2. 中国科学技术大学地球和空间科学学院, 中国科学院壳幔物质与环境重点实验室, 合肥 230026;
3. 中国地质调查局烟台海岸带地质调查中心, 烟台 264004;
4. 安徽省地质勘查局321地质队, 铜陵 244033
2. Key Laboratory of Crust-Mantle Materials and Environments, School of Earth and Space Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China;
3. Yantai Geological Survey Center of Coastal Zone, China Geological Survey, Yantai 264004, China;
4. No. 321 Geological Team, Anhui Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, Tongling 244033, China
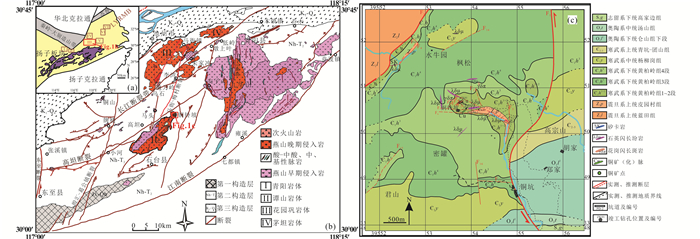
长江中下游成矿带位于扬子板块北缘,是我国重要的铜金铁多金属成矿带之一,安庆-贵池矿集区位于其西段(图 1a;常印佛等,1991)。几十年来,前人对长江中下游成矿带的铜铁金矿床的地质构造特征、地球化学特征、成矿过程及成岩成矿关系进行了大量研究(常印佛等,1991;李曙光,2001;毛景文等,2004;Xie et al., 2008, 2011, 2012a;周涛发等,2008;徐晓春等, 2012, 2018a)。结果表明,长江中下游成矿带由于受到了特提斯构造域、古太平洋构造域以及深部壳幔作用的控制,从而形成了中生代转换构造背景下的断隆-断凹次级构造格局和种类繁多的铁铜金等多金属矿床(常印佛等,1991;Ling et al., 2009; 宋传中等,2010; Yang and Lee, 2011;Yang et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2018; Xie et al., 2018)。安徽贵池矿集区是长江中下游成矿带的重要组成部分之一,区内含有丰富的矿床资源,如铜、铁、金、钼、钨等。近年来,相继发现了铜山铜钼矿、马头铜钼矿、抛刀岭金矿、高家塝钨钼矿、桂林郑钼矿、马石铜矿、安子山铜钼矿等矿床,成矿潜力巨大(Zhu et al., 2014; 徐晓春等,2014;杨晓勇等,2016;Gu et al., 2018)。贵池矿集区燕山期岩浆岩分布广泛,大多以大岩基和复式岩体的形式出露,岩石组合主要以中酸性岩石为主。安徽贵池地区地处下扬子沿江断褶带南部边缘,位于阳新-常州断裂以北。阳新-常州断裂带为沿江断褶带与江南隆起带的界线,区内发育晚中生代中酸性岩体,且均与断裂带延伸方向一致,普遍呈北东向展布(图 1b;杨晓勇等,2016;Gu et al., 2018)。根据岩石类型、空间分布、年代及成矿特征,贵池矿集区燕山期岩浆活动早期(152~136Ma)主要为深成侵位岩体,常以大岩基的形式出露,为复式岩体的早期侵入体,主要以花岗闪长岩为主,为弱过铝质钙碱性系列,具有高Sr、低Y、富集LREE的特征,没有或弱的Eu异常,显示出埃达克(质)岩地球化学特征(Wu et al., 2012, 2018; Yang and Zhang, 2012; Song et al., 2014; 杨晓勇等,2016; Duan et al., 2017; Gu et al., 2017, 2018),如铜山、马头、城安岩体等(Wu et al., 2012; Xie et al., 2012b);第二阶段(135~127Ma)主要是复式岩体的中期侵入体,主要为二长花岗岩,如青阳中期、谭山初期等岩体(Wu et al., 2012; Xie et al., 2012b);晚期多以复式岩体的最晚期侵入体或中期岩体为主,岩性大多为钾长花岗岩,多数具有A型花岗岩特征,具有明显的Eu负异常,如九华山、花园巩、茅坦、谭山、大历山岩体等(Li et al., 2012; Wu et al., 2012; 赵玲和陈志洪, 2014; Yang et al., 2017)。姚孝德等(2013)通过总结前人成果资料,将贵池矿集区划分为三个矿床成矿系列:其一为与燕山早期钙碱性幔壳同熔型首期侵入体有关的W、Mo成矿;其二为燕山早期钙碱性幔壳同熔型闪长岩体主导的Cu、Fe、S、Pb、Zn、W、Mo、(Au、Ag)成矿;其三是与燕山晚期陆壳改造型富硅富碱花岗岩有关的Ag、Cu、Fe、Pb、Zn多金属成矿。
|
图 1 长江中下游地区矿集区和岩浆岩分布图(a,据毛景文等,2004)、贵池地区地质构造-岩浆岩略图(b,据杨晓勇等,2016)及贵池地区铜铃坡铜矿区地质简图(c) LYRMB-长江中下游成矿带;Ⅰ-鄂东;Ⅱ-九瑞;Ⅲ-安庆-贵池;Ⅳ-庐枞;Ⅴ-铜陵;Ⅵ-宁芜;Ⅶ-宁镇 Fig. 1 Distribution of magmatic rochs and ore clusters (districts) in the Middle and Lower Yangtze River metallogenic belt (a, after Mao et al., 2004), geological sketch map of southern Anhui Province (b, modified after Yang et al., 2016) and simplified geological map of the Tonglingpo copper deposit (c) |
尽管长江中下游成矿带近年来对于岩浆活动的年代框架、岩石成因以及地球动力学背景的研究取得了很多成果,但相对于鄂东、九瑞、铜陵、庐枞及宁芜等矿集区,贵池地区岩浆作用研究还较薄弱。铜铃坡铜矿床(图 1b)位于安庆-贵池矿集区的石台县境内,目前只开展了一些基础地质研究,确定为矽卡岩型矿床。铜铃坡矿区内发育石英闪长玢岩和花岗闪长斑岩等岩脉,为进一步确定铜铃坡的成矿时间和含矿石英闪长玢岩对铜富集影响,本文对该矿区含矿石英闪长玢岩进行了锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及地球化学分析,并对其成因及形成的地质背景进行了探讨,从而更好的制约它们与铜成矿关系。
1 矿区地质概况及样品铜铃坡铜矿床位于安徽省池州市石台县境内。大地构造位于沿江拱褶断带和皖南褶断带的交汇部位。矿区地处石门高背斜的倾伏端,谭山岩体与震旦系和寒武纪地层的接触带。本区地层区划属扬子地层区下扬子地层分区贵池地层小区(图 1c)。区域内主要出露地层为寒武系下统黄柏岭组、寒武系中统杨柳岗组、寒武系上统团山组、寒武系上统青坑组及第四系。地层总体呈单斜构造,向东缓倾,倾向110°~170°,倾角10°~30°。区域内大地构造单元属扬子准地台下扬子准台坳的石台穹褶断束,区域主体褶皱构造为七都复背斜,包含三个次级的背向斜构造,自北向南依次为:石门高东西向背斜(山岗尖-杨美桥背斜);东至-杨田埂向斜;葛公镇-雍溪背斜。向斜核部地层为志留系,翼部为震旦系至奥陶系,向北东方向倾伏。断裂构造主要为北东向的逆断层(F1)、北西向性质不明断层F2及北北东向性质不明断层F3。岩浆岩以石英闪长玢岩为主。
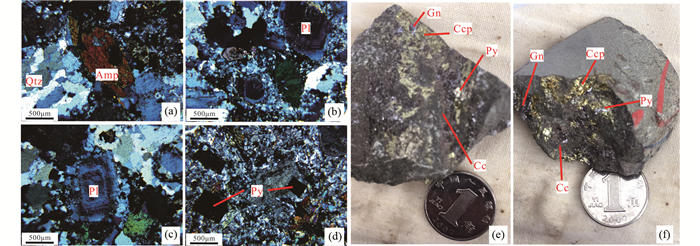
在本次研究中,选取7个铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩样品用于地球化学研究。岩石呈斑状结构和块状结构,主要矿物为斜长石(50%~60%)、石英(15%~20%)、角闪石(5%~10%)和黑云母(~5%)(图 2a-d)。斜长石主要以斑晶形式存在,发育环带状聚片双晶,粒径大小为0.5~5mm。角闪石以斑晶形式存在,部分绿泥石化,粒径大小为0.2~2mm。石英存在于基质中,粒径大小为0.2~0.5mm。副矿物主要有磷灰石、锆石、黄铁矿等矿物。岩石多具绿泥石化、绢云母化、碳酸盐化、硅化。
|
图 2 铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩显微镜下照片(a-d)及矿石照片(e、f) Qtz-石英;Pl-斜长石;Amp-角闪石;Ccp-黄铜矿;Py-黄铁矿;Gn-方铅矿;Cc-辉铜矿 Fig. 2 Microscope photos of the Tonglingpo quartz diorite porphyrite (a-d) and the photographs of ores in Tonglingpo area (e, f) Qtz-quartz; Pl-plagioclase; Amp-amphibole; Ccp-chalcopyrite; Py-pyrite; Gn-galena; Cc-chalcocite |
围岩蚀变类型主要为矽卡岩化,其次为硅化、绢云母化、钾化、碳酸盐化等。矿区主要由两个矿化带组成。第一个为东西向矿(化)带:宽约50m、长大于600m,为断裂破碎带,走向65°~115°。该带发育强烈破碎硅质页岩和石英细脉。矿体发育于破碎带中,为具有黄铁矿化、硅化、黄铜矿化和铅锌矿化的构造角砾岩,宽2~3m,长近百米。矿石矿物有孔雀石、黄铜矿、方铅矿等;脉石矿物主要为石英。分析显示Cu品位为2.06%,Pb品位为1.74%,Zn品位为1.08%,Ag品位为7.78g/t。第二个为北东向矿(化)带,走向NE40°±,主要有以孔雀石、黄铜矿化花岗闪长斑岩脉和铜矿化构造角砾岩两种矿化类型。第一种矿化类型的矿石矿物有孔雀石、黄铜矿、方铅矿等;脉石矿物主要有石英、碳酸盐岩、绿泥石等,局部可见方解石团块或细脉。含有孔雀石化的花岗闪长斑岩的Cu品位为6.95%,Pb品位为6.61%,Zn品位为1.0%,Ag品位为69.8g/t。第二种矿化类型的矿化带宽约30m,矿化沿着硅质页岩层间破碎带发育。矿石矿物以孔雀石和辉铜矿为主;脉石矿物有石英和硅质岩。分析显示Cu品位为2.44%,Pb品位为0.59%,Zn品位为0.04%,Ag品位为3.9g/t。
区内发育石英闪长玢岩和花岗闪长斑岩等岩脉,一般侵入于含碳硅质页岩层间或近EW向和NE向断裂破碎带中。岩脉中黄铁矿化普遍发育,局部岩脉含有大量的黄铜矿化(图 2e, f),构成铜矿(化)体。
2 分析方法为了探究矿区岩浆岩的地球化学特征及与铜多金属成矿作用的关系,本文对矿区内的石英闪长玢岩进行了全岩的主、微量元素,单颗粒锆石U-Pb定年、微量元素分析和Lu-Hf同位素分析。
在广州澳实矿物实验室完成了全岩的主量元素和微量元素分析。主量元素分析采用了X射线荧光熔片法完成,分析精度分别为:SiO2,0.8%;Al2O3,0.5%;Fe2O3,0.4%;MgO,0.4%;CaO,0.6%;Na2O,0.3%;K2O,0.4%;MnO,0.7%;TiO2,0.9%;P2O5,0.8%。采用HF+HNO3溶解样品,加入Rh内标溶液,用PE Elan6000型ICP-MS完成了微量元素的测定,分析精度优于5%。
在河北省地勘局廊坊实验室完成了锆石单矿物分选,将8~10kg的原岩样品粉碎,经常规重选和电磁选后在双目镜下挑选锆石。双目镜下将分选好的锆石根据颜色、自形程度、形态等特征初步分类,挑选出具有代表性的锆石用环氧树脂制靶、打磨和抛光。样品测定之前用体积百分比为3%的HNO3清洗样品表面,以除去样品表面的污染。然后进行锆石显微镜照样(反射光和透射光)和阴极发光(CL)照相, 锆石的透反射和阴极发光照相在中国科学技术大学壳-幔物质与环境重点实验室完成。
锆石的激光剥蚀电感偶合等离子体质谱(LA-ICP-MS)原位U-Pb定年和微量元素分析在中国科学技术大学壳-幔物质与环境重点实验室完成。采用ICPMSDataCal软件(Liu et al., 2008, 2010a)进行数据处理,采用ISOPLOT(3.00版)软件(Ludwig, 2003)完成了年龄计算。详细分析方法见Liu et al. (2010a)。
锆石的微区原位Lu-Hf同位素分析在天津地质矿产研究所同位素实验室完成。所用质谱为NEP TUNE型多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱(LA-MC-ICP-MS),激光剥蚀系统为193nm ArF准分子激光器的NEW WAVE 193nm FX。激光斑束直径为50μm,激光脉冲频率为10Hz。具体分析方法和仪器参数详见耿建珍等(2011)。用176Lu/175Lu=0.02655(De Biévre and Taylor, 1993)和176Yb/172Yb=0.58545(Chu et al., 2002)作为校正因子来进行同质异位干扰校正,计算样品的176Lu/177Hf和176Hf/177Hf。以标准锆石GJ-1作为外标,其推荐的标准值为0.282006±0.000024。在进行εHf(t)计算时,采用176Lu衰变常数=1.867×10-11year-1(Söderlund et al., 2004),球粒陨石现今的176Hf/177Hf=0.282772和176Lu/177Hf=0.0332(Blichert-Toft and Albarède, 1997)。在进行模式年龄计算时,采用现今的亏损地幔176Hf/177Hf=0.28325和176Lu/177Hf=0.0384(Griffin et al., 2000),现今平均大陆壳的176Lu/177Hf=0.015(Griffin et al., 2002)。
3 分析结果 3.1 全岩主微量元素铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩的全岩主、微量元素特征见表 1。
|
|
表 1 铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩的全岩主量(wt%)与微量元素(×10-6)组成 Table 1 Whole rock major elements (wt%) and trace elements (×10-6) compositions of the quartz diorite porphyrites in the Tonglingpo region |
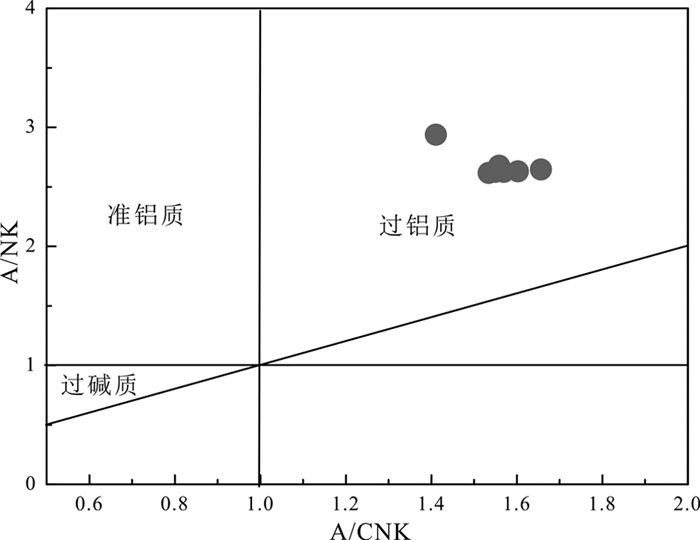
铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩样品SiO2含量变化范围在58.5%~62.8%,K2O含量为2.1%~2.47%,Na2O含量为3.01%~3.87%,全碱含量(Na2O+K2O)在5.48%~6.05%,为闪长岩类岩石,主要显示为亚碱性系列(图 3a)。在SiO2-K2O图解中(图 3b)显示钙碱性特征。样品的MgO含量为2.63%~3.92%(平均为2.84%),Mg#[=Mg/(Mg+FeT)]为0.53~0.57。样品具有过铝质特征(图 4)。

|
图 3 铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩TAS图解(a,据Middlemost, 1994)与K2O-SiO2图解(b,实线据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976; 虚线据Middlemost, 1985) Fig. 3 The plots of the Tonglingpo quartz diorite porphyrites on the TAS (a, after Middlemost, 1994) and K2O vs. SiO2 diagrams (b, solid lines after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976; dashed lines after Middlemost, 1985) |
|
图 4 A/NK-A/CNK图解(据Rickwood, 1989) Fig. 4 Diagram of A/NK vs. A/CNK (after Rickwood, 1989) |
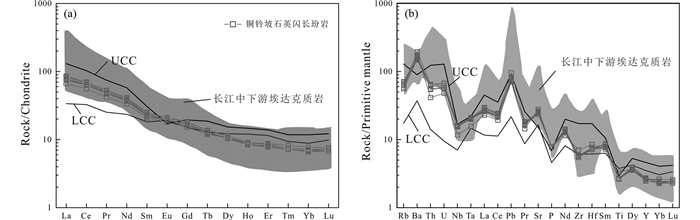
