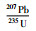2. 中国地质大学地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室, 北京 100083
2. State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China
西南三江地区是研究特提斯演化与成矿的热点区域(莫宣学等,1993;潘桂棠等,1997;邓军等, 2011, 2012, 2014;Deng et al., 2014a;Wang et al., 2014a, 2016;Liu et al., 2015;Geng et al., 2017;Liu and Hou, 2017; Gou et al., 2019)。沿班公湖-怒江缝合带、龙木错-双湖缝合带和金沙江缝合带将三江地区北部分割为拉萨、南羌塘和北羌塘三个微地块(图 1a;Mo et al., 1994;Metcalfe, 2002, 2013;Wang et al., 2014b)。龙木错-双湖缝合带位于羌塘地块中部,与三江南段的昌宁-孟连缝合带被认为是古特提斯洋主洋盆消亡的残迹,代表了冈瓦纳大陆和欧亚大陆的分界线(李才, 1987, 2008;郑洪伟等,2012;Wang et al., 2015a, b;杜斌等,2016;Deng et al., 2018b)。前人多聚焦于对龙木错-双湖缝合带自新元古代以来的特提斯成岩成矿作用及青藏高原隆起的研究(邓军等,2010;Deng et al., 2014b, 2017b, 2018a;Wang et al., 2018a;杜斌等,2018),但由于前寒武纪基底岩石出露较少,缺乏足够的地质证据,因而对该缝合带元古代变质基底的性质和冈瓦纳北缘的构造演化等问题众说纷纭(黄继钧, 2001a, b;王国芝和王成善,2001;赵政璋等,2001;李才,2003;李才等, 2005, 2009b)。
沿藏东他念他翁山东侧出露的吉塘变质杂岩体最早由李璞(1955)首先发现并命名为“吉塘变质岩”,但因受到大面积中生代花岗岩侵入和多期次构造活动后期叠加的影响,其原岩性质和时代属性存在较大争议(Hu et al., 2014;Peng et al., 2015)。早期的野外研究(艾长兴和陈炳蔚,1986)及区域地质资料(西藏地矿局第一地质大队, 1977①)将“吉塘变质岩”称为吉塘群,根据其变质程度不同由上至下分为酉西组和吉塘组,其形成时代均为古生代。随后,雍永源等(1990)通过对察雅县酉西村至吉塘镇多穷沟剖面的野外观测,以花岗闪长侵入体为界,将西侧定为以片岩和变质砂砾岩为主、变质程度较低的酉西群,东侧定为以片麻岩和斜长角闪岩为主、变质程度较高的吉塘群,由此基本确定该区地层序列分为由上到下的酉西群和吉塘群。藏东区域地质调查项目(西藏自治区地质调查院, 2007②)通过进一步研究认为酉西岩群可能属新元古代,吉塘岩群属古-中元古代。昌都幅1:20万区域地质调查报告(西藏自治区地质矿产局, 1999③)将位于酉西群和吉塘群之间的混合岩和混合花岗岩统称“吉塘复式岩体”,形成时代为三叠纪。但这些过于宽泛的年龄结果使吉塘群和酉西群的形成时代变得模糊不清,也制约着对龙木错-双湖缝合带构造演化的认识。近年来,锆石U-Pb同位素定年技术在吉塘地区得到广泛应用,进一步约束了吉塘变质杂岩体的形成时代。李才等(2009a)在类乌齐地区的吉塘群花岗片麻岩得到锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄为227~254Ma;沙绍礼等(2012)利用锆石U-Pb和白云母Ar-Ar法分别得到240±12Ma和226±2Ma的中生代年龄,由此认为吉塘变质杂岩体形成于中生代,很可能不存在变质基底。但另有研究者对吉塘变质杂岩体中出露的花岗岩开展U-Pb定年,显示其年龄为249~220Ma,岩浆源岩为具有变质杂砂岩成分的古元古代吉塘群片麻岩(陶琰等,2011;Hu et al., 2014;Tao et al., 2014)。因此吉塘变质杂岩体古-中生代的锆石年龄很可能代表古特提斯洋俯冲岩浆事件的年龄,并不代表变质基底的形成时代。最新研究显示,在酉西群石英绿泥片岩(何世平等,2012)和变质杂砂岩(金鹭等,2017)中获得了原岩形成时代为中-新元古代的锆石U-Pb年龄,这表明吉塘变质杂岩体作为变质基底的存在且具有中-新元古代的地质事件,其原岩组成和时代归属仍有待进一步研究。
① 西藏地矿局第一地质大队. 1977.西藏察雅县卡贡铁矿外围普查报告
② 西藏自治区地质调查院. 2007.八宿县幅、贡觉县幅、然乌区幅、芒康县幅1:25万区域地质调查报告
③ 西藏自治区地质矿产局. 1999.洛隆幅、昌都幅1:20万区域地质调查报告
基底的性质与时代是板块的“根”(李才等,2006),其在研究和确定板块边界和属性等问题时具有重要意义。吉塘变质杂岩体变质基底的时代和性质是怎样的?这是否可以成为研究羌塘地块大地构造属性及特提斯与冈瓦纳北缘演化新的地质证据?针对以上问题,本文以察雅县吉塘镇附近的酉西群和吉塘群为研究对象,对两个岩群具有代表性的片岩和片麻岩进行锆石LA-ICP-MS年代学和岩石地球化学研究,对原岩组成、时代界限和演化意义等问题进行探讨。研究成果不仅有助于解析龙木错-双湖缝合带变质基底的时代与组成,而且对深入研究羌塘地块基底格架构造演化和区域对比亦具有重要的科学意义。
1 区域地质概况青藏高原被认为是由多个地块在不同时代经历多次碰撞拼合而形成的一个复杂的地质构造单元(Şengör, 1990;潘桂棠等, 1997, 2002;Yin and Harrison, 2000;许志琴等,2006)。龙木错-双湖缝合带是青藏高原北侧一条重要的缝合带,将羌塘地块分为北羌塘地块和南羌塘地块(李才,2008;Xu et al., 2015)。该缝合带以西在龙木错地区被阿尔金大型走滑断裂带错断,向东经双湖、巴青,延入藏东吉塘地区,全长超过2000km。昌宁-孟连缝合带被认为是龙木错-双湖缝合带在西南三江地区的南延部分(图 1a)。龙木错-双湖缝合带两侧的南羌塘和北羌塘地块古-中生代的地层序列、生物组合和沉积建造属于两种不同类型。南羌塘地块奥陶系-泥盆系是一套以浅变质灰岩、砂质灰岩浅海碳酸盐为主的稳定大陆边缘台地型沉积建造;上石炭统至下二叠统以夹碎屑岩基性火山岩的裂谷型建造为主,中-下二叠统以发育枕状玄武岩、复理石建造为特征,具泥盆系与上覆地层层序连续特征,被认为是冈瓦纳大陆北缘的盖层体系(李才等,2004;周志广等,2004;程立人等,2007)。北羌塘地块上石炭统到上二叠统以稳定台地型碳酸盐沉积为主,出露范围较广,发育珊瑚、海绵、类化石的古生物组合;泥盆系到二叠系以浅海、滨浅海碳酸盐建造为主,生物繁盛,但表现出泥盆系以角度不整合覆于奥陶系-志留系地层之上,特征与扬子板块盖层类似(崔建堂等,2006;夏军等,2006)。该缝合带构造活动活跃,中-西段多沿宽窄不一的近东西向负地形走向,地层受东西向断裂为主的构造活动强烈改造,发育以冈玛日-菊花山为代表的新生代逆冲推覆构造(解超明等,2010);东段受到新生代以来印度-欧亚大陆碰撞影响,在藏东昌都一带急转为与澜沧江近平行的北西走向,因强烈挤压而呈高山峡谷地貌。该缝合带以双湖为界分段性清楚(图 1b):在双湖以西由一系列高压变质带、蛇绿混杂岩和火山岩浆弧组成(Kapp et al., 2000;胡培远等,2010; Yang et al., 2011;Zhai et al., 2011, 2013),与古特提斯演化相关的晚古生代至三叠纪岩浆活动大体平行于缝合带发育,持续时间较短(翟庆国等,2006);双湖以东至吉塘地区沿缝合带发育规模巨大的中酸性岩浆岩带,其中,侵入岩出露于类乌齐(Hu et al., 2014)、吉塘(陶琰等,2011; Tao et al., 2014)、东达山(Peng et al., 2015)等地,以中-晚三叠世花岗岩为主,被上三叠统甲丕拉组不整合覆盖,火山岩则平行于他念他翁-东达山中酸性侵入岩带的东侧分布,与中酸性侵入岩共同构成巨大的火山岩浆弧(李才等,2009b)。
|
图 1 区域大地构造简图(a)与青藏高原-三江地区构造单元图解(b)(据Zhu et al., 2013;Deng et al., 2014a改绘) Fig. 1 Simplified regional geological map (a) and tectonic subdivision of the Tibetan Plateau-Sanjiang region (b) (modified after Zhu et al., 2013; Deng et al., 2014a) |
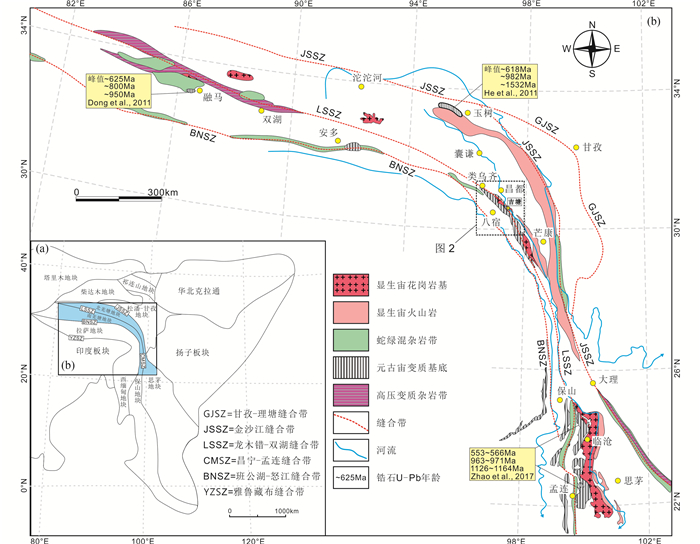
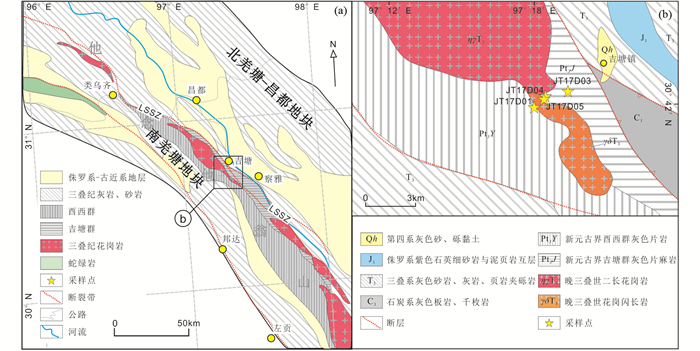
吉塘变质杂岩体为昌都-芒康变质岩系的主体,介于怒江与澜沧江之间,西起巴青县、东至左贡县,长300余千米、宽3~10km(图 2a)。昌都-芒康变质岩系沿龙木错-双湖缝合带北侧的他念他翁山呈北西-南东向长条状展布,是藏东三江地区主要的变质岩系。区域地质资料显示,昌都-芒康变质岩系与班公湖-怒江和冈底斯腾冲变质岩带均具有中-新元古代变质基底,上覆古-中生界地层(图 3)。昌都-芒康变质岩系南北延伸,经历了不同层次的“混杂-构造置换”和“变质均一化作用”(王根厚,2006)。因此,吉塘变质杂岩体在南北两地出露变质岩组成差别较大,其内部包含了不同地层、岩石单元的有序或无序组合,成为形成时代争议较大的变质杂岩体(王根厚等,1996;王根厚,2006)。
|
图 2 类乌齐-吉塘-左贡地质略图(a,据潘桂棠等,2004a修改)和吉塘变质杂岩体简图及采样点位置图(b,据西藏自治区地质调查院, 2007) Fig. 2 Simplified maps of the Leiwuqi-Jitang-Zuogong area (a, modified after Pan et al., 2004a) and simplified geological maps and sample locations of the Jitang metamorphic complex (b) |
|
图 3 藏东变质基底柱状图(据西藏自治区地质调查院, 2007) Fig. 3 Stratigraphic column of the metamorphic basement in eastern Tibet |
研究区位于昌都地区察雅县吉塘镇西侧的多穷沟一带(采样点如图 2b),区内主要出露两套变质岩群,分别为下部的吉塘岩群和上部的酉西岩群。古-中元古代吉塘岩群(Pt1-2J)出露于吉塘镇附近,为一套片麻岩、变粒岩、斜长角闪岩和少量片岩等组成的中深变质岩系,属于南羌塘地块的结晶基底。新元古代酉西群(Pt3Y)出露于酉西村、察兰多一带,岩性组合为绿泥片岩、石英片岩、云母(石英)片岩、绿泥钠长片岩及少量变质石英砾岩组成的浅变质岩系,西与上三叠统甲丕拉组断层接触,东与古-中元古代吉塘岩群断层接触,是南羌塘地块褶皱基底的组成部分。酉西群野外观察未发现明显的混合岩化,与晚三叠世花岗闪长岩侵入体边界可见长英质脉体(图 4a);而吉塘群与中酸性侵入体接触的部分地段则遭受不同程度的混合岩化作用,野外明显可见黑云母团块和不规则石英脉的注入(图 4b)。本区出露的三叠纪中酸性侵入体主要为二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩,大多受到明显的变质作用,野外露头普遍呈灰绿色,黑云母大多蚀变为绿泥石,发育片麻状构造。
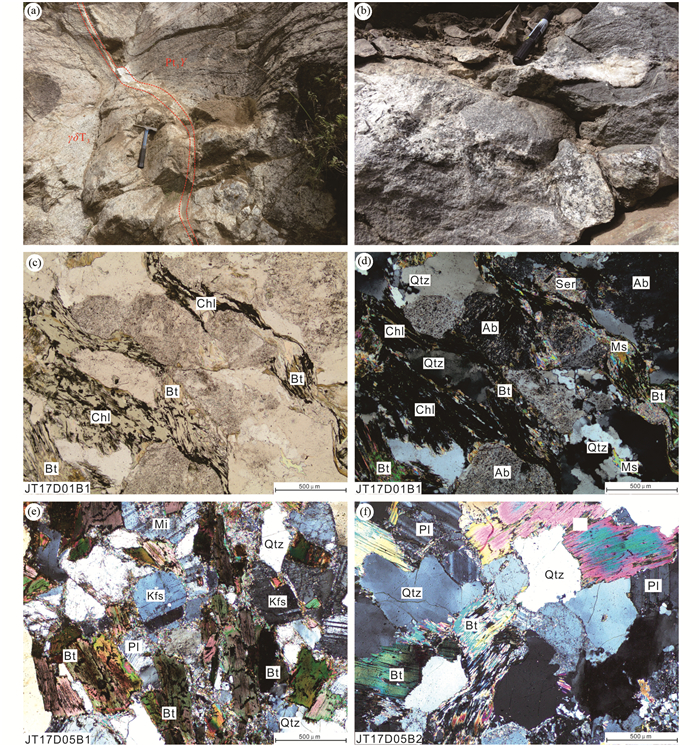
|
图 4 吉塘变质杂岩体野外特征及岩相学特征显微照片 (a)酉西群(Pt3Y)与晚三叠世花岗闪长岩侵入体(γδT3)边界可见长英质脉体;(b)吉塘群(Pt1-2J)与侵入体接触位置可见混合岩化作用;(c、d)酉西群云母绿泥钠长片岩;(e)吉塘群黑云母二长片麻岩;(f)吉塘群黑云母斜长片麻岩. Qtz-石英; Pl -斜长石; Kfs-钾长石; Ab-钠长石; Bt-黑云母; Ms-白云母; Chl-绿泥石; Mi-微斜长石; Ser-绢云母 Fig. 4 Field characteristic and petrographic photomicrographs of the Jitang metamorphic complex (a) the felsic veins can be seen at the boundary between the Youxi Group (Pt3Y) and Late Triassic granodiorite intrusions (γδT3); (b) mixed lithification can be seen in the contact position between Jitang Group (Pt1-2J) and intrusion; (c, d) mica-chlorite-albite schist in Youxi Group; (e) biotite monzonitic gneiss in Jitang Group; (f) biotite plagioclase gneiss in Jitang Group. Qtz-quartz; Pl-plagioclase; Kfs-alkali feldspar; Ab-albite; Bt-biotite; Ms-muscovite; Chl-chlorite; Mi-microcline; Ser-sericite |
样品JT17D01B1为云母绿泥钠长片岩(图 4c, d),采自酉西群,岩石呈深灰绿色,具鳞片粒状变晶结构,片状构造。主要矿物为石英(~25%)、钠长石(~30%)、绿泥石(20%)、黑云母(~15%)、白云母(~5%)、斜长石(~5%)等。钠长石呈粒状变晶,包含石英、云母等矿物而具有残缕构造,且部分发生较强烈的绢云母化,暗色矿物以黑云母和绿泥石为主,呈连续定向排列,绿泥石富铁质而在镜下显暗黑色条带。变质程度为低绿片岩相。
样品JT17D03B1、JT17D03B3、JT17D05B1和JT17D05B4为黑云母二长片麻岩(图 4e),采自吉塘群,岩石呈灰色,鳞片粒状变晶结构,片麻状构造。主要矿物为钾长石(20%~25%)、斜长石(15%~20%,以更长石为主,An = 12~17)、石英(20%~25%)、黑云母(20%~25%)、微斜长石(10%~15%),以及少量的白云母(<5%)和绿泥石(<5%)。钾长石呈半自形-他形,部分发生泥化蚀变。石英颗粒微定向特征,颗粒间有白云母分布。条带矿物主要为黑云母等暗色矿物,具有不连续定向性。
样品JT17D05B2为黑云母斜长片麻岩(图 4f),采自吉塘群,岩石呈灰色,鳞片粒状变晶结构,片麻状构造。主要矿物为斜长石(~35%)、石英(~25%)、黑云母(~25%)、白云母(~10%)以及少量的钾长石(~5%)。斜长石呈半自形板状-他形,粒径约为0.2~0.5mm,An = 11~16,以更长石为主,部分发育简单双晶和聚片双晶,可见石英、云母等包裹体矿物。岩石后期受动力作用,长石双晶弯曲,石英压碎并具波状消光。暗色矿物以黑云母为主,具有不连续定向性。
2.2 测试方法本次对昌都地区酉西群片岩和吉塘群片麻岩等共计6件新鲜的岩石样品进行主量、微量和稀土元素分析。全岩粉末样样品的初步加工在河北省廊坊欣航测绘院完成,采用人工碎样等步骤,获得200目的新鲜全岩粉末样品,并选取部分作全岩主微量分析测试。全岩主微量测试分析在国家地质实验测试中心完成。主量元素使用X射线荧光光谱仪(PW4400)分析,采用GB/T 14506.28—2010标准。微量稀土元素在等离子质谱仪(PE300D)上分析测试,采用GB/T 14506.30—2010标准。
本文对采自酉西群和吉塘群的3件样品(JT17D01B1、JT17D03B1和JT17D05B2)进行了锆石U-Pb定年。锆石挑选在河北省廊坊欣航测绘院进行,将岩石样品破碎至自然粒度,经摇床、淘洗、电磁分选及重液分选后分离出锆石单矿物,在双目镜下挑纯。锆石制靶及拍照工作均在北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成。锆石制靶筛选原则是挑选颗粒大、表面洁净,透明度高的锆石。挑选出的锆石在环氧树脂上制成样靶,并对锆石进行阴极发光(CL)、透射光、反射光拍照,分析锆石结构特征,为测年工作做准备。
锆石U-Pb定年和微量元素测试工作均是在中国地质大学(北京)矿物激光微区分析实验室(Milma Lab)通过LA-ICP-MS方法完成的。实验中,使用NewWave 193UC型ArF准分子激光器进行剥蚀取样,Angilent 7900四级杆型等离子质谱仪测试离子信号强度。实验过程中采用NIST 610作为元素含量外标,锆石91500(Wiedenbeck et al., 2004)作为U-Pb同位素比值外标,锆石GJ-1(Jackson et al., 2004)和Plesovice(Sláma et al., 2008)作为未知样品的数据质量监控标来进行分析。数据处理采用ICPMSDataCal软件(Liu et al., 2008, 2010a, b;Hu et al., 2012),同位素比值及年龄误差均为1σ。普通铅采用Andersen(2002)程序进行校正,谐和图和年龄均值图均采用Isoplot软件(Ludwig, 2001)进行绘制。同时,本文对协和度小于90%的测点暂不考虑,对大于1000Ma的锆石采用207Pb/206Pb年龄,对小于1000Ma的锆石采用206Pb/238U年龄。
3 实验结果 3.1 地球化学特征表 1列出了所分析的6件样品的常量、微量及稀土元素测试结果和计算所得的相关参数,显示6件样品具有较为一致的地球化学变化特征。
|
|
表 1 吉塘变质杂岩体主量(wt%)及微量元素(×10-6)组成 Table 1 Major (wt%) and trace element (×10-6) concentrations of the Jitang metamorphic complex |
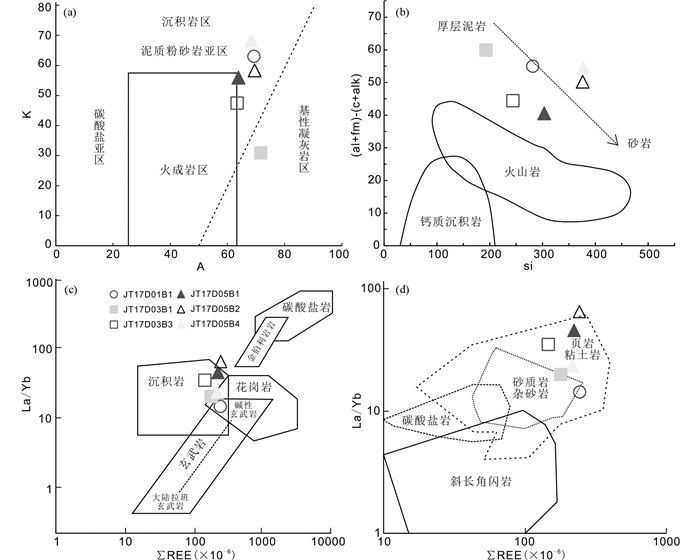
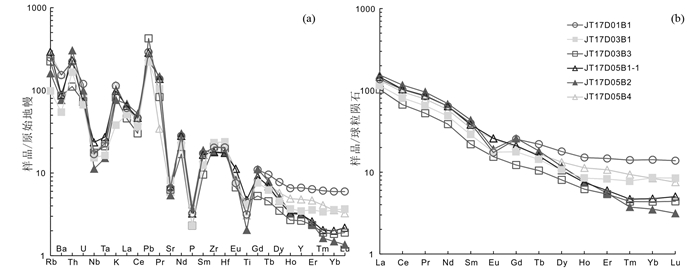
