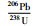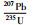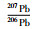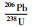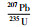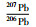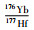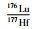2. 中国地质调查局, 北京 100037;
3. 中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心, 天津 300170;
4. Department of Earth and Environment Sciences, University of Kentucky, Lexington KY 40506 0053;
5. Department of Geology, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati OH 45221 0013
2. China Geological Survey, Beijing 100037, China;
3. Tianjin Center, China Geological Survey, Tianjin 300170, China;
4. Department of Earth and Environment Sciences, University of Kentucky, Lexington KY 40506 0053, USA;
5. Department of Geology, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati OH 45221 0013, USA
著名的蓟县剖面位于天津市蓟县(现蓟州区)北部山区,主要代表了中-新元古代华北克拉通燕辽裂陷槽沉积的巨厚地层(图 1)。蓟县剖面具有地质构造简单、岩层完整连续、顶底界面清晰、变质变形轻微、化石丰富、地理位置优越等优点(陈晋镳等, 1980, 1997),是世所罕见的珍贵地层剖面,具有很高的科学研究价值。特别是近年来,研究者们围绕蓟县剖面在早期生命起源和演化(Zhu and Chen, 1995; Peng et al., 2009; Zhu et al., 2016; Huang et al., 2017; Shi et al., 2017a, b ; Guo et al., 2018; Qu et al., 2018; Miao et al., 2019)、古海洋沉积环境(Li et al., 2003; Chu et al., 2004, 2007; Mei, 2006;梅冥相等, 2008, 2009;王德海等, 2009; Mei and Tucker, 2011;朱祥坤等, 2013; Ding et al., 2017; Ma et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2018)、LIP与全球古大陆再造(Zhang et al., 2017)、微生物成因沉积构造(MISS)(Yang et al., 2017)等方面,相继取得了一系列新的重要进展,使这一剖面更受世人关注。
|
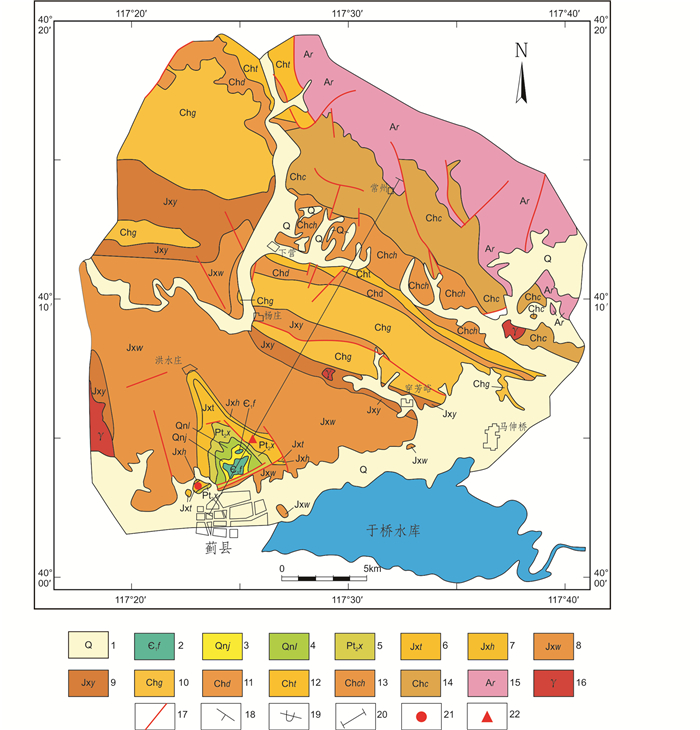
图 1 蓟县北部地区地质图与采样位置(据李怀坤等, 2014修改) 1-第四系; 2-府君山组; 3-景儿峪组; 4-长龙山组; 5-下马岭组; 6-铁岭组; 7-洪水庄组; 8-雾迷山组; 9-杨庄组; 10-高于庄组; 11-大红峪组; 12-团山子组; 13-串岭沟组; 14-常州沟组; 15-太古宙遵化岩群; 16-中生代花岗岩; 17-断层; 18-地层产状; 19-倒转地层; 20-蓟县标准剖面; 21-大喻山剖面采样点; 22-大五尖剖面采样点 Fig. 1 Geological map of northern Jixian area and the sampling locations (modified after Li et al., 2014) |
作为以上各类研究的基础,华北地台及中国中-新元古代地层格架的建立与完善具有十分重要的意义,蓟县剖面则见证了其间复杂的研究历史。“震旦系”最早被明确为代表中国寒武系之下、五台群或泰山群之上的沉积单元(Grabau, 1922),稍后建立的三峡震旦系剖面(Lee and Chao, 1924)成为中国震旦系的代表。自1934年被首次报道后(Kao et al., 1934),蓟县剖面成为华北震旦系的标准剖面(Lee, 1939)。然而,随着工作的不断深入,研究者们逐渐认识到,三峡剖面震旦系层位应高于蓟县剖面震旦系(王曰伦和陆宗斌, 1962;张丕孚, 1988),于是又将中国震旦系重新划分为四个“系”,统称“震旦亚界”(陈晋镳等, 1980),与南方震旦系合称“上前寒武系”(王曰伦等, 1980;邢裕盛和刘桂芝, 1982;曹瑞骥等, 1988)。自20世纪80年代中后期开始,蓟县剖面逐渐成为中国中-新元古界地层标准剖面,用以指代1800~800Ma间华北地台的地质历史,并被学术界长期引用(邢裕盛等, 1996;陈晋镳等, 1999;全国地层委员会, 2001, 2002; Lu et al., 2008)。
众所周知,一个地区地层格架的建立与完善,除了传统的地层学和古生物学研究,主要来自于相关地层的年代学研究,特别是取决于测年对象以及相关测试技术的不断改进和应用,蓟县剖面也是如此。该剖面相关地层直接定年的最早尝试,可追溯到20世纪50年代苏联学者对景儿峪组自生海绿石的K-Ar法测年(转于荣炳和张学祺, 1984)。利用相同方法,研究者们陆续测定了蓟县剖面景儿峪组、铁岭组、大红峪组、团山子组等地层单位的形成年龄(中国科学院地质研究所绝对年龄实验室, 1965; LIGKIGAS, 1977;于荣炳和张学祺, 1984)。20世纪70年代后,研究者又在蓟县剖面地层中开展了包括云母或全岩K-Ar法、沉积岩U-Pb法、自生海绿石或粘土Rb-Sr法、燧石K-Ar法和40Ar-39Ar法以及页岩或碳酸盐岩Pb-Pb法等多方面的测年研究(LIGKIGAS, 1977;于荣炳和张学祺, 1984;王松山等, 1995;李明荣等, 1996;王松山和裘冀, 1999)。现在人们知道,上述这些技术和方法中,由于其测年矿物同位素系统大都会在后期的构造-热事件中受到严重的干扰和改造,因此其测年结果对相关地层形成时代的实际约束是非常有限的。
随着以锆石为测年对象的高精度U-Pb同位素测年法的应用和推广,研究者相继在蓟县剖面大红峪组碱性火山岩(陆松年和李惠民, 1991)以及团山子组火山岩(李怀坤等, 1995)分别获得了1625.3±6.2Ma和1683±67Ma的锆石U-Pb年龄。这是首批利用火山岩锆石对蓟县剖面下部地层形成时代的直接约束。除此之外,研究者也一直设法在蓟县剖面其他层位寻找火山成因的沉积夹层,以期获得更多直接而精确的年龄,但未能成功。进入21世纪以来,研究者首先在燕山地区原来划归“新元古界青白口系(1000~800Ma)”的下马岭组黑色页岩中发现钾质斑脱岩(K-bentonite)这类火山成因夹层(陈晓雨, 2005;杨红梅, 2006),为华北中-新元古界中-上部序列的直接测年带来了新的契机。依靠该组钾质斑脱岩锆石测年研究的突破(高林志等, 2007; Gao et al., 2008; Su et al., 2008)以及随后在其他地区相应层位获得的一系列新进展(Lu et al., 2008;李怀坤等, 2009a, 2010, 2011; Su et al., 2010;苏文博等, 2012; Li et al., 2013;张拴宏等, 2013; Zhang et al., 2015),华北克拉通“中-新元古界”的地层格架终于得到了较全面的重新厘定(苏文博等, 2012; Li et al., 2013;苏文博, 2014, 2016)。然而,蓟县剖面的中上部,以碳酸盐岩为主的层段,即蓟县系(群),一直还缺乏类似的精确而直接的测年约束。2014年笔者等在蓟县城北西铁岭组及雾迷山组中分别发现了钾质斑脱岩,并获得了其锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄分别为1439±14Ma、1483±13Ma和1487±16Ma(李怀坤等, 2014),其中雾迷山组钾质斑脱岩锆石测年在整个华北北缘还是首次。这一进展为蓟县剖面继续作为华北克拉通中-新元古界标准剖面,提供了直接而强有力的年代学新依据,成为精确约束该剖面蓟县系相关地层单位年代格架的新“锚点”。
遗憾的是,由于上述大喻山剖面紧邻蓟县城区,最近几年来该地区的市政建设使得剖面的绝大部分已被道路和其他设施覆盖。这给后续围绕蓟县剖面铁岭组开展研究带来了极大不便,也在客观上影响了该剖面的科学性及权威性。鉴于此,笔者在蓟县附近相关地点开展了一系列新的工作,终于在位于蓟县城东北约5km的大五尖采石场发现了铁岭组新剖面,并在该组二段近底部相关层位确认了类似的钾质斑脱岩夹层。经过前期分析,笔者选取该剖面的2件斑脱岩样品开展了LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb测年研究。为对比起见,笔者还将此前在原大喻山剖面铁岭组相关层位采集的1件样品一起开展了测年。鉴于样品锆石具有确凿的岩浆成因特征,笔者还对这3件样品的测年锆石颗粒开展了系统的Lu-Hf同位素分析。新的测年结果与笔者等早先在蓟县西北原大喻山剖面(李怀坤等, 2014)、河北平泉刘家沟剖面(Su et al., 2010)铁岭组二段近底部钾质斑脱岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年结果,在误差范围内是完全可比的;而其Lu-Hf同位素结果则显示,当前钾质斑脱岩所代表的源岩主要来源于地壳物质的熔融。大五尖剖面的发现及其相关研究,可望弥补大喻山剖面被破坏的缺憾,因而具有重要的科学意义。
1 区域地质背景基于碰撞造山带的系统对比,研究者们提出2000~1800Ma期间曾形成了全球性的Columbia超大陆,华北克拉通保留了与超大陆聚合相关的古老碰撞造山带,是Columbia超大陆的组成部分(Zhao et al., 2000, 2002, 2004; Rogers and Santosh, 2002)。Columbia超大陆在1800Ma前后进入裂解期(Zhao et al., 2000; Rogers and Santosh, 2002),华北克拉通基底整体抬升,紧随着开始发生裂谷作用(Zhai and Liu, 2003;翟明国, 2004;翟明国和彭澎, 2007),主要表现为在其边缘首先形成数个裂陷槽(坳拉谷),海水再沿着这些裂陷槽向克拉通内部不断侵进。位于华北北缘大体呈北东-南西方向展布的燕辽裂陷槽(Lu et al., 2008;翟明国等, 2014;陆松年等, 2016)便是其中之一,天津蓟县一带则为这一裂陷槽的沉降中心,形成了巨厚的滨浅海相中-新元古代地层(王鸿祯, 1985)。
整个蓟县剖面地层的总厚度接近10000m,自下而上一般划分为长城系、蓟县系、青白口系3个系(群),含12个组(Kao et al., 1934;全国地层委员会, 1962, 2001, 2002;王曰伦, 1963;河北省、天津市区域地层表编写组, 1979;陈晋镳等, 1980, 1997, 1999;邢裕盛等, 1996)。区域上,这套地层自东北向西南,由老到新依次展布,中心则为府君山-洪水庄向斜(图 1)。其底部的常州沟组砂砾岩呈角度不整合覆盖于太古界迁西群(密云群)混合岩化的片麻岩、角闪岩、变粒岩等变质杂岩之上,其顶部景儿峪组灰岩、页岩的上覆地层则为寒武系府君山组灰岩和白云岩,其间也为平行不整合接触(Kao et al., 1934;陈晋镳等, 1980)。
铁岭组属于上述序列中的蓟县系顶部,其底部与洪水庄组整合接触,上覆下马岭组,之间为平行不整合接触。后者曾被命名为“芹峪上升”,代表一次区域地壳抬升(乔秀夫, 1976)。高振西等最早将蓟县城北约5km的铁岭村附近灰岩命名为“铁岭灰岩”(Kao et al., 1934),后改称“铁岭组”(全国地层委员会, 1962, 2001;陈晋镳等, 1980, 1999)。铁岭组可被分为上、下两个亚组,即“老虎顶亚组”和“代庄子亚组”(陈晋镳等, 1980),亦对应铁岭组二段和一段(陈晋镳等, 1999)。在华北北部燕山和太行山地区,铁岭组以普遍发育各类叠层石礁丘的滨、浅海相潮间带-潮下带碳酸盐岩为主,夹少量细碎屑岩(杜汝霖等, 1980)。一般认为该组形成于北半球中低纬度(Zhang et al., 2006; Chen et al., 2013),属于热带-亚热带气候环境(屈原皋等, 2004)。笔者此前关于该组顶部风化壳的研究结果,也支持类似认识(郭文琳和苏文博, 2014)。
在蓟县剖面上,铁岭组一段底部为中厚层砂岩与下伏洪水庄组整合接触,向上为页岩和灰色含砂含锰白云岩互层,上部以紫色、绿色和黑色页岩为主,也有含锰白云岩,白云岩含叠层石。顶部有硅质角砾,或锰土质古土壤,厚153m。二段下部为含锰内碎屑白云岩与白云质灰岩互层,向上为巨大叠层石礁灰岩夹内碎屑质灰岩。顶部为薄层白云质灰岩,厚180m(陈晋镳等, 1980)。
2 剖面及样品特征本文新剖面位于天津蓟州区北部府君山东北坡(图 1),整体上沿大五尖灰岩采坑西侧及桃园村-和平村之间乡村公路延伸,其起始位置GPS参考坐标为(40°4′57″ N、117°25′35″ E)。当前剖面总体走向190°左右,岩层倾向一般为230°左右,倾角接近30°。除铁岭组外,沿该剖面自北向南还依次出露有下马岭组、长龙山组、景儿峪组等(图 2)。需要说明的是,由于该采石场主要采集铁岭组二段灰岩,其实际揭示的露头主体沿北西-南东的地层走向横向展布,其东西向最宽处接近1500m,南北向则接近500m,因此在当前剖面的中东侧,也有多处为层序连续、岩石新鲜的露头剖面可供观测。

|
图 2 采样点剖面示意图(A、B)及野外露头(a-f) (a)铁岭组一段泥页岩与二段灰岩整合接触;(b)铁岭组与下马岭组平行不整合接触;样品JX321 (c)、样品JX323 (d)、样品JX324 (e)和样品JX325 (f)露头,箭头指示斑脱岩层位,铁锤等为比例尺. 1-灰岩;2-含锰灰岩;3-叠层石灰岩;4-杂色泥页岩;5-砂岩;6-钾质斑脱岩层 Fig. 2 Stratigraphic profiles with sampling sites (A, B) and field outcrops (a-f) |
该处铁岭组一段以灰岩为主,顶部为含锰-钙质的灰绿色-紫红色-褐色等杂色泥页岩,与其上的含锰灰岩呈现逐渐过渡、连续沉积的特征(图 2a)。其二段底部为灰色-浅褐色中厚层状含锰灰岩,向上逐渐过渡为质地纯净的灰白色中厚层状灰岩及厚层-块状叠层石礁丘,整个二段厚度大于200m。往南则可见铁岭组上覆下马岭组砂岩,其间发育风化壳,两者为平行不整合接触(图 2b)。
采样层位为该处铁岭组二段近底部灰岩,分别见于相隔约300m的两段露头(分别称之剖面A和剖面B)(图 2A, B)。因采石挖掘,露头上可见多层钾质斑脱岩,均呈夹层状产于灰岩中。其层厚5~20cm,上下层位相距3~10m不等。此处共采集4件样品,样品编号JX322、JX323、JX324、JX325,其采样层位参见图 2。此处所见钾质斑脱岩夹层呈灰白、浅灰绿色或浅豆绿色,单层厚度一般为1~10cm。其表面略呈土状,结构疏松,遇水易膨胀;舌尖舔其新鲜断口处,具有明显的吸附-粘滞感;这些均为典型的斑脱岩特征(Huff et al., 1992; Kolata et al., 1996;苏文博等, 2006;周明忠等, 2007; Huff, 2008, 2016; Su et al., 2010)。其中JX324(图 2e)位于剖面露头SE100°方向约300m处的剖面B所在小山包近顶部(即大五尖),其层厚约20cm;JX325(图 2f)位于小山包西南侧的剖面A采坑内,层厚也约为20cm。需要说明的是,上述两者露头横向上相距大约300m,其间因发育有南北向小断层及褶曲,使其层位无法直接追索对比。然而通过反复观测表明,这两层样品所在的斑脱岩夹层距离铁岭组二段底界的地层厚度均为27m左右,同时其斑脱岩夹层厚度、岩性特征也相似,其上覆及下伏岩性也可比,特别是其相邻层位灰岩中也没有其他斑脱岩夹层,因此这两处夹层很可能属于同一层斑脱岩(图 2)。
为对比起见,笔者在早先获得蓟县剖面铁岭组钾质斑脱岩锆石U-Pb年龄的大喻山剖面铁岭组二段近底部钾质斑脱岩(李怀坤等, 2014)同一层位中也曾采集了1件样品,样品编号为JX321。此处钾质斑脱岩呈浅豆绿色,层厚约25cm(图 2c)。值得注意的是,根据早先观测记录,该层斑脱岩也位于铁岭组二段底界厚约25m处。这与上述大五尖测年样品JX324及JX325的层位(距二段底界厚约27m)是基本一致的。考虑到当前样品所在层位的上下地层中也同样再无其他更厚的斑脱岩夹层,同时该斑脱岩厚度、岩性也与大五尖测年样品所在层基本一致,笔者认为,本文大喻山剖面样品JX321与大五尖样品JX324及JX325,很可能都属于不同地点的同一层斑脱岩。
3 测试方法及结果 3.1 测试方法钾质斑脱岩的锆石分选使用常规方法和流程,其分选与制靶的具体过程参见相关文献(宋彪等, 2002; Su et al., 2010;李怀坤等, 2014)。锆石微区原位U-Pb同位素年龄测定和Lu-Hf同位素分析在中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心同位素实验室分别采用LA-ICPMS和LA-MC-ICPMS完成,详细分析流程及原理参见文献(Wu et al., 2006;侯可军等, 2007;李怀坤等, 2009b;耿建珍等, 2011)。
锆石年龄计算采用源自澳大利亚Macquarie大学的标准锆石GJ-1作为外标,数据采用中国地质大学(武汉)刘勇胜研发的ICPMS Data Cal程序(Liu et al., 2010)和Kenneth R. Ludwig的Isoplot程序(Ludwig, 2003)进行处理,普通Pb采用Andersen的3D坐标法校正(Andersen, 2002),利用NIST612玻璃标样作为外标计算锆石样品的Pb、U含量。单个测试点的同位素比值和同位素年龄误差为1σ,207Pb/206Pb年龄加权平均值置信度为95%。
锆石Lu-Hf同位素测试,选择了相关样品中同位素年龄谐和度(指206Pb/238U年龄与207Pb/206Pb年龄比值的百分数)大于90%的颗粒来进行。测试时采用标样91500作为外标,Lu-Hf同位素计算公式及标准值参见文献(吴福元等, 2007)。现今球粒陨石176Lu/177Hf=0.0332,176Hf/177Hf=0.282772(Blichert-Toft and Albarède, 1997),现今亏损地幔的(176Lu/177Hf)DM=0.0384,(176Hf/177Hf)DM=0.28325(Nowell et al., 1998),λ(176Lu)=1.867×10-11y-1(Söderlund et al., 2004)。需要说明的是,该测试是在其U-Pb测年三年多之后才进行的,因此在测试前又按规定程序对样靶进行了轻微抛光、清洗等前处理,并根据测年时的样品靶图,选择了在与锆石U-Pb年龄测试相同的测定域开展测试(图 3)。

