2. 合肥工业大学资源与环境工程学, 合肥 230009
2. School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China
增生杂岩(accretionary complex)是洋-洋或洋-陆俯冲过程中大洋俯冲板块在仰冲板块前端遭受刮削、无序逆冲、底侵和底辟等作用共同形成的以发育双冲构造和紧闭褶皱为典型特征的楔形地质体(Karig, 1980; Moore and Silver, 1987; Isozaki et al., 1990; Von Huene and Scholl, 1991; 方爱民等, 2003; 付长垒等, 2018; 闫臻等, 2003, 2018a)。它们形成并分布于全球现代和古汇聚板块边缘。其中大洋板块地层(Oceanic Plate Stratigraphy, OPS)是增生杂岩的基本组成,主要由海沟复理石、远洋-半远洋沉积以及洋岛/海山/大洋高原岩石共同组成(Isozaki et al., 1990; Bangs et al., 2006; 闫臻等, 2008; Strasser et al., 2009; Wakita, 2012, 2015),也可包含有少量高压-超高压变质岩和微陆块残片(Robertson, 1994; 潘桂棠等, 2008; Wakabayashi, 2015; Safonova et al., 2016),如美国加利福尼亚Franciscan杂岩、日本Shimanto增生楔、新西兰Torlesse增生楔、希腊中部Rhodope增生楔以及我国北祁连造山带托莱山-走廊南山增生楔等。
增生杂岩、蛇绿岩、弧前盆地和岛弧/大陆边缘弧是增生型造山带的基本组成单元(Matsuda and Uyeda, 1971; Şengör and Natal’In, 1996; Maruyama, 1997; 李继亮, 2004; Cawood et al., 2009),它们的时空配置关系可直接指示大洋板块俯冲极性并揭示洋盆形成-演化-俯冲消亡的过程(Dickinson, 1976; Windley et al., 1990; Şengör and Natal’In, 1996; Xiao et al., 2003, 2015; Cawood et al., 2009; 闫臻等, 2012, 2018a, b; 张继恩等, 2018)。增生杂岩与蛇绿岩在造山带内紧密共存,通常被视为古洋盆俯冲消亡的最终位置(Dewey and Bird, 1970; Moores, 1982; Isozaki et al., 1990; Shervais, 2006),二者的组成和构造变形特征是恢复大洋板块地层序列和重建洋盆演化历史的直接依据(Isozaki et al., 1990; Shervais et al., 2011; Wakabayashi, 2015)。造山带内增生杂岩的识别,不仅可为确定古俯冲带相对位置、古洋盆存在以及造山作用类型提供直接证据,而且它的组成、结构及形成过程也可为古洋盆恢复和造山带结构研究提供最基本地质依据。
柴北缘构造带位于祁连造山带和柴达木地块之间,向西被阿尔金断裂切割,向东与西秦岭构造带相邻(图 1)。前人曾对该构造带中的高压-超高压变质作用、前寒武纪变质岩以及蛇绿岩等进行了大量研究并取得了诸多认识(Song et al., 2003, 2006, 2014; 吴才来等, 2004; Zhang et al., 2008, 2009a, b, 2010, 2011, 2012; Chen et al., 2009; Xiong et al., 2011, 2012; 张建新等, 2015; 朱小辉等, 2015; 周桂生等, 2017),然而该构造带的组成及形成演化过程目前依然存在分歧。其中,柴北缘构造带内“滩间山群”的组成、形成时代及构造属性争议最为强烈,严重影响着人们对柴北缘构造带与相邻构造带以及原特提斯洋构造演化的合理认识。

|
图 1 柴北缘构造带与邻区地质图 Fig. 1 Geological map of the northern margin of Qaidam and adjacent area |
根据区域地质资料,“滩间山群”在柴北缘构造带发育广泛,呈北西-南东向展布,西起赛什腾山吉绿素,向东经绿梁山、锡铁山至都兰地区,是一套早古生代浅变质中基性火山岩和碎屑岩为主夹硅质岩、生物碎屑灰岩以及超基性岩的岩石组合,与下伏元古代达肯大坂岩群和上覆泥盆系之间均为角度不整合接触(青海省地质矿产局, 1991)。“滩间山群”岩石组合空间变化较大,不同学者根据自己的研究结果将“滩间山群”的形成时代先后分别厘定为晚奥陶世-志留纪(青海省地质矿产局, 1991)、早奥陶世(李怀坤等, 1999; 赵风清等, 2003)、早-晚奥陶世(李峰等, 2006, 2007)或晚奥陶世(庄儒新和李峰, 2007);同时,“滩间山群”形成的构造环境有大陆裂谷(邬介人等, 1987; 熊兴武和陈忆元, 1994; 赵风清等, 2003; 李峰等, 2006, 2007; 童海奎等, 2009)或者岛弧(袁桂邦等, 2002; 王惠初等, 2003, 2005; 史仁灯等, 2004; 庄儒新和李峰, 2006; 高晓峰等, 2011)或者弧后盆地(孙华山等, 2012; 张孝攀等, 2015)等不同认识。此外,朱小辉等(2015)根据同位素年代学与地球化学综合分析认为,柴北缘“滩间山群”变火山岩是寒武纪-中奥陶世古洋盆俯冲-增生过程中形成的并包含不同成因类型岩块的混杂岩。这些不同认识主要是基于火山岩地球化学和同位素年代学的研究结果,相对而言对其岩石组合序列及其时空变化特征研究薄弱,特别是对“滩间山群”碎屑岩组合的研究相对较少。
为了查明柴北缘构造带原“滩间山群”的结构、组成和构造属性,我们在综合分析前人研究资料的基础上,近年来重点对乌兰县赛坝沟地区原“滩间山群”开展了详细地质调查和地质廊带填图工作。填图结果表明,赛坝沟地区原“滩间山群”碎屑岩主要是一套遭受剪切变形并发育透入性面理的浊积岩、凝灰岩、硅质岩和硅质泥岩组合,同时裹夹有不同形状和不同尺度的硅质岩、玄武岩和灰岩块体,具有混杂岩特有的“基质裹夹块体”结构特征(Hsü, 1968; Raymond, 1984; Festa et al., 2013; 闫臻等, 2018a),应属于增生杂岩。区域上,该增生杂岩与北侧蛇绿岩和岛弧火山岩之间呈现断层接触,向南共同仰冲于元古代达肯大坂岩群之上。该增生杂岩的厘定,可为柴北缘构造带组成及早古生代构造演化重建提供重要证据。
1 区域地质概况柴北缘构造带位于祁连造山带与柴达木地块之间,以乌兰-鱼卡断裂为界分为北侧的欧龙布鲁克微陆块以及南侧的早古生代俯冲杂岩。
欧龙布鲁克微陆块由德令哈杂岩、达肯大坂岩群和万洞沟岩群组成的结晶基底以及全吉群沉积盖层共同构成(陆松年等, 2002; 查显锋等, 2013)。德令哈杂岩以紫红色二长花岗片麻岩为主,含有大量的斜长角闪岩透镜体;达肯大坂岩群岩石类型相对复杂,是一套经历了从高角闪岩相到麻粒岩相变质的变火山-碎屑沉积岩系,表现为石英岩、斜长角闪岩、含石榴石矽线石石英片岩和云母片岩为主的表壳岩组合。前人根据年代学研究结果,认为二者的形成时代为元古代(张建新等, 2001; 陆松年等, 2002; 王惠初等, 2005)。王惠初等(2006)根据达肯大坂岩群变基性火山岩地球化学特征以及区域地质资料和同位素年代学研究结果,进一步推断达肯大坂岩群形成于新元古代晚期-早古生代早期的弧后盆地环境。
早古生代俯冲-增生杂岩主要由高压/超高压变质岩、火山-沉积岩和岩浆岩共同组成,包括正片麻岩、副片麻岩、“滩间山群”变火山-沉积岩系、镁铁质-超镁铁质岩、中酸性侵入岩以及少量的榴辉岩、石榴子石橄榄岩等(王惠初等, 2005, 2006)。根据岩石组合的时空分布,该带可进一步分为南、北2个单元,分别为高压-超高压变质带和蛇绿混杂岩-岛弧带。其中,高压-超高压变质岩出露并分布于研究区西南侧绿梁山、锡铁山和南侧沙柳河一带,表现为正、副片麻岩以及少量的榴辉岩和石榴子石橄榄岩透镜体组合(杨经绥等, 1998, 2003; Yang et al., 2002; Zhang et al., 2009b)。副片麻岩主要有云母石英片岩、二云母片麻岩以及石英岩,其原岩为泥岩、砂岩和少量的灰岩,可见花岗片麻岩呈脉状顺层侵入(Wan et al., 2006)。大量锆石U-Pb同位素年代学数据表明,柴北缘高压-超高压变质岩的原岩年龄集中在~1000Ma以及800~750Ma,可能分别与Rodinia超大陆的形成、裂解有关(杨经绥等, 2003; Yang et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2006),而与俯冲相关的变质年龄主要集中在460~420Ma(Song et al., 2005, 2006, 2014; Zhang et al., 2008, 2009a, 2010, 2017, 2011, 2012; Chen et al., 2009; Xiong et al., 2011, 2012)。Zhang et al.(2008)对沙柳河超高压变质岩研究认为其原岩为蛇绿岩,变质年龄为445Ma,并通过区域分析将柴北缘高压-超高压变质作用分为460~440Ma洋壳俯冲以及440~420Ma陆壳俯冲相关的2期变质作用。
蛇绿岩和岛弧带分布于高压-超高压变质带的北东侧,主要由“滩间山群”变火山-沉积岩、基性-超基性岩和早古生代中酸性侵入岩共同组成(王惠初等, 2005, 2006; 张建新等, 2015)。赖绍聪等(1996)将北起苏干湖、鱼卡、大柴旦、托素湖,南至柴达木盆地的广大区域内的超基性岩、辉长岩以及“滩间山群”海相火山岩统归为蛇绿岩组合。之后,不同学者也先后在绿梁山和赛坝沟地区陆续识别出由变质橄榄岩、辉长岩、辉长辉绿岩、枕状玄武岩以及少量硅质岩和斜长花岗岩组成的蛇绿岩(韩英善和彭琛, 2000; 孙延贵等, 2000; 杨经绥等, 2004; 王惠初等, 2005; Yang et al., 2006; Menold et al., 2009; 朱小辉等, 2014)。朱小辉等(2014)根据斜长花岗岩和辉长岩的锆石U-Pb同位素年代学以及玄武岩地球化学研究结果,认为柴北缘蛇绿岩属于SSZ型蛇绿岩,形成时代为535~493Ma。同时,Zhang et al.(2008)通过地球化学和锆石U-Pb同位素年代学研究,认为沙柳河一带的蓝晶石榴辉岩、绿帘石榴辉岩、多硅白云母榴辉岩以及蛇纹岩属于蛇绿岩组合,形成时代为516Ma。岛弧火山岩由分布于绿吉素、双口山、锡铁山和都兰地区的“滩间山群”玄武岩、玄武安山岩、英安岩、安山岩和流纹岩组成(史仁灯等, 2003, 2004; 庄儒新和李峰, 2006; 张孝攀等, 2015)。已有地球化学数据分析表明,这些岛弧火山岩具有岛弧拉班玄武岩和钙碱性玄武岩两种地球化学特征(史仁灯等, 2003; 庄儒新和李峰, 2006)。锆石U-Pb同位素年龄资料表明,该岛弧火山岩以及侵入其中的辉长岩形成年龄为522~460Ma(袁桂邦等, 2002; 赵风清等, 2003; 史仁灯等, 2004; 王惠初等, 2005; 朱小辉等, 2010)。显然,该年龄与蛇绿岩的形成年龄在误差范围内一致。此外,在柴北缘广泛发育石英闪长岩、英云闪长岩、奥长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩,同时有少量闪长岩和二长花岗岩。Wu et al.(2001, 2014)根据锆石U-Pb同位素年龄和地球化学特征,认为它们形成于大洋俯冲作用相关的岛弧环境,形成时代为494~460Ma。从这些同位素年龄、地球化学特征及岩石组合可以看出,柴北缘在寒武纪时期曾发生古洋盆俯冲、增生造山作用,并伴随有岛弧火山岩的形成,且该洋盆可能于晚奥陶世-早志留世闭合。
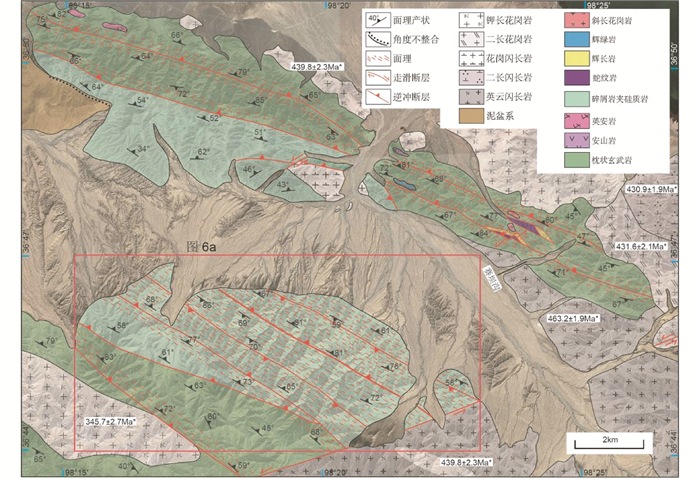
在柴北缘构造带东段赛坝沟地区,广泛出露有变火山-沉积岩、基性-超基性岩、中酸性侵入岩和少量泥盆系(图 1)。长期以来,这些变火山-沉积岩和基性、超基性岩在以往区域地质资料中被划归为滩间山群。野外地质调查结果表明,这些岩石组合虽然遭受不同程度构造破坏和低绿片岩相变质作用改造,但是在部分露头上可见保留完好的枕状构造以及正粒序、底冲刷面、波纹斜层理等原始沉积构造。区域上,中-基性火山岩和基性-超基性岩组合主要出露于赛坝沟北侧,包括枕状玄武岩、英安岩、安山岩、蛇纹岩、辉长岩、辉绿岩和斜长花岗岩;沉积岩主要出露在南侧,表现为砂质浊积岩、凝灰岩和硅质岩组合,与北侧中-基性和基性-超基性岩组合之间均为断层接触(图 2)。泥盆纪牦牛山组不整合在这些中-基性火山岩之上,主要由砾岩、含砾粗砂岩、粗砂岩、粉砂岩以及泥岩组成,发育板状、槽状斜层理以及滑塌褶曲和波痕等沉积构造(夏文静等, 2014)。中酸性侵入岩主要包括二长花岗岩、钾长花岗岩、花岗闪长岩、英云闪长岩和二长闪长岩,锆石U-Pb同位素年龄结果表明这些侵入岩形成于463~430Ma。其中英云闪长岩遭受韧性剪切变形,LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为463.2±1.9Ma,而侵入于英云闪长岩和碎屑岩系且未发生变形的石英闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为439.8±2.3Ma(河南省地质矿产勘查开发局, 2016)。NWW向逆断层和NE向左行走滑断层普遍发育,其中NWW向逆断层被NE向左行走滑断层所截,显示NWW向逆断层形成较早。