酉西群云母绿泥钠长片岩(JT17D01B1)样品中SiO2含量为66.60%,Na2O+K2O含量为5.39%,显示全碱含量较低;K2O/Na2O为1.72,具有富钾的特征;CaO和MgO分别为1.15%和3.24%;Al2O3含量高达15.15%,且分子数大于K2O、Na2O和CaO分子数之和,A/CNK = 1.67,具有明显过铝质特点;该样品Al2O3/SiO2为0.23,与杂砂岩(0.20~0.23)相当(Roser and Korsch, 1986);全铁(FeOT)为5.91%,显示较为富铁。由DF判别式(Shaw, 1972)计算的得到DF值为-5.23(表 1),明显小于0,可能属于副变质岩(王仁民等,1987)。对该样品的岩石化学数据进行计算得到K值和A值并进行K-A图解,显示样品落入沉积岩的泥质-粉砂质岩亚区(图 5a),在尼格里指数(al+fm)-(c+alk)对Si原岩恢复图中样品同样落入沉积岩范围(图 5b)。由稀土元素配分模式显示,该样品稀土元素总量较高(ΣREE = 231.6×10-6),且轻重稀土比值LREE/HREE = 3.52,(La/Yb)N = 9.64,反映轻稀土元素相对富集,重稀土元素相对亏损,具有较强的轻、重稀土元素分馏。样品δEu = 0.53,体现较明显的Eu负异常,而δCe = 0.92,异常不明显。在球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图中(图 6b),样品显示为明显向右倾斜且中间呈V字型。在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图中(图 6a),样品呈现出右倾的多峰谷模式,富集K、Rb、Th等大离子亲石元素(LILE),而Ba则明显亏损;高场强元素(HFSE)如Ti、Nb和Ta呈现负异常,而Zr和Hf显示出正异常的特点,体现较为稳定的地化特征。
|
图 5 吉塘杂岩体变质岩原岩恢复判别图解 (a)K-A关系图(周世泰,1984;齐秋菊等,2011);(b)尼格里指数-Si原岩恢复图解(Winkler, 1976);(c、d)La/Yb-∑REE原岩判别图解(Allègre and Minster, 1978;王仁民等,1987) Fig. 5 Protolith restoration of metamorphic rocks diagrams for the Jitang metamorphic complex (a) the K-A diagram (Zhou et al., 1984; Qi et al., 2011); (b) protolith discrimination diagram of Niggli index (al+fm)-(c+alk) vs. Si (Winkler, 1976); (c, d) protolith discrimination diagram of La/Yb vs. ∑REE (Allègre and Minster, 1978; Wang et al., 1987) |
|
图 6 吉塘变质杂岩体原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(a, 标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)和球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线(b, 标准化值据Boynton, 1984) Fig. 6 Primitive mantle-normalized multi-element diagrams (a, normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) and chondrite-normalized rare earth element patterns (b, normalization values after Boynton, 1984) for the Jitang metamorphic complex |
吉塘群黑云母二长片麻岩(JT17D03B1、JT17D03B3、JT17D05B1和JT17D05B4)样品整体SiO2含量较高,为58.85%~68.77%;全碱含量较低,Na2O+K2O = 3.67%~5.27%,Na2O/K2O = 0.45~2.17,没有明显富钾或富钠的特征;CaO和MgO分别为2.44%~2.87%和2.43%~4.88%,除1件样品(JT17D05B1)CaO和MgO值接近外,其余样品均有MgO>CaO的特点;Al2O3 = 14.08%~16.07%,含量较高且分子数大于K2O、Na2O和CaO分子数之和,A/CNK = 1.16~1.61>1.1,具有明显的过铝质特征;全铁(FeOT)为4.74%~8.54%,其中样品JT17D03B1更为富铁(FeOT = 8.54%)。样品的DF值为-4.05~-6.35<0,在(al+fm)-(c+alk)对Si原岩恢复图解中落入沉积岩区(图 5b),但K-A关系判别图中除JT17D03B1落入基性凝灰岩区外,其余点均投点位于火成岩与沉积岩的判别线附近(图 5a)。由稀土元素配分模式显示,该样品稀土元素总量较高(ΣREE = 140.3×10-6~211.2×10-6),且轻重稀土比值比值较高,LREE/HREE = 4.55~6.86,(La/Yb)N = 13.4~30.6,反映出轻稀土元素相对富集,重稀土元素相对亏损,具有较强的轻、重稀土元素分馏特征。样品δEu = 0.76~0.93,δCe = 0.86~0.91,Eu和Ce均无异常或显示弱负异常。在球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图中(图 6b),样品显示为具陡立状的右倾特征。在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图中(图 6a),样品呈现出右倾的多峰谷模式,富集除Ba之外的K、Rb、Th等大离子亲石元素(LILE);高场强元素(HFSE)如Ti、Nb和Ta呈现负异常,而Zr和Hf显示出正异常的特点,与酉西群样品特征类似,均体现了其较为稳定的地化特征。
吉塘群黑云母斜长片麻岩(JT17D05B2)样品SiO2含量较高,为72.33%;Na2O+K2O为3.93%,全碱含量较低,Na2O/K2O = 1.41>1,具有富钠贫钾的特征;CaO/MgO = 1.47>1,MgO相对于CaO明显富集;Al2O3为13.04%,与其他样品相比略低,但分子数仍大于K2O、Na2O和CaO分子数之和,A/CNK = 1.60>1.1,具有明显的过铝质特征;全铁(FeOT) = 3.78%,与其他样品相比较为贫铁。样品的DF值为-5.53<0,在(al+fm)-(c+alk)对Si原岩恢复图解和K-A关系判别图中均落入沉积岩区(图 5a, b)。由稀土元素配分模式显示,样品具有高稀土元素总量(ΣREE = 230.4×10-6),高轻重稀土比值(LREE/HREE = 7.06),高(La/Yb)N值((La/Yb)N = 43.6)的特征,具有与另外两组样品类似的轻、重稀土元素配分形式。但样品中δEu = 0.55,具有较明显的Eu负异常,在球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图中(图 6b),样品显示为明显右倾且中间呈V字型的稀土元素配分模式。在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图中(图 6a),样品的微量元素特征与样品类似,富集除Ba之外的K、Rb、Th等大离子亲石元素(LILE);高场强元素(HFSE)中亏损Ti、Nb和Ta,富集Zr和Hf元素。
3.2 锆石U-Pb定年结果本文对采自酉西群和吉塘群的3件样品(JT17D01B1、JT17D03B1和JT17D05B2)进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年(表 2、表 3、表 4)。
|
|
表 2 吉塘变质杂岩体云母绿泥钠长片岩(样品JT17D01B1)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb分析结果 Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb analytical data of mica-chlorite-albite schist (Sample JT17D01B1) in the Jitang metamorphic complex |
|
|
表 3 吉塘变质杂岩体黑云母二长片麻岩(样品JT17D03B1)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb分析结果 Table 3 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb analytical data of biotite monzonitic gneiss (Sample JT17D03B1) in the Jitang metamorphic complex |
|
|
表 4 吉塘变质杂岩体黑云母斜长片麻岩(样品JT17D05B2)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb分析结果 Table 4 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb analytical data of biotite plagioclase gneiss (Sample JT17D05B2) in the Jitang metamorphic complex |
样品JT17D01B1锆石颗粒大部分呈半自形、具有一定磨圆度的次棱角状或次圆状,半透明-透明,粒径长在80~170μm,长宽比介于1.1~2.5之间。在锆石阴极发光图像(CL)中,绝大部分锆石具有典型的核边结构,由一个弱发光效应的核部(黑色或暗灰色)以及强发光效应的边部(浅灰或白色)组成(图 7a)。锆石核部一般自形程度较好且具有清晰细密的岩浆震荡环带,显示典型岩浆结晶成因的锆石特征(吴元保和郑永飞,2004)。锆石边部无明显内部结构,部分切割核部震荡环带,应为后期变质增生锆石,由于锆石的变质增生边宽度一般为5~20μm,小于本次原位剥蚀束斑直径(32μm),因此测点均集中锆石核部。从中随机挑选了25颗锆石进行U-Pb年龄测定,同时选点时避开了CL图像中可见的裂隙和包体。

|
图 7 吉塘变质杂岩体锆石的阴极发光(CL)图像 Fig. 7 Cathodoluminescene (CL) images of zircons from metasedimentary rocks in the Jitang metamorphic complex |
样品LA-ICP-MS原位U-Pb年龄测试结果见表 2。测点的Th和U含量及比值差异较大,U含量为148.7×10-6~3570×10-6,Th含量为72.6×10-6~851.1×10-6,对应的Th/U值在0.03~0.9之间,其中大部分测点Th/U大于0.1(除点9、12、21外),具有典型的岩浆锆石特征(Hoskin and Schaltegger, 2003)。但也有研究表明,部分快速生长、变质不彻底的变质锆石仍可残留相对较高的Th/U值(Whitehouse and Kamber, 2002),因而不能作为区分锆石成因的唯一标准。锆石测点的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图如图 8b所示,除8和10号点可能热液熔蚀而显示轻稀土相对于重稀土富集,20号点可能为变质成因锆石而显示重稀土下降外(Dempster et al., 2004),其余锆石总体呈轻稀土亏损重稀土强烈富集的,显示出较高的稀土总量(REE)以及重稀土含量(HREE),分别为330.0×10-6~6054×10-6和335.3×10-6~3217×10-6。所有测点均具有明显的Eu负异常(δEu = 0.01~0.47);除8和10号点外,其余点位均具有明显的Ce正异常(δCe = 2.52~160),显示出典型的岩浆锆石特征。锆石原位U-Pb年龄结果显示出一组较为分散的年龄特征,排除协和度较差以及受到热液混杂影响的测点后,获得的20个锆石谐和年龄的范围变化为685~1109Ma,在累计频率图上形成多个年龄峰值(图 8a),主要集中在864~865Ma(n = 3)、914~932Ma(n = 4)、968~973Ma(n = 5)和1042~1087Ma(n = 4)四个年龄区段。
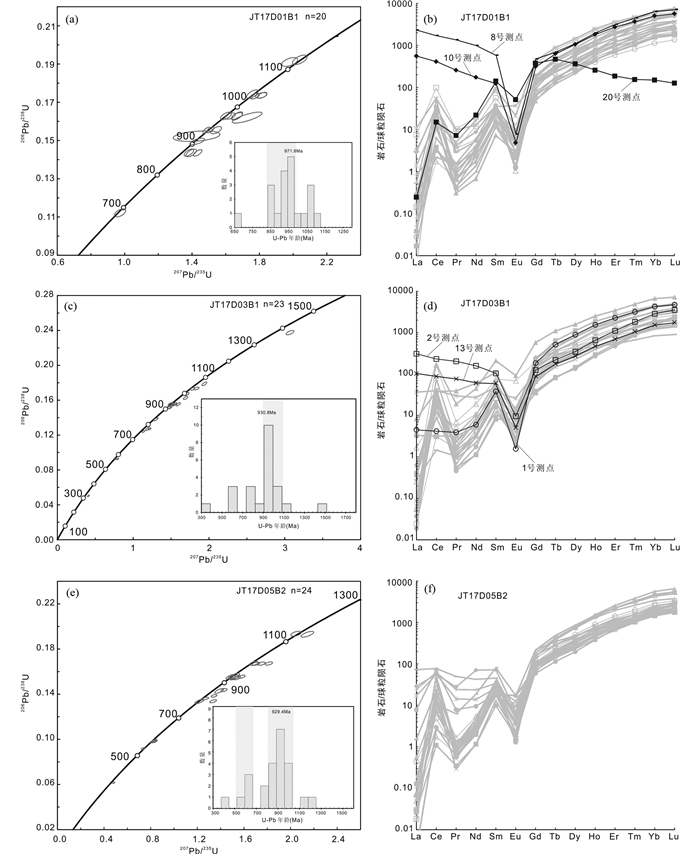
|
图 8 吉塘变质杂岩体锆石的U-Pb年龄谐和图及锆石球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线(标准化值据Boynton, 1984) Fig. 8 U-Pb concordia plot of detrital zircons from metasedimentary rocks and chondrite-normalized rare earth element patterns (normalization values after Boynton, 1984) of zircons in the Jitang metamorphic complex |
样品JT17D03B1锆石颗粒形态与JT17D01B1类似,大部分呈半自形次棱角状或次圆状,半透明-透明,粒径长在70~160μm,长宽比介于1.2~2.5之间。在锆石阴极发光图像(CL)中,绝大部分锆石具有典型亮暗特征的核边结构,锆石核部一般具有显示典型岩浆结晶成因的震荡环带结构。锆石边部即可见无明显内部结构的变质增生边,也可见较狭窄的晚期岩浆环带,锆石的边部宽度一般为5~40μm(图 7b)。从中随机挑选了25颗锆石进行U-Pb年龄测定,同时选点时避开了CL图像中可见的裂隙和包体。
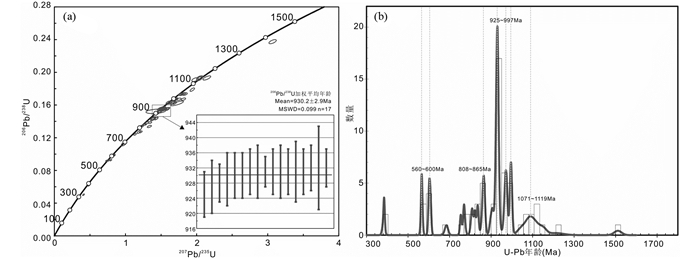
样品LA-ICP-MS原位U-Pb年龄测试结果见表 3。测点的Th和U含量及比值差异较大,U含量为290.7×10-6~2028×10-6,Th含量为95.5×10-6~1619×10-6,对应的Th/U = 0.1~1.28>0.1,其中大部分测点Th/U大于0.4。锆石测点的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图如图 8d所示,除2和13号点可能受到热液溶蚀显示轻稀土相对于重稀土富集,其余锆石总体呈轻稀土亏损重稀土强烈富集的,体现了岩浆成因的锆石稀土分配趋势。测点的稀土总量(REE)以及重稀土含量(HREE)较高,分别为551.3×10-6~3595×10-6和541.3×10-6~3379×10-6。所有测点均具有明显的Eu负异常(δEu = 0.01~0.54);除1、2、13和20号点外,其余点位均具有明显的Ce正异常(δCe = 1.16~148)。锆石原位U-Pb年龄结果显示跨度较大的年龄特征,排除协和度较差以及受到热液混杂影响的测点后,获得的23个锆石谐和年龄的范围变化为316~1161Ma,其中7个点组成的加权平均年龄为930.8±4.2Ma,为该组样品的峰值年龄(图 8c)。17号点位于锆石外围边部,测得的本组最小年龄值为316Ma,该点位具有明显指示岩浆成因锆石的特征环带,可能代表受晚期岩浆事件影响(图 7b)。
3.2.3 吉塘群黑云母斜长片麻岩(JT17D05B2)样品JT17D05B2锆石颗粒大部分呈半自形次棱角状,半透明-透明,粒径长在80~190μm,长宽比介于1.5~3之间。在锆石阴极发光图像(CL)中,绝大部分锆石具有典型亮暗特征的核边结构,锆石核部大多具有窄而密的震荡环带,显示其可能多为酸性岩浆结晶成因的锆石。可见无明显结构的变质增生边,也可见少部分锆石边部也具有环带特征,可能形成于晚期岩浆事件。锆石的变质增生边宽度一般为10~45μm(图 7c)。从中随机挑选了25颗锆石进行U-Pb年龄测定,选点时避开了CL图像中可见的裂隙和包体。
样品LA-ICP-MS原位U-Pb年龄测试结果见表 4。测点的Th和U含量明显低于JT17D01B1和JT17D03B1,U含量为297.0×10-6~1032×10-6,Th含量为44.3×10-6~482.1×10-6,对应的Th/U = 0.06~0.8。锆石测点的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图如图 8f所示,锆石总体呈轻稀土亏损、重稀土强烈富集,显示出典型的岩浆锆石特征。测点的稀土总量(REE)以及重稀土含量(HREE)较高,分别为724.8×10-6~2479×10-6和680.5×10-6~2466×10-6。所有测点均具有明显的Eu负异常(δEu = 0.01~0.44)和Ce正异常(δCe = 1.27~97.1)。锆石原位U-Pb年龄结果显示跨度较大的年龄特征,排除协和度较差以及受到热液混杂影响的测点后,获得的23个锆石谐和年龄的范围变化为385~1211Ma,其中7个点组成的加权平均年龄为929.4±4.6Ma,为该组样品的峰值年龄;其余测点在602~608Ma(n = 3)、808~822Ma(n = 3)和995~997Ma(n = 4)形成三个次峰值年龄区段(图 8e)。20号点位于锆石外围增生边,获得的变质增生年龄为385Ma,可能代表锆石受到后期变质重结晶的影响。
