2. 中国科学院大学地球与行星科学学院, 北京 100049
2. College of Earth and Planetary Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
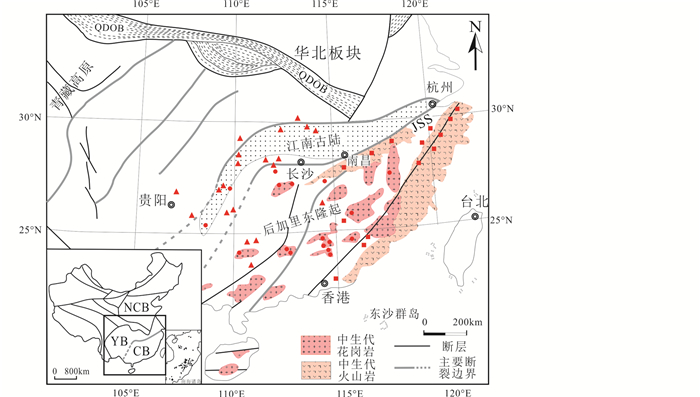
华南陆块由扬子地块和华夏地块在约830Ma的新元古代沿江绍缝合带碰撞拼贴而形成(Zhao et al., 2011)。该地块由于三叠纪印支运动的结果而沿秦岭-大别造山带、松马缝合带和龙门山断裂带,分别与北部的华北地块、南部的印支地块和西南部的青藏高原相连接(Zhou et al., 2006; Wang et al., 2007; Faure et al., 2014; 图 1)。
|
图 1 华南铀矿床区域分布略图(据Hu et al., 2008) JSS-江绍缝合带;NCB-华北地块;YB-扬子地块;CB-华夏地块;QDOB-秦岭-大别造山带.实心三角形为碳硅泥岩型铀矿床;实心方块为火山岩型铀矿床;实心圆为花岗岩型铀矿床 Fig. 1 Simplified geological map showing distribution of uranium deposits in South China (after Hu et al., 2008) JSS-Jiangshan-Shaoxin suture; NCB-North China block; YB-Yangtze block; CB-Cathaysian block; QDOB-Qingling-Dabie orogenic belt. Solid triangle: carbonaceous, siliceous and pelitic sedimentary rock-hosted uranium deposits; solid square: volcanic-hosted uranium deposits; solid circle: granite-hosted uranium deposits |
华南陆块的前寒武纪基底地层主要出露于扬子地块东南部,由新元古代浅变质杂砂岩、板岩、碳酸盐岩和硅质、泥质沉积岩组成,铀含量较高(邓平等, 2003a),大致呈北东向展布,形成千余千米并向西北凸出的弧形带,该带通称江南古陆(Zhao and Cawood, 2012)。华南的沉积盖层由寒武纪至三叠纪海相沉积岩和侏罗纪至新生代陆相沉积岩组成(Yan et al., 2003)。华南中生代的一个显著特点是,主要在华夏地块一侧发生了强烈的中酸性岩浆活动,分别形成了相互平行的内陆花岗岩带和沿海火山岩带(图 1)并显示出朝沿海方向成岩年龄变年轻的趋势(Zhou and Li, 2000)。其中,造山成因的花岗岩大致形成于145Ma前,早白垩纪的火成岩则为非造山成因。前者与太平洋板块俯冲有关,后者则是岩石圈伸展背景下的产物(李献华等, 1997; li2000; Li and Li, 2007)。与早白垩世以来的岩石圈伸展背景相对应,华南形成了一系列总体呈NE走向、充填红色陆相砂岩为主的断陷盆地,同时形成了一套幔源基性脉岩(Hu et al., 2008)。
华南以中生代W、Sn、Cu、Pb、Zn、Au、Sb、U等多金属大爆发成矿著称于世(Hu and Zhou, 2012; Mao et al., 2013; Hu et al., 2017a, b;胡瑞忠等, 2015)。根据赋矿围岩的不同,以往通常将华南广泛分布的铀矿床划分为花岗岩型、火山岩型和碳硅泥岩型等三大主要类型。碳硅泥岩型铀矿床主要分布于江南古陆及其两侧,花岗岩型铀矿床主要分布于华南后加里东隆起带上,火山岩型铀矿床则主要分布于东南沿海的大陆板块边缘地区(图 1),反映了华南主要富铀岩石的空间分布规律(Hu et al., 2008)。近年来,华南铀矿研究取得重要进展,限于篇幅和掌握的资料,以下仅是对其中部分进展的总结。
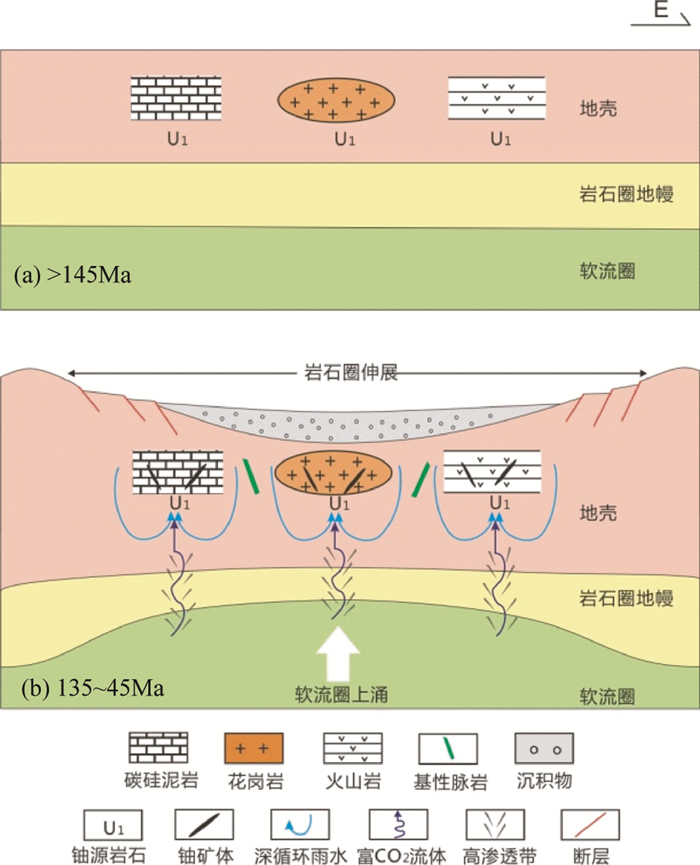
1 华南铀矿床成矿动力学研究进展对华南的上述三类铀矿床以往进行了系统研究,取得重要研究成果(北京铀矿地质研究所, 1982;陈肇博等, 1982;杜乐天, 1982, 2001; 李子颖, 2006; Hu et al., 2008)。杜乐天和王玉民(1984)认为,不同类型铀矿床的矿化特征虽存在一定差异,但具有很多共同之处。几个重要事实是:(1)都为脉型热液铀矿床。华南铀矿床多呈脉状、网脉状和似层状产出,成矿温度约为150~250℃,矿物组合以沥青铀矿、石英、萤石、方解石、黄铁矿和赤铁矿等为主,是在赋矿花岗岩、火山岩和碳硅泥岩的断层、裂隙和层间破碎带等开放空间运移的成矿流体中沉淀形成的后生脉型铀矿床(Ruzicka, 1993);(2)存在很大矿-岩时差。与华南钨锡多金属矿床同相关花岗岩时代基本一致(Hu and Zhou, 2012; Mao et al., 2013; 胡瑞忠等, 2015)很不相同,华南铀矿床与赋矿围岩存在很大时差,可达20~700Myr(杜乐天和王玉民, 1984);(3)不同类型矿床同时成矿。已有定年结果显示,虽然少数铀矿床可能形成于175~160Ma(Bonnetti et al., 2018),但华南不同类型的铀矿床主要是在白垩-古近纪形成的,且具有约~135Ma、~115Ma、~85Ma、~65Ma和~45Ma±等彼此同时的几个主成矿期(Hu et al., 2008及其中参考文献)。近年的研究发现,华南不同类型铀矿床是受白垩-古近纪岩石圈伸展事件统一控制的有机整体,三类铀矿床存在密切的内在联系(Hu et al., 2008, 2009)。通过综合分析,可用以下成矿动力学模型(图 2)进行表征,要点包括四个方面。
|
图 2 华南铀矿床成矿动力学模型 Fig. 2 The geological sketch map of metallogenic geodynamic model for uranium deposits in South China |
(一)铀矿区或邻区存在铀成矿前形成的富铀岩石。华南各类铀矿床分布区或邻区,均存在比铀成矿超前形成的相对富铀地质体,它们多形成于145Ma以前从前寒武纪至侏罗纪的各个时代。虽然这些富铀地质体的岩性和时代很不相同,但它们的铀含量远高于同类岩石的铀克拉克值(Hu et al., 2008)。
(二)铀成矿时代与岩石圈伸展时代一致。华南铀矿空间分布的重要特点之一是,与白垩纪-古近纪岩石圈伸展背景下形成的断陷盆地以及幔源辉绿岩和煌斑岩等基性脉岩伴生。这些幔源基性脉岩是板内地质作用的产物。铀成矿时代(~135Ma、~115Ma、~85Ma、~65Ma和~45Ma)与反映岩石圈伸展的板内幔源基性脉岩的时代能较好地一一对应(李献华等, 1997; Hu et al., 2008, 2009; Luo et al., 2015a)。
(三)铀成矿热液的形成需要CO2。众所周知,铀源岩石和矿床中的铀主要以四价形式存在,但热液中的铀则主要以六价形式迁移。要实现铀从相对深部较还原环境自铀源岩石氧化转入热液,然后在近地表相对浅部较氧化环境自热液还原沉淀这一“矛盾”过程,需要与富铀岩石相互作用的热液富含CO2,以及在热液的后期演化过程中CO2的逃逸进而导致UO2(CO3)22-(或UO2(CO3)34-)分解成UO22+(或UF42+等)。因为中低温条件下UO2可以在较还原环境氧化成UO2(CO3)22-,而UO22+则可在较氧化环境(相对于形成UO2(CO3)22-的Eh值)还原成UO2形成矿床(胡瑞忠和金景福, 1990)。
(四)受岩石圈伸展控制的幔源CO2驱动铀成矿。华南铀矿成矿流体中的水主要是深循环雨水,CO2则主要受白垩纪-古近纪岩石圈伸展控制来自地幔(Hu et al., 1993, 2008, 2009)。其成矿过程是:白垩纪-古近纪时期华南板内软流圈上涌导致岩石圈伸展(地幔与地壳沟通)驱动幔源CO2上升、加入原在地壳浅层断裂系统中循环的贫CO2雨水形成富CO2热液;富CO2热液与富铀岩石(富铀花岗岩、火山岩和碳硅泥岩等)相互作用形成富CO2富铀热液[主要以UO2(CO3)22-(或UO2(CO3)34-)存在];富CO2和铀的热液在沿花岗岩、火山岩和碳硅泥岩中的断裂系统继续上升的途中,因流体外压降低导致其中CO2去气促使UO2(CO3)22-分解成UO22+等并被还原为沥青铀矿,从而分别形成按围岩划分的三类铀矿床;白垩纪-古近纪,华南岩石圈伸展的多期性导致了铀成矿的多期性。
2 铀矿物微区原位U-Pb年代学研究进展矿床的精确定年,是深入探讨矿床成因和成矿动力学背景等问题的重要基础(胡瑞忠等, 2014),是矿床学研究的基本内容,也是其前沿研究领域之一。
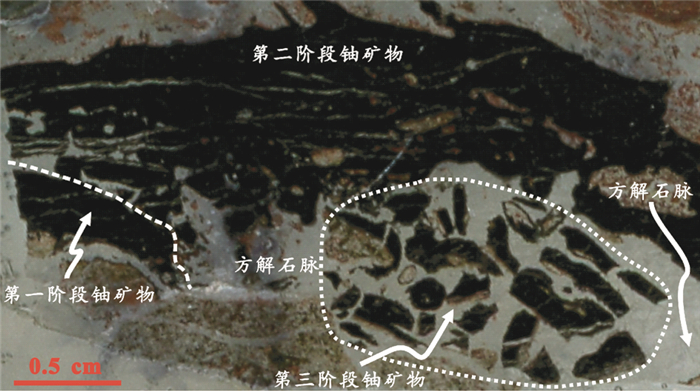
热液铀矿床中的矿石矿物沥青铀矿通常结晶非常细小,且易蚀变成铀的次生矿物,加上有可能受多期铀矿化叠加的影响(图 3),传统铀矿物溶样方法往往难以获得精确的成矿年龄,制约了对铀成矿作用与相应地质事件关系的正确认识。得益于微区原位测年技术的快速发展,近年建立的铀矿物微区原位U-Pb定年方法,可有效克服湿法化学溶样难以辨识多阶段叠加和矿物后生变化的弊端,进而精确揭示单矿物微尺度同位素组成的空间变化。尽管电子探针也具有很高的空间分辨率,可以获得微细铀矿物的化学年龄(Bowles, 1990, 2015; Kempe, 2003; Cross et al., 2011; Förster et al., 2012; Pal and Rhede, 2013; Luo et al., 2015b, 2017)。但该技术的Pb检测限较低,制约了最终的测年精度。基于原位、高灵敏度和高空间分辨率等优势,SHRIMP/SIMS/LA-ICP-MS等测试技术,则已成为近年微区原位分析研究的重点。
|
图 3 粤北仙石铀矿床微区范围多期产出的铀矿物(据Luo et al., 2015a) Fig. 3 Multi-stage uranium minerals observed within micro-scale thin section from the Xianshi uranium deposit, South China (after Luo et al., 2015a) |
Fayek课题组较早采用微区原位分析技术,对铀矿床中的沥青铀矿成功进行了U-Pb精确定年(Fayek et al., 2000, 2002a, b; Sharpe and Fayek, 2011, 2016)。近年来,铀矿物微区U-Pb定年技术亦成功应用到华南铀矿床的年代学研究中,为华南铀矿床的精确定年提供了范例。
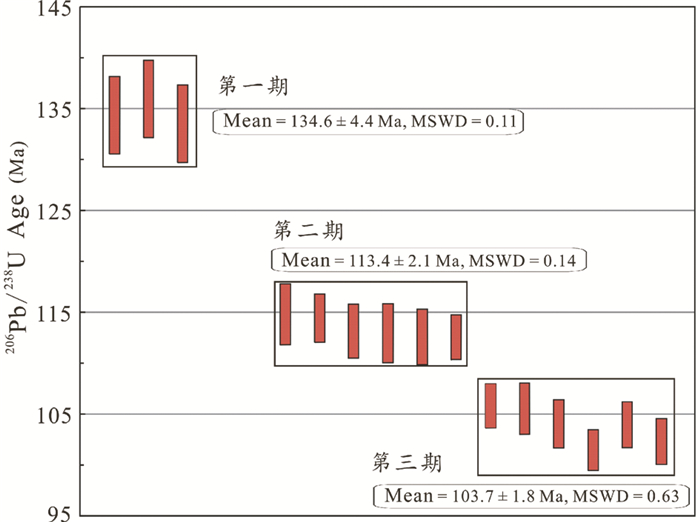
2.1 仙石(339)花岗岩型铀矿床该铀矿床产于粤北贵东复式花岗岩体的断裂构造中。邓平等(2003b)根据划分的成矿阶段,选取该铀矿床中早期角砾状沥青铀矿和晚期脉状沥青铀矿,用铀矿物U-Pb传统溶液法测定,得到~125Ma和81Ma两组年龄。在详细的铀矿物矿相学研究的基础上(图 3),Luo et al.(2015a)采用SIMS铀矿物U-Pb定年方法开展了沥青铀矿微区原位U-Pb年代学研究,确定仙石铀矿床存在三期成矿年龄,分别为135±4Ma、113±2Ma和104±2Ma(图 4),且这三组年龄与区域上岩石圈伸展背景下形成的幔源基性岩脉的侵位年龄可以一一对应。
|
图 4 仙石铀矿床不同铀矿化阶段铀矿物SIMS U-Pb年龄分布图(据Luo et al., 2015b) Fig. 4 In-situ SIMS U-Pb age distribution of multi-stage uranium minerals from the Xianshi uranium deposit (after Luo et al., 2015b) |
该铀矿床产于粤北诸广山复式花岗岩体的断裂构造中。采用传统的沥青铀矿U-Pb溶液法,以往对该铀矿床的成矿年龄已有较多研究。如张国全(2008)获得该矿床角砾状矿石和猪肝色硅化碎裂花岗岩型“红化”矿石的矿化年龄分别为~127Ma和~54Ma;黄国龙等(2010)对采自该铀矿床不同部位的沥青铀矿进行U-Pb和Sm-Nd等时线定年,确定棉花坑铀矿床的成矿年龄为~70Ma。Zhong et al.(2018)利用fs-LA-ICP-MS沥青铀矿微区原位U-Pb方法,结合不同类型矿石的岩相学特征,确定该矿床的成矿年龄应为~60Ma。
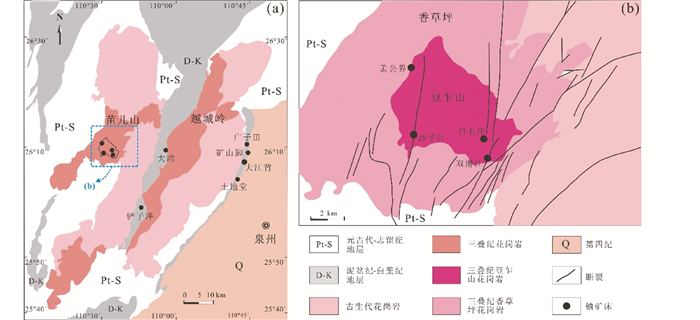