|
图 2 赛坝沟地区地质简图 图中同位素年龄*引自河南省地质矿产勘查开发局(2016①) Fig. 2 Geological map of Saibagou area |
① 河南省地质矿产勘查开发局. 2016. 1:50000托莫尔日特幅区域地质报告
2 赛坝沟增生杂岩的组成特征柴北缘赛坝沟增生杂岩是由发生强烈构造变形的复理石和少量凝灰岩夹层以及玄武岩、硅质岩、灰岩块体共同组成,呈现出混杂岩特有的“基质裹夹块体”基本特征。
2.1 基质组成特征基质在露头上总体由深灰色泥岩、浅灰-红色薄层硅质岩、硅质泥岩以及灰绿色凝灰岩共同组成。空间上,自北而南可分为3种岩石组合类型。其中,北部主要为硅质凝灰岩、硅质泥岩、砂岩和少量薄层凝灰岩组合,砂岩层厚度一般为8~15cm,发育正粒序层理和底冲刷面构造;凝灰岩覆于砂岩层之上,厚度一般为1~3cm,发育平行层理;中-薄层红色硅质泥岩、灰绿色硅质凝灰岩韵律层中发育波纹斜层理(图 3a)。这些基本特征共同表明其为浊流沉积,以发育典型的鲍马序列Tabc组合。中部主要表现为灰绿色中-薄层凝灰质砂岩、泥岩、薄层硅质岩韵律层,夹厚层硅质岩透镜体(图 3b)。该组合中硅质岩透镜体在侧向上断续出露,呈现出“总体有序、局部无序”的结构特征,具有“破碎地层(broken formation)”典型特征(Raymond, 1984)。在研究区南段,主体表现为互层状浅灰色泥岩和薄层硅质岩基质(图 3c, d),局部夹薄层灰绿色凝灰岩和大小不同的灰岩(现为大理岩)、玄武岩透镜体(图 3e, f)。它们分别呈现出与海沟浊积岩型、正常洋壳砂岩-硅质岩型以及海山/洋岛玄武岩-灰岩型OPS混杂岩(Wakita and Metcalfe, 2015; Safonova et al., 2016)相一致的岩性组合和沉积相特征。这些特征表明,赛坝沟增生杂岩的岩石组合自北而南呈现出由海沟向深海盆地地层序列过渡的基本岩石组合特征。

|
图 3 赛坝沟增生杂岩露头照片 (a)由具有正粒序结构(Ta)、平行层理砂岩(Tb)和发育波纹斜层理红色硅质泥岩(Tc)或灰绿色硅质凝灰岩(Tc)构成的浊积岩;(b)薄层砂岩、泥岩互层夹硅质岩透镜体;(c)泥岩夹薄层硅质岩;(d)深灰色薄层硅质岩;(e)硅质岩与薄层泥岩互层夹灰岩透镜体;(f)灰岩与枕状玄武岩整合接触,且灰岩中夹薄层玄武岩 Fig. 3 Photographs of the Saibagou accretionary complex (a) turbidites composed of sandstone with normal grading (Ta) and parallel bedding (Tb), red siliceous mudstone with ripple (Tc), and/or green-gray siliceous tuff (Tc); (b) interlayers of thinner sandstone and mudstone with chert lenses; (c) mudstone with interlayer of thinner chert; (d) deep-grey chert; (e) interlayers of chert and thinner mudstone with limestone lenses; (f) limestone with basalt interlayer conformably overlies pillow basalt |
块体主要有灰岩、玄武岩、硅质岩,大小混杂,一般为数厘米到数米(图 4),被硅质泥岩、硅质岩或凝灰岩包裹。这些块体通常与基质的产状明显不协调。露头上,可见硅质岩基质发生明显的剪切变形,而被包裹灰岩块体未见明显变形(图 4a)。红色、绿色硅质岩与硅质泥岩块体大小混杂,但是部分硅质岩块体中可见同沉积滑塌褶曲(图 4b)。硅质岩块体周边的黑色硅质泥岩基质也发生明显的变形,表明这些混杂岩是滑塌沉积作用形成的(图 4c)。这些滑塌沉积组合在空间上与灰绿色硅质凝灰岩、凝灰岩及凝灰质砂岩紧密相伴,进一步表明它们可能是形成于海沟斜坡环境(Strasser et al., 2009; Wakita, 2012)。部分玄武岩透镜体长轴与发生构造变形硅质岩、凝灰质砂岩的片理呈现出大角度相交(图 4d)。灰岩块体(图 4e)与硅质岩块体(图 4f)分布于强烈变形的硅质岩、凝灰岩中。

|
图 4 赛坝沟增生杂岩露头典型照片 (a)硅质泥岩中的不同类型块体;(b)滑塌堆积中硅质岩块体发生滑塌褶曲;(c)滑塌堆积中的大小不同硅质岩块被硅质泥岩所包裹;(d)硅质泥岩、灰绿色强烈片理化凝灰质砂岩与薄层硅质岩基质中的玄武岩块体;(e)发生强烈褶皱变形凝灰岩、硅质岩基质中的灰岩块体;(f)发生强烈片理化凝灰岩与硅质泥岩基质中的厚层状硅质岩块体 Fig. 4 Typical photographs of the Saibagou accretionary complex (a) different blocks within siliceous mudstone matrix; (b) sliding folds of chert block within olistostrome; (c) chert blocks in various size within siliceous mudstone of olistostrome; (d) basalt block within the flysch matrix composed of siliceous mudstone, grey-green strongly foliated tuffaceous sandstone, and thinly bedded chert; (e) limestone block in the strongly deformed matrix of tuff and chert; (f) thickly bedded chert block in strongly foliated matrix of tuff and siliceous mudstone |
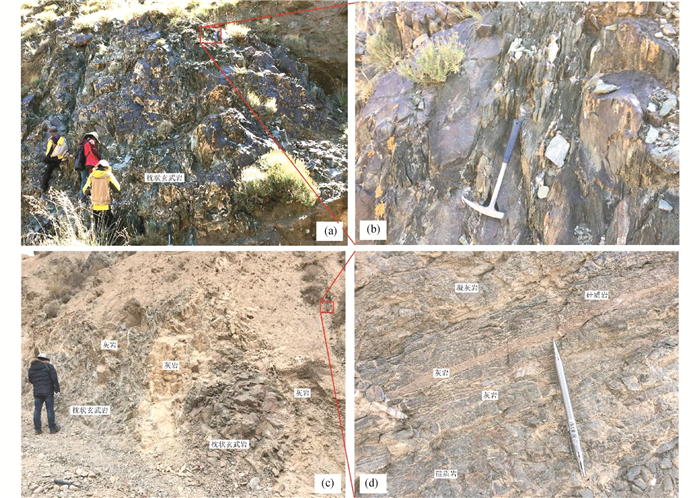
区域上,本文研究区南段和北段,均可见出露头宽度为7~9m玄武岩、灰岩组合块体(图 5a),被强烈剪切变形的深灰色泥岩、薄层硅质岩组合所包裹。玄武岩通常在局部地段保留有完好的枕状构造(图 5b)。灰岩与枕状玄武岩构成互层(图 5c),同时也以夹层形式出现于硅质岩中(图 5d),具有与日本Akiyoshi海山(Sano and Kanmera, 1988)相一致的岩石组合。这些岩石组合在露头上现以构造透镜体形式夹持于硅质岩、薄层泥岩构成的复理石中,但在其中和周边未见到陆源碎屑岩出露,表明它们形成于远离大陆边缘的深海环境,为海山岩石组合(Sano and Kanmera, 1988; Robertson, 1994)。

|
图 5 赛坝沟增生杂岩中海山岩石组合露头照片 (a)凝灰岩、硅质岩、薄层灰岩和泥岩组合中的枕状玄武岩透镜体;(b)枕状玄武岩;(c)枕状玄武岩、灰岩组合透镜体夹持于薄层硅质岩、凝灰岩和灰岩组合中;(d)薄层硅质岩、凝灰岩和灰岩构成的浊积岩 Fig. 5 Photographs of rock assemblages of sea-mountain of the Saibagou accretionary complex (a) pillow basalt lenses in the assemblage of tuff, chert, thinner limestone, and mudstone; (b) pillow basalt; (c) lenses of pillow basalt and limestone in the matrix of thinner chert, tuff and limestone; (d) turbidite consists of thinner chert, tuff, and limestone |
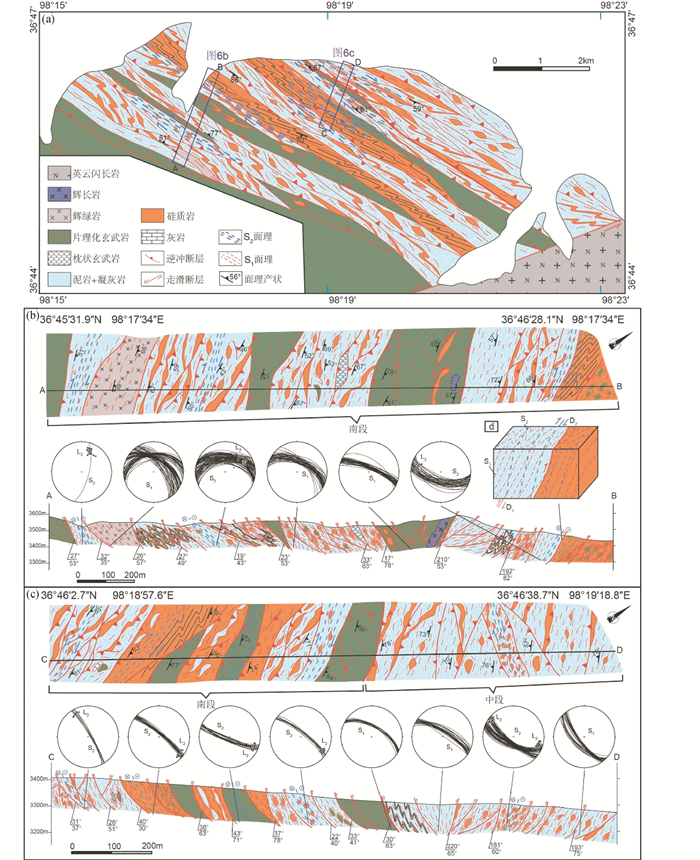
根据构造变形强度和变形样式组合特征,赛坝沟地区增生杂岩自北而南可分为北、中和南三段。其中北段主要见于赛坝沟西侧(图 2),发育宽缓褶皱,局部地段发生强烈挤压变形,以紧闭褶皱和密集片理为特征,总体变形相对较弱,且原始层序保存相对完整。中段和南段出露于赛坝沟南侧,构造变形复杂(图 6),以NW-SE向逆冲断层构造和强烈紧闭褶皱为典型特征,且不同逆冲席体(thrust sheet)内部发生强烈的剪切变形,发育透入性面理、紧闭褶皱和不对称褶皱,构成双冲构造(duplex)。从这些构造变形特征来看,赛坝沟增生杂岩具有与日本西南部增生杂岩(Wakita, 2012, 2015)和Nankai增生楔一致的构造变形组合样式(Strasser et al., 2009)。根据交切关系以及各类变形形迹的系统测量和统计结果,构造变形主要表现为两期(D1和D2),增生杂岩北段仅发育第一期构造变形(D1),中段和南段发育两期变形(D1,D2)且叠加关系明显。本文重点对增生杂岩中段和南段的变形行迹进行了测量,以下将从面理(S0、S1和S2)、线理(L2)以及褶皱(F1和F2)等方面对这些构造变形进行详细分析。
|
图 6 赛坝沟增生杂岩中-南段岩性-构造地质图和剖面图 (a)赛坝沟增生杂岩岩性-构造地质图;(b) A-B剖面图;(c) C-D剖面图;(d) D1和D2两期变形露头素描图. S1-第一期面理;S2-第二期面理;L2-第二期矿物拉伸线理;D1-第一期变形;D2-第二期变形 Fig. 6 Lithologic-structural map and cross sections of the southern and middle portions of the Saibagou accretionary complex (a) lithologic-structural map; (b) Section A-B; (c) Section C-D; (d) sketches of D1 and D2 deformations. S1-the first foliation; S2-the second foliation; L2-the second mineral elongation lineation; D1-the first deformational event; D2-the second deformational event |
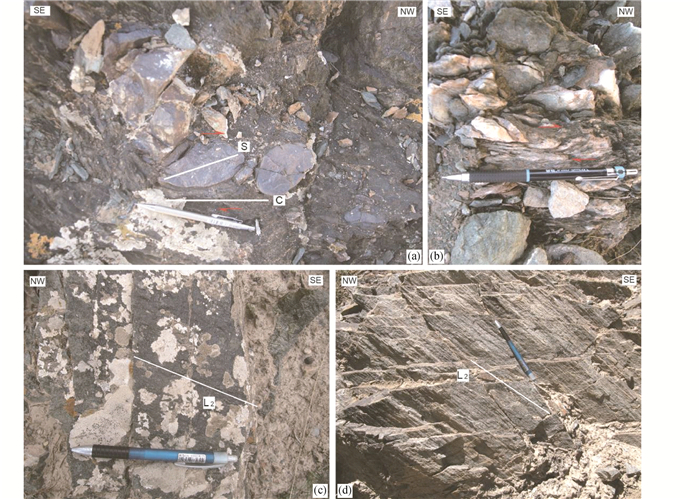
第一期变形(D1):主体表现为NW-SE逆冲断层,主体倾向NE,倾角变化大(30°~82°;图 7a-c)。与该期断层同时发生的是不同逆冲席体中的同斜紧闭褶皱(F1)、透入性面理(S1)和S-C组构。露头上,S1主体倾向NE,局部地段倾向SW,倾角中等-陡倾(38°~86°;图 6),并通常与原始层面S0及逆冲断层相互平行(图 7a, b、图 8)。显微组构分析表明,硅质岩、泥岩和凝灰质砂岩中S1普遍发育,其中S1在凝灰质砂岩中表现为辉石和长石矿物的定向排列(图 7e),而S1在泥岩和硅质岩中表现为石英、云母和黏土矿物的定向排列(图 7f)。同斜紧闭褶皱(F1)轴面与S1面理基本平行(图 8a)。逆冲席体中的玄武岩、灰岩及硅质岩块体在剪切挤压作用下发生旋转,其长轴方向与S1平行,且部分块体内部发生韧性变形,发育S-C组构(图 7d)。少量石英脉在该期变形过程中发生变形并成布丁状(D1)。这些现象表明,该期逆冲断层上盘向SW运动特征。

|
图 7 第一期构造变形(D1)露头和显微照片 (a)双冲构造;(b)指示逆冲断层的S-C组构;(c) S-C组构指示逆冲断层;(d)玄武岩块体发生旋转,内部发育S-C组构;(e)凝灰质砂岩中的S1面理;(f)硅质岩中的S1面理. Px-辉石;Pl-斜长石;Q-石英;Se-绢云母 Fig. 7 Photographs of field occurrences and photomicrographs of the first deformational event D1 (a) duplex; (b) S-C fabric indicated thrust fault; (c) S-C fabric indicated thrust fault; (d) S-C fabric within the rotated basalt block; (e) foliation (S1) within tuffaceous sandstone; (f) foliation (S1) within chert. Px-pyroxene; Pl-plagioclase; Q-quartz; Se-sericite |

|