在稀土元素配分图上(图 5a),铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩和长江中下游埃达克质岩类似,都显示出右倾模式,富集轻稀土。铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩稀土总量变化为83.36×10-6~102.4×10-6,(La/Yb)N值在8.73~12.23之间,反映轻重稀土分异明显。Eu异常不明显(0.98~1.01),表明岩浆演化过程中斜长石的结晶分异不明显,这与岩浆演化过程中Al2O3的含量较稳定一致(图 5a)。
|
图 5 铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素模式图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) 长江中下游埃达克质岩数据来源于王元龙等(2004),Wang et al. (2006),Xie et al.(2012a, b, 2018),Deng et al. (2016), Liu et al. (2010b), Zhu et al. (2014), Yan et al. (2015), Wu et al. (2018);LCC和UCC数据来源于Rudnick and Gao (2003) Fig. 5 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider trace element variation diagram (b) of the Tonglingpo quartz diorite porphyrites (normalization values from Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩具高Ba(>640×10-6)和Sr含量(>483×10-6,平均533×10-6)、高Sr/Y(>41.3)、低Yb(1.12×10-6~1.29×10-6,平均为1.2×10-6)和Y含量(11.2×10-6~12.4×10-6,平均为11.9×10-6)。通过原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(图 5b)可以看出,所有样品具有强烈的Pb正异常,富集LREE和大离子亲石元素LILE,如Rb、Sr、Ba、U、Th,亏损高场强元素,如Nb、Ta、P和Ti,显示岛弧岩浆岩的特征。由于Ba的主要载体矿物是钾长石和黑云母,而Sr的主要载体矿物是富钙斜长石和磷灰石,由此可见,铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩Ba、Sr的富集与岩石富钙富碱的特征一致,微量元素特征与岛弧岩浆岩的特征相似。Nb、Ta、Ti的亏损表明岩浆演化过程中有钛铁矿、金红石等富钛相矿物的分离结晶或源区残留。
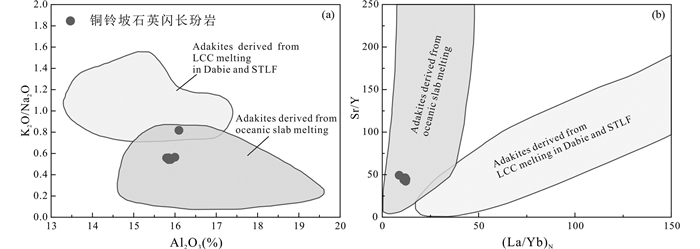
铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩与长江中下游埃达克质岩具有相似的稀土元素及微量元素配分模式。而且铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩富集Sr,具有高的Sr/Y、La/Yb比值以及低Y、Yb含量,与埃达克(质)岩具有相似的地球化学特征(Defant and Drummond, 1990; Martin et al., 2005)。在Sr/Y-Y和(La/Yb)N-YbN判别图解上,贵池地区含矿侵入岩大都投在了埃达克岩范围内(图 6),指示其为埃达克质岩。
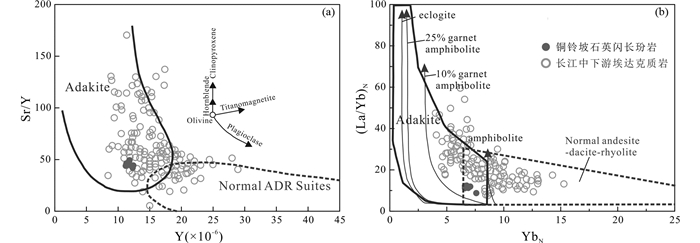
|
图 6 铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩Y-Sr/Y(a, 底图据Martin et al., 2005)及YbN-(La/Yb)N(b, 底图据Defant and Drummond, 1990)判别图解 长江中下游埃达克质岩数据来源同图 5 Fig. 6 Discrimination diagrams of Y vs. Sr/Y (a, after Martin et al., 2005) and YbN vs. (La/Yb)N(b, after Defant and Drummond, 1990) of the Tonglingpo quartz diorite porphyrites |
铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩样品中锆石为无色透明,具有自形晶晶型,大多呈短柱状。除个别锆石为继承锆石外,其余锆石阴极发光图像显示出锆石颗粒的内部具有明显的岩浆振荡环带结构,表明锆石为岩浆结晶产物(Belousova et al., 2002; Hoskin, 2000; Möller et al., 2003)(图 7)。通过对锆石的透射光以及反射光照片的观察,避开含有包裹体的部位或核部可能存在继承锆石的部位,在相对纯净的部位进行激光剥蚀从而对年龄测定和Hf同位素分析。LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄分析结果见表 2。
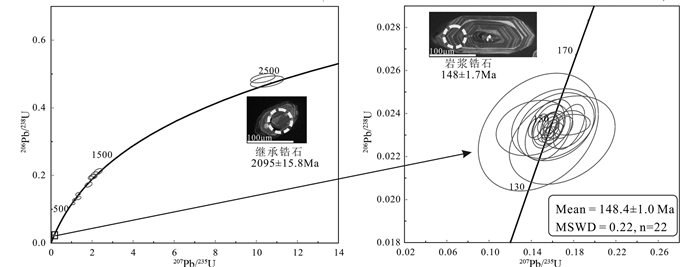
|
图 7 铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩锆石U-Pb谐和图和代表性锆石CL图像 Fig. 7 Zircon concordia diagrams and cathodoluminescence (CL) images of zircons from the Tonglingpo quartz diorite porphyrites |
|
|
表 2 铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩LA-ICP-MS锆石分析数据 Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon analytical data for the quartz diorite porphyrites in the Tonglingpo region |
Th和U含量变化范围较大(Th为151.8×10-6~3361×10-6,U为531.8×10-6~9131×10-6),Th/U比值的变化范围是0.14到1.33,绝大部分都大于0.1,这与岩浆成因锆石一致。锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年结果显示206Pb/238U加权平均年龄分别为148.4±1.0Ma,代表了铜铃坡含矿石英闪长玢岩的侵位年龄。在铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩样品中的继承锆石中具有486~2095Ma的年龄范围,主要集中在755~1138Ma之间,说明在岩石的形成过程中,有古老地壳物质的参与。
铜铃坡埃达克质岩样品中锆石LA-ICP-MS微量元素成分分析结果列于表 3中。在锆石球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图中(图 8a),轻稀土含量低,具有明显的Ce异常和微弱的Eu异常,显示出典型岩浆锆石的特征(Hoskin, 2005)。锆石样品Ce/Ce*(Ce/Ce*=2CeN/(LaN+PrN))变化为8.58~136.3,平均为60.02,表明高Ce异常(低Ce异常 < 50;高Ce异常>50;Xie et al., 2009),暗示高氧逸度特征(Ballard et al., 2002; Xie et al., 2009)。
|
|
表 3 铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩LA-ICP-MS锆石微量元素分析结果(×10-6) Table 3 LA-ICP-MS zircon trace elements (×10-6) analytical result of the quartz diorite porphyrite in the Tonglingpo region |

|
图 8 铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩岩浆氧逸度判别图解 (a)铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩锆石球粒陨石标准化稀土元素模式图(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989);(b)锆石Ce4+/Ce3+-EuN/EuN*氧逸度判别图解(底图据Ballard et al., 2002);(c)铜铃坡埃达克质岩的岩浆氧化状态; (d)岩浆氧逸度(底图据Wang et al., 2015; Sun et al., 2015) Fig. 8 The magma oxygen fugacity discrimination diagrams of quartz diorite porphyrite in the Tonglingpo region (a) chondrite-normalized REE diagram of zircon from quartz diorite porphyrite in the Tonglingpo region (normalizing values after Sun and McDonough, 1989); (b) zircon Ce4+/Ce3+-EuN/EuN* oxygen fugacity discrimination diagram (after Ballard et al., 2002); (c) magma oxidation states; (d) magma oxygen fugacity (after Wang et al., 2015; Sun et al., 2015) |
铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩样品锆石Hf同位素分析结果见表 4,其初始176Hf/177Hf比值为0.281539~0.283033,平均为0.282482,εHf(t)为-18.5~12.4,平均值为-1.3(图 9)。Hf同位素地壳模式年龄(tDM2)为1.01~2.56Ga,平均为1.55Ga。
|
|
表 4 铜铃坡埃达克质岩的锆石Hf同位素组成 Table 4 Zircon Hf isotope data for the adakitic rocks in the Tonglingpo region |
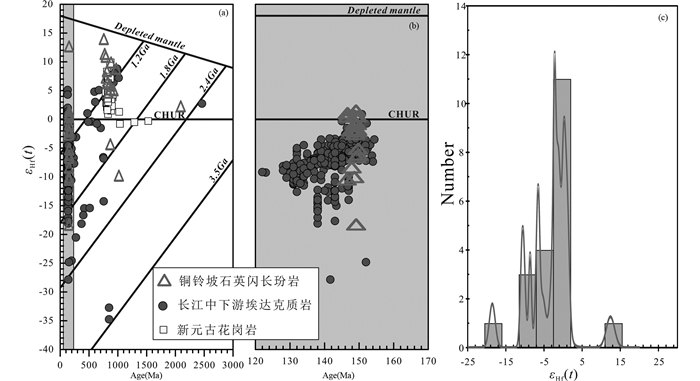
|
图 9 铜铃坡埃达克质岩锆石Hf同位素组成 长江中下游埃达克质岩数据李亮和蒋少涌(2009), 袁峰等(2011), Yang and Zhang (2012), Wu et al.(2012, 2018), Song et al. (2014), Xie et al.(2011, 2018), Deng et al. (2011), 徐晓春等(2018b);新元古花岗岩数据来源于Wu et al. (2006), Wang et al. (2013) Fig. 9 Zircon Hf isotopic compositions of the Tonglingpo adakitic rocks |
长江中下游地区中生代岩浆活动强烈,并伴随了大规模的Cu-Au-Fe成矿作用。长江中下游地区在中生代岩浆作用主要发生在三个阶段(图 10):第一阶段152~136Ma,该时期为重要的铜金多金属成矿阶段,主要与鄂东南、九瑞、铜陵、安庆等隆起区的侵入岩相关,主要为高钾钙碱性系列,岩石类型以辉石闪长(二长)岩-石英闪长(二长)岩-花岗闪长岩为主,其中,闪长岩类为该期最为重要的成矿岩浆岩(Wang et al., 2007, 2015; Li et al., 2008; 蒋少涌等,2008;Xie et al., 2009, 2012b, 2018; 李亮和蒋少涌,2009;Liu et al., 2010b; Wu et al., 2012, 2018);第二阶段135~127Ma,主要包括金牛、怀宁、庐枞、繁昌、宁芜、溧阳和溧水盆地等凹陷区的火山岩及次火山岩(Wang et al., 2006; 周涛发等,2008;薛怀民等,2010; Xie et al., 2011;袁峰等,2011;Yan et al., 2015),其中金牛、怀宁和繁昌盆地火山岩为钙碱性系列,晚期火山岩显示出双峰式特征,其它盆地火山岩具有高钾富碱特征,属于shoshonite岩石系列,其中盆地内同期次火山岩与玢岩型铁矿成矿密切相关;第三阶段127~123Ma,既可产出于隆起区,又可产出于凹陷区,主要为A型花岗岩和宁芜地区的辉长质侵入岩,主导了小规模的热液型金矿和铀矿成矿(范裕等, 2008;Yan et al., 2015; Li et al., 2012; Wu et al., 2012)。
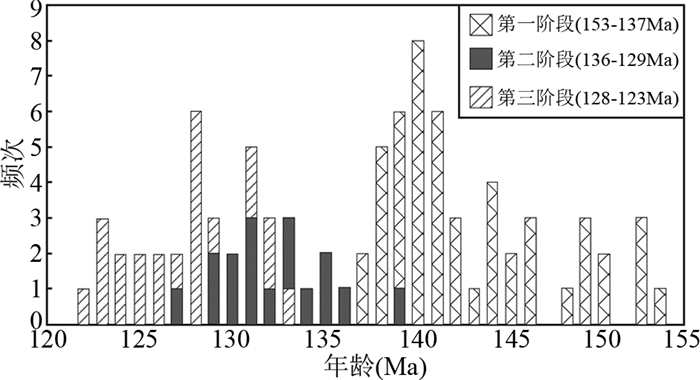
|
图 10 长江中下游成矿带燕山期岩浆岩年龄分布图 年龄数据来源于Wang et al. (2007),Xie et al.(2012b, 2018),Li et al. (2008),Liu et al. (2010b),Wu et al.(2012, 2018),Wang et al. (2015),Yan et al. (2015),范裕等(2008),袁峰等(2011),薛怀民等(2010) Fig. 10 Zircon U-Pb ages from Late Mesozoic magmatic rocks in the Lower Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt |
铜铃坡铜矿埃达克质岩侵位于148.4±1.0Ma,与长江中下游早期岩浆活动相对应。铜铃坡埃达克质岩中继承锆石2095Ma表明了基底岩石年龄,说明扬子克拉通存在古元古代基底(Qiu et al., 2000; Gao et al., 2001; Zhang et al., 2006)。铜铃坡埃达克质岩中来自古元古代物质的继承锆石的发现,不仅证明了扬子板块东北缘古元古代基底物质的存在,同时暗示铜铃坡埃达克质岩的形成过程中有古元古代基底物质的参与。
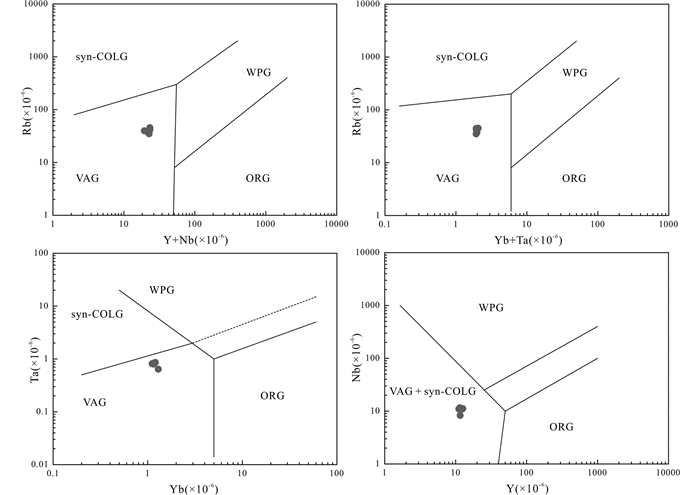
4.2 岩体成因铜铃坡埃达克质岩富集轻稀土LREE、Sr、Ba,亏损重稀土HREE、Y、Yb,以及高的Sr/Y和(La/Yb)N比值,与长江中下游地区早白垩世埃达克质岩的地球化学特征相似(许继峰等,2001;王元龙等,2004;Wang et al., 2006; 李进文等,2007;Li et al., 2008; Xie et al., 2008, 2012a, b; 蒋少涌等,2008;周涛发等,2008;Zhu et al., 2014)。对长江中下游地区含矿埃达克质岩的成岩机制一直以来存在较多争论。主要有以下几种观点:①加厚下地壳(至少少于40km)的部分熔融或拆沉下地壳部分熔融并经地幔混染(Xu et al., 2002; Wang et al., 2007; 蒋少涌等,2008);②幔源岩浆与壳源岩浆的混合作用(Wang et al., 2003; 王元龙等,2004);③富集岩石圈地幔来源的玄武质岩浆的分离结晶或同化混染(AFC)(Li et al., 2008; Deng et al., 2016);④俯冲洋壳+沉积物部分熔融的产物(Ling et al., 2009; Liu et al., 2010b; Sun et al., 2010, 2011; Deng et al., 2016),可能受到部分陆壳物质同化混染(Wang et al., 2011; Yang et al., 2014),形成于板片后撤(Yang et al., 2014)或板片断离(Wang et al., 2014),或洋脊俯冲(Ling et al., 2009; Li et al., 2012)等动力学背景之下;⑤幔源岩浆结晶分异或AFC过程(杜杨松等,2007; Li et al., 2008; Xie et al., 2008, 2011)。