2.3 发现华南迄今最年轻的铀成矿事件——桂北孟公界花岗岩型铀矿床苗儿山铀矿田是华南最重要的铀矿田之一, 其内分布有铲子坪碳硅泥岩型铀矿床及孟公界、沙子江和双滑江等规模较大的花岗岩型铀矿床。孟公界铀矿床位于由古生代和三叠纪花岗岩组成的广西苗儿山复式花岗岩体内的三叠纪豆乍山与香草坪岩体的接触带附近(图 5)。矿区花岗岩蚀变发育,呈现出较强的赤铁矿化、黄铁矿化、绿泥石化、钾钠长石化和高岭土化。矿体受断裂控制多呈透镜状、脉状和网脉状。矿石矿物主要为沥青铀矿,呈脉状、肾状及球粒状等形式产出。脉石矿物主要有微晶石英、紫黑色萤石及方解石等。
|
图 5 苗儿山花岗岩体(a)以及豆乍山和香草坪岩体内铀矿分布简图(b)(据Luo et al., 2017) Fig. 5 The Miao'ershan granitic batholith (a) and the uranium deposits in the Douzhashan and Xiangcaoping granitic intrusions (b)(after Luo et al., 2017) |
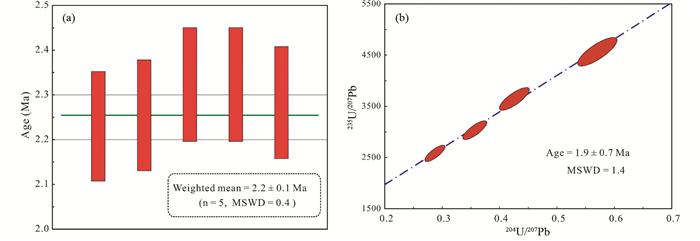
Luo et al.(2017)采用沥青铀矿U-Th-totalPb化学年龄和SIMS微区原位U-Pb定年相结合的方法,确定该矿床的成矿年龄为~2.0Ma(图 6),可能代表了华南新发现的一期最年轻的铀成矿事件。
|
图 6 孟公界花岗岩型铀矿床沥青铀矿U-Th-Pb化学年龄图(a)和SIMS U-Pb年龄图(b)(据Luo et al., 2017) Fig. 6 Pitchblende U-Th-Pb chemical age (a) and SIMS U-Pb age (b) diagrams for the Mengongjie granite-hosted uranium deposit (after Luo et al., 2017) |
Bonnetti et al.(2018)对粤北诸广和下庄地区代表性铀矿床进行了SIMS沥青铀矿微区原位U-Pb定年与铀矿物稀土元素地球化学研究。研究发现,部分花岗岩型铀矿床的成矿年龄为175~160Ma,明显早于先前报道的华南地区已确认的最老的铀成矿年龄~135Ma。这些成矿年龄较老的花岗岩型铀矿的成因机制,需要进一步深入研究。
综上所述,铀矿物微区U-Pb同位素定年,避免了传统方法在铀矿物分选过程中有可能造成的混染,可根据铀矿物的岩相学特征在微小区域分别进行多期次铀矿物的同位素组成分析(图 3),显示了在精确确定铀成矿时代上的相对优势,为进一步约束铀矿床的形成机理和成矿地球动力学背景提供了重要支撑。但是,迄今为止我国铀矿物微区原位U-Pb同位素年代学研究,还有很大的进步空间,尤其是铀矿物标准物质的开发与研究,还亟待深入。
3 铀矿物学研究进展自然界的铀通常以+3、+4、+5、+6价化合物存在,其中铀的+4和+6价化合物最稳定。四价铀通常以含铀副矿物和铀矿物(晶质铀矿、沥青铀矿等)形成于岩浆、热液、沉积和变质作用产物中,而六价铀通常以铀酰离子(UO22+)化合物溶于水体或以硫酸盐、碳酸盐、钒酸盐、磷酸盐等各种盐类铀矿物形式存在。因此,天然条件下铀通常普遍以U4+和U6+形式存在。然而,近年详细的铀矿物学研究发现,华南铀矿床中的铀,不仅可以金属铀(零价铀)形式存在于沥青铀矿中,而且可以六价铀形式大量存在于新识别的矿石矿物高铀酸钙[(CaU6+)O4]中。
3.1 高铀酸钙高铀酸钙[(CaU6+/4+)O4]是一罕见的具有萤石型结构的Ca-U氧化物矿物[Fm3m, a=5.381(2)Å, V=156.87Å3, Z=2],与沥青铀矿(U4+O2)具有相同的构型。近年,已在俄罗斯高加索(Caucasus)以北Chegem火山口上部(Galuskin et al., 2011)、墨西哥的Nopal Ⅰ铀矿床(Othmane et al., 2013)和以色列的Jabel Harmun地区(Galuskin et al., 2013)陆续发现。Galuskin et al. (2012)认为,Caucasus地区高铀酸钙矿物为立方晶系,在α-衰变的影响下Ca和U无序排列,可形成三方晶系Ca的铀酸盐矿物(trigonal CaUO4)偏高铀酸钙(protovorlanite, R3m, a=3.878Å, c=17.564Å)。在750℃以上高温条件下,Caucasus以北Chegem火山口黑红色的高铀酸钙和Jabel Harmun地区灰黑色的高铀酸钙,均可转化为不可逆的亮黄色的偏高铀酸钙(Galuskin et al., 2012, 2013)。前人的这些研究表明,高铀酸钙主要以独立矿物形式出现。
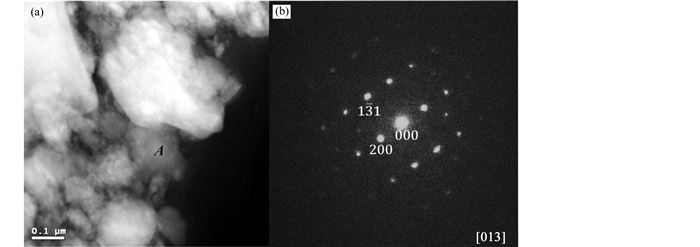
粤北仙石铀矿床位于贵东复式岩体的东部,赋矿围岩为鲁溪-仙人嶂辉绿岩和燕山早期笋洞二云母花岗岩(邓平等, 2003b), 笋洞岩体的侵位年龄为189.1±0.7Ma(凌洪飞等, 2004)。矿体主要赋存在NWW向辉绿岩脉与NNE向硅化带的交点部位。贵东复式岩体内基性脉岩的40Ar/39Ar年龄为140~102Ma(李献华等, 1997)。铀矿床中的铀矿物呈灰黑色,其原位-X射线衍射谱峰与高铀酸钙[(CaU6+)O4]和沥青铀矿(U3O7)类似。但是,透射电镜(TEM)研究进一步表明,矿物的晶胞参数与高铀酸钙[(CaU6+)O4] [Fm3m, a=5.381(2)Å, V=156.87Å3, Z=2](Galuskin et al., 2011)基本一致(图 7)。结合矿物的电子探针化学成分、拉曼光谱特征和铀矿物稀土元素特征(Luo et al., 2015a, 2018),发现仙石铀矿床中主要含铀矿物可能并不是前人认为的铀的氧化物—沥青铀矿或晶质铀矿,而是首次发现以矿床规模富集的高铀酸钙[(CaU6+)O4]。
|
图 7 仙石铀矿床铀矿物粉末样品的HAADF成像图(a)及其代表性区域A在晶轴[013]方向上与高铀酸钙[(CaU6+)O4]一致的立方晶系结构晶胞参数(a=5.381Å)衍射图(b) Fig. 7 HAADF image of the Xianshi powder sample of uranium mineral (a) and selected area diffraction pattern taken from point A in [013] zone axis corresponding to vorlanite having a cubic structure with lattice parameter of 5.381Å (b) |
沥青铀矿中的铀通常以四价和六价存在。Li et al.(2015)利用X射线光电子能谱方法,分析了华南诸广和贵东地区典型热液铀矿床中天然沥青铀矿的元素组成和价态。在此基础上,开展了与人造金属铀和不同铀矿物的对比分析,发现这些矿床中的沥青铀矿同时存在U0、U4+和U6+三种价态的铀,新识别出了零价金属铀(natural native uranium)的存在,并确定了不同价态铀的原子百分比。铀矿床中上述价态铀矿物的识别,为进一步揭示铀成矿机理和控矿因素提供了新的信息。
4 “攻深找盲”取得新成效 4.1 华南深部找矿具有重要潜力华南是我国重要铀矿产区,发育大量热液铀矿床。受技术条件和成矿规律把握程度的限制,该区铀矿的勘探深度以往普遍较浅(多在地下500m以内),面临资源逐渐枯竭的危机。近年来,得益于对成矿规律认识的深入和深部勘查技术的进步,华南热液铀矿床的深部找矿勘查取得了重要进展,尤其在广东长江矿田的棉花坑铀矿床和江西相山矿床深部找矿取得了重要突破。
早期的探索性钻孔资料显示,棉花坑铀矿床在垂幅500m及以下仍存在规模较大的矿体(覃慕陶和刘师先, 1998)。近年来,棉花坑铀矿床的勘查深度已超过1100m,在垂深800~1000m处发现了富-特富铀矿体,且铀矿体向深部有变大变富趋势(冯海生等, 2009; 朱捌, 2010; 黄国龙等, 2015; 许丽丽等, 2017)。该矿床的深部铀矿体基本保持原生特点,未受到成矿后次生氧化改造(黄国龙等, 2015),显示了广阔的深部找矿远景,有望成为我国资源储量最大的花岗岩型铀矿床(谭忠银等, 2015)。另一方面,江西相山铀矿田的邹家山、河元背、居隆庵等矿床的勘探深度目前均已超过1000m,部分地区深部铀矿化有变富变大的趋势。其中,居龙庵矿床深部1000m处仍发现有很好的工业铀矿化,目前控制的最低见矿标高为-755m,该矿床综合矿化垂幅已超过1300m(杨庆坤等, 2017a)。
以上进展表明,华南地区热液铀矿床可能有较好的深部成矿找矿潜力。需要进一步加强深部成矿规律研究,为深部找矿突破提供坚实的科技支撑。
4.2 对铀多金属成矿系统的勘查和研究取得新进展大量事实证明,火山岩系统中的铀矿可与其它金属矿化共伴生,如澳大利亚Olympic Dam超大型Cu-Au-U矿床中发育大量Au-Ag矿化(Dmitrijeva et al., 2019), 俄罗斯Streltsovsky超大型U-Mo矿床发育Cu-Au矿化(Aleshin et al., 2007)等。我国华南火山岩型铀床中也发育少量多金属矿化,如江西盛源铀矿田内发育金、银、锌、铅等矿床(胡茂梅, 2000),广东仁差盆地发育了察甘铀-钼金银多金属矿床(刘峤, 2019)等。相山是我国规模最大也是开采历史最悠久的火山岩型铀矿田,前人很早就发现其中发育少量共生或伴生的铅锌铜等多金属矿化(赵永祥, 1995),但由于规模较小而未引起足够重视。近年来,随着勘探深度的增加,特别是超深钻CUSD3的实施,证实相山地区深部(标高-500m以下)发育有大量铅-锌-铜等多金属矿化,初步显示出一个上铀、中铅锌、下铜的铀多金属矿田雏形,其中已控制的多金属储量已达小型矿床规模,呈现出较大的经济价值和重要的科学价值。
近年来,相山矿田深部的多金属矿化引起了众多学者的关注,对其矿化特征(吴志坚和胡志华, 2014; 刘军港等, 2017a, 2019a; 姚佳蕾等, 2017; 王建国等, 2018)、成矿流体特征(聂江涛等, 2015; 王健等, 2015, 2016; 刘军港等, 2017b, 2019b; 杨庆坤等, 2017b; Guo et al., 2018; 邱林飞等, 2019)、成矿物质来源(杨庆坤等, 2015; 聂江涛等, 2018; 刘斌等, 2018)和成矿时代(杨庆坤等, 2017a; Guo et al., 2018; 刘军港等, 2019c)等方面进行了较多探讨。有学者认为,铀矿化与多金属矿化可能发育于火山-岩浆热液成矿系统的不同阶段,其中多金属矿化具有早阶段浅成中-高温特征,而铀矿化则具有晚阶段中-低温特征(杨庆坤等, 2017a; 聂江涛等, 2018;司志发, 2018)。但是,对成矿流体性质、幔源物质参与形式以及成矿时代等问题仍存在很大争议(聂江涛等, 2015; 杨庆坤等, 2017a, b; 司志发, 2018; 刘斌等, 2018; 邱林飞等, 2019)。
5 本专辑主要内容在以往研究的基础上,本专辑报道了近年华南铀矿研究的部分新进展,包括15篇文章,主要涉及这些铀矿床的地质地球化学特征、成矿时代、成矿过程、成矿动力学背景和找矿潜力等。
陈峰等(2019)以产于江南造山带西南段摩天岭穹隆两种不同地质特征的代表性铀矿床为对象,对新元古代三防花岗岩体及其周缘主要含矿构造与典型铀矿床的成矿关系进行了研究。结果表明,脆韧性构造体制转换条件下的递进变形过程严格控制了铀矿床的分布。在此基础上,建立了构造和蚀变因素复合作用下的铀成矿模式。
陈佑纬等(2019)利用电子探针、LA-ICPMS和SIMS等原位分析技术,对桂北沙子江花岗岩型铀矿床的沥青铀矿开展了U-Pb年代学及元素组成研究。研究表明,沥青铀矿U-Pb年龄为101.3±4.5Ma;沥青铀矿化学年龄-SiO2趋势线上SiO2趋于零时的化学年龄基本可代表其形成年龄;受岩石圈伸展控制形成的富CO2流体浸取豆乍山花岗岩中的铀并在合适部位沉淀形成了沙子江铀矿床。
徐争启等(2019)对桂北摩天岭花岗岩体的岩石学、地球化学、年代学及其铀成矿作用进行了研究。结果表明,岩体为S型花岗岩,形成于850~760Ma,其中的铀矿床形成于360~401Ma和47Ma两个时期。矿床中的铀源自元古界四堡群、丹州群和摩天岭岩体本身,成矿流体主要为大气降水,同时有深部流体参与,热源主要与加里东期区域变质和喜山期伸展背景下的构造作用有关。
骆金诚等(2019)对粤北下庄铀矿田基性岩脉中的角闪石开展了40Ar-39Ar年代学研究。研究表明,该区存在一期形成于200~190Ma的基性岩脉,说明印支期碰撞造山结束后岩石圈伸展可能至少在200~190Ma已经开始。通过探究基性岩脉与铀成矿的时空关系,认为铀矿区内基性岩脉的侵位早于铀矿化或与铀矿化作用近同时,基性岩脉均可为铀成矿提供有利条件,进而促进铀的成矿作用。