图 8 第二期构造变形(D2)不同类型褶皱野外照片 (a)互层的薄层硅质岩和硅质泥岩形成顶厚紧闭褶皱;(b)硅质岩与硅质泥岩中的不对称宽缓褶皱,并发育第二期破裂面理(S2);(c)强烈片理化的硅质泥岩中硅质岩形成紧闭褶皱,翼部减薄并发生细颈化,形成破裂面理(S2);(d)凝灰岩中的硅质泥岩形成等厚褶皱;(e、f)互层的薄层硅质岩与硅质泥岩发育膝折,并形成破裂面理(S2) Fig. 8 Photographs of different types of fold in the second deformational event (D2) (a) top-thick tight fold formed by interlayers of thinly bedded chert and siliceous mudstone; (b) asymmetry broad and gentle fold of interlayers of chert and siliceous mudstone with cleavage S2; (c) tight fold with necking and cleavage S2 of chert within strongly foliated siliceous mudstone; (d) equal thick fold of siliceous mudstone within tuff; (e, f) interbedding of thinly bedded chert and siliceous mudstone with kink and cleavage S2 |
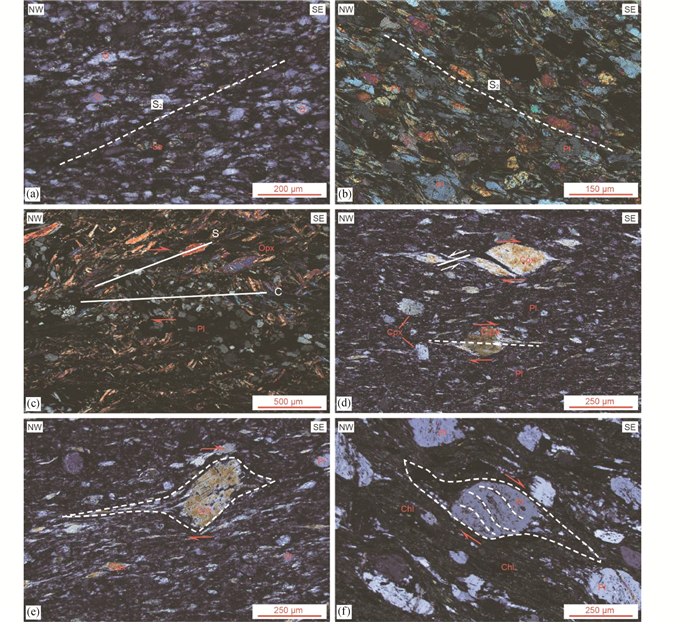
第二期变形(D2):以发育韧性剪切作用相关的不同几何形态和类型的褶皱、S2面理、矿物拉伸线理(L2)、S-C组构以及叠瓦状构造为典型特征。该期变形在赛坝沟增生杂岩硅质岩和硅质泥岩岩石组合中最为发育。露头上,该期褶皱F2主要表现为顶厚紧闭褶皱(图 8a)、非对称宽缓褶皱(图 8b)、紧闭褶皱(图 8c)、等厚褶皱(图 8d)以及膝折(图 8e, f)等。紧闭褶皱(F2)核部增厚,翼部减薄并发生细颈化甚至被断开(图 8c)。S2面理主体倾向NE,倾角较陡(图 6),S2与S1基本平行或有小夹角(图 6d和图 8)。布丁状石英脉(D1)在第二期变形中在持续剪切作用(D2)下形成叠瓦状构造(图 9a)和S-C组构(图 9b)。区域上,L2倾伏NW或SE,倾角在5°~25°之间(图 6)。L2在凝灰质砂岩中通常表现为辉石和斜长石的定向排列(图 9c),在硅质岩和硅质泥岩中表现为石英的定向排列(图 9d)。在硅质岩和硅质泥岩中,S2通常表现为石英、云母和黏土矿物的定向排列(图 10a),构成紧闭褶皱和不对称褶皱的轴面;在凝灰质砂岩中,S2通常表现为长石和辉石的定向排列(图 10b)。显微组构分析表明,该期剪切作用使得凝灰质砂岩中的斜长石和辉石晶屑发生定向排列并形成S-C组构(图 10c),辉石形成“云母鱼”状构造(图 10d)和σ旋转残斑(图 10e),同时,斜长石斑晶发育雪球构造(图 10f)。这些特征共同表明,赛坝沟增生杂岩第二期变形(D2)为高角度右行韧性剪切作用形成。

|
图 9 布丁状石英脉和第二期构造线理 (a)布丁状石英脉发育叠瓦状构造;(b)石英脉剪切形成S-C组构;(c)凝灰岩中的第二期构造线理(L2);(d)硅质泥岩中的第二期拉伸线理(L2) Fig. 9 Photography of pudding-like quartz vein and lineation L2 (a) pudding-like quartz vein with imbricate structure; (b) S-C fabric formed by sheared quartz vein; (c) lineation (L2) in tuff; (d) stretching lineation (L2) in siliceous mudstone |
|
图 10 赛坝沟增生杂岩显微构造照片 (a)硅质岩中第二期面理(S2);(b)凝灰质砂岩中第二期面理(S2);(c)凝灰质砂岩中斜方辉石晶屑构成S-C组构;(d)单斜辉石的鱼状构造与σ旋转残斑;(e)辉石斑晶发育σ旋转残斑;(f)斜长石斑晶发育σ旋转残斑. Chl-绿泥石;Cpx-单斜辉石;Opx-斜方辉石 Fig. 10 Microphotographs of the Saibagou accretionary complex (a) foliation S2 formed by chert; (b) foliation S2 formed by tuffaceous sandstone; (c) orthopyroxene phenocryst with S-C fabric in tuffaceous sandstone; (d) clinopyroxene phenocryst with fish structure and σ rotated porphyroblast; (e) clinopyroxene phenocryst with σ rotated porphyroblast; (f) plagioclase phenocryst with σ rotated porphyroblast. Chl-chlorite; Cpx-clinopyroxene; Opx-orthopyroxene |
岩石组合、构造变形组合样式及其运动学特征以及不同岩石构造单元的时空配置特征是确定增生杂岩形成过程和俯冲极性的重要依据(闫臻等, 2018a)。尽管增生杂岩是由发生强烈构造变形的洋壳物质组成,但在每个逆冲席体(thrust sheet)中依然可以保留相对完好的大洋板块地层“片段”序列信息(闫臻等, 2018a),因此通过对增生杂岩岩石组合及其成分时空变化特征研究,可以恢复和重建大洋板块地层与大洋板块俯冲过程(Wakita, 2012)。
赛坝沟增生杂岩总体表现为硅质岩、硅质泥岩、凝灰岩和砂岩组合,在靠近蛇绿岩一侧的北段部分主要为海沟沉积组合序列,由砂岩、硅质泥岩、薄层硅质凝灰岩共同构成,以发育底冲刷面、波纹斜层理以及鲍马序列Tabc组合为典型特征。中段主要为中-薄层凝灰质砂岩、泥岩、薄层硅质岩韵律层,夹中-厚层硅质岩透镜体,具有“破碎地层”特征的混杂岩。南段主要表现为海山OPS岩石组合类型,呈现为硅质岩和薄层泥岩组合,局部夹灰岩和玄武岩的块体。它们分别与浊积岩型、砂岩-硅质岩型以及玄武岩-灰岩型OPS混杂岩(Wakita, 2015)相类似,而且这些岩石组合中的火山物质成分和砂岩层总体呈现出自北而南逐渐减少,表明它们在形成时,火山喷发中心和陆缘碎屑物源供给区主要位于北侧,是北侧海沟沉积序列的重要物源区。另外,这些岩石组合及相关沉积构造特征也进一步表明,自北而南表现为海沟浊流沉积逐渐向半深海、深海盆地沉积过渡。总之,这些岩石组合类型及其构造变形样式均与日本增生杂岩结构、组成相似(Isozaki et al., 1990; Wakita, 2012),进一步反映了其初始岩石组合表现为自北向南由海沟OPS逐渐过渡为正常洋壳及海山OPS的岩石组合(Wakita and Metcalfe, 2005)。
根据变形行迹测量和统计结果,第一期构造变形虽然经历了第二期构造事件的叠加改造,但是依然保留了清晰的变形行迹,包括双冲构造、逆冲断层、同斜紧闭褶皱以及S1面理等。S1面理与逆冲断层基本平行,倾向NE,结合块体发生旋转形成的S-C组构,共同表明上盘向南逆冲,这些构造变形是增生杂岩典型的特征(Wakita, 2012; Festa et al., 2013; 闫臻等, 2018a)。区域地质资料分析表明,在赛坝沟地区岛弧火山岩、蛇绿岩和增生杂岩在空间上呈现出自北而南依次出露,蛇绿岩与其南、北两侧的增生杂岩和岛弧火山岩与之间为断层接触,且岛弧火山岩向南逆冲于蛇绿岩之上,而增生杂岩与蛇绿岩分别位于断层下盘和上盘(图 2和图 6)。这些特征与弗朗西斯科增生杂岩(Wakabayashi, 2015)相一致。区域上,蛇绿岩和岛弧火山岩的形成时代集中在535~460Ma(袁桂邦等, 2002; 史仁灯等, 2004; 王惠初等, 2005; 朱小辉等, 2010)。这些事实进一步表明,柴北缘在寒武纪-中奥陶世时期存在古洋盆,且该洋盆发生向北俯冲作用。
4.2 增生杂岩的就位过程大洋俯冲以及最终洋盆闭合导致陆-陆碰撞过程,使得增生杂岩内部构造变形复杂化同时也引起增生杂岩最终就位。赛坝沟增生杂岩是由发生强烈褶皱的凝灰质砂岩、泥岩、薄层硅质岩组合以及“破碎地层”和海山OPS混杂岩共同组成,这些岩石组合及其组成的空间展布特征表明其初始形成位置自北而南逐渐远离火山喷发中心和大陆边缘并向深海盆地变化特征;赛坝沟增生杂岩以发育强烈紧闭褶皱、双冲构造变形为特征,与其北侧蛇绿岩断层接触且位于断层下盘;同时,岩石地球化学和同位素年代学研究表明,出露于赛坝沟增生杂岩北侧的蛇绿岩形成于480Ma,为SSZ型蛇绿岩(河南省地质矿产勘查开发局, 2016)。这些事实共同表明,赛坝沟增生杂岩是大洋俯冲过程中,洋壳物质随同古洋盆向北俯冲过程中逐渐发生拼贴,实现增生杂岩向南侧向增长。
野外宏观特征和显微组构分析表明,赛坝沟增生杂岩遭受晚期NW-SE向高角度右行韧性剪切作用(D2)的叠加改造和破坏,从而形成不对称褶皱以及相关的面理(S2)和线理(L2)。该期构造与柴北缘NW-SE向韧性剪切带产状相一致。付建刚等(2016)通过对锡铁山韧性剪切带中花岗质糜棱岩白云母Ar-Ar同位素测年并结合区域地质资料综合分析,认为该期构造形成于400Ma左右,且与柴北缘超高压变质岩形成时代相一致,是柴达木地块向北东斜向俯冲碰撞形成的。然而,前人曾获得侵入于赛坝沟增生杂岩中未发生剪切变形的石英闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄439.8±2.3Ma(河南省地质矿产勘查开发局, 2016)。据此,我们推断赛坝沟增生杂岩形成时代应早于440Ma,在440~400Ma左右的陆-陆碰撞过程向南仰冲、就位。
5 结论(1) 赛坝沟增生杂岩由正常深海OPS、海山OPS和海沟OPS共同构成,主要岩性为硅质岩、凝灰岩和硅质泥岩,同时裹夹玄武岩、灰岩、硅质岩等块体,具有混杂岩特征。增生杂岩与北侧蛇绿岩和岛弧火山岩带共同构成了相对完整和沟-弧系,是寒武纪-中奥陶世时期古洋盆向北发生俯冲-增生造山作用的结果。
(2) 赛坝沟增生杂岩发育两期构造变形(D1、D2),总体主要构造样式表现为双冲构造、不对称褶皱、同斜紧闭褶皱、S-C组构和透入性面理。其中第一期变形(D1)形成于大洋俯冲阶段,时代为寒武纪-中奥陶世;第二期变形(D2)为高角度右行韧性剪切变形,可能形成于440~400Ma柴达木地块与祁连地块碰撞过程中。
致谢 三位匿名审稿人和本刊编辑对本文提出了建设性修改意见,在此谨表谢意。
Bangs NLB, Gulick SPS and Shipley TH. 2006. Seamount subduction erosion in the Nankai Trough and its potential impact on the seismogenic zone. Geology, 34(8): 701-704. DOI:10.1130/G22451.1 |
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Qinghai Province. 1991. Regional Geology of Qinghai Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-662 (in Chinese)
|
Cawood PA, Kröner A, Collins WJ, Kusky TM, Money WD and Windley BF. 2009. Accretionary orogens through Earth history. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 318: 1-36. DOI:10.1144/SP318.1 |
Chen DL, Liu L, Sun Y and Liou JG. 2009. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb dating and its implications of the Yukahe HP/UHP terrane, the North Qaidam, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(3-4): 259-272. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.12.001 |
Dewey JF and Bird JM. 1970. Mountain belts and the new global tectonics. Journal of Geophysical Research, 75(14): 2625-2647. DOI:10.1029/JB075i014p02625 |
Dickinson WR. 1976. Sedimentary basins developed during evolution of Mesozoic-Cenozoic arc-trench system in western North America. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 13(9): 1268-1287. DOI:10.1139/e76-129 |
Fang AM, Hou QL, Li JL, Hao J, Xiao WJ and Zhou H. 2003. Turbiditic facies and their characteristics of abyssal turbidites in the Kuda mélange belt in West Kunlun, Xinjiang. China. Chinese Journal of Geology, 38(1): 1-12. |
