镁铁-超镁铁岩中的角闪石成分特征记录了岩浆演化的物理化学条件等重要信息(Hammarstrom and Zen, 1986; 陈光远等, 1988; Ernst and Liu, 1998; King et al., 1999; Ridolfi et al., 2010; Molina et al., 2015),其中的角闪石通常有两种成因:(1)岩浆成因,由堆晶矿物固化最后阶段间隙中的富集熔体结晶而成(Coogan et al., 2001);(2)热液成因,由岩浆矿物与后期流体反应形成(Gillis and Meyer, 2001)。岩浆成因角闪石的成分受温度、压力以及氧逸度控制(Ridolfi et al., 2010),因此通过对该类角闪石的研究可以获得岩体形成时的温度、压力和氧逸度等方面的信息(吕林素等, 2012; 栾燕等, 2014; 王坤明等, 2016)。夏日哈木镁铁-超镁铁岩含有超大型岩浆铜镍硫化物矿床(李世金等, 2012; Li et al., 2015),矿体主要赋存在橄榄方辉岩和斜方辉石岩中(Song et al., 2016)。虽然前人对赋矿岩体的形成时代、母岩浆特征以及可能的成矿机制进行过讨论(李世金等, 2012; 王冠等, 2014a; Li et al., 2015; 姜常义等, 2015; Song et al., 2016),但含矿岩体形成的温度、压力和氧逸度条件仍不清楚,制约了对成矿机制的深入探讨。本文将对含长橄榄方辉岩中的角闪石产状和化学成分进行研究,进而探讨含长橄榄方辉岩形成的温度、压力和氧逸度条件,为夏日哈木铜镍矿的成因提供新的矿物学依据。
1 区域地质背景东昆仑造山带位于青藏高原的东北部,北部以柴达木盆地南缘断裂为界与柴达木盆地分隔,南邻布青山-阿尼玛卿构造混杂岩带及巴颜喀拉造山带,东部大致以温泉断裂与秦岭相接(李荣社等, 2007)。东昆仑造山带以昆中和昆南两条缝合带为界分为3个地体单元,从北到南依次为东昆北地体、东昆南地体和巴颜喀拉地体(图 1)(姜春发等, 1992; 许志琴等, 2006)。东昆仑造山带经历了早古生代和晚古生代-早中生代两个不同构造旋回的演化过程,侵入岩和火山岩分布广泛(莫宣学等, 2007)。已有多位学者阐述了东昆仑造山带多旋回、多板块、多期次拼贴的构造演化历史(姜春发等, 1992; 朱云海等, 1999; 边千韬等, 2002; 许志琴等, 2006),早古生代的地质体在后期经历了海西期和印支期强烈的构造变形叠加,发生急剧肢解和位移(Pan et al., 1996; 许志琴等, 2006)。东昆仑造山带东段出露早古生代镁铁-超镁铁质杂岩体,多数被认为属于蛇绿岩的残片(Yang et al., 1996; Bian et al., 2004; 谌宏伟等, 2006; 冯建赟等, 2010; 祁晓鹏等, 2016; Li et al., 2018),部分为与洋壳俯冲有关的镁铁质岩石(任军虎等, 2009; 刘彬等, 2013; 刘战庆等, 2011),还有部分与碰撞后伸展背景有关的镁铁质岩石(刘彬等, 2012; Xiong et al., 2014)。与铜镍矿有关的镁铁-超镁铁质岩体主要出露在夏日哈木(李世金等, 2012; 王冠等, 2014a; 姜常义等, 2015; 张照伟等, 2015; Li et al., 2015; Song et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2017, 2018a; 汤庆艳等, 2017)、冰沟南(闫佳铭等, 2016)、阿克楚克塞和石头坑德(Zhang et al., 2018b)。

|
图 1 东昆仑造山带构造格架简图(据张建新等,2015) CEKF-东昆中断裂; NKT-昆北地体; SKT-昆南地体; SEKF-东昆南断裂.锆石U-Pb年代学数据:(1)辉长岩,祁晓鹏等,2016;(2)辉长岩,Yang et al., 1996;(3)辉长岩,Bian et al., 2004;(4)辉长岩,冯建赟等,2010;(5)辉长岩,谌宏伟等,2006;(6)辉绿岩,任军虎等, 2009, ;(7)角闪辉绿岩,刘彬等,2013;(8)辉长岩,刘战庆等,2011;(9)变质辉长岩,Li et al., 2019;(10)辉长岩,Xiong et al., 2014;(11)辉长岩,闫佳铭等,2016 Fig. 1 Tectonic framework of the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt (after Zhang et al., 2015) CEKF-Central Eastern Kunlun Fault; NKT-North Kunlun Terrane; SKT-South Kunlun Terrane; SEKF-South Eastern Kunlun Fault. Zircon U-Pb age data: (1) gabbro, Qi et al., 2016; (2) gabbro, Yang et al., 1996; (3) gabbro, Bian et al., 2004; (4) gabbro, Feng et al., 2010; (5) gabbro, Chen et al., 2006; (6) diabase, Ren et al., 2009; (7) hornblende diabase, Liu et al., 2013; (8) gabbro, Liu et al., 2011; (9) metagabbro, Li et al., 2019; (10) gabbro, Xiong et al., 2014; (11) gabbro, Yan et al., 2016 |
东昆北地体以大面积出露中元古代变质基底金水口群(Liu et al., 2005; He et al., 2016)和加里东期-印支期的侵入岩为特征。金水口群主要为一套高角闪岩相-麻粒岩相-榴辉岩相的深变质岩系,以发育变形强烈的斜长角闪岩-片麻岩-大理岩为主,后期经历了新元古代和早古生代变质热事件(张建新等, 2003; Liu et al., 2005; 李怀坤等, 2006; Meng et al., 2013; 祁生胜等, 2014; 孟繁聪等, 2015; He et al., 2016; Song et al., 2018; 范亚洲等, 2018)。该区还分布大量加里东期-印支期的侵入岩,其中加里东期侵入岩主要出露泥盆纪花岗岩、少量的闪长岩和辉长岩,印支期侵入岩主要出露晚二叠世-三叠世花岗岩、较多的基性岩体及基性岩墙群。
2 矿区地质概况夏日哈木位于青海省格尔木市以西约150km,大地构造位置上隶属于东昆北地体(图 1)。区内以中元古代金水口岩群为主(图 2),被新元古代花岗片麻岩(920~915Ma)侵入(王冠等, 2016),并整体经历了早古生代榴辉岩相变质作用,榴辉岩代表了深俯冲的陆壳(祁生胜等, 2014; 范亚洲等, 2018)。区内岩浆活动强烈,镁铁-超镁铁岩侵位于金水口群片麻岩和大理岩中,主要划分为4个岩体(图 2),其中Ⅰ号岩体为主要的含矿岩体,Ⅱ号岩体仅见零星矿化,Ⅲ号岩体和Ⅳ号岩体为不含矿的岩体。镁铁-超镁铁岩形成时代为晚志留-早泥盆纪(表 1),其中辉长岩形成时代439~423Ma,辉石岩形成时代~410Ma。Ⅰ号岩体被中泥盆世闪长玢岩(382Ma)侵入破坏(奥琮等, 2014)。矿区北侧为早泥盆世(391Ma)正长花岗岩(王冠等, 2013),区内还出现少量印支期(243Ma)闪长岩(王冠等, 2014b)。Ⅰ号岩体内部岩性复杂,大部分为渐变过渡关系。与矿化有关的岩性包括方辉橄榄岩、橄榄方辉岩、斜方辉石岩,橄榄方辉岩和斜方辉石岩是主要的含矿岩性,其中橄榄方辉岩与围岩大理岩接触(图 3a),含矿斜方辉石岩具有海绵陨铁结构(图 3b)。

