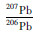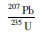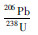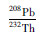2. 山东理工大学资源与环境工程学院, 淄博 255000
2. School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, Shandong University of Technology, Zibo 255000, China
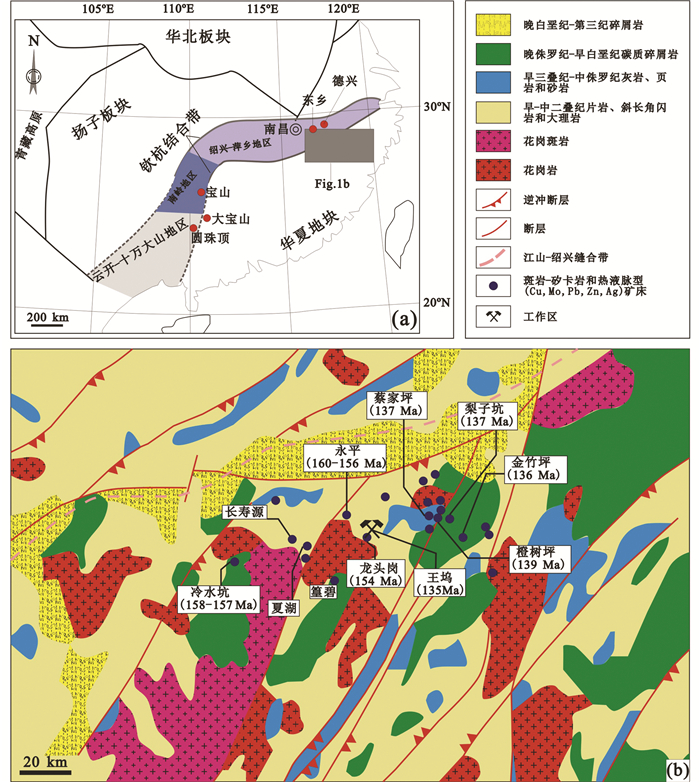
钦杭带位于扬子板块和华夏板块之间,为一条新元古代的碰撞拼接带,是我国重要的Cu、Mo、W、Pb、Zn、Ag多金属成矿带(图 1a,b; 杨明桂和梅勇文,1997;Mao et al., 2011, 2013)。钦杭成矿带内发育有多个大型斑岩-矽卡岩铜多金属矿床,如德兴斑岩型Cu矿床(华仁民等, 2000; 毛景文等, 2010, 2011; Zhou et al., 2012; Hou et al., 2013)、永平矽卡岩型Cu(W)矿床(李晓峰等, 2007; 田明君等, 2014)、宝山矽卡岩型Cu-Mo-W-Pb-Zn-Ag矿床(路远发等, 2006)、大宝山斑岩-矽卡岩型Cu-Mo-W矿床(毛伟等, 2013)、圆珠顶斑岩型Cu-Mo矿床(陈富文等, 2012; Zhong et al., 2013;楚克磊等, 2013)以及东乡Cu矿床(付守会和陈广浩, 2003; 欧阳学才, 2015)等矿床。北武夷地区位于钦-杭成矿带的东北部(图 1a; 杨明桂和梅勇文,1997),区内发育多个Cu-Pb-Zn-Ag多金属矿床,如冷水坑大型火山热液-斑岩型Ag-Pb-Zn矿床(罗诒爵, 1985; 董绍芳, 1994; 卢燃等, 2012; Wang et al., 2013, 2014)和永平矽卡岩型Cu(W)矿床等(张万祥, 1995; 肖志宏, 1996;张学书, 1997; Jiang et al., 2008; Yu et al., 2012;苏慧敏, 2013)。近些年,该地区的找矿勘查工作,取得了很多新的进展,发现了一批新的斑岩-矽卡岩Cu-Mo矿床,如龙头岗矽卡岩-热液脉型Cu-Zn矿床和王坞斑岩型Mo-Cu矿床,表明该地区具有巨大的找矿前景,也指示我国的华南地区仍具有很好的找矿潜力。
|
图 1 华南板块构造简图(a)及北武夷地区地质矿产略图(b)(据Yu et al., 2012; Wu et al., 2015修改) Fig. 1 Simplified tectonic maps of South China (a) and sketch map of ore deposits in North Wuyi area (b) (modified after Yu et al., 2012; Wu et al., 2015) |
王坞Mo-Cu矿床位于龙头岗矽卡岩-热液脉型Cu-Zn矿矿区北东1.5km处。该矿床于2009年被江西省地矿局赣东北大队发现,目前矿区有5个钻孔见Mo矿化,矿化带最厚430余米且未被揭穿,Mo矿体主要由网脉状石英-辉钼矿矿石组成。从钻孔见矿情况分析,该矿区具有发现中、大型以上Mo-Cu多金属矿床的找矿潜力。目前,虽然在找矿工作方面已取得突破,但是对该矿床的形成时代方面的认识还不清楚。尽管魏娟娟等(2016)测得该矿区内的花斑岩脉的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为127.5±1.8Ma,且获得石英-辉钼矿细脉中辉钼矿的Re-Os等时线年龄为153.7±3.2Ma,但对该矿床形成时代和与成矿相关的岩体的认定方面还存在争议。本文在前人研究工作的基础上,对王坞矿区内的花岗斑岩和主要矿石类型(网脉状石英-辉钼矿矿石)分别进行了高精度的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年和辉钼矿Re-Os定年,重新厘定了该矿床的成岩、成矿时限,并在此基础上结合前人的研究资料,讨论了北武夷山地区斑岩-矽卡岩-热液脉型Cu多金属矿床的成矿时代和动力学背景。
1 区域地质背景华南地区由位于该区西北部的扬子板块和东南部的华夏板块组成(Xie et al., 2018a, b)。钦州-杭州成矿带位于扬子板块与华夏陆块的碰撞拼接带(杨明桂和梅勇文,1997; 毛景文等, 2011; 徐德明等, 2012),该带形成于新元古代扬子板块与华夏板块之间的碰撞拼接,之后又经历了加里东、印支和燕山运动的叠加改造(张国伟等, 2013)。该矿带全长近2000km,宽约100~150km,从西南端的广西钦州湾、经湘东和赣中一直延伸到东北端的浙江杭州湾,整体呈北东向反S状弧形展布(图 1a,b; 杨明桂和梅勇文,1997; 周永章等, 2010, 2012;毛景文等, 2011)。钦杭带可以分为北段、中段和南段三个部分(毛景文等, 2011),北武夷地区位于钦杭带的北段(图 1a; Wu et al., 2015)。钦杭带是我国重要的铜多金属成矿带,毛景文等(2011)将钦杭带内及旁侧矿床归纳为两个成矿系列和三个成矿亚系列,即:新元古代海底喷流沉积型Cu-Zn矿床成矿系列及燕山期与花岗岩有关的W-Sn-Cu-Pb-Zn多金属矿床成矿系列,又把后者进一步划分为中-晚侏罗世斑岩-矽卡岩-热液脉状Cu多金属矿床成矿亚系列、晚侏罗世与花岗岩有关的W-Sn多金属矿床成矿亚系列和白垩纪与次火山活动有关的浅成低温热液型Au-Ag-Pb-Zn-W-Sn矿床成矿亚系列。尽管钦杭带主要形成于新元古代,但该带绝大多数矿床形成于中晚侏罗世至白垩纪(毛景文等, 2011)。
1.1 地层北武夷地区的地层由中元古代和新元古代的高绿片岩相-低角闪岩相的变质岩基底及与其呈不整合接触的上覆早古生代、晚石炭世到新生代地层组成(Yu et al., 2012)。前者包括蓟县系周潭岩组云母片岩、石英片岩、黑云斜长片麻岩夹斜长角闪岩、斜长变粒岩和凝灰岩,以及青白口系万源岩组黑云斜长变粒岩、片麻岩夹云母片岩、石英片岩、变余砂岩(原岩为一套海相泥砂质碎屑沉积岩夹火山碎屑及熔岩的复理石建造)(罗平, 2005, 2010);后者包括震旦-寒武系属稳定型沉积的泥砂质含火山物质夹炭硅质、碳酸盐建造的洪山组和外管坑组,一套滨、浅海相泥砂质、碳酸盐建造夹海陆交互相碎屑建造和含煤建造的石炭系上统、二叠系以及三叠系下统和中统地层,属于陆相河湖碎屑岩及火山岩建造的三叠系上统-侏罗系,红色碎屑岩夹火山碎屑岩的白垩系,以及沿沟谷零星分布的新生代沉积物。
1.2 岩浆岩北武夷地区的岩浆岩分布广泛,且类型齐全,超基性-酸性岩类均有发育,其中以中-酸性岩类更为重要(江西省地质矿产局, 1984)。区内岩浆岩整体受区域构造控制,主体多呈带状展布,延伸方向以北东向和北北东向为主,其次为北西和北东东向。
该地区在晋宁期、加里东期、海西-印支期和燕山期等都有岩浆活动,其中以燕山期的岩浆活动规模最大(苏慧敏, 2013; 秦晓峰, 2014)。晋宁期岩浆岩主要为基性、超基性喷出岩和侵入岩;加里东期火山岩主要为钙碱性英安岩-流纹岩组合;海西-印支期岩浆岩主要为小规模的海相中基性、酸性喷出岩和小规模的铁镁质侵入体;燕山期侵入岩呈现多期次性,且类型繁多,超基性-酸性岩类均有发育,但主要是以中酸性岩为主(苏慧敏, 2013)。燕山期花岗岩的岩性主要为花岗斑岩、中细粒黑云母花岗岩、黑云母花岗斑岩以及碱长花岗岩。
1.3 构造自中新元古代以来,北武夷地区经历了多次构造运动,形成了一系列不同方向、不同性质、不同规模的断裂构造(罗平, 2010),这些断裂的展布方向可分为东西向、北东向、北北东向、北西向和南北向五组(罗平, 2010)。其中北东向鹰潭-安远大断裂和东西向广丰-萍乡深断裂联合控制了区域范围内整体的构造格局(苏慧敏等, 2013)。区域内发育的褶皱构造主要有晋宁-加里东期的基底褶皱和华力西-印支期形成并受燕山运动影响和改造的盖层褶皱(罗平, 2010)。基底褶皱为近东西向复式倒转褶皱,盖层褶皱则以宽缓开阔的短轴向斜或背斜为主,轴向主要为北东向和北东东向(魏娟娟等, 2016)。此外,区域内还广泛发育有推覆构造,这些推覆构造对矿床的形成和保存起到了重要的作用(余心起等, 2008; 邱骏挺等, 2011; 狄永军等, 2013; 董越等, 2015),冷水坑Pb-Zn-Ag矿和永平Cu矿等都受到了推覆构造的控制或影响。区内发育多个中生代盆地(江西省地质矿产局, 1984),主要包括铅山火山断陷盆地、天华山火山盆地、黄岗山火山盆地和铜钹山火山盆地(罗平, 2010)。
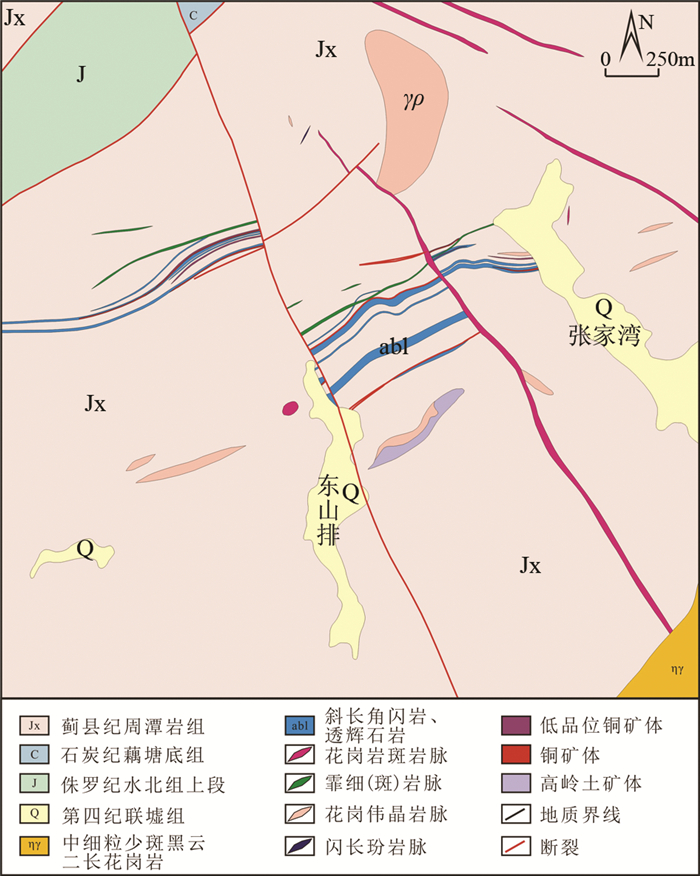
2 矿床地质铅山县王坞Mo-Cu矿床位于龙头岗矿床北东方向约1.5km处。矿区内出露的地层较为简单,主要为蓟县系周潭岩组片岩(云母片岩、石英片岩)、变粒岩(斜长变粒岩)、片麻岩(黑云斜长片麻岩)夹斜长角闪岩、斜长变粒岩、凝灰岩等变质岩;下侏罗统水北组粉砂岩、炭质页岩和泥岩(图 2),其中周潭岩组为该矿床主要的赋矿层位。矿区内褶皱构造不发育,断裂构造可分为北东向和北西向二组(图 2),其中北东向断裂规模较大。矿区内的侵入岩主要有花岗斑岩及少量的石英闪长玢岩等,呈岩脉、岩枝、岩墙状产出,走向以北东东向和北西向为主。
|
图 2 王坞Mo-Cu矿矿床地质图 Fig. 2 Geological map of the Wangwu Mo-Cu deposit |
矿区内的花岗斑岩整体呈灰白色,细粒斑状结构,块状构造。斑晶主要为石英(35%)和钾长石(45%),以及少量斜长石(10%)和黑云母(10%),粒径为0.1~1mm,一般为0.2~0.6mm。部分钾长石斑晶发生了绿泥石化和泥化。基质主要由石英和长石组成。
矿区内的围岩蚀变主要有硅化、绢英岩化、云英岩化、绿泥石化、钾化、绿帘石化、阳起石化和透辉石化等。其中,硅化和绢英岩化与钼矿化关系密切。
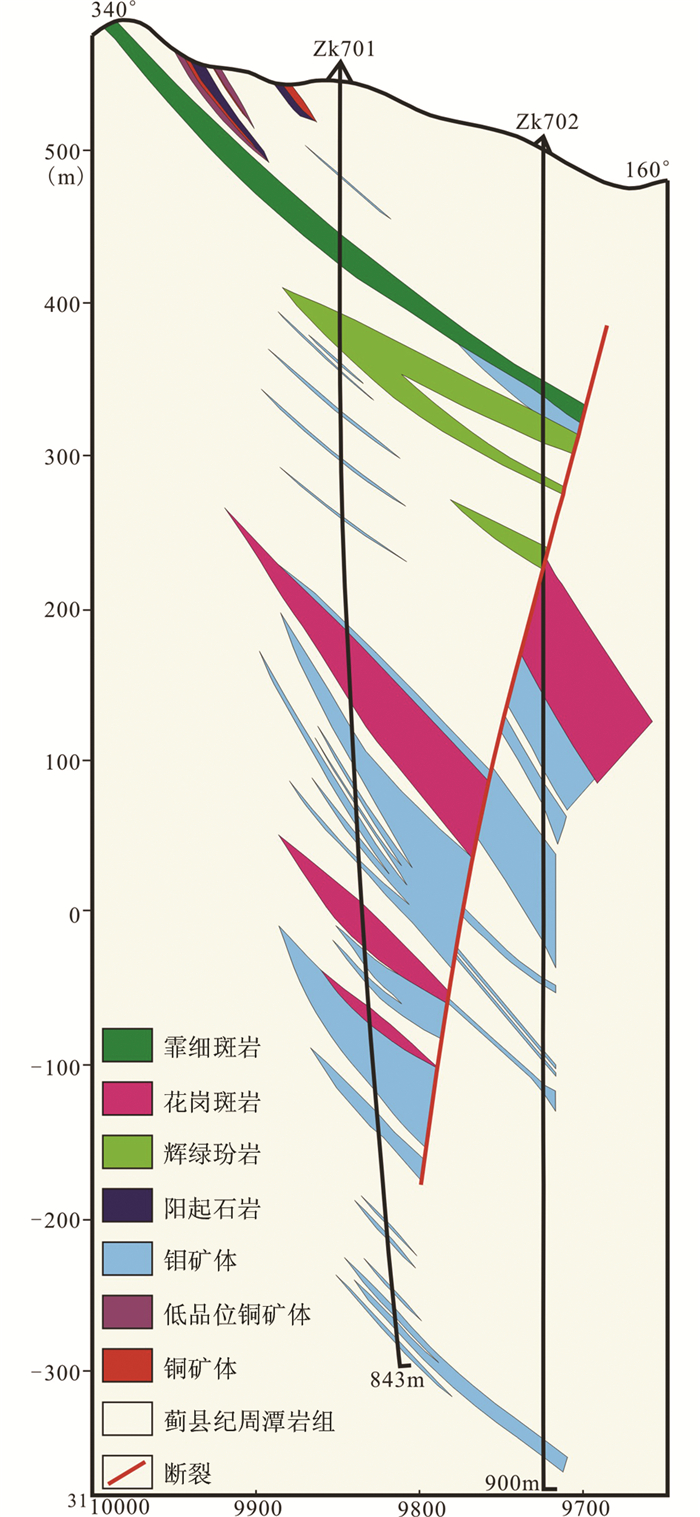
该矿床的矿体主要产出于周潭岩组及花岗斑岩的接触带(图 3)。Cu矿体主要分布在浅部,呈透镜状、似层状产出。矿区深部也有铜矿化,ZK803孔于孔深309~383m段发育视厚度达74m的云英岩脉带,云英岩脉普遍具黄铜矿和闪锌矿化,铜锌矿化视厚度40m以上。Mo矿体主要在标高400m以下,主要由脉状和网脉状石英-辉钼矿矿石组成(图 4),其次为细脉型和细脉浸染型。石英脉宽一般为0.1~3.0cm,以0.2~1.5cm为主。石英脉中的金属矿物主要为辉钼矿(图 4),其次少量的黄铁矿和黄铜矿(图 4e);脉石矿物主要为石英(图 4),其次白云母和少量的黑云母(图 4d)。辉钼矿主要以板状、片状、鳞片状集合体的形式产出于石英脉内及两侧,粒径可达2mm;周潭岩组岩石中的浸染状辉钼矿粒度通常较小,一般小于1mm。
|
图 3 王坞Mo-Cu矿床7线地质剖面图 Fig. 3 Geological section along No.7 line of Wangwu Mo-Cu deposit |

|
图 4 王坞Mo-Cu矿典型钼矿化特征 Qz-石英; Mo-辉钼矿; Ms-白云母; Py-黄铁矿 Fig. 4 Typical molybdenum mineralization characteristics Qz-quartz; Mo-molybdenite; Ms-muscovite; Py-pyrite |
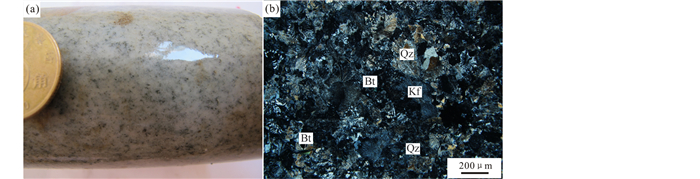
本次研究采集了1件花岗斑岩(图 5)样品进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年,5件网脉状石英-辉钼矿矿石中的辉钼矿样品进行Re-Os同位素测试。
|
图 5 花岗斑岩手标本及显微镜下照片 Kf-钾长石; Bt-黑云母 Fig. 5 Photo and photomicrograph of granite porphyry Kf-K-feldspar; Bt-biotite |
将花岗斑岩样品人工破碎至60~80目以下,经淘洗后用电磁选、重选的方法选出重矿物,再在双目镜下挑选出单颗粒锆石。从锆石颗粒中选出晶形完好和透明度较好的锆石,然后用环氧树脂制靶、抛光,之后对靶中的锆石进行阴极发光、透射光和反射光照相,最后根据这些照片选取环带明显、干净、透明的点位,为LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年测试分析做好准备。
用于Re-Os同位素分析的5件辉钼矿样品均采自于王坞Mo-Cu矿床的矿化石英脉中(图 4)。辉钼矿为铅灰色板状、片状和鳞片状集合体。将样品破碎,选出辉钼矿,在双目镜下分选辉钼矿至纯度达99%以上,并用玛瑙研钵研磨至200目,用于Re-Os同位素分析。
LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年测试分析在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所LA-MC-ICP-MS实验室完成,锆石定年分析所用仪器为FinniganNeptune型MC-ICP-MS及与之配套的NewwaveUP213激光剥蚀系统。激光剥蚀所用斑束直径为25μm,频率为10Hz,能量密度约为2.5J/cm2,以He为载气。信号较小的207Pb、206Pb、204Pb(+204Hg)、202Hg用离子计数器(multi-ion-counters)接收,208Pb、232Th、238U信号用法拉第杯接收,实现了所有目标同位素信号的同时接收并且不同质量数的峰基本上都是平坦的,进而可以获得高精度的数据,均匀锆石颗粒207Pb/206Pb、206Pb/238U、207Pb/235U的测试精度(2σ)均为2%左右,对锆石标准的定年精度和准确度在1%(2σ)左右。LA-MC-ICP-MS激光剥蚀采样采用单点剥蚀的方式,数据分析前用锆石GJ-1进行调试仪器,使之达到最优状态,锆石U-Pb定年以锆石GJ-1为外标,U、Th含量以锆石M127为外标进行校正。测试过程中在每测定7-10个样品前后重复测定两个锆石GJ-1对样品进行校正,并测量一个锆石91500,观察仪器的状态以保证测试的精确度。数据处理采用ICPMSDataCal程序(Liu et al., 2008),测量过程中绝大多数分析点206Pb/204Pb>1000, 未进行普通铅校正,204Pb含量异常高的分析点可能受包体等普通Pb的影响,在计算时剔除,锆石年龄谐和图用Isoplot3.0程序获得。详细实验测试过程可参见侯可军等(2009)。
Re-Os同位素分析测试在国家地质测试中心Re-Os同位素实验室完成。采用Carius管封闭溶样分解样品,Re-Os同位素分析原理及详细分析流程依据Shirey and Walker(1995)和Du et al.(2004)。采用美国TJA公司生产的TJA X-series电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(美国Thermo公司)测定同位素比值。对于Re,选择质量数185、187,用190监测Os;对于Os,选择质量数为186、187、188、189、190、192,用185监测Re。TJA X-series ICP-MS测得的Re、Os和187Os的空白值分别为(0.0035±0.0002)×10-9、(0.0001±0.00002)×10-9和(0.00021±0.00006)×10-9。远小于标样和所测样品中的Re、Os和187Os含量,不会对实验结果造成影响。辉钼矿Re-Os定年实验误差为2σ,普Os是根据原子量表(Wieser, 2006)和同位素丰度表(Bohlkea et al., 2005),通过192Re/190Os测量比计算得出(Bohlkea et al., 2005; Wieser, 2006)。Re、Os含量的不确定度包括样品和稀释剂的称量误差、稀释剂的标定误差、质谱测量的分馏校正误差、待分析样品同位素比值测量误差。模式年龄的不确定度还包括衰变常数的不确定度(1.02%),置信度为95%。实验采用国家标准物质GBW04436(JDC)为标样,来监控化学流程和分析数据等过程的可靠性。实验测得标样GBW04436(JDC)的Re、187Os和模式年龄值都与标准值(Du et al., 2004)在误差范围内完全一致,可以说明所获得的辉钼矿Re-Os分析结果准确可靠。
4 分析结果王坞Mo-Cu矿区花岗斑岩样品中的锆石均为短柱状或长柱状,粒径约为88~147μm,长宽比约为1.5:1~3.5:1。阴极发光图像显示,锆石具有明显的韵律环带(图 6),是典型的岩浆成因锆石(Corfu et al., 2003)。
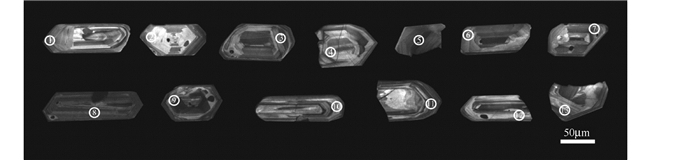
|
图 6 王坞花岗斑岩锆石阴极发光(CL)图像 Fig. 6 Cathodoluminescene (CL) images of zircons from the granite porphyry of the Wangwu deposit |
本次研究对13个锆石颗粒进行了LA-ICP-MS U-Pb分析,结果列于表 1,U-Pb年龄谐和图及加权平均年龄图见图 7。锆石中的Th/U比值可以指示锆石的成因。岩浆锆石的Th/U比一般大于0.5,而变质锆石的Th/U比常小于0.01(Hoskin et al., 2003)。王坞矿区花岗斑岩中锆石的Th/U比值为1.1~2.4,具有岩浆锆石的特点(Hoskin et al., 2003)。锆石的232Th和238U含量变化范围分别为96.97×10-6~1212×10-6和88.32×10-6~986.4×10-6。13个点的206Pb/238U年龄值为131.0±3.2Ma~144.4±9.2Ma,加权平均值为136.7±2.2Ma(MSWD=0.80),该年龄代表了花岗斑岩的成岩年龄。
|
|
表 1 花岗斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb分析结果 Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb analyses results of the granite porphyry |
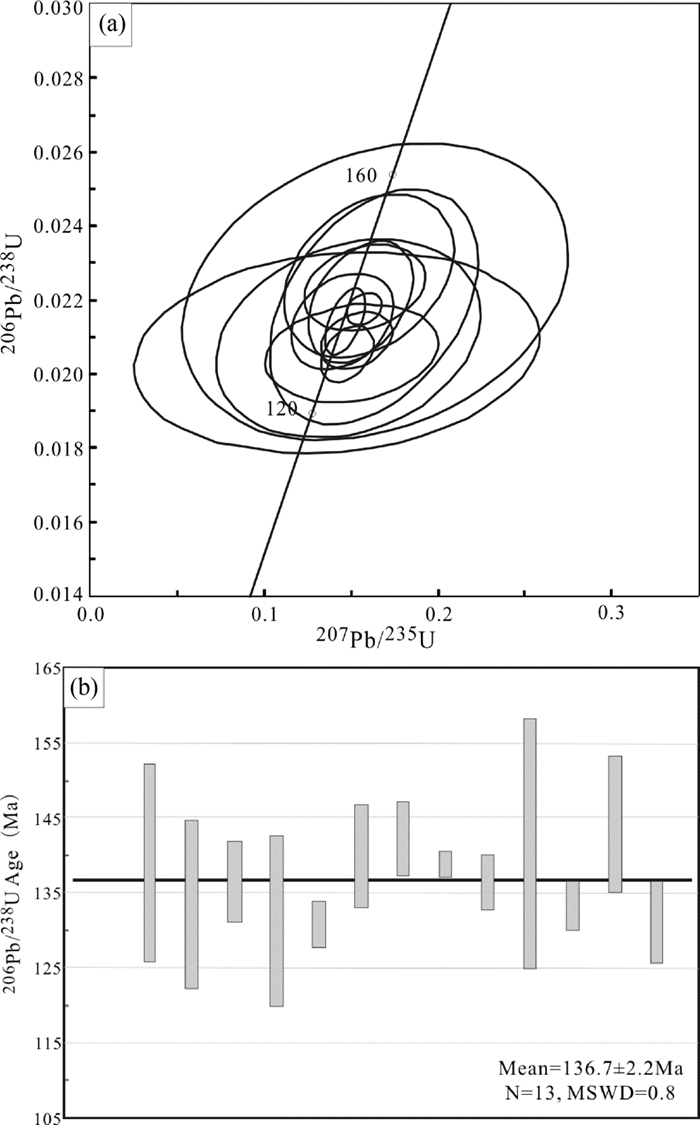
|
图 7 花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图(a)及加权平均年龄图(b) Fig. 7 U-Pb concordia age diagram (a) and weighted average age diagram (b) of the granite porphyry |
王坞Mo-Cu矿床5件辉钼矿样品的Re-Os同位素测试结果列于表 2。5件辉钼矿样品的Re含量为(3.727±0.036)×10-6~(17.30±0.14)×10-6,Re-Os模式年龄为132.6±1.8Ma~134.5±2.0Ma,加权平均值为133.74±0.94Ma (MSWD=0.57)(图 8)。采用ISOPLOT软件对辉钼矿数据进行等时线拟合(Ludwig, 2009),获得Re-Os等时线年龄为134.8±2.1Ma (MSWD=0.74)。
|
|
表 2 王坞Mo-Cu矿辉钼矿Re-Os定年结果 Table 2 Re-Os isotopic data of molybdenites from the Wangwu Mo-Cu deposit |
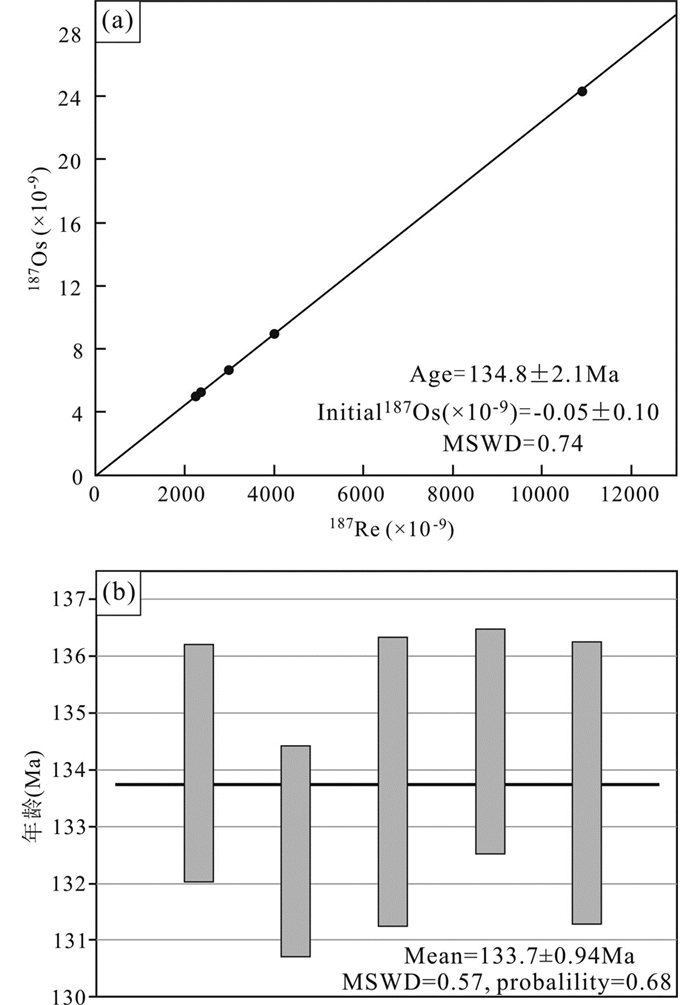
|
图 8 王坞Mo-Cu矿辉钼矿Re-Os等时线年龄图(a)与加权平均年龄图(b) Fig. 8 Re-Os isochron (a) and weighted average (b) ages of molybdenite from the Wangwu Mo-Cu deposit |
本次分析的王坞Mo-Cu矿床中辉钼矿的Re-Os模式年龄为132.6±1.8Ma~134.5±2.0Ma,其加权平均值为133.74±0.94Ma,与Re-Os等时线年龄134.8±2.1Ma在误差范围内一致。辉钼矿Re-Os体系中的解耦现象对辉钼矿Re-Os体系的精确定年有重要的影响(Košler et al., 2003;Stein et al., 2003; Selby and Creaser, 2004; Xie et al., 2007; 杜安道等, 2007; 李超等, 2009)。通常较年轻的及颗粒较小的辉钼矿中Re和187Os的解耦非常弱,仅用少量的样品(1mg的等分样品)就可以获得精确的辉钼矿Re-Os年龄。而年龄较老、颗粒较大的辉钼矿可能需要40mg的等分样品才能克服Re和187Os的解耦对测试精度的影响(Selby and Creaser, 2004; Xie et al., 2007)。采自王坞Mo-Cu矿床中的辉钼矿的粒度为0.1~2mm,本次分析分选粒度较小的辉钼矿进行辉钼矿Re-Os同位素测试,因此可以较好地避免解耦现象,以保证测试精度。辉钼矿Re-Os等时线年龄可以代表辉钼矿的形成年龄。由于辉钼矿为矿石矿物,所以其Re-Os等时线年龄(134.8±2.1Ma)可以直接代表该矿床的Mo成矿年龄。
本次测得矿区内花岗斑岩的锆石U-Pb年龄为136.7±2.2Ma,可以代表王坞矿床内花岗斑岩的成岩年龄。这些网脉状和脉状矿体常常发育在花岗斑岩脉与围岩的接触带周围(图 3),且成岩年龄与成矿年龄一致。因此,可以推断王坞矿区内的花岗斑岩与Mo矿化具有成因联系。
魏娟娟等(2016)测得王坞Mo-Cu矿区花斑岩脉的加权平均年龄为127.5±1.8Ma,辉钼矿Re-Os等时线年龄为153.7±3.2Ma,指出两者无成因联系,并推断王坞矿区成钼岩体为酸性花岗斑岩或黑云母花岗岩。魏娟娟等(2016)文中的花斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄测试数据很分散,得出两组年龄分别为127.5±1.8Ma和137.0±2.4Ma,文中解释137.0±2.4Ma为花斑岩脉在侵位过程中捕获的大量相对较早的岩浆锆石的年龄,而相对较新的年龄127.5±1.8Ma代表了花斑岩岩浆结晶的年龄。然而,从锆石CL图像来看,137.0±2.4Ma年龄值的测点也均位于韵律环带发育较好的部位,并且对应的锆石的晶型也都较好,没有显示出明显的被包裹或者捕虏的特征。魏娟娟等(2016)文中所测试的辉钼矿为石英细脉中的辉钼矿样品,而本次测试所选辉钼矿为网脉状石英-辉钼矿脉中的辉钼矿样品,魏娟娟等(2016)测得辉钼矿的Re-Os等时线年龄为153.7±3.2Ma,若该年龄也为可靠年龄,可能说明了该矿床成矿作用的复杂性,矿床可能存在两期成矿作用。然而由于当前矿床勘查总体上仍处于初步阶段,现有的地表及深部工程还未能完全揭露矿体,因此,对于是否存在两期成矿作用以及两者的精确关系还未能完全确定,仍需待进一步的勘查以及研究工作。
5.2 北武夷地区Cu、Mo、W、Pb、Zn多金属矿成岩成矿时限探讨北武夷地区是我国华南地区重要的Cu-Mo-W-Pb-Zn多金属矿集区。对区域内成岩成矿事件的发生时间的确定,是识别重大成岩成矿事件的基础。Mao et al.(2013)把我国华南地区中生代的成矿事件划分为三个阶段,分别是晚三叠世(230~210Ma)与过铝质花岗岩有关的W-Sn-Nb-Ta矿床;中-晚侏罗世(170~150Ma)与I-型花岗岩有关的斑岩-矽卡岩型Cu矿床和脉型Pb-Zn-Ag矿床(170~160Ma)以及与准铝质花岗岩有关的W-Sn多金属矿床(160~150Ma);早-中白垩世(120~80Ma)与次火山活动有关的Fe矿、与I型钙碱性花岗岩体有关的斑岩型Cu-Mo矿床和斑岩-低温热液型Cu-Au-Ag矿床、与S型过铝质和准铝质花岗岩侵入体有关的Sn多金属矿床。Yu et al.(2012)将北武夷地区古生代和中生代与成矿作用有关的岩浆活动划分为加里东期(530~430Ma)、早-中侏罗世(183~160Ma)、早白垩世(140~110Ma)和晚白垩世(63~85Ma)四个阶段。Wu et al.(2015)认为北武夷地区的斑岩-矽卡岩-热液脉型Cu-Mo-Pb-Zn-Ag多金属矿床主要形成于燕山晚期,且具有两期显著的成矿作用:斑岩-矽卡岩Cu成矿作用(160~154Ma)和热液脉型Pb-Zn-Ag-Mo成矿作用(139~136Ma)。
虽然北武夷地区的岩浆活动的时限比较广,但以燕山期的岩浆活动成矿强度最大(李晓峰等, 2007; 代堰锫等, 2010; 左力艳等, 2010; Yu et al., 2012; Su et al., 2014)。前人对北武夷地区进行过很多关于火山活动和岩浆作用年代学的研究工作(丁昕等, 2005; 罗平等, 2005, 2009; 左力艳等, 2010; 狄永军等, 2013; 徐贻赣等, 2013; Dai et al., 2014; Su et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2015),但是关于该地区矿床的成矿时间的研究工作有限,一方面是由于几个近些年勘查发现的矿床的工作程度还比较低,另一方面是由于部分矿床较难找到可以直接进行精确定年的目标矿物。有人通过对金属矿物如闪锌矿的Rb-Sr定年(徐贻赣等, 2013)以及与矿石矿物共生的脉石矿物如钾长石的Ar-Ar定年(万浩章等, 2013)来限定成矿年龄,也有学者通过与成矿有关的花岗岩的精确定年来限定成矿时间(罗平等, 2009; 左力艳等, 2010; 狄永军等, 2013; Dai et al., 2014)。Dai et al.(2014)通过对蔡家坪流纹斑岩的高精度SIMS锆石U-Pb定年,得到156.0±1.2Ma的年龄,推测蔡家坪成矿作用晚于156Ma。狄永军等(2013)测得冷水坑矿田A7号矿体底板打鼓顶组凝灰岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄为157.6±3.2Ma,指出该年龄代表成矿作用的下限年龄。本文在前人研究成果的基础上,对近年来新获得的北武夷地区的高精度成岩成矿年龄数据(罗平等, 2009; Yu et al., 2012; 张家菁等, 2012; 狄永军等, 2013; 邱骏挺等, 2013; 万浩章等, 2013; Su et al., 2014; Dai et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2015; Yan et al., 2015)进行了统计,结果显示,该地区燕山期的岩浆作用可以划分为175~150Ma和145~130Ma两期,这两期岩浆作用分别对应165~150Ma的Cu、Mo、W、Pb、Zn、Ag和140~125Ma的Pb、Zn、Ag、Mo两期成矿作用(表 3、图 9)。本文测得江西省铅山县王坞Mo-Cu矿床的Mo成矿年龄为134.8±2.1Ma,矿区内花岗斑岩的成岩年龄为136.7±2.2Ma,表明王坞Mo-Cu矿床与区域内蔡家坪Pb-Zn矿床和金竹坪Mo多金属矿床等矿床成矿时代相近,为该地区燕山期大规模成矿作用的一部分。