|
图 3 锆石阴极发光(CL)图像 内部黄色圆圈为LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb同位素分析点位置,外部白色圆圈为Lu-Hf同位素测试位置,数字分别为年龄值和样点号 Fig. 3 Cathodoluminescence images of zircons |
本文对采自大五尖剖面的2件样品JX324、JX325以及采自蓟县大喻山剖面的1件样品JX321分别开展了锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb测年和LA-MC-ICPMS Lu-Hf同位素测定。
3.2.1 锆石U-Pb年龄所测锆石Pb含量为26×10-6~137×10-6,U含量为93×10-6~488×10-6(表 1)。锆石阴极发光(CL)图像(图 3)结果显示,3件样品的锆石粒径约为80~150μm,长宽比约为11~13之间。绝大部分锆石颗粒呈自形-半自形晶,多呈短柱状或柱状,个别呈不规则形,发育有双锥,显示其未经过明显的搬运及磨蚀。锆石晶体内部结构清晰,振荡环带明显,高Th/U比值(0.6~3.4),具有典型的岩浆锆石特征(Hoskin and Black, 2000; Corfu et al., 2003; Wu and Zheng, 2004)。
|
|
表 1 铁岭组钾质斑脱岩锆石LA-ICPMS U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果 Table 1 LA-ICPMS zircon U-Th-Pb isotopic data of the K-bentonite samples from the Tieling Formation |
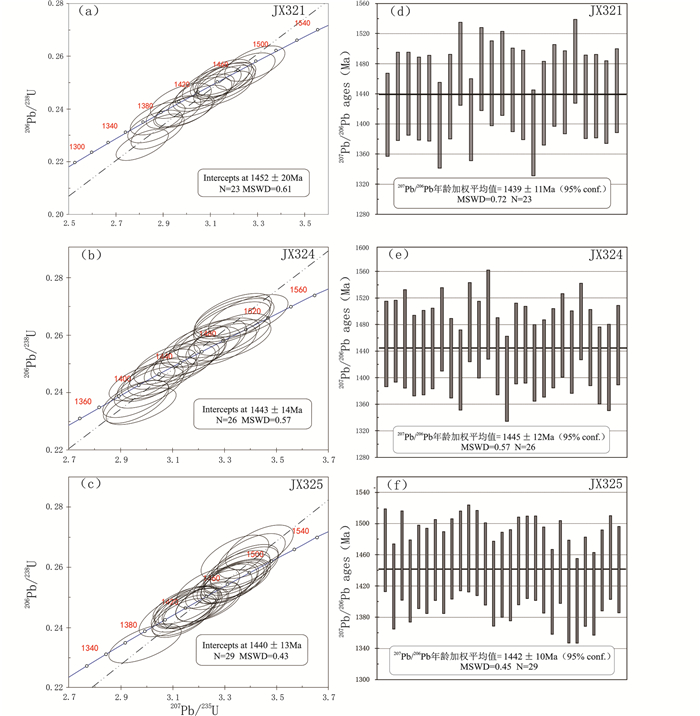
样品JX321一共测定了32个锆石U-Pb同位素数据点,除JX321-21外,其余均具有基本一致的U-Pb同位素年龄(表 1)。其中JX321-21年龄值明显偏大(2182Ma),可能为碎屑或继承锆石,因此将其与另外8个谐和度小于90%的数据点一并剔除,剩余数据点构成的不一致线与谐和线的上交点年龄为1452±20Ma (图 4a)(置信度95%;N=23),207Pb/206Pb表面年龄加权平均值为1439±11Ma (图 4d),二者在误差范围内一致。以207Pb/206Pb年龄加权平均值(1439±11Ma)代表该钾质斑脱岩中锆石结晶年龄。
|
图 4 铁岭组钾质斑脱岩样品锆石U-Pb谐和图 Fig. 4 Zircon U-Pb concordia diagrams of the K-bentonites from the Tieling Formation |
样品JX324也测定了32个锆石U-Pb同位素数据点(表 1),绝大部分都具有基本一致的U-Pb同位素年龄,谐和度较高,71%的数据点谐和度大于90%。其中JX324-13、JX324-28两个点年龄值明显偏大(分别为2731Ma和2176Ma),可能为碎屑或继承锆石,因此将其与4个谐和度小于90%的数据点予以剔除,剩余数据点构成的不一致线与谐和线的上交点年龄为1443±14Ma(图 4b)(置信度95%;N=26),207Pb/206Pb表面年龄加权平均值为1445±12Ma(图 4e),二者在误差范围内一致。以207Pb/206Pb年龄加权平均值(1445±12Ma)代表该钾质斑脱岩中锆石结晶年龄。
样品JX325一共测定了40个锆石U-Pb同位素数据点,绝大部分具有基本一致的U-Pb同位素年龄(表 1)。其中谐和度较低(小于90%),以及具有较大年龄值(2446Ma),可能为碎屑锆石的共11个数据点予以剔除,剩余数据点构成的不一致线与谐和线的上交点年龄为1440±13Ma(图 4c)(置信度95%;N=29),207Pb/206Pb表面年龄加权平均值为1442±10Ma(图 4f),二者在误差范围内一致。以207Pb/206Pb年龄加权平均值(1442±10Ma)代表该钾质斑脱岩中锆石结晶年龄。
3.2.2 锆石Lu-Hf同位素在上述测年基础上,在3件样品测年的同岩浆期锆石中一共选择测定了54个Lu-Hf同位素数据点(表 2)。所有锆石的176Lu/177Hf比值均小于0.002,表明锆石形成后具有较低的放射性成因Hf的积累,其176Hf/177Hf比值能够较好反映形成过程中Hf同位素组成特征。根据上述测年结果,分别取1439Ma、1445Ma和1442Ma作为年龄值对样品JX321、JX324、JX325的Lu-Hf同位素数据进行计算。
|
|
表 2 铁岭组钾质斑脱岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果 Table 2 Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic data of the K-bentonite samples from the Tieling Formation |
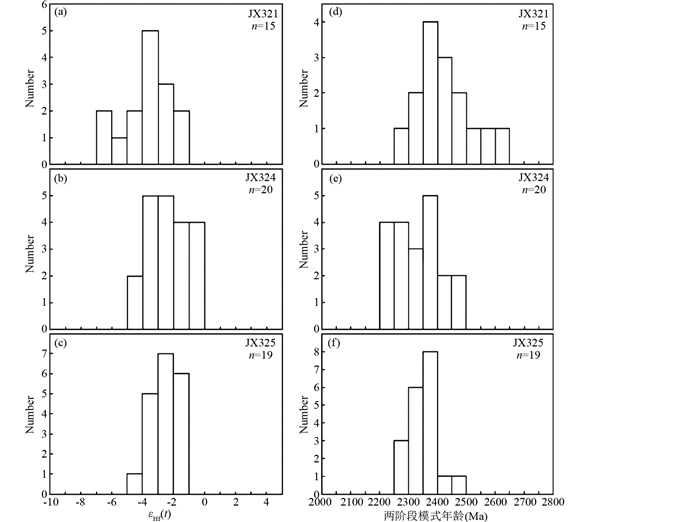
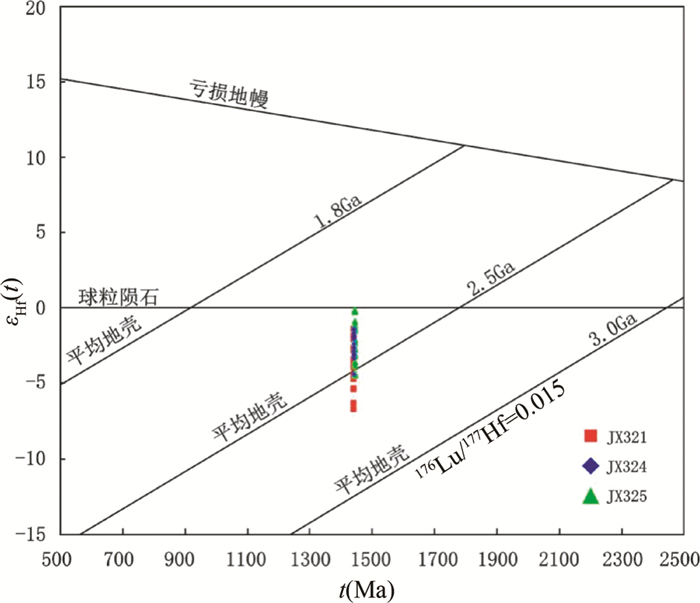
样品JX321测定了15个Lu-Hf同位素数据点(表 2、图 5a, d),数据点176Hf/177Hf比值为0.281703~0.281851,εHf(t)=-6.7~-1.4,两阶段Hf模式年龄tDM2为2271~2603Ma。
样品JX324测定了20个Lu-Hf同位素数据点(表 2、图 5b, e),数据点176Hf/177Hf比值为0.281758~0.281880,εHf(t)=-4.5~-0.2,两阶段Hf模式年龄tDM2为2200~2471Ma。
样品JX325测定了19个Lu-Hf同位素数据点(表 2、图 5c, f),数据点176Hf/177Hf比值为0.281758~0.281847,εHf(t)=-4.4~-1.4,两阶段Hf模式年龄tDM2为2275~2464Ma。
3件样品锆石的εHf(t)值(图 6)、两阶段Hf模式年龄tDM2变化范围均相近,176Hf/177Hf=0.281703~0.281880,εHf(t)=-6.7~-0.2,tDM2=2200~2603Ma,高斯分布峰值为~2360Ma。这一结果显示,这些锆石样品所代表的钾质斑脱岩夹层,应来自时代和组分基本一致的岩浆源区。
|
图 5 铁岭组钾质斑脱岩样品锆石Lu-Hf同位素组成直方图 Fig. 5 Histograms of zircon Lu-Hf isotopic compositions of the K-bentonite samples from the Tieling Formation |
如前所述,华北克拉通铁岭组年代地层学的研究始于20世纪60年代。早期研究者们给出的该组测年结果(1000~1200Ma)主要是通过K-Ar和40Ar-39Ar法测量灰岩中自生海绿石得到的(中国科学院地质研究所绝对年龄实验室, 1965; LIGKIGAS, 1977;王曰伦等, 1980;于荣炳和张学祺, 1984;李明荣等, 1996)(表 3)。
|
|
表 3 华北克拉通铁岭组年代学研究沿革表 Table 3 Chronological researches of the Tieling Formation, NCC |
作为对Columbia超大陆裂解的响应,华北克拉通、尤其是其北缘自中元古代初期开始出现一系列裂陷槽盆地(翟明国和彭澎, 2007; Lu et al., 2008;翟明国等, 2014; Zhai et al., 2015;陆松年等, 2016),这使得该地区中元古界下部长城群的火山活动记录相对上部更加明确(陈晋镳等, 1980),因而在华北北缘长城群的各组中,研究者也已率先获得了较多的锆石U-Pb年龄支撑(陆松年和李惠民, 1991;李怀坤等, 1995; Lu et al., 2008; Li et al., 2013;张拴宏等, 2013)。然而并非所有层位均发育适合锆石测年的火山岩,研究者开始寻找火山成因的沉积夹层,以期获得新的突破。
一般认为,钾质斑脱岩(K-bentonite)是中酸性火山喷发所产生的火山灰经过沉降、水解和成岩作用,形成的粘土岩沉积夹层(Huff et al., 1992)。由于主要来自爆发式的火山成因背景,钾质斑脱岩具有天然的等时性和空间广泛分布等优势(Huff et al., 1992; Kolata et al., 1996; Calarge et al., 2003;苏文博等, 2006;周明忠等, 2007; Huff, 2008, 2016; Su et al., 2010),这使其在前寒武纪研究、特别是针对缺乏显生宙那样实体化石约束的前寒武纪“哑地层”的年代框架的修正和完善工作中,可以发挥越来越重要的作用(陈晓雨, 2005;杨红梅, 2006;高林志等, 2007; Gao et al., 2008; Su et al., 2008;王泽九, 2010)。正是基于华北中元古界上部的下马岭组三段所发现的钾质斑脱岩(陈晓雨, 2005;杨红梅, 2006),研究者获得其锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄为~1380Ma(高林志等, 2007; Gao et al., 2008; Su et al., 2008),由此将下伏铁岭组的上限推定为1400Ma。稍后,笔者等在河北平泉刘家沟剖面铁岭组二段近底部发现钾质斑脱岩夹层,并获得其岩浆型锆石的SHRIMP U-Pb年龄为1437±21Ma,从而首次直接标定了铁岭组的形成时代(Su et al., 2010)。而在蓟县剖面上,经过近10年的不断努力,笔者等终于在蓟县北西大喻山铁岭组二段底部以及附近的无名山北侧雾迷山组四段底部均识别出质地良好的钾质斑脱岩夹层,并分别获得了1439±14Ma、1483±13Ma和1487±16Ma的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄(李怀坤等, 2014)。由此,蓟县剖面蓟县系上部、即华北克拉通中-新元古界上部碳酸盐岩为主的代表性层段,也就第一次获得了直接而精确的年代约束。显然,大喻山剖面对于整个蓟县剖面而言,其重要性是不言而喻的。
本文对2件蓟县大五尖剖面铁岭组二段近底部的钾质斑脱岩样品、1件原蓟县大喻山剖面(李怀坤等, 2014)的钾质斑脱岩样品开展了系统的锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb同位素测年。研究表明,样品锆石具有典型的岩浆锆石特征,所测得的锆石结晶年龄可以代表其成岩年龄,并可限定其所在地层序列的形成时代。以上3件样品分别获得了1445±12Ma、1442±10Ma、1439±11Ma的精确年龄。这3个新测年结果在误差允许范围内彼此是高度一致的,同时与笔者等早先在河北平泉刘家沟剖面(Su et al., 2010)和蓟县大喻山剖面(李怀坤等, 2014)的铁岭组二段钾质斑脱岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年结果(1437±21Ma、1439±14Ma)也均可对比。
与前人研究相一致的新测年,首先充分说明了其高可信度。这既为铁岭组高精度年代约束提供了可靠的新依据,也再次肯定了之前笔者等提出的对华北克拉通北部铁岭组形成年龄的限定(~1440Ma),同时也支持应将该组由原对应于国际地层委员会中元古代狭带纪(Stenian Period,1200~1000Ma)划归为中元古代盖层纪(Calymmian Period,1600~1400Ma)(Su et al., 2010; Li et al., 2013;李怀坤等, 2014)的认识。
其次,新的测年也表明,位于蓟县北东大五尖剖面的铁岭组与早先报道的蓟县北西大喻山剖面该组在层位上是完全一致的,并且也同样获得了精确可信的年代学约束,完全可以作为蓟县地区铁岭组新的研究剖面(关于大五尖剖面详见下文)。这一进展既为蓟县剖面及整个燕山地区铁岭组及年代地层格架厘定等增加了更多、更富有说服力的年代学证据,同时也及时弥补了大喻山剖面被毁的缺憾,增强了蓟县剖面作为华北克拉通中-新元古界标准剖面的立典意义,进一步地夯实了其科学性与代表性。
4.2 铁岭组钾质斑脱岩源区的讨论关于钾质斑脱岩的源区实际包括了两层含义:其一是指其所对应的母岩岩浆来源,其二是指其对应的火山喷发-岩浆活动带、即空间来源。对于前者,本文将结合铁岭组Hf同位素分析结果来加以讨论;对于后者,限于本文的主要内容和目前资料,这里仅做一个初步而粗略的探讨。
研究表明,准确的锆石Hf同位素可作为岩浆源区判断的重要依据(Patchett et al., 1982; Amelin et al., 1999; Griffin et al., 2000;吴福元等, 2007)。一般来说,Hf的模式年龄与形成年龄相近,表明岩浆源区为源自亏损地幔或新生地壳物质;Hf模式年龄大于形成年龄,岩浆源区受地壳物质混染或来自于富集型地幔(吴福元等, 2007)。原始地幔发生壳幔分异后,亏损地幔的εHf(t)值为正值,地壳的εHf(t)值为负值(Blichert-Toft and Albarède, 1997)。
当前铁岭组新测年样品的锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果表明,其176Hf/177Hf=0.281703~0.281880,εHf(t)=-6.7~-0.2;其两阶段模式年龄变化范围2200~2603Ma,年龄分布相对集中,高斯分布峰值约为2360Ma;在锆石εHf(t)值-年龄比值图(图 6)上,数据点也表现出明显富集的特征。这些均表明,其岩浆源岩物质主要来源于新太古代-古元古代早期地壳物质部分熔融。
|
图 6 铁岭组钾质斑脱岩锆石εHf(t)值-年龄比值图 Fig. 6 Zircon εHf(t)vs. age diagram of the K-bentonite samples from the Tieling Formation |
根据现有资料,在2500Ma前后,华北克拉通岩石圈地幔由太古宙的亏损状态开始转变为富集型地幔(任康绪等, 2006),新太古代晚期至古元古代晚期,岩浆源区主要来自富集地幔的熔融(Wu et al., 2005a, b ; Zhang et al., 2007; Yang et al., 2009;翟明国等, 2014;张健等, 2015),古-中元古代的岩浆活动主要为新太古代地壳物质的循环和改造(任荣等, 2011;陈岳龙等, 2012; Liu et al., 2014)。进入中元古代蓟县群沉积时期,华北克拉通由裂陷槽背景盆地逐渐转换为浅海相碳酸盐盆地,且海侵范围不断扩大,蓟县剖面所在的燕辽裂陷槽已相对稳定,岩浆作用也明显减弱(Lu et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2009; Meng et al., 2011;乔秀夫和王彦斌, 2014;陆松年等, 2016)。
显然,根据锆石Hf同位素分析所获得的铁岭组二段近底部钾质斑脱岩的源岩特征,与目前有关该阶段华北克拉通岩浆源区主要为地壳物质循环改造的认识是基本吻合的,但是其源岩产生的主要年代(峰值~2360Ma),并非目前公认的新太古代-古元古代阶段华北克拉通岩浆活动的两个高峰期(~2500Ma及~1850Ma)。另一方面,虽然~2300Ma的岩浆活动在华北克拉通中部及南北缘均有发育(耿元生等, 2006;赵凤清等, 2006;第五春荣等, 2007; Dong et al., 2007; Wan et al., 2009;黄道袤等, 2012;包创等, 2013),1440Ma前后的碎屑锆石(陈岳龙等, 2012; Hu et al., 2012;王盟等, 2013)也频见于华北克拉通不同时代地层中,但就整个华北克拉通本体而言,则普遍缺乏~1440Ma的岩浆侵入-喷发记录。这使得铁岭组斑脱岩对应火山-岩浆活动带的分析与探讨,目前还存在着相当大的不确定性。
如前所述,钾质斑脱岩往往来源于远离火山源头的中酸性火山喷发所产生的火山灰降尘(Huff et al., 1992; Kolata et al., 1996; Calarge et al., 2003;苏文博等, 2006;周明忠等, 2007; Huff, 2008, 2016; Su et al., 2010),由此可以认为,蓟县剖面及燕山地区铁岭组内这些斑脱岩夹层,在很大程度上不大可能像该地区团山子组-大红峪组碱性火山岩那样,来自于该组所沉积的燕山裂陷槽内部。相反,它们很有可能来源于燕山裂陷槽之外,即华北克拉通其他区域的火山带,甚至来自当时与华北克拉通邻近的古板块及其边缘的岛弧岩浆带。
如果说产生该组斑脱岩的火山活动来源于华北克拉通其他地区,那么目前来看,至少下面这两方面信息是值得关注的:
首先,有学者(He et al., 2009)在研究传统的豫西南地区熊耳群火山岩过程中,曾在熊耳山地区熊耳群鸡蛋坪组内识别出少量1.45Ga左右的长英质岩浆记录。从测年结果看,其与当前铁岭组二段斑脱岩年龄是基本一致的,其位置则在华北克拉通南缘的熊耳裂陷槽内。有趣的是,在该文这一样品当中,除去~1.45Ga岩浆锆石群,同时还有少量2275~2352Ma的继承锆石(He et al., 2009),后者与当前铁岭组斑脱岩Hf同位素所获得的源岩峰值时代(~2360Ma)也非常接近。因此,不排除该地区在该时期曾发生较大规模的火山喷发,所产生的火山灰被季风搬运到华北北缘的燕山裂陷槽后,形成了当前铁岭组二段近底部的这些斑脱岩夹层。当然,要想真正验证这一推测,至少关于上述长英质岩浆记录的性质、组分、规模和区域分布等,都还有待更进一步的研究;
其次,有学者(曾令君等, 2013)在位于华北克拉通南缘的河南卢氏潘河地区确认了一组LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年龄为1469±8Ma的正长岩岩脉,其岩石εHf(t)=-14.79~+8.16,Hf模式年龄为2.93~1.74Ga,指示其成岩物质主要来源于富集岩石圈地幔的部分熔融并有地壳物质的加入。虽然其Hf同位素揭示的源岩信息与本文铁岭组斑脱岩锆石比较接近,但必须看到,这些岩脉规模非常有限、且侵位时代也较早,因此无论是推测它们属于当前铁岭组斑脱岩的源区所在,抑或仅推测与之相关,都还需要更多工作来加以验证。