Festa A, Dilek Y, Codegone G, Cavagna S and Pini GA. 2013. Structural anatomy of the Ligurian accretionary wedge (Monferrato, NW Italy), and evolution of superposed mélanges. GSA Bulletin, 125(9-10): 1580-1598. DOI:10.1130/B30847.1 |
Fu CL, Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Buckman S, Aitchison JC, Niu ML, Cao B, Guo XQ, Li XC, Li YS and Li JL. 2018. Lajishankou ophiolite complex:Implications for Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional events in the South Qilian belt. Tectonics, 37(5): 1321-1346. DOI:10.1029/2017TC004740 |
Fu CL, Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Niu ML, Guo XQ, Yu LJ and Li JL. 2018. Texture and composition of the Lajishankou accretionary wedge of the South Qilian belt, NW China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(7): 2049-2064. |
Fu JG, Liang XQ, Wang C, Jiang Y, Zhou Y, Pan CC, Yang YQ, Wang ZL and Zhong YS. 2016. Characteristics and muscovite 40Ar/39Ar age of ductile shear zone in the Xitieshan area, North Qaidam. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 40(1): 14-28. |
Gao XF, Xiao PX and Jia QZ. 2011. Redetermination of the Tanjianshan Group:Geochronological and geochemical evidence of basalts from the margin of the Qaidam basin. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(9): 1452-1463. |
Han YS and Peng C. 2000. Geological characteristics of Tuomuoerrite ophilite mélange belt and its tectonic significance. Qinghai Geology, 9(1): 18-25. |
Hsü KJ. 1968. Principles of mélanges and their bearing on the Franciscan-Knoxville paradox. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 79(8): 1063-1074. DOI:10.1130/0016-7606(1968)79[1063:POMATB]2.0.CO;2 |
Isozaki Y, Maruyama S and Furuoka F. 1990. Accreted oceanic materials in Japan. Tectonophysics, 181(1-4): 179-205. DOI:10.1016/0040-1951(90)90016-2 |
Karig DE. 1980. Material transport within accretionary prisms and the "Knocker" problem. The Journal of Geology, 88(1): 27-39. DOI:10.1086/628471 |
Lai SC, Deng JF and Zhao HL. 1996. Paleozoic ophiolites and its tectonic significance on north margin of Qaidam basin. Geoscience, 10(1): 18-28. |
Li F, Wu ZL, Li BZ and Wang LF. 2006. Revision of the Tanjianshan Group on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin. Northwestern Geology, 39(3): 83-90. |
Li F, Wu ZL and Li BZ. 2007. Recognition on formation age of the Tanjianshan Group on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin and its geological significance. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 31(2): 226-233. |
Li HK, Lu SN, Zhao FQ, Yu HF and Zheng JK. 1999. Determination and significance of the coesite eclogite of the Yuqia river on the north margin of the Qaidam basin. Geoscience, 13(1): 43-50. |
Li JL. 2004. Basic characteristics of accretion-type orogens. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(9-10): 947-951. |
Lu SN, Wang HC, Li HK, Yuan GB, Xin HT and Zheng JK. 2002. Redefinition of the 'Dakendaban Group' on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin. Geological Bulletin of China, 21(1): 19-23. |
Maruyama S. 1997. Pacific-type orogeny revisited:Miyashiro-type orogeny proposed. The Island Arc, 6(1): 91-120. DOI:10.1111/iar.1997.6.issue-1 |
Matsuda T and Uyeda S. 1971. On the Pacific-type orogeny and its model-extension of the paired belts concept and possible origin of marginal seas. Tectonophysics, 11(1): 5-27. DOI:10.1016/0040-1951(71)90076-X |
Menold CA, Walsh EO, Manning CE and Yin A. 2009. Relationship between the Early Paleozoic SSZ ophiolite complex and North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt in NW China. In: AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts. AGU: 90(52): T21A-1781
|
Moore JC and Silver EA. 1987. Continental margin tectonics:Submarine accretionary prisms. Reviews of Geophysics, 25(6): 1305-1312. DOI:10.1029/RG025i006p01305 |
Moores EM. 1982. Origin and emplacement of ophiolites. Reviews of Geophysics, 20(4): 735-760. DOI:10.1029/RG020i004p00735 |
Pan GT, Xiao QH, Lu SN, Deng JF, Feng YM, Zhang KX, Zhang ZY, Wang FG, Xing GF, Hao GJ and Feng YF. 2008. Definition, classification, characteristics and diagnostic indications of tectonic facies. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(10): 1613-1637. |
Raymond LA. 1984. Classification of mélanges. In: Melanges: Their Nature, Origin, and Significance. Geological Society of America, 198: 669-684
|
Robertson AHF. 1994. Role of the tectonic facies concept in orogenic analysis and its application to Tethys in the Eastern Mediterranean region. Earth-Science Reviews, 37(3-4): 139-213. DOI:10.1016/0012-8252(94)90028-0 |
Safonova I, Maruyama S, Kojima S, Komiya T, Krivonogov S and Koshida K. 2016. Recognizing OIB and MORB in accretionary complexes:A new approach based on ocean plate stratigraphy, petrology and geochemistry. Gondwana Research, 33: 92-114. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.013 |
Sano H and Kanmera K. 1988. Paleogeographic reconstruction of accreted oceanic rocks, Akiyoshi, Southwest Japan. Geology, 16(7): 600-603. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0600:PROAOR>2.3.CO;2 |
Şengör AMC and Natal'In BA. 1996. Turkic-type orogeny and its role in the making of the continental crust. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 24(1): 263-337. DOI:10.1146/annurev.earth.24.1.263 |
Shervais JW. 2006. The significance of subduction-related accretionary complexes in early Earth processes. Geological Society of America Special Papers, 405: 173-192. |
Shervais JW, Choi SH, Sharp WD, Ross J, Zoglman-Schuman M and Mukasa SB. 2011. Serpentinite matrix mélange:Implications of mixed provenance for mélange formation. Geological Society of America Special Papers, 480: 1-30. DOI:10.1130/9780813724805 |