|
|
表 3 北武夷地区燕山期成岩成矿年龄 Table 3 Petrogenetic and metallogenic ages of Yanshanian igneous rocks and deposits in the North Wuyi area |
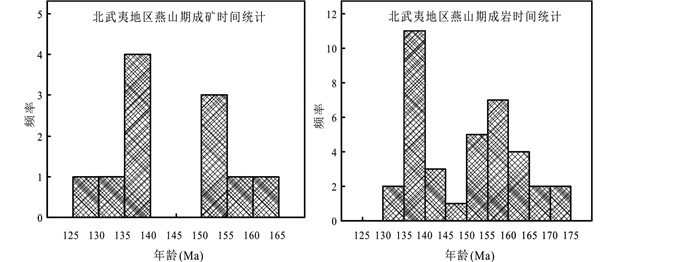
|
图 9 北武夷地区燕山期成岩成矿年龄直方图 Fig. 9 Histogram of petrogenetic and metallogenic ages of Yanshanian igneous rocks and deposits in the North Wuyi area |
钦杭带位于华南地区扬子板块和华夏板块之间,北武夷地区位于钦杭带的东北部。虽然华南地区自晚中生代以来就受到了古太平洋板块俯冲作用影响的观点已经被大多数学者所接受(Zhou and Li, 2000; Xie et al., 2006;毛景文等, 2007, 2008, 2011;蒋少涌等, 2008; Mao et al., 2011, 2013;张达等, 2011a; Sun et al., 2012; Wu et al., 2018),但是,对于华南地区晚中生代大规模成岩成矿作用的动力学背景还存在争议(John et al., 1990; Charvet et al., 1994; Li and Li, 2007; Li et al., 2007, 2014; Chen et al., 2008; Jiang et al., 2009, 2011; Xie et al., 2011, 2012)。Li and Li(2007)认为华南地区在250~190Ma受到了古太平洋板块的平板俯冲作用,随后俯冲板片发生了折断和拆沉,诱发了华南地区中生代的大规模成岩成矿作用。Su et al.(2014)和Yan et al.(2015)根据天华山盆地打鼓顶组和鹅湖岭组岩浆岩的岩石地球化学特征,认为俯冲的古太平板块在晚中生代发生了折返,从而使得钦杭带在该时期处于伸展的构造背景下。Mao et al.(2013)认为俯冲板块(古太平洋板块)在170~160Ma沿着钦杭带撕裂,诱发了该地区I型花岗岩类岩石以及斑岩型Cu矿和脉型Pb-Zn-Ag矿的形成;160~150Ma俯冲板片窗引发的软流圈地幔上涌,诱发了南岭地区的花岗岩以及与这些花岗岩相关的W-Sn多金属矿床的形成;从135Ma左右起,古太平洋板块由斜向俯冲改变为几乎平行大陆边缘沿NE方向走滑,导致了大陆岩石圈的伸展,引发了区域内NE向断裂的活化,形成了NE向的拉分盆地,并诱发了一系列的火山-岩浆作用及成矿作用。
北武夷地区的年代学数据显示,北武夷地区在晚中生代有两期的岩浆-热液成矿作用,分别为与175~150Ma的花岗斑岩、流纹斑岩、二长花岗斑岩有关的Cu、Mo、Pb、Zn、Ag、W成矿作用以及与145~130Ma的火山岩-次火山岩和花岗斑岩有关的Pb、Zn、Mo、Ag成矿作用。虽然王坞Mo-Cu矿床与龙头岗Cu-Zn矿床仅相距1.5km,但龙头岗矽卡岩-热液脉型Cu-Zn矿的成矿年龄为153.6Ma(Wu et al., 2015),所以龙头岗矿床的成岩成矿作用发生在较早的阶段,而王坞Mo-Cu矿床的成岩成矿作用发生在较晚的阶段。中侏罗世以来东亚岩石圈大规模的板块运动造成中国大陆及周缘地带产生了强烈的构造变形,华南大陆岩石圈总体上处于持续挤压的状态,产生了大规模褶皱及逆冲推覆构造(张达等, 2011b)。北武夷地区的推覆构造影响着矿床的生成与保存,推覆构造兼具成矿和破矿两个方面的作用(余心起等, 2008; Yu et al., 2012)。北武夷地区多个矿床都受到了推覆构造的影响,如永平Cu矿(余心起等, 2008)、冷水坑Ag-Pb-Zn矿(余心起等, 2008)、篁碧Mo-Pb-Zn矿(邱骏挺等, 2011)等。然而,在王坞矿区逆冲推覆构造与成矿作用的关系仍需进一步的工作进行研究。
从上述的构造模型可以看出,虽然诱发机制还存在争议,但是前人普遍认为北武夷地区在早白垩世处于伸展的构造背景下。北武夷地区发育了一系列早白垩世北北东向火山盆地(天华山火山盆地、黄岗山火山盆地、铜锣山(梨子坑)火山盆地、仙霞岭火山盆地等);这些火山盆地中广泛发育早白垩世火山-次火山岩;这些火山岩-次火山岩都具有相似的稀土元素分配模式,富集轻稀土元素,表现出明显的负Eu异常,亏损Sr、Ba、P、Ti、Nb、Ta等微量元素(秦晓峰, 2014; Yan et al., 2015),全岩εNd(t)值为-12.07~-8.69,锆石εHf(t)值为-21.9~+2.31,且锆石Hf的二阶段模式年龄为2550~1051Ma,全岩的Nd二阶段模式年龄为1915~1639Ma(Su et al., 2014; Yan et al., 2015),这些地球化学特征指示这些火山岩-次火山岩的形成是由于软流圈地幔上涌导致岩石圈的部分熔融而引起的(Su et al., 2014;秦晓峰, 2014)。广泛发育的火山盆地和火山盆地中火山岩-次火山岩的地球化学特征,指示北武夷地区在早白垩世处于伸展的构造背景下。
6 结论(1) 王坞Mo-Cu矿床花岗斑岩的锆石U-Pb年龄为136.7±2.2Ma,辉钼矿的Re-Os等时线年龄为134.8±2.1Ma,王坞Mo-Cu矿床的成矿作用和矿区内花岗斑岩的成岩作用都发生在早白垩世。
(2) 王坞矿床的花岗斑岩和Mo矿化在空间上关系密切,且二者形成时间一致,指示王坞Mo-Cu矿床的钼矿化可能与区内的花岗斑岩具有密切的成因联系。
(3) 北武夷地区在燕山期有两期岩浆和成矿作用。两期岩浆作用的时间分别为175~150Ma和145~130Ma,两期成矿作用分别为165~150Ma的斑岩-矽卡岩型Cu、Mo、Pb、Zn、Ag、W成矿作用和140~125Ma的斑岩-热液脉以及火山-次火山热液型Pb、Zn、Mo、Ag成矿作用。王坞Mo-Cu矿床形成于较晚的一期成岩成矿作用中。
(4) 钦杭带在晚侏罗到早白垩世受到了古太平洋板块俯冲作用的影响,在早白垩世开始处于伸展的构造环境中,发育了与火山-侵入岩相关的Mo-Pb-Zn-Ag矿化作用。
致谢 在野外工作中,得到江西省地质矿产勘查开发局赣东北大队罗平和魏英文高工的大力支持和帮助; 在LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测试过程中得到中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所成矿作用与资源评价重点实验室LA-ICP-MS实验室侯可军老师和王倩老师的帮助; 辉钼矿Re-Os测试得到了国家地质测试中心Re-Os同位素实验室杜安道研究员、屈文俊研究员和李超老师的帮助; 在此深表感谢。同时,感谢审稿人对本文的认真审阅并提出宝贵的修改意见。
Bohlkea JK, Laeter JR, Bievre PD, Peiserb HS, Rosman KJR and Taylor PDP. 2005. Isotopic compositions of the elements, 2001. Journey of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 34(1): 57-67. DOI:10.1063/1.1836764 |
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Jiangxi Province. 1984. Regional Geology of Jiangxi Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-921.
|
Charvet J, Lapierre H and Yu YW. 1994. Geodynamic significance of the Mesozoic volcanism of southeastern China. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 9(4): 387-396. DOI:10.1016/0743-9547(94)90050-7 |
Chen CH, Lee CY and Shinjo R. 2008. Was there Jurassic paleo-Pacific subduction in South China? Constraints from 40Ar/39Ar dating, elemental and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic geochemistry of the Mesozoic basalts. Lithos, 106(1): 83-92. |
Chen FW, Li HQ, Wang DH, Xiao GM, Yang XJ, Gao YW, Mei YP and Lin XG. 2012. Geological characteristics and diagenetic-metallogenic chronological study of the Yuanzhuding porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, western Guangdong Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(8): 1298-1305. |
Chu KL, Mao JW, Chen MH, Yu CF, Lin LZ and Lin XG. 2013. Source of metallogenic materials and ore-forming fluids, and metallogenic mechanism of the Yuanzhuding porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, western Guangdong Province, South China. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(5): 115-125. |
Corfu F, Hanchar JM, Hoskin PWO and Kinny P. 2003. Atlas of zircon textures. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 469-500. DOI:10.2113/0530469 |
Dai YP, Yu XQ, Wu GG, Di YJ, Li CL, Qiu JT, Zhang JJ and Luo P. 2010. Sulfide features and Ar-Ar age of F4 fault of Caijiaping lead-zinc deposit of Shangrao, Jiangxi. Mineral deposits, 29(Suppl.): 425-426. |
Dai YP, Yu XQ, Wu GG, Li CL, Qiu JT, Zhang JJ and Luo P. 2011. Characteristics of sulfide minerals, genetic type and metallogenic epoch of the Caijiaping lead-zinc deposit, North Wuyi area, Jiangxi Province. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(2): 321-338. |
Dai YP, Yu XQ, Zhang LC, Cao WT, Zhu YD and Li CL. 2014. Geology, isotopes and geochronology of the Caijiaping Pb-Zn deposit in the North Wuyi area, South China:Implications for petrogenesis and metallogenesis. Ore Geology Reviews, 57: 116-131. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.09.015 |
Di YJ, Xu YG, Wu GG, Zhang D, Xiao MZ, Lai SH, Yu XQ, Qin ST, Yan PC, Gong Y and Qin XF. 2013. The formation era of nappe structure in Lengshuikeng Ag-Pb-Zn ore field, Jiangxi:Constraints from geochronology. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(4): 340-349. |
