2. 中国科学院地球科学研究院, 北京 100029;
3. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049;
4. 卢氏县国土资源局, 卢氏 472200
2. Institutions of Earth Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029, China;
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China;
4. Lushi Country Bureau of Land and Resource, Lushi 472200, China
卢氏多金属矿集区的楼房银铜矿和柳关铅锌矿位于华北克拉通南缘秦岭成矿带东段,秦岭成矿带由大量金矿、钼矿和铅锌多金属矿床组成,是世界上规模最大的钼矿带(Mao et al., 2011; Zeng et al., 2013),也是我国重要的金矿带之一(Li et al., 2012a)。前人对秦岭成矿带内的钼、金成矿作用进行了大量的研究工作,成矿带内钼矿床主要形成于晚侏罗世-早白垩世(150~130Ma)(Chen et al., 2000; Du et al., 2004; 焦建刚等, 2009; Mao et al., 2011; 晏国龙等, 2012; 赵海杰等, 2013; 向君峰等, 2016),少数矿床形成于三叠纪(Du et al., 2004; Zhu et al., 2011a; Song et al., 2015),另有个别形成于元古代(魏庆国等, 2009;Li et al., 2011; Deng et al., 2013)。成矿带内金矿床主要形成于早白垩世(130~110Ma)(Li et al., 2012a, b)。相对于钼矿床、金矿床而言,东秦岭铅锌银矿床的成矿时代研究相对较少,在这些矿床中较难找到合适的传统同位素定年的矿物。目前东秦岭成矿带中,铅锌银矿床只有蒿坪沟银多金属矿(134.9±0.8Ma,叶会寿,2006)、铁炉坪银铅矿床(134.6±1.2Ma,高建京等, 2011)、沙沟银铅锌矿床(140.0±1.0Ma,Li et al., 2013)等有相应的成矿时代报道。卢氏多金属矿集区是秦岭成矿带内一个非常重要的多金属矿化集中区,包括夜长坪钼钨矿、八宝山铁铜矿、楼房银铜矿、柳关铅锌矿、银家沟硫铁多金属矿等矿床。该矿集区内矿床年代学研究非常薄弱,除银家沟硫铁多金属矿床外(143Ma, 武广等, 2013)和夜长坪钼钨矿(147~144Ma,毛冰等,2011; 晏国龙等,2012)的成矿年龄有文献报道外,其它多金属矿床缺少成矿年代学研究,这也极大地限制了对该矿集区成矿地球动力学背景、矿床成因等方面的认识。所以,对于该矿集区的矿床,特别是银铅锌多金属矿床的年代学研究是十分必要且有意义的。
本文通过对楼房银铜矿、柳关铅锌矿中黄铜矿、黄铁矿的Rb-Sr等时线年龄测定,以查明卢氏多金属矿集区多金属矿床的形成时代,从而进一步探讨其与区域上构造、岩浆岩的关系,判断其成矿流体的物质来源,揭示其成矿规律并探讨成矿构造背景。
1 区域地质背景东秦岭成矿带位于华北克拉通南缘(图 1),该地区经历过复杂的、多期次的造山运动(Meng and Zhang, 2000; 张国伟等, 2001; Dong et al., 2011)。东秦岭地区地层主要由太古代太华群、中元古代熊耳群、中元古代官道口群、中元古代宽坪群、上元古代栾川群组成。太古代太华群由片岩、大理岩、石英岩、角闪岩、片麻岩组成,锆石U-Pb年龄为2.8~2.6Ga(Kröner et al., 1988; Xue et al., 1996)。熊耳群不整合覆盖于太华群之上(Peng et al., 2008; Zhao and Zheng, 2009),其Rb-Sr和锆石U-Pb年龄为1.8~1.4Ga(任富根和李维明, 1996),分为大古石组、许山组、鸡蛋坪组、马家河组。其中,大古石组主要为砾岩、砂岩和泥岩(陈衍景和富士谷, 1992);许山组为玄武安山岩、安山岩、少量英安岩和流纹岩;鸡蛋坪组由玄武安山质至流纹质岩浆组成,夹少量火山碎屑岩和沉积岩;马家河组主要包括玄武安山岩、安山岩、火山碎屑岩和沉积岩(Yang et al., 2015)。官道口群以石英砂岩和白云岩为主,为一套陆源碎屑岩-碳酸盐岩沉积序列,自下而上分为高山河组、龙家园组、巡检司组、杜关组和冯家湾组。高山河组由紫红色石英砂岩、泥岩及泥须粉砂岩组成;龙家园组由砾屑白云岩、砾岩组成;巡检司组由泥晶白云岩来燧石条带组成;杜关组由碎屑细晶白云岩、泥质白云岩组成;冯家湾组由纹层状细晶白云岩和粉晶白云岩组成(胡国辉等,2013)。宽坪群包括绿片岩相变质火山岩和变质沉积岩(王宗起等, 2009; 第五春荣等, 2010)。栾川群自下而上主要分为白术沟组、三川组、南泥湖组和煤窑沟组,其岩性主要为千枚岩、变质长石石英岩、白云石大理岩、绢云(钙质)片岩等(蒋干清等, 1994)。
|
图 1 东秦岭地区地质与矿产略图(据叶会寿,2006) Fig. 1 Geological and mineral sketch map of eastern Qinling area (modified after Ye, 2006) |
东秦岭地区断裂构造发育,包括区域性断裂如北部边界断裂三门峡-宝丰断裂、南部边界断裂栾川断裂、近EW走向的马超营断裂等;次一级断裂如康山-星星阴断裂、洛宁断裂等。区域断裂及次级断裂控制区域中酸性岩体的侵入,小规模断裂则是区内重要的容矿构造(叶会寿, 2006)。东秦岭花岗岩体主要包括老牛山、华山、文峪、娘娘山、花山、五丈山、合峪等,主要岩性有二长花岗岩、黑云母花岗岩、花岗闪长岩等,主要有两期岩浆活动,分别为155~130Ma和120~105Ma(Wang et al., 2015)。该地区的成矿作用复杂,以金、钼、多金属成矿为特色,伴随多期岩浆侵入作用所引发的多期成矿作用。区内金矿床主要发育于文峪岩体周围,钼矿主要集中在东秦岭西部老牛山、华山岩体周围、东部的花山、五丈山、合峪岩体周围,成矿与小岩体有关(图 2)。前人发现这些金、钼矿床与岩体之间存在时空耦合关系(Mao et al., 2002, 2011)。其他已发现的多金属矿床多在距离岩体较远、断裂交汇处的位置产出。

|
图 2 卢氏多金属矿集区小岩体与矿床分布图(据胡浩等,2011修绘) Fig. 2 The distribution map of the small intrusions and deposits in Lushi polymetallic ore-concentrated area (modified after Hu et al., 2011) |
卢氏多金属矿集区内出露地层主要包括太古代太华群角闪岩和片麻岩、中元古代熊耳群火山岩和中元古代官道口群白云岩。区内小岩体发育,包括后瑶峪、银家沟、八宝山、曲里、秦池、柳关、圪佬湾等花岗斑岩体以及蒲阵沟、西沟、郭家河等闪长岩体和石英闪长岩体,小岩体在空间上具有NE向成带分布的特点,受NE向断裂构造控制明显(胡浩等, 2011)。这些小岩体与区内斑岩型钨钼矿化、多金属矿化具有密切的成因联系,在小岩体内部或边部发生矿化。
2 矿床地质特征 2.1 楼房银铜矿楼房银铜矿区地层包括太古代太华群片麻岩,中元古代熊耳群大古石组砂岩、砂板岩、砾岩,中元古代熊耳群许山组安山岩以及第四系黄土和砂砾石层。侵入岩主要包括石英闪长岩、闪长岩、辉绿玢岩及花岗斑岩。石英闪长岩呈岩株状、细粒闪长岩呈脉状、辉绿玢岩呈小岩株状、花岗斑岩主要呈脉状产出。矿区含矿构造主要为走向NNE-NEE的断裂,包括F1、F2、F3、F4和F5。其中F1、F3、F4和F5位于矿区东部,F2位于矿区西部,为分叉断裂,其由北向南分为2支。这些断裂控制了矿区内矿脉的分布(图 3)。

|
图 3 楼房银铜矿矿区地质图(据河南省国土资源科学研究院,2008①) Fig. 3 Geological map of Loufang Ag-Cu deposit |
① 河南省国土资源科学研究院.2008.卢氏县楼房银矿详查地质报告
楼房银铜矿共由5条矿脉组成。其中,1号矿体赋存于F1断裂内(图 4),为银铜矿脉,倾向NWW-近N,倾角为55°~85°;2号矿体赋存于F2断裂内,为铅锌银矿脉;3号矿体赋存于F3断裂内,为铜矿脉;4号矿体赋存于F4断裂内,为铅矿脉;5号矿体赋存于F5断裂内,为含铜矿脉。

|
图 4 楼房银铜矿03线钻孔剖面图(据河南省国土资源科学研究院,2008) Fig. 4 Vertical drill section of 3rd line in Loufang Ag-Cu deposit |
楼房银铜矿矿石矿物主要为黄铜矿、黄铁矿、方铅矿、闪锌矿,并含有少量毒砂,脉石矿物主要为石英、方解石(图 5a-d)。围岩蚀变以硅化、绢云母化为主,其次为碳酸盐化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化等。围岩蚀变严格受构造破碎带控制。结合野外观察、钻孔剖面,将该矿床的成矿阶段划分为两个:(1)石英-黄铁矿-黄铜矿;(2)石英-黄铁矿-方铅锌-闪锌矿-方解石。前者为铜矿化阶段,后者为铅锌矿化阶段。

|
图 5 楼房银铜矿(a-d)、柳关铅锌矿(e-h)的矿石手标本、反射光镜下照片 (a)石英-黄铁矿-黄铜矿脉;(b)黄铜矿中的自形毒砂矿物包体,说明毒砂形成于黄铜矿之前;(c)黄铜矿交代黄铁矿呈交代港湾状结构;(d)网脉状黄铜矿沿黄铁矿裂隙充填;(e)铅锌矿块状矿石,由方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿构成;(f)黄铁矿被方铅矿、闪锌矿交代呈交代港湾状结构,方铅矿交代闪锌矿呈交代星状结构;(g)晚期细粒脉状黄铁矿-闪锌矿脉穿切早期粗粒他形的黄铁矿颗粒;(h)隐爆角砾岩中放射状阳起石.Act-阳起石;Apy-毒砂;Ccp-黄铜矿;Gn-方铅矿;Py-黄铁矿;Q-石英;Sp-闪锌矿 Fig. 5 Hand specimen and reflected-light photomicrographs of the ores in Loufang (a-d) and Liuguan (e-h) deposits (a) quartz-pyrite-chalcopyrite veins; (b) euhedral-shaped arsenopyrite inclusion in chalcopyrite, which demonstrate that arsenopyrite forms before chalcopyrite; (c) the chalcopyrite replace pyrite which present as metasomatic bay-like texture; (d) the stockwork chalcopyrite filled in the fractures of pyrite; (e) massive ore mainly consists of galena, sphalerite and pyrite; (f) pyrite is replaced by sphalerite and galena in metasomatic star-like texture, galena replaces pyrite by metasomatic star-like texture; (g) earlier fine-grained pyrite-sphalerite vein cut the course-grained anhedral pyrite of early stage; (h) the radial actinolite in cryptoexplosive breccia. Act-actinolite; Apy-arsenopyrite; Ccp-chalcopyrite; Gn-galena; Py-pyrite; Q-quartz; Sp-sphalerite |