庞雅庆等(2019)以诸广南部铀矿田花岗岩型铀矿床成矿期萤石、方解石和黄铁矿中流体包裹体为对象,研究了成矿流体的He、Ar同位素地球化学。研究表明,成矿流体由两个端元组成:一是含一定放射性成因Ar的大气成因地壳流体,二是含幔源He的地幔流体。相较于受NE向断裂控制的一些铀矿床,受NNW向断裂带控制的棉花坑、书楼丘、长排等铀矿床受地幔流体影响较大。
祁家明等(2019)以粤北棉花坑(302)花岗岩型铀矿床成矿期脉石矿物和黄铁矿为对象,研究了流体包裹体热力学、流体包裹体组成和黄铁矿的微量元素地球化学。研究表明,随成矿流体温度、压力的逐渐降低,流体的∑M+/∑M-逐渐升高,矿物沉淀按萤石、方解石、微晶石英的顺序进行,沉淀出的黄铁矿U/Th比值亦逐渐升高,铀在流体演化的最晚阶段才大量与微晶石英一同沉淀。
钟福军等(2019)对长江铀矿田棉花坑、书楼坵和长排三个花岗岩型铀矿床中的沥青铀矿开展了LA-ICP-MS原位U-Pb定年研究。结果表明,长江铀矿田至少存在三期热液铀矿化,成矿年龄分别为~75Ma、~70Ma和~60Ma,成矿年龄与诸广地区北东向断裂带、断陷盆地的强烈拉张时期(80~60Ma)同步,成矿统一受制于华南白垩纪-古近纪岩石圈伸展的动力学背景。
吴德海等(2019)以粤北长江铀矿田棉花坑铀矿床的矿化剖面为对象,研究了新鲜花岗岩、蚀变岩和矿石的主微量元素地球化学特征,运用质量平衡方法探讨了元素的迁移规律。结果表明,矿床成矿物质主要来自赋矿花岗岩,成矿流体富含挥发分(CO2等)、碱金属和重稀土元素,是地幔流体与深循环大气水的混合流体。挥发分的带入是重要的矿质迁移机制,CO2逸出是重要的矿质沉淀机制。
刘军港等(2019c)对相山铀矿田深部多金属矿脉中的闪锌矿、毒砂、黄铁矿等硫化物和围岩进行了Rb-Sr同位素研究。结果显示,深部多金属矿化形成于121.0±3.5Ma,与围岩火山岩存在较大时差,可能与晚于围岩的深部次火山有关。虽然相山矿田铀矿化和多金属矿化具有一致的成矿动力学背景,但是多金属矿化的成矿流体可能来自深部壳源岩浆体系,与铀成矿流体非同一来源。
刘斌等(2019)对比研究了相山铀矿田西部的居隆庵和北部的沙洲两个铀矿床新鲜围岩、蚀变围岩及矿石的微量和稀土元素地球化学特征。研究表明,从新鲜围岩到蚀变围岩再到矿石,两个矿床的Zr、Hf、U、REE等元素具有不同的变化趋势,居隆庵铀矿床铀品位较高,这可能与居隆庵铀矿床的成矿流体富F、而沙洲铀矿床的成矿流体相对贫F有关。
田建吉等(2019)对赣杭铀成矿带东段最重要的大茶园火山岩型铀矿床的脉石矿物开展了C-O和Sr-Nd同位素研究。结果表明,成矿流体中矿化剂ΣCO2主要来源于地幔,成矿物质主要来自赋矿流纹岩。岩石圈伸展控制着富CO2热液的形成,富CO2热液在上升过程中萃取富铀火山岩中成矿物质,并在有利的成矿部位通过CO2去气导致铀沉淀成矿。
林锦荣等(2019)应用沥青铀矿和矿化岩石U-Pb等时线、黄铁矿Rb-Sr等时线、绢云母40Ar-39Ar法和锆石裂变径迹法等多种方法,对相山铀矿田铀多金属成矿热事件的时代进行了限定。结果显示,铀成矿热事件与华南花岗岩型热液铀矿床的区域成矿热事件时代基本吻合,为利用锆石裂变径迹年龄(峰值年龄)限定热液铀多金属成矿热事件的时代提供了较好范例。
金中国等(2019)对近年发现的贵州第一个大型碳硅泥岩型铀矿床——三穗龙湾铀矿床开展了较系统的矿物学和地质地球化学研究。结果表明,矿床成矿物质主要来自赋矿围岩,成矿流体为深部流体与大气降水的混合,铀及其伴生元素的富集与炭质泥岩中富含有机质等密切相关,矿床具有沉积-热液叠加改造成因的特点,震旦-寒武系老堡组及其发育的炭质泥岩是铀矿床形成的必要条件。
宋昊等(2019)对桂西大新碳硅泥岩型铀矿床和邻区的辉绿岩开展了较系统的地质地球化学和锆石U-Pb年代学研究。研究表明,辉绿岩属于具富集地幔特征的板内碱性玄武岩系列,成岩年龄约为86.7±0.9Ma~91.6±8.3Ma,是岩石圈伸展构造背景下的产物,与华南一次重要铀成矿事件的时代一致。辉绿岩的成岩过程及其伸展背景,对矿源岩中铀的活化迁移和成矿具有重要控制作用。
Aleshin AP, Velichkin VI and Krylova TL. 2007. Genesis and formation conditions of deposits in the unique Strel'tsovka molybdenum-uranium ore field:New mineralogical, geochemical, and physicochemical evidence. Geology of Ore Deposits, 49(5): 392-412 DOI:10.1134/S1075701507050054 |
Beijing Institute of Uranium Geology. 1982. Compiled Papers on the Carbonaceous-Siliceous-Pelitic Rock-Type Uranium Deposits. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 1-208 (in Chinese)
|
Bonnetti C, Liu XD, Mercadier J, Cuney M, Deloule E, Villeneuve J and Liu WQ. 2018. The genesis of granite-related hydrothermal uranium deposits in the Xiazhuang and Zhuguang ore fields, North Guangdong Province, SE China:Insights from mineralogical, trace elements and U-Pb isotopes signatures of the U mineralisation. Ore Geology Reviews, 92: 588-612 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.12.010 |
Bowles JFW. 1990. Age dating of individual grains of uraninite in rocks from electron microprobe analyses. Chemical Geology, 83(1-2): 47-53 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(90)90139-X |
Bowles JFW. 2015. Age dating from electron microprobe analyses of U, Th, and Pb:Geological advantages and analytical difficulties. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 21(S5): 1114-1122 DOI:10.1017/S1431927615000446 |
Chen F, Yan DP, Qiu L, Yang WX, Tang SL, Guo QY and Zhang YX. 2019. The brittle-ductile shearing and uranium metallogenesis of the Motianling dome in the southwestern Jiangnan Orogenic Belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2637-2659 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.02 |
Chen YW, Hu RZ, Luo JC and Dong SH. 2019. In-situ mineral chemistry and chronology analyses of the pitchblende in the Shazijiang uranium deposit and their implications for mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2679-2694 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.04 |
Chen ZB, Xie YX, Wan GL, Ji SF, Wang CL and Fang XH. 1982. Uranium deposits in Mesozoic volcanics in Southeast China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 56(3): 235-243 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Cross AJ, Jaireth S, Rapp R and Armstrong R. 2011. Reconnaissance-style EPMA chemical U-Th-Pb dating of uraninite. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 58(6): 675-683 DOI:10.1080/08120099.2011.598190 |
Deng P, Shu LS and Tan ZZ. 2003a. The geological setting for the formation of rich uranium ores in Zhuguang-Guidong large-scale uranium metallogenetic area. Geological Review, 49(5): 486-494 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Deng P, Shen WZ, Ling HF, Ye HM, Wang XC, Pu W and Tan ZZ. 2003b. Uranium mineralization related to mantle fluid:A case study of the Xianshi deposit in the Xiazhuang uranium orefield. Geochimica, 32(6): 520-528 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.1016/S0955-2219(02)00073-0 |
Dmitrijeva M, Ehrig KJ, Ciobanu CL, Cook NJ, Verdugo-Ihl MR and Metcalfe AV. 2019. Defining IOCG signatures through compositional data analysis:A case study of lithogeochemical zoning from the Olympic Dam deposit, South Australia. Ore Geology Reviews, 105: 86-101 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.12.013 |
Du LT. 1982. The Granite-Type Uranium Deposits. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 1-404 (in Chinese)
|
Du LT and Wang YM. 1984. The integration of metallogenic mechanisms of the granite-type, volcanic rock-type, carbonaceous-siliceous-pelitic rocktype, and sandstone-type uranium deposits in South China. Radioactive Geology, (3): 1-10 (in Chinese) |
Du LT. 2001. Fundamental Metallogenic Rules and General Hydrothermal Mineralization. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 217-237 (in Chinese)
|