然而,上述两处岩浆活动可能都无法圆满解释这一现象:为何在华北克拉通整体缺乏~1440Ma岩浆侵入-喷发记录的同时,却可以在华北不同地点的不同地层中频频见到这一年龄(但不一定同源)的碎屑锆石(陈岳龙等, 2012; Hu et al., 2012;王盟等, 2013)?须知,仅仅依靠那么一点铁岭组斑脱岩夹层、以及上述有可能与之对应的豫西南地区那么一点火山岩-侵入岩,是绝对无法让整个华北克拉通后来的地层里几乎都可以出现~1440Ma的碎屑锆石的。相反,如果考虑铁岭组斑脱岩并非来自华北克拉通本身,而可能来自当时其附近的某个地块-克拉通板块,包括附近曾经存在过、但后期已被剥蚀了的岛弧岩浆带时,上述现象也许可以得到更为合理的解释。
最近有中国学者(Yuan et al., 2019)提出,在亚洲中部造山带南部(即塔里木-华北北缘)存在一条残余的1.45~1.36Ga的岩浆岩带。其包括多个I型和A型花岗岩体,代表了从挤压到拉张背景的连续变化。其中不乏与当前铁岭组斑脱岩形成年代基本一致、形成于挤压背景下的I型花岗岩体,被认为属于该时期主动大陆边缘的岩浆弧,并处于Nuna(Columbia)超大陆的边缘。显然,这一岩浆弧的存在,从空间上和时间上,为本文铁岭组斑脱岩及华北克拉通多个层位出现的~1440Ma碎屑锆石,提供了一处可能的、紧邻华北克拉通北缘的物源区。
值得注意的是,欧美学者曾提出,大约在1.45~1.35Ga期间,在劳伦古陆西南部存在一次特征尚不甚明确的造山事件(Nyman et al., 1994; Karlstrom and Humphreys, 1998; Williams et al., 1999; Daniel and Pyle, 2006),产生了相关的沉积及岩浆记录。最近有学者(Doe et al., 2013)则认为,这可能表明在此期间劳伦西南与澳大利亚东部有着更为密切的关系。而一些学者(Karlstrom et al., 2001)认为,劳伦西南-东南缘曾经存在过一个延续时限长达1.0Ga(1.8~0.8Ga)汇聚型造山带,其中包括了1.5~1.3Ga等四个阶段。这个造山带可与澳大利亚、波罗的等古陆周缘同时代造山带相对比,表明这些古陆在此期间应彼此相连,属于同一个古陆群、即后来Rodinia的一部分。
近年来古地磁(Zhang et al., 2012)及大火成岩省LIP(Zhang et al., 2017)等方面的进展表明,中元古代的华北克拉通与西伯利亚、劳伦、北澳大利亚及印度等克拉通板块应存在紧密的联系。特别是基于燕辽地区1.33~1.30Ga基性岩墙群LIP与澳大利亚北部时代相同、岩性一致的Derim Derim-Galiwinku LIP,以及古元古代-中元古代阶段燕辽地区与澳洲北部McArthur Basin地层序列的相似性,最近张拴宏等学者(Zhang et al., 2017)明确提出,这两个地区及所在克拉通实际上很可能在同一个LIP的影响范围内。
另一方面,笔者(苏文博, 2016)曾指出,根据现有年代学研究(苏文博等, 2012)等,华北克拉通南缘含有大型具刺疑源类Tappania-Shuiyousphaeridium-Valaria等真核生物组合(Xiao et al., 1997; Yin, 1997)的层位——山西永济北大尖组,其形成时代应厘定为~1.65Ga。由于目前这一生物群在印度北部(~1.63Ga, Butterfield, 2015)、澳大利亚北部(~1.45Ga, Javaux et al., 2001)、西伯利亚(~1.1Ga, Nagovitsin, 2009)及劳伦西部(~1.5Ga, Adam et al., 2014)等均有发现,这可能说明,至少从~1.65Ga开始到稍后一个阶段即中元古代早-中期,上述古陆彼此之间应相距不远并有海域畅通(苏文博, 2016)。
基于上述进展和认识,并考虑到钾质斑脱岩多来源于中酸性火山喷发、后者又多与岛弧及板内中酸性岩浆活动相关,本文推测:目前来看,可能形成当前铁岭组二段钾质斑脱岩的、非华北克拉通本体的火山源岩岩浆区,除了紧邻华北克拉通北缘的亚洲造山带南部1.45~1.36Ga岩浆岩带,还应当考虑来自北澳及劳伦古陆的同时代造山带(但也不排除印度、西伯利亚等),包括它们周缘或附近曾经存在过的同时代的岛弧岩浆带。
显然,关于铁岭组斑脱岩更具体而准确的源区等信息,将是一个很有科学价值、并有待今后深入而系统工作的重要研究,它将有助于进一步揭示中元古代阶段华北克拉通大地构造背景、及其与Columbia-Rodinia超大陆演化之间的内在关系。
4.3 蓟县大五尖剖面的推介前已述及,此前笔者等(李怀坤等, 2014)在蓟县大喻山剖面获得并报道了铁岭组钾质斑脱岩锆石的精确测年结果,但是由于近年来的市政公路建设,剖面露头遭受严重破坏。这使得未来围绕蓟县剖面铁岭组的其他相关研究无法继续进行,并会在相当程度上影响蓟县剖面作为华北中-新元古界标准剖面的科学性和代表性。
显然,本文新发现并获得其钾质斑脱岩锆石新测年龄的大五尖铁岭组剖面,可以作为一个新的替代剖面,适时弥补上述缺憾。概括而言,新剖面具有以下明显优势:
(1) 本文研究表明,新发现的蓟县大五尖剖面的铁岭组同样具备精确和可信的地质年代学约束。其测年结果与早先报道的蓟县北西大喻山剖面以及河北平泉刘家沟剖面铁岭组斑脱岩锆石测年在误差范围内完全可比,均为~1440Ma。这充分说明了其科学性和代表性;
(2) 大五尖剖面位于府君山东北坡的大型灰岩采石场,露头良好。前已述及,由于该采石场主要采集铁岭组二段灰岩,因此其实际露头的主体沿北西-南东的地层走向横向展布,其东西方向最宽处接近1500m,南北方向也接近500m,露头资源相当充裕(实际上,在该采石场最东端边缘,也有一条近南北向、沿原采石场便道展布、层序比较连续、露头新鲜的铁岭组剖面可供观测)。需要补充的是,除铁岭组外,沿剖面A(参见图 2)自北向南还依次出露有下马岭组、长龙山组、景儿峪组等。由于早先的河谷冲蚀作用以及近年来“村村通”公路修筑等,这段剖面露头良好而连续,上述各组间界线也非常明显,相信该剖面在未来将会有很大的研究潜力;
(3) 大五尖剖面采石场周边交通便利。其东南和西北方向皆有新修建的可以连接蓟县市区环路的乡村公路,可以很方便快捷地到达。同时,不像津(天津)-围(围场)公路那样处于交通要道,当前乡村公路车辆稀少,具有更为稳妥安全的观测空间;
(4) 大五尖剖面地处府君山北坡,属于蓟县北郊农村及蓟县剖面核心区,远离城区、特别是其规划的开发区,在相当长时间内有望不会遭受城市未来建设的影响和破坏。特别是根据最新的环保要求,这个采石场目前已经封矿,今后将不再进行更大规模的开采,适合持续的科研观测及相关研究。因此,该剖面将为后续围绕蓟县剖面及华北克拉通铁岭组等层位开展相关工作,提供一个良好的、可供长期观测研究的剖面和平台。
5 结论(1) 在蓟县府君山东北坡采石场发现了新的大五尖铁岭组剖面,并在该组二段近底部再次确认多层钾质斑脱岩,分别获得了1445±12Ma和1442±10Ma的U-Pb年龄。同时对采自原大喻山剖面铁岭组二段的钾质斑脱岩样品也开展了LA-ICPMS锆石测年,其U-Pb年龄为1439±11Ma。这三者在误差范围内基本一致;
(2) 大五尖剖面及原大喻山剖面铁岭组二段近底部钾质斑脱岩的LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年龄,与早先在河北平泉刘家沟剖面及蓟县城北西大喻山剖面铁岭组二段近底部钾质斑脱岩夹层所获SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄,也是完全可比的。这一新的结果再次确认了蓟县剖面及华北北缘铁岭组年龄应为~1440Ma,也进一步表明了目前有关铁岭组钾质斑脱岩测年结果的可信性和科学性;
(3) 蓟县系铁岭组二段底部钾质斑脱岩中锆石的Hf同位素εHf(t)=-6.7~-0.2,两阶段模式年龄变化范围2200~2603Ma,高斯分布峰值为2360Ma,说明岩浆源岩主要来源于新太古代-古元古代早期地壳物质部分熔融。这是首次报道华北中元古界钾质斑脱岩夹层中锆石Lu-Hf同位素研究结果,为继续深入探讨类似沉积的岩浆来源及其它相关研究提供了新思路;
(4) 大五尖剖面位于府君山东北坡的一个大型采石场,其铁岭组露头良好并具备精确年龄限定,远离蓟县城区、交通便利,特别是因环保因素,今后将不再进行大规模开采,因此将会成为一条非常有利于长期开展研究工作的新剖面。
致谢 样品粉碎和锆石挑选由河北廊坊宇能公司帮助完成。锆石制靶由北京凯德正公司完成,锆石样品透射光与反射光照相、阴极发光(CL)扫描电镜照相在中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心同位素实验室完成。衷心感谢王建华、叶青、许雅雯、郭虎、耿建珍、肖志斌、崔玉荣、章敬若、李晓双、张师语、古丽米拉等在实验及成文过程中的大力支持和帮助。在论文评审过程中,赵太平研究员、张拴宏研究员、祝禧艳博士和梁新权博士等学者对本文的认真审读和中肯意见,以及期间与王世炎高工、赵太平研究员等学者的深入讨论,极大地提高了论文的质量和水平。
Absolute-Age Laboratory of Institute of Geology and Geophysics, CAS. 1965. Report on the petrological and mineralogical dating with K-Ar method Ⅱ. Scientia Geologica Sinica, (2): 106-112 (in Chinese) |
Adam ZR, Mogk DW, Skidmore M and Butterfield NJ. 2014. Microfossils from the Greyson Formation, Lower Belt Supergroup:Support for Early Mesoproterozoic biozonation. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, 46(5): 71 |
All China Commission of Stratigraphy. 1962. Academic Reports Compilation of the National Stratigraphic Conference:Precambrian of China. Beijing: Science Press: 1-80 (in Chinese)
|
All China Commission of Stratigraphy. 2001. Guide to Stratigraphy in China and the Introduction to the Guide. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-59 (in Chinese)
|
All China Commission of Stratigraphy. 2002. Explanation of China Regional Stratigraphic Chart. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-72 (in Chinese)
|
Amelin Y, Lee DC, Halliday AN and Pidgeon RT. 1999. Nature of the Earth's earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons. Nature, 399(6733): 252-255 DOI:10.1038/20426 |
Andersen T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2): 59-79 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X |
Bao C, Chen YL and Li DP. 2013. LA-MC-ICP-MS zircons U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic compositions of the Paleoproterozoic amphibolite in Bayan Ul area, Inner Mongolia. Geological Bulletin of China, 32(10): 1513-1524 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Blichert-Toft J and Albarède F. 1997. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 148(1-2): 243-258 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00040-X |
Butterfield NJ. 2015. Early evolution of the Eukaryota. Palaeontology, 58(1): 5-17 DOI:10.1111/pala.12139 |
Calarge LM, Meunier A and Formoso MLL. 2003. A bentonite bed in the Aceguá (RS, Brazil) and Melo (Uruguay) areas:A highly crystallized montmorillonite. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 16(2): 187-198 DOI:10.1016/S0895-9811(03)00029-4 |
Cao RJ, Tang TF and Xue YS. 1988. The connection of the Upper Precambrian in N. China with the Sinian System in S. China. Geological Review, 34(2): 175-178 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Chen JB, Zhang HM, Zhu SX, Zhao Z and Wang ZG. 1980. Research on Sinian Suberathem of Jixian, Tianjin. In: Tianjin Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (ed.). Research on Precambrian Geology-Sinian Suberathem in China. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Press, 56-114 (in Chinese)
|
Chen JB, Wu TS, Zhang PY and You WD. 1997. Regional Stratigraphy of North China. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press: 1-199 (in Chinese)
|
Chen JB, Zhang PY, Gao ZJ and Sun SF. 1999. Lexicon of China Stratigraphy:Mesoproterozoic Era. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-89 (in Chinese)
|
Chen LW, Huang BC, Yi ZY, Zhao J and Yan YG. 2013. Paleomagnetism of ca. 1.35Ga sills in northern North China Craton and implications for paleogeographic reconstruction of the Mesoproterozoic supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 228: 36-47 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2013.01.011 |
Chen XY. 2005. Preliminary study on the K-bentonites from the Middle-Upper Xiamaling Formation (Neoproterozoic) at Xishan, Beijing. Bachelor Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-28 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Chen YL, Li DP, Wang Z, Liu JB and Liu CZ. 2012. History of formation and evolution on the crust around the Ordos Basin:Evidences from U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic composition of zircons. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(3): 147-166 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Chu XL, Zhang TG, Zhang QR, Feng LJ and Zhang FS. 2004. Carbon isotopic variations of Proterozoic carbonates in Jixian, Tianjin, China. Science in China (Series D), 47(2): 160-170 DOI:10.1360/02yd0384 |
Chu XL, Zhang TG, Zhang QR and Lyons TW. 2007. Sulfur and carbon isotope records from 1700 to 800Ma carbonates of the Jixian Section, northern China:Implications for secular isotope variations in Proterozoic seawater and relationships to global supercontinental events. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(19): 4668-4692 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2007.07.017 |
