2. 有色金属矿山深部资源勘查工程技术研究中心, 北京 100012;
3. 中国地质大学地球科学与资源学院, 北京 100083
2. Technical Research Center for Deep Resources Exploration in Non-ferrous Metal Mines, Beijing 100012, China;
3. School of Earth Sciences and Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China
富钠质岩石和铁(铜)等多金属矿床有着密切的联系(Williams, 1994;Frietsch et al., 1997;Oliver et al., 2004;Smith et al., 2007;毛景文等,2008;Sheibi, 2014),这些与成矿有关的岩石不仅具有钠含量高的特点(杨峰华,2001;Fei et al., 2005;姜福芝和王玉往,2005;张招崇等,2016),而且矿床的形成与富钠质岩石具有时间上耦合(Oliver et al., 2004;Bonyadi et al., 2011;钟富明,2016)、空间上密切共生的关系(沈保丰等,1977;Mark and Foster, 2000;刘妍等,2002;Kontonikas-Charos et al., 2014)。阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带是中亚造山带南缘新疆地区重要的铁(铜)等矿产资源产区(王登红等,2006;董连慧等,2011),带内发育多种成因矿床类型(王京彬等,2006),但尤以赋存于火山地层中的铁(铜)矿床最为突出(姜福芝等,2002;徐仕琪等,2011;董连慧等,2011;李厚民等,2014;Hou et al., 2014)。带内大面积发育近东西向展布的石炭系火山岩地层,占其总面积的四分之三以上。前人已对该带内火山岩进行了大量的年代学和岩石地球化学等方面的研究工作(方维萱等,2006;苏春乾等,2009;罗婷等,2012;Hou et al., 2014;杨富全等,2016),但对带内火山岩的富钠特征研究较为缺乏,特别是对钠长石(化)的形成过程与带内铁(铜)等多金属成矿关系的研究,目前尚属空白。为此,本文拟通过对带内富钠火山岩的成岩时代的厘定、不同类型钠长石(化)的原位主量和微量元素分析,试图探讨其成岩时代、揭示其形成条件及其与成矿的关系,结合带内富钠火山岩与矿床的时空分布特征,为找矿勘查提供另一种思路。
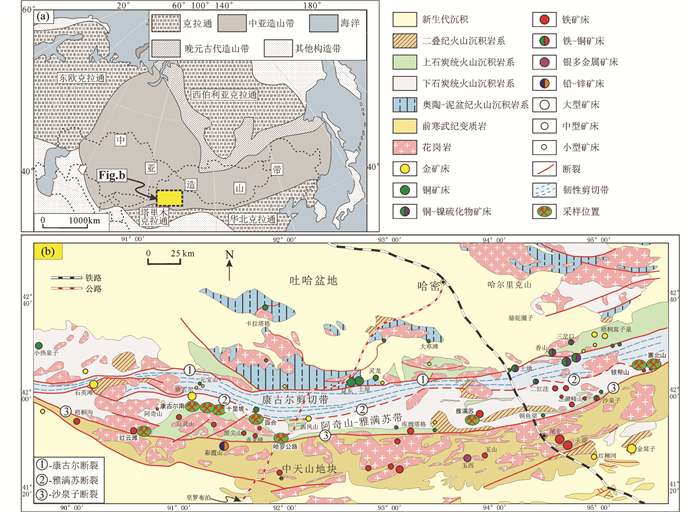
1 地质背景中亚造山带位于西伯利亚克拉通、东欧克拉通、塔里木克拉通和华北克拉通之间(图 1a),是全球主要造山带或成矿域之一(Şengör et al., 1993;Windley et al., 2007;Xiao et al., 2010)。新疆东天山作为中亚造山带的重要组成部分,在古生代经历了复杂的构造演化和成矿,成矿条件十分优越(肖序常等,1992;Gao et al., 1998;李锦轶等,2006),形成了新疆乃至我国重要的铁、铜、金、镍、铅、锌和钼等矿床成矿区带(秦克章等,2002;Mao et al., 2005;王京彬等,2006)。东天山在构造上以近东西向的深大断裂为界,将其从北向南依次划分为博格达-哈尔里克构造带、觉罗塔格构造带和中天山地块(图 1b)。根据断裂和矿床展布特点,觉罗塔格构造带进一步可划分为三个次一级的构造单元,自北向南分别为:吐哈盆地南缘大南湖-头苏泉铜矿带(北带)、康古尔金矿带(中带)和阿奇山-雅满苏铁(铜)银多金属矿带(南带)(王京彬等,2006)。
|
图 1 中亚造山带构造简图(a, 据Jahn et al., 2000)和东天山地区地质矿产简图(b, 据王京彬等,2006) Fig. 1 Tectonic sketch map of the Central Asia Orogenic Belt (a, modified after Jahn et al., 2000) and geological map and deposits distribution in the Eastern Tianshan (b, modified after Wang et al., 2006) |
大南湖-头苏泉带位于吐哈盆地以南,康古尔断裂以北,带内主要发育奥陶系-石炭系火山岩地层,火山岩属于岛弧拉斑和岛弧钙碱性系列(马瑞士等,1993;芮宗瑶等,2002;王京彬等,2006),且火山岩时空分布指示该带弧岩浆前锋带的演化具有向南逐渐迁移的特点(李锦轶等,2006)。其中奥陶系大柳沟组(O2d)主要为海相长英质火山岩地层,属于钠质的钙碱性系列岩石,该组中发育海相环境下的VMS型矿床,以卡拉塔格红海矿床为代表(毛启贵等,2010)。至泥盆纪末到早石炭世,演化成陆相环境,含铜花岗质岩浆上升侵位到浅部形成土屋、延东等斑岩型矿床(韩春明等,2006)。带内南部西段下石炭统小热泉子组(C1x)为海相火山岩地层,由长英质火山岩组成,两个火山喷发旋回的火山沉积层中发育小热泉子VMS型矿床(王京彬等,2006)。
康古尔-黄山韧性剪切带位于康古尔和雅满苏大断裂之间,为一套变质变形较强的石炭系火山-沉积岩系(张达玉,2012),具有右行韧性剪切变形的特点(张连昌,1999),可划分为4~6条强变形的糜棱岩带(杨兴科等,1998),韧性剪切变形时代在260~240Ma左右(陈文等,2005)。该带内金、铜-镍成矿作用发育,金矿床主要赋存于雅满苏组和干墩组地层中,受构造变形控制明显(陈文等,2005;张达玉,2012),铜-镍矿床主要分布于带内东部的北缘地区,成矿时代主要集中在二叠纪(刘威,2017)。
阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带位于东天山觉罗塔格构造带南部,向北以雅满苏断裂为界和康古尔韧性剪切带相邻,向南以阿奇克库都克断裂为界和中天山地块相邻(图 1b),是东天山重要的铁(铜)等多金属成矿带。带内主要出露石炭系火山岩地层,少量二叠系和第四系地层。其中石炭系地层包括下石炭统阿奇山组(C1a)、雅满苏组(C1y)和上石炭统土古土布拉克组(C2tgt)。阿奇山组主要分布于该带西部沙泉子断裂以北,该组主要由灰绿色玄武岩、灰褐色蚀变安山岩、熔结角砾岩、熔结凝灰岩组成,夹透镜状砂岩和灰岩等,苏春乾等(2009)获得该组中流纹英安岩锆石U-Pb年龄为341.7±2.7Ma。雅满苏组在带内分布范围广泛,主要为一套海相火山岩-碳酸盐建造。杨兴科等(1998)在雅满苏组安山岩下灰岩中采集有棱菊石化石,认为其属于早石炭世;罗婷等(2012)对雅满苏组英安岩、流纹岩进行锆石U-Pb定年,从东至西,年龄分别为348.0±1.7Ma、335.9±2.4Ma、334.0±2.5Ma。土古土布拉克组主要分布在阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带西段的南部,在阿其克库都克断裂带以北,南接中天山地块,为一套火山熔岩、火山碎屑岩夹正常沉积岩,以火山熔岩为主,含有海百合茎和腕足化石。宋安江等(2006)对其中含砾岩屑砂岩的锆石进行SHRIMP U-Pb定年,获得年龄为314±4.2Ma。二叠系阿奇克布拉克组(P1a)主要分布在雅满苏东部景峡-木头井子地区,主要岩石组合为砾岩、砂砾岩。带内侵入岩体有闪长质岩体和花岗质岩体,包括花岗闪长岩、石英闪长岩、正长花岗岩岩体等,主要为晚古生代岩体(吴昌志等,2006;周涛发等,2010;Zhao et al., 2018),部分早中生代岩体(雷如雄等,2013)。成矿带内矿床类型主要有赋存于海相火山岩中的铁(铜)矿、矽卡岩型矿床、火山-次火山热液型铜矿以及产于玄武岩中的自然铜矿等。与海相火山岩有关的“雅满苏式”铁矿,包括红云滩铁矿、阿奇山铁矿、雅满苏铁矿等,主要产于早石炭世火山岩地层中,部分产于晚石炭世火山岩地层中,矿体大都呈层状、似层状产出,成矿时代为石炭纪(Hou et al., 2014;黄小文等,2014;Huang et al., 2018;Sun et al., 2019)。与火山-次火山热液活动型有关的铜矿主要有寨北山铜矿、铜鱼梁铜矿和景峡铜矿等(龙灵利等,2018),张达玉(2012)将该类矿床与上述“雅满苏式”铁矿同归为火山岩型铁(铜)矿。与花岗岩侵入体有关的矽卡岩型维权银多金属矿床,其成矿年龄为297±3Ma(王龙生等,2005)。