|
图 2 夏日哈木镁铁-超镁铁质岩体地质简图(据王冠等,2014a) 锆石U-Pb年代学数据:(1)王冠等,2013;(2)奥琮等,2014; (3)王冠等,2014b Fig. 2 Sketch geological map of the Xiarihamu mafic-ultramafic intrusion (after Wang et al., 2014a) Zircon U-Pb age data: (1)Wang et al., 2013; (2)Ao et al., 2014; (3)Wang et al., 2014b |
|
|
表 1 夏日哈木镁铁-超镁铁岩年代学结果 Table 1 Published zircon U-Pb age of Xiarihamu mafic-ultramafic intrusion |

|
图 3 夏日哈木Ⅰ号岩体接触带产状及含矿岩心照片 (a)Ⅰ号岩体超基性岩与大理岩接触带; (b)含矿斜方辉石岩具有海绵陨铁结构 Fig. 3 Outcrop and core sample of the Xiarihamu mafic-ultramafic intrusion (a) contact zone between ultramafic rocks and marble in Xiarihamu No.1 intrusion; (b) ore-bearing orthopyroxenites show sideronitic texture |
含长斜方辉石岩样品主要由堆晶相斜方辉石和填隙相斜长石及硫化物组成(图 4a),斜长石和硫化物结晶都晚于斜方辉石。含长橄榄方辉岩主要由橄榄石(20%)、斜方辉石(55%)、角闪石(10%)、斜长石(10%)以及少量硫化物组成(图 4b)。样品中可见斜方辉石包裹橄榄石,表明橄榄石结晶早于斜方辉石(图 4c)。斜长石与角闪石充填在斜方辉石颗粒之间,且两者接触界线较为平直(图 4d),表明两者可能同时结晶,但都晚于斜方辉石。硫化物与角闪石的结晶顺序不易观察,但角闪石与斜长石基本同时结晶,推测角闪石和硫化物也是同时结晶的产物。在单偏光下角闪石核部呈较深的棕色,边部为淡黄色,由核部到边部多色性呈渐变过渡(图 4d, e),暗示其成分存在差异;角闪石还与金云母共生(图 4f)。

|
图 4 夏日哈木岩体含长斜方辉石岩(a, 样品K15-4-6.1)和含长橄榄方辉岩(b-f, 样品K13-14-1.1)显微照片 (a)斜长石和硫化物充填在斜方辉石颗粒之间(正交偏光);(b)斜长石和角闪石充填在斜方辉石颗粒间(单偏光);(c)橄榄石被斜方辉石包裹(正交偏光);(d)角闪石呈填隙状,包裹斜方辉石(单偏光);(e)角闪石核边多色性具有差异(单偏光);(f)角闪石与金云母共生(单偏光). Ol-橄榄石;Opx-斜方辉石;Ti-prg-富钛韭闪石;Krs-钛闪石;Phl-金云母;Pl-斜长石; Sul-硫化物 Fig. 4 Micrographs of the Pl-orthopyroxenite (a, Sample K15-4-6.1) and the Pl-bearing Ol-orthopyroxenite (b-f, Sample K13-14-1.1) from the Xiarihamu intrusion (a) interstitial plagioclase and sulfide between orthopyroxenes (CPL); (b) interstitial plagioclase and amphibole between orthopyroxenes (PPL); (c) poikilitic olivine with pyroxene (CPL); (d) poikilitic orthopyroxene with interstitial amphibole (PPL); (e) different core-rim pleochroism of interstitial amphibole (PPL); (f) Ti-rich pargasite and phlogopite assemblage (PPL). Ol-olivine; Opx-orthopyroxene; Ti-prg-Ti-rich pargasite; Krs-kaersutite; Phl-phlogopite; Pl-plagioclase; Sul-sulfide |
样品采自夏日哈木矿区地表,选取较为新鲜的样品制备成0.03mm厚的光薄片,对角闪石进行电子探针分析测试。电子探针分析测试在中国地质科学院地质研究所电子探针(EPMA)实验室完成,实验仪器型号为JXA-8100,工作加速电压为15kV,电流为2.00×10-8A,束斑直径为5μm,标样采用天然矿物或合成金属国家标准,分析精度为0.01。实验数据经过ZAF修正。
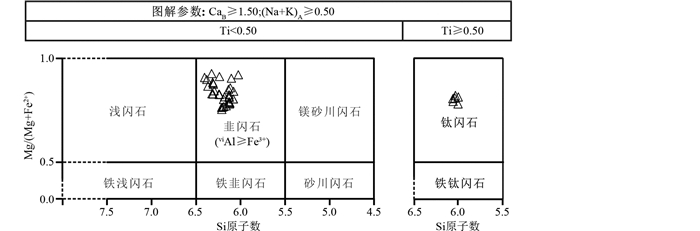
5 分析结果对含长橄榄方辉岩中的59个角闪石测试结果基于标准分子式A0-1B2C5T8O22(OH)2计算得到角闪石的阳离子数(表 2)。含长橄榄方辉岩中的角闪石阳离子特征为:Si=5.99~6.40,Ti=0.07~0.61,CaB=1.60~1.86,(Na+K)A=0.51~0.86,Mg/(Mg+Fe2+)=0.78~0.94。根据国际矿物协会(IMA)角闪石委员会提出的分类命名方案(Leake et al., 1997),含长橄榄方辉岩中的角闪石属于钙角闪石(CaB≥1.5,(Na+K)A≥0.5),按照钙角闪石的进一步分类命名原则(刘显凡等, 2015),其种属分别属于韭闪石和钛闪石(图 5),韭闪石中有41个测点属于富钛韭闪石(0.25≤Ti≤0.49)。钙角闪石总体显示贫镁(14.46%~16.75%)、贫硅(40.97%~44.63%)、富铝(12.56%~13.95%)和富钾、钠(K2O=0.72%~1.45%,Na2O=2.48%~3.23%)特征。其中部分钙角闪石核边具有成分差异,其中核部TiO2、Al2O3、MgO含量较高,向边部含量先降低后升高,SiO2含量则与其相反。
|
|
表 2 夏日哈木含长橄榄方辉岩中代表性角闪石的矿物化学成分(wt%) Table 2 Chemical compositions of representative amphiboles in Pl-bearing Ol-othorpyroxenite from Xiarihamu mafic-ultramaic intrusions (wt%) |
|
图 5 夏日哈木含长橄榄方辉岩中的角闪石分类图(据Leake et al., 1997) Fig. 5 Discrimination diagram for amphiboles in Pl-bearing Ol-pyroxenite of the Xiarihamu mafic-ultramafic intrusion (after Leake et al., 1997) |
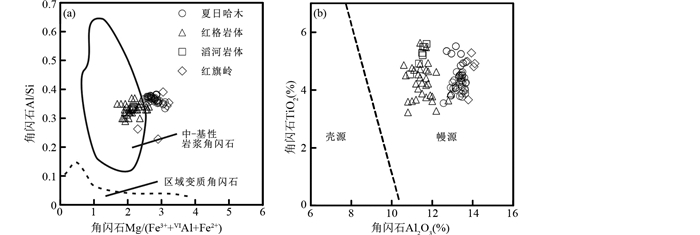
