2. 青岛海洋科学与技术试点国家实验室, 海洋矿产资源评价与探测技术功能实验室, 青岛 266237;
3. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049;
4. 中国科学院海洋大科学研究中心, 青岛 266071
2. Laboratory for Marine Mineral Resources, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao 266237, China;
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China;
4. Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266071, China
铼(Re),自然界中最难熔的元素之一,最初主要用于催化剂和高温加热电离带等。由于具有难熔难蚀及良好的塑性等物化条件,目前,铼的最重要的用途是制造在高温下保持足够机械强度的超级合金,其价格也因此飞涨至每吨数百万乃至千万美元。超级铼合金是高性能飞机发动机涡轮的核心材料,其目的是保证飞机发动机叶片在高温下不变形。自二十世纪中后期开始,铼合金被陆续应用于F-22、F-35的发动机中。因此,铼被誉为改变航空业的金属。
迄今为止,斑岩型铜钼金矿床是世界铼产量的主要来源。从目前探明储量看,全球近一半(约55%)的铼产出于智利的斑岩铜钼矿床,据美国地质调查局估计智利的铼探明储量约1300吨(Polyak, 2013; John et al., 2017)。其他国家依次是美国、俄罗斯、秘鲁等国,均在300吨左右。从前景储量看,美国地质调查局估计美国铼的前景储量在5千吨,全球其他国家总的前景储量在6千吨(Polyak, 2013; John et al., 2017)。在哈萨克斯坦和波兰,大部分铼矿产量主要来自受沉积物影响的层控铜矿床(Bartlett et al., 2013)。我国铼资源储量目前并没有较为明确的统计数据,截止2003年,我国铼的储量为237吨,有铼矿11处,分布于9个省,主要分布于江西德兴、湖南宝山、陕西洛南和金堆城、河南栾川及吉林大黑山等地。据前人估计,陕西金堆城钼矿、河南栾川钼矿、吉林大黑山钼矿、黑龙江多宝山铜(钼)矿等矿床中,合计占全国铼总储量的近90%(吴贤等, 2008)。但是,实际上秦岭钼矿带斑岩钼矿中铼的品位很低(约十万分之一),急需寻找更好的铼矿资源。
铼的地球化学性质与钼接近,在地表风化过程中容易被氧化成钼酸盐而溶解于水,随地表径流运移,在还原条件下被固定,进入富含有机质的还原性沉积物中(孙卫东等, 2015; Sun et al., 2016; Liao et al., 2019)。研究表明,在寒武纪(~550Ma)以后,由于大气氧的大幅度升高,氧化还原敏感元素的活化迁移加强,富含有机质的沉积物中钼含量大幅度升高(Kump, 2008; Scott et al., 2008; Saltzman et al., 2011; Lyons et al., 2014; Smit and Mezger, 2017)。相应地,其铼含量也应该有较大幅度的升高。
本文尝试通过对Re的地球化学性质的分析,探讨我国铼成矿前景,为进一步指导铼矿找矿提供依据。
1 铼的地球化学性质与富集铼的原子序数为75,原子质量为186.2mol/g。在元素周期表中,铼位于锰和锝下方,与钨和铂族元素(PGE)相邻,并且在钼的斜下方。铼的密度为21.02g/cm3,是第四密度元素(铱、锇和铂的密度较高)。它具有六角密排晶体结构。
铼的价态范围变化宽,总共有9个,从-1到+7,其中+7、+6、+4和+2是最常见的离子,对硫逸度、氧逸度敏感。铼形成三种稳定的氧化物,分别是七氧化铼(Re2O7)、三氧化铼(ReO3)和二氧化铼(ReO2),其中ReO3是最常见的氧化物。七氧化铼,又名铼庚醚,是一种明亮的黄色挥发性固体(Colodner et al., 1995),溶于水中形成高铼酸(HReO4)和高铼酸盐。铼对硫有很强的亲和力,同时因Re4+与Mo4+的半径相似,故铼经常类质同象置换钼而富集于辉钼矿中。铼化合物的不寻常特征,包括七氧化铼异常高的挥发性及其在水中的高溶解度等,都有助于将铼从辉钼矿精矿焙烧产生的烟尘中回收。
在硅酸盐地球中,铼通常以+4和+6价存在,表现为中度不相容元素的特征。铼是长半衰期的放射性元素中唯一的中度不相容的亲铜、亲铁元素(Shirey and Walker, 1998;Sun et al., 2003a)。铼有两种主要的天然同位素,185Re(稳定,占天然Re的37.4%)和187Re(具有放射性,占天然Re的62.6%)。铼有多种衰变体系,目前最常利用的是187Re通过β衰变为187Os,半衰期约为4.1×1010y (Bosch et al., 1996)。铼-锇同位素系统常被用来测定矿床中硫化物矿物(最常见的是辉钼矿)的年龄(McCandless and Ruiz, 1993;Stein et al., 2001)以及示踪壳-幔相互作用(杜安道等, 1994, 2009; 孙亚莉等, 1997; Gao et al., 2002; Du et al., 2018, 2019a, b)。
铼是地球陆壳中最稀有的元素之一,目前报道的铼在地壳中的丰度变化范围较大,在0.2×10-9~2×10-9之间(Taylor and McLennan, 1995;Rudnick and Gao, 2014)。铼具有很强的挥发性,通过火山岩获得的铼的丰度值偏低,而由于铼在表生过程中易于被氧化,所以根据黄土获得的铼的丰度也偏低。考虑到大洋玄武岩中铼的丰度为1×10-9,本文倾向认为铼的地壳丰度在2×10-9左右(Sun et al., 2003b)。铼在地幔中的丰度为50×10-12(McDonough and Sun, 1995)。
铼是极度分散元素,很少作为一种金属或其独立矿物存在,主要为辉铼矿、铜铼矿和锇铜铼矿(Kuleshevich et al., 2010),但含铼矿物种类繁多,包括辉钼矿、铌铁矿、辉铜矿、白钨矿等61种,有的地区黑色岩系中也富集铼(Figueiredo et al., 2014; 田立强等, 2016)。辉钼矿是铼富集的矿物,不同类型的辉钼矿中铼的含量差别很大。已有报道中,辉钼矿中铼的含量最高可以含有百分之十(Ishihara, 1988; Bernard et al., 2003; 毛景文等, 2004; Yudovskaya et al., 2008; 魏庆国等, 2009; 应立娟等, 2009)。从矿床的角度看,斑岩铜金矿床中伴生的辉钼矿中铼含量最高,可以达到辉钼矿的千分之三的平均品位,是铼的主要来源。相比之下,斑岩钼矿中辉钼矿的铼含量普遍很低,可以低到百万分之一(杜安道等, 1994; 张兴国等, 2008; Li et al., 2012a; 聂凤军等, 2013; 卢志强等, 2016),目前国际上一般不将其作为铼矿开采。此外,在同一矿床中,低温下形成的辉钼矿铼含量高。例如,在一些火山通道中形成的辉钼矿,随温度降低,铼含量升高,低温部位辉钼矿中铼的含量可以达到10%(Bernard et al., 2003; Yudovskaya et al., 2008)。
自然界中也发现了一些含铼量非常高的硫化物,如1986年首次在日本Usu火山的喷气孔中发现了辉铼矿显微晶体(ReS2) (Bernard and Dumortier, 1986),1994年在俄罗斯千岛群岛地区Iturup岛上的Kudryavy火山的高温喷气孔中发现了铼矿石晶体,主要成分为ReS2 (Korzhinsky et al., 1994),在希腊北部的帕戈里拉奇斑岩中也曾报道过(Voudouris et al., 2009),在芬兰Nivala的Nivala镍-铜-PGE矿的硫化物精矿中发现了富含铼的(Cu, Fe)(Re, Mo)4S8的显微(≤75μm)晶体(Kojonen et al., 2004),2008年在俄罗斯远东勘察加半岛的火山喷气口也发现有纯的硫化铼矿物(Kremenetsky and Chaplygin, 2010)。另外,美国南部的一些铀矿、俄罗斯的页岩及某些石油产品燃烧后的烟灰中也含有一定量的铼,但具体的含量数据未见报道(吴贤等, 2008)。
矿石中提取铼的方法主要包括溶剂萃取法、离子交换法、沉淀法、氧化还原法、碱浸置换法、电渗析法等,不同赋存矿物及赋存状态所采用的回收方法不同(曹冲等, 2014; 彭真等, 2012; 夏瑜等, 2017)。由于铼的氧化物Re2O7具有挥发性,且溶于水,辉钼矿冶炼的烟道气中可以提取铼,通常以高铼酸铵的形式产出。对于黑色页岩中铼的分离,目前还缺乏相关的研究。
国际上铼的储量主要来自斑岩铜金矿床中的辉钼矿。我国辉钼矿储量占全球的近一半,主要是斑岩钼矿,多数辉钼矿中铼含量低(1×10-9~10×10-9)。钼矿主要分布在秦岭-大别山钼矿带(陈衍景等, 2000, 2009; Mao et al., 2008; Li et al., 2012b; Mi et al., 2017),按照该钼矿带探明斑岩钼矿中钼的储量(约800万吨)、其辉钼矿中铼的含量在十万分之一的量级计算,秦岭-大别山斑岩钼矿中的铼仅为80吨。由于含量太低,回收率很难保证。迄今为止,国际上没有从此类矿床中提取铼的案例。因此,我国急需寻找更好的铼矿资源。
不同类型含铼钼矿床中铼的含量不一,差别巨大。我国著名的特大型斑岩钼矿床,如陕西金堆城钼矿床的辉钼矿含铼17×10-6~20×10-6(符新科和尹孝刚, 2004)。特大型斑岩矽卡岩型钼钨矿床,如河南栾川地区钼矿床的辉钼矿含铼10×10-6~20×10-6(李永峰等, 2003),铼总量约135.39吨(崔世俊和郭娜娜, 2013)。葫芦岛地区大型矽卡岩型钼矿床的辉钼矿含铼10×10-6~20×10-6。而江西德兴斑岩铜钼矿床的辉钼矿含铼近600×10-6~700×10-6(王诚华, 2006),按照其钼储量20万吨和辉钼矿中600×10-6的品位计算,德兴斑岩铜矿的铼储量可以达到120吨。不过,这些钼矿大部分已被开采,铼回收量尚不清楚,剩余储量也不清楚。湖南宝山斑岩铜钼矿床的辉钼矿含铼300×10-6~450×10-6(路远发等, 2006),陕西洛南地区钼矿床的辉钼矿中铼含量约为250×10-6~300×10-6、个别地段的辉钼矿含铼高达350×10-6~370×10-6(袁海潮等, 2014)。但是这些地区的钼储量较小。相应地,我国钼矿中铼资源分布也是不均匀的,铼与钼储量之间缺乏对应关系。本文根据文献统计结果显示(图 1),我国钼矿床及其相关的矿床中铼资源总量超过1300吨,其中10吨以上的钼矿床主要分布在东北、兴蒙造山带、秦岭-大别造山带和冈底斯造山带,合计占全国铼总量的近90%,集中分布在陕西金堆城钼矿、河南栾川钼(钨)矿、吉林大黑山钼矿、黑龙江多宝山铜(钼)矿、西藏纳日贡玛钼铜矿、帮浦钼铜矿、新疆白山钼矿、内蒙古乌努格吐山铜钼矿等矿床中。另外,西部地区的一些斑岩钼矿和斑岩铜钼矿值得重点关注,如西藏南木铜矿、新疆东戈壁钼矿。此外,紫金山、玉龙等斑岩铜钼矿床有可能提供较多的铼。黄龙铺、杨家杖子等矽卡岩型钼矿,辉钼矿中铼的含量也可以达到万分之几,也值得重点关注
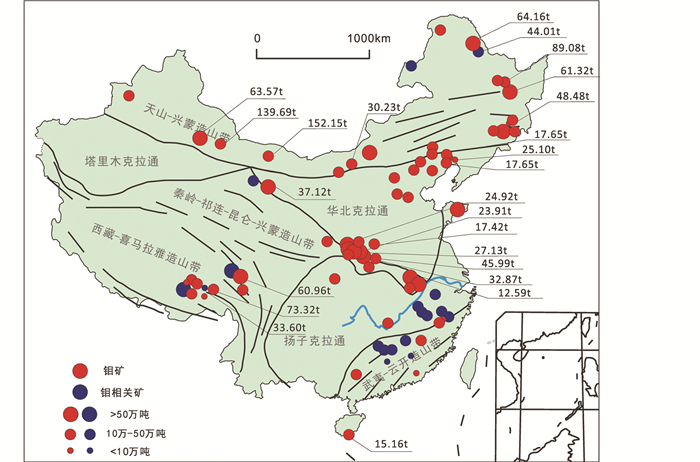
|
图 1 我国典型辉钼矿的分布图及其估计铼资源量(底图据Zeng et al., 2013;范羽等,2014修改) 图中铼估计储量计算方法:根据钼矿床及钼相关矿床中辉钼矿的铼平均浓度、整个矿床的平均钼品位和矿床总吨位进行乘积计算.数据选自王召林等, 2008; 张绮玲等, 2003; 孟祥金等, 2003; 李孙雄等, 2014; 黄凡等, 2012; 刘晓煌等, 2007; 袁海潮等, 2014; 李诺等, 2007; 李永峰等, 2003; 李法岭, 2011; 晏国龙等, 2012; 周珂等, 2009; 黄典豪等, 1996; Dai et al., 2009; 黄超勇等, 2011; 邓刚等, 2004; 刘永慧等, 2014; 谭钢等, 2010; 聂凤军等, 2007a, b, 2011; 刘翼飞等, 2011; 崔根等, 2008; 赵元艺等, 1997; 邵军等, 2012; 王成辉等, 2009 Fig. 1 Schematic showing the distribution of the typical molybdenite ore-deposits in China and their estimated rhenium resources (base map modified after Zeng et al., 2013, Fan et al., 2014) The calculating method of rhenium reserves is based on the average rhenium concentration, molybdenum content and rhenium content of molybdenite in molybdenum ore-deposits and molybdenum related ore-deposits. The average grade of molybdenum and the total tonnage of the deposit are calculated by product. Data are selected from Wang et al., 2008, 2009; Zhang et al., 2003; Meng et al., 2003; Li et al., 2003, 2007, 2014; Huang et al., 2011, 2012, 2012; Liu et al., 2007, 2011, 2014; Yuan et al., 2014; Li, 2011; Yan et al., 2012; Zhou et al., 2009; Huang et al., 1996, Dai et al., 2009; Deng et al., 2004; Tan et al., 2010; Nie et al., 2007a, b, 2011; Cui et al., 2008; Zhao et al., 1997; Shao et al., 2012 |
表生沉积过程是铼富集的另一个重要途径(Sun et al., 2016; Liao et al., 2019)。我国华南地区广泛分布寒武纪黑色页岩,这些黑色页岩中富集铼。从已有的少量数据看,这些黑色页岩的铼品位可以达到0.1×10-6~0.6×10-6(Jiang et al., 2007)。由于这些黑色页岩中铼主要富集于硫化物(黄铁矿等)中,实际开采成本应该接近或低于同等品位的金矿。因此,这些黑色页岩很多可能都已达到可采品位,初步估计,黑色页岩中铼资源量可以达到万吨以上(图 2)。在上述地区寻找高品位铼矿是一个好的找矿方向。