2 样品采集和岩相学特征 2.1 样品采集用于年代学测试的样品采自康古尔南地区土古土布拉克组的安山岩。用于显微镜下研究、原位电子探针主量元素和LA-ICP-MS微量元素分析的样品分别采自红云滩、雅满苏、银帮山和寨北山地区雅满苏组的火山岩;哈罗公路、十里坡西、康古尔南、十里坡和百合地区土古土布拉克组的火山岩;以及红云滩矿区的蚀变岩石、矿石等。各样品的采集分布地区见图 1b,各地区采样位置及样品描述等详见表 1。
|
|
表 1 阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带样品采样位置及特征 Table 1 The locations of samples collected from the Aqishan-Yamansu belt and their characteristics |
阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带内富钠火山岩几乎均产于石炭系海相火山-沉积环境中,岩性类型包括火山熔岩和火山碎屑岩。本次对不同地(矿)区(表 1)石炭系火山岩进行显微镜下研究,包括下石炭统雅满苏组火山岩和上石炭统土古土布拉克组火山岩。
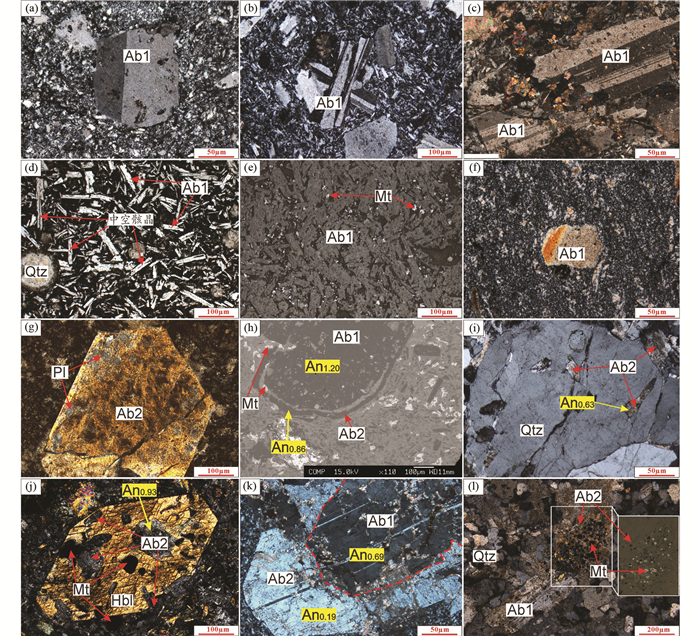
下石炭统雅满苏组可识别出两种不同类型钠长石。第一类钠长石(Ab1)常具有斜长石的典型结构特征,自形晶发育较好,呈自形-半自形,长条状、板条状,发育卡斯巴双晶(图 2a)、卡钠复合双晶和贯穿双晶(图 2b),部分发育聚片双晶(图 2c)。该类型钠长石在火山岩中常呈斑状结构或聚合斑状结构,斑晶长轴直径在100~1000μm之间,常被绿泥石、绿帘石、方解石以及晚期钠长石(第二类钠长石Ab2)交代。火山熔岩中(玄武岩、安山岩和流纹岩)中该类型钠长石常呈微晶结构,构成淬火状中空骸晶结构(图 2d)、玻晶交织结构(图 2e)、霏细结构(图 2f)等。第二类钠长石(Ab2)通常无斜长石晶形或不具有斜长石的典型结构特征,或虽有斜长石的几何形状,但其结构与第一类钠长石截然不同。该类型钠长石常呈半自形-他形,粒状、短柱状,或碎片状、面状杂乱分布(图 2g),不发育钠长石双晶、卡钠复合双晶或聚片双晶等(图 2g, j),而且其表面较模糊。该类型钠长石在火山岩中粒径大小不一,亦无固定形状,常与绿泥石、绿帘石、方解石等形成面状集合体。第二类钠长石(Ab2)通常交代火山岩中早期结晶的辉石、角闪石、斜长石、石英等呈交代残余结构(图 2g)、交代净边结构(图 2h)、交代穿孔结构(图 2i, j)、交代镶边结构(图 2k)等,有时可见被交代的暗色矿物等附近有细粒的磁铁矿颗粒(图 2h, j, l),暗示晚期钠长石化可能与带内铁矿化有关。
|
图 2 阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带雅满苏组富钠火山岩显微照片 (a) Ab1呈卡式双晶结构;(b) Ab1呈卡钠复合双晶和贯穿双晶;(c) Ab1呈聚片双晶;(d)玄武岩中Ab1呈中空骸晶结构;(e)安山岩呈玻晶交织结构,微粒磁铁矿分布其中;(f)流纹岩具霏细结构,含微晶钠长石;(g) Ab2交代早期斜长石,呈交代残余结构;(h) Ab2(边部,斜长石牌号An0.86)交代Ab1(核部,斜长石牌号An1.20),呈交代净边结构;(i)石英被Ab2(斜长石牌号An0.63)交代,呈交代穿孔结构;(j)角闪石被Ab2(斜长石牌号An0.93)交代,呈交代穿孔结构,有磁铁矿与Ab2共生;(k) Ab2(边部白色部分,斜长石牌号An0.19)交代Ab1(核部灰色部分,斜长石牌号An0.69),呈交代镶边结构;(l) Ab2交代Ab1,有磁铁矿微粒集合体与Ab2共生. (e)为反射光照片,(h)为背散射照片,其他均为正交偏光照片.缩写:Ab1-第一类钠长石;Qtz-石英;Mt-磁铁矿;Ab2-第二类钠长石;Pl-斜长石;Hbl-角闪石 Fig. 2 Photomicrographs of Na-rich volcanic rocks from the Yamansu Formation in the Aqishan-Yamansu belt (a) Ab1 showing carlsbad twin; (b) Ab1 showingcarlsbad-albite compound twin and interpenetranttwin; (c) Ab1 showing polysynthetic albite twin; (d) Ab1 showing central absent skelecton crystal texture in the basalt; (e) Ab1 showing pilotaxitic texture in the andesite; (f) the felsic texture in the rhyolite with microlite albite; (g) early plagioclase replaced by Ab2, showing metasomatic relict texture; (h) Ab1 (in the center, gray, with An1.20) replaced by Ab2 (at the edge, with An0.86); (i) quartz replaced by Ab2 (with An0.63) showing perforation texture; (j) hornblende replaced byAb2 (with An0.93) showing perforation texture, and the intergrowth between magnetite and Ab2 at the edge; (k) Ab1 (in the center, gray, An0.69) replaced by Ab2 (at the edge, white, An0.19) showing metasomatic rimmed texture; (l) Ab1 replaced by Ab2 and showing the co-existence of magnetite and Ab2. Imaging light source: (e) based on reflected light; (h) based on back-scattered electron (BSE); the rest of others based on cross-polarized light. Abbreviations: Ab1-the first type albite; Qtz-quartz; Mt-magnetite; Ab2-the second type albite; Pl-plagioclase; Hbl-hornblende |
上石炭统土古土布拉克组火山岩中钠长石呈自形-半自形,长条状、板条状,发育聚片双晶,安山岩中可见角闪石镶嵌其中(图 3a)。矿区火山岩中钠长石表面常被碳酸盐化和帘石化。英安玢岩中钠长石呈自形-半自形的长条状或磨圆状,基质呈隐晶质或微晶质结构(图 3b)。
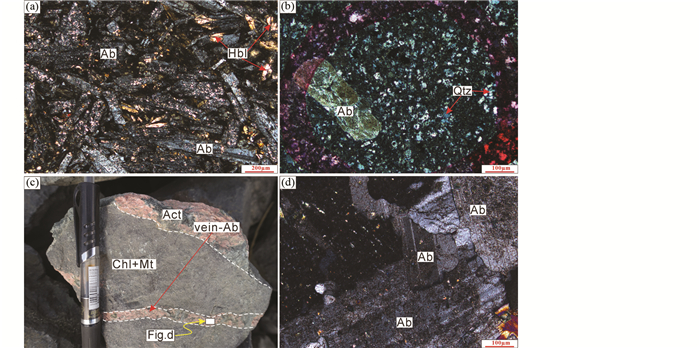
|