含长橄榄方辉岩中的角闪石呈填隙相,与流体中结晶出来的矿物组合具有较大区别。在岩浆演化晚期,很多矿物可以直接从流体中结晶形成,形成流体晶组合,流体结晶的矿物之间边界平直、没有相互交代穿插的现象,同时矿物组合不符合熔体结晶的原理,如内蒙文圪乞铂族矿床、金川铜镍矿床等(Su and Lesher, 2012; 苏尚国等, 2014)。本区含长橄榄方辉岩中角闪石和斜长石呈填隙相,包裹斜方辉石等早期结晶矿物,且矿物之间的关系并不符合流体晶组合的特征,暗示其为熔体中结晶的产物。角闪石成分显示Al2O3含量较高(12.56%~13.95%),Si/(Si+Ti+Al)=0.676~0.735,具有幔源岩浆角闪石特征(薛君治等, 1986),与红旗岭含铜镍矿岩体、红格岩体以及滔河岩体中的岩浆成因角闪石成分相似,与区域变质角闪石特征具有明显差别(图 6),结合钙质角闪石的Al2O3-TiO2分类图解(图 6b)可知,其属于幔源岩浆角闪石(姜常义和安三元, 1984),表明夏日哈木岩体含长橄榄方辉岩中的角闪石是与幔源岩浆作用有关的原生矿物。
|
图 6 夏日哈木岩体角闪石Mg/(Fe3++ⅥAl+Fe2+)-Al/Si图解(a, 据姜常义和安三元, 1984)和TiO2-Al2O3图解(b,据薛君治等, 1986) 数据来源:红旗岭(吕林素等, 2012);红格岩体(栾燕等, 2014);滔河岩体(王坤明等, 2016) Fig. 6 Discrimination diagram of Mg/(Fe3++ⅥAl+Fe2+) vs. Al/Si (a, after Jiang and An, 1984) and TiO2 vs. Al2O3 (b, after Xue et al., 1986) for amphiboles in the Xiarihamu mafic-ultramafic intrusion Data source: Hongqiling (Lv et al., 2012); Hongge intrusion (Luan et al., 2014); Taohe intrusion (Wang et al., 2016) |
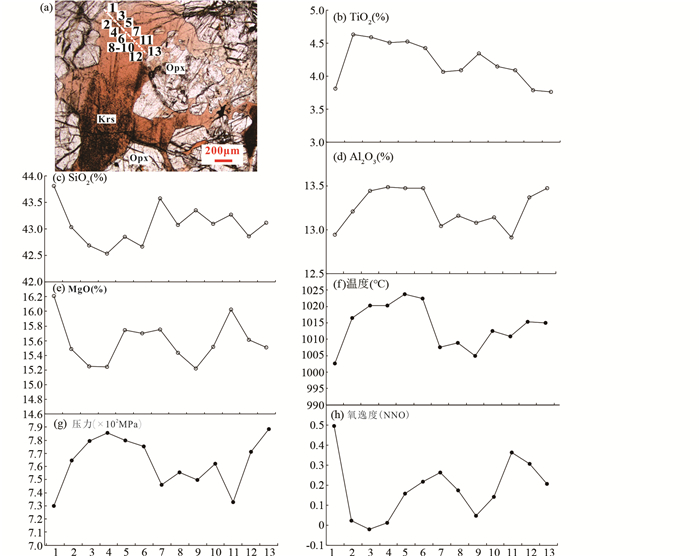
岩浆结晶角闪石的形成主要受温度、压力、及氧逸度等条件影响(Holloway and Burnham, 1972; Brown, 1977; Hammarstrom and Zen, 1986; Adam and Green, 1994; Ernst and Liu, 1998; King et al., 1999)。对含长橄榄方辉岩中的角闪石成分进行测定,结果显示其核部具有较高的TiO2、MgO和Al2O3含量,以及较低的SiO2含量,边部与核部成分具有明显差别(图 7a-e)。实验岩石学表明,钙质角闪石Ti含量随温度升高而增加(Hammarstrom and Zen, 1986),而SiO2含量随压力升高而降低(Adam and Green, 1994; Ernst and Liu, 1998; King et al., 1999),同时Ti含量会随着氧逸度升高而降低(King et al., 1999; Niida and Green, 1999)。深成岩体中结晶分异的环带角闪石具有由核部向边部TiO2含量降低,MgO和SiO2含量升高的规律,反映了矿物结晶时降温降压的过程(Hammarstrom and Zen, 1986; 刘飞等, 2013)。本区角闪石的成分变化总体上与降温降压结晶的过程一致,但内部存在TiO2、MgO和Al2O3含量升高的趋势(图 7),其变化并不符合降温降压的规律,因此该角闪石的形成并不是简单的岩浆降温降压冷却结晶过程,可能在结晶过程中受到了围岩同化混染以及同源岩浆注入等作用的影响。
|
图 7 夏日哈木角闪石的显微照片及其电子探针线扫描分析主要化学成分及相关参数变化曲线 (a)角闪石的显微照片及电子探针扫描剖面; TiO2 (b)、SiO2 (c)、Al2O3 (d)、MgO (e)、温度(f)、压力(g)和氧逸度(h)变化曲线,横坐标为测点号 Fig. 7 The micrograph of the amphibole in Xiarihamu mafic-ultramafic intrusion and the variation curves of the major chemical compositions and calculated index along the measured section by EPMA (a) micrograph of the amphibole and measured section; the variation curves of TiO2 (b), SiO2 (c), Al2O3 (d), MgO (e), pressure (f), temperature (g) and oxygen fugacity (h), the abscissa is the measuring point number |
利用Ridolfi et al. (2010)提出的基性-超基性岩中的岩浆成因角闪石的Si*温度计进行计算,计算得到角闪石的结晶温度为980~1040℃,其中钛闪石的平均温度(1030℃)略高于韭闪石的平均温度(990℃)。Li et al. (2015)利用MELTS模拟了夏日哈木岩体的形成过程,提出最早结晶的橄榄石(Fo=88)温度约为1270℃,当橄榄石Fo值降低到85时,结晶温度为1228℃,含长橄榄方辉岩中的被斜方辉石包裹的橄榄石Fo值约为84,表明其结晶温度可能稍低于1230℃;斜方辉石岩中的斜方辉石的结晶温度为1200~1250℃(杜伟, 2015)。角闪石温度计算结果低于橄榄石和斜方辉石,与角闪石结晶晚于橄榄石和斜方辉石的岩相观察一致。实验表明角闪石中Al含量与压力呈正相关关系(Holloway and Burnham, 1972; Adam and Green, 1994; Ernst and Liu, 1998; King et al., 1999)。角闪石具有高Na(0.69~0.91,平均值0.76),高Al(1.95~2.48,平均值2.25)特征,与低压角闪石Al<2.0具有明显的区别,反映高压成因的特征(樊祺诚等, 1992)。依据角闪石全铝压力计算公式(Schmidt, 1992),计算得到角闪石结晶压力范围为:700~840MPa。姜常义等(2015)报道了堆晶相单斜辉石与填隙相的角闪石和少量单斜辉石共存的现象,表明角闪石晚于或与单斜辉石同时结晶。Zhang et al. (2018a)利用单斜辉石Na2O含量计算获得其结晶压力为500~1000MPa,与岩相观察结果一致。具有成分差异的角闪石核部平均温度1021℃,平均压力777MPa,边部平均温度1009℃,平均压力754MPa,反映矿物结晶过程中总体具有降温降压的规律(图 7f, g)。