Ding X, Jiang SY, Ni P, Gu LX and Jiang YH. 2005. Zircon SIMS U-Pb geochronology of host granitoids in Wushan and Yongping copper deposits, Jiangxi Province. Geological Journal of China Universities, 11(3): 383-389. |
Dong SF. 1994. The characteristics of Lengshuikeng auriferous porphyry and its gold mineralization in Jiangxi. Geology of Jiangxi, 8(1): 14-20. |
Dong Y. 2015. Thrust nappe structure tectonics in Yongping-Shitang area, and analysis of ore-controlling structure of the Longtougang deposit, northeastern Jiangxi. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-51 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Du AD, Wu SQ, Sun DZ, Wang SX, Qu WJ, Markey RHS, Morgan J and Malinovskiy D. 2004. Preparation and certification of Re-Os dating reference materials:Molybdenite HLP and JDC. Geostandard and Geoanalytical Research, 28(1): 41-52. DOI:10.1111/ggr.2004.28.issue-1 |
Du AD, Qu WJ, Wang DH, Li HM, Feng CY, Liu H, Ren J and Zeng FG. 2007. Subgrain-size decoupling of Re and 187Os within molybdenite. Mineral Deposits, 26(5): 572-580. |
Fu SH and Chen GH. 2003. Metallogenic features and prospecting research of Dongxiang porphyry copper deposit. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 27(3): 282-286. |
Hoskin PWO and Schaltegger U. 2003. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 27-62. DOI:10.2113/0530027 |
Hou KJ, Li YH and Tian YR. 2009. In situ U-Pb zircon dating using laser ablation-multi ion counting-ICP-MS. Mineral Deposits, 28(4): 481-492. |
Hou ZQ, Pan XF, Li QY, Yang ZM and Song YC. 2013. The giant Dexing porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposit in East China:Product of melting of juvenile lower crust in an intracontinental setting. Mineralium Deposita, 48: 1019-1045. DOI:10.1007/s00126-013-0472-5 |
Hua RM, Li XF, Lu JJ, Chen PR, Qiu DT and Wang G. 2000. Study on the tectonic setting and ore-forming fluids of Dexing large ore-concentrating area, Northeast Jiangxi Province. Advance in Earth Sciences, 15(5): 525-533. |
Huang SB, Mao DH, Di YJ, Wei Y, Luo P and Bochun L. 2012. Genetic relationship between rhyolite porphyries and lead-zinc mineralization in Lizikeng volcanic basin, northern Wuyishan. Resources Survey and Environment, 33(3): 152-157. |
Jiang SY, Zhu B, Ding X and Jiang YH. 2008. Origin of hydrothermally altered granites from the Yongping copper deposit, Jiangxi Province, China:Constraints from immobile elements and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72(Suppl.): 430. |
Jiang SY, Zhao KD, Jiang YH and Dai BZ. 2008. Characteristics and genesis of Mesozoic A-type granites and associated mineral deposits in the southern Hunan and northern Guangxi provinces along the Shi-Hang belt, South China. Geological Journal of China Universities, 14(4): 496-509. |
Jiang YH, Jiang SY, Dai BZ, Liao SY, Zhao KD and Ling HF. 2009. Middle to Late Jurassic felsic and mafic magmatism in southern Hunan Province, Southeast China:Implications for a continental arc to rifting. Lithos, 107(3): 185-204. |
Jiang YH, Zhao P, Zhou Q, Liao SY and Jin GD. 2011. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Early Cretaceous S-and A-type granites in the northwest of the Gan-Hang rift, SE China. Lithos, 121(1): 55-73. |
John BM, Zhou XH and Li JL. 1990. Formation and tectonic evolution of southeastern China Mainland and Taiwan area:Isotopic and geochemical constraints. Tectonophysics, 183(1-4): 145-160. DOI:10.1016/0040-1951(90)90413-3 |
Košler J, Simonetti A, Sylvester PJ, Cox RA, Tubrett MN and Wilton DHC. 2003. Laser-ablation ICP-MS measurements of Re/Os in molybdenite and implications for Re-Os geochronology. The Canadian Mineralogist, 41(2): 307-320. DOI:10.2113/gscanmin.41.2.307 |
Li C, Qu WJ and Du AD. 2009. Decoupling of Re and Os and migration model of 187Os in coarse-grained molybdenite. Mineral Deposits, 28(5): 707-712. |
Li XF, Yasushi W and Qu WJ. 2007. Textures and geochemical characteristic of granitics rocks in the Yongping climax-type Cu-Mo deposit, Jiangxi, southeastern China, and their alteration, mineralization and tectonic regime. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(10): 2353-2365. |
Li XH, Li ZX, Li WX, Liu Y, Yuan C, Wei GJ and Qi CS. 2007. U-Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of Jurassic I-and A-type granites from central Guangdong, SE China:A major igneous event in response to foundering of a subducted flat-slab?. Lithos, 96(1): 186-204. |
Li Z, Qiu JS and Yang XM. 2014. A review of the geochronology and geochemistry of Late Yanshanian (Cretaceous) plutons along the Fujian coastal area of southeastern China:Implications for magma evolution related to slab break-off and rollback in the Cretaceous. Earth-Science Reviews, 128: 232-248. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.09.007 |
Li ZX and Li XH. 2007. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen andpostorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China:A flat-slab subduction model. Geology, 35(2): 179-182. DOI:10.1130/G23193A.1 |
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Gao S, Gunther D, Xu J, Gao C and Chen H. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemincal geology, 257(1-2): 34-43. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 |
Lu R, Mao JW, Gao JJ, Su HM and Zheng JH. 2012. Geological characteristics and occurrence of silver in Xiabao Ag-Pb-Zn deposit, Lengshuikeng ore field, Jiangxi Province, East China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(1): 105-121. |
Lu YF, Ma LY, Qu WJ, Mei YP and Chen XQ. 2006. U-Pb and Re-Os isotope geochronology of Baoshan Cu-Mo polymetallic ore deposit in Hunan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(10): 2483-2492. |