图 3 阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带土古土布拉克组富钠火山岩显微照片(a、b)和红云滩矿区脉状钠长石(c)及其显微镜下特征(d) (a)安山岩中钠长石自形杂乱分布,角闪石等镶嵌其中;(b)英安玢岩中自形钠长石,基质微晶质结构;(c)绿泥石+磁铁矿矿石被晚期钠长石+阳起石脉切穿;(d)钠长石呈卡钠复合双晶和聚片双晶双晶结构. (a、b、d)为正交偏光照片.缩写:Act-阳起石;Chl-绿泥石 Fig. 3 Photomicrographs of Na-rich volcanic rocks from the Tugutu Bulak Formation in the Aqishan-Yamansu belt (a, b) and vein-Ab in the Hongyuntan ore district (c) and its photomicrograph (d) (a) Ab irregularly distributed in andesite and hornblende inlayed; (b) euhedral Ab in dacite porphyry, showing microcrystalline texture; (c) massive chlorite and magnetite crosscut by vein-Ab and actinolite; (d) Ab showing carlsbad-albite compound twin and polysynthetic twin. Abbreviations: Act-actinolite; Chl-chlorite |
此外,矿区(如红云滩矿区)发育有脉状钠长石(vein-Ab)(图 3c),它们主要呈脉状,切穿块状矿石,指示形成于成矿后期。镜下特征显示该类型钠长石形晶完整,大都呈自形集合体,单晶体呈长条状、短柱状,发育卡钠复合双晶和聚片双晶双晶(图 3d)。为了进行对比,本次亦对该类型钠长石进行了研究(详见下述)。
3 分析方法 3.1 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年样品重约10kg。锆石单矿物分选工作由河北廊坊地质服务有限公司实验室完成,将样品清洗后粉碎至80目,采用重力和磁选方法分选出锆石,然后在显微镜下挑出实验所用锆石,锆石纯度大于99.9%。将分选出的锆石和标样TEMORA一起粘在玻璃板上,用环氧树脂浇铸,待环氧树脂固化后将样品制成样品靶。分析测试前,在显微镜下对锆石进行透射光、反射光照相和阴极发光(CL)扫描电镜照相。制靶和照相在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所完成。SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年实验在中国地质科学院地质研究所北京离子探针中心的SHRIMPII上完成,在实验时尽量选择显微照片下完整、无裂隙、环带结构清晰的锆石颗粒且选择锆石核部与边部之间的过度位置为最佳测试点。锆石测年实验时为5组扫描,一次离子流O2-强度为3~4nA,束斑为30μm,每分析4个样品数据则分析1个标准锆石样品(TEMORA,年龄为417Ma;Black et al., 2003)。对样品数据处理采用SQUID(Ludwig, 2001)和ISOPLOT3.0程序(Ludwig,2003),根据实测204Pb进行普通Pb校正。单个数据误差为1σ,加权平均年龄误差为95%置信度。详细测试原理、流程和方法等参考Williams(1997)和Compston et al.(1992)。
3.2 斜长石电子探针分析分析前需对样品进行岩石薄片的制备,磨制工作由北京久仁伟业矿产品加工公司制作完成。电子探针实验工作在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所电子探针(EMPA)实验室进行。在电子探针测试之前需对光薄片进行喷涂炭膜前处理。实验过程中工作仪器为JXA-8100型,分析条件选择加速电压为15kV,加速电流20nA,束斑直径3μm。实验时,在二次电子像下选择所测试对象,然后放大聚焦,选定测试点后进行测试。
3.3 斜长石原位LA-ICP-MS分析分析前需对样品进行岩石薄片的制备,磨制工作由北京久仁伟业矿产品加工公司制作完成。激光剥蚀等离子质谱(LA-ICP-MS)实验在中国中国科学院广州地球化学研究所完成。使用仪器为Thermo Element II等离子质谱仪,激光剥蚀系统为New Wave UP-213。实验采用He作为载气,波长213nm、激光束斑40μm、脉冲频率10Hz、能量0.176mJ、密度23~25J/cm2,测试中首先遮挡激光束进行空白背景采集15s,然后连续剥蚀采集45s,停止剥蚀后继续吹扫15s清洗进样系统,单点分析时间75s。等离子质谱测试参数为冷却气流速(Ar)15.55L/Min,辅助气流速(Ar)0.67L/Min,载气流速(He)0.58L/Min,样品气流速0.819L/Min,射频发生器功率1205W。测试数据采用内标和外标相结合的方法。斜长石原位LA-ICP-MS微量元素分析内标选择为Si元素,外标使用NIST SRM-610。
4 分析结果 4.1 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄康古尔南地区安山岩中挑选出的锆石在透射光下均为无色透明-半透明,阴极发光图像中形态呈自形粒状、短柱状结构,粒径多在100~200μm,大都显示出清晰的震荡韵律环带(图 4a),应属岩浆锆石。对挑选最佳的6颗锆石进行离子探针分析,U-Pb同位素分析结果见表 2。结果显示所测锆石Th/U比值均大于0.40,表明锆石为岩浆成因(Belousova et al., 2002)。获得206Pb/238U年龄分布在308.8~324.6Ma之间,样品点年龄数据均在协和线上或附近,得到加权平均年龄为313.9±5.8Ma(MSWD=1.4)(图 4b)。
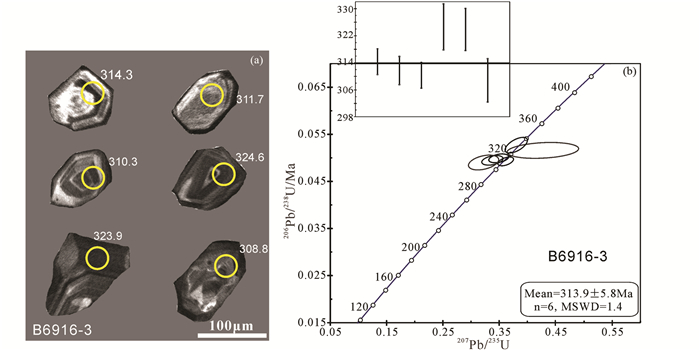
|
图 4 土古土布拉克组安山岩中锆石CL图像(a)和锆石U-Pb协和图及加权平均年龄(b) Fig. 4 Zircon CL images (a) and U-Pb concordia plot, age data bar mean ages (b) of the andesite in the Tugutu Bulak Formation |
|
|
表 2 康古尔南地区安山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb同位素分析结果 Table 2 SHRIMP zircons U-Pb isotopic data of andesite from the southern Kangguer area |
阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带不同地区石炭系富钠火山岩中斜长石主量元素分析测试结果列于表 3。测试过程可能存在系统误差和偶然误差,结果显示,所测81个样品点,除1个样品Total值大于101(可能是由于仪器不稳定造成的系统误差)和4个样品Total值小于97(可能是由于电子束的聚焦偏转所致的偶然误差)外,样品均在误差范围内。
|
|
表 3 阿奇山-雅满苏带不同地区斜长石电子探针主量元素分析结果(wt%) Table 3 Electron microprobe analyses of plagioclases from different areas in the Aqishan-Yamansu belt (wt%) |
下石炭统雅满苏组中第一类钠长石(Ab1)SiO2含量在65.24%~69.41%之间,平均为67.95%,Al2O3含量在18.31%~21.30%之间,平均为19.62%,Na2O含量在10.27%~11.75%之间,平均为11.30%,CaO和K2O含量较低,分别在0.03%~2.66%和0.02%~1.01%之间,平均分别为0.36%和0.16%,MnO、MgO和TiO2含量均很低,平均分别为0.01%、0.01%和0.01%。第一类钠长石(Ab1)An值变化很大,在0.14%~12.38%之间,平均为1.70%,Ab值在86.61%~99.60%之间,平均为97.38%,Or值在0.14%~5.86%之间,平均为0.92%。第二类钠长石(Ab2)SiO2含量在66.41%~68.98%之间,平均为67.96%,Al2O3含量在19.05%~20.27%之间,平均为19.56%,Na2O含量在10.22%~12.01%之间,平均为11.32%,CaO和K2O含量较低,分别在0.04%~1.43%和0.05%~0.43%之间,平均分别为0.29%和0.17%。第二类钠长石(Ab2)An、Ab和Or值分别在0.19%~7.04%、90.82%~99.51%和0.27%~2.44%之间,平均分别为1.41%、97.64%和0.94%。