角闪石成分的差异还可能受到氧逸度变化的影响。氧逸度通过影响流体相的赋存状态间接地影响含挥发分条件下的上地幔部分熔融作用和地幔交代作用(O'Neill and Wall, 1987)。利用角闪石化学式计算矿物结晶氧逸度的公式和校正公式(Ridolfi et al., 2008, 2010),计算得到角闪石结晶时岩浆的氧逸度变化范围为NNO-0.54~NNO+1.36(图 8),韭闪石氧逸度变化范围为NNO+0.27~NNO+1.36,钛闪石氧逸度范围为NNO-0.54~NNO-0.02。角闪石氧逸度具有由核部向边部先升高后降低的规律(图 7h),其中边部氧逸度变化范围NNO+0.04~NNO+0.49(平均值NNO+0.25),核部氧逸度变化范围NNO-0.02~NNO+0.21(平均值NNO+0.08)。同时夏日哈木钛闪石氧逸度与Li et al.(2015)利用二辉橄榄岩中的橄榄石和硫化物中Ni含量计算的氧逸度FMQ+0.3~FMQ+1(相当于NNO-0.4~NNO+0.3)接近,而与岛弧玄武岩和阿拉斯加侵入体所代表的岩浆氧逸度(FMQ=+2, Ballhaus et al., 1991)明显不同。

|
图 8 夏日哈木镁铁-超镁铁岩角闪石lgfO2-T曲线图 实线代表氧缓冲剂(Eugster and Wones, 1962),虚线代表夏日哈木岩体角闪石结晶氧逸度.QFI=quartz+fayalite+iron; WI=wüstite+iron; MW=magnetite+wüstite; QFM=quartz+fayalite+magnetite; NNO=nickel+nickel oxide; HM=hematite+magnetite Fig. 8 Plots of lgfO2 vs. T diagram of the amphibole from Xiarihamu mafic-ultramafic intrusion The solid line represents oxygen buffer (Eugster and Wones, 1962), and the dotted line represents amphibole crystallization oxygen fugacity |
角闪石的成分特征对结晶分异、同化混染等过程较全岩成分更加敏感,所以矿物成分的变化特征能够准确地反映岩体的形成过程。结晶分异作用贯穿岩浆演化的始终,而同化混染和新的岩浆注入则是阶段性的,这些过程可以反映在矿物成分上(苏本勋等, 2009)。夏日哈木岩体中的角闪石成分反映了矿物结晶时普遍的降温降压过程,同时TiO2、MgO和Al2O3含量的变化则对岩浆演化过程中的阶段性变化有所反映。夏日哈木岩体以结晶大量斜方辉石为特征,典型的阿拉斯加型岩体以出现大量角闪石而少有斜方辉石的结晶,表明其原始岩浆富水的特征(Irvine, 1974; Burg et al., 2009; Eyuboglu et al., 2010)。原生角闪石与金云母等矿物的出现(图 4c),暗示其岩浆演化过程中局部可能存在流体组分的富集(王冠等, 2014a; 丰成友等, 2016)。
角闪石的氧逸度变化反映了岩浆氧逸度先升高后降低的变化过程,角闪石核部成分特征反映了成矿母岩浆氧逸度较低,但都高于FMQ(图 8)。在氧逸度较低(<FMQ)情况下需要25%以上的部分熔融才能产生有利于形成硫化物矿床的岩浆(Keays, 1995);而当氧逸度>FMQ时,则仅需较低程度部分熔融即可将源区硫化物耗尽,并将亲硫元素(PGE、Ni、Cu等)转移到岩浆当中(Lee et al., 2012)。夏日哈木岩体由地幔约15%部分熔融形成(姜常义等, 2015),需要较高的氧逸度才能使成矿元素在母岩浆中富集。通过角闪石的氧逸度计算,夏日哈木岩体的母岩浆氧逸度>FMQ有利于形成铜镍硫化物矿床。
角闪石氧逸度的变化反映岩浆氧逸度有逐渐升高的过程(图 7h)。影响岩浆氧逸度的主要因素包括岩浆去气作用、溶解水的加入、分离结晶作用以及同化混染作用(柏忠杰等, 2019)。汤庆艳等(2017)报道了夏日哈木不同岩性中辉石流体挥发分的组成特征,认为其H2O含量较低而H2含量较高的原因与岩浆上升过程中的脱气过程有关。Brounce et al.(2017)提出岩浆氧逸度会随着H2O含量降低而降低,与角闪石反映的氧逸度先升高的过程不一致,因此去气作用可能并不是其氧逸度变化的主要原因。溶解水的加入造成氧逸度的变化范围不大(小于0.5log单位),早期镁铁质矿物(橄榄石、辉石)的分离结晶的氧逸度的改变很小(赖绍聪, 1994; 柏中杰等, 2019)。玄武质岩浆上升过程中同化混染作用可以显著改变岩浆中的氧逸度(Thakurta et al., 2008),母岩浆同化混染碳酸盐围岩能够导致氧逸度升高(Ganino et al., 2008, 2013)。夏日哈木岩体形成过程中经历了广泛的同化混染作用(王冠等, 2014a; Li et al., 2015; 姜常义等, 2015)。汤庆艳等(2017)研究认为夏日哈木矿床的形成,受到来源于地幔、地壳端元及有机质热成因组分混合的流体挥发分的影响,其中壳源组分可能来自岩浆房中围岩的混染。由于含长橄榄方辉岩样品采在岩体与围岩大理岩接触带附近(图 3a),岩石结晶位置可能位于岩浆上涌的前锋带,推测岩浆同化混染组分很可能来自于围岩金水口群大理岩(Li et al., 2015; 姜常义等, 2015; Zhang et al., 2017)。
同源岩浆注入是铜镍硫化物成矿的关键因素之一(Naldrett, 2004)。夏日哈木岩体中出现大量的富镁矿物,形成大量的斜方辉石岩(Song et al., 2016),表明岩浆极度富镁。通常情况下,由于早期富镁矿物的结晶,岩浆会向贫镁方向演化,同时地壳混染作用也不会导致岩浆富镁,因此岩浆中镁含量增高,说明有新岩浆的补充(吕林素等, 2012)。同时夏日哈木岩体橄榄石Fo-Ni含量(Li et al., 2015)、PGE含量与同位素之间的关系(Zhang et al., 2017)以及流体挥发份的研究(汤庆艳等, 2017)都表明存在多阶段的岩浆注入过程。研究表明夏日哈木岩体的母岩浆性质为高镁玄武质岩浆(姜常义等, 2015; Zhang et al., 2018a),同时角闪石MgO含量和Mg#值从核部到边部过程中有突然升高的趋势(图 7e),很可能受到了同源富镁岩浆注入作用的影响。角闪石幔部到边部的成分变化反映了岩浆氧逸度降低的过程。一般来说,磁铁矿的结晶可以显著降低岩浆氧逸度(Morse, 2015),但在夏日哈木各类岩石中未见到岩浆阶段形成的磁铁矿,因此氧逸度降低与磁铁矿分离结晶可能没有关系。由于母岩浆具有低氧逸度特征,因此角闪石氧逸度下降的趋势可能也受到同源岩浆注入作用的影响。当氧逸度<FMQ和>FMQ+2条件下,S分别以硫化物(S2-)和硫酸盐(S6+)的形式存在(Jugo et al., 2010),S6+/S2-比值会随着氧逸度升高而增大,由于S6+溶解度较S2-高一个数量级,因此成矿作用多是在由氧化条件向还原条件转变时发生(Naldrett, 1999; Li et al., 2001)。同源岩浆注入可以降低岩浆氧逸度,使岩浆由氧化条件向还原条件转变,降低岩浆中S的溶解度,促进硫化物的熔离,形成夏日哈木铜镍硫化物矿床。
7 结论(1) 含长橄榄方辉岩中出现岩浆成因的韭闪石和钛闪石,其结晶温度为980~1040℃,压力为700~840MPa,结晶时的氧逸度变化范围为NNO=-0.54~+1.36,反映角闪石结晶时岩浆降温降压的过程。
(2) 角闪石成分特征反映岩浆氧逸度先升高后降低的过程:核部具有低氧逸度特征,表明母岩浆有利于成矿物质的富集;早期氧逸度升高可能受到围岩金水口群大理岩同化混染作用影响;后期氧逸度降低可能与同源高镁玄武质岩浆注入有关,新的岩浆注入促进了硫化物的熔离成矿。
致谢 贾丽辉、冯惠彬、刘强、田广阔在野外工作中给予了协助;中国地质科学院地质研究所探针实验室在测试以及数据处理等方面给予了帮助;曾令森、苏尚国和熊发挥对论文初稿提出了宝贵的修改意见;在此一并表示衷心感谢!