Shi RD, Yang JS and Wu CL. 2003. The discovery of adakitic dacite in Early Palaeozoic island arc volcanic rocks on the northern margin of Qaidam basin and its geological significance. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 22(3): 229-236. |
Shi RD, Yang JS, Wu CL, Iizuka T and Hirata T. 2004. Island arc volcanic rocks in the North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78(1): 52-64. |
Song SG, Yang JS, Xu ZQ, Liou JG and Shi RD. 2003. Metamorphic evolution of the coesite-bearing ultrahigh-pressure terrane in the North Qaidam, Northern Tibet, NW China. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 21(6): 631-644. DOI:10.1046/j.1525-1314.2003.00469.x |
Song SG, Zhang LF, Niu YL, Su L, Jian P and Liu DY. 2005. Geochronology of diamond-bearing zircons from garnet peridotite in the North Qaidam UHPM belt, Northern Tibetan Plateau:A record of complex histories from oceanic lithosphere subduction to continental collision. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 234(1-2): 99-118. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.036 |
Song SG, Zhang LF, Niu YL, Su L, Song BA and Liu DY. 2006. Evolution from oceanic subduction to continental collision:A case study from the Northern Tibetan Plateau based on geochemical and geochronological data. Journal of Petrology, 47(3): 435-455. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egi080 |
Song SG, Niu YL, Su L, Zhang C and Zhang LF. 2014. Continental orogenesis from ocean subduction, continent collision/subduction, to orogen collapse, and orogen recycling:The example of the north Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China. Earth-Science Reviews, 129: 59-84. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.11.010 |
Strasser M, Moore GF, Kimura G, Kitamura Y, Kopf AJ, Lallemant S, Park JO, Screaton EJ, Su X, Underwood MB and Zhao XX. 2009. Origin and evolution of a splay fault in the Nankai accretionary wedge. Nature Geoscience, 2(9): 648-652. DOI:10.1038/ngeo609 |
Sun HS, Zhao LJ, Wu GB, Ning JT, Chen QM and Jiang CL. 2012. Metallogenic tectonic setting and ore-finding potential of Xitieshan massive sulfide lead-zinc deposit:Evidence from lithochemistry and geochemistry of ore-hosted volcanic strata, Tanjianshan Group. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(2): 652-664. |
Sun YG, Hao WJ, Han YS and Liu YA. 2000. Characteristics of the Tomorit ophiolite-like assemblage in the eastern sector of the northern margin of the Qaidam basin. Regional Geology of China, 19(3): 258-264. |
Tong HK, Zhang SG, Xu GW and Huang YB. 2009. Characteristic and genesis of ductile-shear zone related gold deposits in Saibagou of Wulan County. Northwestern Geology, 42(1): 88-94. |
Von Huene R and Scholl DW. 1991. Observations at convergent margins concerning sediment subduction, subduction erosion, and the growth of continental crust. Reviews of Geophysics, 29(3): 279-316. DOI:10.1029/91RG00969 |
Wakabayashi J. 2015. Anatomy of a subduction complex:Architecture of the Franciscan Complex, California, at multiple length and time scales. International Geology Review, 57(5-8): 669-746. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2014.998728 |
Wakita K and Metcalfe I. 2005. Ocean plate stratigraphy in East and Southeast Asia. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(6): 679-702. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.04.004 |
Wakita K. 2012. Mappable features of mélanges derived from Ocean Plate Stratigraphy in the Jurassic accretionary complexes of Mino and Chichibu terranes in Southwest Japan. Tectonophysics, 568-569: 74-85. DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2011.10.019 |
Wakita K. 2015. OPS mélange:A new term for mélanges of convergent margins of the world. International Geology Review, 57(5-8): 529-539. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2014.949312 |
Wan YS, Zhang JX, Yang JS and Xu ZQ. 2006. Geochemistry of high-grade metamorphic rocks of the North Qaidam Mountains and their geological significance. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 28(2-3): 174-184. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.018 |
Wang HC, Lu SN, Yuan GB, Xin HT, Zhang BH, Wang QH and Tian Q. 2003. Tectonic setting and age of the "Tanjianshan Group" on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin. Geological Bulletin of China, 22(7): 487-493. |
Wang HC, Lu SN, Mo XX, Li HK and Xin HT. 2005. An Early Paleozoic collisional orogen on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin, northwestern China. Geological Bulletin of China, 24(7): 603-612. |
Wang HC, Li HK, Lu SN, Yuan GB and Xin HT. 2006. Geological characteristics and tectonic setting of the Dakendaba Group in Iqe area, northern margin of Qaidam basin. Geological Survey and Research, 29(4): 253-262. |
Windley BF, Allen MB, Zhang C, Zhao ZY and Wang GR. 1990. Paleozoic accretion and Cenozoic redeformation of the Chinese Tien Shan Range, central Asia. Geology, 18(2): 128-131. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<0128:PAACRO>2.3.CO;2 |
Wu CL, Yang JS, Ireland T, Wooden J, Li HB, Wan YS and Shi RD. 2001. Zircon SHRIMP ages of Aolaoshan granite from the south margin of Qilianshan and its geological significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(2): 215-221. |
Wu CL, Yang JS, Xu ZQ, Wooden JL, Ireland T, Li HB, Shi RD, Meng FC, Chen SY, Persing H and Meibom A. 2004. Granitic magmatism on the Early Paleozoic UHP belt of northern Qaidam, NW China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78(5): 658-674. |
Wu CL, Gao YH, Li ZL, Lei M, Qin HP, Li MZ, Liu CH, Frost RB, Robinson PT and Wooden JL. 2014. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of granites from Dulan and the chronological framework of the North Qaidam UHP belt, NW China. Science China (Earth Sciences), 57(12): 2945-2965. DOI:10.1007/s11430-014-4958-5 |