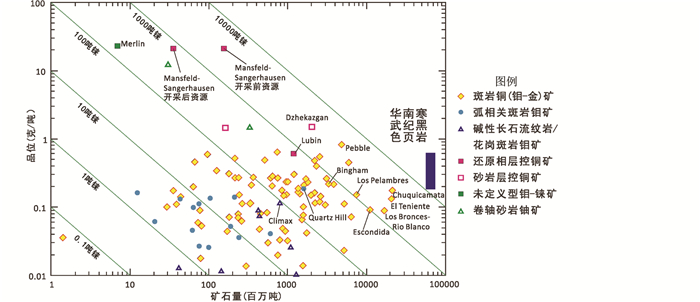
|
图 2 世界主要含铼矿床的品位-品级(据John et al., 2017修改) 华南寒武纪黑色页岩中铼金属量估算方法:黑色页岩分布范围、厚度及其平均铼含量三者的乘积 Fig. 2 Diagram showing the tonnages v.s. grades of the major rhenium-bearing ore-deposits in the world (modified after John et al., 2017) Estimating method for the amount of rhenium in the Cambrian black shale of the South China: The product of the distribution range, thickness and average rhenium content of the black shale |
我国华南广泛发育晚震旦世和早寒武世黑色岩系(范德廉等, 2004; 杨剑和易成发, 2005),该页岩层地理上横跨云南、贵州、湖南、湖北、江西和浙江等地(图 3)(范德廉等, 1973; 陈南生和杨秀珍, 1987; Coveney et al., 1992; 毛景文等, 2001; Mao et al., 2002),呈北东向展布,平均厚约数十米,绵延约1600km,如此大的规模为我国所独有(Mao et al., 2002);现多采用“牛蹄塘组”命名发育这套黑色页岩的地层(罗超等, 2014; 吴陈君等, 2014; 李海等, 2016)。

|
图 3 华南寒武纪黑色页岩构造背景及分布图(据Mao et al., 2002修改) Fig. 3 Tectonic background and distribution map of the Cambrian black shale in the South China (modified after Mao et al., 2002) |
华南牛蹄塘组整体从下往上的典型层序为硅质岩、含磷结核和磷块岩的黑色页岩、Ni-Mo多金属硫化物矿层、黑色页岩,其下覆地层为新元古代灯影组白云岩或留茶坡组硅质岩(范德廉等, 2004; 蒋少涌等, 2008),两者间为平行不整合接触。不同地区,牛蹄塘组及其中黑色页岩分布不一,如鄂西地区牛蹄塘组在剖面上可大致分为两段:下段主要为灰黑色-黑色炭质页岩和炭质泥岩,见灰岩透镜体;上段地层中灰岩比例增加,页岩逐渐减少。平面上,牛蹄塘组黑色页岩厚度基本呈环带状分布(图 4),最高值位于宣恩-咸丰一线,平均厚度介于160~280m,以此为中心向四周逐渐减薄,向西北至建始、利川一带变为80~100m,向东则多在60m以下(李海等, 2016)。而黔东北地区牛蹄塘组暗色泥页岩厚度横向展布稳定,优质页岩平均厚度约40~50m,整体厚度大于30m,但平面分布不均(王玉芳等, 2016)。
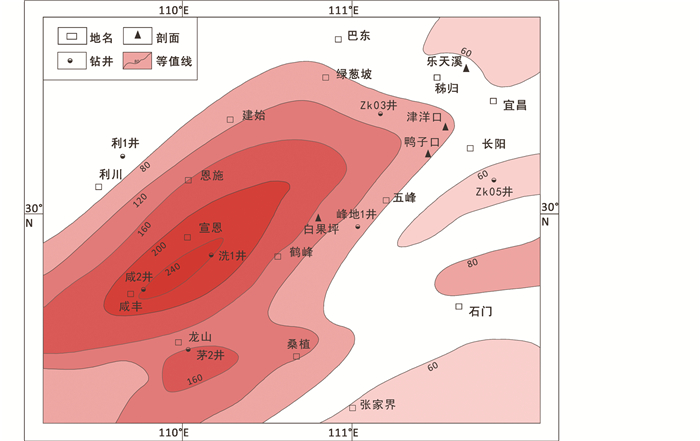
|
图 4 鄂西黑色页岩平均厚度图(据李海等,2016修改) Fig. 4 Average thickness map of black shale in the western Hubei (modified after Li et al., 2016) |
关于这套黑色页岩的沉积相,前人进行了大量研究。陈兰等(2006)通过生物标志化合物特征参数和碳同位素组成特征的研究,认为湘黔地区早寒武世黑色岩系沉积环境为贫氧-缺氧的还原环境,这与前人认为的华南黑色页岩属于滞留缺氧沉积环境一致(李任伟等, 1999; Steiner et al., 2001; 陈兰等, 2006; 杨兴莲等, 2008)。
华南寒武系黑色页岩素有“多元素富集层”之称,其底部赋存有一层极富各种金属元素的硫化物矿层,尤以富集Ni、Mo和PGE为特征,如湘西北Ni-Mo-PGE矿化带(Xu et al., 2013)、遵义Ni-Mo-PGE矿化带(Mao et al., 2002)等,这些黑色页岩也富集铼(图 5)。
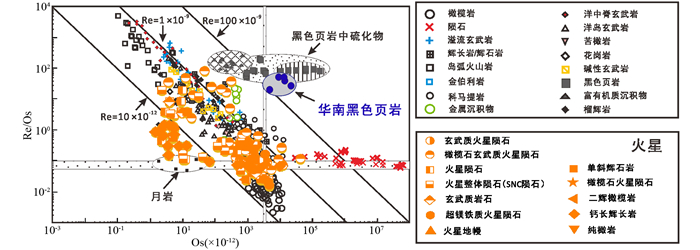
|
图 5 华南寒武纪黑色页岩中富集铼(底图孙卫东等, 2010; 华南黑色页岩数据选自Jiang et al., 2007) Fig. 5 Enrichment of rhenium in the Cambrian black shale of the South China (base map after Sun et al., 2010; data of the South China black shale from Jiang et al., 2007) |
对于黑色页岩中这些多金属矿床的形成机理及形成环境,主要有两种假说:①海底热液成因说(李胜荣和高振敏, 1995; Steiner et al., 2001; Coveney, 2003; 杨瑞东等, 2005; Jiang et al., 2006, 2007; Orberger et al., 2007; 蒋少涌等, 2008; Chen et al., 2009; Han et al., 2017);②海水成因说(Mao et al., 2002; Lehmann et al., 2007; Yin et al., 2017)。最近,Lan et al.(2017)通过对湖南、贵州等地牛蹄塘组黑色页岩内Ni-Mo-PGE矿床地球化学特征的分析,认为其成矿物质具有海水、热液以及陆源碎屑三者混合成因。华南寒武系黑色页岩中另一类重要资源就是页岩气,目前的研究已经划定了一些页岩气勘探区和远景区(何金先等, 2011; 李海等, 2016; 王玉芳等, 2016)。
本文初步的研究认为华南寒武纪黑色页岩多种性质迥异的金属同时富集可能与埃迪卡拉纪大气氧突然升高(图 6a)(Smit and Mezger, 2017; Lyons et al., 2014; Saltzman et al., 2011; Scott et al., 2008; Sahoo et al., 2012)和生命大爆发(朱茂炎, 2010; Orberger et al., 2007)有关。在大气氧升高之前,铼在表生过程中被氧化的量很少。寒武纪时大气氧的突然升高到原来的100倍以上,导致大量的铼在表生过程中集中被氧化,聚集到水体中。而生命大爆发促进了还原性物质的累积(Butterfield, 2009, 2011),形成黑色页岩,将水体中的铼富集到黑色页岩中(图 6b)。甚至铼可能与镍钼等金属一同参与了生命过程中。

|
图 6 地球大气氧含量随时间演化图(a, 据Lyons et al., 2014; Smit and Mezger, 2017修改)及海洋体系铼的物质来源和主要的迁移和沉积过程简图(b, 据Jiang et al., 2006修改) PO2-大气氧分压;PAL-当前大气水平;左纵轴表示相对于当前大气水平的氧分压;右纵轴表示氧分压 Fig. 6 The evolution of the earth's atmospheric oxygen content over time (a, modified after Lyons et al., 2014; Smit and Mezger, 2017) and chematic diagram of the material sources and main migration and sedimentary processes of Re in marine systems (b, modified after Jiang et al., 2006) PO2-atmospheric partial pressure of oxygen; PAL-present atmospheric level; left longitudinal axis, partial pressure of oxygen relative to the present atmospheric level; right longitudinal axis, partial pressure of oxygen |
黑色页岩中的铼金属含量巨大。我国华南广泛分布寒武纪黑色页岩,仅鄂西分布范围就有数千平方千米,其中铼含量达到0.1×10-6~0.6×10-6,据保守估计,前景资源量在万吨以上(表 1)。但是,黑色页岩中的铼作为一种远景战略资源,目前的研究程度及勘查力度都相对薄弱,一方面是因为目前还缺乏将铼元素从页岩中进行工业分离、回收的工艺(于世昆和伍艳辉, 2010; 冯宝奇等, 2013; 邬建辉等, 2015);另一方面则是由于目前的铼矿产量研究多集中在硫化物、铂族元素及铀矿物等伴生矿物(Mao et al., 2002; Aminzadeh et al., 2011; Xu et al., 2013),对黑色页岩中铼的地球化学行为及其伴生矿物形式认识不足。基于我国目前面临的铼矿形势及未来对铼矿的需求,本文建议加大对黑色页岩中铼的研究,包括地质勘查、分离、回收等,以满足国家经济发展的需要。
|
|
表 1 部分华南黑色页岩中铼含量及其中Ni-Mo硫化物层中铼含量 Table 1 Rhenium contents of the black shale and Ni-Mo sulfides from the South China |
铼因其具有耐高温、耐熔蚀的特性,在航空制造业中占有十分重要的地位。作为中度不相容的亲铜、亲铁元素,铼对地表环境敏感,在表生过程中强烈富集。斑岩铜矿伴生的辉钼矿和还原性沉积岩是铼的主要富集类型。我国斑岩钼矿床分布不均,辉钼矿中铼含量总体偏低,很多没有达到回收利用的伴生矿品位。我国华南广泛分布寒武纪黑色页岩,其中铼含量达到0.1×10-6~0.6×10-6,远景资源量在万吨以上,是寻找铼矿的最佳选区。
致谢 感谢四位匿名审稿人对本文提出的宝贵意见和建议。
Aminzadeh B, Shahabpour J and Maghami M. 2011. Variation of rhenium contents in molybdenites from the Sar Cheshmeh porphyry Cu-Mo deposit in Iran. Resource Geology, 61(3): 290-295 DOI:10.1111/j.1751-3928.2011.00165.x |
Bartlett SC, Burgess, Harry, Dajanovic, Bogdan, Gowans RM and Lattanzi CR. 2013. Technical report on the copper-silver production operations of KGHM Polska Miedz' S.A. in the Legnica Glogów copper belt area of southwestern Poland. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Micon International Ltd
|
Bernard A and Dumortier P. 1986. Identification of natural rhenium sulfide (ReS2) in volcanic fumaroles from the Usu volcano, Hokkaido, Japan. In: Imura T, Maruse S and Suzuki T (eds.). Proceedings of the XIth International Congress on Electron Microscopy. Tokyo, Japan: Japanese Society of Electron Microscopy, 1691-1692
|
Bernard A, Symonds RB and Rose WI Jr. 1990. Volatile transport and deposition of Mo, W and Re in high temperature magmatic fluids. Applied Geochemistry, 5(3): 317-326 |
Bosch F, Faestermann T, Friese J, Heine F, Kienle P, Wefers E, Zeitelhack K, Beckert K, Franzke B, Klepper O, Kozhuhariv C, Menzel G, Moshammer R, Nolden F, Reich H, Schlitt B, Steck M, Stohlker Th, Winkler Th and Takahashi K. 1996. Observation of bound-state β-decay of fully ionized 187Re:187Re-187Os cosmochronometry. Physical Review Letters, 77(26): 5190-5193 DOI:10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.5190 |
Butterfield NJ. 2009. Macroevolutionary turnover through the Ediacaran transition:Ecological and biogeochemical implications. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 326(1): 55-66 DOI:10.1144/SP326.3 |
Butterfield NJ. 2011. Animals and the invention of the Phanerozoic Earth system. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 26(2): 81-87 |
Cao C, Zhao YY, Shui XF, Chang YH, Shen W and Yang YQ. 2014. Occurrence and distribution regularity of by-product elements in porphyry Cu-Mo deposits. Contributions to Geology & Mineral Resources Research, 29(1): 1-12 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Chen DZ, Wang JG, Qing HR, Yan DT and Li RW. 2009. Hydrothermal venting activities in the Early Cambrian, South China:Petrological, geochronological and stable isotopic constraints. Chemical Geology, 258(3-4): 168-181 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.10.016 |