Ludwig K. 2009. Isoplot/Ex, version 2.0: A geochronogical toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Geochronology Center
|
Luo P. 2005. Metallogenic regularities and prediction of copper-lead-zinc-silver mineralization in the area of Chenfang-Yongping, Yanshan County, Jiangxi Province. Master Degree Thesis. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 1-67 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Luo P, Wei YW and Wang YQ. 2005. Geology of the Changshouyuan silver-lead (-zinc) deposit in northern Wuyi area. Resources Survey and Environment, 26(1): 33-42. |
Luo P, Wu GG, Zhang D, Di YJ, Wang CM and Wang YQ. 2009. Geochemistry and genesis of Shengmikeng lead-zinc deposit in northern Wuyi, eastern China. Journal of Geomechanics, 15(4): 349-362. |
Luo P. 2010. Research on metallogenic regularities and prospecting orientation of copper polymetal mineral resources in the northern Wuyi region of Jiangxi Province. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-187 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Luo YJ. 1985. Geochemical characteristics of the Lengshuikeng porphyry type Pb-Zn deposit in Guixi County, Jiangxi Province. Mineral Deposits, 4(4): 15-24. |
Mao JW, Xie GQ, Guo CL and Chen YC. 2007. Large-scale tungsten-tin mineralization in the Nanling region, South China:Metallogenic ages and corresponding geodynamic processes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(10): 2329-2338. |
Mao JW, Xie GQ, Guo CL, Yuan SD, Cheng YB and Chen YC. 2008. Spatial-temporal distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their metallogenic settings. Geological Journal of China Universities, 14(4): 510-526. |
Mao JW, Zhang JD and Guo CL. 2010. Porphyry Cu, epithermal Ag-Pb-Zn, distal hydrothermal Au deposits:A new model of mineral deposit, taking the Dexing area as an example. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 32(1): 1-14. |
Mao JW, Franco P and Cook NJ. 2011. Mesozoic metallogeny in East China and corresponding geodynamic settings:An introduction to the special issue. Ore Geology Review, 43: 1-7. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.09.003 |
Mao JW, Chen MH, Yuan SD and Guo CL. 2011. Geological characteristics of theQinhang (Shihang) metallogenic belt in South China spatial-temporal distribution of mineral deposits. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(5): 636-658. |
Mao JW, Cheng YB, Chen MH and Franco P. 2013. Major types and time-space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings. Mineralium Deposita, 48(3): 267-294. DOI:10.1007/s00126-012-0446-z |
Mao W, Li XF and Yang FC. 2013. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages of granites at Dabaoshan polymetallic deposit and its geological significance, Guangdong, South China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(12): 4104-4120. |
Meng XJ, Hou ZQ, Dong GY, Liu JG, Qu WJ, Yang ZS, Zou LY, Wan LJ and Xiao MZ. 2007. The geological characteristics and Re-Os isotope age of molybdenite of the Xiongjiashan molybdenum deposit, Jiangxi Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(7): 946-951. |
Meng XJ, Xu WY, Yang ZS, Hou ZQ, Li ZQ, Yu YS, Xiao MZ, He XR and Wan HZ. 2012. Time limit of volcanic-magmatic action in Lengshuikeng orefield, Jiangxi:Evidence from SHRIMP zircon U-Pb ages. Mineral Deposits, 31(4): 831-838. |
Ouyang XC. 2015. Geological and geochemical characteristics and its genesis of the Dongxiang copper deposit, Jiangxi Province. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-78 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Qiu JT, Yu XQ, Wu GG, Qu WJ, Di YJ, Zhang D, Luo P and Du AD. 2011. Research on the nappe structure and its relevance to the mineralization in the Huangbi deposit, North Wuyi, Southeast China. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(5): 243-255. |
Qiu JT, Yu XQ, Wu GG, Liu JG and Xiao MZ. 2013. Geochronology of igneous rocks and nappe structures in Lengshuikeng deposit, Jiangxi Province, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(3): 812-826. |
Qin XF. 2014. A preliminary framework for the sequence of Yanshanian volcanic-intrusive magma of relation to mineralization in the North Wuyi area. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-79 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Selby D and Creaser RA. 2004. Macroscale NTIMS and microscale LA-MC-ICP-MS Re-Os isotopic analysis of molybdenite:Testing spatial restrictions for reliable Re-Os age determinations, and implications for the decoupling of Re and Os within molybdenite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(19): 3897-3908. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2004.03.022 |
Shirey SB and Walker RJ. 1995. Carius tube digestion for low-blank rhenium-osmium analysis. Analytical Chemistry, 67: 2136-2141. DOI:10.1021/ac00109a036 |
Stein H, Scherstén A, Hannah J and Markey R. 2003. Subgrain-scale decoupling of Re and 187Os and assessment of laser ablation ICP-MS spot dating in molybdenite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(19): 3673-3686. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00269-2 |
Su HM. 2013. Petrogenedsis of lata Mesozoic volcanic-intrusive rocks in the Tianhuashan basin in the north Wuyishan area and relation to Pb-Zn-Cu mineralization. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-134 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Su HM, Mao JW, He XR and Lu R. 2013. Timing of the formation of the Tianhuashan Basin in northern Wuyi as constrained by geochronology of volcanic and plutonic rocks. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 43(5): 745-759. |