Compilation Group of the Regional Stratigraphic Chart of Hebei Province and Tianjin City. 1979. Regional Stratigraphic Chart of the North China Region, Hebei Province and Tianjin City(1). Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-312 (in Chinese)
|
Corfu F, Hanchar JM, Hoskin PWO and Kinny P. 2003. Atlas of zircon textures. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 469-500 DOI:10.2113/0530469 |
Daniel CG and Pyle JM. 2006. Monazite-Xenotime thermochronometry and Al2SiO5 reaction textures in the Picuris Range, northern New Mexico, USA:New evidence for a 1450~1400Ma orogenic event. Journal of Petrology, 47(1): 97-118 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egi069 |
Ding TP, Gao JF, Tian SH, Fan CF, Zhao Y, Wan DF and Zhou JX. 2017. The δ30Si peak value discovered in Middle Proterozoic chert and its implication for environmental variations in the ancient ocean. Scientific Reports, 7: 44000 DOI:10.1038/srep44000 |
Diwu CR, Sun Y, Lin CL, Liu XM and Wang HL. 2007. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes and their geological significance of Yiyang TTG gneisses from Henan Province, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 253-262 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Doe MF, Jones JV Ⅲ, Karlstrom KE, Dixon B, Gehrels G and Pecha M. 2013. Using detrital zircon ages and Hf isotopes to identify 1.48~1.45Ga sedimentary basins and fingerprint sources of exotic 1.6~1.5Ga grains in southwestern Laurentia. Precambrian Research, 231: 409-421 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2013.03.002 |
Dong CY, Liu DY, Li JJ, WanYS, Zhou HY, Li CD, Yang YH and Xie LW. 2007. Palaeoproterozoic khondalite belt in the western North China Craton:New evidence from SHRIMP dating and Hf isotope composition of zircons from metamorphic rocks in the Bayan Ul-Helan Mountains area. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(21): 2984-2994 DOI:10.1007/s11434-007-0404-9 |
Du RL, Li PJ and Wu ZS. 1980. Sinian suberathem in the western Yanshan ranges. In: Tianjin Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (ed.). Research on Precambrian Geology-Sinian Suberathem in China. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Press, 341-357 (in Chinese)
|
Gao LZ, Zhang CH, Shi XY, Zhou HR and Wang ZQ. 2007. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of the tuff bed in the Xiamaling Formation of the Qingbaikouan System in North China. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(3): 249-255 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Gao LZ, Zhang CH, Shi XY, Song B, Wang ZQ and Liu YM. 2008. Mesoproterozoic age for Xiamaling Formation in North China Plate indicated by zircon SHRIMP dating. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(17): 2665-2671 |
Geng JZ, Li HK, Zhang J, Zhou HY and Li HM. 2011. Zircon Hf isotope analysis by means of LA-MC-ICP-MS. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(10): 1508-1513 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Geng YS, Wang XS, Shen QH and Wu CM. 2006. Redefinition of the Alxa Group-complex (Precambrian metamorphic basement) in the Alxa area, Inner Mongolia. Geology in China, 33(1): 138-145 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Grabau AW. 1922. The Sinian System. Bulletin of the Geological Society of China, 1(1-4): 44-88 |
Griffin WL, Pearson NJ, Belousova E, Jackson SE, Van Achterbergh E, O'Reilly SY and Shee SR. 2000. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle:LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(1): 133-147 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9 |
Guo WL and Su WB. 2014. Geochemistry and implication to paleoclimate of the~1.4Ga ancient weathering crust in the northern North China Craton. Geoscience, 28(2): 243-255 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Guo ZX, Peng XT, Czaja AD, Chen S and Ta KW. 2018. Cellular taphonomy of well-preserved Gaoyuzhuang microfossils:A window into the preservation of ancient cyanobacteria. Precambrian Research, 304: 88-98 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2017.11.007 |
He YH, Zhao GC, Sun M and Xia XP. 2009. SHRIMP and LA-ICP-MS zircon geochronology of the Xiong'er volcanic rocks:Implications for the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic evolution of the southern margin of the North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 168(3-4): 213-222 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2008.09.011 |
Hoskin PWO and Black LP. 2000. Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 18(4): 423-439 |
Hou KJ, Li YH, Zou TR, Qu XM, Shi YR and Xie GQ. 2007. Laser ablation-MC-ICP-MS technique for Hf isotope microanalysis of zircon and its geological applications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(10): 2595-2604 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu B, Zhai MG, Li TS, Li Z, Peng P, Guo JH and Kusky TM. 2012. Mesoproterozoic magmatic events in the eastern North China Craton and their tectonic implications:Geochronological evidence from detrital zircons in the Shandong Peninsula and North Korea. Gondwana Research, 22(3-4): 828-842 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.03.005 |
Huang DM, Zhang DH, Wang SY, Zhang YX, Dong CY, Liu DY and Wan YS. 2012. 2.3Ga magmatism and 1.94Ga metamorphism in the Xiatang area, southern margin of the North China craton:Evidence from whole-rock geochemistry and zircon geochronology and Hf isotope. Geological Review, 58(3): 565-576 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Huang M, Lu CM, Jiang ZK, Liu BP, Chu ZH and Zhao YX. 2017. Investigation of controlling factors for growth in stromatolites of the Tieling Formation, Jixian, Tianjin. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(1): 347-348 DOI:10.1111/1755-6724.13084 |
Huff WD, Bergström SM and Kolata DR. 1992. Gigantic Ordovician volcanic ash fall in North America and Europe:Biological, tectonomagmatic, and event-stratigraphic significance. Geology, 20(10): 875-878 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0875:GOVAFI>2.3.CO;2 |
Huff WD. 2008. Ordovician K-bentonites:Issues in interpreting and correlating ancient tephras. Quaternary International, 178(1): 276-287 DOI:10.1016/j.quaint.2007.04.007 |
Huff WD. 2016. K-bentonites:A review. American Mineralogist, 101(1): 43-70 DOI:10.2138/am-2016-5339 |
Javaux EJ, Knoll AH and Walter MR. 2001. Morphological and ecological complexity in early Eukaryotic ecosystems. Nature, 412(6842): 66-69 DOI:10.1038/35083562 |
Kao CS, Hsiung YH and Kao P. 1934. Preliminary notes on Sinian stratigraphy of North China. Bulletin of the Geological Society of China, 8(13): 243-288 |
Karlstrom KE and Humphreys ED. 1998. Persistent influence of Proterozoic accretionary boundaries in the tectonic evolution of southwestern North America:Interaction of cratonic grain and mantle modification events. Rocky Mountain Geology, 33(2): 161-179 DOI:10.2113/33.2.161 |
Karlstrom KE, Åhäll KI, Harlan SS, Williams ML, McLelland J and Geissman JW. 2001. Long-lived (1.8~0.8Ga) convergent orogen in southern Laurentia, its extensions to Australia and Baltica, and implications for refining Rodinia. Precambrian Research, 111(1-4): 5-30 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(01)00154-1 |
Kolata DR, Huff WD and Bergström SM. 1996. Ordovician K-bentonites of eastern North America. Boulder, Colorado: The Geological Society of America, 313
|
Laboratory of Isotope Geology, Kweiyang Institute of Geochemistry, Academia Sinica (LIGKIGAS). 1977. On the Sinian geochronological scale of China based on isotopic ages for the Sinian strata in the Yenshan region, North China. Scientia Sinica, 20(6): 818-834 |
Lee JS and Chao YT. 1924. Geology of the gorge district of the Yangtze (from Ichang to Tzekuei) with special reference to the development of the Gorges. Bulletin of the Geological Society of China, 3(3-4): 351-392 |
Lee JS. 1939. The Geology of China. London: Thomas Murby & Co, 528
|
Li C, Peng PA, Sheng GY, Fu JM and Yan YZ. 2003. A molecular and isotopic geochemical study of Meso-to Neoproterozoic (1.73~0.85Ga) sediments from the Jixian Section, Yanshan Basin, North China. Precambrian Research, 125(3-4): 337-356 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(03)00111-6 |