上石炭统土古土布拉克组中斜长石SiO2含量在62.80%~69.56%之间,平均为67.28%,Al2O3含量在17.95%~22.35%之间,平均为19.80%,Na2O含量在8.28%~11.67%之间,平均为10.57%,CaO含量在0.13%~3.74%之间,平均为1.02%,K2O含量在0.04%~1.80%之间,平均为0.31%,MnO、MgO和TiO2含量均很低,部分低于检测线以下。斜长石An值变化较大,在0.62%~18.80%之间,平均为5.04%,Ab值在76.94%~98.61%之间,平均为93.10%,Or值变化较大,在0.21%~10.99%之间,平均为1.86%。
脉状钠长石(vein-Ab)SiO2含量在65.51%~68.97%之间,平均为66.78%,Al2O3含量在19.14%~20.66%之间,平均为19.84%,Na2O含量在10.03%~11.78%之间,平均为10.94%,CaO含量变化较大,0.15%~2.20%之间,均为1.12%,K2O含量较低,在0.04%~0.20%,平均为0.12%。脉状钠长石(vein-Ab)An值变化较大,0.70%~10.70%之间,平均为5.35%,Ab和Or值分别在88.50%~98.91%和0.23%~1.09%之间,平均分别为93.99%和0.66%。
整体上,下石炭统雅满苏组,从Ab1到Ab2,SiO2含量和K2O含量几乎不变,Al2O3含量和CaO含量降低,Na2O含量升高,An值降低、Ab值升高。从下石炭统雅满苏组到上石炭统土古土布拉克组,斜长石中的SiO2含量和Na2O含量降低,Al2O3含量、CaO含量和K2O含量升高,An值和Or值升高、Ab值降低。在Or-Ab-An判别图中(图 5),下石炭统雅满苏组第一类钠长石(Ab1)除红云滩地区1个样品外,均落入到钠长石区域(图 5a),第二类钠长石(Ab2)全部落入到钠长石区域(图 5b)。上石炭统土古土布拉克组中斜长石除十里坡西和哈罗公路地区的四个样品落入到更长石区域外,大都落入到钠长石区域(图 5c)。红云滩矿区成矿后的脉状钠长石(vein-Ab)除1个样品外,其余样品均落入到钠长石区域(图 5d)。
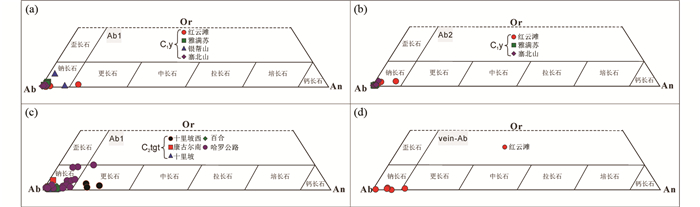
|
图 5 阿奇山-雅满苏带石炭系火山岩中不同类型斜长石成分分类图解(底图据Dana et al., 1993) Fig. 5 Classifications of different plagioclases in Carboniferous Na-rich volcanic rocks from the Aqishan-Yamansu belt (base map after Dana et al., 1993) |
斜长石原位LA-ICP-MS微量元素分析列于表 4。
|
|
表 4 阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带不同类型钠长石LA-ICP-MS微量元素组成(×10-6) Table 4 LA-ICP-MS trace element analyses of different plagioclases in the Aqishan-Yamansu belt (×10-6) |
第一类钠长石(Ab1)的稀土元素总量(∑REE)在5.16×10-6~18.90×10-6之间,平均为10.93×10-6;LREE/HRRR值在15.87~49.81之间,平均为28.07,重稀土较轻稀土亏损;δEu=5.28~17.78,平均为10.59,具有明显的正Eu异常;δCe=0.84~1.17,平均为0.98,Ce异常不明显;Rb含量在0.23×10-6~27.05×10-6之间,平均为7.49×10-6;Sr含量在228.3×10-6~336.7×10-6之间,平均为285.8×10-6;Ba含量在40.30×10-6~87.95×10-6之间,平均为59.08×10-6。
第二类钠长石(Ab2)的稀土元素总量在1.19×10-6~59.32×10-6之间,平均为13.46×10-6;LREE/HRRR值在0.71~18.69之间,平均为8.64,重稀土相对亏损;δEu=1.42~6.44,平均为3.17,具有正的Eu异常;δCe=0.84~1.06,平均为0.95,Ce异常不明显或弱的负Ce异常;Rb含量在22.97×10-6~106.7×10-6之间,平均为80.42×10-6;Sr含量在604.3×10-6~ 909.6×10-6之间,平均为727.3×10-6;Ba含量在31.85×10-6~824.5×10-6之间,平均为258.1× 10-6。
脉状钠长石(veined Ab)稀土元素总量在0.06×10-6~6.24×10-6之间,平均为1.93×10-6;LREE/HRRR值在0.98~54.13之间,平均为28.59,重稀土相对亏损;δEu=0~386.8,平均为69.01,具有明显的正Eu异常;δCe=0.70~0.95,平均为0.78,Ce负异常较明显;Rb含量在0.12×10-6~92.32×10-6之间,平均为24.35×10-6;Sr含量在0.18×10-6~167.72×10-6之间,平均为86.39×10-6;Ba含量在0.08×10-6~255.3×10-6之间,平均为66.32×10-6。
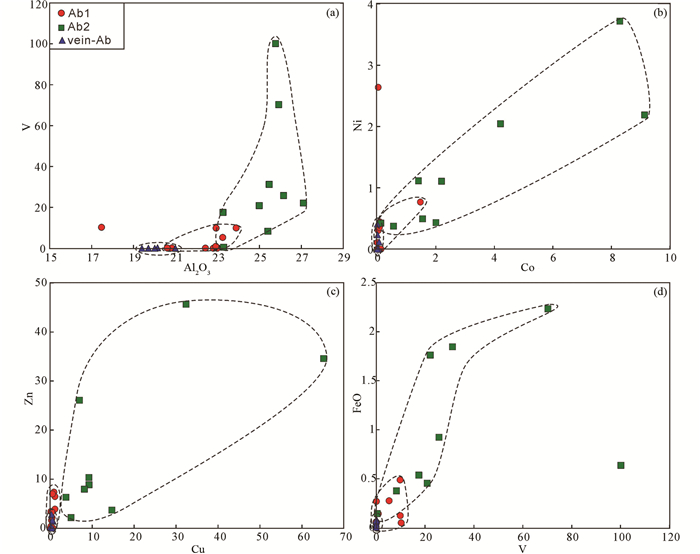
5 讨论 5.1 钠长石(化)及其与成矿关系斜长石的岩相学特征表明阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带发育有两种类型钠长石,且主量和微量元素特征亦均表明两种类型钠长石存有差异。从Ab1到Ab2,SiO2和K2O含量几乎不变,Al2O3和CaO含量降低,而Na2O含量升高(An值降低、Ab值升高),表明在Ab2形成过程中,更多富钠的流体参与了其中,暗示Ab2与区域的蚀变交代矿化有关。稀土元素和微量元素标准化图(图 6)显示,Ab2相对Ab1的元素含量和变化范围均较大,而vein-Ab的各微量元素成分总体上均很低,部分低于检测线以下。不同微量元素协变图中显示(图 7),Ab2相对于Ab1具有较大微量元素成分变化范围、较高的Al、Sr、Ca、Ba、Y、Rb和较低的Ti、LREE/HREE、δEu,表明Ab2在形成过程中可能有流体成分参与了作用(赵振华,1997),而成矿后的vein-Ab几乎任何元素含量均比Ab1和Ab2都要低,暗示成矿过程中耗尽了流体中成矿元素或其他微量元素成分,致使最晚的vein-Ab各成分含量均很低。有意义的是,相对于Ab1,Ab2含有更高的有利成矿元素(如Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、V、Zn等,图 8),该现象指示Ab2可能参与了区域的成矿作用,这和上述Ab2常与磁铁矿等金属矿物共生的岩相学证据相吻合。

|
图 6 阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带石炭系雅满苏组火山岩中不同类型钠长石及矿区脉状钠长石球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a-c)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(d-f,底图据Norman et al., 2005)(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized REE pattern diagram (a-c) and primitive-mantle normalized trace element spider diagram (d-f, base map after Norman et al., 2005) of different plagioclases in the Carboniferous Yamansu Formation Na-rich volcanic rocks and vein-Ab in the Aqishan-Yamansu belt (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