不同成因的埃达克岩具有不同的地球化学特征,比如,K2O、MgO、TiO2、P2O5、Th和U含量差异,K2O/Na2O,Th/Ce、Th/U、Sr/Y和(La/Yb)N等比值也不同。铜铃坡埃达克质岩MgO含量为2.63%~3.92%,与SiO2含量具有明显的负相关关系。Mg#值是一个可以判断是否存在地幔作用的有用指标。不管熔融程度如何,玄武质下地壳熔融具有低Mg#(< 0.4)特征,而Mg#>0.4,则说明有地幔物质的参与(Rapp and Watson, 1995)。铜铃坡埃达克质岩具有相对较高的相容元素含量(V=91×10-6~144×10-6,平均为99×10-6;Cr=72×10-6~80×10-6,平均为76×10-6;Co=10.5×10-6~14.2×10-6,平均为11.4×10-6;Ni=16.4×10-6~18.9×10-6,平均为18.1×10-6)和高的Mg#(0.53~0.56,平均为0.54),与长江中下游地区埃达克质岩一致(0.35~0.76;许继峰等,2001;Wang et al., 2003; Xie et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2010b)一致,表明有地幔成分的参与。铜铃坡埃达克质岩的Al2O3含量较高(平均15.9%),K2O/Na2O比值变化在0.55到0.82(平均值为0.6),位于俯冲洋壳熔融型埃达克岩区域内,与大别造山带加厚下陆壳部分熔融形成的埃达克岩具有明显区别(Wang et al., 2007; Huang et al., 2008)(图 11a)。
|
图 11 铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩K2O/Na2O-Al2O3(a)和Sr/Y-(La/Yb)N(b)图解(底图据Sun et al., 2012; Liu et al., 2010b; Ling et al., 2013) 大别加厚下地壳埃达克质岩数据据Petford and Atherton (1996),Wang et al. (2007),Huang et al. (2008),Zhao and Zhou (2008);洋壳板块而来埃达克岩数据据Defant and Drummond (1990),Drummond et al. (1996),Stern and Kilian (1996),Aguillón-Robles et al. (2001) Fig. 11 Diagrams of K2O/Na2O vs. Al2O3(a) and Sr/Y vs. (La/Yb)N (b) of the quartz diorite porphyrites in the Tonglingpo region (base map after Sun et al., 2012; Liu et al., 2010b; Ling et al., 2013) Data of thickened lower crust-derived adakitic rocks from the Dabie orogen from Petford and Atherton (1996), Wang et al. (2007), Huang et al. (2008), Zhao and Zhou (2008); data of oceanic slab-derived adakites from Defant and Drummond (1990), Drummond et al. (1996), Stern and Kilian (1996), Aguillón-Robles et al. (2001) |
高Sr/Y和(La/Yb)N比值是判别埃达克质岩的两个最重要参数(Defant and Drummond, 1990; Martin et al., 2005)。铜铃坡埃达克质岩的(La/Yb)N比值(8.7~12.2,平均为11.2)较低,Sr/Y比值(42.1~49.4,平均为44.7)较高,落在俯冲洋壳熔融型埃达克岩区域内,支持板块熔体的解释(Martin et al., 2005)(图 11b),主要由低温海水蚀变洋壳部分熔融导致。陆壳Ce/Pb(约4~5;Taylor and McLennan, 1985; Rudnick and Gao, 2003)比值比洋壳(~24;Sun and McDonough, 1989)低。由于N-MORB亏损LREE和海水蚀变富集Sr,蚀变洋壳相对下陆壳而言具有更高的Sr/La比值。Sr/La-Ce/Pb图解可以对来自下陆壳和俯冲洋壳的岩石进行判别(Liu et al., 2010b; Sun et al., 2012; Ling et al., 2013)。铜铃坡埃达克质岩与长江中下游埃达克质岩具有相似的Ce/Pb和Sr/La比值,暗示其起源于俯冲洋壳(图 12)。铜铃坡及长江中下游埃达克质岩低Nb/U比值(8.1~9.4)和高Ba/Th(192.5~342.9)比值,进一步表明其起源于俯冲洋壳板块部分熔融(Plank and Langmuir, 1998)。
|
图 12
铜铃坡埃达克质岩与长江中下游埃达克质岩Sr/La-Ce/Pb图解(据Liu et al., 2010b; Rudnick and Gao, 2003)
长江中下游地区埃达克质岩数据来源同图 5]]>
|
|
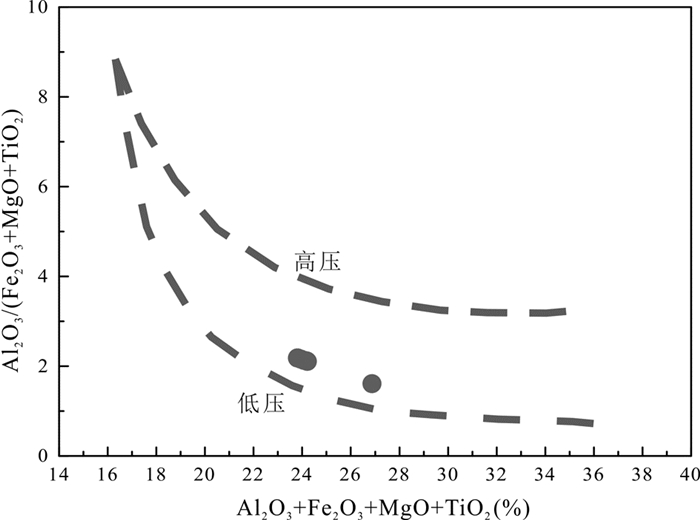
图 15 铜铃坡埃达克质岩(Al2O3+Fe2O3+MgO+TiO2)-Al2O3/(Fe2O3+MgO+TiO2)图解 高压和低压曲线引自Patiňo Douce (1999) Fig. 15 (Al2O3+Fe2O3+MgO+TiO2) vs. Al2O3/(Fe2O3+MgO+TiO2) diagram of the Tonglingpo adakitic rocks The area between the high- and low-pressure curves encompasses the range of depths at which mantle-crust interaction takes place after Patiňo Douce (1999) |
铜铃坡埃达克质岩富集大离子亲石元素LILE(如Rb、Ba、Th),亏损高场强元素(Nb、Ta、Zr)(图 5),与板块消减带火成岩具有相似的地球化学特征,区别于形成于板内环境的富集高场强元素的火成岩。结合地球物理资料,吕庆田等(2014)认为在早白垩世时期整个长江中下游地区处于大陆边缘岩浆弧的内陆一侧,古太平洋板块的斜向俯冲形成了大规模的岩浆活动;随着板片俯冲角度的加大,发育的岩浆岩显示出弧后环境特征。Sun et al. (2007)通过将中国东部岩浆活动的时间与太平洋板块对欧亚大陆的俯冲方向进行比较,认为中国东部白垩纪以来的主要构造岩浆活动与太平洋板块转向密切相关。进一步研究表明,太平洋板块向南西俯冲以及相应的板块后撤,导致了华南地区晚侏罗世岩浆活动和成矿作用的发生(Wang et al., 2011)。
铜铃坡埃达克质岩地球化学特征表明本区岩浆岩形成于大陆边缘岩浆弧的内陆一侧环境,与古太平洋板块俯冲密切相关。铜铃坡埃达克质岩的形成于148Ma左右(图 6),其地球化学特征指示了由于太平洋板块俯冲使得俯冲洋壳加沉积物熔融产生的埃达克岩浆在上升的过程中,混染了岩石圈地幔,从而形成了铜铃坡埃达克质岩。因此,我们认为铜铃坡埃达克质岩形成于早白垩世低压板块俯冲环境。
4.4 铜金成矿指示意义根据Watson and Harrison (1983)提出的岩浆Zr饱和温度计(TZr=12900/[2.95+0.85M+ln(496000/Zrmelt)]),得到铜铃坡埃达克质岩的岩浆锆饱和温度为689~701℃(表 1)。锆石中Ti元素是对岩浆形成温度的灵敏指示剂,铜铃坡埃达克质岩锆石中Ti的含量为2.5×10-6~26.7×10-6,得到锆石的结晶温度范围在632~835℃ (表 3,Watson et al., 2006),平均温度为762℃。岩浆Zr饱和温度计与锆石Ti温度计得到的结果一致,低于正常的岩浆温度。锆石结晶处于岩浆分异演化的早期阶段,锆石结晶时岩浆的温度较低,可能指示岩浆是在减压条件下由源区物质部分熔融导致。
Ballard et al. (2002)提出锆石的Ce4+/Ce3+是一种很好的氧逸度指示剂,根据Blundy and Wood (1994)的公式计算出铜铃坡埃达克质岩锆石的Ce4+/Ce3+为20.1~792,绝大多数为74~366,平均值为323,指示岩体具有高氧逸度特征,岩体源区物质可能受到了俯冲洋壳脱水形成的高氧逸度流体的交代(Mungall, 2002)。同时,根据Trail et al. (2012)提出的氧逸度计算方法,计算出贵池地区铜金矿床含矿埃达克(质)岩的氧逸度大多数位于MH(磁铁矿-赤铁矿缓冲对)之上(图 8c, d),平均值为FMQ+6.7,氧逸度较高。研究表明,高氧逸度对于Cu、Au成矿具有重要作用(Mungall, 2002; Sun et al., 2015, 2017)。氧逸度作为一个经验性的指标可以判断岩体与成矿的关系(Ballard et al., 2002)。研究表明(Sun et al., 2012, 2015, 2017; Li et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2017; Deng et al., 2017, 2019),在高氧逸度下,俯冲洋壳的部分熔融是形成大型超大型斑岩铜金矿床的最佳地质过程。铜铃坡埃达克质岩高氧逸度的特征指示铜铃坡岩体具有较好的成矿潜力(图 8b-d)。研究表明,俯冲带的氧逸度比板内更高(Sun et al., 2004, 2011; Ling et al., 2009)。铜铃坡岩体的锆石高氧逸度特征进一步证明该地区可能经历了太平洋俯冲,在其上升过程中与富集地幔发生相互作用。因此,铜铃坡铜成矿作用是俯冲洋壳部分熔融结果,为本区Cu、Au矿床勘探提供了一个新方向。
磷灰石具有独特的含流体元素的特征,热液蚀变、热液流体活化迁移成矿物质以及矿石矿物的富集主要受到花岗质岩浆和岩浆热液流体中的F、Cl的配分影响(Treloar and Colley, 1996; Sotnikov et al., 2003; Li et al., 2017)。富含F、Cl的岩浆热液流体对成矿物质的迁移、搬运起着至关重要的作用,是反映岩浆氧逸度条件和流体活动性的标志性矿物(Tollari et al., 2008; Li et al., 2017)。磷灰石是花岗质岩石中较早结晶、接近液相线的矿物,通过岩浆成因磷灰石端元组分计算得到流体中HF、HCl含量可以指示岩浆期液相线组分(Piccoli and Candela, 2002)。王蝶等(2010)运用电子探针分析得到了德兴铜厂与成矿相关的花岗闪长斑岩中斑晶磷灰石的F-、Cl-、OH-浓度,结合角闪石Al压力计和Zr饱和温度计得到矿物结晶的温压值,进而运用热力学方法计算出磷灰石结晶时与之平衡的原始岩浆分异的初始流体中的HF、HCl含量。根据铜铃坡含矿石英闪长玢岩中角闪石电子探针数据,计算得到角闪石平均结晶压力值为P=189±50MPa,通过全岩锆石饱和温度计计算得到的铜铃坡含矿石英闪长玢岩的平均结晶温度为693℃,结合磷灰石电子探针数据及磷灰石端元组分热力学反应平衡原理(Zhu and Sverjensky, 1991),计算得到磷灰石结晶时与之平衡的流体中的HF的活度为0.00049mol/L,HCl活度为0.018mol/L(数据另文发表),岩浆结晶早期分异的流体中HCl的浓度是HF的30多倍。因而,相比F-,铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩在结晶分异过程中能够较多地分异出Cl-,为携带Cu等成矿元素在流体中的运移提供了重要的络合剂。上述结果进一步表明,铜铃坡铜矿成矿流体主要为铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩成岩过程中分异出的岩浆流体。
5 结论(1) 铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩为埃达克质岩,主要显示亚碱性系列钙碱性过铝质特征,属于俯冲洋壳俯冲成因,明显不同于加厚或底侵下地壳型埃达克岩。
(2) 铜铃坡埃达克质岩形成于晚侏罗世,年龄为148.4±1.0Ma。岩石地球化学特征、Hf同位素特征显示岩浆来源于有限俯冲沉积物贡献的俯冲洋壳部分熔融,在上升过程中不仅与富集地幔发生相互作用,同时混染了古老地壳物质。
(3) 俯冲洋壳的部分熔融形成了高氧逸度的铜铃坡埃达克质岩浆,有利于铜金成矿。铜铃坡石英闪长玢岩磷灰石端元组分表明在岩浆结晶早期,成矿流体主要为石英闪长玢岩成岩过程中分异出的岩浆流体。
致谢 感谢中国科学院海洋研究所孙卫东研究员及两位审稿专家对本文提出的建设性修改意见。野外工作得到了安徽省地勘局324地质队的帮助与指导;同时也感谢胡青、汪海在实验过程中给予的帮助。
Aguillón-Robles A, Calmus T, Benoit M, Bellon H, Maury RC, Cotton J, Bourgois J and Michaud F. 2001. Late Miocene adakites and Nb-enriched basalts from Vizcaino Peninsula, Mexico:Indicators of East Pacific Rise subduction below southern Baja California?. Geology, 29(6): 531-534 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0531:LMAANE>2.0.CO;2 |
Ballard JR, Palin MJ and Campbell IH. 2002. Relative oxidation states of magmas inferred from Ce(Ⅳ)/Ce(Ⅲ) in zircon:Application to porphyry copper deposits of northern Chile. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 144(3): 347-364 DOI:10.1007/s00410-002-0402-5 |
Bedard JH. 1999. Petrogenesis of boninites from the Betts Cove ophiolite, Newfoundland, Canada:Identification of subducted source components. Journal of Petrology, 40(12): 1853-1889 DOI:10.1093/petroj/40.12.1853 |
Belousova E, Griffin W, O'Reilly SY and Fisher N. 2002. Igneous zircon:Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 143(5): 602-622 DOI:10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7 |
Blichert-Toft J and Albarède F. 1997. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 148(1-2): 243-258 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00040-X |