Wu JR, Ren BC, Zhang M, Gao DC, Zhao T, Zhang HW, Song ZG and Zhang QL. 1987. The genetic type and geological characteristics of the Xitieshan massive sulfide deposit, Qinghai. Bulletin of Xi'an Institute of Geological Mineral Resources, Chinese Academic Geological Sciences, (20): 1-30 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Xia WJ, Niu ML, Yan Z, Wu Q, Guo XQ, Fu CL and Li JL. 2014. Sedimentary facies of the Maoniushan Formation in Maoniushan area along the northern margin of Qaidam terrane. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(5): 943-955. |
Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Hao J and Zhai MG. 2003. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China:Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt. Tectonics, 22(6): 1069. DOI:10.1029/2002TC001484 |
Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Sun S, Li JL, Huang BC, Han CM, Yuan C, Sun M and Chen HL. 2015. A tale of amalgamation of three Permo-Triassic collage systems in Central Asia:Oroclines, sutures, and terminal accretion. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 43(1): 477-507. DOI:10.1146/annurev-earth-060614-105254 |
Xiong Q, Zheng JP, Griffin WL, O'Reilly SY and Zhao JH. 2011. Zircons in the Shenglikou ultrahigh-pressure garnet peridotite massif and its country rocks from the North Qaidam terrane (western China):Meso-Neoproterozoic crust-mantle coupling and Early Paleozoic convergent plate-margin processes. Precambrian Research, 187(1-2): 33-57. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2011.02.003 |
Xiong Q, Zheng JP, Griffin WL, O'Reilly SY and Pearson NJ. 2012. Decoupling of U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircon from the UHP North Qaidam orogen, NE Tibet (China):Tracing the deep subduction of continental blocks. Lithos, 155: 125-145. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.08.022 |
Xiong XW and Chen YY. 1994. Problems of the Early Palaeozoic aulacogen on the northern border of the Qaidam Massif. In: Wang HZ, Wang ZQ, Zhang LH et al. (eds.). Tectonic Evolution of the Mesoproterozoic, Neoproterozoic and Palaeozoic Continental Margins of China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. 114-131 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Yan QR and Wang T. 2003. Advances on fluid of accretionary wedge in the orogene of subduction-accretion. Geological Science and Technology Information, 22(1): 7-12. |
Yan Z, Li JL, Yong Y, Xiao WJ, Wang ZQ and Xiang YS. 2008. Tectonic environment of Ordovician carbonate-chert in the Shihuigou area, North Qilian orogen. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(10): 2384-2394. |
Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Li JL, Xu ZQ and Deng JF. 2012. Tectonic settings and accretionary orogenesis of the West Qinling Terrane, northeastern margin of the Tibet Plateau. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(6): 1808-1828. |
Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Fu CL, Niu ML, Ji WH, Li RS, Qi SS and Mao XC. 2018a. Characteristics and thematic geological mapping of mélanges. Geological Bulletin of China, 37(2-3): 167-191. |
Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Yan QR, Fang AM and Chen JL. 2018b. Identification and reconstruction of tectonic archetype of the sedimentary basin within the orogenic belt developed along convergent margin. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(7): 1943-1958. |
Yang JS, Xu ZQ, Li HB, Wu CL, Cui JW, Zhang JX and Chen W. 1998. Discovery of eclogite at northern margin of Qaidam basin, NW China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 43(20): 1755-1760. DOI:10.1007/BF02883981 |
Yang JS, Xu ZQ, Zhang JX, Song SG, Wu CL, Shi RD, Li HB and Maurice B. 2002. Early Palaeozoic North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt on the north-eastern Tibetan Plateau and a paired subduction model. Terra Nova, 14(5): 397-404. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-3121.2002.00438.x |
Yang JS, Zhang JX, Meng FC, Shi RD, Wu CL, Xu ZQ, Li HB and Chn SY. 2003. Ultrahigh pressure eclogites of the North Qaidam and Altun mountains, NW China and their protoliths. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(3): 291-314. |
Yang JS, Shi RD, Wu CL and Chen SY. 2004. Recognition of Neoproterozoic ophiolite on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin:Evidence of the breakup of Rodinia?. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(9-10): 892-898. |
Yang JS, Wu CL, Zhang JX, Shi RD, Meng FC, Wooden J and Yang HY. 2006. Protolith of eclogites in the North Qaidam and Altun UHP terrane, NW China:Earlier oceanic crust?. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 28(2-3): 185-204. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.020 |
Yuan GB, Wang HC, Li HM, Hao GJ, Xin HT, Zhang BH, Wang QH and Tian Q. 2003. Zircon U-Pb age of the gabbros in Luliangshan area on the northern margin of Qaidam basin and its geological implication. Progress in Precambrian Research, 25(1): 36-40. |
Zha XF, Gu PY, Ji WH, Dong ZC, Chen RM and Zhang HD. 2013. The material composition and deformation characteristics of Dakendaban Rock Group, in western Oulongbuluke micro-block, north to Lenghu in Qinghai Province. Chinese Journal of Geology, 48(4): 1103-1114. |
Zhang C, Zhang LF, van Roermund H, Song SG and Zhang GB. 2011. Petrology and SHRIMP U-Pb dating of Xitieshan eclogite, North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 42(4): 752-767. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.04.002 |
Zhang C, van Roermund H, Zhang LF and Spiers C. 2012. A polyphase metamorphic evolution for the Xitieshan paragneiss of the North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt, western China:In-situ EMP monazite-and U-Pb zircon SHRIMP dating. Lithos, 136-139: 27-45. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.07.024 |