4 讨论 4.1 构造-岩浆热事件年龄约束前人认为西南特提斯北侧的龙木错-双湖缝合带与南侧的昌宁-孟连缝合带代表古特提斯主洋盆,且大多集中于对特提斯闭合以及之后的造山作用对岩浆活动、成岩成矿过程的研究(杨立飞等,2016;Deng et al., 2017a;Qiu and Deng, 2017;Wang et al., 2017, 2018b;王长明等,2017;Qiu et al., 2018;Yang et al., 2019;Yu et al., 2019)。最新的研究发现,在东特提斯沿龙木错-双湖缝合带和昌宁-孟连缝合带中存在可以代表泛非期和格林威尔造山期构造-岩浆热事件的变质基底(图 1b)。Dong et al.(2011)在龙木错-双湖缝合带北段戎马乡温泉石英岩获得的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄峰值为950Ma和625Ma,认为来源可能与冈瓦纳变质基底有关。He et al.(2011)在北羌塘地块玉树县宁多岩群变质岩的碎屑锆石中发现了以982Ma和618Ma为峰值的年龄,认为其分别对应着Rodinian超级大陆和泛非期造山运动的形成。Zhao et al.(2017)通过测定保山地体沿昌宁-孟连缝合带出露的澜沧组和勐统组沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄,得到了中元古代晚期(~1150Ma)、新元古代早期(~960Ma)和泛非期(600~500Ma)三个构造-岩浆热事件的年龄峰值。龙木错-双湖缝合带东段吉塘地区出露面积较大的变质基底,由于该区域受到较强的后期构造热事件改造,酉西群和吉塘群的变质岩形成时代长期存在争论,已有的年代学成果显示了从元古宙到晚古生代较大的时间跨度。我们对酉西群和吉塘群的3个变沉积岩样品进行锆石U-Pb定年研究,共计得到有效数据点67个,3件样品具有类似的锆石年龄分布模式和锆石稀土元素分配模式,其整体沿谐和线分布的年龄范围从316Ma到1511Ma,锆石年龄峰值范围为560~600Ma、808~865Ma、925~997Ma以及1071~1119Ma(图 9a, b)。不同类型的锆石代表了变质基底形成过程中不同的构造热事件,碎屑锆石最老的年龄峰值为1071~1119Ma,揭示了中元古代的信息,这一年龄区间在整个龙木错-双湖缝合带发现较少,仅在北羌塘地块宁多群变质杂岩体(He et al., 2011)和西南三江澜沧组和勐统组沉积岩碎屑锆石(Zhao et al., 2017)中有所记录。大多数碎屑锆石具有925~995Ma和808~865Ma两组峰值,主峰值年龄为932Ma,显示了新元古代的信息,代表了该区存在格林威尔造山期的构造-岩浆热事件。吉塘变质杂岩体碎屑锆石最年轻的年龄范围为560~600Ma,表明其遭受了后期构造-热事件,这与泛非期造山运动年龄记录相近。此外,本次测得的最年轻的岩浆成因的锆石为316Ma,可能代表了晚泥盆世之后古特提斯南向俯冲有关的岩浆记录(Pullen et al., 2011;Zhu et al., 2013;Wang et al., 2017)。来自锆石变质增生边的年龄为385Ma,代表了晚于吉塘变质杂岩体沉积时代的变质事件;最年轻的构造-岩浆热事件峰值为560~600Ma,从而限定它们的沉积时代不会早于这个时间。前人研究认为南羌塘地块在早奥陶世到泥盆纪具有大陆边缘浅海相的稳定沉积序列(李才等,2004),吉塘群上部层位获得了泥盆纪孢子和几丁虫微体化石(陈炳蔚,1987),金鹭等(2017)将酉西群沉积时代限定为410~360Ma;同时,来自昌宁-孟连缝合带澜沧江组和勐统组最新的碎屑锆石年龄也表明其沉积作用开始于奥陶纪,并非之前推测的新元古代(Zhao et al., 2017)。以上研究与本文得到的限定吉塘群和酉西群沉积时代大致为寒武纪之后到早泥盆世之间的推测一致。
|
图 9 吉塘变质杂岩体样品锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图(a)和碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄谱(b)由各样品中谐和度>90%的锆石年龄组成 Fig. 9 U-Pb concordia plot of detrital zircons from metasedimentary rocks in the Jitang metamorphic complex (a) and U-Pb age spectra of detrital zircons (b) Age data used are those with a concordance > 90% |
前人研究表明酉西群是岩性不一、成因不一的岩片集合体,自上而下主要为一套石英片岩、钠长石片岩、绿泥片岩和变质砾岩、砂岩夹千枚岩构成的变质岩系(雍永源等,1990;沙绍礼等,2012;金鹭等,2017)。酉西群在他念他翁山南麓的左贡地区尖灭,该处以变质砂砾岩为主的特征岩性以及微层理、粒序层理等原生层面构造可以基本判断其原岩为沉积岩(雍永源等,1990;金鹭等,2017)。本次在吉塘镇酉西村一带的野外考察中,露头可见较为明显成层的片状构造,矿物具有明显的定向性。从矿物学角度看,多发育为浅变质岩系,新生变质矿物有绢云母、白云母、黑云母、绿泥石等富铝质的低变质级、低绿片岩相的变质矿物组合。在地球化学方面,样品具有高硅富铝富钾贫钙的岩石地球化学的特征,属于富铝系列,原岩类型很可能为泥质沉积岩(贺同兴等,1988)。酉西群样品主量元素中K2O>Na2O和MgO>CaO,显示其原岩可能含有沉积岩成分。通过DF函数判别式、周世泰(1984)K-A图解和尼格里指数原岩恢复图解(表 1、图 5a, b),酉西群样品显示出较明显的副变质岩特征。由于稀土元素和高场强元素可以将地球化学信息继承到沉积岩中,在两个稀土元素La/Yb-∑REE原岩判别图中(图 5c, d),酉西群样品既落入了沉积岩、花岗岩和碱性玄武岩的重合部分,又落入砂质岩与页岩相交接的位置,指示其原岩以泥沙质沉积岩为主,可能还有酸性岩浆岩和中基性玄武岩成分的加入。这与样品中片状矿物黑云母占有一定比例说明其原岩可能含有中基性凝灰质成分的判断一致。结合前人曾在酉西群发现原岩为基性火山岩的斜长角闪岩、原岩为中酸性凝灰岩的绿泥钠长片岩和白云石英片岩、以及原岩为含凝灰质长石石英砂岩的二云石英片岩(雍永源等,1990)等资料,我们认为该群原岩自下而上可能为砂砾岩夹长石石英砂岩-砂泥质岩夹基性火山岩-中酸性火山岩、凝灰岩夹基性火山岩等的原岩组合,其中上部未见明显露头。
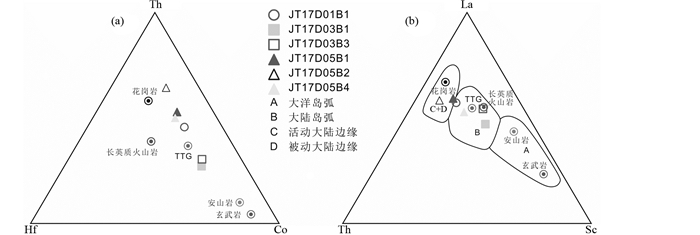
吉塘群变质程度较高,且由受到部分混合岩化的改造,因此原岩的组构特征残留很少。在变质作用过程中,大离子亲石元素(如Sr、K、Rb、Ba)和主量元素等活动性元素的含量会发生明显变化(Becker et al., 2000),但是稀土元素(REE)、高场强元素(如Zr、Ti、Hf、Y、Nb)和过渡族元素(如Co、Ni、V)等具有更为稳定的性质,在变质过程甚至是高级变质作用过程中其含量基本不变,能较好地反映原岩的性质和源区特征(Hajash, 1984;Taylor and McLennan, 1985;王中刚等,1989;Zheng et al., 2004)。本文运用稳定元素解析吉塘群黑云母二长片麻岩和黑云母斜长片麻岩的源区特征,进而对其原岩形成的构造背景进行制约。为避免各种交代作用的影响,La/Yb-∑REE原岩判别图利用化学稳定性较大的稀土元素(Allègre and Minster, 1978)。吉塘群部分样品落入沉积岩与花岗岩和碱性玄武岩的重合部位,对样品的进一步判别显示其成分为以粘土质为主,混入少量砂质岩成分(图 5c-d)。这些特征指示吉塘群原岩成分较为复杂,结合其镜下照片可见细小白云母和石英分布于石英颗粒间、长英质矿物含量高且有较多的黑云母等片柱状矿物定向排列的现象,反映其原岩性质具有碎屑岩或杂砂岩的特征(雍永源等,1990)。此外,该样品的主量元素体现了富硅富铝、高钾贫钙的特征,推断其原岩可能为以长英质粘土岩和砂砾岩为主,并混入了基性或中酸性的火山岩组分。研究表明长英质源区通常含有较多的Th、Zr、Hf、La,而镁铁质-超镁铁质源区则相对含有较多的Co、Sc、Cr(Jahn and Condie, 1995)。吉塘群样品投点大多靠近聚集在长英质火山岩和TTG成分之间,表明变沉积岩的碎屑物质主要来自花岗质岩石、长英质火山岩或类似TTG的源岩(图 10a, b)。前人在北侧类乌齐地区发现的吉塘群片麻岩原岩为一套碎屑岩夹中-基性火山岩(陈炳蔚,1987;李才等,2009a),而本次采集的南侧吉塘镇附近吉塘群片麻岩原岩以长英质的粘土岩和砂砾岩为主,从而证明了吉塘群南北岩石组成差异较大,其原岩成分也有一定区别。
|
图 10 Th-Hf-Co(a)和La-Th-Sc(b)图解(据Jahn and Condie, 1995修改; 平均成分据Condie, 1993) Fig. 10 Diagrams of Th-Hf-Co (a) and La-Th-Sc (b) (after Jahn and Condie, 1995; reference compositions from Condie, 1993) |
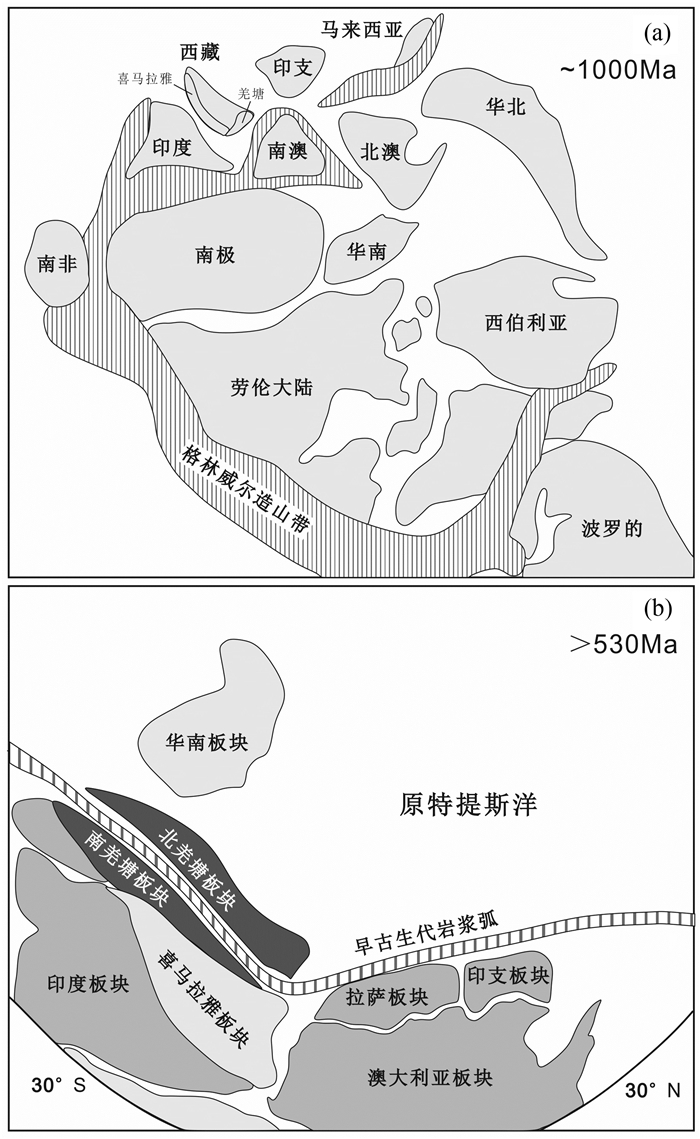
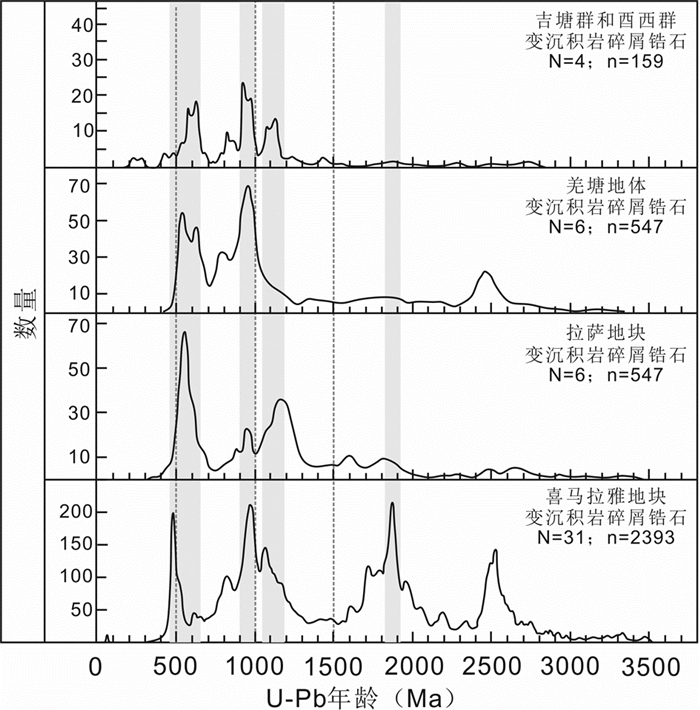
格林威尔造山运动是形成新元古代Rodinia超大陆的全球性造山作用,它形成了以劳伦大陆为中心,聚合澳大利亚、南极、印度、西伯利亚、波罗的、亚马逊、西非、刚果和北非等陆块的超大陆(Hoffman, 1991;Condie, 2001;图 11a)。格林威尔造山运动主要发生于中元古代(1300~1000Ma),之后在新元古代(900~700Ma)Rodinia超大陆逐渐发生裂解,但其过程具有明显的时空分布不均一性,聚合与裂解的时限在全球各地也略有不同。其中,印度东部Eastern Ghats带连接东南极大陆的格林威尔造山事件发生在960Ma左右(Mezger and Cosca, 1999),东南极北查尔斯王子山的格林威尔造山带形成于990~900Ma之间(Boger et al., 2000)。自二十世纪四十年代晋宁运动提出以来,其大地构造性质和时代可以与国际上格林威尔造山运动进行对比,并可以代表我国中元古代末会聚与新元古代裂解(1000~850Ma)的构造-岩浆热事件(Wang and Mo, 1995;白瑾等,1996;Zhang et al., 2012)。最新研究显示,除在喜马拉雅泛非基底和拉萨地块泛非基底中得到较多的格林威尔-晋宁构造-岩浆热事件年龄记录外,在羌塘地块及沿龙木错-双湖缝合带两侧均发现了中-新元古代构造-岩浆热事件的年龄纪录,例如在龙木错-双湖缝合带南侧戎马乡温泉石英岩中存在大量800~1200Ma的碎屑锆石,且主峰值为950Ma(Dong et al., 2011);在北羌塘地块玉树县宁多岩群变质岩的形成时代则被限定为990~1044Ma之间,且发现了年龄为990.5±3.7Ma的片麻状黑云母花岗岩侵入体(何世平等,2013)。本次研究测得碎屑锆石的主要年龄峰值范围为808~865Ma、925~997Ma以及1071~1119Ma,且主峰值为932Ma,代表了格林威尔-晋宁期构造-岩浆热事件在本区域十分发育。虽然现有的地球化学数据难以对形成变质基底的原岩源区性质进行进一步判断,但研究区碎屑锆石具有925~997Ma的峰值范围与南羌塘地块和喜马拉雅地块古生代碎屑锆石的峰值范围相近(Dong et al., 2011;Zhu et al., 2011),而1071~1119Ma的峰值范围与拉萨地块和高喜马拉雅地块发现的碎屑锆石年龄峰值范围类似(Zhu et al., 2011, 2013),这显示出吉塘变质杂岩体与喜马拉雅、拉萨和南羌塘地块具有类似的碎屑锆石年龄谱(图 12),成为南羌塘地块在中-新元古代期间可能属冈瓦纳大陆一部分的有力的佐证。
|
图 11 新元古代Rodinia超大陆古地理重建图(a,据Condie, 2001;Zhou et al., 2019)和青藏高原泛非期古地理重建图(b,据朱弟成等,2012;Zhu et al., 2013) Fig. 11 Palaeogeographic reconstruction of Neoproterozoic Rodinia (a, modified after Condie, 2001; Zhou et al., 2019) and palaeogeographic reconstruction of Pan-African in the Tibet Plateau (b, modified after Zhu et al., 2012, 2013) |
|
图 12 区域屑碎锆石年龄频谱对比图 重要年龄峰值用灰色条带标识.数据来源:吉塘群和酉西群(本文;金鹭等,2017);羌塘地体(Dong et al., 2011;Zhu et al., 2011);拉萨地体(Zhu et al., 2011);喜马拉雅地体(Gehrels et al., 2006a, b;McQuarrie et al., 2008, 2013;Myrow et al., 2009, 2010). N-样品数;n-锆石测试点 Fig. 12 Comparison of age distributions of detrital zircons from different regions Important age peaks are shown in grey bands. Data sources: Youxi Group (this study; Jin et al., 2017); Qiangtang metamorphic rocks (Dong et al., 2011; Zhu et al., 2011); Lhasa Terrane (Zhu et al., 2011); Himalaya Terrane (Gehrels et al., 2006a, b; McQuarrie et al., 2008, 2013; Myrow et al., 2009, 2010). N-number of samples; n-zircon test point |
泛非期造山运动以发生于600~500Ma之间的构造-岩浆热事件为主要形式,导致冈瓦纳超大陆在新元古代末至古生代初由东冈瓦纳和西冈瓦纳等几个大陆块体合并,在南极、印度和澳大利亚西南部之间形成了普雷兹-达令造山带(Fitzsimons, 2000;许志琴等,2005;Cawood and Buchan, 2007)。大量的泛非期构造-岩浆热事件的年龄可能与冈瓦纳超大陆的形成有关,在~530Ma的年龄峰值变质作用记录了冈瓦纳东部和西部的最终碰撞时间(Shabeer et al., 2005)。前人通过大量的研究与野外地质调查证明班公湖-怒江缝合带以南包括喜马拉雅地块以及拉萨地块的基底均为泛非基底,广泛发育前奥陶纪变质基底的泛非期构造-岩浆热事件(潘桂棠等, 1997, 2002, 2004b;DeCelles et al., 2000;许志琴等,2005;Cawood et al., 2007;李才,2008;Zhu et al., 2013),而近年来在北部羌塘地块变质基底中也相继发现了泛非期的年龄记录(Dong et al., 2011;He et al., 2011;何世平等,2013;Zhao et al., 2017)。冈瓦纳大陆前奥陶纪的变质基底泛非构造-岩浆热事件广泛发育,但其北部欧亚大陆南缘与之相邻地区的变质基底中却缺乏这一时期的年龄记录,这些年龄信息所代表的岩浆和变质事件可以成为判断碎屑岩物质来源及构造背景分析的有力证据(Rainbird et al., 1992;Morton et al., 1996)。在吉塘变质杂岩体碎屑锆石得到的一组年龄峰值在560~600Ma之间,成为沿龙木错-双湖缝合带南侧在藏东昌都地区首次发现可以代表泛非期构造-岩浆热事件的年龄记录。本次研究在吉塘变质杂岩体中获得的年龄与典型的泛非期造山运动时代(520~570Ma)相近(Cawood et al., 2007),略早于冈瓦纳大陆闭合的时间,表明原岩源区受泛非期造山事件的影响,碎屑物质可能来自洋盆闭合过程中岩浆活动产生的火成岩,支持了藏东南羌塘地块属冈瓦纳大陆的观点(图 11b)。而冈瓦纳大陆与欧亚大陆的边界是否需要北移则有待进一步详细的研究。
5 结论本文通过对藏东南羌塘地块酉西群变质岩和吉塘群变质岩进行系统的岩石学、岩相学、地球化学及锆石年代学研究,分析变质基底原岩组成、时代界限和地质意义,取得如下主要认识和成果:
(1) 酉西群片岩和吉塘群片麻岩的锆石整体为岩浆成因锆石,测得碎屑锆石的年龄峰值范围为560~600Ma、808~865Ma、925~997Ma和1071~1119Ma,认为变质基底的年龄主要由泛非期和格林威尔造山期的构造-岩浆热事件组成。
(2) 吉塘变质杂岩体岩性为副变质岩,其中酉西群片岩的原岩以泥沙质沉积岩为主,吉塘群片麻岩的原岩以长英质粘土岩和砂砾岩为主,两个岩群的变沉积岩碎屑物质主要来自花岗质岩石、长英质火山岩或类似TTG的源岩。
(3) 吉塘变质杂岩体所在的南羌塘地块与喜马拉雅地块和拉萨地块具有相近的物源区,认为南羌塘地块在中-新元古代期间可能属冈瓦纳大陆的一部分。
致谢 恰逢著名矿床学家翟裕生院士九十华诞,谨以此文感谢翟老师多年来的教导、关心和帮助,并表达对他的衷心祝愿!论文的完成得益于邓军教授等老师的指导。实验过程中得到了国家地质实验测试中心、中国地质大学(北京)矿物激光微区分析实验室(Milma Lab)的帮助,在此一并感谢。
Ai CX and Chen BW. 1986. Discussion on the geological age of Jiayuqiao Group and Jitang Group in eastern Tibet. Tibet Geology, (1): 13-17 (in Chinese) |
Allègre CJ and Minster JF. 1978. Quantitative models of trace element behavior in magmatic processes. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 38(1): 1-25 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(78)90123-1 |
Andersen T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2): 59-79 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X |
Bai J, Huang XG, Wang HC, Guo JJ, Yan YY, Xiu QY, Dai FY, Xu WZ and Wang GF. 1996. Precambrian Crustal Performance in China. 2nd Edition. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Becker H, Jochum KP and Carlson RW. 2000. Trace element fractionation during dehydration of eclogites from high-pressure terranes and the implications for element fluxes in subduction zones. Chemical Geology, 163(1-4): 65-99 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00071-6 |