Blundy J and Wood B. 1994. Prediction of crystal-melt partition-coefficients from elastic-moduli. Nature, 372(6505): 452-454 DOI:10.1038/372452a0 |
Chang YF, Liu XP and Wu YC. 1991. The Iron-Copper Ore-Forming Belt of Middle-Lower Yangtze River. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Chu NC, Taylor RN, Chavagnac V, Nesbitt RW, Boella RM, Milton JA, German CR, Bayon G and Burton K. 2002. Hf isotope ratio analysis using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry:An evaluation of isobaric interference corrections. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 17(12): 1567-1574 DOI:10.1039/b206707b |
De Biévre P and Taylor PDP. 1993. Table of the isotopic compositions of the elements. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Ion Processes, 123(2): 149-166 DOI:10.1016/0168-1176(93)87009-H |
Defant MJ and Drummond MS. 1990. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature, 347(6294): 662-665 DOI:10.1038/347662a0 |
Deng J, Wang QF, Xiao CH, Yang LQ, Liu H, Gong QJ and Zhang J. 2011. Tectonic-magmatic-metallogenic system, Tongling ore cluster region, Anhui Province, China. International Geology Review, 53(5-6): 449-476 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2010.501538 |
Deng JH, Yang XY, Li S, Gu HL, Mastoi AS and Sun WD. 2016. Partial melting of subducted paleo-Pacific plate during the Early Cretaceous:Constraint from adakitic rocks in the Shaxi porphyry Cu-Au deposit, Lower Yangtze River Belt. Lithos, 262: 651-667 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2016.07.039 |
Deng JH, Yang XY, Qi HS, Zhang ZF, Mastoi AS and Sun WD. 2017. Early Cretaceous high-Mg adakites associated with Cu-Au mineralization in the Cebu Island, Central Philippines:Implication for partial melting of the paleo-Pacific Plate. Ore Geology Reviews, 88: 251-269 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.05.006 |
Deng JH, Yang XY, Qi HS, Zhang ZF, Mastoi AS, Berador AEG and Sun WD. 2019. Early Cretaceous adakite from the Atlas porphyry Cu-Au deposit in Cebu Island, Central Philippines:Partial melting of subducted oceanic crust. Ore Geology Reviews, 110: 102937 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.102937 |
Duan LA, Gu HL and Yang XY. 2017. Geological and geochemical constraints on the newly discovered Yangchongli gold deposit in Tongling Region, Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(6): 2078-2108 DOI:10.1111/1755-6724.13451 |
Drummond MS, Defant MJ and Kepezhinskas PK. 1996. Petrogenesis of slab-derived trondhjemite-tonalite-dacite/adakite magmas. In: Brown M, Candela PA, Peck DL, Stephens WE, Walker RJ and Zen EA (eds.). The Third Hutton Symposium on the Origin of Granites and Related Rocks. Geological Society of America, 205-215
|
Du YS, Li ST, Cao Y, Qin ZL and Lou YE. 2007. UAFC-related origin of the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous intrusions in the Tongguanshan ore field, Tongling, Anhui Province, East China. Geoscience, 21(1): 71-77 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Fan Y, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Qian CC, Lu SM and Cooke D. 2008. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages of the A-type granites in the Lu-Zong (Lujiang-Zongyang) area and their geological significances. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8): 1715-1724 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Gao S, Qiu YM, Ling WL, McNaughton NJ and Grove DI. 2001. Single zircon U-Pb dating of the Kongling high-grade metamorphic terrain:Evidence for >3.2Ga old continental crust in the Yangtze Craton. Science in China (Series D), 44(4): 326-335 DOI:10.1007/BF02907103 |
Geng JZ, Li HK, Zhang J, Zhou HY and Li HM. 2011. Zircon Hf isotope analysis by means of LA-MC-ICP-MS. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(10): 1508-1513 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Griffin WL, Pearson NJ, Belousova E, Jackson SE, van Achterbergh E, O'Reilly SY and Shee SR. 2000. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle:LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(1): 133-147 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9 |
Griffin WL, Wang X, Jackson SE, Pearson NJ, O'Reilly SY, Xu XS and Zhou XM. 2002. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China:In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes. Lithos, 61(3-4): 237-269 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00082-8 |
Gu HL, Yang XY, Deng JH, Duan LA and Liu L. 2017. Geochemical and zircon U-Pb geochronological study of the Yangshan A-type granite:Insights into the geological evolution in south Anhui, eastern Jiangnan Orogen. Lithos, 284-285: 156-170 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2017.04.007 |
Gu HL, Yang XY, Nie ZX, Deng JH, Duan LA, Hu Q, Shakoor MA, Gao EG and Jasmi Hafiz AA. 2018. Study of Late-Mesozoic magmatic rocks and their related copper-gold-polymetallic deposits in the Guichi ore-cluster district, Lower Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt, East China. International Geology Review, 60(11-14): 1404-1434 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2017.1422442 |
Hawkesworth CJ, Turner SP, McDermott F, Peate DW and van Calsteren P. 1997. U-Th isotopes in arc magmas:Implications for element transfer from the subducted crust. Science, 276(5312): 551-555 DOI:10.1126/science.276.5312.551 |
Hoskin PWO. 2000. Patterns of chaos:Fractal statistics and the oscillatory chemistry of zircon. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(11): 1905-1923 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00330-6 |
Hoskin PWO. 2005. Trace-element composition of hydrothermal zircon and the alteration of Hadean zircon from the Jack Hills, Australia. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(3): 637-648 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2004.07.006 |
Hou ZQ, Pan XF, Yang ZM and Qu XM. 2007. Porphyry Cu-(Mo-Au) deposits no related to oceanic-slab subduction:Examples from Chinese porphyry deposits in continental settings. Geoscience, 21(2): 332-351 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Huang F, Li SG, Dong F, He YS and Chen FK. 2008. High-Mg adakitic rocks in the Dabie orogen, Central China:Implications for foundering mechanism of lower continental crust. Chemical Geology, 255(1-2): 1-13 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.02.014 |
Jiang SY, Li L, Zhu B, Ding X, Jiang YH, Gu LX and Ni P. 2008. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic compositions of granodiorite from the Wushan copper deposit, Jiangxi Province and their implications for petrogenesis. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8): 1679-1690 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Kepezhinska P, McDermott F, Defant MJ, Hochstaedter A, Drummond MS, Hawkesworth CJ, Koloskov A, Maury RC and Bellon J. 1997. Trace element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic constraints on a three-component model of Kammchatka Arc petrogenesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61(3): 577-600 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00349-3 |