Zhang GB, Song SG, Zhang LF and Niu YL. 2008. The subducted oceanic crust within continental-type UHP metamorphic belt in the North Qaidam, NW China:Evidence from petrology, geochemistry and geochronology. Lithos, 104(1-4): 99-118. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.12.001 |
Zhang GB, Zhang LF, Song SG and Niu YL. 2009a. UHP metamorphic evolution and SHRIMP geochronology of a coesite-bearing meta-ophiolitic gabbro in the North Qaidam, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(3-4): 310-322. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.11.013 |
Zhang JE, Chen YC, Xiao WJ, Chen ZY and Song SH. 2018. Buoyant units on oceanic crust and their contributions to components of ophiolitic mélanges in orogenic belts. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(7): 1977-1990. |
Zhang JX, Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Zhang ZM and Cui JW. 2001. Petrology, geochemistry and geochronology of eclogites from the western segment of the Altun tectonic belt, northwestern China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 75(2): 186-197. |
Zhang JX, Yang JS, Meng FC, Wan YS, Li HM and Wu CL. 2006. U-Pb isotopic studies of eclogites and their host gneisses in the Xitieshan area of the North Qaidam mountains, western China:New evidence for an Early Paleozoic HP-UHP metamorphic belt. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 28(2-3): 143-150. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.017 |
Zhang JX, Mattinson CG, Meng FC, Yang HJ and Wan YS. 2009b. U-Pb geochronology of paragneisses and metabasite in the Xitieshan area, North Qaidam Mountains, western China:Constraints on the exhumation of HP/UHP metamorphic rocks. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(3-4): 245-258. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.08.008 |
Zhang JX, Mattinson CG, Yu SY, Li JP and Meng FC. 2010. U-Pb zircon geochronology of coesite-bearing eclogites from the southern Dulan area of the North Qaidam UHP terrane, northwestern China:Spatially and temporally extensive UHP metamorphism during continental subduction. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 28(9): 955-978. DOI:10.1111/jmg.2010.28.issue-9 |
Zhang JX, Yu SY, Li YS, Yu XX, Lin YH and Mao XH. 2015. Subduction, accretion and closure of Proto-Tethyan Ocean:Early Paleozoic accretion/collision orogeny in the Altun-Qilian-North Qaidam orogenic system. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(12): 3531-3554. |
Zhang JX, Yu SY and Mattinson CG. 2017. Early Paleozoic polyphase metamorphism in northern Tibet, China. Gondwana Research, 41: 267-289. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.11.009 |
Zhang XP, Wang QF, Hui J, Chang X and Tong HK. 2015. Chemical characteristics of volcanic rocks from the Tanjianshan Group on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin and its tectonic environment. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 35(1): 18-26. |
Zhao FQ, Guo JJ and Li HK. 2003. Geological characteristics and isotopic age of Tanjianshan Group along northern margin of Qaidam basin. Geological Bulletin of China, 22(1): 28-31. |
Zhou GS, Zhang JX, Li YS, Yu SY, Yu XX, Mao XH and Lu ZL. 2017. Redefinition of the polyphase tectonothermal events of the North Qaidaim HP/UHP metamorphic terrane:Evidence from zircon and monazite U-Pb geochronology of the Yuka HP metapelites. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(12): 3801-3814. |
Zhu XH, Chen DL, Liu L and Li D. 2010. Zicon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of the Wanggaxiu gabbro complex in the Dulan area, northern margin of Qaidam Basin, China and its geological significance. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(2-3): 227-236. |
Zhu XH, Chen DL, Liu L, Zhao J and Zhang L. 2014. Geochronology, geochemistry and significance of the Early Paleozoic back-arc type ophiolite in Lvliangshan area, North Qaidam. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(3): 822-834. |
Zhu XH, Chen DL, Wang C, Wang H and Liu L. 2015. The initiation, development and termination of the Neoproterozoic-Early Paleozoic ocean in the northern margin of Qaidam basin. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(2): 234-251. |
Zhuang RX and Li F. 2006. The characteristics and formation environment of Tanjianshan Group volcanic rock of north margin of Chaidamu basin. Yunnan Geology, 25(2): 209-217. |
方爱民, 侯泉林, 李继亮, 郝杰, 肖文交, 周辉. 2003. 西昆仑库地混杂岩带中深海浊积岩的浊积相划分及其特征. 地质科学, 38(1): 1-12. |
付长垒, 闫臻, 王宗起, 牛漫兰, 郭现轻, 俞良军, 李继亮. 2018. 南祁连拉脊山口增生楔的结构与组成特征. 岩石学报, 34(7): 2049-2064. |
付建刚, 梁新权, 王策, 蒋英, 周云, 潘传楚, 杨永强, 王泽利, 钟永生. 2016. 柴北缘锡铁山韧性剪切带的基本特征及其形成时代. 大地构造与成矿学, 40(1): 14-28. |
高晓峰, 校培喜, 贾群子. 2011. 滩间山群的重新厘定——来自柴达木盆地周缘玄武岩年代学和地球化学证据. 地质学报, 85(9): 1452-1463. |
韩英善, 彭琛. 2000. 托莫尔日特蛇绿混杂岩带地质特征及其构造意义. 青海地质, 9(1): 18-25. |
赖绍聪, 邓晋福, 赵海玲. 1996. 柴达木北缘古生代蛇绿岩及其构造意义. 现代地质, 10(1): 18-28. |
李峰, 吴志亮, 李保珠, 汪林峰. 2006. 柴达木盆地北缘滩间山群新厘定. 西北地质, 39(3): 83-90. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2006.03.012 |
李峰, 吴志亮, 李保珠. 2007. 柴达木北缘滩间山群时代及其地质意义. 大地构造与成矿学, 31(2): 226-233. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2007.02.012 |
李怀坤, 陆松年, 赵风清, 于海峰, 郑健康. 1999. 柴达木盆地北缘鱼卡河含柯石英榴辉岩的确定及其意义. 现代地质, 13(1): 43-50. |
李继亮. 2004. 增生型造山带的基本特征. 地质通报, 23(9-10): 947-951. |
陆松年, 王惠初, 李怀坤, 袁桂邦, 辛后田, 郑健康. 2002. 柴达木盆地北缘"达肯大坂群"的再厘定. 地质通报, 21(1): 19-23. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.01.004 |
潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 邓晋福, 冯益民, 张克信, 张智勇, 王方国, 邢光福, 郝国杰, 冯艳芳. 2008. 大地构造相的定义、划分、特征及其鉴别标志. 地质通报, 27(10): 1613-1637. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.10.004 |
青海省地质矿产局. 1991. 青海省区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-662.