Li HK, Li HM and Lu SN. 1995. Grain Zircon U-Pb ages for volcanic rocks from Tuanshanzi Formation of Changcheng System and their geological implications. Geochimica, 24(1): 43-48 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li HK, Lu SN, Li HM, Sun LX, Xiang ZQ, Geng JZ and Zhou HY. 2009a. Zircon and beddeleyite U-Pb precision dating of basic rock sills intruding Xiamaling Formation, North China. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(10): 1396-1404 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li HK, Geng JZ, Hao S, Zhang YQ and Li HM. 2009b. Zircon U-Pb dating technique using LA-MC-ICPMS. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 29(S1): 600-601 (in Chinese) |
Li HK, Zhu SX, Xiang ZQ, Su WB, Lu SN, Zhou HY, Geng JZ, Li S and Yang FJ. 2010. Zircon U-Pb dating on tuff bed from Gaoyuzhuang Formation in Yanqing, Beijing:Further constraints on the new subdivision of the Mesoproterozoic stratigraphy in the northern North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7): 2131-2140 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li HK, Su WB, Zhou HY, Geng JZ, Xiang ZQ, Cui YR, Liu WC and Lu SN. 2011. The base age of the Changchengian System at the northern North China Craton should be younger than 1670Ma:Constraints from zircon U-Pb LA-MC-ICPMS dating of a granite-porphyry dike in Miyun County, Beijing. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(3): 108-120 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li HK, Lu SN, Su WB, Xiang ZQ, Zhou HY and Zhang YQ. 2013. Recent advances in the study of the Mesoproterozoic geochronology in the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 72: 216-227 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.02.020 |
Li HK, Su WB, Zhou HY, Xiang ZQ, Tian H, Yang LG, Huff WD and Ettensohn FR. 2014. The first precise age constraints on the Jixian System of the Meso-to Neoproterozoic standard section of China:SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of bentonites from the Wumishan and Tieling formations in the Jixian Section, North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(10): 2999-3012 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li MR, Wang SS and Qiu J. 1996. The ages of glauconites from Tieling and Jingeryu formations, Beijing-Tianjin area. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 12(3): 416-423 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu CH, Zhao GC and Liu FL. 2014. Detrital zircon U-Pb, Hf isotopes, detrital rutile and whole-rock geochemistry of the Huade Group on the northern margin of the North China Craton:Implications on the breakup of the Columbia supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 254: 290-305 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2014.09.011 |
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Zong KQ, Gao CG, Gao S, Xu J and Chen HH. 2010. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(15): 1535-1546 DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4 |
Lu SN and Li HM. 1991. A precise U-Pb single zircon age determination for the volcanics of Dahongyu Formation Changcheng System in Jixian. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 22: 137-146 (in Chinese) |
Lu SN, Zhao GC, Wang HC and Hao GJ. 2008. Precambrian metamorphic basement and sedimentary cover of the North China Craton:A review. Precambrian Research, 160(1-2): 77-93 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.017 |
Lu SN, Hao GJ and Xiang ZQ. 2016. Precambrian major geological events. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(6): 140-155 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ludwig KR. 2003. User's manual for Isoplot/Ex, Version 3.00:A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 4(2): 1-70 |
Ma K, Hu SY, Wang TS, Zhang BM, Qin SF, Shi SY, Wang K and Huang QY. 2017. Sedimentary environments and mechanisms of organic matter enrichment in the Mesoproterozoic Hongshuizhuang Formation of northern China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 475: 176-187 DOI:10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.02.038 |
Mei MX. 2006. Origin of molar-tooth structure based on sequence-stratigraphic position and macroscopic features:Example from Mesoproterozoic Gaoyuzhuang Formation at Jixian Section, Tianjin, North China. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 17(3): 201-208, 271 DOI:10.1016/S1002-0705(06)60029-0 |
Mei MX, Yang FJ, Gao JH and Meng QF. 2008. Glauconites formed in the high-energy shallow-marine environment of the Late Mesoproterozoic:A case study from Tieling Formation at Jixian Section in Tianjin North China. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(4): 146-158 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.1016/S1872-5791(08)60048-2 |
Mei MX, Gao JH, Meng QF and Liu ZR. 2009. Microbial mat-related silty dykes of the Precambrian:An example from the Paleoproterozoic Chuanlinggou Formation at Jixian Section in Tianjin. Journal of Palaeogeography, 11(1): 37-50 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Mei MX and Tucker ME. 2011. Molar tooth structure:A contribution from the Mesoproterozoic Gaoyuzhuang Formation, Tianjin City, North China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(5): 1084-1099 DOI:10.1111/j.1755-6724.2011.00542.x |
Meng QR, Wei HH, Qu YQ and Ma SX. 2011. Stratigraphic and sedimentary records of the rift to drift evolution of the northern North China Craton at the Paleo-to Mesoproterozoic transition. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 205-218 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.12.010 |
Miao LY, Moczydłowska M, Zhu SX and Zhu MY. 2019. New record of organic-walled, morphologically distinct microfossils from the late Paleoproterozoic Changcheng Group in the Yanshan Range, North China. Precambrian Research, 321: 172-198 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2018.11.019 |
Nagovitsin K. 2009. Tappania-bearing association of the Siberian platform:Biodiversity, stratigraphic position and geochronological constraints. Precambrian Research, 173(1-4): 137-145 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2009.02.005 |
Nowell GM, Kempton PD, Noble SR, Fitton JG, Saunders AD, Mahoney JJ and Taylor RN. 1998. High precision Hf isotope measurements of MORB and OIB by thermal ionisation mass spectrometry:Insights into the depleted mantle. Chemical Geology, 149(3-4): 211-233 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00036-9 |
Nyman MW, Karlstrom KE, Kirby E and Graubard CM. 1994. Mesoproterozoic contractional orogeny in western North America:Evidence from ca.4Ga plutons. Geology, 22(10): 901-904 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0901:MCOIWN>2.3.CO;2 |
Patchett PJ, Kouvo O, Hedge CE and Tatsumoto M. 1982. Evolution of continental crust and mantle heterogeneity:Evidence from Hf isotopes. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 78(3): 279-297 DOI:10.1007/BF00398923 |
Peng YB, Bao HM and Yuan XL. 2009. New morphological observations for Paleoproterozoic acritarchs from the Chuanlinggou Formation, North China. Precambrian Research, 168(3-4): 223-232 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2008.10.005 |
Qiao XF. 1976. Investigation on stratigraphy of the Qingbaikou Group of the Yenshan Mountains, North China. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 11(3): 246-265 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Qiao XF and Wang YB. 2014. Discussions on the lower boundary age of the Mesoproterozoic and basin tectonic evolution of the Mesoproterozoic in North China Craton. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(9): 1623-1637 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Qu YG, Xie GW and Gong YM. 2004. Relationship between Earth-Sun-Moon 1000Ma ago:Evidence from the stromatolite. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(21): 2288-2295 DOI:10.1360/03wd0616 |
Qu YG, Zhu SX, Whitehouse M, Engdahl A and McLoughlin N. 2018. Carbonaceous biosignatures of the earliest putative macroscopic multicellular eukaryotes from 1630Ma Tuanshanzi Formation, north China. Precambrian Research, 304: 99-109 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2017.11.004 |