Chen L, Zhong H, Hu RZ and Xiao JF. 2006. Composition of organic carbon isotope of Early Cambrian black shale in the Xiang-Qian area and its significances. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 26(1): 81-85 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Chen NS and Yang XZ. 1987. Studies of Lizhe molybdenum ore deposit of sedimentary-magmatic hydropneumatic, origin, Lizhe, Zhejiang Province. Geochimica, (3): 208-214 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Chen YJ, Li C, Zhang J, Li Z and Wang HH. 2000. Sr and O isotopic characteristics of porphyries in the Qinling molybdenum deposit belt and their implication to genetic mechanism and type. Science in China (Series D), 43(Suppl.1): 82-94 |
Chen YJ, Zhai MG and Jiang SY. 2009. Significant achievements and open issues in study of orogenesis and metallogenesis surrounding the North China continent. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11): 2695-2726 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Colodner D, Edmond J and Boyle E. 1995. Rhenium in the Black Sea:Comparison with molybdenum and uranium. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 131(1-2): 1-15 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(95)00010-A |
Coveney RM Jr, Murowchick JB, Grauch RI, Glascock MD and Denison JR. 1992. Gold and platinum in shales with evidence against extraterrestrial sources of metals. Chemical Geology, 99(1-3): 101-114 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(92)90033-2 |
Coveney RM. 2003. Re-Os dating of polymetallic Ni-Mo-PGE-Au mineralization in Lower Cambrian black shales of South China and its geological significance:A discussion. Economic Geology, 98(3): 661-662 |
Cui G, Wang JY, Zhang JX and Cui G. 2008. U-Pb SHRIMP dating of zircons from Duobaoshan granodiorite in Heilongjiang and its geological significance. Global Geology, 27(4): 387-394 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Cui SJ and Guo NN. 2013. Comprehensive utilization of 277 tailings reservoirs in Luanchuan County. Resource Guide, (9): 34 (in Chinese) |
Dai JZ, Mao JW, Zhao CS, Xie GQ, Yang FQ and Wang YT. 2009. New U-Pb and Re-Os age data and the geodynamic setting of the Xiaojiayingzi Mo (Fe) deposit, western Liaoning Province, northeastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 35(2): 235-244 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2008.10.001 |
Deng G, Wu H and Lu QM. 2004. Geological characteristics and prospecting mark of the Baishan porphyry Mo deposit, East Tianshan. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(11): 1132-1138 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Du AD, He HL, Yin NW, Zou XQ, Sun YL, Sun DZ, Chen SZ and Qu WJ. 1994. A study on the rhenium-osmium geochronometry of molybdenites. Acta Geologica Sinica, 68(4): 339-347 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Du AD, Qu WJ, Li C and Yang G. 2009. A review on the development of Re-Os isotopic dating methods and techniques. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 28(3): 288-304 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Du L, Long XP, Yuan C, Zhang YY, Huang ZY, Sun M and Xiao WJ. 2018. Petrogenesis of Late Paleozoic diorites and A-type granites in the central Eastern Tianshan, NW China:Response to post-collisional extension triggered by slab breakoff. Lithos, 318-319: 47-59 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2018.08.006 |
Du L, Yuan C, Li XP, Zhang YY, Huang ZY and Long XP. 2019a. Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications of the Carboniferous granitoids in the DananhuBelt, Eastern Tianshan Orogenic Belt. Journal of Earth Science, 30(6): 1243-1252 DOI:10.1007/s12583-019-1256-3 |
Du L, Zhang YY, Huang ZY, Li XP, Yuan C, Wu B and Long XP. 2019b. Devonian to Carboniferous tectonic evolution of the Kangguer Ocean in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China:Insights from three episodes of granitoids. Lithos, 350-351: 105243 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2019.105243 |
Fan DL, Yang XZ, Wang LF and Chen NS. 1973. Petrological and geochemical characteristics of a nickel-molybdenum-multi-element-bearing Lower-Cambrian black shale from a certain district in South China. Geochimica, (3): 143-164 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Fan DL, Zhang T and Ye J. 2004. Black Rock Series and Its Related Deposits in China. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese)
|
Fan Y, Zhou TF, Zhang DY, Yuan F, Fan Y, Ren Z and White N. 2014. Spatial and temporal distribution and metallogical background of the Chinese molybdenum deposits. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(4): 784-804 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Feng BQ, Guo JL, Ma GF, Wang W, Bai HB, Tian SS, Xie YN and Wang ZC. 2013. Research on separation and extraction of rhenium. China Molybdenum Industry, 37(1): 12-15 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Figueiredo MO, da Silva TP, Veiga JP, de Oliveira DD and Batista MJ. 2014. Towards the recovery of by-product metals from mine wastes:An X-ray absorption spectroscopy study on the binding state of rhenium in debris from a Centennial Iberian pyrite belt mine. Journal of Minerals & Materials Characterization & Engineering, 2(2): 135-143 |
Fu XK and Yin XG. 2004. Discussion on distilling rhenium from molybdnite in Jinduicheng. China Molybdenum Industry, 28(4): 37-39 (in Chinese) |
Gao S, Rudnick RL, Carlson RW, McDonough WF and Liu YS. 2002. Re-Os evidence for replacement of ancient mantle lithosphere beneath the North China Craton. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 198(3-4): 307-322 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00489-2 |
Han T, Fan HF, Zhu XQ, Wen HJ, Zhao CH and Xiao F. 2017. Submarine hydrothermal contribution for the extreme element accumulation during the Early Cambrian, South China. Ore Geology Reviews, 86: 297-308 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.030 |