Faure M, Lepvrier C, van Nguyen V, van Vu T, Lin W and Chen ZC. 2014. The South China Block-Indochina collision:Where, when, and how?. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 79: 260-274 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.09.022 |
Fayek M, Harrison TM, Grove M and Coath CD. 2000. A rapid in situ method for determining the ages of uranium oxide minerals:Evolution of the Cigar Lake deposit, Athabasca basin. International Geology Review, 42(2): 163-171 DOI:10.1080/00206810009465075 |
Fayek M, Harrison TM, Ewing RC, Grove M and Coath CD. 2002a. O and Pb isotopic analyses of uranium minerals by ion microprobe and U-Pb ages from the Cigar Lake deposit. Chemical Geology, 185(3-4): 205-225 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00401-6 |
Fayek M, Kyser TK and Riciputi LR. 2002b. U and Pb isotope analysis of uranium minerals by ion microprobe and the geochronology of the Mcarthur River and Sue Zone uranium deposits, Saskatchewan, Canada. The Canadian Mineralogist, 40(6): 1553-1569 DOI:10.2113/gscanmin.40.6.1553 |
Feng HS, Yin ZP, Xu WX and Huang GL. 2009. Minerogenetic characteristic and prospecting potential of the deeping of Mianhuakeng uranium deposit in southern Zhuguang granite batholith. Journal of East China Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 32(2): 101-107 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Förster HJ, Rhede D, Stein HJ, Romer RL and Tischendorf G. 2012. Paired uraninite and molybdenite dating of the Königshain granite:Implications for the onset of Late-Variscan magmatism in the Lausitz Block. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 101(1): 57-67 DOI:10.1007/s00531-010-0631-1 |
Galuskin EV, Armbruster T, Galuskina IO, Lazic B, Winiarski A, Gazeev VM, Dzierzanowski P, Zadov AE, Pertsev NN, Wrzalik R, Gurbanov AG and Janeczek J. 2011. Vorlanite (CaU6+)O4:A new mineral from the Upper Chegem caldera, Kabardino-Balkaria, northern Caucasus, Russia. American Mineralogist, 96(1): 188-196 DOI:10.2138/am.2011.3610 |
Galuskin EV, Galuskina IO, Dubrovinsky LS and Janeczek J. 2012. Thermally induced transformation of vorlanite to "protovorlanite":Restoration of cation ordering in self-irradiated CaUO4. American Mineralogist, 97(5-6): 1002-1004 DOI:10.2138/am.2012.4092 |
Galuskin EV, Kusz J, Armbruster T, Galuskina IO, Marzec K, Vapnik Y and Murashko M. 2013. Vorlanite, (CaU6+)O4, from Jabel Harmun, Palestinian Autonomy, Israel. American Mineralogist, 98(11-12): 1938-1942 DOI:10.2138/am.2013.4548 |
Guo J, Li ZY, Nie JT, Huang ZZ, Wang J and Lai CK. 2018. Genesis of Pb-Zn mineralization beneath the Xiangshan uranium orefield, South China:Constraints from H-O-S-Pb isotopes and Rb-Sr dating. Resource Geology, 68(3): 275-286 DOI:10.1111/rge.12170 |
Hu MM. 2000. Characteristics of basement and uranium and polymetallic mineralizations in Shengyuan basin. Uranium Geology, 16(3): 150-156,163 |
Hu RZ and Jin JF. 1990. Mechanism of the migration and deposition of uranium in ascending hydrothermal solutions:Evidence from the Xiwang uranium deposit. Geological Review, 36(4): 317-325 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu RZ, Li CY, Ni SJ, Liu J and Yu JS. 1993. Research on ΣCO2 source in ore-forming hydrothermal solution of granite-type uranium deposit, South China. Science in China (Series B), 36(10): 1252-1261 |
Hu RZ, Bi XW, Zhou MF, Peng JT, Su WC, Liu S and Qi HW. 2008. Uranium metallogenesis in South China and its relationship to crustal extension during the Cretaceous to Tertiary. Economic Geology, 103(3): 583-598 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.103.3.583 |
Hu RZ, Burnard PG, Bi XW, Zhou MF, Peng JT, Su WC and Zhao JH. 2009. Mantle-derived gaseous components in ore-forming fluids of the Xiangshan uranium deposit, Jiangxi Province, China:Evidence from He, Ar and C isotopes. Chemical Geology, 266(1-2): 86-95 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.07.017 |
Hu RZ and Zhou MF. 2012. Multiple Mesozoic mineralization events in South China:An introduction to the thematic issue. Mineralium Deposita, 47(6): 579-588 DOI:10.1007/s00126-012-0431-6 |
Hu RZ, Wen HJ, Su WC, Peng JT, Bi XW and Chen YW. 2014. Some advances in ore deposit geochemistry in last decade. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 33(2): 127-144 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu RZ, Mao JW, Hua RM and Fan WM. 2015. Intra-Continental Mineralization of South China Craton. Beijing: Science Press, 1-903 (in Chinese)
|
Hu RZ, Chen WT, Xu DR and Zhou MF. 2017a. Reviews and new metallogenic models of mineral deposits in South China:An introduction. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 137: 1-8 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.02.035 |
Hu RZ, Fu SL, Huang Y, Zhou MF, Fu SH, Zhao CH, Wang YJ, Bi XW and Xiao JF. 2017b. The giant South China Mesozoic low-temperature metallogenic domain:Reviews and a new geodynamic model. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 137: 9-34 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.10.016 |
Huang GL, Yin ZP, Ling HF, Deng P, Zhu B and Shen WZ. 2010. Formation age, geochemical characteristics and genesis of pitchblende from No. 302 uranium deposit in northern Guangdong. Mineral Deposits, 29(2): 352-360 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Huang GL, Cao HJ, Xu WX and Shen WZ. 2015. Vertical zoning model and prospecting potential in depth of Mianhuakeng uranium deposit in Zhuguang. Uranium Geology, 31(3): 355-362 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Jin ZG, Liu KK, Luo K, Zheng MH, Yang SF, Li YT, Fan YF and Wang Q. 2019. Geological, geochemical features and origin of the Longwan uranium deposit in Sansui, Guizhou Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2830-2844 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.14 |