Ren KX, Yan GH, Cai JH, Mu BL, Li FT and Chu ZY. 2006. Nd, Sr and Pb isotopic geochemistry of Paleo-Mesoproterozoic alkaline-rich intrusions from the northern part of the North China Craton:Evidence of the lithospheric mantle enrichment. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(12): 2933-2944 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ren R, Han BF, Zhang ZC, Li JF, Yang YH and Zhang YB. 2011. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic studies of basement gneiss and overlying Meso-Neoproterozoic sedimentary rocks from the Changping area, Beijing, and their geological implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(6): 1721-1745 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Rogers JJW and Santosh M. 2002. Configuration of Columbia, a Mesoproterozoic supercontinent. Gondwana Research, 5(1): 5-22 DOI:10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70883-2 |
Shi M, Feng QL, Khan MZ, Awramik S and Zhu SX. 2017a. Silicified microbiota from the Paleoproterozoic Dahongyu Formation, Tianjin, China. Journal of Paleontology, 91(3): 369-392 DOI:10.1017/jpa.2016.163 |
Shi M, Feng QL, Khan MZ and Zhu SX. 2017b. An eukaryote-bearing microbiota from the Early Mesoproterozoic Gaoyuzhuang Formation, Tianjin, China and its significance. Precambrian Research, 303: 709-726 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2017.09.013 |
Söderlund U, Patchett PJ, Vervoort JD and Isachsen CE. 2004. The176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 219(3-4): 311-324 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00012-3 |
Song B, Zhang YH, Wan YS and Jian P. 2002. Mount making and procedure of the SHRIMP dating. Geological Review, 48(Suppl.): 26-30 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Su WB, Li ZM, Shi XY, Zhou HR, Huang SJ, Liu XM, Chen XY, Zhang JE, Yang HM, Jia LJ, Huff WD and Ettensohn FR. 2006. K-bentonites and black shales from the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations (Early Paleozoic, South China) and Xiamaling Formation (Early Neoproterozoic, North China):Implications for tectonic processes during two important transitions. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(6): 82-95 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Su WB, Zhang SH, Huff WD, Li HK, Ettensohn FR, Chen XY, Yang HM, Han YG, Song B and Santosh M. 2008. SHRIMP U-Pb ages of K-bentonite beds in the Xiamaling Formation:Implications for revised subdivision of the Meso-to Neoproterozoic history of the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 14(3): 543-553 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2008.04.007 |
Su WB, Li HK, Huff WD, Ettensohn FR, Zhang SH, Zhou HY and Wan YS. 2010. SHRIMP U-Pb dating for a K-bentonite bed in the Tieling Formation, North China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(29): 3312-3323 DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-4007-5 |
Su WB, Li HK, Xu L, Jia SH, Geng JZ, Zhou HY, Wang ZH and Pu HY. 2012. Luoyu and Ruyang Group at the south margin of the North China Craton (NCC) should belong in the Mesoproterozoic Changchengian System:Direct constraints from the LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb age of the tuffite in the Luoyukou Formation, Ruzhou, Henan, China. Geological Survey and Research, 35(2): 96-108 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Su WB. 2014. A review of the revised Precambrian Time Scale (GTS2012) and the research of the Mesoproterozoic chronostratigraphy of China. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(2): 119-138 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Su WB. 2016. Revision of the Mesoproterozoic chronostratigraphic subdivision both of North China and Yangtze Cratons and the relevant issues. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(6): 156-185 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wan YS, Liu DY, Dong CY, Xu ZY, Wang ZJ, Wilde SA, Yang YH, Liu ZH and Zhou HY. 2009. The Precambrian Khondalite Belt in the Daqingshan area, North China Craton: Evidence for multiple metamorphic events in the Palaeoproterozoic Era. In: Reddy SM, Mazumder R, Evans DAD and Collins AS (eds.). Palaeoproterozoic Supercontinents and Global Evolution. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 323(1): 73-97
|
Wang DH, Meng XH, Guo F, Ren GX and Ge M. 2009. Discussion on the sedimentary environment and origin of the microsparite carbonates of Mesoproterozoic Gaoyuzhuang Formation in Jixian area, Tianjin, China. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 39(6): 1023-1030 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang HZ. 1985. Atlas of the Palaeogeography of China. Beijing: Cartographic Publishing House: 1-143 (in Chinese)
|
Wang M, Luo JL, Li M, Bai XJ, Cheng C and Yan LW. 2013. Provenance and tectonic setting of sandstone-type uranium deposit in Dongsheng area, Ordos basin:Evidence from U-Pb age and Hf isotopes of detrital zircons. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(8): 2746-2758 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang SS, Sang HQ, Qiu J, Chen ME and Li MR. 1995. The forming ages of Yangzhuang and Wumishan formations in Jixian Section, Northern China. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 30(2): 166-173 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang SS and Qiu J. 1999. A study of saddle-shaped 40Ar-39Ar age spectrum of chert:Examples from Tieling Formation, Jixian Section. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 20(4): 363-367 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang YL and Lu ZB. 1962. Discussion on Precambrian stratigraphic problems based on absolute age. Acta Geologica Sinica, 42(2): 186-197 (in Chinese) |
Wang YL. 1963. The boundary between the Sinian and Cambrian systems in northern China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 43(2): 116-140 (in Chinese) |
Wang YL, Lu ZB, Xing YS, Gao ZJ, Lin WX, Ma GG, Zhang LY and Lu SN. 1980. Subdivision and correlation of the Upper Precambrian in China. In: Tianjin Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (ed.). Research on Precambrian Geology-Sinian Suberathem in China. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Press, 1-30 (in Chinese)
|
Wang ZJ. 2010. Zircon SHRIMP dating of the K-bentonite in the Precambrian strata. Journal of Stratigraphy, 34(1): 56-59 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Williams ML, Karlstrom KE, Lanzirotti A, Read AS, Bishop JL, Lombardi CE, Pedrick JN and Wingsted MB. 1999. New Mexico middle-crustal cross sections:1.65Ga macroscopic geometry, 1.4Ga thermal structure, and continued problems in understanding crustal evolution. Rocky Mountain Geology, 34(1): 56-66 |
Wu FY, Yang JH, Liu XM, Li TS, Xie LW and Yang YH. 2005a. Hf isotopes of the 3.8Ga zircons in eastern Hebei Province, China:Implications for early crustal evolution of the North China Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50(21): 2473-2480 DOI:10.1360/982005-629 |
Wu FY, Zhao GC, Wilde SA and Sun DY. 2005b. Nd isotopic constraints on crustal formation in the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 523-545 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.10.011 |
Wu FY, Yang YH, Xie LW, Yang JH and Xu P. 2006. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology. Chemical Geology, 234(1-2): 105-126 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.003 |
Wu FY, Li XH, Zheng YF and Gao S. 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185-220 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wu YB and Zheng YF. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(15): 1554-1569 DOI:10.1007/BF03184122 |
Xiao SH, Knoll AH, Kaufman AJ, Yin LM and Zhang Y. 1997. Neoproterozoic fossils in Mesoproterozoic rocks? Chemostratigraphic resolution of a biostratigraphic conundrum from the North China Platform. Precambrian Research, 84(3-4): 197-220 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(97)00029-6 |
Xing YS and Liu GZ. 1982. Late Precambrian microflora of China and its stratigraphical significance. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 4(1): 57-69 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xing YS, Gao ZJ, Wang ZQ, Gao LZ and Yin CY. 1996. Lexicon of China Stratigraphy:Neoproterozoic Era. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-117 (in Chinese)
|
Yang H, Chen ZQ and Fang YH. 2017. Microbially induced sedimentary structures from the 1.64Ga Chuanlinggou Formation, Jixian, North China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 474: 7-25 DOI:10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.04.038 |