Adam J and Green TH. 1994. The effects of pressure and temperature on the partitioning of Ti, Sr and REE between amphibole, clinopyroxene and basanitic melts. Chemical Geology, 117(1-4): 219-233 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(94)90129-5 |
Ao C, Sun FY, Li BL, Li SJ and Wang G. 2014. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb dating and geological significance of diorite porphyrite in Xiarihamu deposit, eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Qinghai. Northwestern Geology, 47(1): 96-106 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Bai ZJ, Zhong H and Zhu WG. 2019. Redox state of mantle derived-magma and constraints on the genesis of magmatic deposits. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(1): 204-214 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.01.16 |
Ballahaus C, Berry RF and Green DH. 1991. High pressure experimental calibration of the olivine-orthopyroxene-spinel oxygen geobarometer:Implications for the oxidation state of the upper mantle. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 127(1): 27-40 |
Bian QT, Zhao DS, Ye ZR, Chang CF, Luo XQ and Gao SL. 2002. A preliminary study of the Kunlun-Qilian-Qinling Suture System. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 23(6): 501-508 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Bian QT, Li DH, Pospelov I, Yin LM, Li HS, Zhao DS, Chang CF, Luo XQ, Gao SL, Astrakhantsev O and Chamov N. 2004. Age, geochemistry and tectonic setting of Buqingshan ophiolites, North Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 23(4): 577-596 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.09.003 |
Brounce M, Stolper E and Eiler J. 2017. Redox variations in Mauna Kea lavas, the oxygen fugacity of the Hawaiian plume, and the role of valcanic gases in Earth's oxygenation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114(34): 8997-9002 DOI:10.1073/pnas.1619527114 |
Brown EH. 1977. The crossite content of Ca-amphibole as a guide to pressure of metamorphism. Journal of Petrology, 18: 53-72 DOI:10.1093/petrology/18.1.53 |
Burg JP, Bodinier JL, Gerya T, Bedini RM, Boudier F, Dautria JM, Prikhodko V, Efimov A, Pupier E and Balanec JL. 2009. Translithospheric mantle diapirism:Geological evidence and numerical modelling of the Kondyor zoned ultramafic complex (Russian Far-East). Journal of Petrology, 50(2): 289-321 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egn083 |
Chen GY, Sun DS and Yin HA. 1988. Genetic Mineralogy and Prospecting Mineralogy. 2nd Edition. Chongqing: Chongqing Press, 555-647 (in Chinese)
|
Chen HW, Luo ZH, Mo XX, Zhang XT, Wang J and Wang BZ. 2006. SHRIMP ages of Kayakedengtage complex in the East Kunlun Mountains and their geological implications. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 25(1): 25-32 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Coogan LA, Wilson RN, Gillis KM and Macleod CJ. 2001. Near-solidus evolution of oceanic gabbros:Insights from amphibole geochemistry. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(23): 4339-4357 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00714-1 |
Du W. 2015. Study on the mafic-ultramafic rocks of Xiarihamu nickel mining area in East Kunlun. Master Degree Thesis. Xi'an: ChangAn University, 1-106 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Ernst WG and Liu J. 1998. Experimental phase-equilibrium study of Al-and Ti-contents of calcic amphibole in MORB:A semiquantitative thermobarometer. American Mineralogist, 83(9-10): 952-969 DOI:10.2138/am-1998-9-1004 |
Eugster HP and Wones DR. 1962. Stability relations of the ferruginous biotite, annite. Journal of Petrology, 3(1): 82-125 DOI:10.1093/petrology/3.1.82 |
Eyuboglu Y, Dilek Y, Bozkurt E, Bektas O, Rojay B and Sen C. 2010. Structure and geochemistry of an Alaskan-type ultramafic-mafic complex in the Eastern Pontides, NE Turkey. Gondwana Research, 18(1): 230-252 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.01.008 |
Fan QC, Liu RX and Ma BL. 1984. Upper-mantle amphiboles from China and their genetic implications. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 12(4): 353-358 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Fan YZ, Meng FC and Duan XP. 2018. The protoliths of the Xiarihamu eclogites from the western part of East Kunlun and continent/arc-continent collision. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(3): 482-502 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Feng CY, Zhao YM, Li DX, Liu JN and Liu CZ. 2016. Mineralogical Characteristics of the Xiarihamu nickel deposit in the Qiman Tagh Mountain, East Kunlun, China. Geological Review, 62(1): 215-228 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Feng JY, Pei XZ, Yu SL, Ding SP, Li RB, Sun Y, Zhang YF, Li ZC, Chen YX, Zhang XF and Chen GC. 2010. The discovery of the mafic-ultramafic melange in Kekesha area of Dulan County, East Kunlun region, and its LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age. Geology in China, 37(1): 28-38 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ganino C, Arndt NT, Zhou MF, Gaillard F and Chauvel C. 2008. Interaction of magma with sedimentary wall rock and magnetite ore genesis in the Panzhihua mafic intrusion, SW China. Mineralium Deposita, 43(6): 677-694 DOI:10.1007/s00126-008-0191-5 |
Ganino C, Harris C, Arndt NT, Prevec SA and Howarth GH. 2013. Assimilation of carbonate country rock by the parent magma of the Panzhihua Fe-Ti-V deposit (SW China):Evidence from stable isotopes. Geoscience Frontiers, 4(5): 547-554 DOI:10.1016/j.gsf.2012.12.006 |
Gillis KM and Meyer PS. 2001. Metasomatism of oceanic gabbros by late stage melts and hydrothermal fluids:Evidence from the rare earth element composition of amphiboles. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2(3): 2000GC000087 |
Hammarstrom JM and Zen EA. 1986. Aluminum in hornblende:An empirical igneous geobarometer. American Mineralogist, 71(11-12): 1297-1313 |
He DF, Dong YP, Liu XM, Yang Z, Sun SS, Cheng B and Li W. 2016. Tectono-thermal events in East Kunlun, northern Tibetan Plateau:Evidence from zircon U-Pb geochronology. Gondwana Research, 30: 179-190 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.08.002 |
Holloway Jr and Burnham CW. 1972. Melting relations of basalt with equilibrium water pressure less than total pressure. Journal of Petrology, 13(1): 1-29 DOI:10.1093/petrology/13.1.1 |
Irvine TN. 1974. Petrology of the Duke Island Ultramafic Complex Southeastern Alaska. Boulder:Geological Society of American, 138: 240 |
Jiang CF, Yang JS, Feng BG, Zhu ZZ, Zhao M, Chai YC, Shi XD, Wang HD and Hu JQ. 1992. Opening-closing Tectonics of Kunlun Mountains. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-224 (in Chinese)
|
Jiang CY and An SY. 1984. On chemical characteristics of calcic amphiboles from igneous rocks and their petrogenesis significance. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, (3): 1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Jiang CY, Ling JL, Zhou W, Du W, Wang ZX, Fan YZ, Song YF and Song ZB. 2015. Petrogenesis of the Xiarihamu Ni-bearing layered mafic-ultramafic intrusion, East Kunlun:Implications for its extensional island arc environment. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(4): 1117-1136 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Jugo PJ, Wilke M and Botcharnikov RE. 2010. Sulfur K-edge XANES analysis of natural and synthetic basaltic glasses:Implicatons for S speciation and S content as function of oxygen fugacity. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(20): 5926-5938 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2010.07.022 |
Keays RR. 1995. The role of komatiitic and picritic magmatism and S-saturation in the formation of ore deposits. Lithos, 34(1-3): 1-18 DOI:10.1016/0024-4937(95)90003-9 |
King PL, Hervig RL, Holloway JR, Vennemann TW and Righter K. 1999. Oxy-substitution and dehydrogenation in mantle-derived amphibole megacrysts. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(21): 3635-3651 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00162-3 |
Lai SC. 1994. Influence of separation crystallization on oxygen fugacity of magma. Earth Science Frontiers, 1(Suppl.1): 12 (in Chinese) |
Leake BE, Woolley AR, Arps CES, Birch WD, Gilbert MC, Grice JD, Hawthorne FC, Kato A, Kisch HJ, Krivovichev VG, Linthout K, Laird J, Mandarino J, Maresch WV, Nickel EH, Rock NMS, Schumacher JCS, Smith DC, Stephenson NCN, Ungaretti L, Whittaker EJW and Guo YZ. 1997. Nomenclature of amphiboles:Report of the Subcommittee on Amphiboles of the International Mineralogical Association, Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names. The Canadian Mineralogist, 35(1): 219-246 |
Lee CTA, Luffi P, Chin EJ, Bouchet R, Dasgupta R, Morton DM, Le Roux V, Yin QZ and Jin D. 2012. Copper systematics in arc magmas and implications for crust-mantle differentiation. Science, 336(6077): 64-68 DOI:10.1126/science.1217313 |