Kempe U. 2003. Precise electron microprobe age determination in altered uraninite:Consequences on the intrusion age and the metallogenic significance of the Kirchberg granite (Erzgebirge, Germany). Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 145(1): 107-118 DOI:10.1007/s00410-002-0439-5 |
Li XH, Hu RZ and Rao B. 1997. Geochronology and geochemistry of Cretaceous mafic dikes from northern Guangdong, SE China. Geochimica, 26(2): 14-31 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li XH. 2000. Cretaceous magmatism and lithospheric extension in Southeast China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 18(3): 293-305 DOI:10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00060-7 |
Li ZX and Li XH. 2007. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China:A flat-slab subduction model. Geology, 35(2): 179-182 DOI:10.1130/G23193A.1 |
Li ZY. 2006. Hostspot uranium metallogenesis in South China. Uranium Geology, 22(2): 65-69,82 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li ZY, Huang ZZ, Li XZ, Guo J and Fan C. 2015. The discovery of natural native uranium and its significance. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(5): 1561-1567 DOI:10.1111/1755-6724.12564 |
Lin JR, Hu ZH, Wang YJ, Zhang S and Tao Y. 2019. Ore-forming age and thermal history of uranium-polymetallic mineralization in Xiangshan uranium orefield. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2801-2816 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.12 |
Ling HF, Shen WZ, Deng P, Jiang SY, Gao JF, Ye HM, Pu W and Tan ZZ. 2004. Age, geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Sundong granite, northern Guangdong Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(3): 413-424 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu B, Chen WF, Fang QC, Tang XS, Mao YF, Sun LQ, Gao S, Yan YJ, Wei X and Ling HF. 2018. Study on in situ sulfur isotope compositions of sulfides: Implication for the source of Pb-Zn mineralized body of Niutoushan in the Xiangshan area. Earth Science, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20181221.0947.004.html (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu B, Chen WF, Fang QC, Mao YF, Tang XS, Yan YJ, Wei X and Ling HF. 2019. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids in the Xiangshan uranium ore-field:Constraints from trace elements and rare earth elements. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2774-2786 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.10 |
Liu JG, Li ZY, Huang ZZ, Li XZ and Nie JT. 2017a. The element mobility study of uranium mineralization alteration zones in Xiangshan, Jiangxi using the drill core CUSD3. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(4): 896-912 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu JG, Li ZY and Nie JT. 2017b. The S isotope geochemical characteristics and its geological implications of lead-zinc polymetallic mineralization in Xiangshan ore field, Jiangxi Province. Geological Review, 63(Suppl.): 237-238 (in Chinese) |
Liu JG, Li ZY, Nie JT, Wang J and Li XZ. 2019a. Ore fabric and mineralogy of polymetallic mineralization in western Xiangshan uranium orefield, Jiangxi Province. Mineral Deposits, 38(2): 367-381 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu JG, Li ZY, Nie JT and Wang J. 2019b. Origin of ore-forming fluids in the deep polymetallic mineralization in western Xiangshan uranium ore field, Jiangxi Province, China:Constraints from He-Ar Isotopes. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 43(2): 271-282 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu JG, Li ZY, Nie JT, Zhang WL, Wang YJ and Tian MM. 2019c. The timing and ore-forming fluid evolution of deep polymetalic mineralization in western Xiangshan uranium ore field, South China:Constraints from Rb-Sr isotope systematics. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2787-2800 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.11 |
Liu Q. 2019. Characteristics and metallogenic mechanism of Chagan volcanic-type uranium-polymetal deposits in Rencha Basin, northeastern Guangdong. Mineral Resources and Geology, 33(1): 77-82 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Luo JC, Hu RZ, Fayek M, Li CS, Bi XW, Abdu Y and Chen YW. 2015a. In-situ SIMS uraninite U-Pb dating and genesis of the Xianshi granite-hosted uranium deposit, South China. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 968-978 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.06.016 |
Luo JC, Hu RZ and Shi SH. 2015b. Timing of uranium mineralization and geological implications of Shazijiang granite-hosted uranium deposit in Guangxi, South China:New constraint from chemical U-Pb age. Journal of Earth Science, 26(6): 911-919 DOI:10.1007/s12583-015-0542-y |
Luo JC, Hu RZ, Fayek M, Bi XW, Shi SH and Chen YW. 2017. Newly discovered uranium mineralization at~2. 0Ma in the Menggongjie granite-hosted uranium deposit, South China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 137: 241-249 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.01.021 |