Yang HM. 2006. Implication of the depositional environment and the tectonic setting of the K-bentonite-bearing black shales in the Xiamaling Formation, Early Neoproterozoic, North China. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-62 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Yang J, Gao S, Chen C, Tang YY, Yuan HL, Gong HJ, Xie SW and Wang JQ. 2009. Episodic crustal growth of North China as revealed by U-Pb age and Hf isotopes of detrital zircons from modern rivers. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(9): 2660-2673 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2009.02.007 |
Yin LM. 1997. Acanthomorphic acritarchs from Meso-Neoproterozoic shales of the Ruyang Group, Shanxi, China. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 98(1-2): 15-25 DOI:10.1016/S0034-6667(97)00022-5 |
Yu RB and Zhang XQ. 1984. Study of geochronology of Late Precambrian in the Yanshan Ranges. In: Bulletin of Tianjin Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources (11). Beijing: China Geological Society, 1-23 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yuan Y, Zong KQ, Cawood PA, Cheng H, Yu YY, Guo JL, Liu YS, Hu ZC, Zhang W and Li M. 2019. Implication of Mesoproterozoic (~1.4Ga) magmatism within microcontinents along the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Precambrian Research, 327: 314-326 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2019.03.014 |
Zeng LJ, Bao ZW, Zhao TP, Yao JM and Zhou D. 2013. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Mesoproterozoic Panhe syenites in the southern margin of North China Craton and its tectonic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(7): 2425-2436 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai MG and Liu WJ. 2003. Palaeoproterozoic tectonic history of the North China Craton:A review. Precambrian Research, 122(1-4): 183-199 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00211-5 |
Zhai MG. 2004. 2.1~1.7Ga geological event group and its geotectonic significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(6): 1343-1354 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai MG and Peng P. 2007. Paleoproterozoic events in the North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(11): 2665-2682 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai MG, Hu B, Peng P and Zhao TP. 2014. Meso-Neoproterozoic magmatic events and multi-stage rifting in the NCC. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(1): 100-119 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai MG, Hu B, Zhao TP, Peng P and Meng QR. 2015. Late Paleoproterozoic-Neoproterozoic multi-rifting events in the North China Craton and their geological significance:A study advance and review. Tectonophysics, 662: 153-166 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2015.01.019 |
Zhang J, Tian H, Li HK, Su WB, Zhou HY, Xiang ZQ, Geng JZ and Yang LG. 2015. Age, geochemistry and zircon Hf isotope of the alkaline basaltic rocks in the middle section of the Yan-Liao aulacogen along the northern margin of the North China Craton:New evidence for the breakup of the Columbia Supercontinent. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(10): 3129-3146 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang K, Zhu XK, Wood RA, Shi Y, Gao ZF and Poulton SW. 2018. Oxygenation of the Mesoproterozoic ocean and the evolution of complex eukaryotes. Nature Geoscience, 11(5): 345-350 DOI:10.1038/s41561-018-0111-y |
Zhang PF. 1988. A complete Sinian section in North China. Journal of Stratigraphy, 12(2): 125-132 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang SC, Wang XM, Hammarlund EU, Wang HJ, Costa MM, Bjerrum CJ, Connelly JN, Zhang BM, Bian LZ and Canfield DE. 2015. Orbital forcing of climate 1.4 billion years ago. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(12): E1406-E1413 |
Zhang SH, Li ZX and Wu HC. 2006. New Precambrian palaeomagnetic constraints on the position of the North China Block in Rodinia. Precambrian Research, 144(3-4): 213-238 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2005.11.007 |
Zhang SH, Liu SW, Zhao Y, Yang JH, Song B and Liu XM. 2007. The 1.75~1.68Ga anorthosite-mangerite-alkali granitoid-rapakivi granite suite from the northern North China Craton:Magmatism related to a Paleoproterozoic orogen. Precambrian Research, 155(3-4): 287-312 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.02.008 |
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Yang ZY, He ZF and Wu H. 2009. The 1.35Ga diabase sills from the northern North China Craton:Implications for breakup of the Columbia (Nuna) supercontinent. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 288(3-4): 588-600 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2009.10.023 |
Zhang SH, Li ZX, Evans DAD, Wu HC, Li HY and Dong J. 2012. Pre-Rodinia supercontinent Nuna shaping up:A global synthesis with new paleomagnetic results from North China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 353-354: 145-155 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2012.07.034 |
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Ye H, Hu JM and Wu F. 2013. New constraints on ages of the Chuanlinggou and Tuanshanzi formations of the Changcheng System in the Yan-Liao area in the northern North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(7): 2481-2490 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Li XH, Ernst RE and Yang ZY. 2017. The 1.33~1.30Ga Yanliao large igneous province in the North China Craton:Implications for reconstruction of the Nuna (Columbia) supercontinent, and specifically with the North Australian Craton. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 465: 112-125 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2017.02.034 |
Zhao FQ, Li HM, Zuo YC and Xue KQ. 2006. Zircon U-Pb ages of Paleoproterozoic granitoids in the Zhongtiao Mountains, southern Shanxi, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(4): 442-447 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao GC, Cawood PA, Wilde SA, Sun M and Lu LZ. 2000. Metamorphism of basement rocks in the central zone of the North China Craton:Implications for Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution. Precambrian Research, 103(1-2): 55-88 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00076-0 |
Zhao GC, Cawood PA, Wilde SA and Sun M. 2002. Review of global 2.1~1.8Ga orogens:Implications for a pre-Rodinia supercontinent. Earth-Science Reviews, 59(1-4): 125-162 DOI:10.1016/S0012-8252(02)00073-9 |
Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA and Li SZ. 2004. A Paleo-Mesoproterozoic supercontinent:Assembly, growth and breakup. Earth-Science Reviews, 67(1-2): 91-123 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2004.02.003 |
Zhou MZ, Luo TY, Huang ZL, Long HS and Yang Y. 2007. Advances in research on K-bentonite. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 27(3): 351-359 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhu SX and Chen HN. 1995. Megascopic multicellular organisms from the 1700-million-year-old Tuanshanzi Formation in the Jixian area, North China. Science, 270(5236): 620-622 DOI:10.1126/science.270.5236.620 |
Zhu SX, Zhu MY, Knoll AH, Yin ZJ, Zhao FC, Sun SF, Qu YG, Shi M and Liu H. 2016. Decimetre-scale multicellular eukaryotes from the 1.56-billion-year-old Gaoyuzhuang Formation in North China. Nature Communications, 7: 11500 DOI:10.1038/ncomms11500 |
Zhu XK, Zhang K, Zhang FF, Gao ZF, Dong AG, Bao C, Guo YL, Yan B and Liu H. 2013. Discovery of siderite concretes in Mesoproterozoic Xiamaling Formation, Jixian Section. Geological Review, 59(5): 816-822 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
包创, 陈岳龙, 李大鹏. 2013. 内蒙古巴彦乌拉山古元古代斜长角闪岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成. 地质通报, 32(10): 1513-1524. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.10.003 |
曹瑞骥, 唐天福, 薛耀松. 1988. 关于华北上前寒武系与华南震旦系之间衔接问题的讨论. 地质论评, 34(2): 175-178. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1988.02.009 |
陈晋镳, 张惠民, 朱士兴, 赵震, 王振刚. 1980.蓟县震旦亚界的研究.见: 中国地质科学院天津地质矿产研究所编.中国震旦亚界.天津: 天津科学技术出版社, 56-114
|
陈晋镳, 武铁山, 张鹏远, 游文澄. 1997. 华北区区域地层. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社: 1-199.