Su HM, Mao JW, Santosh M and Xie GQ. 2014. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous volcanic-intrusive complex in the Tianhuashan basin, South China. Ore Geology Reviews, 56: 566-583. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.05.004 |
Sun WD, Yang XY, Fan WM and Wu FY. 2012. Mesozoic large scale magmatism and mineralization in South China:Preface. Lithos, 150: 1-5. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.06.028 |
Tian MJ, Li YG, Wan HZ, Zhang Y and Gao TT. 2014. Characteristics of skarn minerals in Yongping copper deposit, Jiangxi Province, and geological significances. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(12): 3741-3758. |
Wan HZ, Zhang D, Di YJ, Luo P, Lv LJ, Dong Y and Lu JH. 2013. Altered potassium feldspar Ar-Ar age of Tieshajie copper deposit of Yiyang, Jiangxi. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, (Suppl.2): 613-614. |
Wang CM, Zhang D, Wu GG, Xu YG, Carranza EJM, Zhang YY, Li HK and Geng JZ. 2013. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of rhyolitic tuff, granite porphyry and syenogranite in the Lengshuikeng ore district, SE China:Implications for a continental arc to intra-arc rift setting. Journal of Earth System Science, 122(3): 809-830. DOI:10.1007/s12040-013-0302-2 |
Wang CM, Zhang D, Wu GG, Santosh M, Zhang J, Xu YG and Zhang YY. 2014. Geological and isotopic evidence for magmatic-hydrothermal origin of the Ag-Pb-Zn deposits in the Lengshuikeng district, east-central China. Mineralium Deposita, 49(6): 733-749. DOI:10.1007/s00126-014-0521-8 |
Wei JJ, Di YJ, Wei YW, Zhang D, Luo P, Luo GH, Qin XF, Dong Y, Yang Q and Chen J. 2016. Relationship between granophyres and molybdenum ore of Wangwu mining district in North Wuyi region:Evidences from zircon U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os dating. Geoscience, 30(1): 59-68. |
Wieser ME. 2006. Atomic weights of the elements 2005 (IUPAC technical report). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 78(11): 2051-2066. DOI:10.1351/pac200678112051 |
Wu SH, Mao JW, Xie GQ, Geng JZ and Xiong BK. 2015. Geology, geochronology, and Hf isotope geochemistry of the Longtougang skarn and hydrothermal vein Cu-Zn deposit, North Wuyi area, southeastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 70: 136-150. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.04.012 |
Wu SH, Mao JW, Yuan SD, Dai P and Wang XD. 2018. Mineralogy, fluid inclusion petrography, and stable isotope geochemistry of Pb-Zn-Ag veins at the Shizhuyuan deposit, Hunan Province, southeastern China. Mineralium deposita, 53(1): 89-103. DOI:10.1007/s00126-017-0725-9 |
Xiao ZH. 1996. Discussion on metallogenic regularity of Yongping mining area. Copper Engineering of Jiangxi, 2: 41-45. |
Xie GQ, Hu RZ, Mao JW, Pirajno F, Li RL, Cao JJ, Jiang GH and Zhao JH. 2006. K-Ar dating, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic systematics of Late Mesozoic mafic dikes, southern Jiangxi Province, Southeast China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. International Geology Review, 48(11): 1023-1051. DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.48.11.1023 |
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Li RL, Qü WJ, Pirajno F and Du AD. 2007. Re-Os molybdenite and Ar-Ar phlogopite dating of Cu-Fe-Au-Mo (W) deposits in southeastern Hubei, China. Mineralogy and Petrology, 90(3-4): 249-270. DOI:10.1007/s00710-006-0176-y |
Xie GQ, Mao JW and Zhao HJ. 2011. Zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic intrusions in the southeast Hubei Province, Middle-Lower Yangtze River belt (MLYRB), East China. Lithos, 125: 693-710. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.04.001 |
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Zhao HJ, Duan C and Yao L. 2012. Zircon U-Pb and phlogopite 40Ar-39Ar age of the Chengchao and Jinshandian skarn Fe deposits, Southeast Hubei Province, Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt, China. Mineralium Deposita, 47(6): 633-652. DOI:10.1007/s00126-011-0367-2 |
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Bagas L, Fu B and Zhang ZY. 2018a. Mineralogy and titanite geochronology of the Caojiaba W deposit, Xiangzhong metallogenic province, southern China:Implications for a distal reduced skarn W formation. Mineralium Deposita. DOI:10.1007/s00126-018-0816-2 |
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Li W, Fu B and Zhang ZY. 2018b. Granite-related Yangjiashan tungsten deposit, southern China. Mineralium Deposita,. DOI:10.1007/s00126-018-0805-5 |
Xu DM, Lin ZY, Long WG, Zhang K, Wang L, Zhou D and Huang H. 2012. Research history and current situation of Qinzhou-Hangzhou Metallogenic Belt, South China. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 28(4): 277-289. |
Xu QS, Wei YW, Huang AJ, Luo P, Wu CL, Zhao HS and Di YJ. 2014. Geochemical features, zircon U-Pb ages and relationshio to Pb-Zn mineralization of the subvolcanic rocks in Lizikeng volcanic basin, Shangrao, Jiangxi. Geological Review, 60(4): 932-943. |
Xu WX, Xiao MH and Chen MY. 2001. A study of the isotope geochemistry of the Lenshuikeng Ag-Pb-Zn ore deposit, Jiangxi Province. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, 20(4): 370-372. |
Xu YG, Wu GG, Wang CM, Zhang D and Zhang YY. 2013. Rb-Sr dating of sphalerites from the Lengshuikeng Ag-Pb-An deposit, Jiangxi, and its geological significances. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(5): 621-633. |
Yan X, Jiang SY and Jiang YH. 2015. Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic significance of the Late Mesozoic volcanic sequences in the northern Wuyi Mountain volcanic belt of South China. Gondwana Research, 37: 362-383. |
Yang MG and Mei YW. 1997. Characteristics of geology and metallization in the Qinzhou-Hangzhou paleoplate juncture. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 3: 52-59. |