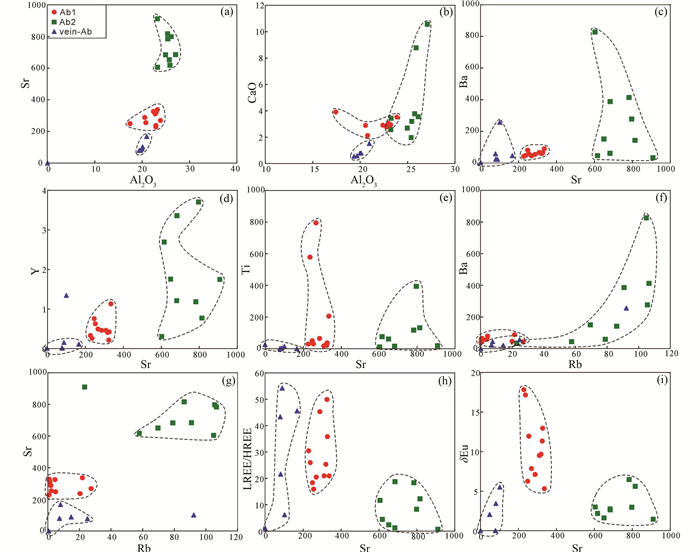
|
图 7 阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带石炭系雅满苏组火山岩中不同类型钠长石和脉状钠长石微量元素成分变化图 Fig. 7 Contents variation diagrams for different plagioclases in the Carboniferous Yamansu Formation Na-rich volcanic rocks and vein-An in the Aqishan-Yamansu belt |
|
图 8 阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带石炭系雅满苏组火山岩中不同类型钠长石及矿区脉状钠长石中的成矿微量元素成分变化图 Fig. 8 Contents variation diagrams of ore-forming trace element in different plagioclases in the Carboniferous Yamansu Formation Na-rich volcanic rocks and vein-Ab in the Aqishan-Yamansu belt |
不仅如此,在众多铁(铜)等多金属矿床的钠长石(化)过程中,均出现有多期次(或多世代)的钠长石化。如贺节明(1980)在四川拉拉铁铜矿区发现钠长石特征具有一定规律:单纯的钠长石化,或者叫做第一期钠长石化的产物,往往保留原岩外貌,继承原岩的结构构造特征,后期蚀变作用常引起钠长石化变熔岩的重结晶,使钠长石颗粒变粗,出现各种交代结构,为第二期钠长石化,且第二期钠长石化的长石牌号An值比第一期钠长石化降低5%左右。陈毓川等(1981)研究梅山铁矿发现有两期碱长石蚀变矿化,早期钠长石化一般是基质斜长石蚀变成钠长石,析出细粒磁铁矿,中期产生钠长石和钾长石,该期矿化表现在磁铁矿的假象赤铁矿化,并认为铁质的来源是由于钠长石化过程中岩石中铁的析出。Battles and Barton(1995)报道美国西部火山岩钠质蚀变有两期,早期为Na+Ca蚀变,与区域Fe矿化有关,晚期为Na蚀变,与Cu±Zn矿化有关。Oliver et al.(2004)对澳大利亚Cloncurry矿区的矿床研究发现存在多时期的钠长石化叠加,早期钠长石化与1600~1590Ma的变质事件有关,后期与1550~1500Ma期间William岩套侵位所引起的热事件有关,且矿床钠长石化过程中的地球化学特征表明,后期钠长石化过程中Na被带入,而Fe、Ba、Rb(Co、V、Mn、Pb、Zn)等被带出,被带出的元素主要富集在富铜金的铁矿石中。
综上可知,碱质交代,特别是钠长石交代,是铁(铜)等多金属矿床的一种热液蚀变作用过程(Simurkova et al., 2016)。无论含矿流体的最终沉淀方式如何,钠长石(化)交代都是成矿物质被带出、迁移和富集的重要作用(李九玲等,1979;王玉荣等,1981;杨峰华等,2001;Oliver et al., 2004;Alexandre, 2010)。阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带内广泛发育富钠火山岩及钠长石化,岩相学和矿物地球化学特征均指示钠长石化与区域蚀变矿化有密切联系,因此带内矿床的成矿物质的迁出和运移可能与钠长石(化)有关。
5.2 富钠火山岩对找矿的启示国内外关于富钠火山岩与铁(铜)矿床有密切成因联系的研究一直都受到极大关注,这些赋矿火山岩的钠含量总是偏高的,如瑞典北部的Kiruna矿区铁矿赋存在钠含量高的细碧岩-角斑岩系中(Martinsson et al., 2016);智利中生代铁矿产在富钠安山-粗面岩的火山岩中(Ménard, 1995);俄罗斯土尔盖地区铁矿主要产在钙碱性系列的富钠安山玄武岩和凝灰岩中、俄罗斯安格拉依利姆型铁矿产在钠含量高的粗玄玢岩和集块岩中、阿尔泰山地区铁矿产在角斑岩和石英斑岩等火山碎屑岩中(冶金工业部情报标准研究所,1977);伊朗中部Choghart铁氧化物-磷灰石(IOA)矿床赋存于前寒武纪富钠的火山-沉积岩中(Khoshnoodi et al., 2017)。我国宁芜-庐枞地区与铁矿有关的火山岩-次火山岩,是偏基性富钠质的闪长玢岩,且大量发育的钠长石化与铁成矿具有明显的分带关系(毛景文等,2008)。甘肃黑鹰山铁矿赋矿围岩为富钠质火山岩(角斑岩-石英角斑岩系),钠长石化与铁矿关系密切(刘妍等,2002)。近些年研究程度较高的我国西天山海相火山岩型铁矿赋矿围岩也为富钠火山岩系(张招崇等,2016)。
成矿地质体是指与矿床形成在时间、空间和成因上有密切联系的地质体(叶天竺等,2014)。赋存于海相火山岩中的铁(铜)矿床一般产于火山岩地层中,为火山同期活动的产物,成矿地质体即为海相火山岩。国内外与海相火山岩有关的铁(铜)矿床的成岩、成矿年代学研究显示,在误差范围内,矿床的成矿年龄和赋矿火山岩年龄具有高度的一致性,或成矿年龄略晚于成岩年龄,如瑞典Kiruna矿床(Cliff et al., 1990;Romer et al., 1994)、伊朗Bafq矿床(Ramezani and Tucker, 2003;Bonyadi et al., 2011)以及我国的云南大红山矿床(张招崇等,2016)和新疆的蒙库矿床(张保江等,2012;张招崇等,2016)、查岗诺尔矿床(汪帮耀,2011;洪为,2012)、智博矿床(蒋宗胜,2014)等。以上研究表明铁(铜)矿床的形成与海底火山活动有密切关系。阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带火山机构广泛发育,显示以中心式和裂隙喷发为主,铁(铜)等矿床的分布受火山机构的控制,矿床的形成几乎均与火山喷发中心有密切关系(王正铤,1980;张安和丁天府,1984;丁天府,1990;徐仕琪等,2011)。而且近年来成岩和成矿年代学研究亦发现,矿床的成矿年龄与火山岩的成岩年龄在误差范围内一致,如沙泉子矿床(杨富全等,2016)、黑峰山-双峰山矿床(杨富全等,2016;Huang et al., 2013)、雅满苏矿床(Hou et al., 2014;Huang et al., 2018)和红云滩矿床(郑仁乔,2015;Sun et al., 2019)等。因此带内铁(铜)矿床可能与火山作用有关,成矿受火山活动控制。
矿床成因是矿床勘查的向导,而成矿地质体的厘定是寻找同类型矿床的先决条件。阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带石炭纪火山岩浆活动强烈,矿床受火山机构控制作用明显,且矿床与海相富钠火山岩有空间上和时间上的耦合关系,因此,对带内该类型矿床的勘查指导应该围绕火山活动中心及其周围构造单元,并重点对富钠火山岩系来展开。
6 结论(1) 阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带内石炭系海相火山岩为富钠火山岩系,获得康古尔南地区上石炭统土古土布拉克组安山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄为313.9±5.8Ma,形成于晚石炭世。
(2) 下石炭统雅满苏组富钠火山岩中斜长石为钠长石,少量更长石,识别出两种类型钠长石(Ab1和Ab2)的存在,Ab2不仅在形态和结构上,而且在元素成分上均与Ab1相异。上石炭统土古土布拉克组富钠火山岩中斜长石亦为钠长石和少量更长石。从下石炭统雅满苏组到上石炭统土古土布拉克组,其火山岩中斜长石的SiO2含量和Na2O含量降低,Al2O3含量、CaO含量和K2O含量升高,An值和Or值升高、Ab值降低。
(3) 雅满苏组Ab2形成过程中,更多富钠流体、更多成矿元素参与其中,Ab2可能与带内的蚀变交代及矿化有关。阿奇山-雅满苏成矿带内海相富钠火山岩与矿床有空间上和时间上的耦合关系,指示找矿勘查工作应重视富钠火山岩。
谨以此文祝贺肖序常院士90华诞!祝先生青松不老、万寿无疆、身体安康、幸福吉祥!