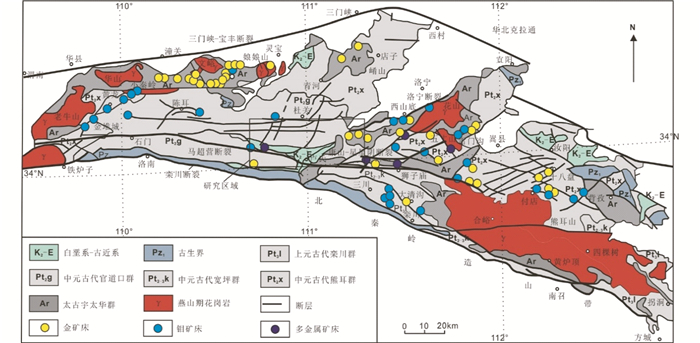
柳关铅锌矿出露地层主要包括中元古代熊耳群马家河组安山岩夹凝灰岩、中元古代官道口群龙家园组含燧石条带的条纹状白云岩,第四系河谷沉积物。官道口群龙家园组是区内主要赋矿围岩。侵入岩主要包括中生代花岗斑岩和隐爆角砾岩,二者侵入到官道口群龙家园组白云岩和熊耳群安山岩中。
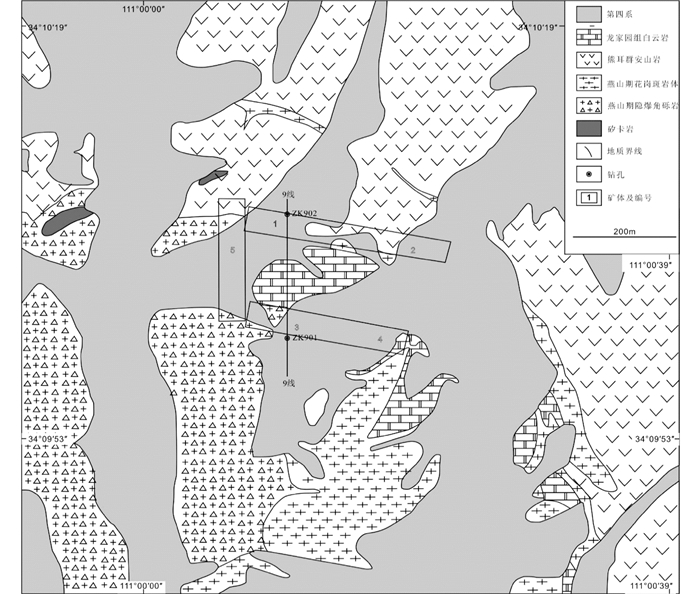
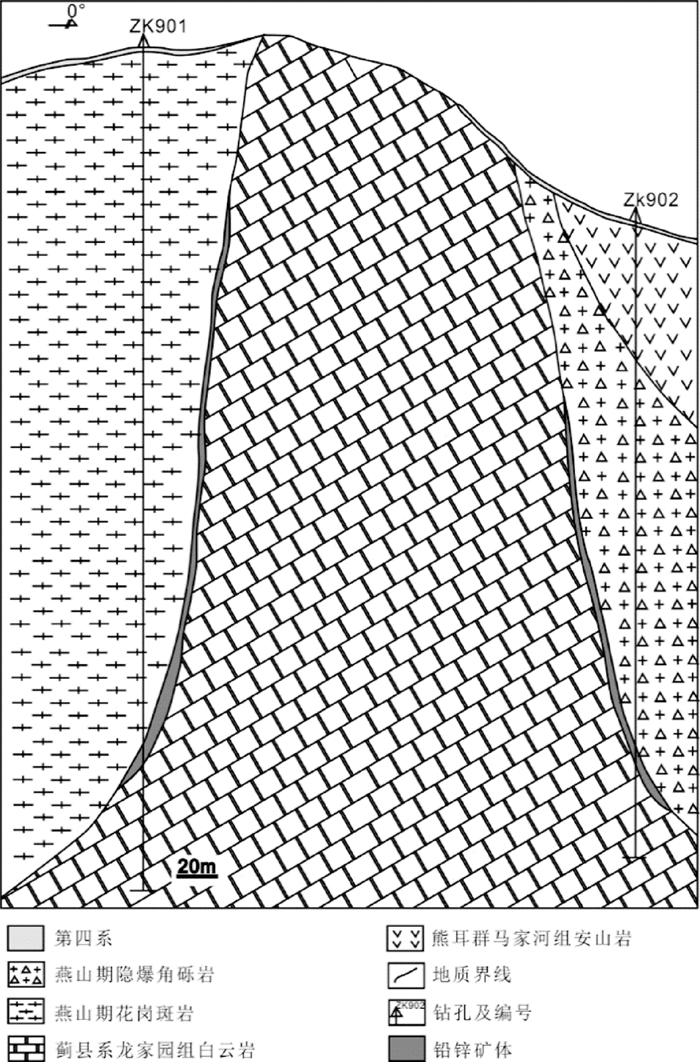
柳关铅锌矿共有3条矿带5个铅锌矿体,主要分布在花岗斑岩体与官道口群龙家园组白云岩和燕山期隐爆角砾岩的外接触带上(图 6),其形成主要与花岗斑岩的侵位有关。矿体均为隐伏矿体(图 7),1号矿体分布在北矿带西段,呈近东西向展布,走向270°~290°,倾向0°~20°,倾角65°~85°,一般在80°左右。2号矿体发育于北矿带东段,产于花岗斑岩与白云岩接触带的矽卡岩中,走向85°~105°,倾向355°~15°,倾角65°~81°。3号矿体发育于南矿带西段,走向85°~110°,倾向175°~200°,倾角68°~85°,总体陡倾。4号矿体发育在南矿带东段,走向275°~290°,倾向180°,倾角68°~85°,平均75°左右。5号矿体位于西矿带,走向175°~190°,倾向265°~280°,倾角75°~85°,平均80°左右。
|
图 6 柳关铅锌矿地质图(中科远航矿业有限公司, 2015①) Fig. 6 Geological map of Liuguan Pb-Zn deposit |
① 中科远航矿业有限公司.2015.卢氏县柳关栾卢铅锌矿生产勘探报告
|
图 7 柳关铅锌矿9号勘探线剖面图(中科远航矿业有限公司, 2015) Fig. 7 Vertical section of 9th prospecting line in Liuguan deposit |
柳关铅锌矿矿石矿物主要为闪锌矿、方铅矿、黄铁矿、磁铁矿,脉石矿物主要为透辉石、石榴石、阳起石、透闪石、绿帘石、蛇纹石、方解石; 围岩蚀变主要为矽卡岩化,其次为硅化、绿泥石化、碳酸盐化等(图 5e-h)。成矿阶段可以划分为两个:透辉石-透闪石-阳起石-石榴石-磁铁矿(早期矽卡岩阶段)和方铅矿-闪锌矿-黄铁矿-石英-绿帘石-绿泥石-蛇纹石-方解石(晚期热液阶段),其中晚阶段是铅锌矿的主成矿阶段。
3 样品及实验方法楼房银铜矿用于Rb-Sr定年的黄铜矿样品取自1号脉平硐中黄铜矿石英脉(图 5a),柳关铅锌矿用于Rb-Sr定年的黄铁矿样品采于块状多金属矿石(图 5e)。
Rb-Sr定年分析实验是在南京大学现代分析中心同位素分析室完成。将楼房银铜矿的黄铜矿和柳关铅锌矿中的黄铁矿碎样至40~60目,在双目镜下挑纯,每个样品选取1~2g表面新鲜的、纯度较高的单颗粒黄铜矿或黄铁矿。挑选出的黄铜矿或黄铁矿尽量小,以尽量避免次生流体的干扰。之后将纯净的单颗粒样品放入玛瑙研钵研磨至200目左右待测。
黄铜矿、黄铁矿颗粒(称取500mg)在超声浴中用分析纯乙醇洗净后,经过超纯水的漂洗放入Teflon vessels封闭器皿中加入87Sr和84Sr混合的稀释剂。样品在80℃下用盐酸和硝酸比例为1:3的混合酸溶解,取清液上离子交换柱分离,采用高压密闭熔样和阳离子交换技术分离和提纯。Rb和Sr的分离和纯化用Horwitz et al.(1992)的方法,其他有关实验的信息详见Li et al.(2008)。同位素比值的测量使用英国VG354多接收同位素质谱仪,测定方法见文献(Wang et al., 2007; 王银喜等, 2007)。Sr同位素数据标准化为88Sr/86Sr=8.375219,87Sr/86Sr使用NBS987标准:0.71025(Faure and Mensing, 2005),测定值为0.710233±6。整个过程中使用的对照组Rb和Sr均为0.2ng。年龄计算的回归分析使用ISOPLOT(Ludwig, 2003)。计算时使用的衰变常数为λ87Rb=1.42×10-11a-1(Steiger and Jäger, 1977)。
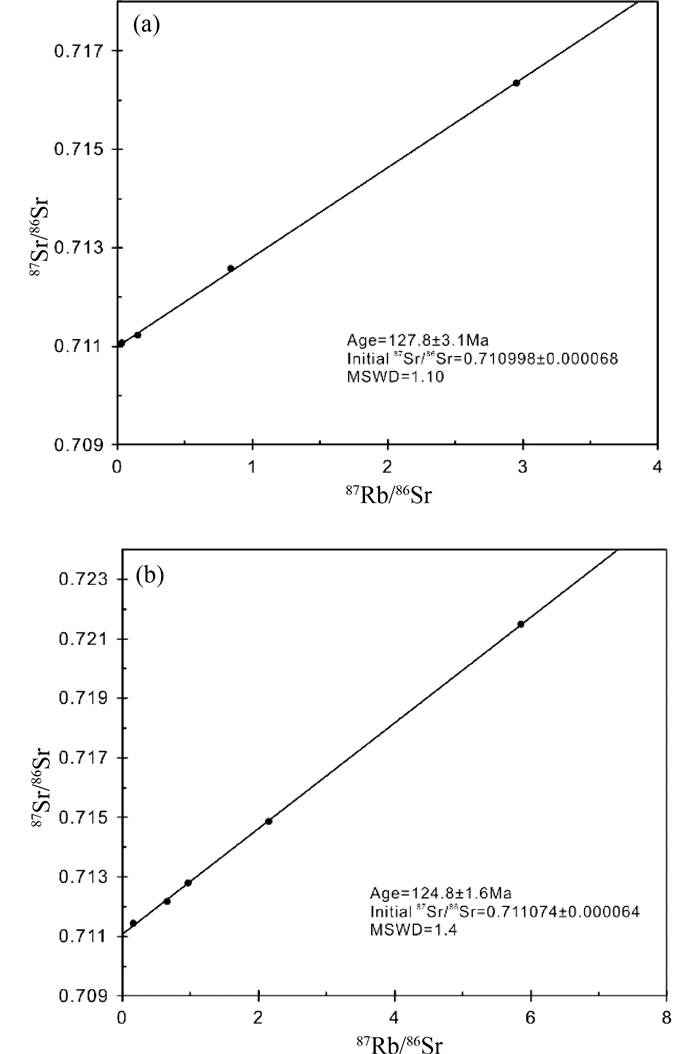
4 实验结果Rb-Sr同位素的分析结果呈现在表 1、图 8中,楼房银铜矿矿石中黄铜矿的87Rb/86Sr比值为0.0331~2.954,柳关铅锌矿矿石中黄铁矿的87Rb/86Sr比值为0.1649~5.863,实验得到的87Rb/86Sr-87Sr/86Sr均表现出很好的线性关系(图 8a, b)(Lüders and Ziemann, 1999)。
|
|
表 1 楼房银铜矿黄铜矿、柳关铅锌矿黄铁矿Rb-Sr同位素测定结果 Table 1 The Rb/Sr isotope contents and ratios of chalcopyrite in Loufang Ag-Cu deposit and pyrite in Liuguan Pb-Zn deposit |
|
图 8 楼房银铜矿黄铜矿(a)和柳关铅锌矿黄铁矿(b)Rb-Sr年龄 Fig. 8 Rb-Sr isochron age plot of chalcopyrites of the Loufang Ag-Cu deposit (a) and pyrites of the Liuguan Pb-Zn deposit (b) |
对楼房银铜矿和柳关铅锌矿各采用6个样品进行Rb-Sr等时线定年,使用ISOPLOT(Ludwig, 2003)软件计算出各矿床的Rb-Sr等时线年龄。楼房银铜矿的4个样品点构筑出一条等时线,其Rb-Sr等时线年龄为127.8±3.1Ma,初始87Rb/86Sr为0.710998±0.000068 (MSWD=1.1)(图 8a);柳关铅锌矿的5个样品点构筑出一条等时线,其Rb-Sr等时线年龄为124.8±1.6Ma,初始87Rb/86Sr为0.711074±0.000064 (MSWD=1.4)(图 8b)。
5 讨论 5.1 成矿时代硫化物Rb-Sr定年的方法起源于Reesman(1968)对加拿大Noranda矿区硫化物(黄铜矿、黄铁矿、磁黄铁矿、闪锌矿等)中Rb、Sr、Rb-Sr同位素组成的测定,研究发现这些硫化物具有足量可分析的Rb/Sr比值变化范围。Medford et al.(1983)发现闪锌矿中Sr同位素存在均一化过程,证明闪锌矿满足Rb-Sr等时线定年的前提条件,具有铅锌矿床直接定年的潜力。Nakai et al.(1990)首次直接使用Rb-Sr等时线法测定密西西比河Coy铅锌矿的闪锌矿Rb-Sr年龄,也是世界上首例使用硫化物Rb-Sr定年的成功案例,之后不断得到应用(Yang and Zhou, 2001; Schneider et al., 2007; Zhou et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2014)。
使用同位素地质年代学方法的基本前提是同时、同源、封闭。本文中我们选取同一地区同一期矿脉中的黄铜矿、黄铁矿进行定年,这样可以保证样品的同时性和同源性。选取的样品还应具有相同的(87Sr/86Sr)i和不同的(87Rb/86Sr)i(李文博等,2002),这样可以保证每个样品中Rb/Sr比值具有差异性而得到更精确的年龄,所以在选取样品时应使每个测定样品之间在空间上间隔一定距离。硫化物Rb-Sr等时线定年最大的干扰因素在于次生包裹体。但由于次生包裹体多形成于矿物的裂隙、解理等相对薄弱的部位,故相对容易破坏以排除次生包裹体的影响(刘建明等,1998)。实验前我们通过对样品进行研磨来达到破坏样品中次生包裹体的目的,将样品碎至200目以下以尽可能降低误差。综上,我们的实验满足同位素定年体系的基本前提,在实验过程中尽可能降低实验误差,最终得到楼房银铜矿成矿年龄为127.8±3.1Ma,柳关铅锌矿的成矿年龄为124.8±1.6Ma。
梁涛等(2015)对楼房银铜矿附近的蒿坪沟黑云母花岗岩进行锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb定年得到年龄为130.5±1.1Ma,与楼房银铜矿床黄铜矿Rb-Sr等时线实验结果127.8±3.1Ma接近,证明成矿可能与这一时期花岗质岩浆的侵入活动有关。胡浩等(2011)得到柳关岩体U-Pb年龄为132±1Ma,也与测定出的柳关铅锌矿黄铁矿Rb-Sr年龄124.8±1.6Ma比较接近,这说明柳关铅锌矿床成矿可能与柳关岩体有关。这些研究表明,卢氏多金属矿集区内多金属矿床主要形成于早白垩世。
5.2 成矿物质来源初始87Sr/86Sr比值是判断成岩成矿物质来源的重要指标。在矿床地质研究中,常利用87Sr/86Sri来示踪成矿物质来源、岩浆流体、深源流体的壳幔混染作用(侯明兰等,2006)。楼房银铜矿锶同位素的测试结果表明,同位素87Rb/86Sr比值变化较大,为0.0331~2.954,平均值为0.9955,初始87Sr/86Sr比值变化相对较小,为0.71095~0.71106,平均值为0.71100;柳关铅锌矿锶同位素的测试结果显示,同位素87Rb/86Sr比值变化较大,为0.1649~5.863,平均值为1.96,初始87Sr/86Sr比值变化相对较小,为0.71100~0.71115,平均值0.71107。而西秦岭晚中生代玄武岩初始87Sr/86Sr比值为0.7025~0.7050(李晓勇和范立勇,2006),大别地区地幔来源闪长岩-辉长岩杂岩体初始87Sr/86Sr比值为0.7076~0.7097(Jahn et al., 1999),区域内与成矿相关的晚中生代花岗岩初始87Sr/86Sr比值为0.7033~0.7105(王晓霞等,2011)。如华山复式岩体(132Ma, Hu et al., 2012)、花山岩体(128±1Ma,聂政融等,2015)、伏牛山岩体(131~115Ma, Gao et al., 2014b)等均为壳幔混合成因。柳关铅锌矿为矽卡岩型矿床,在时空及成因关系上与柳关岩体密切相关,岩体年龄为132Ma(胡浩等,2011),柳关岩体与区域内晚中生代成矿岩体特征及时代一致,它们形成于相同的地球动力学环境,推测具有相似的壳幔混合成因。