|
史仁灯, 杨经绥, 吴才来. 2003. 柴北缘早古生代岛弧火山岩中埃达克质英安岩的发现及其地质意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 22(3): 229-236. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2003.03.004 |
史仁灯, 杨经绥, 吴才来, Iizuka T, Hirata T. 2004. 柴达木北缘超高压变质带中的岛弧火山岩. 地质学报, 78(1): 52-64. |
孙华山, 赵立军, 吴冠斌, 宁钧陶, 陈巧妹, 姜楚灵. 2012. 锡铁山块状硫化物铅锌矿床成矿构造环境及矿区南部找矿潜力:来自滩间山群火山岩岩石化学、地球化学证据. 岩石学报, 28(2): 652-664. |
孙延贵, 郝维杰, 韩英善, 刘永安. 2000. 柴达木盆地北缘东段托莫尔日特似蛇绿岩岩石组合特征. 中国区域地质, 19(3): 258-264. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2000.03.008 |
童海奎, 张顺桂, 许国武, 黄银宝. 2009. 乌兰县赛坝沟韧性剪切带型金矿特征及成因. 西北地质, 42(1): 88-94. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2009.01.009 |
王惠初, 陆松年, 袁桂邦, 辛后田, 张宝华, 王青海, 田琪. 2003. 柴达木盆地北缘滩间山群的构造属性及形成时代. 地质通报, 22(7): 487-493. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.07.005 |
王惠初, 陆松年, 莫宣学, 李怀坤, 辛后田. 2005. 柴达木盆地北缘早古生代碰撞造山系统. 地质通报, 24(7): 603-612. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2005.07.003 |
王惠初, 李怀坤, 陆松年, 袁桂邦, 辛后田. 2006. 柴北缘鱼卡地区达肯大坂岩群的地质特征与构造环境. 地质调查与研究, 29(4): 253-262. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2006.04.004 |
吴才来, 杨经绥, Ireland T, Wooden J, 李海兵, 万渝生, 史仁灯. 2001. 祁连南缘嗷唠山花岗岩SHRIMP锆石年龄及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 17(2): 215-221. |
吴才来, 杨经绥, 许志琴, Wooden JL, Ireland T, 李海兵, 史仁灯, 孟繁聪, 陈松永, Persing H, Meibom A. 2004. 柴达木盆地北缘古生代超高压带中花岗质岩浆作用. 地质学报, 78(5): 658-674. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2004.05.010 |
邬介人, 任秉琛, 张莓, 高栋丞, 赵统, 张汉文, 朱志高, 张群力. 1987. 青海锡铁山块状硫化物矿床的类型及地质特征. 中国地质科学院西安地质矿产研究所文集, (20): 1-30. |
夏文静, 牛漫兰, 闫臻, 吴齐, 郭现轻, 付长垒, 李继亮. 2014. 柴北缘牦牛山地区牦牛山组沉积相组合特征. 地质学报, 88(5): 943-955. |
熊兴武, 陈忆元. 1994.柴达木地块北缘早古生代裂陷槽.见: 王鸿祯, 王自强, 张玲华等著.中国古大陆边缘中、新元古代及古生代构造演化.北京: 地质出版社, 114-131
|
闫臻, 王宗起, 闫全人, 王涛. 2003. 俯冲-增生型造山带增生楔流体研究进展. 地质科技情报, 22(1): 7-12. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2003.01.002 |
闫臻, 李继亮, 雍拥, 肖文交, 王宗起, 向永生. 2008. 北祁连石灰沟奥陶纪碳酸盐岩-硅质岩形成的构造环境. 岩石学报, 24(10): 2384-2394. |
闫臻, 王宗起, 李继亮, 许志琴, 邓晋福. 2012. 西秦岭楔的构造属性及其增生造山过程. 岩石学报, 28(6): 1808-1828. |
闫臻, 王宗起, 付长垒, 牛漫兰, 计文化, 李荣社, 祁生胜, 毛晓长. 2018a. 混杂岩基本特征与专题地质填图. 地质通报, 37(2-3): 167-191. |
闫臻, 王宗起, 闫全人, 方爱民, 陈隽璐. 2018b. 造山带汇聚板块边缘沉积盆地的鉴别与恢复. 岩石学报, 7(34): 1943-1958. |
杨经绥, 许志琴, 李海兵, 吴才来, 崔军文, 张建新, 陈文. 1998. 我国西部柴北缘地区发现榴辉岩. 科学通报, 43(14): 1544-1549. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.14.023 |
杨经绥, 张建新, 孟繁聪, 史仁灯, 吴才来, 许志琴, 李海兵, 陈松永. 2003. 中国西部柴北缘-阿尔金的超高压变质榴辉岩及其原岩性质探讨. 地学前缘, 10(3): 291-314. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.03.026 |
杨经绥, 史仁灯, 吴才来, 陈松永. 2004. 柴达木盆地北缘新元古代蛇绿岩的厘定——罗迪尼亚大陆裂解的证据?. 地质通报, 23(9-10): 892-898. |
袁桂邦, 王惠初, 李惠民, 等. 2002. 柴北缘绿梁山地区辉长岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及意义. 前寒武纪研究进展, 25(1): 36-40. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2002.01.005 |
查显锋, 辜平阳, 计文化, 董增产, 陈锐明, 张海迪. 2013. 欧龙布鲁克地块西段达肯大坂岩群物质组成及变形特征研究. 地球科学, 48(4): 1103-1114. |
张建新, 许志琴, 杨经绥, 张泽明, 崔军文. 2001. 阿尔金西段榴辉岩岩石学、地球化学和同位素年代学研究及其构造意义. 地质学报, 75(2): 186-197. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2001.02.007 |
张建新, 于胜尧, 李云帅, 喻星星, 林宜慧, 毛小红. 2015. 原特提斯洋的俯冲、增生及闭合:阿尔金-祁连-柴北缘造山系早古生代增生/碰撞造山作用. 岩石学报, 31(12): 3531-3554. |
张继恩, 陈艺超, 肖文交, 陈振宇, 宋帅华. 2018. 洋底凸起地质体及其对造山带中蛇绿岩组分的贡献. 岩石学报, 34(7): 1977-1990. |
张孝攀, 王权锋, 惠洁, 常鑫, 童海奎. 2015. 柴北缘滩间山群火山岩岩石化学特征及构造环境. 矿物岩石, 35(1): 18-26. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.01.002 |
赵风清, 郭进京, 李怀坤. 2003. 青海锡铁山地区滩间山群的地质特征及同位素年代学. 地质通报, 22(1): 28-31. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.01.005 |
周桂生, 张建新, 李云帅, 于胜尧, 喻星星, 毛小红, 路增龙. 2017. 柴北缘HP-UHP变质带多期构造热事件的再厘定:鱼卡地区高压变泥质岩锆石和独居石U-Pb定年. 岩石学报, 33(12): 3801-3814. |
朱小辉, 陈丹玲, 刘良, 李涤. 2010. 柴达木盆地北缘都兰地区旺尕秀辉长杂岩的锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄及地质意义. 地质通报, 29(2-3): 227-236. |
朱小辉, 陈丹玲, 刘良, 赵姣, 张乐. 2014. 柴北缘绿梁山地区早古生代弧后盆地型蛇绿岩的年代学、地球化学及大地构造意义. 岩石学报, 30(3): 822-834. |
朱小辉, 陈丹玲, 王超, 王红, 刘良. 2015. 柴达木盆地北缘新元古代-早古生代大洋的形成、发展和消亡. 地质学报, 89(2): 234-252. |
庄儒新, 李峰. 2006. 柴达木盆地北缘滩间山群火山岩及形成环境. 云南地质, 25(2): 209-217. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2006.02.010 |
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35