He JX, Duan Y, Zhang XL and Wu BX. 2011. Geologic characteristics and hydrocarbon resource implication of the black shale in Niutitang Formation of the Lower Cambrian, Guizhou Province. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 26(3): 37-42 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Huang CY, Lang YF, Dong LJ and Fu ZG. 2011. Geological characteristics and genesis research of the Dornogobi oversize molybdenum deposit in eastern Tianshan. China Molybdenum Industry, 35: 8-17 (in Chinese) |
Huang DH, Du AD, Wu CY, Liu LS, Sun YL and Zou XQ. 1996. Metallochronology of molybdenum (copper) deposits in the North China platform:Re-Os age of molybdenite and its geological significance. Mineral Deposits, 15(4): 365-373 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Huang F, Wang DH, Zeng ZL, Zhang YZ, Zeng Y and Wen ZL. 2012. Petro-geochemical characteristics and isotope chronology study on the Yuanlingzhai porphyry Mo deposit in southern Jiangxi Province. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 36(3): 363-376 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ishihara S. 1988. Rhenium contents of molybdenites in granitoid-series rocks in Japan. Economic Geology, 83(5): 1047-1051 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.83.5.1047 |
Jiang SY, Chen YQ, Ling HF, Yang JH, Feng HZ and Ni P. 2006. Trace-and rare-earth element geochemistry and Pb-Pb dating of black shales and intercalated Ni-Mo-PGE-Au sulfide ores in Lower Cambrian strata, Yangtze Platform, South China. Mineralium Deposita, 41(5): 453-467 DOI:10.1007/s00126-006-0066-6 |
Jiang SY, Yang JH, Ling HF, Chen YQ, Feng HZ, Zhao KD and Ni P. 2007. Extreme enrichment of polymetallic Ni-Mo-PGE-Au in Lower Cambrian black shales of South China:An Os isotope and PGE geochemical investigation. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 254(1-2): 217-228 DOI:10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.03.024 |
Jiang SY, Ling HF, Zhao KD, Zhu MY, Yang JH and Chen YQ. 2008. A discussion on Mo isotopic compositions of black shale and Ni-Mo sulfide bed in the Early Cambrian Niutitang Formation in South China. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 27(4): 341-345 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
John DA, Seal RR II and Polyak DE. 2017. Rhenium. In: Schulz KJ, DeYoung JH Jr, Seal RR II and Bradley DC (eds.). Critical Mineral Resources of the United States: Economic and Environmental Geology and Prospects for Future Supply. U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1802, 1-49
|
Kojonen KK, Roberts AC, Isomaki OP, Knauf VV, Johanson BO and Pakkanen L. 2004. Tarkianite, (Cu, Fe)(Re, Mo)4S8, a new mineral species from the Hitura Mine, Nivala, Finland. The Canadian Mineralogist, 42(2): 539-544 DOI:10.2113/gscanmin.42.2.539 |
Korzhinsky MA, Tkachenko SI, Shmulovich KI, Taran YA and Steinberg GS. 1994. Discovery of a pure rhenium mineral at Kudriavy volcano. Nature, 369(6475): 51-52 DOI:10.1038/369051a0 |
Kremenetsky AA and Chaplygin IV. 2010. Concentration of rhenium and other rare metals in gases of the Kudryavy Volcano (Iturup Island, Kurile Islands). Doklady Earth Sciences, 430: 114-119 |
Kuleshevich LV, Golubev AI and Lavrov OB. 2010. Paleoproterozoic gold-bearing copper deposits and occurrences of the Karelian Craton. Doklady Earth Sciences, 432(1): 677-681 DOI:10.1134/S1028334X10050272 |
Kump L R. 2008. The rise of atmospheric oxygen. Nature, 451(7176): 277-278 DOI:10.1038/nature06587 |
Lan ZW, Li XH, Chu XL, Tang GQ, Yang SH, Yang HW, Liu H, Jiang T and Wang T. 2017. SIMS U-Pb zircon ages and Ni-Mo-PGE geochemistry of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in South China:Constraints on Ni-Mo-PGE mineralization and stratigraphic correlations. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 137: 141-162 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.12.046 |
Lehmann B, Nägler TF, Holland HD, Wille M, Mao JW, Pan JY, Ma DS and Dulski P. 2007. Highly metalliferous carbonaceous shale and Early Cambrian seawater. Geology, 35(5): 403-406 DOI:10.1130/G23543A.1 |
Li CY, Zhang H, Wang FY, Liu JQ, Sun YL, Hao XL, Li YL and Sun WD. 2012a. The formation of the Dabaoshan porphyry molybdenum deposit induced by slab rollback. Lithos, 150: 101-110 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.001 |
Li CY, Wang FY, Hao XL, Ding X, Zhang H, Ling MX, Zhou JB, Li YL, Fan WM and Sun WD. 2012b. Formation of the world's largest molybdenum metallogenic belt:A plate-tectonic perspective on the Qinling molybdenum deposits. International Geology Review, 54(9): 1093-1112 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2011.623039 |
Li FL. 2011. Geological characteristics and metallogenic epoch of Qianechong large-size porphyry Mo deposit at the northern foot of Dabie Mountains, Henan Province. Mineral Deposits, 30(3): 457-468 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li H, Liu A, Wei K and Li JT. 2016. Geological characteristic of Cambrian black shale and prediction of shale gas prospective area in western Hubei Province. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 32(2): 117-125 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li J, Zhang J and Yin L. 2018. Advances and problems of Re-Os isotope analysis of geological samples. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 37(2): 242-249 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li N, Chen YJ, Zhang H, Zhao TP, Deng XH, Wang Y and Ni ZY. 2007. Molybdenum deposits in East Qinling. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(5): 186-198 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li RW, Lu JL, Zhang SK and Lei JJ. 1999. Organic carbon isotopes of the Sinian and Early Cambrian black shale on Yangtze Platform, China. Science in China (Series D), 42(6): 595-603 DOI:10.1007/BF02877787 |
Li SR and Gao ZM. 1995. REE characteristics of black rock series of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Hunan-Guizhou provinces, China, with a discussion on the REE patterns in marine hydrothermal sediments. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 15(2): 225-229 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li SX, Chen ML, Yang DS and Wang YH. 2014. The molybdenite Re-Os age and analysis of geodynamic background in Hainan Island. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 30(3): 272-279 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li T and Ni SB. 1990. Abundance of Chemical Elements in the Earth and its Crust. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Li YF, Mao JW, Bai FJ, Li JP and He ZJ. 2003. Re-Os isotopic dating of molybdenites in the Nannihu molybdenum (tungsten) orefield in the Eastern Qinling and its geological significance. Geological Review, 49(6): 652-659 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liao RQ, Li CY, Liu H, Chen Q and Sun WD. 2019. Rhenium enrichment in the Northwest Pacific arc. Ore Geology Reviews, 115: 103176 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103176 |