Li CY, Hao XL, Liu JQ, Ling MX, Ding X, Zhang H and Sun WD. 2017. The formation of Luoboling porphyry Cu-Mo deposit:Constraints from zircon and apatite. Lithos, 272-273: 291-300 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2016.12.003 |
Li H, Ling MX, Li CY, Zhang H, Ding X, Yang XY, Fan WM, Li YL and Sun WD. 2012. A-type granite belts of two chemical subgroups in central eastern China:Indication of ridge subduction. Lithos, 150: 26-36 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.09.021 |
Li JW, Pei RF, Zhang DQ, Mei YX, Zang WS, Meng GX, Zeng PS, Li TJ and Di YJ. 2007. Geochemical characteristics of the Yanshanian intermediate-acid intrusive rocks in the Tongling mineralization concentration area, Anhui Province, and their geological implications. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 28(1): 11-22 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li JW, Zhao XF, Zhou MF, Vasconcelos P, Ma CQ, Deng XD, de Souza ZS, Zhao YX and Wu G. 2008. Origin of the Tongshankou porphyry-skarn Cu-Mo deposit, eastern Yangtze craton, eastern China:Geochronological, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints. Mineralium Deposita, 43(3): 315-336 DOI:10.1007/s00126-007-0161-3 |
Li L and Jiang SY. 2009. Petrogenesis and geochemistry of the Dengjiashan porphyritic granodiorite, Jiujiang-Ruichang metallogenic district of the Middle-Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11): 2877-2888 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li SG. 2001. Infrastructure of Mesozoic magmatic rocks and copper-iron metallogenic belt in the Middle and Lower Yangtze River Reaches. Geology of Anhui, 11(2): 118-122 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li ZX and Li XH. 2007. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China:A flat-slab subduction model. Geology, 35(2): 179-182 DOI:10.1130/G23193A.1 |
Ling MX, Wang FY, Ding X, Hu YH, Zhou JB, Zartman RE, Yang XY and Sun WD. 2009. Cretaceous ridge subduction along the Lower Yangtze River Belt, eastern China. Economic Geology, 104(2): 303-321 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.104.2.303 |
Ling MX, Li Y, Ding X, Teng FZ, Yang XY, Fan WM, Xu YG and Sun WD. 2013. Destruction of the North China Craton induced by Ridge Subductions. Journal of Geology, 121(2): 197-213 DOI:10.1086/669248 |
Liu SA, Li SG, He YS and Huang F. 2010b. Geochemical contrasts between Early Cretaceous ore-bearing and ore-barren high-Mg adakites in central-eastern China:Implications for petrogenesis and Cu-Au mineralization. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(24): 7160-7178 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2010.09.003 |
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Gao S, Günther D, Xu J, Gao CG and Chen HH. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34-43 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 |
Liu YS, Gao S, Hu ZC, Gao CG, Zong KQ and Wang DB. 2010a. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2): 537-571 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egp082 |
Liu Z, Yang XY, Liu CM, Huang DZ, Zhou WJ, Teng X, Liang EY and Dai TG. 2018. Genesis of Early Cretaceous porphyrite-type iron deposits and related sub-volcanic rocks in the Ningwu Volcanic Basin, Middle-Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt, Southeast China. International Geology Review, 60(11-14): 1507-1528 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2017.1419883 |
Ludwig KR. 2003. User's Manual for Isoplot/Ex, Version 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publications, 4(2): 1-70 |
Lv QT, Dong SW, Shi DN, Tang JT, Jiang GM, Zhang YQ, Xu T and Sinoprobe-03-CJ Group. 2014. Lithosphere architecture and geodynamic model of Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze Metallogenic Belt:A review from SinoProbe. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(4): 889-906 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Mao JW, Stein H, Du AD, Zhou TF, Mei YX, Li YF, Zang WS and Li JW. 2004. Molybdenite Re-Os precise dating for molybdenite from Cu-Au-Mo deposits in the Middle-Lower Reaches of Yangtze River Belt and its implications for mineralization. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78(1): 121-131 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Martin H, Smithies RH, Rapp R, Moyen JF and Champion D. 2005. An overview of adakite, tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG), and sanukitoid:Relationships and some implications for crustal evolution. Lithos, 79(1-2): 1-24 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.04.048 |
Middlemost EAK. 1985. Magmas and Magmatic Rocks. London: Longman, 1-266
|
Middlemost EAK. 1994. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth-Science Reviews, 37(3-4): 215-224 DOI:10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9 |
Möller A, O'Brien PJ, Kennedy A and Kröner A. 2003. Linking growth episodes of zircon and metamorphic textures to zircon chemistry:An example from the ultrahigh-temperature granulites of Rogaland (SW Norway). Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 220(1): 65-81 DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.2003.220.01.04 |
Mungall JE. 2002. Roasting the mantle:Slab melting and the genesis of major Au and Au-rich Cu deposits. Geology, 30(10): 915-918 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0915:RTMSMA>2.0.CO;2 |
Patiňo Douce AE. 1999. What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas? In: Castro A, Fermandez C and Vigneresse JL (eds.). Understanding Granites: Integrating New and Classical Techniques. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 168(1): 55-75
|
Pearce JA, Harris NBW and Tindle AG. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983 DOI:10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 |
Peccerillo A and Taylor SR. 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic-rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1): 63-81 DOI:10.1007/BF00384745 |
Petford N and Atherton M. 1996. Na-rich partial melts from newly underplated basaltic crust:The Cordillera Blanca Batholith, Peru. Journal of Petrology, 37(6): 1491-1521 DOI:10.1093/petrology/37.6.1491 |
Piccoli PM and Candela PA. 2002. Apatite in igneous systems. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 48(1): 255-292 DOI:10.2138/rmg.2002.48.6 |
Plank T and Langmuir CH. 1998. The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle. Chemical Geology, 145(3-4): 325-394 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00150-2 |
Qiu YM, Gao S, McNaughton NJ, Groves DI and Ling WL. 2000. First evidence of >3.2Ga continental crust in the Yangtze Craton of south China and its implications for Archean crustal evolution and Phanerozoic tectonics. Geology, 28(1): 11-14 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2000)028<0011:FEOGCC>2.0.CO;2 |