Boger SD, Carson CJ, Wilson CML and Fanning CM. 2000. Neoproterozoic deformation in the Radok Lake region of the Northern Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica:Evidence for a single protracted orogenic event. Precambrian Research, 104(1-2): 1-24 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00079-6 |
Boynton WV. 1984. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements:Meteorite studies. Developments in Geochemistry, 2: 63-114 DOI:10.1016/B978-0-444-42148-7.50008-3 |
Cawood PA and Buchan C. 2007. Linking accretionary orogenesis with supercontinent assembly. Earth-Science Reviews, 82(3-4): 217-256 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2007.03.003 |
Cawood PA, Johnson MRW and Nemchin AA. 2007. Early Palaeozoic orogenesis along the Indian margin of Gondwana:Tectonic response to Gondwana assembly. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 255(1-2): 70-84 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.12.006 |
Chen BW. 1987. Geotectonics of the Nujiang-Lancangjiang-Jinshajiang Region. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Cheng LR, Chen SM and Zhang YC. 2007. Discovery of Early Paleozoic strata in south of Qiangtang, Northern Tibet and its significance. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 32(1): 59-62 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Condie KC. 1993. Chemical composition and evolution of the upper continental crust:Contrasting results from surface samples and shales. Chemical Geology, 104(1-4): 1-37 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(93)90140-E |
Condie KC. 2001. Continental growth during formation of Rodinia at 1.35~0.9Ga. Gondwana Research, 4(1): 5-16 DOI:10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70650-X |
Cui JT, Bian XW, Wang JC, Yang KJ, Zhu HP and Zhang JL. 2006. Discovery of an unconformity between the Lower Silurian and Middle Devonian in the Tianshuihu area, southern Kangxiwar, West Kunlun, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(12): 1437-1440 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
DeCelles PG, Gehrels GE, Quade J, LaReau B and Spurlin M. 2000. Tectonic implications of U-Pb zircon ages of the Himalayan Orogenic Belt in Nepal. Science, 288(5465): 497-499 DOI:10.1126/science.288.5465.497 |
Dempster TJ, Hay DC and Bluck BJ. 2004. Zircon growth in slate. Geology, 32(3): 221-224 DOI:10.1130/G20156.1 |
Deng J, Yang LQ, Ge LS, Yuan SS, Wang QF, Zhang J, Gong QJ and Wang CM. 2010. Character and post-ore changes, modifications and preservation of Cenozoic alkali-rich porphyry gold metallogenic system in western Yunnan, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(6): 1633-1645 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Deng J, Yang LQ and Wang CM. 2011. Research advances of superimposed orogenesis and metallogenesis in the Sanjiang Tethys. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2501-2509 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Deng J, Wang CM and Li GJ. 2012. Style and process of the superimposed mineralization in the Sanjiang Tethys. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(5): 1349-1361 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ, Li CS and Wang CM. 2014a. Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region, SW China. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 419-437 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.08.002 |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ and Santosh M. 2014b. Cenozoic tectono-magmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China. Earth-Science Reviews, 138: 268-299 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.05.015 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Li WC, Yang LQ and Wang QF. 2014. The situation and enlightenment of the research of the tectonic evolution and metallogenesis in the Sanjiang Tethys. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(1): 52-64 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Deng J, Wang QF and Li GJ. 2017a. Tectonic evolution, superimposed orogeny, and composite metallogenic system in China. Gondwana Research, 50: 216-266 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.02.005 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Selvaraja V, Jeon H, Wu B and Yang LF. 2017b. Insights into ore genesis of the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan Province, China:Evidence from Zn and in-situ S isotopes. Ore Geology Reviews, 90: 943-957 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.036 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Santosh M and Yao EY. 2018a. Crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the south-eastern North China Craton. Earth-Science Reviews, 182: 251-272 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.05.001 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Zi JW, Xia R and Li Q. 2018b. Constraining subduction-collision processes of the Paleo-Tethys along the Changning-Menglian Suture:New zircon U-Pb ages and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf-O isotopes of the Lincang Batholith. Gondwana Research, 62: 75-92 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.10.008 |
Dong CY, Li C, Wan YS, Wang W, Wu YW, Xie HQ and Liu DY. 2011. Detrital zircon age model of Ordovician Wenquan quartzite south of Lungmuco-Shuanghu suture in the Qiangtang area, Tibet:Constraint on tectonic affinity and source regions. Science China (Earth Sciences), 54(7): 1034-1042 DOI:10.1007/s11430-010-4166-x |
Du B, Wang CM, He XY, Yang LF, Chen JY, Shi KX, Luo Z and Xia JS. 2016. Advances in research of bulk-rock Nd and zircon Hf isotopic mappings:Case study of the Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2555-2570 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Du B, Wang CM, Yang LF, Shi KX, Zhang D, Chen Q, Zhu JX and Zhang SH. 2018. Magma source and formation mechanism of the Zhuopan alkaline complex in Yongping, Southwest China:Constraints from geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(5): 1376-1396 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Fitzsimons ICW. 2000. Grenville-age basement provinces in East Antarctica:Evidence for three separate collisional orogens. Geology, 28(10): 879-882 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<879:GBPIEA>2.0.CO;2 |
Gehrels GE, DeCelles PG, Ojha TP and Upreti BN. 2006a. Geologic and U-Th-Pb geochronologic evidence for Early Paleozoic tectonism in the Kathmandu thrust sheet, central Nepal Himalaya. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 118(1-2): 185-198 DOI:10.1130/B25753.1 |
Gehrels GE, DeCelles PG, Ojha TP and Upreti BN. 2006b. Geologic and U-Pb geochronologic evidence for Early Paleozoic tectonism in the Dadeldhura thrust sheet, far-west Nepal Himalaya. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 28(4-6): 385-408 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.012 |
Geng JZ, Qiu KF, Gou ZY and Yu HC. 2017. Tectonic regime switchover of Triassic Western Qinling Orogen:Constraints from LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology and Lu-Hf isotope of Dangchuan intrusive complex in Gansu, China. Geochemistry, 77(4): 673-651 |
Gou ZY, Yu HC, Qiu KF, Geng JZ, Wu MQ, Wang YG, Yu MH and Li J. 2019. Petrogenesis of ore-hosting diorite in the Zaorendao gold deposit at the Tongren-Xiahe-Hezuo polymetallic district, West Qinling, China. Minerals, 9(2): 76 DOI:10.3390/min9020076 |
Hajash A Jr. 1984. Rare earth element abundances and distribution patterns in hydrothermally altered basalts:Experimental results. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 85(4): 409-412 DOI:10.1007/BF01150297 |