Liu XH, Sun BN, Qu WJ, Kang HJ and Wu JY. 2007. Re-Os dating of molybdenite in Xiliugou W-Mo deposits in western part of North Qilin Mountains and its geological significance, 23(10): 2434-2442 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu YF, Nie FJ, Sun ZJ, Lv KP, Zhang K and Liu Y. 2011. Discovery of Chalukou superlarge scale molybdenum polymetallic deposit, northern Daxing'anlin Mountain, China, and its significance. Mineral Deposits, 30(4): 759-764 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu YH, Xi Z, Zhang ZG and Zhao QX. 2014. Geological characteristics and ore-prospecting criteria of Chaganhua Cu-Mo deposit in Houqi, Wulateh County, Inner Mongolia. Western Resources, (2): 200-202 (in Chinese) |
Lu YF, Ma LY, Qu WJ, Mei YP and Chen XQ. 2006. U-Pb and Re-Os isotope geochronology of Baoshan Cu-Mo polymetallic ore deposit in Hunan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(10): 2483-2492 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Lu ZQ, Li XJ, Qiu C and Liang BS. 2016. Geology, geochemistry and geochronology of ore-bearing intrusions in Jidetun molybdenum deposit in mid-east Jilin Province. Mineral Deposits, 35(2): 349-364 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Luo C, Liu SG, Sun W, Ran B, Wang SY, Yang D, Bai ZQ, Yu YH, Zhang X and Deng B. 2014. Pore structure characterization of black shale in the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in western Hubei and eastern Chongqing area. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 38(2): 8-17 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Lyons TW, Reinhard CT and Planavsky NJ. 2014. The rise of oxygen in Earth's early ocean and atmosphere. Nature, 506(7488): 307-315 DOI:10.1038/nature13068 |
Mao JW, Zhang GD, Du AD, Wang YT and Zeng MG. 2001. Geology, geochemistry, and Re-Os isotopic dating of the Huangjiawan Ni-Mo-PGE deposit, Zunyi, Guizhou Province:With a discussion of the polymetallic mineralization of basal Cambrian black shales in South China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 75(2): 234-243 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Mao JW, Lehmann B, Du AD, Zhang GD, Ma DS, Wang YT, Zeng MG and Kerrich R. 2002. Re-Os dating of polymetallic Ni-Mo-PGE-Au mineralization in Lower Cambrian black shales of South China and its geologic significance. Economic Geology, 97(5): 1051-1061 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.97.5.1051 |
Mao JW, Stein H, Du AD, Zhou TF, Mei YX, Li YF, Zang WS and Li JW. 2004. Molybdenite Re-Os precise dating for molybdenite from Cu-Au-Mo deposits in the Middle-Lower Reaches of Yangtze River Belt and its implications for mineralization. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78(1): 121-131 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Mao JW, Xie GQ, Bierlein F, Qü WJ, Du AD, Ye HS, Pirajno F, Li HM, Guo BJ, Li YF and Yang ZQ. 2008. Tectonic implications from Re-Os dating of Mesozoic molybdenum deposits in the East Qinling-Dabie orogenic belt. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72(18): 4607-4626 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2008.06.027 |
McCandless TE and Ruiz J. 1993. Rhenium-osmium evidence for regional mineralization in southwestern North America. Science, 261(5126): 1282-1286 DOI:10.1126/science.261.5126.1282 |
McDonough WF and Sun SS. 1995. The composition of the Earth. Chemical Geology, 120(3-4): 223-253 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(94)00140-4 |
Meng XJ, Hou ZQ, Gao YF, Huang W, Qu XM and Qu WJ. 2003. Development of porphyry copper-molybdenum-lead-zinc ore-forming system in East Gangdese belt, Tibet:Evidence from Re-Os age of molybdenite in Bangpu copper polymetallic deposit. Mineral Deposits, 22(3): 246-252 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Mi M, Li CY, Sun WD, Li DF and Zhu CH. 2017. Yaochong Mo deposit, a low-F porphyry Mo deposit from the Qinling-Dabie orogenic belt. Ore Geology Reviews, 88: 188-200 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.03.029 |
Nie FJ, Zhang WY, Du AD, Jiang SH and Liu Y. 2007a. Re-Os isotopic dating on molybdenite separates from the Xiaodonggou porphyry Mo deposit, Hexigten Qi, Inner Mongolia. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(7): 898-905 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Nie FJ, Zhang WY, Jiang SH and Liu Y. 2007b. Geological features and origin of Xiaodonggou porphyry molybdenum deposit in Hexigten Banner, Inner Mongolia. Mineral Deposits, 26(6): 609-620 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Nie FJ, Sun ZJ, Li C, Liu YF, Lü KP, Zhang K and Liu Y. 2011. Re-Os isotopic dating of molybdenite separates from Chalukou porphyry Mo polymetallic deposit in Heilongjiang Province. Mineral Deposits, 30(5): 828-836 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Nie FJ, Li XZ, Li C, Zhao YA and Liu YF. 2013. Re-Os isotopic age dating of the molybdenite separated from the Caosiyao giant molybdenum deposit, Xinghe County, Inner Mongolia, and its geological significances. Geological Review, 59(1): 175-181 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Orberger B, Vymazalova A, Wagner C, Fialin M, Gallien JP, Wirth R, Pasava J and Montagnac G. 2007. Biogenic origin of intergrown Mo-sulphide-and carbonaceous matter in Lower Cambrian black shales (Zunyi Formation, southern China). Chemical Geology, 238(3-4): 213-231 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.11.010 |
Peng Z, Luo MB, Hua R and Liao ZW. 2012. Research situation on recovery of rhenium from uranium ore. Hydrometallurgy of China, 31(2): 76-80 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Polyak DE. 2013. Rhenium, in metals and minerals. U.S. Geological Survey Minerals Yearbook 2012
|
Rudnick RL and Gao S. 2014. Composition of the continental crust. In: Holland HD and Turwkian KK (eds.). Treatise on Geochemistry. 2nd Edition. Elsevier, 1-51
|