Rapp RP and Watson EB. 1995. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8~32kbar:Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling. Journal of Petrology, 36(4): 891-931 DOI:10.1093/petrology/36.4.891 |
Rickwood PC. 1989. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements. Lithos, 22(4): 247-263 DOI:10.1016/0024-4937(89)90028-5 |
Rudnick RL and Gao S. 2003. Composition of the continental crust. In: Rudnick RL, Holland HD and Turekian KK (eds.). Treatise on Geochemistry, Volume 3. Oxford: Elsevier, 1-64
|
Seghedi I, Downes H, Pécskay Z, Thirlwall MF, Szakács A, Prychodko M and Mattey D. 2001. Magmagenesis in a subduction-related post-collisional volcanic arc segment:The Ukrainian Carpathians. Lithos, 57(4): 237-262 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(01)00042-1 |
Söderlund U, Patchett JP, Vervoort JD and Isachsen CE. 2004. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 219(3-4): 311-324 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00012-3 |
Song CZ, Lin SF, Zhou TF, Yan J, Ren SL, Li JH, Tu WC and Zhang Y. 2010. Mesozoic tectonic regime transition of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River and its adjacent area. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(9): 2835-2849 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Song GX, Qin KZ, Li GM, Evans NJ and Li XH. 2014. Mesozoic magmatism and metallogeny in the Chizhou area, Middle-Lower Yangtze Valley, SE China:Constrained by petrochemistry, geochemistry and geochronology. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 91: 137-153 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.04.025 |
Sotnikov VI, Berzina AN, Berzina AP, Ponomarchuk VA and Gimon VO. 2003. Fluorine and chlorine in magmatic and metasomatic ore processes in the Cu-Mo porphyry deposits of Siberia and Mongolia. Petrology, 11(3): 301-304 |
Stern CR and Kilian R. 1996. Role of the subducted slab, mantle wedge and continental crust in the generation of adakites from the Andean Austral volcanic zone. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 123(3): 263-281 DOI:10.1007/s004100050155 |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in Oceanic Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345
|
Sun WD, Arculus RJ, Kamenetsky VS and Binns RA. 2004. Release of gold-bearing fluids in convergent margin magmas prompted by magnetite crystallization. Nature, 431(7011): 975-978 DOI:10.1038/nature02972 |
Sun WD, Ding X, Hu YH and Li XH. 2007. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the west Pacific. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 262(3-4): 533-542 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.08.021 |
Sun WD, Ling MX, Yang XY, Fan WM, Ding X and Liang HY. 2010. Ridge subduction and porphyry copper-gold mineralization:An overview. Science China Earth Sciences, 53(4): 475-484 DOI:10.1007/s11430-010-0024-0 |
Sun WD, Zhang H, Ling MX, Ding X, Chung SL, Zhou JB, Yang XY and Fan WM. 2011. The genetic association of adakites and Cu-Au ore deposits. International Geology Review, 53(5-6): 691-703 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2010.507362 |
Sun WD, Ling MX, Chung SL, Ding X, Yang XY, Liang HY, Fan WM, Goldfarb R and Yin QZ. 2012. Geochemical constraints on adakites of different origins and copper mineralization. Journal of Geology, 120(1): 105-120 DOI:10.1086/662736 |
Sun WD, Huang RF, Li H, Hu YB, Zhang CC, Sun SJ, Zhang LP, Ding X, Li CY, Zartman RE and Ling MX. 2015. Porphyry deposits and oxidized magmas. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 97-131 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.09.004 |
Sun WD, Wang JT, Zhang LP, Zhang CC, Li H, Ling MX, Ding X, Li CY and Liang HY. 2017. The formation of porphyry copper deposits. Acta Geochimica, 36(1): 9-15 DOI:10.1007/s11631-016-0132-4 |
Taylor SR and McLennan SM. 1985. The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1-100
|
Tollari N, Baker DR and Barnes SJ. 2008. Experimental effects of pressure and fluorine on apatite saturation in mafic magmas, with reference to layered intrusions and massif anorthosites. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 156(2): 161-175 DOI:10.1007/s00410-008-0279-z |
Trail D, Watson EB and Tailby ND. 2012. Ce and Eu anomalies in zircon as proxies for the oxidation state of magmas. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 97: 70-87 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2012.08.032 |
Treloar PJ and Colley H. 1996. Variations in F and Cl contents in apatites from magnetite-apatite ores in northern Chile, and their ore-genetic implications. Mineralogical Magazine, 60(399): 285-301 DOI:10.1180/minmag.1996.060.399.04 |
Wang D, Bi XW and Shang LB. 2010. The concentration characteristics of HF and HCl deriving from early crystal of granodiorite porphyry in Dexing County, Jiangxi Province, China. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 30(3): 331-337 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang FY, Ling MX, Ding X, Hu YH, Zhou JB, Yang XY, Liang HY, Fan WM and Sun WD. 2011. Mesozoic large magmatic events and mineralization in SE China:Oblique subduction of the Pacific plate. International Geology Review, 53(5-6): 704-726 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2010.503736 |
Wang FY, Liu SA, Li SG, Akhtar S and He YS. 2014. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf-O isotopes and trace elements of Mesozoic high Sr/Y porphyries from Ningzhen, eastern China:Constraints on their petrogenesis, tectonic implications and Cu mineralization. Lithos, 200-201: 299-316 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.05.004 |
Wang Q, Xu JF, Zhao ZH, Xiong XL and Bao ZW. 2003. Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Tongling area, Anhui Province, China and their constraint on geodynamic process. Science in China (Series D), 46(8): 801-815 DOI:10.1007/BF02879524 |
Wang Q, Wyman DA, Xu JF, Zhao ZH, Jian P, Xiong XL, Bao ZW, Li CF and Bai ZH. 2006. Petrogenesis of Cretaceous adakitic and shoshonitic igneous rocks in the Luzong area, Anhui Province (eastern China):Implications for geodynamics and Cu-Au mineralization. Lithos, 89(3-4): 424-446 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2005.12.010 |
Wang Q, Wyman DA, Xu JF, Zhao ZH, Jian P and Zi F. 2007. Partial melting of thickened or delaminated lower crust in the middle of eastern China:Implications for Cu-Au mineralization. Journal of Geology, 115(2): 149-161 DOI:10.1086/510643 |
Wang SW, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Fan Y, White NC and Lin FJ. 2015. Geological and geochemical studies of the Shujiadian porphyry Cu deposit, Anhui Province, eastern China:Implications for ore genesis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 103: 252-275 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.08.004 |