除此之外,在区域上存在晚侏罗世-早白垩世华北克拉通南缘发生壳幔混合的证据:(1)小秦岭金矿集区中各个晚侏罗世-早白垩世金矿床的稀有气体和稳定同位素分析结果反映它们的成矿流体和成矿物质来源于地幔或岩浆,说明在这期间曾因为地壳减薄发生过大规模的热液成矿事件(Li et al., 2012a, b; Liu et al., 2013);(2)华北克拉通南缘晚侏罗世-早白垩世花岗岩由古老地壳部分熔融形成,并有新生岩石圈、软流圈地幔的物质加入(Gao et al., 2014a, b; Li et al., 2012c),许多岩体含有丰富的镁铁质微颗粒包体,说明在这些岩体的形成过程中,曾发生过镁铁质和长石质岩浆的混合(丁丽雪等,2010; Liu et al., 2013); (3)部分花岗岩体被镁铁质岩脉侵入,而镁铁质岩脉的年龄和岩体以及岩体中包含的镁铁质微颗粒包体年龄相吻合(包志伟等, 2009; 丁丽雪等,2010; Li et al., 2012b; Liu et al., 2013)。根据矿床与岩体的耦合关系,说明这些矿床的物质来源也是壳幔混合。
综上所述,推测柳关铅锌矿和楼房银铜矿的成矿物质均为壳幔混合。
5.3 成矿构造环境中生代是华北克拉通重要的叠加岩浆活动期,峰期为120~127Ma(Zhu et al., 2011b; Zhang et al., 2012; Gao and Zhao., 2017)。晚侏罗世-早白垩世,华北克拉通减薄和活化的速率得到明显加快,太平洋板块的俯冲方向发生明显变化(Bartolini and Larson, 2001; Sun et al., 2007; Li et al., 2012b),太平洋板块的深部俯冲使地幔流失稳(Xu et al., 2011),俯冲板片脱水使上地幔的固相线和粘度降低,显著加剧了岩石圈的底侵作用(Niu, 2005)。在早白垩世,华北克拉通东部发育变质核杂岩、A型花岗岩、粗玄岩、双峰式火山岩等反映了华北克拉通在这一时期发生了强烈的岩石圈伸展及减薄作用(Zhang and Zheng, 1999; 谢桂青等, 2007; 周红升等, 2008; Mao et al., 2010; 王晓霞等, 2011),处于伸展的构造环境,也是华北克拉通破坏的环境(Zhu et al., 2011b; Zhu et al., 2015)。
华北克拉通南缘的熊耳山地区发育大量晚中生代花岗岩侵入体,它们的锆石U-Pb年龄多集中在晚侏罗世-早白垩世(157~127Ma; 郭波等,2009; Mao et al., 2010; 高昕宇等,2010)。前人对小秦岭地区的金矿床硫化物Re-Os年龄和绢云母Ar-Ar年龄进行测定,它们的年龄分布在154~119Ma之间,这些岩体与相关的金矿床均形成于克拉通破坏的构造环境(Li et al., 2012a, b; Liu et al., 2013)。
卢氏多金属矿集区位于熊耳山地区,区内花岗质侵入岩体也主要形成于早白垩世(133.8±1.1Ma,郭波等, 2009; 127.7±0.6Ma, Li et al., 2012b),与华北克拉通南缘花岗岩形成峰期一致。而卢氏多金属矿集区广泛分布的花岗岩类侵入体,多伴生与侵入体相关的多金属矿化,这些岩体也主要形成于早白垩世。除此之外,Sr-Nd-Hf同位素研究也可以从另一个角度说明矿集区内这些早白垩世花岗岩类侵入体源区具有壳源混合源的特点(Gao and Zhao, 2017),反映了这一地区在早白垩世克拉通发生了破坏(Li et al., 2012a),而区内包括楼房银铜矿、柳关铅锌矿在内的多金属矿床成矿与这些早白垩世岩体密切相关,因此,卢氏多金属矿集区成矿作用也是华北克拉通破坏的产物,楼房银铜矿和柳关铅锌矿均形成于与克拉通破坏的构造环境。
6 结论(1) 楼房脉状银铜矿床成矿年龄为127.8±3.1Ma,柳关矽卡岩型铅锌矿床成矿年龄为124.8±1.6Ma,二者均形成于早白垩世。
(2) 根据楼房银铜矿床黄铜矿、柳关铅锌矿床黄铁矿初始87Sr/86Sr比值,推测两个矿床成矿物质来源均为壳幔混合来源。
(3) 楼房银铜矿和柳关铅锌矿成矿与早白垩世侵入体密切相关,形成于华北克拉通破坏的构造环境。
致谢 感谢卢氏中科领导与技术人员、楼房银铜矿、大洞沟铅矿领导与技术人员等为我们在卢氏县野外考察期间所提供的大量帮助与支持!两位匿名审稿人对本文提出了具体的修改意见,在此表示感谢!
谨以此文祝贺叶大年院士80华诞,感谢叶先生的关怀与指导。
Bao ZW, Li CJ and Qi JP. 2009. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age of the gabbro dyke in the Luanchuan Pb-Zn-Ag orefield, East Qinling orogen and its constraint on mineralization time. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11): 2951-2956 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Bartolini A and Larson RL. 2001. Pacific microplate and the Pangea supercontinent in the Early to Middle Jurassic. Geology, 29(8): 735-738 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0735:PMATPS>2.0.CO;2 |
Chen YJ and Fu SG. 1992. Gold Mineralization in West Henan. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Chen YJ, Li C, Zhang J, Li Z and Wang HH. 2000. Sr and O isotopic characteristics of porphyries in the Qinling molybdenum deposit belt and their implication to genetic mechanism and type. Science in China (Series D), 43(S1): 82-94 DOI:10.1007/BF02911935 |
Deng XH, Chen YJ, Santosh M and Yao JM. 2013. Genesis of the 1.76Ga Zhaiwa Mo-Cu and its link with the Xiong'er volcanics in the North China Craton:Implications for accretionary growth along the margin of the Columbia supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 227: 337-348 |
Ding LX, Ma CQ, Li JW, Wang LX, Chen L and She ZB. 2010. LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb ages of the Lantian and Muhuguan granitoid plutons, southern margin of the North China craton:Implications for tectonic setting. Geochimica, 39(5): 401-413 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Diwu CR, Sun Y, Liu L, Zhang CL and Wang HL. 2010. The disintegration of Kuanping Group in North Qinling orogenic belts and Neo-Proterozoic N-MORB. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7): 2025-2038 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Dong YP, Zhang GW, Neubauer F, Liu XM, Genser J and Hauzenberger C. 2011. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, China:Review and synthesis. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 41(3): 213-237 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.002 |
Du AD, Wu SQ, Sun DZ, Wang SX, Qu WJ, Markey R, Stain H, Morgan JW and Malinovskiy D. 2004. Preparation and certification of Re-Os dating reference materials:Molybdenites HLP and JDC. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 28(1): 41-52 DOI:10.1111/ggr.2004.28.issue-1 |
Faure G and Mensing T. 2005. Isotopes: Principles and Applications. 3rd Edition. John Wiley Sons, 75-112