Sahoo SK, Planavsky NJ, Kendall B, Wang XQ, Shi XY, Scott C, Anbar AD, Lyons TW and Jiang GQ. 2012. Ocean oxygenation in the wake of the Marinoan glaciation. Nature, 489(7417): 546-549 DOI:10.1038/nature11445 |
Saltzman MR, Young SA, Kump LR, Gill BC, Lyons TW and Runnegar B. 2011. Pulse of atmospheric oxygen during the Late Cambrian. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(10): 3876-3881 DOI:10.1073/pnas.1011836108 |
Scott C, Lyons TW, Bekker A, Shen Y, Poulton SW, Chu X and Anbar AD. 2008. Tracing the stepwise oxygenation of the Proterozoic ocean. Nature, 452(7186): 456-459 DOI:10.1038/nature06811 |
Shao J, Yang HZ, Jia B and Peng MS. 2012. Geological characteristics and ore-forming age of Luming Mo deposit in Heilongjiang Province. Mineral Deposits, 31(6): 1301-1310 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Shirey SB and Walker RJ. 1998. The Re-Os isotope system in cosmochemistry and high-temperature geochemistry. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 26(1): 423-500 |
Smit MA and Mezger K. 2017. Earth's early O2 cycle suppressed by primitive continents. Nature Geoscience, 10(10): 788-792 DOI:10.1038/ngeo3030 |
Stein HJ, Markey RJ, Morgan JW, Hannah JL and Scherstén A. 2001. The remarkable Re-Os chronometer in molybdenite:How and why it works. Terra Nova, 13(6): 479-486 DOI:10.1046/j.1365-3121.2001.00395.x |
Steiner M, Wallis E, Erdtmann BD, Zhao YL and Yang RD. 2001. Submarine-hydrothermal exhalative ore layers in black shales from South China and associated fossils:Insights into a Lower Cambrian facies and bio-evolution. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 169(3-4): 165-191 DOI:10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00208-5 |
Sun WD, Bennett VC, Eggins SM, Arculus RJ and Perfit MR. 2003a. Rhenium systematics in submarine MORB and back-arc basin glasses:Laser ablation ICP-MS results. Chemical Geology, 196(1-4): 259-281 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00416-3 |
Sun WD, Bennett VC, Eggins SM, Kamenetsky VS and Arculus RJ. 2003b. Enhanced mantle-to-crust rhenium transfer in undegassed arc magmas. Nature, 422(6929): 294-297 DOI:10.1038/nature01482 |
Sun WD, Ling MX and Yin QZ. 2010. Chemical evolution of the Moon:A review. Geochimica, 39(2): 131-141 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun WD, Li CY, Ling MX, Ding X, Yang XY, Liang HY, Zhang H and Fan WM. 2015. The geochemical behavior of molybdnum and mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(7): 1807-1817 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun WD, Li CY, Hao XL, Ling MX, Ireland T, Ding X and Fan WM. 2016. Oceanic anoxic events, subduction style and molybdenum mineralization. Solid Earth Sciences, 1(2): 64-73 DOI:10.1016/j.sesci.2015.11.001 |
Sun YL, Guan XY and Du AD. 1997. Preconcentration of precious metal elements by nickel sulphide fire assay: Ⅰ. Determination of platinum group elements in geological samples by ICP-MS. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 16(1): 12-17 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Tan G, Chang GX, She HQ, Li JW, Zhang DQ, Yang XC, Zhang B, Xiang AP and Dong YJ. 2010. Rhenium-osmium isotope dating of molybdate from Wunuetushan porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, Inner Mongolia and its geological significance. Mineral Deposits, 29(Suppl.1): 506-508 (in Chinese) |
Taylor SR and McLennan SM. 1995. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(2): 241-265 |
Tian LQ, Fan SY, Wang HM and Liu SL. 2016. Study of enrichment of scattered rhenium in Xuchang coal mine in Jining City. Shandong Land and Resources, 32(2): 35-38 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Voudouris PC, Melfos V, Spry PG, Bindi L, Kartal T, Arikas K, Moritz R and Ortelli M. 2009. Rhenium-rich molybdenite and rheniite in the Pagoni Rachi Mo-Cu-Te-Ag-Au prospect, northern Greece:Implications for the Re geochemistry of porphyry-style Cu-Mo and Mo mineralization. Canadian Mineralogist, 47(5): 1013-1036 DOI:10.3749/canmin.47.5.1013 |
Wang CH. 2006. Production practice of recovering associated valuable elements in Dexing copper mine. Metal Mine, (5): 77-79 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang CH, Song QH, Wang DH, Li LX, Yu C, Wang ZG, Qu WJ, Du AD and Ying LJ. 2009. Re-Os isotopic dating of molybdenite from the Daheishan molybdenum deposit of Jilin Province and its geological significance. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 28(3): 269-273 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang YF, Leng JG, Li P and Li F. 2016. Characteristics and its main enrichment controlling factors of shale gas of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in northeastern Guizhou Province. Journal of Palaeogeography, 18(4): 605-614 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang ZL, Yang ZM, Yang ZS, Tian SH, Liu YC, Ma YQ, Wang GR and Qu WJ. 2008. Narigongma porphery molybdenite copper deposit, northern extension of Yulong copper belt:Evidence from the age of Re-Os isotope. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(3): 503-510 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wei QG, Yao JM, Zhao TP, Sun YL, Li J, Yuan ZL and Qiao B. 2009. Discovery of a~1.9Ga Mo deposit in the eastern Qinling orogen:Molybdenite Re-Os ages of the Longmendian Mo deposit in Henan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11): 2747-2751 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wu CJ, Zhang MF, Ma WY, Liu Y, Xiong DM, Sun LN and Tuo JC. 2014. Organic matter characteristic and sedimentary environment of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang shale in southeastern Chongqing. Natural Gas Geoscience, 25(8): 1267-1274 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wu JH, Zhang WH, Liu G, Su T, Wei T, Zhang GH, Dong JL and Luo MM. 2015. Research progress on resources and extraction technology of rhenium. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2: 40-44 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wu X, Li LP, Zhang WZ and Zhang X. 2008. Properties of rhenium and distribution of rhenium resources. Express Information of Mining Industry, 24(11): 67-69 (in Chinese) |