Li CS, Naldrett AJ and Ripley EM. 2001. Critical factors for the formation of a nickel-copper deposit in an evolved magma system:lessons from a comparison of the pants lake and Voisey's Bay sulfide occurrences in Labrador, Canada. Mineralium Deposita, 36(1): 85-92 DOI:10.1007/s001260050288 |
Li CS, Zhang ZW, Li WY, Wang YL, Sun T and Ripley EM. 2015. Geochronology, petrology and Hf-S isotope geochemistry of the newly-discovered Xiarihamu magmatic Ni-Cu sulfide deposit in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau, western China. Lithos, 216-217: 224-240 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.01.003 |
Li HK, Lu SN, Xiang ZQ, Zhou HY, Guo H, Song B, Zheng JK and Gu Y. 2006. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon age of the granulite from the Qingshuiquan area, central eastern Kunlun Suture Zone. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(6): 311-321 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li RB, Pei XZ, Wei B, Li ZC, Pei L, Chen YX, Liu CJ, Cheng GC, Wang M and Feng K. 2019. Constraints of late Cambrian mafic rocks from the Qushi'ang ophiolite on a back-arc system in a continental margin, East Kunlun Orogen, western China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 169: 117-129 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.08.006 |
Li RS, Ji WH, Zhao ZM, Chen SJ, Meng Y, Yu PS and Pan XP. 2007. Progress in the study of the Early Paleozoic Kunlun orogenic belt. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(4): 373-382 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li SJ, Sun FY, Gao YW, Zhao JW, Li LS and Yang QA. 2012. The theoretical guidance and the practice of small intrusions forming large deposits:The enlightenment and significance for searching breakthrough of Cu-Ni sulfide deposit in Xiarihamu, East Kunlun, Qinghai. Northwestern Geology, 45(4): 185-191 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu B, Ma CQ, Zhang JY, Xiong FH, Huang J and Jiang HA. 2012. Petrogenesis of Early Devonian intrusive rocks in the east part of Eastern Kunlun Orogen and implication for Early Palaeozoic orogenic processes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(6): 1785-1807 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu B, Ma CQ, Jiang HA, Guo P, Zhang JY and Xiong FH. 2013. Early Paleozoic tectonic transition from ocean subduction to collisional orogeny in the Eastern Kunlun region:Evidence from Huxiaoqin mafic rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(6): 2093-2106 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu F, Su SG, Yu XY, Liang FH, Hu Y and Niu XL. 2013. Characteristics and petrogenesis of zoned amphiboles in Wengeqi mafic-ultramafic complex, Inner Mongolia. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(1): 206-222 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu XF, Wang L, Li H, Liu J, Zhao FF, Lu QX and Hu L. 2015. Systematic mineralogical classifications and nomenclatures of amphibole and pyroxene group minerals. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 35(1): 19-28 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu YJ, Genser J, Neubauer F, Jin W, Ge XH, Handler R and Takasu A. 2005. 40Ar/39Ar mineral ages from basement rocks in the Eastern Kunlun Mountains, NW China, and their tectonic implications. Tectonophysics, 398(3-4): 199-224 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2005.02.007 |
Liu ZQ, Pei XZ, Li RB, Li ZC, Zhang XF, Liu ZG, Chen GC, Chen YX, Ding SP and Guo JF. 2011. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology of the two suites of ophiolites at the Buqingshan area of the A'nyemaqen Orogenic Belt in the southern margin of East Kunlun and its tectonic implication. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(2): 185-194 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Luan Y, Song XY, Chen LM, Zheng WQ, Tian XL and Ran QY. 2014. Mineralogical features and petrogenetic significances of the hornblende and phlogopite of the Hongge layered intrusion, Sichuan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(5): 1457-1471 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Lü LS, Mao JW, Zhou ZH, Li HB, Zhang ZH and Wang YF. 2012. Mineral chemistry of ore-bearing ultramafic rocks from the Hongqiling No.1 and 7 instrusions in Jilin Province:Constraints on the magmatic processes and the metallogenesis of Ni-Cu sulfide deposits. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(1): 319-344 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Meng FC, Cui MH, Wu XK and Ren YF. 2013. Discovery of Early Paleozoic eclogite from the East Kunlun, western China and its tectonic significance. Gondwana Research, 23(2): 825-836 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.06.007 |
Meng FC, Cui MH, Jia LH, Ren YF and Feng HB. 2015. Paleozoic continental collision of the East Kunlun orogen:Evidence from protoliths of the eclogites. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(12): 3581-3594 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Mo XX, Luo ZH, Deng JF, Yu XH, Liu CD, Chen HW, Yuan WM and Liu YH. 2007. Granitoids and crustal growth in the East-Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13(3): 403-414 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Molina JF, Moreno JA, Castro A, Rodríguez C and Fershtater GB. 2015. Calcic amphibole thermobarometry in metamorphic and igneous rocks:New calibrations based on plagioclase/amphibole Al-Si partitioning and amphibole/liquid Mg partitioning. Lithos, 232: 286-305 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.027 |
Morse SA. 2015. Kiglapait intrusion, Labrador. In: Charlier B, Namur O, Latypov R and Tegner C (eds.). Layered Intrusions. Dordrecht: Springer, 589-648
|
Naldrett AJ. 1999. World-class Ni-Cu-PGE deposits:Key factors in their genesis. Mineralium Deposita, 34(3): 227-240 DOI:10.1007/s001260050200 |
Naldrett AJ. 2004. An overview of Ni-Cu mineralization with conclusion guide in exploration. International Geological Correlation Programme IGCP479 Short Course Notes, 154-164
|
Niida K and Green DH. 1999. Stability and chemical composition of pargasitic amphibole in MORB pyrolite under upper mantle conditions. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 135(1): 18-40 DOI:10.1007/s004100050495 |
O'Neill HSC and Wall VJ. 1987. The olivine-orthopyroxene-spinel oxygen geobarometer:The nickel precipitation curve, and the oxygen fugacity of the earth's upper mantle. Journal of Petrology, 28(6): 1169-1191 DOI:10.1093/petrology/28.6.1169 |
Pan YS, Zhou WM, Xu RM, Wang DA, Zhang YQ, Xie YW, Chen TE and Luo H. 1996. Geological characteristics and evolution of the Kunlun Mountains region during the Early Paleozoic. Science in China (Series D), 39(4): 337-347 |
Peng B, Sun FY, Li BL, Wang G, Li SJ, Zhao TF, Li L and Zhi YB. 2016. The geochemistry and geochronology of the Xiarihamu Ⅱ mafic-ultramafic complex, eastern Kunlun, Qinghai Province, China:Implications for the genesis of magmatic Ni-Cu sulfide deposits. Ore Geology Reviews, 73: 13-28 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.10.014 |
Qi SS, Song SG, Shi LC, Cai HJ and Hu JC. 2014. Discovery and its geological significance of Early Paleozoic eclogite in Xiarihamu-Suhaitu area, western part of the East Kunlun. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(11): 3345-3356 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Qi XP, Yang J, Fan XG, Cui JT, Cai ZF, Zeng XW, Wei W, Qu XX and Zhai LM. 2016. Age, geochemical characteristics and tectonic significance of Changshishan ophiolite in central East Kunlun tectonic mélange belt along the east section of East Kunlun Mountains. Geology in China, 43(3): 797-816 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ren JH, Liu YQ, Feng Q, Han WZ, Gao H and Zhou DW. 2009. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon dating and geochemical characteristics of diabase-dykes from the Qingshuiquan area, eastern Kunlun orogenic belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(5): 1135-1145 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ridolfi F, Puerini M, Renzulli A, Menna M and Toulkeridis T. 2008. The magmatic feeding system of El Reventador volcano (Sub-Andean zone, Ecuador) constrained by texture, mineralogy and thermobarometry of the 2002 erupted products. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 176(1): 94-106 DOI:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2008.03.003 |
Ridolfi F, Renzulli A and Puerini M. 2010. Stability and chemical equilibrium of amphibole in calc-alkaline magmas:An overview, new thermobarometric formulations and application to subduction-related volcanoes. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 160(1): 45-66 DOI:10.1007/s00410-009-0465-7 |