Yu MG, Zhao XL, Qian MP, Duan Z, Zhang XH, Wan HZ, Xiao MZ and Sun JD. 2015. The discovery of Late Jurassic volcanic rocks in Lengshuikeng, Jiangxi and their geological significance. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 34(1): 138-149. |
Yu XQ, Wu GG, Zhang D, Di YJ, Dai YP and Qiu JT. 2008. Thrust nappe structure and its ore-controlling effects in the North Wuyi area, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(10): 1667-1677. |
Yu XQ, Wu GG, Zhao XX, Zhang D, Di YJ, Qiu JT, Dai YP and Li CL. 2012. New geochronological data from the Paleozoic and Mesozoic nappe structures, igneous rocks, and molybdenite in the North Wuyi area, Southeast China. Gondwana Research, 22(2): 519-533. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.11.013 |
Zhang D, Wu GG, Di YJ, Lü LJ and Yao JM. 2011a. Evolution of tectonic stress field in southwestern Wuyishan mountain area and relationship with mineralization. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(4): 505-513. |
Zhang D, Wu GG, Di YJ, Wang CM, Lü LJ, Zhang YY, Shi JJ and Yao JM. 2011b. Ore-controlling features of Mesozoic nappe stuctures on iron deposits in Southwest Fujian Province. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 31(Suppl.1): 128-129. |
Zhang GW, Guo AL, Wang YJ, Li SZ, Dong YP, Liu SF, He DF, Cheng SY and Lu RK. 2013. Tectonics of South China continent and its implications. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 43(10): 1553-1582. |
Zhang JJ, Wu MS, Chen ZH, Liu SB, Li LX, Qiu LM, Wu B, Huang AJ and Zhu PJ. 2009. Geochronologic study on the Jinzhuping molybdenum-polymetallic deposit from Shangrao of Jiangxi Province. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 28(3): 228-232. |
Zhang JJ, Wang DH, Liu SB, Chen ZHi, Shi GH, Wang J, Wang YQ and Wei YW. 2012. Geochronology and isotopic compositions of the Huangbi lead-zinc deposits, Jiangxi, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(10): 3325-3333. |
Zhang WX. 1995. The basic features and ore-forming process of Yongping-Tongshan strata-bound Cu-Pb-Zn deposits. Geology of Jiangxi, 9(4): 249-258. |
Zhang XS. 1997. Characteristics of chemical composition and mineral inclusions of ore minerals in Yongping copper deposit. Jiangxi Geology, 11(2): 40-48. |
Zhou Q, Jiang YH, Zhao P, Liao SY, Jin GD, Liu Z and Jia RY. 2012. SHRIMP U-Pb dating on hydrothermal zircons:Evidence for an Early Cretaceous epithermal event in the middle Jurassic Dexing porphyry copper deposit, southeast China. Economic Geology, 107(7): 1507-1514. DOI:10.2113/econgeo.107.7.1507 |
Zhou XM and Li WX. 2000. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China:Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas. Tectonophysics, 326(3): 269-287. |
Zhou YZ, Zeng CY, Li HZ, Yang ZJ, Chen BH, Wang ZH, Liang J, Lu WJ and Chen Q. 2010. Typical ore-types and ore deposit distribution characteristics of Qin-Hang metgallogenic belt. Mineral Deposits, 29(Suppl.): 34-34. |
Zhou YZ, Zeng CY, Li HZ, An YF, Liang J, Lü WC, Yang ZJ, He JG and Shen WJ. 2012. Geological evolution and ore-prospecting targets in southern segment of Qinzhou Bay-Hangzhou Bay juncture orogenic belt, southern China. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(2-3): 486-491. |
Zhong LF, Li J, Peng TP, Xia B and Liu LW. 2013. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic compositions of the Yuanzhuding granitoid porphyry within the Shi-Hang Zone, South China:Petrogenesis and implications for Cu-Mo mineralization. Lithos, 177: 402-415. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.07.003 |
Zuo LY. 2008. Research on mineralization of the Lengshuikeng porphyry silver-lead-zinc deposit in Jiangxi province, China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1-140 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zuo LY, Hou ZQ, Meng XJ, Yang ZM, Song YC and Li Z. 2010. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of the ore-bearing rock in the Lengshuikeng porphyry type Ag-Pb-Zn deposit. Geology in China, 37(5): 1450-1456. |
陈富文, 李华芹, 王登红, 肖光铭, 杨晓君, 高亦文, 梅玉萍, 林秀广. 2012. 粤西圆珠顶斑岩型铜钼矿床成矿地质特征及成岩成矿作用年代学研究. 地质学报, 86(8): 1298-1305. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.08.012 |
楚克磊, 毛景文, 陈懋弘, 赵军, 余长发, 林良庄, 林秀广. 2013. 广东圆珠顶斑岩型铜钼矿床成矿物质、成矿流体来源和成矿机理研究. 地学前缘, 20(5): 115-125. |
代堰锫, 余心起, 吴淦国, 狄永军, 李春麟, 邱骏挺, 张家菁, 罗平. 2010. 江西上饶蔡家坪铅锌矿床硫化物特征及F4断裂的Ar-Ar年龄. 矿床地质, 29(增): 425-426. |
代堰锫, 余心起, 吴淦国, 李春麟, 邱骏挺, 张家菁, 罗平. 2011. 北武夷蔡家坪铅锌矿床硫化物特征、矿床成因类型及成矿时代. 地学前缘, 18(2): 321-338. |
杜安道, 屈文俊, 王登红, 李厚民, 丰成友, 刘华, 任静, 曾法刚. 2007. 辉钼矿亚晶粒范围内Re和187Os的失耦现象. 矿床地质, 26(5): 572-580. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.05.010 |
狄永军, 徐贻赣, 吴淦国, 张达, 肖茂章, 来守华, 余心起, 秦思婷, 闫鹏程, 龚勇, 秦晓峰. 2013. 江西冷水坑银铅锌矿田推覆构造的形成时代:来自年代学的约束. 地学前缘, 20(4): 340-349. |
丁昕, 蒋少涌, 倪培, 顾连兴, 姜耀辉. 2005. 江西武山和永平铜矿含矿花岗质岩体锆石SIMSU-Pb年代学. 高校地质学报, 11(3): 383-389. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.03.009 |
董绍芳. 1994. 江西冷水坑含金斑岩及金矿化特征. 江西地质, 8(1): 14-20. |
董越. 2015.江西永平-石塘推覆构造及龙头岗矿区控矿构造分析.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学, 1-51
|
付守会, 陈广浩. 2003. 江西东乡铜矿成矿地质特征与找矿实践. 大地构造与成矿学, 27(3): 282-286. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2003.03.011 |
华仁民, 李晓峰, 陆建军, 陈培荣, 邱德同, 王果. 2000. 德兴大型铜金矿集区构造环境和成矿流体研究进展. 地球科学进展, 15(5): 525-533. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2000.05.007 |
黄水保, 毛大华, 狄永军, 魏英文, 罗平, 李伯春. 2012. 北武夷梨子坑火山盆地流纹斑岩与铅锌矿的成因关系. 资源调查与环境, 33(3): 152-157. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2012.03.003 |
侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. 2009. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位U-Pb定年技术. 矿床地质, 28(4): 481-492. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.04.010 |
江西省地质矿产局. 1984. 江西省区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-921.