He SP, Li RS, Wang C, Zhang HF, Ji WH, Yu PS, Gu PY and Shi C. 2011. Discovery of~4.0Ga detrital zircons in the Changdu block, North Qiangtang, Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56(7): 647-658 DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-4320-z |
He SP, Li RS, Yu PS, Gu PY, Wang C, Yang YS and Zhang WJ. 2012. The age of Youxi Formation of Jitang rock group in Taniantaweng Mountains, northern Qiangtang, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(6): 985-993 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
He SP, Li RS, Wang C, Gu PY, Yu PS, Shi C and Zha XF. 2013. Research on the formation age of Ningduo rock group in Changdu block:Evidence for the existence of basement in the North Qiangtang. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(5): 15-24 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
He TX, Lu LZ, Li SX and Lan YQ. 1988. Metamorphic Rock Petrology. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Hoffman PF. 1991. Did the breakout of Laurentia turn Gondwanaland inside-out?. Science, 252(5011): 1409-1412 DOI:10.1126/science.252.5011.1409 |
Hoskin POW and Schaltegger U. 2003. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 27-62 DOI:10.2113/0530027 |
Hu PY, Li C, Yang HT, Zhang HB and Yu H. 2010. Characteristic, zircon dating and tectonic significance of Late Triassic granite in the Guoganjianianshan area, central Qiangtang, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(12): 1825-1832 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu PY, Li C, Li J, Wang M, Xie CM and Wu YW. 2014. Zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopes and whole-rock geochemistry of gneissic granites from the Jitang complex in Leiwuqi area, eastern Tibet, China:Record of the closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Tectonophysics, 623: 83-99 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2014.03.018 |
Hu ZC, Liu YS, Gao S, Liu WG, Zhang W, Tong XR, Lin L, Zong KQ, Li M, Chen HH, Zhou L and Yang L. 2012. Improved in situ Hf isotope ratio analysis of zircon using newly designed X skimmer cone and jet sample cone in combination with the addition of nitrogen by laser ablation multiple collector ICP-MS. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 27(9): 1391-1399 DOI:10.1039/c2ja30078h |
Huang JJ. 2001a. Tectonic characteristics and evolution of the Qiangtang Basin. Regional Geology of China, 20(2): 178-186 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Huang JJ. 2001b. Structural characteristics of the basement of the Qiangtang Basin. Acta Geologica Sinica, 75(3): 333-337 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Jackson SE, Pearson NJ, Griffin WL and Belousova EA. 2004. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology. Chemical Geology, 211(1-2): 47-69 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.06.017 |
Jahn BM and Condie KC. 1995. Evolution of the Kaapvaal craton as viewed from geochemical and Sm-Nd isotopic analyses of intracratonic pelites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(11): 2239-2258 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(95)00103-7 |
Jin L, Wang Q, Zhu DC, Xie JC and Zhang LL. 2017. Age and provenance of some key strata from Zuogong-Zhuka in Eastern Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(8): 2523-2534 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Kapp P, Yin A, Manning CE, Murphy M, Harrison TM, Spurlin M, Ding L, Deng XG and Wu CM. 2000. Blueschist-bearing metamorphic core complexes in the Qiangtang block reveal deep crustal structure of northern Tibet. Geology, 28(1): 19-22 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<19:BMCCIT>2.0.CO;2 |
Li C. 1987. The Longmucuo-Shuanghu-Lancangjiang plate suture and the north boundary of distribution of Gondwana facies Permo-Carboniferous system in northern Xizang, China. Journal of Changchun College of Geology, 17(2): 155-166 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li C. 2003. Question about the basement of the Qiangtang micro-plate. Geological Review, 49(1): 5-9 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li C, Cheng LR, Zhang YC and Zhai QG. 2004. Discovery of Ordovician-Devonian strata in the south of the Qiangtang area, Tibet. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(5-6): 602-604 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li C, Zhai QG, Cheng LR, Xu F and Huang XP. 2005. Thought on some key geological problems in the Qiangtang area, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geological Bulletin of China, 24(4): 295-301 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li C, Huang XP, Zhai QG, Zhu TX, Yu YS, Wang GH and Zeng QG. 2006. The Longmu Co-Shuanghu-Jitang plate suture and the northern boundary of Gondwanaland in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(4): 136-147 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li C. 2008. A review on 20 years' study of the Longmu Co-Shuanghu-Lancang River suture zone in Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau. Geological Review, 54(1): 105-119 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li C, Xie YW, Dong YS, Qiangba ZX and Jiang GW. 2009a. Discussion on the age of Jitang Group around Leiwuqi area, eastern Tibet, China and primary understanding. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(9): 1178-1180 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li C, Xie YW, Dong YS, Xu F, Qiangba ZX and Jiang GW. 2009b. The North Lancangjiang suture:The boundary between Gondwana and Yangtze?. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(12): 1711-1719 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li P. 1955. Preliminary understanding of geology in eastern Tibet. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52-71: 62-71, 52 (in Chinese) |
Liu Y, Zhu ZM, Chen C, Zhang SP, Sun X, Yang ZS and Liang W. 2015. Geochemical and mineralogical characteristics of weathered ore in the Dalucao REE deposit, Mianning-Dechang REE Belt, western Sichuan Province, southwestern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 71: 437-456 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.06.009 |
Liu Y and Hou ZQ. 2017. A synthesis of mineralization styles with an integrated genetic model of carbonatite-syenite-hosted REE deposits in the Cenozoic Mianning-Dechang REE metallogenic belt, the eastern Tibetan Plateau, southwestern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 137: 35-79 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.01.010 |
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Gao S, Günther D, Xu J, Gao CG and Chen HH. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34-43 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 |
Liu YS, Gao S, Hu ZC, Gao CG, Zong KQ and Wang DB. 2010a. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the trans-North China orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2): 537-571 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egp082 |
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Zong KQ, Gao CG, Gao S, Xu J and Chen HH. 2010b. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(15): 1535-1546 DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4 |
Ludwig KR. 2001. Users manual for Isoplot/ex rev. 2.49:A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Centre Special Publication, 1a: 1-56 |
McQuarrie N, Robinson D, Long S, Tobgay T, Grujic D, Gehrels G and Ducea M. 2008. Preliminary stratigraphic and structural architecture of Bhutan:Implications for the along strike architecture of the Himalayan System. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 272(1-2): 105-117 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.04.030 |
McQuarrie N, Long SP, Tobgay T, Nesbit JN, Gehrels G and Ducea MN. 2013. Documenting basin scale, geometry and provenance through detrital geochemical data:Lessons from the Neoproterozoic to Ordovician Lesser, Greater, and Tethyan Himalayan strata of Bhutan. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1491-1510 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.09.002 |