Schmidt MW. 1992. Amphibole composition in tonalite as a function of pressure:An experimental calibration of the Al-in-hornblende barometer. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 110(2-3): 304-310 DOI:10.1007/BF00310745 |
Song SG, Bi HZ, Qi SS, Yang LM, Alle MB, Niu YL, Su L and Li WF. 2018. HP-UHP metamorphic belt in the East Kunlun Orogen:Final closure of the Proto-Tethys Ocean and formation of the Pan-North-China Continent. Journal of Petrology, 59(11): 2043-2060 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egy089 |
Song XY, Yi JN, Chen LM, She YW, Liu CZ, Dang XY, Yang QA and Wu SK. 2016. The giant Xiarihamu Ni-Co sulfide deposit in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, northern Tibet Plateau, China. Economic Geology, 111(2): 29-55 |
Su BX, Qin KZ, Sun H, Tang DM, Xiao QH and Cao MJ. 2009. Petrological and mineralogical characteristics of Hongshishan mafic-ultramafic complex in Beishan area, Xinjiang:Implications for assimilation and fractional crystallization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(4): 873-887 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Su SG and Lesher CM. 2012. Genesis of PGE mineralization in the Wengeqi mafic-ultramafic complex, Guyang County, Inner Mongolia, China. Mineralium Deposita, 47(1-2): 197-207 DOI:10.1007/s00126-011-0351-x |
Su SG, Tang ZL, Luo ZH, Deng JF, Wu GY, Zhou MF, Song C and Xiao QH. 2014. Magmatic conduit metallogenic system. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(11): 3120-3130 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Tang QY, Li JP, Zhang MJ, Song Z, Dang YX and Du L. 2017. The volatile conditions of ore-forming magma for the Xiarihamu Ni-Cu sulfide deposit in East Kunlun orogenic belt, western China:Constraints from chemical and carbon isotopic compositions of volatiles. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(1): 104-114 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Thakurta J, Ripley EM and Li CS. 2008. Geochemical constraints on the origin of sulfide mineralization in the Duke Island complex, southeastern Alaska. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 9(7): Q07003 |
Wang G, Sun FY, Li BL, Li SJ, Zhao JW, Yang QA and Ao C. 2013. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the Early Devonian syenogranite in the Xiarihamu ore district from East Kunlun, with implications for the geodynamic setting. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 37(4): 685-697 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang G, Sun FY, Li BL, Li SJ, Zhao JW, Ao C and Yang QA. 2014a. Petrography, zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the mafic-ultramafic intrusion in Xiarihamu Cu-Ni deposit from East Kunlun, with implications for geodynamic setting. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(6): 381-401 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang G, Sun FY, Li BL, Li SJ, Zhao JW and Yang QA. 2014b. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of diorite in Xiarihamu ore district from East Kunlun and its geological significance. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 44(3): 876-891 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang G, Sun FY, Li BL, Ao C, Li SJ, Zhao JW and Yang QA. 2016. Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implication of Early Neoproterozoic monzogranite in Xiarihamu ore district from East Kunlun. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 40(6): 1247-1260 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang KM, Wang ZQ, Zhang YL and Wang G. 2016. Determination of kaersutite and its implication for mafic rock in Taohe area, North Daba Mountain. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 35(3): 506-516 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xiong FH, Ma CQ, Jiang HA, Liu B and Huang J. 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of Middle Devonian mafic dykes in the East Kunlun orogenic belt, Northern Tibet Plateau:Implications for the transition from Prototethys to Paleotethys orogeny. Geochemistry, 74(2): 225-235 DOI:10.1016/j.chemer.2013.07.004 |
Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Li HB and Yao JX. 2006. The early Palaeozoic terrene framework and the formation of the High-Pressure (HP) and Ultra-High Pressure (UHP) metamorphic belts at the Central Orogenic Belt (COB). Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(12): 1793-1806 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xue JZ, Bai XR and Chen W. 1986. Genetic Mineralogy. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press: 114-121 (in Chinese)
|
Yan JM, Sun FY, Chen GJ, Qian Y, Li L, Wang C and He SY. 2016. Geochemical characteristics of gabbro from Binggounan Cu-Ni deposit in the north of eastern Kunlun metallogenic belt. Global Geology, 35(3): 729-737 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang JS, Robinson PT, Jiang CF and Xu ZQ. 1996. Ophiolites of the Kunlun Mountains, China and their tectonic implications. Tectonophysics, 258(1-4): 215-231 DOI:10.1016/0040-1951(95)00199-9 |
Zhang JX, Meng FC, Wan YS, Yang JS and Dong GA. 2003. Early Paleozoic tectono-thermal event of the Jinshuikou Group on the southern margin of Qaidam:Zircon U-Pb SHRIMP age evidence. Geological Bulletin of China, 22(6): 397-404 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang JX, Yu SY, Li YS, Yu XX, Lin YH and Mao XH. 2015. Subduction, accretion and closure of Proto-Tethyan Ocean:Early Paleozoic accretion/collision orogeny in the Altun-Qilian-North Qaidam orogenic system. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(12): 3531-3554 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang JY, Lei HL, Ma CQ, Li JW and Pan YM. 2018a. Geochemical and thermodynamical modeling of magmatic sources and processes for the Xiarihamu sulfide deposit in the eastern Kunlun Orogen, western China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 190: 345-356 DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.04.005 |
Zhang ZW, Tang QY, Li CS, Wang YL and Ripley EM. 2017. Sr-Nd-Os-S isotope and PGE geochemistry of the Xiarihamu magmatic sulfide deposit in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Mineralium Deposita, 52(1): 51-68 DOI:10.1007/s00126-016-0645-0 |
Zhang ZW, Wang YL, Qian B, Liu YG, Zhang DY, Lü PR and Dong J. 2018b. Metallogeny and tectonomagmatic setting of Ni-Cu magmatic sulfide mineralization, number I Shitoukengde mafic-ultramafic complex, East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 96: 236-246 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.04.027 |
Zhang ZW, Li WY, Qian B, Wang YL, Li SJ, Liu CZ, Zhang JW, Yang QA, You MX and Wang ZA. 2015. Metallogenic epoch of the Xiarihamu magmatic Ni-Cu sulfide deposit in eastern Kunlun orogenic belt and its prospecting significance. Geology in China, 42(3): 438-451 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhu YH, Zhang KX, Pan YM, Chen NS, Wang GC and Hou GJ. 1999. Determination of different ophiolitic belts in eastern Kunlun orogenic zone and their tectonic significance. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 24(2): 134-138 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
奥琮, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 李世金, 王冠. 2014. 青海夏日哈木矿区中泥盆世闪长玢岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其地质意义. 西北地质, 47(1): 96-106. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2014.01.007 |
柏中杰, 钟宏, 朱维光. 2019. 幔源岩浆氧化还原状态及对岩浆矿床成矿的制约. 岩石学报, 35(1): 204-214. |
边千韬, 赵大升, 叶正仁, 常承法, 罗小全, 高山林. 2002. 初论昆祁秦缝合系. 地球学报, 23(6): 501-508. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.06.004 |
陈光远, 孙岱生, 殷辉安. 1988. 成因矿物学与找矿矿物学. 第2版. 重庆: 重庆出版社: 555-647.
|
谌宏伟, 罗照华, 莫宣学, 张雪亭, 王瑾, 王秉璋. 2006. 东昆仑喀雅克登塔格杂岩体的SHRIMP年龄及其地质意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 25(1): 25-32. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2006.01.003 |
杜玮. 2015.东昆仑夏日哈木镍矿区镁铁-超镁铁质岩石研究.硕士学位论文.西安: 长安大学, 1-106 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1015802121.htm
|
樊祺诚, 刘若新, 马宝林. 1992. 中国上地幔角闪石及其成因意义. 矿物学报, 12(4): 353-358. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1992.04.010 |
范亚洲, 孟繁聪, 段雪鹏. 2018. 东昆仑西段夏日哈木榴辉岩原岩属性及陆(弧)陆碰撞. 地质学报, 92(3): 482-502. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.03.005 |
丰成友, 赵一鸣, 李大新, 刘建楠, 刘长征. 2016. 东昆仑祁漫塔格山地区夏日哈木镍矿床矿物学特征. 地质论评, 62(1): 215-228. |
冯建赟, 裴先治, 于书伦, 丁仨平, 李瑞保, 孙雨, 张亚峰, 李佐臣, 陈有炘, 张晓飞, 陈国超. 2010. 东昆仑都兰可可沙地区镁铁-超镁铁质杂岩的发现及其LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄. 中国地质, 37(1): 28-38. |
姜常义, 安三元. 1984. 论火成岩中钙质角闪石的化学组成特征及其岩石学意义. 矿物岩石, (3): 1-9. |
姜常义, 凌锦兰, 周伟, 杜玮, 王子玺, 范亚洲, 宋艳芳, 宋忠宝. 2015. 东昆仑夏日哈木镁铁质-超镁铁质岩体岩石成因与拉张型岛弧背景. 岩石学报, 31(4): 1117-1136. |
姜春发, 杨经绥, 冯秉贵, 朱志直, 赵民, 柴耀楚, 施希德, 王怀达, 胡金庆. 1992. 昆仑开合构造. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-224.