Luo JC, Hu RZ, Bi XW and Chen YW. 2018. REE characteristics of a new uranium mineral from the Xianshi uranium deposit, South China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(4): 1667-1669 DOI:10.1111/1755-6724.13658 |
Luo JC, Qi YQ, Wang LX, Tian JJ, Shi SH and Chen YW. 2019. Ar-Ar dating of mafic dykes from the Xiazhuang uranium ore field in northern Guangdong, South China:A reevaluation of the role of mafic dyke in uranium mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2660-2678 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.03 |
Mao JW, Cheng YB, Chen MH and Pirajno F. 2013. Major types and time-space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings. Mineralium Deposita, 48(3): 267-294 DOI:10.1007/s00126-012-0446-z |
Nie JT, Li ZY, Wang J and Guo J. 2015. Characteristics of polymetallic ore-forming fluid and metallogenesis of the Xiangshan ore-field in Jiangxi. Geological Bulletin of China. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(2-3): 535-547 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Nie JT, Li ZY, Wang J, Guo J, Lin JR, Huang ZZ, Li ZX, Tian MM, Liu JG and Si ZF. 2018. Isotopic feature and provenance of lead-zinc mineralization ores of the scientific drilling in Xiangshan ore field. Uranium Geology, 34(6): 353-359 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Othmane G, Allard T, Menguy N, Morin G, Esteve I, Fayek M and Calas G. 2013. Evidence for nanocrystals of vorlanite:A rare uranate mineral, in the Nopal Ⅰ low-temperature uranium deposit (Sierra Pena Blanca, Mexico). American Mineralogist, 98(2-3): 518-521 DOI:10.2138/am.2013.4295 |
Pal DC and Rhede D. 2013. Geochemistry and chemical dating of uraninite in the Jaduguda uranium deposit, Singhbhum shear zone, India:Implications for uranium mineralization and geochemical evolution of uraninite. Economic Geology, 108(6): 1499-1515 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.108.6.1499 |
Pang YQ, Fan HH, Gao F, Wu JY and Xie XZ. 2019. Helium and argon isotopic compositions of fluid inclusions and tracing to the source of ore-forming fluids for the southern Zhuguang uranium ore field in northern Guangdong Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2765-2773 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.09 |
Qi JM, Zhu B, Wu JY, Cao HJ, Liu WQ and Xu ZQ. 2019. The evolution of ore-forming fluid and its constraint on mineralization process in Mianhuakeng uranium deposit, northern Guangdong, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2711-2726 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.06 |
Qin MT and Liu SX. 1998. Granite Type and Volcanic Rock Type Uranium Deposits in Nanling. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 96-122 (in Chinese)
|
Qiu LF, Wu D, Wu Y, Jin GS, Han J, Liu JG and Guo J. 2019. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids and sources of polymetallic ore-forming materials in deep segment of uranium deposits in Niutoushan area, Xiangshan. Mineral Deposits, 38(2): 291-302 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ruzicka V. 1993. Vein uranium deposits. Ore Geology Reviews, 8(3-4): 247-276 DOI:10.1016/0169-1368(93)90019-U |
Sharpe R and Fayek M. 2011. The World's oldest observed primary uraninite. The Canadian Mineralogist, 49(5): 1199-1210 DOI:10.3749/canmin.49.5.1199 |
Sharpe R and Fayek M. 2016. Mass bias corrections for U-Pb isotopic analysis by secondary ion mass spectrometry:Implications for U-Pb dating of uraninite. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 30(13): 1601-1611 DOI:10.1002/rcm.7595 |
Si ZF. 2018. Comparative study of uranium and polymetallic mineralization in Xiangshan ore field, Jiangxi Province. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, 1-60
|
Song H, Xu ZQ, Song SW, Ni SJ, Zhang CJ, Yan WQ, Cheng FG and Li YP. 2019. Geochemistry and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronological dating of diabase dykes and their relationship with mineralization of the carbonate-siliceous-pelitic rock type uranium deposits in Daxin-Qinjia, western Guangxi. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2845-2863 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.15 |
Tan ZY, Zhang DC, Kuang ZP, Zhu QZ and Li Y. 2015. Analysis of deep prospecting at Mianhuakeng uranium deposit in the southern Zhuguang massif in northern Guangdong. Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 34(2): 78-81,86 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Tian JJ, Zhang GQ, Shang PQ and Qi YQ. 2019. Ore-forming material sources of the Dachayuan uranium deposit, Zhejiang Province:Evidence from C-O and Sr-Nd isotopes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2817-2829 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.13 |
Wang J, Nie JT and Guo J. 2015. Characteristic of copper mineralization and ore-forming fluid evolution in Xiangshan ore field, Jiangxi Province. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 35(4): 74-84 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang J, Nie JT, Guo J, Huang ZZ and Li XZ. 2016. Characteristics of deep polymetallic mineralization in the Xiangshan uranium ore field of Jiangxi Province. Geology and Exploration, 52(1): 47-59 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang JG, Ma YY, Tang GP, Zhang YT, Pang WJ, Yao YJ, Qiu LF and Guo J. 2018. Study on composition feature polymetallic minerals and metallogenic stages of Niutoushan area, Xiangshan uranium field. World Nuclear Geoscience, 35(3): 143-149 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang YJ, Fan WM, Sun M, Liang XQ, Zhang YH and Peng TP. 2007. Geochronological, geochemical and geothermal constraints on petrogenesis of the Indosinian peraluminous granites in the South China Block:A case study in the Hunan Province. Lithos, 96(3-4): 475-502 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.11.010 |