Alexandre P. 2010. Mineralogy and geochemistry of the sodium metasomatism-related uranium occurrence of Aricheng South, Guyana. Mineralium Deposita, 45(4): 351-367 DOI:10.1007/s00126-010-0278-7 |
Battles DA and Barton MD. 1995. Arc-related sodic hydrothermal alteration in the western United States. Geology, 23(10): 913-916 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0913:ARSHAI>2.3.CO;2 |
Belousova EA, Griffin WL, O'Reilly SY and Fisher NI. 2002. Igneous zircon:Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 143(5): 602-622 DOI:10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7 |
Black LP, Kamo SL, Allen CM, Aleinikoff JN, Davis DW, Korsch RJ and Foudoulis C. 2003. TEMORA 1:A new zircon standard for Phanerozoic U-Pb geochronology. Chemical Geology, 200(1-2): 155-170 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(03)00165-7 |
Bonyadi Z, Davidson GJ, Mehrabi B, Meffre S and Ghazban F. 2011. Significance of apatite REE depletion and monazite inclusions in the brecciated Se-Chahun iron oxide-apatite deposit, Bafq district, Iran:Insights from paragenesis and geochemistry. Chemical Geology, 281(3-4): 253-269 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.12.013 |
Chen W, Sun S, Zhang Y, Xiao WJ, Wang YT, Wang QL, Jiang LF and Yang JT. 2005. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Qiugemingtashi-Huangshan ductile shear zone in East Tianshan, Xinjiang, NW China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(6): 790-804 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Chen YC, Sheng JF and Ai YD. 1981. Meishan iron deposit:An ore-magma-hydrothermal deposit. Journal of Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2(1): 26-48 (in Chinese) |
Cliff RA, Rickard D and Blake K. 1990. Isotope systematics of the Kiruna magnetite ores, Sweden:Part 1, Age of the ore. Economic Geology, 85(8): 1770-1776 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.85.8.1770 |
Compston W, Williams IS, Krischvink JL, Zhang ZC and Ma GG. 1992. Zircon U-Pb ages for the Early Cambrian time-scale. Journal of the Geological Society, 149(2): 171-184 DOI:10.1144/gsjgs.149.2.0171 |
Dana JD, Klein C and Hurlbut CS Jr. 1993. Manual of Mineralogy. New York: Wiley
|
Ding TF. 1990. The geological characteristics of stratabound iron deposits in the Yamansu Formation in Xinjiang. Regional Geology of China, (3): 269-272 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Dong LH, Feng J, Zhuang DZ, Li FM, Qu X, Liu DQ and Tang YL. 2011. Discussion of metallogenic models, mineralization characteristic and main type of rich-iron ore of Xinjiang. Xinjiang Geology, 29(4): 416-422 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Fang WX, Gao ZQ, Jia RX, Liu ZT, Li FS and Xu GD. 2006. Geological exploration potentials and geochemical study on rocks and ores in Shaquanzi copper and copper-iron deposits, East Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5): 1413-1424 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Fei HC, Xiao RG, Cheng L and Wang CZ. 2005. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of Na-rich rocks in the Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. In: Mao J and Bierlein FP (eds.). Mineral Deposit Research: Meeting the Global Challenge. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 385-388
|
Frietsch R, Tuisku P, Martinsson O and Perdahl JA. 1997. Early Proterozoic Cu-(Au) and Fe ore deposits associated with regional Na-Cl metasomatism in northern Fennoscandia. Ore Geology Reviews, 12(1): 1-34 DOI:10.1016/S0169-1368(96)00013-3 |
Gao J, Li MS, Xiao XC, Tang YQ and He GQ. 1998. Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Tianshan orogen, northwestern China. Tectonophysics, 287(1-4): 213-231 DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00211-4 |
Han CM, Xiao WJ, Cui B, Mao QG, Zhang JE and Ao SJ. 2006. Major types and characteristics of Late Paleozoic copper deposits in north Xinjiang, northwest China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(1): 74-89 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
He JM. 1980. The albite metasomatites and their original rocks, Lala Huili, western Sichuan. Bulletin of Chengdu Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, The Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1(1): 59-79 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hong W. 2012. Geological characteristics and ore genesis of the Chagangnuoer iron deposit in the western Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang, NW China. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1-124(in Chinese)
|
Hou T, Zhang ZC, Santosh M, Encarnacion J and Zhu Jand Luo WJ. 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of submarine volcanic rocks in the Yamansuiron deposit, eastern Tianshan mountains, NW China:Constraints on the metallogenesis. Ore Geology Reviews, 56: 487-502 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.03.008 |
Huang XW, Qi L, Gao JF and Zhou MF. 2013. First reliable Re-Os ages of pyrite and stable isotope compositions of Fe(-Cu) deposits in the Hami region, Eastern Tianshan orogenic belt, NW China. Resource Geology, 63(2): 166-187 DOI:10.1111/rge.12003 |
Huang XW, Qi L, Wang YC and Liu YY. 2014. Re-Os dating of magnetite from the Shaquanzi Fe-Cu deposit, eastern Tianshan, NW China. Science China (Earth Sciences), 57(2): 267-277 DOI:10.1007/s11430-013-4660-z |
Huang XW, Zhou MF, Beaudoin G, Gao JF and Qi Land Lyu C. 2018. Origin of the volcanic-hosted Yamansu Fe deposit, eastern Tianshan, NW China:Constraints from pyrite Re-Os isotopes, stable isotopes, and in situ magnetite trace elements. Mineralium Deposita, 53(7): 1039-1060 DOI:10.1007/s00126-018-0794-4 |
Institute of Information Standards and Ministry of Metallurgical Industry. 1977. Volcanic Rock-type Rich Iron Deposits from Abroad. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press (in Chinese)
|
Jahn BM, Wu FY and Chen B. 2000. Granitoids of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and continental growth in the Phanerozoic. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 91(1-2): 181-193 DOI:10.1017/S0263593300007367 |
Jiang FZ, Qin KZ, Fang TH and Wang SL. 2002. Types, geological characteristics, metallogenic regularity and exploration target of iron deposits in Eastern Tianshan Mountains. Xinjiang Geology, 20(4): 379-383 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Jiang FZ and Wang YW. 2005. Marine Volcanic Rocks and Related Metallic Ore Deposits. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press (in Chinese)
|
Jiang ZS. 2014. Carboniferous volcanism and Fe mineralization at the Zhibo iron deposit in the Western Tianshan. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1-179(in Chinese)
|
Khoshnoodi K, Behzadi M, Gannadi-Maragheh M and Yazdi M. 2017. Alkali metasomatism and Th-REE mineralization in the Choghart deposit, Bafq district, Central Iran. Geologia Croatica, 70(1): 53-69 DOI:10.4154/gc.2017.03 |
Kontonikas-Charos A, Ciobanu CL and Cook NJ. 2014. Albitization and redistribution of REE and Y in IOCG systems:Insights from Moonta-Wallaroo, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. Lithos, 208-209: 178-201 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.09.001 |
Lei RX, Wu CZ, Zhang ZZ, Gu LX, Tang JH and Li GR. 2013. Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic significances of the Yamansubei pluton in Eastern Tianshan, Northwest China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(8): 2653-2664 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li HM, Ding JH, Li LX and Yao T. 2014. The genesis of the skarn and the genetic type of the Yamansuiron deposit, Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(12): 2477-2489 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li JL, Liu YS, Miao WP and Qu GL. 1979. Experimental studies on the albitization of diorite-porphyrite. Acta Geologica Sinica, (1): 60-73 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li JY, Wang KZ, Sun GH, Mo SG, Li WQ, Yang TN and Gao LM. 2006. Paleozoic active margin slices in the southern Turfan-Hamibasin:Geological records of subduction of the Paleo-Asian Ocean Plate in Central Asian Regions. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5): 1087-1102 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu W. 2017. The genesis of Aqishan first iron deposit of Jueluotage tectonic belt in the Eastern Tianshan. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Liu Y, Nie FJ, Jiang SH, Su XX and Wang XJ. 2002. Petrographic study on sodium-rich volcanic rocks in Heiyingshan xenotime-iron deposit. Mineral Deposits, 21(Suppl.): 334-337 (in Chinese) |
Long LL, Wang JB, Wang YW, Sun ZY, Zhao LT and Shi Y. 2018. Geological characteristics, metallogenic age of hydrothermal vein-type copper deposit, Zhaibeishan, eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang and discussion of the deposit genesis. Mineral Exploration, 9(12): 2282-2291 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ludwig KR. 2001. Squid 1. 02: A User's Manual. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, No. 2
|
Ludwig KR. 2003. Using ISOPLOT/Ex: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel Version 3.0. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication, 1-40
|
Luo T, Liao QA, Chen JP, Zhang XH, Guo DB and Hu ZC. 2012. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of the volcanic rocks from Yamansu Formation in the eastern Tianshan, and its geological significance. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 37(6): 1338-1352 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ma RS, Wang CG and Ye SF. 1993. Tectonic Framework and Crust Evolution of Eastern Tianshan Mountains. Nanjing: Nanjing University Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Mao JW, Goldfarb RJ, Wang YT, Hart CJ, Wang ZL and Yang JM. 2005. Late Paleozoic base and precious metal deposits, East Tianshan, Xinjiang, China:Characteristics and geodynamic setting. Episodes, 28(1): 23-36 DOI:10.18814/epiiugs/2005/v28i1/003 |
Mao JW, Yu JJ, Yuan SD, Cheng YB, Xie GQ, Hou KJ, Xiang JF and Yang ZX. 2008. Iron oxide-copper-gold deposits:Characteristics, present research situationand ore prospecting. Mineral Deposits, 27(3): 267-278 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Mao QG, Fang TH, Wang JB, Wang SL and Wang N. 2010. Geochronology studies of the Early Paleozoic Honghai massive sulfide deposits and its geological significance in Kalatage area, eastern Tianshan Mountain. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(10): 3017-3026 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Mark G and Foster DRW. 2000. Magmatic-hydrothermal albite-actinolite-apatite-rich rocks from the Cloncurry district, NW Queensland, Australia. Lithos, 51(3): 223-245 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00069-9 |
Martinsson O, Billström K, Broman C, Weihed P and Wanhainen C. 2016. Metallogeny of the northern Norrbottenore Province, northern Fennoscandian Shield with emphasis on IOCG and apatite-iron ore deposits. Ore Geology Reviews, 78: 447-492 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.02.011 |
Ménard JJ. 1995. Relationship between altered pyroxene diorite and the magnetite mineralization in the Chilean iron belt, with emphasis on the El Algarrobo iron deposits (Atacama region, Chile). Mineralium Deposita, 30(3-4): 268-274 DOI:10.1007/BF00196362 |