|
陈晋镳, 张鹏远, 高振家, 孙淑芬. 1999. 中国地层典——中元古界. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-89.
|
陈晓雨. 2005.北京西山新元古代下马岭组中上部斑脱岩初步研究.学士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学, 1-28
|
陈岳龙, 李大鹏, 王忠, 刘金宝, 刘长征. 2012. 鄂尔多斯盆地周缘地壳形成与演化历史:来自锆石U-Pb年龄与Hf同位素组成的证据. 地学前缘, 19(3): 147-166. |
第五春荣, 孙勇, 林慈銮, 柳小明, 王洪亮. 2007. 豫西宜阳地区TTG质片麻岩锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素地质学. 岩石学报, 23(2): 253-262. |
杜汝霖, 李培菊, 吴振山. 1980.燕山西段震旦亚界.见: 中国地质科学院天津地质矿产研究所编.前寒武地质研究——中国震旦亚界.天津: 天津科学技术出版社, 341-357
|
高林志, 张传恒, 史晓颖, 周洪瑞, 王自强. 2007. 华北青白口系下马岭组凝灰岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年. 地质通报, 26(3): 249-255. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.03.001 |
耿建珍, 李怀坤, 张健, 周红英, 李惠民. 2011. 锆石Hf同位素组成的LA-MC-ICP-MS测定. 地质通报, 30(10): 1508-1513. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.10.004 |
耿元生, 王新社, 沈其韩, 吴春明. 2006. 内蒙古阿拉善地区前寒武纪变质基底阿拉善群的再厘定. 中国地质, 33(1): 138-145. |
郭文琳, 苏文博. 2014. 华北克拉通北部14亿年前古风化壳的地球化学特征及古气候意义. 现代地质, 28(2): 243-255. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.02.001 |
河北省、天津市区域地层表编写组. 1979. 华北地区区域地层表——河北省、天津市分册(一). 北京: 地质出版社.
|
侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 曲晓明, 石玉若, 谢桂青. 2007. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用. 岩石学报, 23(10): 2595-2604. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.025 |
黄道袤, 张德会, 王世炎, 张毅星, 董春艳, 刘敦一, 万渝生. 2012. 华北克拉通南缘豫西下汤地区2.3Ga岩浆作用和1.94Ga变质作用——锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素组成及全岩地球化学研究. 地质论评, 58(3): 565-576. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.03.017 |
李怀坤, 李惠民, 陆松年. 1995. 长城系团山子组火山岩颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义. 地球化学, 24(1): 43-48. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1995.01.004 |
李怀坤, 陆松年, 李惠民, 孙立新, 相振群, 耿建珍, 周红英. 2009a. 侵入下马岭组的基性岩床的锆石和斜锆石U-Pb精确定年——对华北中元古界地层划分方案的制约. 地质通报, 28(10): 1396-1404. |
李怀坤, 耿建珍, 郝爽, 张永清, 李惠民. 2009b. 用激光烧蚀多接收器等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS)测定锆石U-Pb同位素年龄的研究. 矿物学报, 29(增): 600-601. |
李怀坤, 朱士兴, 相振群, 苏文博, 陆松年, 周红英, 耿建珍, 李生, 杨锋杰. 2010. 北京延庆高于庄组凝灰岩的锆石U-Pb定年研究及其对华北北部中元古界划分新方案的进一步约束. 岩石学报, 26(7): 2131-2140. |
李怀坤, 苏文博, 周红英, 耿建珍, 相振群, 崔玉荣, 刘文灿, 陆松年. 2011. 华北克拉通北部长城系底界年龄小于1670Ma——来自北京密云花岗斑岩岩脉锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb年龄的约束. 地学前缘, 18(3): 108-120. |
李怀坤, 苏文博, 周红英, 相振群, 田辉, 杨立公, Huff WD, Ettensohn FR. 2014. 中-新元古界标准剖面蓟县系首获高精度年龄制约——蓟县剖面雾迷山组和铁岭组斑脱岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb同位素定年研究. 岩石学报, 30(10): 2999-3012. |
李明荣, 王松山, 裘冀. 1996. 京津地区铁岭组、景儿峪组海绿石40Ar-39Ar年龄. 岩石学报, 12(3): 416-423. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1996.03.007 |
陆松年, 李惠民. 1991. 蓟县长城系大红峪组火山岩的单颗粒锆石U-Pb法准确定年. 中国地质科学院院报, 22: 137-146. |
陆松年, 郝国杰, 相振群. 2016. 前寒武纪重大地质事件. 地学前缘, 23(6): 140-155. |
梅冥相, 杨锋杰, 高金汉, 孟庆芬. 2008. 中元古代晚期浅海高能沉积环境中的海绿石:以天津蓟县剖面铁岭组为例. 地学前缘, 15(4): 146-158. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.04.017 |
梅冥相, 高金汉, 孟庆芬, 刘智荣. 2009. 前寒武纪与微生物席相关的粉砂岩岩墙——以天津蓟县古元古界串岭沟组为例. 古地理学报, 11(1): 37-50. |
乔秀夫. 1976. 青白口群地层学研究. 地质科学, 11(3): 246-265. |
乔秀夫, 王彦斌. 2014. 华北克拉通中元古界底界年龄与盆地性质讨论. 地质学报, 88(9): 1623-1637. |
屈原皋, 解古巍, 龚一鸣. 2004. 10亿年前的地-日-月关系:来自叠层石的证据. 科学通报, 49(20): 2083-2089. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.20.012 |
全国地层委员会. 1962. 全国地层会议学术报告汇编——中国的前寒武系. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-80.
|
全国地层委员会. 2001. 中国地层指南及中国地层指南说明书. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-59.
|
全国地层委员会. 2002. 中国区域年代地层(地质年代)表说明书. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-72.
|
任康绪, 阎国翰, 蔡剑辉, 牟保磊, 李凤棠, 储著银. 2006. 华北克拉通北部古-中元古代富碱侵入岩的Nd、Sr、Pb同位素地球化学:岩石圈地幔富集的证据. 岩石学报, 22(12): 2933-2944. |
任荣, 韩宝福, 张志诚, 李建锋, 杨岳衡, 张艳斌. 2011. 北京昌平地区基底片麻岩和中-新元古代盖层锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素研究及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 27(6): 1721-1745. |
宋彪, 张玉海, 万渝生, 简平. 2002. 锆石SHRIMP样品靶制作、年龄测定及有关现象讨论. 地质论评, 48(增): 26-30. |
苏文博, 李志明, 史晓颖, 周洪瑞, 黄思骥, 刘晓茗, 陈晓雨, 张继恩, 杨红梅, 贾柳静, Huff WD, Ettensohn FR. 2006. 华南五峰组-龙马溪组与华北下马岭组的钾质斑脱岩及黑色岩系——两个地史转折期板块构造运动的沉积响应. 地学前缘, 13(6): 82-95. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.06.011 |
苏文博, 李怀坤, 徐莉, 贾松海, 耿建珍, 周红英, 王志宏, 蒲含勇. 2012. 华北克拉通南缘洛峪群-汝阳群属于中元古界长城系——河南汝州洛峪口组层凝灰岩锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb年龄的直接约束. 地质调查与研究, 35(2): 96-108. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2012.02.003 |
苏文博. 2014. 2012年全球前寒武纪新年表与中国中元古代年代地层学研究. 地学前缘, 21(2): 119-138. |
苏文博. 2016. 华北及扬子克拉通中元古代年代地层格架厘定及相关问题探讨. 地学前缘, 23(6): 156-185. |
王德海, 孟祥化, 郭峰, 任国选, 葛铭. 2009. 天津蓟县高于庄组微亮晶(MT)碳酸盐岩的沉积环境及成因探讨. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 39(6): 1023-1030. |
王鸿祯. 1985. 中国古地理图集. 北京: 地图出版社: 1-143.
|
王盟, 罗静兰, 李杪, 白雪晶, 程辰, 闫辽伟. 2013. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜地区砂岩型铀矿源区及其构造背景分析——来自碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素的证据. 岩石学报, 29(8): 2746-2758. |
王松山, 桑海清, 裘冀, 陈孟莪, 李明荣. 1995. 蓟县剖面杨庄组和雾迷山组形成年龄的研究. 地质科学, 30(2): 166-173. |
王松山, 裘冀. 1999. 燧石40Ar-39Ar马鞍形年龄谱形成机制探讨——以蓟县剖面铁岭组燧石为例. 地球学报, 20(4): 363-367. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.1999.04.005 |
王曰伦, 陆宗斌. 1962. 根据绝对年龄资料对前寒武纪地层问题的讨论. 地质学报, 42(2): 186-197. |
王曰伦. 1963. 中国北部震旦系和寒武系分界问题. 地质学报, 43(2): 116-140. |
王曰伦, 陆宗斌, 邢裕盛, 高振家, 林蔚兴, 马国干, 张录易, 陆松年. 1980.中国上前寒武系的划分和对比.见: 中国地质科学院天津地质矿产研究所编.中国震旦亚界.天津: 天津科学技术出版社, 1-30
|
王泽九. 2010. 斑脱岩中锆石SHRIMP测年在前寒武纪地层中的应用——前寒武纪年代地层学研究的新思路. 地层学杂志, 34(1): 56-59. |
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185-220. |
邢裕盛, 刘桂芝. 1982. 中国晚前寒武纪微古植物群及其地层意义. 中国地质科学院院报, 4: 57-69. |
邢裕盛, 高振家, 王自强, 高林志, 尹崇玉. 1996. 中国地层典——新元古界. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-117.
|
杨红梅. 2006.华北北部新元古代下马岭组黑色岩系沉积环境及构造古地理意义.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学, 1-62
|
于荣炳, 张学祺. 1984.燕山地区晚前寒武纪同位素地质年代学的研究.见: 中国地质科学院天津地质矿产研究所文集(11).北京: 中国地质学会, 1-23
|
曾令君, 包志伟, 赵太平, 姚军明, 周栋. 2013. 华北克拉通南缘潘河~1.5Ga正长岩的厘定及其构造意义. 岩石学报, 29(7): 2425-2436. |
翟明国. 2004. 华北克拉通2.1~1.7Ga地质事件群的分解和构造意义探讨. 岩石学报, 20(6): 1343-1354. |
翟明国, 彭澎. 2007. 华北克拉通古元古代构造事件. 岩石学报, 23(11): 2665-2682. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.001 |
翟明国, 胡波, 彭澎, 赵太平. 2014. 华北中-新元古代的岩浆作用与多期裂谷事件. 地学前缘, 21(1): 100-119. |
张健, 田辉, 李怀坤, 苏文博, 周红英, 相振群, 耿建珍, 杨立功. 2015. 华北克拉通北缘Columbia超大陆裂解事件:来自燕辽裂陷槽中部长城系碱性火山岩的地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学和Hf同位素证据. 岩石学报, 31(10): 3129-3146. |
张丕孚. 1988. 震旦系在北方的一个完整剖面. 地层学杂志, 12(2): 125-132. |
张拴宏, 赵越, 叶浩, 胡健民, 吴飞. 2013. 燕辽地区长城系串岭沟组及团山子组沉积时代的新制约. 岩石学报, 29(7): 2481-2490. |
赵凤清, 李惠民, 左义成, 薛克勤. 2006. 晋南中条山古元古代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄. 地质通报, 25(4): 442-447. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.04.003 |
中国科学院地质研究所绝对年龄实验室. 1965. 钾-氩法测定岩石矿物绝对年龄数据的报导Ⅱ. 地质科学, (2): 106-112. |
周明忠, 罗泰义, 黄智龙, 龙汉生, 杨勇. 2007. 钾质斑脱岩的研究进展. 矿物学报, 27(3): 351-359. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2007.03.017 |
朱祥坤, 张衎, 张飞飞, 高兆富, 董爱国, 包创, 郭跃玲, 闫斌, 刘辉. 2013. 蓟县中元古界下马岭组中菱铁矿的发现及其意义. 地质论评, 59(5): 816-822. |
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35