|
Gao JJ, Mao JW, Chen MH, Ye HS, Zhang JJ and Li YF. 2011. Vein structure analysis and 40Ar/39Ar dating of sericite from sub-ore altered rocks in the Tieluping large-size Ag-Pb deposit of western Henan Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(7): 1172-1187 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Gao XY, Zhao TP, Yuan ZL, Zhou YY and Gao JF. 2010. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Heyu batholith in the southern margin of the North China block. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(12): 3485-3506 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Gao XY, Zhao TP, Bao ZW and Yang AY. 2014a. Petrogenesis of the early Cretaceous intermediate and felsic intrusions at the southern margin of the North China Craton:Implications for crust-mantle interaction. Lithos, 206: 65-78 |
Gao XY, Zhao TP and Chen WT. 2014b. Petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous Funiushan granites on the southern margin of the North China Craton:Implications for the Mesozoic geological evolution. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 94: 28-44 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.042 |
Gao XY and Zhao TP. 2017. Late Mesozoic magmatism and tectonic evolution in the southern margin of the North China Craton. Science China (Earth Sciences), 60(11): 1959-1975 DOI:10.1007/s11430-016-9069-0 |
Guo B, Zhu LM, Li B, Gong HJ and Wang JQ. 2009. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope composition of the Huashan and Heyu granite plutons at the southern margin of North China Craton:Implications for geodynamic setting. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(2): 265-281 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Horwitz EP, Chiarizia R and Dietz ML. 1992. A novel strontium-selective extraction chromatographic resin. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 10(2): 313-336 DOI:10.1080/07366299208918107 |
Hou ML, Jiang SY, Jiang YH and Ling HF. 2006. S-Pb isotope geochemistry and Rb-Sr geochronology of the Penglai gold field in the eastern Shandong Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(10): 2525-2533 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu GH, Zhao TP, Zhou YY and Wang SY. 2013. Meso-Neoproterozoic sedimentary formation in the southern margin of the North China Craton and its geological implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(7): 2491-2507 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu H, Li JW and Deng XD. 2011. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of granitoid intrusions related to iron-copper polymetallic deposits in Luonan-Lushi area of southern North China Craton and its geological implications. Mineral Deposits, 30(6): 979-1101 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu J, Jiang SY, Zhao HX, Shao Y, Zhang ZZ, Xiao E, Wang YF, Dai BZ and Li HY. 2012. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Huashan granites and their implications for the Mesozoic tectonic settings in the Xiaoqinling gold mineralization belt, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 56: 276-289 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.05.016 |
Jahn BM, Wu FY, Lo CH and Tsai CH. 1999. Crust-mantle interaction induced by deep subduction of the continental crust:geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from post-collisional mafic-ultramafic intrusions of the northern Dabie complex, central China. Chemical Geology, 157: 119-146 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00197-1 |
Jiang GQ, Zhou HR and Wang ZQ. 1994. Stratigraphic sequence, sedimentary environment and its tectono-paleogeographic significance of the Luanchuan Group, Luanchuan area, Henan Province. Geoscience, 8(4): 430-440 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Jiao JG, Yuan HC, He K, Sun T, Xu G and Liu RP. 2009. Zircon U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os dating for the Balipo porphyry Mo deposit in East Qinling, China, and its geological implication. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(8): 1159-1166 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Kröner A, Compston W, Zhang GW, Guo AL and Todt W. 1988. Age and tectonic setting of Late Archean greenstone-gneiss terrain in Henan Province, China, as revealed by single-grain zircon dating. Geology, 16(3): 211-215 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0211:AATSOL>2.3.CO;2 |