Wang XL, Zhou JC, Wan YS, Kitajima K, Wang D, Bonamici C, Qiu JS and Sun T. 2013. Magmatic evolution and crustal recycling for Neoproterozoic strongly peraluminous granitoids from southern China:Hf and O isotopes in zircon. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 366: 71-82 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2013.02.011 |
Wang YL, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Jia XQ and Han S. 2004. The geochemical characteristics of Mesozoic intermediate-acid intrusives of the Tongling area and its metallogenesis-geodynamic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(2): 325-338 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Watson EB and Harrison TM. 1983. Zircon saturation revisited:Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 64(2): 295-304 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X |
Watson EB, Wark DA and Thomas JB. 2006. Crystallization thermometers for zircon and rutile. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 151(4): 413-433 DOI:10.1007/s00410-006-0068-5 |
Wu CL, Dong SW, Wu D, Zhang X and Ernst WG. 2018. Late Mesozoic high-K calc-alkaline magmatism in Southeast China:The Tongling example. International Geology Review, 60(11-14): 1326-1360 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2017.1313137 |
Wu FY, Ji WQ, Sun DH, Yang YH and Li XH. 2012. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions of the Mesozoic granites in southern Anhui Province, China. Lithos, 150: 6-25 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.03.020 |
Wu RX, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Zhao ZF, Zhang SB, Liu XM and Wu FY. 2006. Reworking of juvenile crust:Element and isotope evidence from Neoproterozoic granodiorite in South China. Precambrian Research, 146(3-4): 179-212 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.01.012 |
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Li RL and Bierlein FP. 2008. Geochemistry and Nd-Sr isotopic studies of Late Mesozoic granitoids in the southeastern Hubei Province, Middle-Lower Yangtze River Belt, eastern China:Petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Lithos, 104(1-4): 216-230 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.12.008 |
Xie GQ, Mao JW and Zhao HJ. 2011. Zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic intrusions in the Southeast Hubei Province, Middle-Lower Yangtze River Belt (MLYRB), East China. Lithos, 125(1-2): 693-710 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.04.001 |
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Zhao HJ, Duan C and Yao L. 2012a. Zircon U-Pb and phlogopite 40Ar-39Ar age of the Chengchao and Jinshandian skarn Fe deposits, Southeast Hubei Province, Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley Metallogenic Belt, China. Mineralium Deposita, 47(6): 633-652 DOI:10.1007/s00126-011-0367-2 |
Xie JC, Yang XY, Sun WD, Du JG, Xu W, Wu LB, Wang KY and Du XW. 2009. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on formation of the Tongling metal deposits, middle Yangtze metallogenic belt, east-central China. International Geology Review, 51(5): 388-421 DOI:10.1080/00206810802712004 |
Xie JC, Yang XY, Sun WD and Du JG. 2012b. Early Cretaceous dioritic rocks in the Tongling region, eastern China:Implications for the tectonic settings. Lithos, 150: 49-61 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.05.008 |
Xie JC, Wang Y, Li QZ, Liu JM, Yan J and Sun WD. 2018. Early Cretaceous adakitic rocks in the Anqing region, southeastern China:Constraints on petrogenesis and metallogenic significance. International Geology Review, 60(11-14): 1435-1452 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2017.1362672 |
Xu JF, Wang Q, Xu YG, Zhao ZH and Xiong XL. 2001. Geochemistry of Anjishan intermediate-acid intrusive rocks in Ningzhen area:Constraint to origin of the magma with HREE and Y depletion. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(4): 576-584 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu JF, Shinjo R, Defant MJ, Wang Q and Rapp RP. 2002. Origin of Mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of East China:Partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust. Geology, 30(12): 1111-1114 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<1111:OOMAIR>2.0.CO;2 |
Xu XC, Bai RY, Xie QQ, Lou JW, Zhang ZZ, Liu QN and Chen LW. 2012. Re-understanding of the geological and geochemical characteristics of the Mesozoic intrusive rocks from Tongling area of Anhui Province, and discussions on their genesis. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(10): 3139-3169 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu XC, Liu X, Zhang ZZ, He M, Liu XY, Xie QQ, Fan ZL and He J. 2014. Zircon U-Pb ages of magmatic rocks in Zhaojikou lead-zinc deposits of Dongzhi County, Anhui Province and their geological significance. Chinese Journal of Geology, 49(2): 431-455 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu XC, Zou X, He J and Fu ZY. 2018a. Geological and geochemical characteristics of the intrusive rocks of early and late stages during Late Mesozoic in Tongling district, Anhui Province. Geological Journal of China University, 24(3): 325-339 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu XC, Ji K, Bai RY, Qian SL, Yang QG and Xie ZJ. 2018b. Modes of occurrence of gold and genetic connection between gold and copper in the ores from the Chating porphyry copper-gold deposit, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 37(4): 575-589 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xue HM, Dong SW and Ma F. 2010. Geochemistry of shoshonitic volcanic rocks in the Luzong basin, Anhui Province (eastern China):Constraints on Cretaceous lithospheric thinning of the Lower Yangtze Region. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(5): 664-681 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yan J, Liu JM, Li QZ, Xing GF, Liu XQ, Xie JC, Chu XQ and Chen ZH. 2015. In situ zircon Hf-O isotopic analyses of late Mesozoic magmatic rocks in the Lower Yangtze River Belt, central eastern China:Implications for petrogenesis and geodynamic evolution. Lithos, 227: 57-76 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.03.013 |
Yang W and Zhang HF. 2012. Zircon geochronology and Hf isotopic composition of Mesozoic magmatic rocks from Chizhou, the Lower Yangtze Region:Constraints on their relationship with Cu-Au mineralization. Lithos, 150: 37-48 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.06.026 |
Yang XY and Lee IS. 2011. Review of the stable isotope geochemistry of Mesozoic igneous rocks and Cu-Au deposits along the middle-lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt, China. International Geology Review, 53(5-6): 741-757 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2010.533881 |
Yang XY, Yang XM, Zhang ZW, Chi YY, Yu LF and Zhang QM. 2011. A porphyritic copper (gold) ore-forming model for the Shaxi-Changpushan district, Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt, China:Geological and geochemical constraints. International Geology Review, 53(5-6): 580-611 DOI:10.1080/00206810903211906 |