Norman M, Garcia MO and Pietruszka AJ. 2005. Trace-element distribution coefficients for pyroxenes, plagioclase, and olivine in evolved tholeiites from the 1955 eruption of Kilauea Volcano, Hawai'i, and petrogenesis of differentiated rift-zone lavas. American Mineralogist, 90(5-6): 888-899 DOI:10.2138/am.2005.1780 |
Oliver NHS, Cleverley JS, Mark G, Pollard PJ, Fu B, Marshall LJ, Rubenach MJ, Williams PJ and Baker T. 2004. Modeling the role of sodic alteration in the genesis of iron oxide-copper-gold deposits, Eastern Mount Isa block, Australia. Economic Geology, 99(6): 1145-1176 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.99.6.1145 |
Qin KZ, Fang TH, Wang SL, Zhu BQ, Feng YM, Yu HF and Xiu QY. 2002. Plate tectonics division, evolution and metallogenic settings in eastern Tianshan Mountains, NW China. Xinjiang Geology, 20(4): 302-308 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ramezani Jand Tucker RD. 2003. The Saghand region, Central Iran:U-Pb geochronology, petrogenesis and implications for Gondwana tectonics. American Journal of Science, 303(7): 622-665 DOI:10.2475/ajs.303.7.622 |
Romer RL, Martinsson O and Perdahl JA. 1994. Geochronology of the Kiruna iron ores and hydrothermal alterations. Economic Geology, 89(6): 1249-1261 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.89.6.1249 |
Rui ZY, Wang LS, Wang YT and Liu YL. 2002. Discussion onmetallogenic epoch of Tuwu and Yandong porphyry copper deposits in eastern Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang. Mineral Deposits, 21(1): 16-22 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Şengör AMC, Natal'in BA and Burtman VS. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia. Nature, 364(6435): 299-307 DOI:10.1038/364299a0 |
Sheibi M. 2014. Chemistry of minerals and mass changes of elements during sodiccalcic alteration of the Panj-Kuh intrusive body (Damghan, Iran). Journal of Petrology, 4(1): 87-102 |
Shen BF, Lu SN, Yu EZ, Shan LF and Yu JH. 1977. The characteristics of sodium metasomatism in magnetite deposits of a certain region and its prospecting significance. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 12(3): 263-274 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Simurkova M, Ivan P and Gargulák M. 2016. Subsolidus alkali metasomatism in the metamorphosed Ordovician acid volcanicsand volcaniclastics of the Gelnica Group (Gemeric Superunit, Western Carpathians). Acta Geologica Slovaca, 8(1): 87-98 |
Smith M, Coppard J and Herrington Rand Stein H. 2007. The geology of the Rakkurijarvi Cu-(Au) prospect, Norrbotten:A new iron oxide copper-gold deposit in northern Sweden. Economic Geology, 102(3): 393-414 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.102.3.393 |
Song AJ, Zhu ZX, Shi Y and Li SH. 2006. SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircons from the Tugutu Bulak Formation in the western segment of the Aqqikkuduk fault in the East Tianshan, Xinjiang, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(8): 953-956 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Su CQ, Jiang CY, Xia MZ, Wei W and Pan R. 2009. Geochemistry and zircons SHRIMP U-Pb age of volcanic rocks of Aqishan Formation in the eastern area of North Tianshan, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(4): 901-915 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematic of oceanic basalts: Implicationsfor mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345
|
Sun ZY, Long LL, Wang YW, Luo ZH, Hu QT and Wang ML. 2019. Geology, chronology, fluid inclusions, and H-O-S isotopic compositions of the Hongyuntan magnetite deposit, Eastern Tianshan, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 172: 328-345 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.09.016 |
Wang BY. 2011. Geological characteristics and genesis of Chagangnuoer and Zhibo volcanogenic iron deposit, in Western Tianshan, Xinjiang. Ph. D. Dissertation. Xi'an: Changan University (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Wang DH, Li CJ, Chen ZH, Chen SP, Xiao KY, Li HQ and Liang T. 2006. Metallogenic characteristics and direction in mineral search in the East Tianshan, Xinjiang, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(8): 910-915 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang JB, Wang YW and He ZJ. 2006. Ore deposits as a guide to the tectonic evolution in the East Tianshan Mountains, NW China. Geology in China, 33(3): 461-469 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang LS, Li HQ, Liu DQ and Chen YC. 2005. Geological characteristics and mineralization epoch of Weiquansilver (copper) deposit, Hami, Xinjiang, China. Mineral Deposits, 24(3): 280-284 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang YR, Fan WL and Yu YM. 1981. Geochemical mechamism of alkali metasomatism and the formation of iron deposits. Geochimica, (1): 95-103 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang ZT. 1980. A discussion on minerogenetic model of Hongyuntan iron deposit in the northern Tianshan Mountain. Bulletin of Chinese Academy Geological Science, 1(2): 115-127 (in Chinese) |
Williams IS. 1997. U-Th-Pb geochronology by Ion Microprobe. In: McKibbenMA, Shanks WC and Ridley WI (eds.). Applications of Micro Analytical Techniques to Understanding Mineralizing Processes. Reviews in Economic Geology, 7: 1-35
|
Williams PJ. 1994. Iron mobility during synmetamorphic alteration in the Selwyn Range area, NW Queensland:Implications for the origin of ironstone-hosted Au-Cu deposits. Mineralium Deposita, 29(3): 250-260 |
Windley BF, Alexeiev D, Xiao WJ, Kröner A and Badarch G. 2007. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Journal of the Geological Society, 164(1): 31-47 DOI:10.1144/0016-76492006-022 |
Wu CZ, Zhang ZZ, Zaw K, Della-Pasque F, Tang JH, Zheng YC, Wang CS and San JZ. 2006. Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic significances of the Hongyuntan granitoids in the Qoltagarea, Eastern Tianshan. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5): 1121-1134 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xiao WJ, Mao QG, Windley BF, Han CM, Qu JF, Zhang JE, Ao SJ, Guo QQ, Cleven NR, Lin SF, Shan YH and Li JL. 2010. Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional processes of the Beishan orogenic collage. American Journal of Science, 310(10): 1553-1594 DOI:10.2475/10.2010.12 |
Xiao XC, Tang YQ, Feng YM, Zhu BQ, Li JY and Zhao M. 1992. Tectonic Evolution of the Northern Xinjiang and Its Adjacent Regions. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-167 (in Chinese)
|
Xu LL, Chai FM, Li Q, Zeng H, Geng XX, Xia F and Deng G. 2014. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb age of volcanic rocks from the Shaquanzi Fe-Cu deposit in East Tianshan Mountains and their geological significance. Geology in China, 41(6): 1771-1790 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu SQ, Zhao TY, Feng J, Gao YF, Tian JT, Yang ZF and Liu DQ. 2011. Study on regional metallogenic regularity of marine volcanic type iron ore in the East Tianshan of Xinjiang. Xinjiang Geology, 29(2): 173-177 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang FH. 2001. The relation of natriiumlization and metallogenesis in Daye iron deposit, Hubei. Geology and Prospecting, 37(6): 20-24 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang FQ, Geng XX, Li Q, Chai FM, Zhang ZL, Wang C, Zheng JH and Yang JJ. 2016. Iron Polymetallic Deposits in North Xinjiang. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Yang XK, Ji JS, Zhang LC and Zeng ZR. 1998. Basic features and gold prognosis of the regional ductile shear zone in Eastern Tianshan. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 22(3): 209-218 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ye TZ, Lv ZC and Pang ZS, et al. 2014. Metallogenic Prognosis Theories and Methods in Exploration Areas. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Zhang A and Ding TF. 1984. Paleovolcanic bend and its ore-control character in the Yamansu, Xinjiang. Northwestern Geology, (3): 19-24 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang BJ, Li Q, Geng XX, Yang FQ and Liu F. 2012. SHRIMP U-Pb age of the amphibolite from Mengkuiron deposit and its geological implications in Altay, Xinjiang. Xinjiang Geology, 30(3): 277-282 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang DY. 2012. Petrogenesis, mineralization and geodynamic evolution in Jueluotage area, eastern Tianshan, Northwest China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zhang LC. 1999. Study and prognosis on geological-geochemical dynamics of mineralization in Kanggultag gold copper ore belt, East Tianshan. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zhang ZC, Chai FM and Xie QH. 2016. High-angle subduction in a thermal structure with warm mantle-cool crust:Formation of submarine volcanics-hosted iron deposits. Geology in China, 43(2): 367-379 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao LD, Chen HY, Zhang L, Zhang WF, Yang JT and Yan XL. 2018. The late Paleozoic magmatic evolution of the Aqishan-yamansu belt, Eastern Tianshan:Constraints from geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes of igneous rocks. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 153: 170-192 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.07.038 |
Zhao ZH. 1997. Pinciple of Trace Element Geochemistry. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese)
|
Zheng RQ. 2015. Geological characteristics and genesis of Hongyuntan iron deposits in the Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (in Chinese with English summary) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1015391527.htm
|
Zhong FM. 2016. The research of relationship between alkaline rock and iron of Nihe iron deposit in Luzong basin, Anhui, China. Master Degree Thesis. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology (in Chinese with English summary) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y3028563
|
Zhou TF, Yuan F, Zhang DY, Fan Y, Liu S, Peng MX and Zhang JD. 2010. Geochronology, tectonic setting and mineralization of granitoids in Jueluotage area, eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(2): 478-502 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
陈文, 孙枢, 张彦, 肖文交, 王义天, 王清利, 姜立丰, 杨俊涛. 2005. 新疆东天山秋格明塔什-黄山韧性剪切带40Ar/39Ar年代学研究. 地质学报, 79(6): 790-804. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.06.008 |
陈毓川, 盛继福, 艾永德. 1981. 梅山铁矿——一个矿浆热液矿床. 中国地质科学院院报矿床地质研究所所刊, 2(1): 26-48. |
丁天府. 1990. 新疆雅满苏组层控型铁矿的地质特征. 中国区域地质, (3): 269-272. |
董连慧, 冯京, 庄道泽, 李凤鸣, 屈迅, 刘德权, 唐延龄. 2011. 新疆富铁矿成矿特征及主攻类型成矿模式探讨. 新疆地质, 29(4): 416-422. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2011.04.012 |
方维萱, 高珍权, 贾润幸, 刘正桃, 李丰收, 徐国端. 2006. 东疆沙泉子铜和铜铁矿床岩(矿)石地球化学研究与地质找矿前景. 岩石学报, 22(5): 1413-1424. |
韩春明, 肖文交, 崔彬, 毛启贵, 张继恩, 敖松坚. 2006. 新疆北部晚古生代铜矿床主要类型和地质特征. 地质学报, 80(1): 74-89. |
贺节明. 1980. 川西会理拉拉钠长交代岩及其原岩. 中国地质科学院成都地质矿产研究所文集, 1(1): 59-79. |
洪为. 2012.新疆西天山查岗诺尔铁矿地质特征与矿床成因.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质科学院, 1-124
|
黄小文, 漆亮, 王怡昌, 刘莹莹. 2014. 东天山沙泉子铜铁矿床磁铁矿Re-Os定年初探. 中国科学(地球科学), 44(4): 606-616. |
姜福芝, 秦克章, 方同辉, 王书来. 2002. 东天山铁矿床类型、地质特征成矿规律与找矿方向. 新疆地质, 20(4): 379-383. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2002.04.019 |
姜福芝, 王玉往. 2005. 海相火山岩与金属矿床. 北京: 冶金工业出版社.