Li JW, Bi SJ, Selby D, Chen L, Vasconcelos P, Thiede D, Zhou MF, Zhao XF, Li ZK and Qiu HN. 2012a. Giant Mesozoic gold provinces related to the destruction of the North China craton. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 349-350: 26-37 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2012.06.058 |
Li JW, Li ZK, Zhou MF, Chen L, Bi SJ, Deng XD, Qiu HN, Cohen B, Selby D and Zhao XF. 2012b. The Early Cretaceous Yangzhaiyu lode gold deposit, North China Craton:A link between craton reactivation and gold veining. Economic Geology, 107(1): 43-79 |
Li N, Chen YJ, Santosh M, Yao JM, Sun YL and Li J. 2011. The 1.85Ga Mo mineralization in the Xiong'er Terrane, China:Implications for metallogeny associated with assembly of the Columbia supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 186(1-4): 220-232 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2011.01.019 |
Li N, Chen YJ, Pirajno F, Gong HJ, Mao SD and Ni ZY. 2012c. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating, trace element and Hf isotope geochemistry of the Heyu granite batholith, eastern Qinling, central China:Implications for Mesozoic tectono-magmatic evolution. Lithos, 142-143: 34-47 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.02.013 |
Li QL, Chen FK, Yang JH and Fan HR. 2008. Single grain pyrite Rb-Sr dating of the Linglong gold deposit, eastern China. Ore Geology Review, 34(3): 263-270 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.10.003 |
Li WB, Huang ZL, Xu DR, Chen J, Xu C and Guan T. 2002. Rb-Sr isotopic method on zinc-lead ore deposits:A review. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 26(4): 436-441 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li XY and Fan LY. 2006. Geochemistry of Late Mesozoic mafic volcanic rocks in Western Qinling and its implication. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 45(3): 127-128 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li ZK, Li JW, Zhao XF, Zhou MF, Selby D, Bi SJ, Sui JX and Zhao ZJ. 2013. Crustal-extension Ag-Pb-Zn veins in the Xiong'ershan district, southern North China craton:Constraints from the Shagou deposit. Economic Geology, 108(7): 1703-1729 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.108.7.1703 |
Liang T, Lu R, Luo ZH, Bai FJ and Liu X. 2015. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb age of zircons from Haopinggou biotite granite porphyry in Xiong'er Mountain, western Henan Province, and its geologic implications. Geological Review, 61(4): 901-912 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu JM, Zhao SR, Shen J, Jiang N and Huo WG. 1998. Review on direct isotopic dating of hydrothermal ore-forming processes. Progress in Geophysics, 13(3): 46-55 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu R, Li JW, Bi SJ, Hu H and Chen M. 2013. Magma mixing revealed from in situ zircon U-Pb-Hf isotope analysis of the Muhuguan granitoid pluton, eastern Qinling orogen, China:Implications for Late Mesozoic tectonic evolution. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 102(6): 1583-1602 DOI:10.1007/s00531-013-0900-x |
Lüders V and Ziemann M. 1999. Possibilities and limits of infrared light microthermometry applied to studies of pyrite-hosted ffluid inclusions. Chemical Geology, 154(1-4): 169-178 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00130-2 |
Ludwig KR. 2003. User's manual for Isoplot 3.00:A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center, 4: 25-32 |
Mao B, Ye HS, Li C, Xiao ZJ and Yang GQ. 2011. Molybdenite Re-Os isochron age of Yechangping Mo deposit in western Henan Province and its geological implications. Mineral Deposits, 30(6): 1069-1074 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Mao JW, Goldfarb RJ, Zhang ZW, Xu WY, Qiu YM and Deng J. 2002. Gold deposits in the Xiaoqinling-Xiong'ershan region, Qinling Mountains, central China. Mineralium Deposita, 37(3-4): 306-325 DOI:10.1007/s00126-001-0248-1 |
Mao JW, Xie GQ, Pirajno F, Ye HS, Wang YB, Li YF, Xiang JF and Zhao HJ. 2010. Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous granitoid magmatism in Eastern Qinling, central-eastern China:SHRIMP zircon U-Pb ages and tectonic implications. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 57(1): 51-78 DOI:10.1080/08120090903416203 |
Mao JW, Pirajno F, Xiang JF, Gao JJ, Ye HS, Li YF and Guo BJ. 2011. Mesozoic molybdenum deposits in the East Qinling-Dabie orogenic belt:Characteristics and tectonic settings. Ore Geology Review, 43(1): 264-293 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.07.009 |
Medford GA, Maxwell RJ and Lee Armstrong R. 1983. 87Sr/86Sr ratio measurements on sulfides, carbonates, and fluid inclusions from Pine Point, Northwest Territories, Canada:An 87Sr/86Sr ratio increase accompanying the mineralizing process. Economic Geology, 78(7): 1375-1378 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.78.7.1375 |