Metcalfe I. 2002. Permian tectonic framework and palaeogeography of SE Asia. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 20(6): 551-566 DOI:10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00022-6 |
Metcalfe I. 2013. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion:Tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 66: 1-33 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.020 |
Mezger K and Cosca MA. 1999. The thermal history of the Eastern Ghats Belt (India) as revealed by U-Pb and 40Ar/39Ar dating of metamorphic and magmatic minerals:Implications for the SWEAT correlation. Precambrian Research, 94(3-4): 251-271 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(98)00118-1 |
Mo XX, Lu FX, Shen SY, Zhu QW, Hou ZQ and Yang KH. 1993. Sanjiang Tethyan Volcano and Mineralization. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Mo XX, Deng JF and Lu FX. 1994. Volcanism and the evolution of Tethys in Sanjiang area, southwestern China. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 9(4): 325-333 DOI:10.1016/0743-9547(94)90043-4 |
Morton AC, Claoué-Long JC and Berge C. 1996. SHRIMP constraints on sediment provenance and transport history in the Mesozoic Statfjord Formation, North Sea. Journal of the Geological Society, 153(6): 915-929 DOI:10.1144/gsjgs.153.6.0915 |
Myrow PM, Hughes NC, Searle MP, Fanning CM, Peng SC and Parcha SK. 2009. Stratigraphic correlation of Cambrian-Ordovician deposits along the Himalaya:Implications for the age and nature of rocks in the Mount Everest region. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 121(3-4): 323-332 DOI:10.1130/B26384.1 |
Myrow PM, Hughes NC, Goodge JW, Fanning CM, Williams IS, Peng SC, Bhargava ON, Parcha SK and Pogue KR. 2010. Extraordinary transport and mixing of sediment across Himalayan central Gondwana during the Cambrian-Ordovician. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 122(9-10): 1660-1670 DOI:10.1130/B30123.1 |
Pan GT, Chen ZL and Li XZ. 1997. The Geological Tectonic Evolution in the Eastern Tethys. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Pan GT, Li XZ, Wang LQ, Ding J and Chen ZL. 2002. Preliminary division of tectonic units of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its adjacent regions. Geological Bulletin of China, 21(11): 701-707 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Pan GT, Ding J and Yao DS, et al. 2004a. Guidebook of 1:1500000 Geologic Map of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau and Adjacent Areas. Chengdu: Chengdu Cartographic Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Pan GT, Zhu DC, Wang LQ, Liao ZL, Geng QR and Jiang XS. 2004b. Bangong Lake-Nu River suture zone-the northern boundary of Gondwanaland:Evidence from geology and geophysics. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(4): 371-382 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Peng TP, Zhao GC, Fan WM, Peng BX and Mao YS. 2015. Late Triassic granitic magmatism in the eastern Qiangtang, eastern Tibetan Plateau:Geochronology, petrogenesis and implications for the tectonic evolution of the Paleo-Tethys. Gondwana Research, 27(4): 1494-1508 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2014.01.009 |
Pullen A, Kapp P, Gehrels GE, Ding L and Zhang QH. 2011. Metamorphic rocks in central Tibet:Lateral variations and implications for crustal structure. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 123(3-4): 585-600 DOI:10.1130/B30154.1 |
Qi QJ, Zhang ZC, Dong SY, Zhang DY, Huang H, Zhang S and Ma LT. 2011. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic setting of Mesoproterozoic metamorphic rocks in Aksu area, southwestern Tianshan Mountains. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 30(2): 172-184 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Qiu KF and Deng J. 2017. Petrogenesis of granitoids in the Dewulu skarn copper deposit:Implications for the evolution of the Paleotethys Ocean and mineralization in Western Qinling, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 90: 1078-1098 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.027 |
Qiu KF, Yu HC, Gou ZY, Liang ZL, Zhang JL and Zhu R. 2018. Nature and origin of Triassic igneous activity in the Western Qinling Orogen:The Wenquan composite pluton example. International Geology Review, 60(2): 242-266 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2017.1334598 |
Rainbird RH, Hearnan LM and Young G. 1992. Sampling Laurentia:Detrital zircon geochronology offers evidence for an extensive Neoproterozoic river system originating from the Grenville orogen. Geology, 20(4): 351-354 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0351:SLDZGO>2.3.CO;2 |
Roser BP and Korsch RJ. 1986. Determination of tectonic setting of sandstone-mudstone suites using SiO2 content and K2O/Na2O ratio. The Journal of Geology, 94(5): 635-650 DOI:10.1086/629071 |
Şengör AMC. 1990. Plate tectonics and orogenic research after 25 years:A Tethyan perspective. Earth-Science Reviews, 27(1-2): 1-201 DOI:10.1016/0012-8252(90)90002-D |
Sha SL, Xie YW, Peng DP, Chen YM, Liu XL and Zhang N. 2012. A brief discussion of the Jitang Group in eastern Tibet. Geology and Exploration, 48(4): 768-774 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Shabeer KP, Satish-Kumar M, Armstrong R and Buick IS. 2005. Constraints on the timing of Pan-African granulite-facies metamorphism in the Kerala Khondalite Belt of southern India:SHRIMP mineral ages and Nd isotopic systematics. Journal of Geology, 113(1): 95-106 DOI:10.1086/425971 |
Shaw DM. 1972. The origin of the Apsley gneiss, Ontario. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 9(1): 18-35 DOI:10.1139/e72-002 |
Sláma J, Košler J, Condon DJ, Crowley JL, Gerdes A, Hanchar JM, Horstwood MSA, Morris GA, Nasdala L, Norberg N, Schaltegger U, Schoene B, Tubrett MN and Whitehouse MJ. 2008. Plešovice zircon:A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis. Chemical Geology, 249(1-2): 1-35 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.11.005 |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345
|
Tao Y, Bi XW, Li JG, Zhu FL, Liao MY and Li YB. 2011. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Jitang granitoids in Tibet, SW China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2763-2774 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Tao Y, Bi XW, Li CS, Hu RZ, Li YB and Liao MY. 2014. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the Jitang granitic pluton in eastern Tibet, SW China. Lithos, 184-187: 314-323 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.10.031 |
Taylor SR and McLennan SM. 1985. The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1-312
|
Wang BD, Wang LQ, Chen JL, Liu H, Yin FG and Li XB. 2017. Petrogenesis of Late Devonian-Early Carboniferous volcanic rocks in northern Tibet:New constraints on the Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Tethyan Ocean. Gondwana Research, 41: 142-156 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.09.007 |
Wang CM, Deng J, Carranza EJM and Lai XR. 2014a. Nature, diversity and temporal-spatial distributions of sediment-hosted Pb-Zn deposits in China. Ore Geology Reviews, 56: 327-351 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.06.004 |
Wang CM, Deng J, Carranza EJM and Santosh M. 2014b. Tin metallogenesis associated with granitoids in the southwestern Sanjiang Tethyan Domain:Nature, deposit types, and tectonic setting. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 576-593 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.005 |
Wang CM, Deng J, Santosh M, Lu YJ, McCuaig TC, Carranza EJM and Wang QF. 2015a. Age and origin of the Bulangshan and Mengsong granitoids and their significance for post-collisional tectonics in the Changning-Menglian Paleo-Tethys Orogen. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113: 656-676 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.05.001 |