|
蒋宗胜. 2014.西天山智博铁矿石炭纪火山作用与铁成矿研究.博士学位论文.北京: 中国地质科学院, 1-179
|
雷如雄, 吴昌志, 张遵忠, 顾连兴, 唐俊华, 黎广荣. 2013. 东天山雅满苏北岩体的年代学、地球化学及其构造意义. 岩石学报, 29(8): 2653-2664. |
李厚民, 丁建华, 李立兴, 姚通. 2014. 东天山雅满苏铁矿床矽卡岩成因及矿床成因类型. 地质学报, 88(12): 2477-2489. |
李锦轶, 王克卓, 孙桂华, 莫申国, 李文铅, 杨天南, 高立明. 2006. 东天山吐哈盆地南缘古生代活动陆缘残片:中亚地区古亚洲洋板块俯冲的地质记录. 岩石学报, 22(5): 1087-1102. |
李九玲, 刘玉山, 缪婉萍, 曲国林. 1979. 闪长玢岩钠长石化的实验研究. 地质学报, (1): 60-73. |
刘威. 2017.东天山觉罗塔格地区阿齐山第一铁矿矿床成因研究.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1017125514.htm
|
刘妍, 聂凤军, 江思宏, 苏旭新, 王新建. 2002. 黑鹰山磷钇-铁矿富钠质火山岩的岩相学研究. 矿床地质, 21(增): 334-337. |
龙灵利, 王京彬, 王玉往, 孙志远, 赵路通, 石煜. 2018. 东天山寨北山热液脉状铜矿地质特征、成矿时代及矿床成因初探. 矿产勘查, 9(12): 2282-2291. |
罗婷, 廖群安, 陈继平, 张雄华, 郭东宝, 胡兆初. 2012. 东天山雅满苏组火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 37(6): 1338-1352. |
马瑞士, 王赐银, 叶尚夫. 1993. 东天山构造格架及地壳演化. 南京: 南京大学出版社.
|
毛景文, 余金杰, 袁顺达, 程彦博, 谢桂青, 侯可军, 向君峰, 杨宗喜. 2008. 铁氧化物-铜-金(IOCG)型矿床:基本特征、研究现状与找矿勘查. 矿床地质, 27(3): 267-278. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2008.03.001 |
毛启贵, 方同辉, 王京彬, 王书来, 王宁. 2010. 东天山卡拉塔格早古生代红海块状硫化物矿床精确定年及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 26(10): 3017-3026. |
秦克章, 方同辉, 王书来, 朱宝清, 冯益民, 于海峰, 修群业. 2002. 东天山板块构造分区、演化与成矿地质背景研究. 新疆地质, 20(4): 302-308. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2002.04.002 |
芮宗瑶, 王龙生, 王义天, 刘玉琳. 2002. 东天山土屋和延东斑岩铜矿床时代讨论. 矿床地质, 21(1): 16-22. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2002.01.003 |
沈保丰, 陆松年, 于恩泽, 单莲芳, 郁建华. 1977. 某区磁铁矿床中钠质交代作用的特征及其找矿意义. 地质科学, 12(3): 263-274. |
宋安江, 朱志新, 石莹, 李生虎. 2006. 东天山阿其克库都克断裂西段土古土布拉克组锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年. 地质通报, 25(8): 953-956. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.08.010 |
苏春乾, 姜常义, 夏明哲, 魏巍, 潘荣. 2009. 北天山东段阿奇山组火山岩的地球化学特征及锆石U-Pb年龄. 岩石学报, 25(4): 901-915. |
汪帮耀. 2011.新疆西天山查岗诺尔和智博火山岩型铁矿矿床地质特征与成因研究.博士学位论文.西安: 长安大学 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1012142433.htm
|
王登红, 李纯杰, 陈郑辉, 陈世平, 肖克炎, 李华芹, 梁婷. 2006. 东天山成矿规律与找矿方向的初步研究. 地质通报, 25(8): 910-915. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.08.002 |
王京彬, 王玉往, 何志军. 2006. 东天山大地构造演化的成矿示踪. 中国地质, 33(3): 461-469. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.03.002 |
王龙生, 李华芹, 刘德权, 陈毓川. 2005. 新疆哈密维权银(铜)矿床地质特征和成矿时代. 矿床地质, 24(3): 280-284. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.03.007 |
王玉荣, 樊文苓, 郁云妹. 1981. 碱交代与铁矿形成的地球化学机理探讨. 地球化学, (1): 95-103. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1981.01.012 |
王正铤. 1980. 北天山红云滩铁矿成矿模式探讨. 中国地质科学院院报天津地质矿产所分刊, 1(2): 115-127. |
吴昌志, 张遵忠, Zaw K, Della-Pasque F, 唐俊华, 郑远川, 汪传胜, 三金柱. 2006. 东天山觉罗塔格红云滩花岗岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义. 岩石学报, 22(5): 1121-1134. |
肖序常, 汤耀庆, 冯益民, 朱宝清, 李锦轶, 赵民. 1992. 新疆北部及其邻区大地构造. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-167.
|
徐仕琪, 赵同阳, 冯京, 高永峰, 田江涛, 杨在峰, 刘德权. 2011. 东天山海相火山岩型铁矿区域成矿规律研究. 新疆地质, 29(2): 173-177. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2011.02.011 |
杨峰华. 2001. 湖北大冶铁山矿床钠化蚀变与成矿关系的探讨. 地质与勘探, 37(6): 20-24. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2001.06.006 |
杨富全, 耿新霞, 李强, 柴凤梅, 张振亮, 王成, 郑佳浩, 杨俊杰. 2016. 新疆北部铁多金属矿床. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
杨兴科, 姬金生, 张连昌, 曾章仁. 1998. 东天山大型韧性剪切带基本特征与金矿预测. 大地构造与成矿学, 22(3): 209-218. |
冶金工业部情报标准研究所. 1977. 国外火山岩型富铁矿. 北京: 冶金工业出版社.
|
叶天竺, 吕志成, 庞振山, 等. 2014. 勘查区找矿预测理论与方法. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
张安, 丁天府. 1984. 新疆雅满苏古火山穹窿及其控矿特征. 西北地质, (3): 19-24. |
张保江, 李强, 耿新霞, 杨富全, 刘锋. 2012. 阿尔泰蒙库铁矿斜长角闪岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及地质意义. 新疆地质, 30(3): 277-282. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2012.03.007 |
张达玉. 2012.新疆东天山觉罗塔格地区成岩成矿作用及地球动力学过程.博士学位论文.合肥: 合肥工业大学
|
张连昌. 1999.东天山康古尔塔格金铜矿带成矿地质地球化学动力学研究及预测.博士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-11415-2006044936.htm
|
张招崇, 柴凤梅, 谢秋红. 2016. 热幔-冷壳背景下的高角度俯冲:海相火山岩型铁矿的形成. 中国地质, 43(2): 367-379. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.02.001 |
赵振华. 1997. 微量元素地球化学原理. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
郑仁乔. 2015.新疆东天山红云滩铁矿床地质特征与矿床成因研究.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1015391527.htm
|
钟富明. 2016.安徽庐枞盆地泥河铁矿床碱性岩与铁成矿关系研究.硕士学位论文.合肥: 合肥工业大学 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y3028563
|
周涛发, 袁峰, 张达玉, 范裕, 刘帅, 彭明兴, 张建滇. 2010. 新疆东天山觉罗塔格地区花岗岩类年代学、构造背景及其成矿作用研究. 岩石学报, 26(2): 478-502. |
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35