Meng QR and Zhang GW. 2000. Geologic framework and tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, central China. Tectonophysics, 323(3-4): 183-196 DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00106-2 |
Nakai S, Halliday AN, Kesler SE and Jones HD. 1990. Rb-Sr dating of sphalerites from Tennessee and the genesis of Mississippi valley type ore deposits. Nature, 346(6282): 354-357 DOI:10.1038/346354a0 |
Nie ZR, Wang XX, Ke CH, Yang Y and Lv XQ. 2015. Age, geochemistry and petrogenesis of Huashan granitoid pluton on the southern margin of the North China Block. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(8): 1502-1516 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Niu YL. 2005. Generation and evolution of basaltic magmas:Some basic concepts and a new view on the origin of Mesozoic-Cenozoic basaltic volcanism in Eastern China. Geological Journal of China Universities, 11(1): 9-46 |
Peng P, Zhai MG, Ernst RE, Guo JG, Liu F and Hu B. 2008. A 1.78Ga large igneous province in the North China Craton:The Xiong'er Volcanic Province and the North China dyke swarm. Lithos, 101(3-4): 260-280 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.07.006 |
Reesman RJ. 1968. The Rb-Sr analyses of some sulfide mineralization. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 5: 23-26 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(68)80005-6 |
Ren FG and Li WM. 1996. Ore-forming Geological Conditions and Models for Ore Searching and Ore Evaluation of Gold Deposit in Xiongershan-Xiaoshan Area. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Schneider J, Melcher F and Brauns M. 2007. Concordant ages for the giant Kipushi base metal deposit (DR Congo) from direct Rb-Sr and Re-Os dating of sulfides. Mineralium Deposita, 42(7): 791-797 DOI:10.1007/s00126-007-0158-y |
Song WL, Xu C, Qi L, Zhou L, Wang LJ and Kynicky J. 2015. Genesis of Si-rich carbonatites in Huanglongpu Mo deposit, Lesser Qinling Orogen, China and significance for Mo mineralization. Ore Geology Review, 64: 756-765 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.04.003 |
Steiger RH and Jäger E. 1977. Subcommission on geochronology:Convention on the use of decay constants in geo-and cosmochronology. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 36(3): 359-362 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(77)90060-7 |
Sun WD, Ding X, Hu YH and Li XH. 2007. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the West Pacific. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 262(3-4): 533-542 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.08.021 |
Wang XX, Wang T, Qi QJ and Li S. 2011. Temporal-spatial variations, origin and their tectonic significance of the Late Mesozoic granites in the Qinling, Central China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(6): 1573-1593 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang XX, Wang T, Ke CH, Yang Y, Li JB, Li YH, Qi QJ and Lv XQ. 2015. Nd-Hf isotopic mapping of Late Mesozoic granitoids in the East Qinling orogen, Central China:Constraint on the basements of terranes and distribution of Mo mineralization. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 103: 169-183 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.002 |
Wang YB, Zeng QD and Liu JM. 2014. Rb-Sr dating of gold-bearing pyrites from Wulaga gold deposit and its geological significance. Resource Geology, 64(3): 262-270 DOI:10.1111/rge.12040 |
Wang YX, Yang JD, Chen J, Zhang KJ and Rao WB. 2007. The Sr and Nd isotopic variations of the Chinese Loess Plateau during the past 7Ma:Implications for the East Asian winter monsoon and source areas of Loess. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 249(3-4): 351-361 DOI:10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.02.010 |
Wang YX, Gu LX, Zhang ZZ, Wu CZ, Li HM and Yang JD. 2007. Sr-Nd-Pb isotope geochemistry of rhyolite of the Late Carboniferous Dashitou Group in eastern Tianshan. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(7): 1749-1755 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang ZQ, Yan Z, Wang T, Gao LD, Yan QR, Chen JL, Li QG, Jiang CF, Liu P, Zhang YL, Xie CL and Xiang ZJ. 2009. New advances in the study on ages of metamorphic strata in the Qinling orogenic belt. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 30(5): 561-570 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wei QG, Yao JM, Zhao TP, Sun YL, Li J, Yuan ZL and Qiao B. 2009. Discovery of a~1.9Ga Mo deposit in the eastern Qinling orogen:Molybdenite Re-Os ages of the Longmendian Mo deposit in Henan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11): 2747-2751 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wu G, Chen YC, Li ZY, Yang XS, Liu J and Qiao CJ. 2013. Molybdenite Re-Os and sericite 40Ar-39Ar ages of Yinjiagou pyrite-polymetallic deposit in western Henan Province, and their geological significance. Mineral Deposits, 32(4): 810-822 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xiang JF, Pei RF, Xing B, Wang CY, Tian ZH, Chen XD, Ye HS and Wang HL. 2016. The formation process and Mo (W) mineralizaton of the skarn in the Nannihu-Sandaozhuang Mo (W) deposit. Geology in China, 43(6): 2131-2153 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Li RL, Ye HS, Zhang YX, Wan YS, Li HM, Gao JJ and Zheng RF. 2007. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating for volcanic rocks of the Daying Formation from Baofeng basin in eastern Qinling, China and its implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(10): 2387-2396 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu WW, Zheng TY and Zhao L. 2011. Mantle dynamics of the reactivating North China Craton:Constraints from the topographies of the 410km and 660km discontinuities. Science China (Earth Sciences), 54(6): 881-887 DOI:10.1007/s11430-010-4163-0 |
Xue F, Kröner A, Reischmann T and Lerch F. 1996. Palaeozoic pre-and post-collision calc-alkaline magmatism in the Qinling orogenic belt, central China, as documented by zircon ages on granitoid rocks. Journal of the Geological Society, 153: 406-417 |
Yan GL, Wang ZM, Li YQ, Fu YH and Ding GM. 2012. Re-Os isotope ages of molybdenite and their geological significance of Yechangping molybdenum deposit, Henan. Mineral Exploration, 3(2): 184-193 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang JH and Zhou XH. 2001. Rb-Sr, Sm-Nd, and Pb isotope systematics of pyrite:Implications for the age and genesis of lode gold deposits. Geology, 29(8): 711-714 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0711:RSSNAP>2.0.CO;2 |
Yang YF, Chen YJ, Pirajno F and Li N. 2015. Evolution of ore fluids in the Donggou giant porphyry Mo system, East Qinling, China, a new type of porphyry Mo deposit:Evidence from fluid inclusion and H-O isotope systematics. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 148-164 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.09.011 |
Ye HS. 2006. The Mesozoic tectonic evolution and Pb-Zn-Ag metallogeny in the south margin of North China Craton. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences
|
Zeng QD, Liu JM, Qin KZ, Fan HR, Chu SX, Wang YB and Zhou LL. 2013. Types, characteristics, and time-space distribution of molybdenum deposits in China. International Geology Review, 55(11): 1311-1358 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2013.774195 |
Zhang GW, Zhang BR, Yuan XC and Xiao QH. 2001. Qinling Orogenic Belt and Continental Dynamics. Beijing:Science Press, 1-729 (in Chinese)
|
Zhang HF, Zhu RX, Santosh M, Ying JF, Su BX and Yan H. 2012. Episodic widespread magma underplating beneath the North China Craton in the Phanerozoic:Implications for craton destruction. Gondwana Research, 23(1): 95-107 |
Zhang JJ and Zheng YD. 1999. Multistage extension and age dating of the Xiaoqinling metamorphic core complex, central China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 73(2): 139-147 DOI:10.1111/acgs.1999.73.issue-2 |
Zhao HJ, Ye HS and Li C. 2013. Re-Os dating of molybdenite from the Shijiawan molybdenum deposit in Shaanxi Province and its geological implications. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 32(1): 90-98 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao ZF and Zheng YF. 2009. Remelting of subducted continental lithosphere:Petrogenesis of Mesozoic magmatic rocks in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt. Science in China (Series D), 52(9): 1295-1318 DOI:10.1007/s11430-009-0134-8 |
Zhou HS, Ma CQ, Zhang C, Chen L, Zhang JY and She ZB. 2008. Yanshanian aluminous A-type granitoids in the Chunshui of Biyang, southern margin of North China Craton:Implications from petrology, geochronology and geochemistry. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(1): 49-64 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhou JX, Huang ZL, Zhou MF, Li XB and Jin ZG. 2013. Constraints of C-O-S-Pb isotope compositions and Rb-Sr isotopic age on the origin of the Tianqiao carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, SW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 53: 77-92 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.01.001 |