Xia Y, Peng GJ, Zhou WN, Zhang XH and Ma RK. 2017. Study on the occurrence state of rhenium in copper-molybdenum ore from the Fujiawu deposit, Jiangxi Province and factors affecting Re recovery. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 36(6): 659-665 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu LG, Lehmann B and Mao JW. 2013. Seawater contribution to polymetallic Ni-Mo-PGE-Au mineralization in Early Cambrian black shales of South China:Evidence from Mo isotope, PGE, trace element, and REE geochemistry. Ore Geology Reviews, 52: 66-84 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.06.003 |
Yan GL, Wang ZM, Li YQ, Fu YH and Ding GM. 2012. Re-Os isotope ages of molybdenite and their geological significance of Yechangping molybdenum deposit, Henan. Mineral Exploration, 3(2): 184-193 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang J and Yi FC. 2005. Genesis and organic carbon/sulphur characteristics of the Lower Cambrian black shale series in Guizhou-Hunan. Chinese Journal of Geology, 40(4): 457-463 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang RD, Zhu LJ, Gao H, Zhang WH, Jiang LJ, Wang Q and Bao M. 2005. A study on characteristics of the hydrothermal vent and relating biota at the Cambrian bottom in Songlin, Zunyi County, Guizhou Province. Geological Review, 51(5): 481-492 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang XL, Zhu MY, Zhao YL, Zhang JM, Guo QJ and Pi DH. 2008. REE geochemical characteristics of the Ediacaran-Lower Cambrian black rock series in eastern Guizhou. Geological Review, 54(1): 3-15 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yin RS, Xu LG, Lehmann B, Lepak RF, Hurley JP, Mao JW, Feng XB and Hu RZ. 2017. Anomalous mercury enrichment in Early Cambrian black shales of South China:Mercury isotopes indicate a seawater source. Chemical Geology, 467: 159-167 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.08.010 |
Ying LJ, Tang JX, Wang DH, Chang ZS, Qu W and Zheng WB. 2009. Re-Os isotopic dating of molybdenite in skarn from the Jiama copper polymetallic deposit of Tibet and its metallogenic significance. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 28(3): 265-268 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yu SK and Wu YW. 2010. Progress of research on rhenium separation and enrichment. China Molybdenum Industry, 34(2): 7-12 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yuan HC, Wang RT, Jiao JG, Li W, Liu WQ and Tan W. 2014. Re-Os isotopic ages of molybdenites from Xigou Mo deposit in Huaxian of East Qinling and their geological significance. Journal of Earth Sciences & Environment, 36(1): 120-127 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yudovskaya MA, Tessalina S, Distler VV, Chaplygin IV, Chugaev AV and Dikov YP. 2008. Behavior of highly-siderophile elements during magma degassing:A case study at the Kudryavy volcano. Chemical Geology, 248(3-4): 318-341 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.12.008 |
Zeng QD, Liu JM, Qin KZ, Fan HR, Chu SX, Wang YB and Zhou LL. 2013. Types, characteristics, and time-space distribution of molybdenum deposits in China. International Geology Review, 55(11): 1311-1358 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2013.774195 |
Zhang QL, Qu XM, Xu WY, Hou ZQ and Chen WS. 2003. Study of the fluid inclusions from Nanmu porphyry Cu-Mo deposit in Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 19(2): 251-259 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang XG, Wang BD, Xia BB and Qiong D. 2008. Discovery of the Tangbula porphyry molybdenum-copper deposit in the eastern segment of the Gangdise metallogenic belt and its significance. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(6): 837-843 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao YY, Ma ZH and Zhong CX. 1997. A study on ore-forming geochemistry of Duobaoshan copper deposit, Heilongjiang Province. Journal of Xi'an College of Geology, 19(1): 28-35 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhou K, Ye HS, Mao JW, Qu WJ, Zhou SF, Meng F and Gao YL. 2009. Geological characteristics and molybdenite Re-Os isotopic dating of Yuchiling porphyry Mo deposit in western Henan Province. Mineral Deposits, 28(2): 170-184 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhu MY. 2010. The origin and Cambrian explosion of animals:Fossil evidences from China. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 49(3): 269-287 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
曹冲, 赵元艺, 水新芳, 常玉虎, 申维, 杨永强. 2014. 斑岩型铜钼矿床重要共(伴)生元素赋存状态与分布规律. 地质找矿论丛, 29(1): 1-12. |
陈兰, 钟宏, 胡瑞忠, 肖加飞. 2006. 湘黔地区早寒武世黑色页岩有机碳同位素组成变化及其意义. 矿物岩石, 26(1): 81-85. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2006.01.015 |
陈南生, 杨秀珍. 1987. 浙江漓渚沉积-岩浆气液叠加型钼矿床的研究. 地球化学, (3): 208-214. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1987.03.002 |
陈衍景, 李超, 张静, 李震, 王海华. 2000. 秦岭钼矿带斑岩体锶氧同位素特征与岩石成因机制和类型. 中国科学(地球科学), 30(增1): 64-72. |
陈衍景, 翟明国, 蒋少涌. 2009. 华北大陆边缘造山过程与成矿研究的重要进展和问题. 岩石学报, 25(11): 2695-2726. |
崔根, 王金益, 张景仙, 崔革. 2008. 黑龙江多宝山花岗闪长岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地质意义. 世界地质, 27(4): 387-394. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2008.04.006 |
崔世俊, 郭娜娜. 2013. 栾川县将对二百七十七座尾矿库综合利用. 资源导刊, (9): 34. |
邓刚, 吴华, 卢全敏. 2004. 东天山白山斑岩型钼矿床的地质特征及找矿标志. 地质通报, 23(11): 1132-1138. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.11.014 |
杜安道, 何红蓼, 殷宁万, 邹晓秋, 孙亚利, 孙德忠, 陈少珍, 屈文俊. 1994. 辉钼矿的铼-锇同位素地质年龄测定方法研究. 地质学报, 68(4): 339-347. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1994.04.005 |
杜安道, 屈文俊, 李超, 杨刚. 2009. 铼-锇同位素定年方法及分析测试技术的进展. 岩矿测试, 28(3): 288-304. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2009.03.019 |
范德廉, 杨秀珍, 王连芳, 陈南生. 1973. 某地下寒武统含镍钼多元素黑色岩系的岩石学及地球化学特点. 地球化学, (3): 143-164. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1973.03.001 |
范德廉, 张焘, 叶杰. 2004. 中国的黑色岩系及其有关矿床. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
范羽, 周涛发, 张达玉, 袁峰, 范裕, 任志, White N. 2014. 中国钼矿床的时空分布及成矿背景分析. 地质学报, 88(4): 784-804. |
冯宝奇, 郭金亮, 马高峰, 王伟, 白宏斌, 田莎莎, 谢亚宁, 王子川. 2013. 铼的分离提取技术研究. 中国钼业, 37(1): 12-15. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2602.2013.01.003 |
符新科, 尹孝刚. 2004. 金堆城精矿提取铼金属方法探讨. 中国钼业, 28(4): 37-39. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2602.2004.04.010 |
何金先, 段毅, 张晓丽, 吴保祥. 2011. 贵州地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组黑色页岩地质特征及其油气资源意义. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 26(3): 37-42. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2011.03.007 |
黄超勇, 郎岩峰, 董理践, 付治国. 2011. 东天山东戈壁特大型钼矿床地质特征及成因研究. 中国钼业, 35(3): 8-17. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2602.2011.03.003 |