Wu DH, Xia F, Pan JY, Liu GQ, Huang GL, Liu WQ and Wu JY. 2019. Characteristics of hydrothermal alteration and material migration of the Mianhuakeng uranium deposit in northern Guangdong Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2745-2764 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.08 |
Wu ZJ and Hu ZH. 2014. Uranium-polymetallic metallogenic characteristics and prospecting direction of Niutoushan uranium deposit in Xiangshan orefield. World Nuclear Geoscience, 31(2): 89-94 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu LL, Fu SC and Xu WX. 2017. Analysis on metallogenic characteristics in the deep of Mianhuakeng uranium deposit. World Nuclear Geoscience, 34(2): 63-69 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu ZQ, Song H, Yin MH, Zhang CJ, Cheng FG and Tang CY. 2019. Uranium metallogenic mechanism of Neoproterozoic granites in South China:A case study from the Motianling granite. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2695-2710 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.05 |
Yan DP, Zhou MF, Song HL, Wang XW and Malpas J. 2003. Origin and tectonic significance of a Mesozoic multi-layer over-thrust system within the Yangtze block (South China). Tectonophysics, 361(3-4): 239-254 DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(02)00646-7 |
Yang QK, Huang QT and Sun QZ. 2015. Geological characteristics of sulfur and Lead isotopes in the Xiangshan ore field. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 34(4): 755-762 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang QK, Guo FS, Zhou WP and Qu HJ. 2017a. Geochronology and metallogenic model of the Xiangshan U-Pb-Zn deposits, southern Jiangxi, China. Earth Science Frontiers, 24(5): 283-298 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang QK, Huang QT, Luo Y, Huang BH and Wang QY. 2017b. The characteristics of metallogenic fluid evolution of lead zinc polymetallic in Xiangshan ore field, Jiangxi Province. Science Technology and Engineering, 17(5): 132-141 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yao JL, Zhang C, Ye FW, Xu QJ and Tian MJ. 2017. Hyperspectral alteration mineral feature and its geological significance of drill core in Zoujiashan uranium deposit of Xiangshan orefield. Uranium Geology, 33(6): 376-380 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang GQ. 2008. Geochemistry of hydrothermal uranium deposits in South China: A case study of the No. 302 uranium deposit. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1-96 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zhao GC and Cawood PA. 2012. Precambrian geology of China. Precambrian Research, 222-223: 13-54 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2012.09.017 |
Zhao JH, Zhou MF, Yan DP, Zheng JP and Li JW. 2011. Reappraisal of the ages of Neoproterozoic strata in South China:No connection with the Grenvillian orogeny. Geology, 39(4): 299-302 DOI:10.1130/G31701.1 |
Zhao YX. 1995. Uranium metallogenic series in Xiangshan ore field. Journal of East China Geological Institute, 18(2): 128-134 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhong FJ, Pan JY, Qi JM, Yan J, Liu WQ and Li HD. 2018. New in-situ LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages of uraninite from the Mianhuakeng uranium deposit, northern Guangdong Province, China:Constraint on the metallogenic mechanism. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(2): 852-854 DOI:10.1111/1755-6724.13558 |
Zhong FJ, Yan J, Xia F, Pan JY, Liu WQ, Lai J and Zhao QF. 2019. In-situ U-Pb isotope geochronology of uraninite for Changjiang granite-type uranium ore field in northern Guangdong, China:Implications for uranium mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2727-2744 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.07 |
Zhou XM and Li WX. 2000. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China:Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas. Tectonophysics, 326(3-4): 269-287 DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00120-7 |
Zhou XM, Sun T, Shen WZ, Shu LS and Niu YL. 2006. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China:A response to tectonic evolution. Episodes, 29(1): 26-33 DOI:10.18814/epiiugs/2006/v29i1/004 |
Zhu B. 2010. The study of mantle liquid and uranium metallogenesis: Take uranium ore field of South Zhuguangshan as an example. Ph. D. Dissertation. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 1-104 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
北京铀矿地质研究所. 1982. 碳硅泥岩型铀矿床文集. 北京: 原子能出版社, 1-208.
|
陈峰, 颜丹平, 邱亮, 杨文心, 汤双立, 郭庆银, 张翼西. 2019. 江南造山带西南段摩天岭穹隆脆韧性剪切与铀成矿作用. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2637-2659. |
陈佑纬, 胡瑞忠, 骆金诚, 董少花. 2019. 桂北沙子江铀矿床沥青铀矿原位微区年代学和元素分析:对铀成矿作用的启示. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2679-2694. |
陈肇博, 谢佑新, 万国良, 季树藩, 王灿林, 方锡珩. 1982. 华东南中生代火山岩中的铀矿床. 地质学报, 56(3): 235-243. |
邓平, 舒良树, 谭正中. 2003a. 诸广-贵东大型铀矿聚集区富铀矿成矿地质条件. 地质论评, 49(5): 486-494. |
邓平, 沈渭洲, 凌洪飞, 叶海敏, 王学成, 濮巍, 谭正中. 2003b. 地幔流体与铀成矿作用:以下庄矿田仙石铀矿床为例. 地球化学, 32(6): 520-528. |
杜乐天. 1982. 花岗岩型铀矿文集. 北京: 原子能出版社, 1-404.
|
杜乐天, 王玉明. 1984. 华南花岗岩型、火山岩型、碳硅泥岩型、砂岩型铀矿成矿机理的统一性. 放射性地质, (3): 1-10. |
杜乐天. 2001. 中国热液铀矿基本成矿规律和一般热液成矿学. 北京: 原子能出版社, 217-237.