Wang CM, Deng J, Lu YJ, Bagas L, Kemp AIS and McCuaig TC. 2015b. Age, nature, and origin of Ordovician Zhibenshan granite from the Baoshan Terrane in the Sanjiang region and its significance for understanding Proto-Tethys evolution. International Geology Review, 57(15): 1922-1939 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2015.1043358 |
Wang CM, Bagas L, Lu YJ, Santosh M, Du B and Campbell McCuaig T. 2016. Terrane boundary and spatio-temporal distribution of ore deposits in the Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen:Insights from zircon Hf-isotopic mapping. Earth-Science Reviews, 156: 39-65 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.02.008 |
Wang CM, Deng J, Bagas L and Wang Q. 2017. Zircon Hf-isotopic mapping for understanding crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the Eastern Qinling Orogen. Gondwana Research, 50: 293-310 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.04.008 |
Wang CM, Chen JY, Yang LF, Zhang D, Du B and Shi KX. 2017. Tectonic-fluid-mineral system in the Lanping basin, Sanjiang Tethys. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(7): 1975-1977 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang CM, Yang LF, Bagas L, Evans NJ, Chen JY and Du B. 2018a. Mineralization processes at the giant Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Lanping Basin, Sanjiang Tethys Orogen:Evidence from in situ trace element analysis of pyrite and marcasite. Geological Journal, 53(4): 1279-1294 DOI:10.1002/gj.v53.4 |
Wang CM, Bagas L, Chen JY, Yang LF, Zhang D, Du Bi and Shi KX. 2018b. The genesis of the Liancheng Cu-Mo deposit in the Lanping Basin of SW China:Constraints from geology, fluid inclusions, and Cu-S-H-O isotopes. Ore Geology Reviews, 92: 113-128 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.11.012 |
Wang GH, Zhou X, Pu BCR and Zeng QG. 1996. The Structural Deformation and Evolution of Tanitawen Mt. Range. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Wang GH. 2006. Structural characteristics and emplace mechanism of Tanitawen Mt. Range metamorphic complex in the eastern margin of Tibet Plateau. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-115
|
Wang GZ and Wang CS. 2001. Disintegration and age of basement metamorphic rocks in Qiangtang, Tibet, China. Science in China (Series D), 44(Suppl 1): 86-93 |
Wang HZ and Mo XX. 1995. An outline of the tectonic evolution of China. Episodes, 18(1-2): 6-16 |
Wang RM, He GP, Chen ZZ, Zheng SY and Geng YS. 1987. Graphical Discrimination Method for Metamorphic Rock Original Rock. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Wang ZG, Yu XY and Zhao ZH. 1989. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese)
|
Whitehouse MJ and Kamber BS. 2002. On the overabundance of light rare earth elements in terrestrial zircons and its implication for Earth's earliest magmatic differentiation. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 204(3-4): 333-346 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(02)01000-2 |
Wiedenbeck M, Hanchar JM, Peck WH, Sylvester P, Valley J, Whitehouse M, Kronz A, Morishita Y, Nasdala L, Fiebig J, Franchi I, Girard JP, Greenwood RC, Hinton R, Kita N, Mason PRD, Norman M, Ogasawara M, Piccoli PM, Rhede D, Satoh H, Schulz-Dobrick B, Skår O, Spicuzza MJ, Terada K, Tindle A, Togashi S, Vennemann T, Xie Q and Zheng YF. 2004. Further characterisation of the 91500 zircon crystal. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 28(1): 9-39 DOI:10.1111/ggr.2004.28.issue-1 |
Winkler HGF. 1976. Petrogenesis of Metamorphic Rocks. 2nd Edition. New York: Springer, 1-334
|
Wu YB and Zheng YF. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(16): 1589-1604 (in Chinese) |
Xia J, Zhong HM, Tong JS and Lu RK. 2006. Unconformity between the Lower Ordovician and Devonian in the Sanchakou area in the eastern part of the Lungmu Co, northern Tibet, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(1-2): 113-117 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xie CM, Li C, Dong YS, Wu YW, Wang M and Hu PY. 2010. Gangmari-Juhuashan thrust nappe were discovered in central Qiangtang, northern Tibet, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(12): 1857-1862 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Liang FH, Qi XX, Liu FL, Zeng LS, Liu DY, Li HB, Wu CL, Shi RD and Chen SY. 2005. Pan-African and Early Paleozoic orogenic events in the Himalaya Terrane:Inference from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(1): 1-12 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu ZQ, Li HB and Yang JS. 2006. An orogenic plateau:The orogenic collage and orogenic types of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(4): 1-17 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu ZQ, Dilek Y, Cao H, Yang JS, Robinson P, Ma CQ, Li HQ, Jolivet M, Roger F and Chen XJ. 2015. Paleo-Tethyan evolution of Tibet as recorded in the East Cimmerides and West Cathaysides. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 105: 320-337 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.01.021 |
Yang LF, Shi KX, Wang CM, Wu B, Du B, Chen JY, Xia JS and Chen J. 2016. Ore genesis of the Jinman copper deposit in the Lanping Basin, Sanjiang Orogen:Constraints by copper and sulfur isotopes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2392-2406 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang LF, Wang CM, Bagas L, Du B and Zhang D. 2019. Mesozoic-Cenozoic sedimentary rock records and applications for provenance of sediments and affiliation of the Simao Terrane, SW China. International Geology Review DOI:10.1080/00206814.2019.1587671 |
Yang TN, Zhang HR, Liu YX, Wang ZL, Song YC, Yang ZS, Tian SH, Xie HQ and Hou KJ. 2011. Permo-Triassic arc magmatism in central Tibet:Evidence from zircon U-Pb geochronology, Hf isotopes, rare earth elements, and bulk geochemistry. Chemical Geology, 284(3-4): 270-282 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.03.006 |
Yin A and Harrison TM. 2000. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28: 211-280 DOI:10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211 |
Yong YY, Xiang TX and Wang JM. 1990. Some new observations on North Lancangjiang metamorphic rocks. Contribution to the Geology of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau, 20: 67-71 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yu HC, Guo CA, Qiu KF, McIntire D, Jiang GP, Gou ZY, Geng JZ, Pang Y, Zhu R and Li NB. 2019. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the formation of the giant Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit, West Qinling, China. Minerals, 9(1): 37 DOI:10.3390/min9010037 |
Zhai QG, Li C and Huang XP. 2006. Geochemistry of Permian basalt in the Jiaomuri area, central Qiangtang, Tibet, China, and its tectonic significance. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(12): 1419-1427 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai QG, Jahn BM, Zhang RY, Wang J and Su L. 2011. Triassic subduction of the Paleo-Tethys in northern Tibet, China:Evidence from the geochemical and isotopic characteristics of eclogites and blueschists of the Qiangtang Block. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 42(6): 1356-1370 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.07.023 |
Zhai QG, Jahn BM, Wang J, Su L, Mo XX, Wang KL, Tang SH and Lee HY. 2013. The Carboniferous ophiolite in the middle of the Qiangtang Terrane, Northern Tibet:SHRIMP U-Pb dating, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic characteristics. Lithos, 168-169: 186-199 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.02.005 |
Zhang ZC, Kang JL, Kusky T, Santosh M, Huang H, Zhang DY and Zhu J. 2012. Geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of Neoproterozoic basalts from Sugetbrak, Northwest Tarim block, China:Implications for the onset of Rodinia supercontinent breakup. Precambrian Research, 220-221: 158-176 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2012.08.002 |