|
蒋少涌, 赵葵东, 姜耀辉, 戴宝章. 2008. 十杭带湘南-桂北段中生代A型花岗岩带成岩成矿特征及成因讨论. 高校地质学报, 14(4): 496-509. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.04.004 |
李晓峰, Yasushi W, 屈文俊. 2007. 江西永平铜矿花岗质岩石的岩石结构、地球化学特征及其成矿意义. 岩石学报, 23(10): 2353-2365. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.004 |
李超, 屈文俊, 杜安道. 2009. 大颗粒辉钼矿Re-Os同位素失耦现象及187Os迁移模式研究. 矿床地质, 28(5): 707-712. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.05.016 |
路远发, 马丽艳, 屈文俊, 梅玉萍, 陈希清. 2006. 湖南宝山铜-钼多金属矿床成岩成矿的U-Pb和Re-Os同位素定年研究. 岩石学报, 22(10): 2483-2492. |
罗平. 2005.江西铅山县陈坊-永平地区铜铅锌银成矿规律与成矿预测.硕士学位论文.武汉: 中国地质大学, 1-67
|
罗平, 魏英文, 王永庆. 2005. 北武夷长寿源银铅(锌)矿床地质特征. 资源调查与环境, 26(1): 33-42. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2005.01.006 |
罗平, 吴淦国, 张达, 狄永军, 王长明, 王永庆. 2009. 北武夷生米坑铅锌矿床地质地球化学特征与成因探讨. 地质力学学报, 15(4): 349-362. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.04.004 |
罗平. 2010.江西北武夷地区铜多金属矿成矿规律及找矿方向研究.博士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学, 1-187
|
罗诒爵. 1985. 冷水坑斑岩型铅锌矿床地质特征. 矿床地质, 4(4): 15-24. |
卢燃, 毛景文, 高建京, 苏慧敏, 郑佳浩. 2012. 江西冷水坑矿田下鲍Ag-Pb-Zn矿床地质特征及银的赋存状态研究. 岩石学报, 28(1): 105-121. |
毛景文, 谢桂青, 郭春丽, 陈毓川. 2007. 南岭地区大规模钨锡多金属成矿作用成矿时限及地球动力学背景. 岩石学报, 23(10): 2329-2338. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.002 |
毛景文, 谢桂青, 郭春丽, 袁顺达, 程彦博, 陈毓川. 2008. 华南地区中生代主要金属矿床时空分布规律和成矿环境. 高校地质学报, 14(4): 510-526. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.04.005 |
毛景文, 张建东, 郭春丽. 2010. 斑岩铜矿-浅成低温热液银铅锌-远接触带热液金矿矿床模型:一个新的矿床模型——以德兴地区为例. 地球科学与环境学报, 32(1): 1-14. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2010.01.001 |
毛景文, 陈懋弘, 袁顺达, 郭春丽. 2011. 华南地区钦杭成矿带地质特征和矿床时空分布规律. 地质学报, 85(5): 636-658. |
毛伟, 李晓峰, 杨富初. 2013. 广东大宝山多金属矿床花岗岩锆石LA-ICP-MSU-Pb定年及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 29(12): 4104-4120. |
孟祥金, 侯增谦, 董光裕, 刘建光, 屈文俊, 杨竹森, 左力艳, 万禄进, 肖茂章. 2007. 江西金溪熊家山钼矿床特征及其Re-Os年龄. 地质学, 81(7): 946-951. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.07.010 |
孟祥金, 徐文艺, 杨竹森, 侯增谦, 李振清, 于玉帅, 肖茂章, 何细荣, 万浩章. 2012. 江西冷水坑矿田火山-岩浆活动时限:SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄证据. 矿床地质, 31(4): 831-838. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2012.04.012 |
欧阳学财. 2015.江西东乡铜矿床地质地球化学特征及成因探讨.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学, 1-78
|
秦晓峰. 2014.北武夷地区燕山期与成矿有关的火山-侵入岩浆序列初步框架.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学, 1-79
|
邱骏挺, 余心起, 吴淦国, 屈文俊, 狄永军, 张达, 罗平, 杜安道. 2011. 北武夷篁碧矿区逆冲推覆构造及其与钼、铅-锌成矿作用关系. 地学前缘, 18(5): 243-255. |
邱骏挺, 余心起, 吴淦国, 刘建光, 肖茂章. 2013. 江西冷水坑矿区构造-岩浆活动的年代学约束. 岩石学报, 29(3): 812-826. |
苏慧敏. 2013.北武夷天华山盆地火山-侵入岩的成因及其与成矿关系的研究.博士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学, 1-134
|
苏慧敏, 毛景文, 何细荣, 卢燃. 2013. 北武夷天华山盆地形成时限的约束:来自火山岩-侵入岩的年代学证据. 中国科学(地球科学), 43(5): 745-759. |
田明君, 李永刚, 万浩章, 张宇, 高婷婷. 2014. 江西永平铜矿矽卡岩矿物特征及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 30(12): 3741-3758. |
万浩章, 张达, 狄永军, 罗平, 吕良冀, 董越, 卢俊浩. 2013. 江西弋阳铁砂街铜矿床蚀变钾长石Ar-Ar同位素年龄. 矿物学报, (增2): 613-614. |
魏娟娟, 狄永军, 魏英文, 张达, 罗平, 罗国辉, 秦晓峰, 董越, 杨秋, 陈杰. 2016. 北武夷王坞矿区花斑岩与钼矿的关系:来自锆石U-Pb和辉钼矿Re-Os定年的证据. 现代地质, 30(1): 59-68. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.01.007 |
肖志宏. 1996. 浅谈永平矿区成矿规律. 江西铜业工程, 2: 41-45. |
徐德明, 蔺志永, 龙文国, 张鲲, 王磊, 周岱, 黄皓. 2012. 钦杭成矿带的研究历史和现状. 华南地质与矿产, 28(4): 277-289. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2012.04.001 |
徐庆胜, 魏英文, 黄安杰, 罗平, 吴才来, 赵红松, 狄永军. 2014. 江西上饶梨子坑火山盆地潜火山岩地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及其与铅锌矿成矿关系. 地质论评, 60(4): 932-943. |
徐文炘, 肖孟华, 陈民扬. 2001. 江西冷水坑银-铅-锌矿床同位素地球化学研究. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 20(4): 370-372. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2001.04.046 |
徐贻赣, 吴淦国, 王长明, 张达, 张垚垚. 2013. 江西冷水坑银铅锌矿田闪锌矿铷-锶测年及地质意义. 地质学报, 87(5): 621-633. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.05.003 |
杨明桂, 梅勇文. 1997. 钦-杭古板块结合带与成矿带的主要特征. 华南地质与矿产, 3: 52-59. |
余明刚, 赵希林, 钱迈平, 段政, 张雪辉, 万浩章, 肖茂章, 孙建东. 2015. 江西冷水坑火山-侵入杂岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义. 岩矿测试, 34(1): 138-149. |
余心起, 吴淦国, 张达, 狄永军, 代堰锫, 邱骏挺. 2008. 北武夷地区逆冲推覆构造的特征及其控矿作用. 地质通报, 27(10): 1667-1677. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.10.009 |
张达, 吴淦国, 狄永军, 吕良冀, 姚继明. 2011a. 武夷山西南缘构造应力场演化及其与成矿的关系. 地质通报, 30(4): 505-513. |
张达, 吴淦国, 狄永军, 王长明, 吕良冀, 张垚垚, 石建基, 姚继明. 2011b. 闽西南中生代推覆构造对铁矿床控矿特征研究. 矿物学报, 31(增1): 128-129. |
张万祥. 1995. 永平-铜山地区层控型铜铅锌矿床的成矿地质条件及其成矿作用. 江西地质, 9(4): 249-258. |
张学书. 1997. 江西永平铜矿金属矿物化学成份及矿物包体特征. 江西地质, 11(2): 40-48. |
张国伟, 郭安林, 王岳军, 李三忠, 董云鹏, 刘少峰, 何登发, 程顺有, 鲁如魁, 姚安平. 2013. 中国华南大陆构造与问题. 中国科学(地球科学), 43(10): 1553-1582. |
张家菁, 吴木森, 陈郑辉, 刘善宝, 李立兴, 邱良明, 吴斌, 黄安杰, 祝平俊. 2009. 江西省上饶县金竹坪钼多金属矿床成矿年代学研究. 岩矿测试, 28(3): 228-232. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2009.03.007 |
张家菁, 王登红, 刘善宝, 陈郑辉, 施光海, 王静, 王永庆, 魏英文. 2012. 江西省铅山县篁碧铅锌矿区同位素年代学和稳定同位素组成. 岩石学报, 28(10): 3325-3333. |
周永章, 曾长育, 李红中, 杨志军, 陈炳辉, 王正海, 梁锦, 卢文姬, 陈庆. 2010. 钦-杭成矿带典型矿种及其矿床分布总体特征. 矿床地质, 29(增): 34-34. |
周永章, 曾长育, 李红中, 安燕飞, 梁锦, 吕文超, 杨志军, 何俊国, 沈文杰. 2012. 钦州湾-杭州湾构造结合带(南段)地质演化和找矿方向. 地质通报, 31(2-3): 486-491. |
左力艳. 2008.江西冷水坑斑岩型银铅锌矿床成矿作用研究.博士学位论文.北京: 中国地质科学院, 1-140
|
左力艳, 侯增谦, 孟祥金, 杨志明, 宋玉财, 李政. 2010. 冷水坑斑岩型银铅锌矿床含矿岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究. 中国地质, 37(5): 1450-1456. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.05.021 |
 2018, Vol. 34
2018, Vol. 34