黄典豪, 杜安道, 吴澄宇, 刘兰笙, 孙亚莉, 邹晓秋. 1996. 华北地台钼(铜)矿床成矿年代学研究-辉钼矿铼-锇年龄及其地质意义. 矿床地质, 15(4): 365-373. |
黄凡, 王登红, 曾载淋, 张永忠, 曾跃, 温珍连. 2012. 赣南园岭寨大型钼矿岩石地球化学、成岩成矿年代学及其地质意义. 大地构造与成矿学, 36(3): 363-376. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.03.008 |
蒋少涌, 凌洪飞, 赵葵东, 朱茂炎, 杨竞红, 陈永权. 2008. 华南寒武纪早期牛蹄塘组黑色岩系中Ni-Mo多金属硫化物矿层的Mo同位素组成讨论. 岩石矿物学杂志, 27(4): 341-345. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2008.04.011 |
李法岭. 2011. 河南大别山北麓千鹅冲特大隐伏斑岩型钼矿床地质特征及成矿时代. 矿床地质, 30(3): 457-468. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.03.007 |
李海, 刘安, 危凯, 李继涛. 2016. 鄂西地区寒武系黑色页岩地质特征及页岩气远景预测. 华南地质与矿产, 32(2): 117-125. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2016.02.003 |
李杰, 张晶, 尹露. 2018. 地质样品的Re-Os同位素分析技术及存在的问题. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 37(2): 242-249. |
李诺, 陈衍景, 张辉, 赵太平, 邓小华, 王运, 倪智勇. 2007. 东秦岭斑岩钼矿带的地质特征和成矿构造背景. 地学前缘, 14(5): 188-200. |
李任伟, 卢家烂, 张淑坤, 雷加锦. 1999. 震旦纪和早寒武世黑色页岩有机碳同位素组成. 中国科学(D辑), 29(4): 351-357. |
李胜荣, 高振敏. 1995. 湘黔地区牛蹄塘组黑色岩系稀土特征——兼论海相热水沉积岩稀土模式. 矿物学报, 15(2): 225-229. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1995.02.017 |
李孙雄, 陈沐龙, 杨东生, 汪焰华. 2014. 海南岛钼矿床Re-Os年龄及其成矿地球动力学背景探讨. 华南地质与矿产, 30(3): 272-279. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2014.03.010 |
黎彤, 倪守斌. 1990. 地球和地壳的化学元素丰度. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
李永峰, 毛景文, 白凤军, 李俊平, 和志军. 2003. 东秦岭南泥湖钼(钨)矿田Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义. 地质论评, 49(6): 652-659. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2003.06.014 |
刘晓煌, 孙柏年, 屈文俊, 康鸿杰, 吴靖宇. 2007. 北祁连山西段西柳沟钨钼矿的Re-Os定年及地质意义. 岩石学报, 23(10): 2434-2442. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.012 |
刘翼飞, 聂凤军, 孙振江, 吕克鹏, 张可, 刘勇. 2011. 岔路口特大型钼多金属矿床的发现及其意义. 矿床地质, 30(4): 759-764. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.04.016 |
刘永慧, 席忠, 张志刚, 赵清旭. 2014. 内蒙古乌拉特后旗查干花铜钼矿床地质特征及找矿标志. 西部资源, (2): 200-202. |
路远发, 马丽艳, 屈文俊, 梅玉萍, 陈希清. 2006. 湖南宝山铜-钼多金属矿床成岩成矿的U-Pb和Re-Os同位素定年研究. 岩石学报, 22(10): 2483-2492. |
卢志强, 李绪俊, 秋晨, 梁本胜. 2016. 吉林中东部季德屯钼矿床含矿岩体地质、地球化学及年代学研究. 矿床地质, 35(2): 349-364. |
罗超, 刘树根, 孙玮, 冉波, 王世玉, 杨迪, 白志强, 叶玥豪, 张旋, 邓宾. 2014. 鄂西-渝东地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组黑色页岩孔隙结构特征. 东北石油大学学报, 38(2): 8-17. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2014.02.002 |
毛景文, 张光弟, 杜安道, 王义天, 曾明果. 2001. 遵义黄家湾镍钼铂族元素矿床地质、地球化学和Re-Os同位素年龄测定-兼论华南寒武系底部黑色页岩多金属成矿作用. 地质学报, 75(2): 234-243. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2001.02.013 |
毛景文, Stein H, 杜安道, 周涛发, 梅燕雄, 李永峰, 藏文栓, 李进文. 2004. 长江中下游地区铜金(钼)矿Re-Os年龄测定及其对成矿作用的指示. 地质学报, 78(1): 121-131. |
孟祥金, 侯增谦, 高永丰, 黄卫, 曲晓明, 屈文俊. 2003. 西藏冈底斯东段斑岩铜钼铅锌成矿系统的发育时限:帮浦铜多金属矿床辉钼矿Re-Os年龄证据. 矿床地质, 22(3): 246-252. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2003.03.004 |
聂凤军, 张万益, 杜安道, 江思宏, 刘妍. 2007a. 内蒙古小东沟斑岩型钼矿床辉钼矿铼-锇同位素年龄及地质意义. 地质学报, 81(7): 898-905. |
聂凤军, 张万益, 江思宏, 刘妍. 2007b. 内蒙古小东沟斑岩钼矿床地质特征及成因探讨. 矿床地质, 26(6): 609-620. |
聂凤军, 孙振江, 李超, 刘翼飞, 吕克鹏, 张可, 刘勇. 2011. 黑龙江岔路口钼多金属矿床辉钼矿铼-锇同位素年龄及地质意义. 矿床地质, 30(5): 828-836. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.05.006 |
聂凤军, 李香资, 李超, 赵宇安, 刘翼飞. 2013. 内蒙古兴和县曹四夭特大型钼矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及地质意义. 地质论评, 59(1): 175-181. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2013.01.019 |
彭真, 罗明标, 花榕, 廖桢葳. 2012. 从矿石中回收铼的研究进展. 湿法冶金, 31(2): 76-80. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-2617.2012.02.003 |
邵军, 杨宏智, 贾斌, 彭明生. 2012. 黑龙江鹿鸣钼矿床地质特征及成矿年龄. 矿床地质, 31(6): 1301-1310. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2012.06.014 |
孙卫东, 凌明星, Yin QZ. 2010. 月球的化学演化. 地球化学, 39(2): 131-141. |
孙卫东, 李聪颖, 凌明星, 丁兴, 杨晓勇, 梁华英, 张红, 范蔚茗. 2015. 钼的地球化学性质与成矿. 岩石学报, 31(7): 1807-1817. |
孙亚莉, 管希云, 杜安道. 1997. 锍试金富集贵金属元素: Ⅰ.等离子体质谱法测定地质样品中痕量铂族元素. 岩矿测试, 16(1): 12-17. |
谭钢, 常国雄, 佘宏全, 李进文, 张德全, 杨郧城, 张斌, 向安平, 董英君. 2010. 内蒙古乌奴格吐山斑岩铜钼矿床辉钼矿铼-锇同位素定年及其地质意义. 矿床地质, 29(增1): 506-508. |
田立强, 范士彦, 王红梅, 刘松良. 2016. 济宁许厂煤矿伴生分散元素铼的富集成矿探析. 山东国土资源, 32(2): 35-38. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2016.02.007 |
王诚华. 2006. 德兴铜矿伴生有价元素回收的生产实践. 金属矿山, (5): 77-79. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2006.05.021 |
王成辉, 松权衡, 王登红, 李立兴, 于城, 汪志刚, 屈文俊, 杜安道, 应立娟. 2009. 吉林大黑山超大型钼矿辉钼矿铼-锇同位素定年及其地质意义. 岩矿测试, 28(3): 269-273. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2009.03.015 |
王玉芳, 冷济高, 李鹏, 李飞. 2016. 黔东北地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气特征及主控因素分析. 古地理学报, 18(4): 605-614. |
王召林, 杨志明, 杨竹森, 田世洪, 刘英超, 马彦青, 王贵仁, 屈文俊. 2008. 纳日贡玛斑岩钼铜矿床:玉龙铜矿带的北延-来自辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄的证据. 岩石学报, 24(3): 503-510. |
魏庆国, 姚军明, 赵太平, 孙亚莉, 李晶, 原振雷, 乔波. 2009. 东秦岭发现~1.9Ga钼矿床-河南龙门店钼矿床Re-Os定年. 岩石学报, 25(11): 2747-2751. |
吴陈君, 张明峰, 马万云, 刘艳, 熊德明, 孙丽娜, 妥进才. 2014. 渝东南牛蹄塘组页岩有机质特征及沉积环境研究. 天然气地球科学, 25(8): 1267-1274. |
邬建辉, 张文宏, 刘刚, 苏涛, 魏涛, 张光华, 董俊龙, 罗妹妹. 2015. 铼的资源和提取技术研究进展. 中国资源综合利用, 2: 40-44. |
吴贤, 李来平, 张文钲, 张新. 2008. 铼的性质及铼资源分布. 现代矿业快报, 24(11): 67-69. |
夏瑜, 彭光菊, 周卫宁, 张新海, 马荣锴. 2017. 江西富家坞矿床铜钼矿石中铼元素的赋存状态及其回收影响因素分析. 岩矿测试, 36(6): 659-665. |
晏国龙, 王佐满, 李永全, 傅渊辉, 丁高明. 2012. 河南夜长坪钼矿辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及地质意义. 矿产勘查, 3(2): 184-193. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2012.02.010 |
杨剑, 易发成. 2005. 贵州-湖南黑色岩系的有机碳和有机硫特征及成因意义. 地质科学, 40(4): 457-463. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2005.04.001 |
杨瑞东, 朱立军, 高慧, 张位华, 姜立君, 王强, 鲍淼. 2005. 贵州遵义松林寒武系底部热液喷口及与喷口相关生物群特征. 地质论评, 51(5): 481-492. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2005.05.001 |
杨兴莲, 朱茂炎, 赵元龙, 张俊明, 郭庆军, 皮道会. 2008. 黔东震旦系-下寒武统黑色岩系稀土元素地球化学特征. 地质论评, 54(1): 3-15. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.01.002 |
应立娟, 唐菊兴, 王登红, 畅哲生, 屈文俊, 郑文宝. 2009. 西藏甲玛铜多金属矿床矽卡岩中辉钼矿铼-锇同位素定年及其成矿意义. 岩矿测试, 28(3): 265-268. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2009.03.014 |
于世昆, 伍艳辉. 2010. 铼的分离提取研究进展. 中国钼业, 34(2): 7-12. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2602.2010.02.002 |
袁海潮, 王瑞廷, 焦建刚, 李伍义, 刘文庆, 谭雯. 2014. 东秦岭华县西沟钼矿床Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义. 地球科学与环境学报, 36(1): 120-127. |
张绮玲, 曲晓明, 徐文艺, 侯增谦, 陈伟十. 2003. 西藏南木斑岩铜钼矿床的流体包裹体研究. 岩石学报, 19(2): 251-259. |
张兴国, 王保弟, 夏抱本, 穷达. 2008. 冈底斯成矿带东段汤不拉斑岩钼(铜)矿的发现及意义. 地质通报, 27(6): 837-843. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.06.012 |
赵元艺, 马志红, 仲崇学. 1997. 多宝山铜矿床成矿作用地球化学研究. 西安地质学院学报地球科学与环境学报, 19(1): 28-35. |
周珂, 叶会寿, 毛景文, 屈文俊, 周树峰, 孟芳, 高亚龙. 2009. 豫西鱼池岭斑岩型钼矿床地质特征及其辉钼矿铼-锇同位素年龄. 矿床地质, 28(2): 170-184. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.02.006 |
朱茂炎. 2010. 动物的起源和寒武纪大爆发:来自中国的化石证据. 古生物学报, 49(3): 269-287. |
 2020, Vol. 36
2020, Vol. 36