|
冯海生, 尹征平, 徐文雄, 黄国龙. 2009. 诸广山棉花坑铀矿深部矿化特征及找矿前景. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 32(2): 101-107. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2009.02.001 |
胡茂梅. 2000. 盛源盆地基底特征与铀及多金属矿化. 铀矿地质, 16(3): 150-156,163. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2000.03.004 |
胡瑞忠, 金景福. 1990. 上升热液浸取成矿过程中铀的迁移沉淀机制探讨——以希望铀矿床为例. 地质论评, 36(4): 317-325. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1990.04.004 |
胡瑞忠, 温汉捷, 苏文超, 彭建堂, 毕献武, 陈佑纬. 2014. 矿床地球化学近十年若干研究进展. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 33(2): 127-144. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2014.02.016 |
胡瑞忠, 毛景文, 华仁民, 范蔚茗. 2015. 华南陆块陆内成矿作用. 北京:科学出版社: 1-903. |
黄国龙, 尹征平, 凌洪飞, 邓平, 朱捌, 沈渭洲. 2010. 粤北地区302矿床沥青铀矿的形成时代、地球化学特征及其成因研究. 矿床地质, 29(2): 352-360. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.02.017 |
黄国龙, 曹豪杰, 徐文雄, 沈渭洲. 2015. 诸广棉花坑铀矿床垂向分带模式及深部找矿潜力. 铀矿地质, 31(3): 355-362. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2015.03.001 |
金中国, 刘开坤, 罗开, 郑明泓, 杨胜发, 李艳桃, 范云飞, 王琼. 2019. 贵州三穗龙湾铀矿床地质地球化学特征及成因. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2830-2844. |
李献华, 胡瑞忠, 饶冰. 1997. 粤北白垩纪基性岩脉的年代学和地球化学. 地球化学, 26(2): 14-31. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1997.02.004 |
李子颖. 2006. 华南热点铀成矿作用. 铀矿地质, 22(2): 65-69,82. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2006.02.001 |
林锦荣, 胡志华, 王勇剑, 张松, 陶意. 2019. 相山铀矿田铀多金属成矿时代与成矿热历史. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2801-2816. |
凌洪飞, 沈渭洲, 邓平, 蒋少涌, 高剑峰, 叶海敏, 濮巍, 谭正中. 2004. 粤北笋洞花岗岩的形成时代、地球化学特征与成因. 岩石学报, 20(3): 413-424. |
刘斌, 陈卫锋, 方启春, 唐湘生, 毛玉锋, 孙立强, 高爽, 严永杰, 魏欣, 凌洪飞. 2018.相山西部牛头山铅锌矿化体成矿物质来源——原位硫同位素的制约.地球科学, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20181221.0947.004.html
|
刘斌, 陈卫锋, 方启春, 毛玉锋, 唐湘生, 严永杰, 魏星, 凌洪飞. 2019. 相山铀矿田成矿流体特征——来自微量、稀土元素地球化学证据. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2774-2786. |
刘军港, 李子颖, 黄志章, 李秀珍, 聂江涛. 2017a. 江西相山CUSD3钻孔铀矿化蚀变带元素活动性探讨. 地质学报, 91(4): 896-912. |
刘军港, 李子颖, 聂江涛. 2017b. 相山深部铅锌多金属矿化S同位素特征及其地质意义. 地质论评, 63(增): 237-238. |
刘军港, 李子颖, 聂江涛, 王健, 李秀珍. 2019a. 江西相山西部地区深部多金属矿化矿石组构学、矿物学研究及其地质意义. 矿床地质, 38(2): 367-381. |
刘军港, 李子颖, 聂江涛, 王健. 2019b. 江西相山铀矿田深部多金属矿化成矿流体来源——流体包裹体He-Ar同位素证据. 大地构造与成矿学, 43(2): 271-282. |
刘军港, 李子颖, 聂江涛, 张万良, 王勇剑, 田明明. 2019c. 相山铀矿田西部地区深部多金属矿化成矿年代与成矿流体演化:Rb-Sr同位素体系的制约. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2787-2800. |
刘峤. 2019. 粤东北仁差盆地察甘火山岩型铀-多金属矿床成矿特征及其成矿机理探讨. 矿产与地质, 33(1): 77-82. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2019.01.010 |
骆金诚, 齐有强, 王连训, 田建吉, 石少华, 陈佑纬. 2019. 粤北下庄铀矿田基性岩脉Ar-Ar定年及其与铀成矿关系新认识. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2660-2678. |
聂江涛, 李子颖, 王健, 郭建. 2015. 江西相山矿田多金属成矿流体特征与成矿作用. 地质通报, 34(2-3): 535-547. |
聂江涛, 李子颖, 王健, 郭建, 林锦荣, 黄志章, 李秀珍, 田明明, 刘军港, 司志发. 2018. 相山铀矿田铅锌矿化同位素特征及成矿物质来源探讨. 铀矿地质, 34(6): 353-359. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2018.06.005 |
庞雅庆, 范洪海, 高飞, 吴建勇, 谢小占. 2019. 粤北诸广南部铀矿田流体包裹体的氦氩同位素组成及成矿流体来源示踪. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2765-2773. |
祁家明, 朱捌, 吴建勇, 曹豪杰, 刘文泉, 徐争启. 2019. 粤北仁化棉花坑铀矿床成矿热液演化及其对成矿过程的约束. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2711-2726. |
覃慕陶, 刘师先. 1998. 南岭花岗岩型和火山岩型铀矿床. 北京: 地质出版社, 96-122.
|
邱林飞, 吴迪, 吴玉, 金贵善, 韩娟, 刘军港, 郭娟. 2019. 相山牛头山地区铀矿床深部多金属成矿流体特征与成矿物质来源探讨. 矿床地质, 38(2): 291-302. |
司志发. 2018.江西相山矿田铀与多金属成矿作用对比研究.硕士学位论文.北京: 核工业北京地质研究院, 1-60
|
宋昊, 徐争启, 宋世伟, 倪师军, 张成江, 晏文权, 程发贵, 李亚平. 2019. 桂西大新-钦甲地区辉绿岩脉地球化学与锆石U-Pb同位素年代学特征及其对碳硅泥岩型铀矿床成因的启示. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2845-2863. |
谭忠银, 张德存, 匡正平, 朱全政, 李元. 2015. 粤北诸广南部棉花坑铀矿床深部找矿分析. 铀矿冶, 34(2): 78-81,86. |
田建吉, 张国全, 商朋强, 齐有强. 2019. 大茶园铀矿床成矿物质来源——C-O和Sr-Nd同位素证据. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2817-2829. |
王健, 聂江涛, 郭建. 2015. 江西相山矿田铜矿化特征及成矿流体演化. 矿物岩石, 35(4): 74-84. |
王健, 聂江涛, 郭建, 黄志章, 李秀珍. 2016. 江西相山矿田深部多金属矿化特征. 地质与勘探, 52(1): 47-59. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2016.01.009 |
王建国, 马英英, 汤国平, 张运涛, 庞文静, 姚亦军, 邱林飞, 郭娟. 2018. 相山铀矿田牛头山地区多金属矿石矿物特征及成矿期次. 世界核地质科学, 35(3): 143-149. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2018.03.004 |
吴德海, 夏菲, 潘家永, 刘国奇, 黄国龙, 刘文泉, 吴建勇. 2019. 粤北棉花坑铀矿床热液蚀变与物质迁移研究. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2745-2764. |
吴志坚, 胡志华. 2014. 相山矿田牛头山铀矿床铀-多金属成矿地质特征及找矿方向. 世界核地质科学, 31(2): 89-94. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2014.02.005 |
许丽丽, 伏顺成, 徐文雄. 2017. 棉花坑矿床深部铀成矿特征分析. 世界核地质科学, 34(2): 63-69. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2017.02.001 |
徐争启, 宋昊, 尹明辉, 张成江, 程发贵, 唐纯勇. 2019. 华南地区新元古代花岗岩铀成矿机制——以摩天岭花岗岩为例. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2695-2710. |
杨庆坤, 黄强太, 孙清钟. 2015. 江西相山矿田硫铅同位素地球化学特征. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 34(4): 755-762. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.04.009 |
杨庆坤, 郭福生, 周万蓬, 曲宏建. 2017a. 江西相山矿田铀铅锌多金属年代学特征及成矿模式. 地学前缘, 24(5): 283-298. |
杨庆坤, 黄强太, 罗勇, 黄宝华, 王清亚. 2017b. 江西相山铀矿田深部铅锌矿成矿流体演化特征. 科学技术与工程, 17(5): 132-141. |
姚佳蕾, 张川, 叶发旺, 徐清俊, 田茂杰. 2017. 相山邹家山铀矿区某钻孔岩心高光谱蚀变矿物特征及地质意义. 铀矿地质, 33(6): 376-380. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2017.06.009 |
张国全. 2008.华南热液铀矿床地球化学研究——以302铀矿床为例.博士学位论文.北京: 中国科学院大学, 1-96
|
赵永祥. 1995. 相山矿田铀成矿系列. 华东地质学院学报, 18(2): 128-134. |
钟福军, 严杰, 夏菲, 潘家永, 刘文泉, 赖静, 赵奇峰. 2019. 粤北长江花岗岩型铀矿田沥青铀矿原位U-Pb年代学研究及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2727-2744. |
朱捌. 2010.地幔流体与铀成矿作用研究——以诸广山南部铀矿田为例.博士学位论文.成都: 成都理工大学, 1-104
|
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35