Zhao TY, Feng QL, Metcalfe I, Milan LA, Liu GC and Zhang ZB. 2017. Detrital zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopes and provenance of Late Neoproterozoic and Early Paleozoic sediments of the Simao and Baoshan blocks, SW China:Implications for proto-Tethys and paleo-Tethys evolution and Gondwana reconstruction. Gondwana Research, 51: 193-208 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.07.012 |
Zhao ZZ, Li YT, Ye HF and Zhang YW. 2001. Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese)
|
Zheng HW, He RZ and Yang G. 2012. Geological and geophysical characteristics of Shuanghu-Gangmacuo-Longmucuo structural belt in Qiangtang area. Geology in China, 39(5): 1229-1235 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zheng YF, Wu YB, Chen FK, Gong B, Li L and Zhao ZF. 2004. Zircon U-Pb and oxygen isotope evidence for a large-scale 18O depletion event in igneous rocks during the Neoproterozoic. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(20): 4145-4165 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2004.01.007 |
Zhou ST. 1984. Examination of 17 pertrochemical methods of restoring protoliths of metamorphic rocks. Geological Review, 30(1): 81-84 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhou X, Zheng JP, Li YB, Griffin WL, Xiong Q, Moghadam HS and O'Reilly SY. 2019. Neoproterozoic sedimentary rocks track the location of the Lhasa Block during the Rodinia breakup. Precambrian Research, 320: 63-77 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2018.10.005 |
Zhou ZG, Liu WC and Liang DY. 2004. Discovery of the Ordovician and its basal conglomerate in the Kangmar area, southern Tibet:With a discussion of the relation of the sedimentary cover and unifying basement in the Himalayas. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(7): 655-663 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Niu YL, Dilek Y and Mo XX. 2011. Lhasa terrane in southern Tibet came from Australia. Geology, 39(8): 727-730 DOI:10.1130/G31895.1 |
Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Niu YL, Wang Q, Dilek Y, Dong GC and Mo XX. 2012. Origin and Paleozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Lhasa Terrane. Geological Journal of China Universities, 18(1): 1-15 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Niu YL, Dilek Y, Hou ZQ and Mo XX. 2013. The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1429-1454 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.002 |
艾长兴, 陈炳蔚. 1986. 对西藏东部嘉玉桥群及吉塘群地质时代问题的讨论. 西藏地质, (1): 13-17. |
白瑾, 黄学光, 王惠初, 郭进京, 颜耀阳, 修群业, 戴凤岩, 徐文蒸, 王官福. 1996. 中国前寒武纪地壳演化. 第2版. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
陈炳蔚. 1987. 怒江-澜沧江-金沙江地区大地构造. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
程立人, 陈寿铭, 张以春. 2007. 藏北羌塘南部发现早古生代地层及意义. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 32(1): 59-62. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2007.01.008 |
崔建堂, 边小卫, 王炬川, 杨克俭, 朱海平, 张俊良. 2006. 西昆仑康西瓦南部甜水湖一带下志留统与中泥盆统不整合界面的发现. 地质通报, 25(12): 1437-1440. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.12.012 |
邓军, 杨立强, 葛良胜, 袁士松, 王庆飞, 张静, 龚庆杰, 王长明. 2010. 滇西富碱斑岩型金成矿系统特征与变化保存. 岩石学报, 26(6): 1633-1645. |
邓军, 杨立强, 王长明. 2011. 三江特提斯复合造山与成矿作用研究进展. 岩石学报, 27(9): 2501-2509. |
邓军, 王长明, 李龚健. 2012. 三江特提斯叠加成矿作用样式及过程. 岩石学报, 28(5): 1349-1361. |
邓军, 王长明, 李文昌, 杨立强, 王庆飞. 2014. 三江特提斯复合造山与成矿作用研究态势及启示. 地学前缘, 21(1): 52-64. |
杜斌, 王长明, 贺昕宇, 杨立飞, 陈晶源, 石康兴, 罗政, 夏锦胜. 2016. 锆石Hf和全岩Nd同位素填图研究进展:以三江特提斯造山带为例. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2555-2570. |
杜斌, 王长明, 杨立飞, 石康兴, 张端, 陈奇, 祝佳萱, 张淑花. 2018. 西南三江永平卓潘碱性杂岩体源区与形成机制:全岩元素、锆石U-Pb年代学和Hf同位素联合约束. 岩石学报, 34(5): 1376-1396. |
何世平, 李荣社, 于浦生, 辜平阳, 王超, 杨永成, 张维吉. 2012. 青藏高原北羌塘他念他翁山吉塘岩群酉西岩组时代的确定. 地质学报, 86(6): 985-993. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.06.012 |
何世平, 李荣社, 王超, 辜平阳, 于浦生, 时超, 查显锋. 2013. 昌都地块宁多岩群形成时代研究:北羌塘基底存在的证据. 地学前缘, 20(5): 15-24. |
贺同兴, 卢良兆, 李树勋, 兰玉琦. 1988. 变质岩岩石学. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
胡培远, 李才, 杨韩涛, 张海波, 于红. 2010. 青藏高原羌塘中部果干加年山一带晚三叠世花岗岩的特征、锆石定年及其构造意义. 地质通报, 29(12): 1825-1832. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.12.010 |
黄继钧. 2001a. 藏北羌塘盆地构造特征及演化. 中国区域地质, 20(2): 178-186. |
黄继钧. 2001b. 羌塘盆地基底构造特征. 地质学报, 75(3): 333-337. |
金鹭, 王青, 朱弟成, 谢锦程, 张亮亮. 2017. 藏东左贡-竹卡地区一些关键地层的时代和物源区示踪. 岩石学报, 33(8): 2523-2534. |
李才. 1987. 龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带与石炭二叠纪冈瓦纳北界. 长春地质学院学报, 17(2): 155-166. |
李才. 2003. 羌塘基底质疑. 地质论评, 49(1): 5-9. |
李才, 程立人, 张以春, 翟庆国. 2004. 西藏羌塘南部发现奥陶纪-泥盆纪地层. 地质通报, 23(5-6): 602-604. |
李才, 翟庆国, 程立人, 徐峰, 黄小鹏. 2005. 青藏高原羌塘地区几个关键地质问题的思考. 地质通报, 24(4): 295-301. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2005.04.001 |
李才, 黄小鹏, 翟庆国, 朱同兴, 于远山, 王根厚, 曾庆高. 2006. 龙木错-双湖-吉塘板块缝合带与青藏高原冈瓦纳北界. 地学前缘, 13(4): 136-147. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.04.011 |
李才. 2008. 青藏高原龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带研究二十年. 地质论评, 54(1): 105-119. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.01.012 |
李才, 谢尧武, 董永胜, 强巴扎西, 蒋光武. 2009a. 藏东类乌齐一带吉塘岩群时代讨论及初步认识. 地质通报, 28(9): 1178-1180. |
李才, 谢尧武, 董永胜, 徐锋, 强巴扎西, 蒋光武. 2009b. 北澜沧江带的性质——是冈瓦纳板块与扬子板块的界线吗?. 地质通报, 28(2): 1711-1719. |
李璞. 1955. 西藏东部地质的初步认识. 科学通报, 52(7): 62-71, 52. |
莫宣学, 路凤香, 沈上越, 朱勤文, 侯增谦, 杨开辉. 1993. 三江特提斯火山作用与成矿. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
潘桂棠, 陈智梁, 李兴振, 等. 1997. 东特提斯地质构造形成演化. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
潘桂棠, 李兴振, 王立全, 丁俊, 陈智梁. 2002. 青藏高原及邻区大地构造单元初步划分. 地质通报, 21(11): 701-707. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.11.002 |
潘桂棠, 丁俊, 姚东生, 等. 2004a. 青藏高原及邻区地质图(1:1500000). 成都: 成都地图出版社.
|
潘桂棠, 朱弟成, 王立全, 廖忠礼, 耿全如, 江新胜. 2004b. 班公湖-怒江缝合带作为冈瓦纳大陆北界的地质地球物理证据. 地学前缘, 11(4): 371-382. |
齐秋菊, 张招崇, 董书云, 张东阳, 黄河, 张舒, 马乐天. 2011. 西南天山阿克苏地区中元古代变质岩的地球化学特征及其构造背景. 岩石矿物学杂志, 30(2): 172-184. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.02.002 |
沙绍礼, 谢尧武, 彭道平, 陈应明, 刘学龙, 张娜. 2012. 略谈藏东吉塘群. 地质与勘探, 48(4): 768-774. |
陶琰, 毕献武, 李金高, 朱飞霖, 廖名扬, 李玉帮. 2011. 西藏吉塘花岗岩地球化学特征及成因. 岩石学报, 27(9): 2763-2774. |
王长明, 陈晶源, 杨立飞, 张端, 杜斌, 石康兴. 2017. 三江特提斯兰坪盆地构造-流体-成矿系统. 岩石学报, 33(7): 1957-1977. |
王根厚, 周详, 普布次仁, 曾庆高. 1996. 西藏他念他翁山链构造变形及其演化. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
王根厚. 2006.藏东他念他翁山链变质杂岩系变形特征及表露机制.博士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学, 1-115
|
王国芝, 王成善. 2001. 西藏羌塘基底变质岩系的解体和时代厘定. 中国科学(D辑), 31(增1): 77-82. |
王仁民, 贺高品, 陈珍珍, 郑松彦, 耿元生. 1987. 变质岩原岩图解判别法. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
王中刚, 于学元, 赵振华. 1989. 稀土元素地球化学. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约. 科学通报, 49(16): 1589-1604. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 |
夏军, 钟华明, 童劲松, 鲁如魁. 2006. 藏北龙木错东部三岔口地区下奥陶统与泥盆系的不整合界面. 地质通报, 25(1-2): 113-117. |
解超明, 李才, 董永胜, 吴彦旺, 王明, 胡培远. 2010. 青藏高原羌塘中部冈玛日——菊花山地区大型逆冲推覆构造的基本特征及形成机制. 地质通报, 29(12): 1857-1862. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.12.014 |
许志琴, 杨经绥, 梁凤华, 戚学祥, 刘福来, 曾令森, 刘敦一, 李海兵, 吴才来, 史仁灯, 陈松永. 2005. 喜马拉雅地体的泛非-早古生代造山事件年龄记录. 岩石学报, 21(1): 1-12. |
许志琴, 李海兵, 杨经绥. 2006. 造山的高原——青藏高原巨型造山拼贴体和造山类型. 地学前缘, 13(4): 1-17. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.04.002 |
杨立飞, 石康兴, 王长明, 吴彬, 杜斌, 陈晶源, 夏锦胜, 陈晶. 2016. 西南三江兰坪盆地金满铜矿床成因研究:来自铜和硫同位素的联合约束. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2392-2406. |
雍永源, 向天秀, 王洁民. 1990. 初论北澜沧江变质岩. 青藏高原地质文集, 20: 67-71. |
翟庆国, 李才, 黄小鹏. 2006. 西藏羌塘中部角木日地区二叠纪玄武岩的地球化学特征及其构造意义. 地质通报, 25(12): 1419-1427. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.12.010 |
赵政璋, 李永铁, 叶和飞, 张昱文. 2001. 青藏高原地层. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
郑洪伟, 贺日政, 杨贵. 2012. 羌塘地体内部双湖-冈玛错-龙木错构造带地质与地球物理特征. 中国地质, 39(5): 1229-1235. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.05.010 |
周世泰. 1984. 对17种恢复变质岩原岩的岩石化学方法的检验结果. 地质评论, 30(1): 81-84. |
周志广, 刘文灿, 梁定益. 2004. 藏南康马奥陶系及其底砾岩的发现并初论喜马拉雅沉积盖层与统一变质基底的关系. 地质通报, 23(7): 655-663. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.07.004 |
朱弟成, 赵志丹, 牛耀龄, 王青, Dilek Y, 董国臣, 莫宣学. 2012. 拉萨地体的起源和古生代构造演化. 高校地质学报, 18(1): 1-15. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2012.01.001 |
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35