|
赖绍聪. 1994. 分离结晶对岩浆氧逸度的影响. 地学前缘, 1(增1): 12. |
李怀坤, 陆松年, 相振群, 周红英, 郭虎, 宋彪, 郑健康, 顾瑛. 2006. 东昆仑中部缝合带清水泉麻粒岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究. 地学前缘, 13(6): 311-321. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.06.034 |
李荣社, 计文化, 赵振明, 陈守建, 孟勇, 于浦生, 潘小平. 2007. 昆仑早古生代造山带研究进展. 地质通报, 26(4): 373-382. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.04.002 |
李世金, 孙丰月, 高永旺, 赵俊伟, 李连松, 杨启安. 2012. 小岩体成大矿理论指导与实践:青海东昆仑夏日哈木铜镍矿找矿突破的启示及意义. 西北地质, 45(4): 185-191. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2012.04.017 |
刘彬, 马昌前, 张金阳, 熊富浩, 黄坚, 蒋红安. 2012. 东昆仑造山带东段早泥盆世侵入岩的成因及其对早古生代造山作用的指示. 岩石学报, 28(6): 1785-1807. |
刘彬, 马昌前, 蒋红安, 郭盼, 张金阳, 熊富浩. 2013. 东昆仑早古生代洋壳俯冲与碰撞造山作用的转换:来自胡晓钦镁铁质岩石的证据. 岩石学报, 29(6): 2093-2106. |
刘飞, 苏尚国, 余晓燕, 梁凤华, 胡妍, 牛晓露. 2013. 内蒙古文圪气镁铁-超镁铁质杂岩体中环带角闪石矿物学特征及成因. 地学前缘, 20(1): 206-222. |
刘显凡, 汪灵, 李慧, 刘菁, 赵甫峰, 卢秋霞, 胡琳. 2015. 角闪石族和辉石族矿物的系统矿物学分类命名. 矿物学报, 35(1): 19-28. |
刘战庆, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 李佐臣, 张晓飞, 刘智刚, 陈国超, 陈有炘, 丁仨平, 郭俊峰. 2011. 东昆仑南缘阿尼玛卿构造带布青山地区两期蛇绿岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其构造意义. 地质学报, 85(2): 185-194. |
栾燕, 宋谢炎, 陈列锰, 郑文勤, 田小林, 冉启渝. 2014. 四川红格层状侵入体中角闪石和金云母的矿物学特征及其成因意义. 岩石学报, 30(5): 1457-1471. |
吕林素, 毛景文, 周振华, 李宏博, 张作衡, 汪云峰. 2012. 吉林红旗岭1号和7号岩体中含矿超镁铁质岩的矿物化学特征:对岩浆演化过程以及铜镍硫化物矿床形成机制的约束. 岩石学报, 28(1): 319-344. |
孟繁聪, 崔美慧, 贾丽辉, 任玉峰, 冯惠彬. 2015. 东昆仑造山带早古生代的大陆碰撞:来自榴辉岩原岩性质的证据. 岩石学报, 31(12): 3581-3594. |
莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 喻学惠, 刘成东, 谌宏伟, 袁万明, 刘云华. 2007. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长. 高校地质学报, 13(3): 403-414. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.010 |
祁生胜, 宋述光, 史连昌, 才航加, 胡继春. 2014. 东昆仑西段夏日哈木-苏海图早古生代榴辉岩的发现及意义. 岩石学报, 30(11): 3345-3356. |
祁晓鹏, 杨杰, 范显刚, 崔建堂, 蔡振峰, 曾献文, 魏伟, 屈小明, 翟黎明. 2016. 东昆仑东段东昆中构造混杂岩带长石山蛇绿岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义. 中国地质, 43(3): 797-816. |
任军虎, 柳益群, 冯乔, 韩文中, 高辉, 周鼎武. 2009. 东昆仑清水泉辉绿岩脉地球化学及LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年. 岩石学报, 25(5): 1135-1145. |
苏本勋, 秦克章, 孙赫, 唐冬梅, 肖庆华, 曹明坚. 2009. 新疆北山地区红石山镁铁-超镁铁岩体的岩石矿物学特征:对同化混染和结晶分异过程的启示. 岩石学报, 25(4): 873-887. |
苏尚国, 汤中立, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 伍光英, 周美夫, 宋晨, 肖庆辉. 2014. 岩浆通道成矿系统. 岩石学报, 30(11): 3120-3130. |
汤庆艳, 李建平, 张铭杰, 宋哲, 党永西, 杜丽. 2017. 东昆仑夏日哈木镍铜硫化物矿床成矿岩浆条件:流体挥发份化学组成与碳同位素组成制约. 岩石学报, 33(1): 104-114. |
王冠, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 李世金, 赵俊伟, 杨启安, 奥琮. 2013. 东昆仑夏日哈木矿区早泥盆世正长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其动力学意义. 大地构造与成矿学, 37(4): 685-697. |
王冠, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 李世金, 赵俊伟, 奥琮, 杨启安. 2014a. 东昆仑夏日哈木铜镍矿镁铁质-超镁铁质岩体岩相学、锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其构造意义. 地学前缘, 21(6): 381-401. |
王冠, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 李世金, 赵俊伟, 杨启安. 2014b. 东昆仑夏日哈木矿区闪长岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其地质意义. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44(3): 876-891. |
王冠, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 奥琮, 李世金, 赵俊伟, 杨启安. 2016. 东昆仑夏日哈木矿区新元古代早期二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其构造意义. 大地构造与成矿学, 40(6): 1247-1260. |
王坤明, 王宗起, 张英利, 王刚. 2016. 北大巴山滔河镁铁质岩中钛闪石的厘定及指示意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 35(3): 506-516. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2016.03.010 |
许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 姚建新. 2006. 中央造山带早古生代地体构架与高压-超高压变质带的形成. 地质学报, 80(12): 1793-1806. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.12.002 |
薛君治, 白学让, 陈武. 1986. 成因矿物学. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社: 114-121.
|
闫佳铭, 孙丰月, 陈广俊, 钱桦, 李良, 王超, 何书跃. 2016. 东昆北成矿带冰沟南铜镍矿辉长岩地球化学特征. 世界地质, 35(3): 729-737. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2016.03.013 |
张建新, 孟繁聪, 万渝生, 杨经绥, 董国安. 2003. 柴达木盆地南缘金水口群的早古生代构造热事件:锆石U-Pb SHRIMP年龄证据. 地质通报, 22(6): 397-404. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.06.004 |
张建新, 于胜尧, 李云帅, 喻星星, 林宜慧, 毛小红. 2015. 原特提斯洋的俯冲、增生及闭合:阿尔金-祁连-柴北缘造山系早古生代增生/碰撞造山作用. 岩石学报, 31(12): 3531-3554. |
张照伟, 李文渊, 钱兵, 王亚磊, 李世金, 刘长征, 张江伟, 杨启安, 尤敏鑫, 王志安. 2015. 东昆仑夏日哈木岩浆铜镍硫化物矿床成矿时代的厘定及其找矿意义. 中国地质, 42(3): 438-451. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.03.004 |
朱云海, 张克信, Pan YM, 陈能松, 王国灿, 侯光久. 1999. 东昆仑造山带不同蛇绿岩带的厘定及其构造意义. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 24(2): 134-138. |
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35