Zhu LM, Zhang GW, Chen YJ, Ding ZL, Guo B, Wang F and Lee B. 2011a. Zircon U-Pb ages and geochemistry of the Wenquan Mo-bearing granitioids in West Qinling, China:Constraints on the geodynamic setting for the newly discovered Wenquan Mo deposit. Ore Geology Reviews, 39(1-2): 46-62 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2010.10.001 |
Zhu RX, Chen L, Wu FY and Liu JL. 2011b. Timing, scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton. Science China (Earth Sciences), 54(6): 789-797 DOI:10.1007/s11430-011-4203-4 |
Zhu RX, Fan HR, Li JW, Meng QR, Li SR and Zeng QD. 2015. Decratonic gold deposits. Science China (Earth Sciences), 58(9): 1523-1537 DOI:10.1007/s11430-015-5139-x |
包志伟, 李创举, 祁进平. 2009. 东秦岭栾川铅锌银矿田辉长岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及成矿时代. 岩石学报, 25(11): 2951-2956. |
陈衍景, 富士谷. 1992. 豫西金矿成矿规律. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
第五春荣, 孙勇, 刘良, 张成立, 王洪亮. 2010. 北秦岭宽坪岩群的解体及新元古代N-MORB. 岩石学报, 26(7): 2025-2038. |
丁丽雪, 马昌前, 李建威, 王连训, 陈玲, 佘振兵. 2010. 华北克拉通南缘蓝田和牧护关花岗岩体:LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义. 地球化学, 39(5): 401-413. |
高建京, 毛景文, 陈懋弘, 叶会寿, 张继军, 李永峰. 2011. 豫西铁炉坪银铅矿床矿脉构造解析及近矿蚀变岩绢云母40Ar-39Ar年龄测定. 地质学报, 85(7): 1172-1187. |
高昕宇, 赵太平, 原振雷, 周艳艳, 高剑峰. 2010. 华北陆块南缘中生代合峪花岗岩的地球化学特征与成因. 岩石学报, 26(12): 3485-3506. |
郭波, 朱赖民, 李犇, 弓虎军, 王建其. 2009. 华北陆块南缘华山和合峪花岗岩岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成与成岩动力学背景. 岩石学报, 25(2): 265-281. |
侯明兰, 蒋少涌, 姜耀辉, 凌洪飞. 2006. 胶东蓬莱金成矿区的S-Pb同位素地球化学和Rb-Sr同位素年代学研究. 岩石学报, 22(10): 2525-2533. |
胡国辉, 赵太平, 周艳艳, 王世炎. 2013. 华北克拉通南缘中-新元古代沉积地层对比研究及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 29(7): 2491-2507. |
胡浩, 李建威, 邓晓东. 2011. 洛南-卢氏地区与铁铜多金属矿床有关的中酸性侵入岩锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义. 矿床地质, 30(6): 979-1101. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.06.002 |
蒋干清, 周洪瑞, 王自强. 1994. 豫西栾川地区栾川群的层序、沉积环境及其构造古地理意义. 现代地质, 8(4): 430-440. |
焦建刚, 袁海潮, 何克, 孙涛, 徐刚, 刘瑞平. 2009. 陕西华县八里坡钼矿床锆石U-Pb和辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其地质意义. 地质学报, 83(8): 1159-1166. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.08.014 |
李文博, 黄智龙, 许德如, 陈进, 许成, 管涛. 2002. 铅锌矿床Rb-Sr定年研究综述. 大地构造与成矿学, 26(4): 436-441. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2002.04.015 |
李晓勇, 范立勇. 2006. 西秦岭地区晚中生代OIB型玄武岩的发现及其意义. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 45(3): 127-128. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2006.03.033 |
梁涛, 卢仁, 罗照华, 白凤军, 刘晓. 2015. 豫西熊耳山蒿坪沟黑云母花岗斑岩的锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄及其地质意义. 地质论评, 61(4): 901-912. |
刘建明, 赵善仁, 沈洁, 姜能, 霍卫国. 1998. 成矿流体活动的同位素定年方法评述. 地球物理学进展, 13(3): 46-55. |
毛冰, 叶会寿, 李超, 肖中军, 杨国强. 2011. 豫西夜长坪钼矿床辉钼矿铼-锇同位素年龄及地质意义. 矿床地质, 30(6): 1069-1074. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.06.007 |
聂政融, 王晓霞, 柯昌辉, 杨阳, 吕星球. 2015. 华北地块南缘花山、五丈山岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及成因. 地质通报, 34(8): 1502-1516. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.08.010 |
任富根, 李维明. 1996. 熊耳山-崤山地区金矿成矿地质条件和找矿综合评价模型. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
王晓霞, 王涛, 齐秋菊, 李舢. 2011. 秦岭晚中生代花岗岩时空分布、成因演变及构造意义. 岩石学报, 27(6): 1573-1593. |
王银喜, 顾连兴, 张遵忠, 吴昌志, 李惠民, 杨杰东. 2007. 东天山晚石炭世大石头群流纹岩Sr-Nd-Pb同位素地球化学研究. 岩石学报, 23(7): 1749-1755. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.07.020 |
王宗起, 闫臻, 王涛, 高联达, 闫全人, 陈隽璐, 李秋根, 姜春发, 刘平, 张英利, 谢春林, 向忠金. 2009. 秦岭造山带主要疑难地层时代研究的新进展. 地球学报, 30(5): 561-570. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2009.05.001 |
魏庆国, 姚军明, 赵太平, 孙亚莉, 李晶, 原振雷, 乔波. 2009. 东秦岭发现~1.9Ga钼矿床——河南龙门店钼矿床Re-Os定年. 岩石学报, 25(11): 2747-2751. |
武广, 陈毓川, 李宗彦, 杨鑫生, 刘军, 乔翠杰. 2013. 豫西银家沟硫铁多金属矿床Re-Os和40Ar-39Ar年龄及其地质意义. 矿床地质, 32(4): 810-822. |
向君峰, 裴荣富, 邢波, 王春毅, 田志恒, 陈晓丹, 叶会寿, 王浩琳. 2016. 南泥湖-三道庄钼(钨)矿床中矽卡岩的形成过程及其与钼钨矿化的关系. 中国地质, 43(6): 2131-2153. |
谢桂青, 毛景文, 李瑞玲, 叶会寿, 张毅星, 万渝生, 李厚民, 高建京, 郑熔芬. 2007. 东秦岭宝丰盆地大营组火山岩SHRIMP定年及其意义. 岩石学报, 23(10): 2387-2396. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.007 |
晏国龙, 王佐满, 李永全, 傅渊辉, 丁高明. 2012. 河南夜长坪钼矿辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及地质意义. 矿产勘查, 3(2): 184-193. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2012.02.010 |
叶会寿. 2006.华北陆块南缘中生代构造演化与铅锌银成矿作用.博士学位论文.北京: 中国地质科学院
|
张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 肖庆辉. 2001.秦岭造山带与大陆动力学.北京:科学出版社, 1-729
|
赵海杰, 叶会寿, 李超. 2013. 陕西洛南县石家湾钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及地质意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 32(1): 90-98. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.01.007 |
周红升, 马昌前, 张超, 陈玲, 张金阳, 佘振兵. 2008. 华北克拉通南缘泌阳春水燕山期铝质A型花岗岩类:年代学、地球化学及其启示. 岩石学报, 24(1): 49-64. |
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35