Yang XY, Gu HL, Yan ZZ, Lü QL, Duan LA, Deng JH, Zhu YS, Wang MS and Zhao DK. 2016. Metallogenic relationship between Yanshanian magmatic rocks and Cu-Au-Mo deposits in Guichi region of Anhui:Evidence from geological-geochemical-geophysical characteristics. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 38(4): 444-463 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang YZ, Long Q, Siebel W, Cheng T, Hou ZH and Chen FK. 2014. Paleo-Pacific subduction in the interior of eastern China:Evidence from adakitic rocks in the Edong-Jiurui district. Journal of Geology, 122(1): 77-97 DOI:10.1086/674423 |
Yang YZ, Wang Y, Ye RS, Li SQ, He JF, Wolfgang S and Chen FK. 2017. Petrology and geochemistry of Early Cretaceous A-type granitoids and Late Mesozoic mafic dikes and their relationship to adakitic intrusions in the Lower Yangtze River Belt, Southeast China. International Geology Review, 59(1): 62-79 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2016.1212284 |
Yao XD, Tan DX and Chen F. 2013. Regional metallogenic models for the Chizhou area, Anhui Province. Geology of Anhui, 23(3): 200-204 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yuan F, Zhou TF, Fan Y, Zhang LJ, Ma L and Qian B. 2011. Zircon U-Pb ages and isotopic characteristics of the granitoids in the Ningwu Basin, China, and their significance. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(5): 821-833 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang CC, Sun WD, Wang JT, Zhang LP, Sun SJ and Wu K. 2017. Oxygen fugacity and porphyry mineralization:A zircon perspective of Dexing porphyry Cu deposit, China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 206: 343-363 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2017.03.013 |
Zhang SB, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Zhao ZF, Gao S and Wu FY. 2006. Zircon isotope evidence for >3.5Ga continental crust in the Yangtze craton of China. Precambrian Research, 146(1-2): 16-34 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.01.002 |
Zhao JH and Zhou MF. 2008. Neoproterozoic adakitic plutons in the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, China:Partial melting of a thickened lower crust and implications for secular crustal evolution. Lithos, 104(1-4): 231-248 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.12.009 |
Zhao L and Chen ZH. 2014. Zircon LA-ICP-MS dating of the Tanshan pluton in the area of southern Anhui Province and its geological significances. Resources Survey and Environment, 35(3): 185-191 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhou MF, Yan DP, Wang CL, Qi L and Kennedy A. 2006. Subduction-related origin of the 750Ma Xuelongbao adakitic complex (Sichuan Province, China):Implications for the tectonic setting of the giant Neoproterozoic magmatic event in South China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 248(1-2): 286-300 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.05.032 |
Zhou TF, Fan Y and Yuan F. 2008. Advances on petrogensis and metallogeny study of the mineralization belt of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River area. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8): 1665-1678 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhou XM and Li WX. 2000. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China:Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas. Tectonophysics, 326(3-4): 269-287 DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00120-7 |
Zhu C and Sverjensky DA. 1991. Partitioning of F-Cl-OH between minerals and hydrothermal fluids. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 55(7): 1837-1858 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(91)90028-4 |
Zhu ZY, Jiang SY, Hu J, Gu LX and Li JW. 2014. Geochronology, geochemistry, and mineralization of the granodiorite porphyry hosting the Matou Cu-Mo (±W) deposit, Lower Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt, eastern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 79: 623-640 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.07.033 |
常印佛, 刘湘培, 吴言昌. 1991. 长江中下游铜铁成矿带. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
杜杨松, 李顺庭, 曹毅, 秦新龙, 楼亚儿. 2007. 安徽铜陵铜官山矿区中生代侵入岩的形成过程——岩浆底侵、同化混染和分离结晶. 现代地质, 21(1): 71-77. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.01.008 |
范裕, 周涛发, 袁峰, 钱存超, 陆三明, Cooke D. 2008. 安徽庐江-枞阳地区A型花岗岩的LA-ICP-MS定年及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 24(8): 1715-1724. |
耿建珍, 李怀坤, 张健, 周红英, 李惠民. 2011. 锆石Hf同位素组成的LA-MC-ICP-MS测定. 地质通报, 30(10): 1508-1513. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.10.004 |
侯增谦, 潘小菲, 杨志明, 曲晓明. 2007. 初论大陆环境斑岩铜矿. 现代地质, 21(2): 332-351. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.02.019 |
蒋少涌, 李亮, 朱碧, 丁昕, 姜耀辉, 顾连兴, 倪培. 2008. 江西武山铜矿区花岗闪长斑岩的地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素组成及成因探讨. 岩石学报, 24(8): 1679-1690. |
李进文, 裴荣富, 张德全, 梅燕雄, 臧文拴, 孟贵祥, 曾普胜, 李铁军, 狄永军. 2007. 铜陵矿集区燕山期中酸性侵入岩地球化学特征及其地质意义. 地球学报, 28(1): 11-22. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2007.01.003 |
李亮, 蒋少涌. 2009. 长江中下游地区九瑞矿集区邓家山花岗闪长斑岩的地球化学与成因研究. 岩石学报, 25(11): 2877-2888. |
李曙光. 2001. 长江中下游中生代岩浆岩及铜铁成矿带的深部构造背景. 安徽地质, 11(2): 118-122. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-6157.2001.02.007 |
吕庆田, 董树文, 史大年, 汤井田, 江国明, 张永谦, 徐涛, SinProbe-03-CJ项目组. 2014. 长江中下游成矿带岩石圈结构与成矿动力学模型——深部探测(SinProbe)综述. 岩石学报, 30(4): 889-906. |
毛景文, Stein H, 杜安道, 周涛发, 梅燕雄, 李永峰, 臧文栓, 李进文. 2004. 长江中下游地区铜金(钼)矿Re-Os年龄测定及其对成矿作用的指示. 地质学报, 78(1): 121-131. |
宋传中, Lin SF, 周涛发, 闫峻, 任升莲, 李加好, 涂文传, 张妍. 2010. 长江中下游及其邻区中生代构造体制转换. 岩石学报, 26(9): 2835-2849. |
王蝶, 毕献武, 尚林波. 2010. 德兴铜矿花岗闪长斑岩成岩过程分异的初始岩浆流体HF、HCL浓度特征. 矿物学报, 30(3): 331-337. |
王元龙, 王焰, 张旗, 贾秀琴, 韩松. 2004. 铜陵地区中生代中酸性侵入岩的地球化学特征及其成矿-地球动力学意义. 岩石学报, 20(2): 325-338. |
许继峰, 王强, 徐义刚, 赵振华, 熊小林. 2001. 宁镇地区中生代安基山中酸性侵入岩的地球化学:亏损重稀土和钇的岩浆产生的限制. 岩石学报, 17(4): 576-584. |
徐晓春, 白茹玉, 谢巧勤, 楼金伟, 张赞赞, 刘启能, 陈莉薇. 2012. 安徽铜陵中生代侵入岩地质地球化学特征再认识及成因讨论. 岩石学报, 28(10): 3139-3169. |
徐晓春, 刘雪, 张赞赞, 何苗, 刘晓燕, 谢巧勤, 范子良, 何俊. 2014. 安徽东至兆吉口铅锌矿区岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义. 地质科学, 49(2): 431-455. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2014.02.008 |
徐晓春, 左续, 何俊, 傅仲阳. 2018a. 安徽铜陵地区晚中生代早、晚两期侵入岩的地质和地球化学特征. 高校地质学报, 24(3): 325-339. |
徐晓春, 季珂, 白茹玉, 钱仕龙, 杨前国, 谢祖军. 2018b. 安徽宣城茶亭斑岩铜金矿床金的赋存状态及金铜成因联系. 岩石矿物学杂志, 37(4): 575-589. |
薛怀民, 董树文, 马芳. 2010. 安徽庐枞火山岩盆地橄榄玄粗岩系的地球化学特征及其对下扬子地区晚中生代岩石圈减薄机制的约束. 地质学报, 84(5): 664-681. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.05.009 |
杨晓勇, 古黄玲, 严志忠, 吕启良, 段留安, 邓江洪, 朱永胜, 汪梅生, 赵德奎. 2016. 安徽贵池地区燕山期岩浆岩与铜金钼成矿关系:来自地质-地球化学-地球物理证据. 地球科学与环境学报, 38(4): 444-463. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2016.04.002 |
姚孝德, 谭德兴, 陈芳. 2013. 安徽省池州地区区域成矿模式. 安徽地质, 23(3): 200-204. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-6157.2013.03.008 |
袁峰, 周涛发, 范裕, 张乐骏, 马良, 钱兵. 2011. 宁芜盆地花岗岩类的锆石U-Pb年龄、同位素特征及其意义. 地质学报, 85(5): 821-833. |
赵玲, 陈志洪. 2014. 皖南谭山岩体的锆石定年及地质意义. 资源调查与环境, 35(3): 185-191. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2014.03.006 |
周涛发, 范裕, 袁峰. 2008. 长江中下游成矿带成岩成矿作用研究进展. 岩石学报, 24(8): 1665-1678. |
 2020, Vol. 36
2020, Vol. 36


