2. 北京大学地球与空间科学学院, 北京 100871;
3. 吉林大学地球科学学院, 长春 130061;
4. 长安大学地球科学与资源学院, 西安 710054
2. School of Earth and Space Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China;
3. College of Earth Sciences, Jilin University, Changchun 130061, China;
4. School of Earth Science and Resources, Chang'an University, Xi'an 710054, China
大兴安岭是我国东北重要的银、铅、锌、铜和钼多金属成矿带(徐贵忠等, 1998; 李长珠, 1999; 祁进平等, 2005; 毛景文等, 2013), 带内多数矿床与中生代岩浆活动关系密切,成矿类型以斑岩型、矽卡岩型和浅成低温热液型为主(赵一鸣和张德全, 1997; Chen et al., 2007; Ouyang et al., 2013, 2015)。大兴安岭中生代岩浆广泛发育,被称为大兴安岭中生代岩浆省(Sengor and Natal'in, 1996)。前人对于大兴安岭中生代火成岩形成的构造背景主要持三种观点:(1)与地幔柱活动或板内作用有关(Shao et al., 1995; 林强等, 1998; 邵济安等, 1998; 郭锋等, 2001);(2)形成于蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合后的造山带伸展环境(郭锋等, 2001; Wang et al., 2002; Fan et al., 2003; Meng, 2003);(3)与太平洋板块的俯冲作用有关(葛文春等, 1999; Wang et al., 2006a; Zhang et al., 2008a, b; 张吉衡, 2009)。
研究区位于大兴安岭北端,属天山-兴蒙造山带上黑龙江前陆盆地南缘,地处黑龙江拗陷腰站断陷南缘与十八站隆起北缘交接部位(黑龙江省地质矿产局, 1993)。区内断裂构造发育,岩浆活动频繁,燕山期侵入岩可划分为中-晚侏罗世和早白垩世两期。中-晚侏罗世侵入岩形成于大兴安岭火山岩喷发之前,同位素年龄为167~164Ma,主要岩性为二长花岗岩和钾长花岗岩,其次为闪长岩、花岗闪长岩(武广, 2006)。早白垩世侵入岩与大兴安岭中生代火山岩密切相伴,武广(2006)测得同位素年龄为129.8~126.0Ma(SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄)主要岩石类型有闪长岩、石英闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、花岗斑岩和闪长玢岩等,多为造山期后岩浆活动的产物。早白垩世斑岩类与研究区金、银及有色金属成矿关系密切,与之有关的矿床有:二十一站Cu-Au矿、龙沟河Cu-Au矿点及洛古河Cu-Mo矿点等(武广等, 2002, 2014)。前人没有对二十一站岩体进行过年代学研究,按照区域地质资料把二十一站岩体的时代定为侏罗纪(武广等, 2008),前人指出二十一站成矿母岩花岗斑岩的K-Ar年龄为137~112Ma(武广, 2006),武广等(2009)对上黑龙江盆地的洛古河岩体进行了SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年(130±2Ma),近年研究成果表明,上黑龙江盆地的成矿事件主要集中在早白垩世(刘军等, 2013; 李向文, 2015; 孙琦等, 2015),因此,有必要对二十一站矿区存在的上黑龙江盆地的主要赋矿岩相(闪长岩、花岗闪长斑岩)进行详细的定年和地球化学研究,在此基础上讨论其成岩成矿时代、成矿动力学背景及其找矿意义,指导下一步找矿工作。
1 地质背景 1.1 区域地质背景上黑龙盆地位于兴蒙造山带的东段、大兴安岭北段,介于额尔齐斯-索伦-黑河缝合带与蒙古-鄂霍茨克缝合带之间,西部为额尔古纳地块、南部为北兴安地块和西南部的鄂伦春晚古生代中期增生带(图 1a)(武广, 2006)。其构造演化经历了古元古代变质基底形成阶段;中新元古代浅变质阶段;古生代盖层形成阶段;中生代陆相盆地沉积阶段及晚侏罗-早白垩世构造-岩浆活动阶段。同时,这里也是环太平洋和中亚-兴蒙两大成矿带的交汇区,成矿地质条件十分优越。

|
图 1 区域构造简图(a, 据武广, 2006)和上黑龙江盆地地质简图(b, 据武广等, 2008; 李良等, 2015; 李向文, 2015修改) ①-得尔布干断裂带;②-塔河-漠河断裂;③-漠河韧性剪切带 Fig. 1 Tectonic map of study area (a, after Wu, 2006) and geological sketch map of Upper Heilongjiang Basin (b, after Wu et al., 2008; Li, 2015; Li et al., 2015) |
区域出露的地层主要有古元古代兴华渡口群中级变质岩,早寒武世额尔古纳河组大理岩和早泥盆世泥鳅河组灰岩,下-中侏罗统绣峰组,中侏罗统二十二站组和漠河组陆相砾岩、砂岩、粉砂岩。中生代火山岩形成于中侏罗世-早白垩世,为一套中酸性为主的火山熔岩、火山碎屑岩,从下至上划分为:绣峰组(J2x)、二十二站组(J2e)、漠河组(J2m)、开库康组(J2k)、塔木兰沟组(J2tm)、白音高老组(J3b)、龙江组(K1l)、光华组(K1gh)、甘河组(K1g)(黑龙江省地质矿产局, 1993; 武广, 2006)。
区内主要断裂具多期性和继承性活动特点。主要有北东向的得尔布干断裂、开库康-马林断裂,北西向塔河-漠河断裂,近南北向的二根河断裂。
区内侵入岩发育,主要发育中生代的花岗岩类(图 1b),可分为两个时期:晚侏罗世侵入岩主要分布于洛古河-北极村一带,呈大的岩基出露,岩性以二长花岗岩为主,局部有闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、黑云母花岗岩、中细粒花岗岩、中粗粒花岗岩,与“洛古河式”斑岩型铜多金属矿化关系密切;早白垩期花岗岩分布于额木尔河上游1047高地、二十二站及二十一站等地,均以岩株、岩枝状产出,岩性以闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、花岗闪长斑岩为主,与“二十一站式”斑岩型铜、金矿密切相关(武广等, 2002)。
1.2 矿区地质背景矿区出露地层主要有侏罗系二十二站组(J2er)、白垩系的上库力组(K1s)及第四系,矿体主要受NW向断裂控制(武广, 2006),侵入岩主要有早期浸染状黄铁矿化的闪长岩,与黄铜矿赋矿岩体花岗闪长斑岩,主要的围岩蚀变有:钾长石化、硅化绢云母化、绢云母化高岭土化、绿泥石化绿帘石化和碳酸盐化(李孝敏, 2016),矿区的金矿化主要赋存在硅化、黄铁绢英岩化闪长岩中,铜矿化主要赋存于钾化花岗闪长斑岩中,且矿化与石英网脉和岩石的破碎程度密切相关,网脉越发育,岩体越破碎含矿性越好。前人根据二十一站矿床的矿石类型、矿石组构及围岩蚀变组合,将矿床类型定为斑岩型矿床(张炯飞等, 2002; 武广, 2006; 李孝敏, 2016)。
2 岩相学特征和样品描述作者根据岩芯编录认为闪长岩与花岗闪长斑岩分别与金铜矿化关系密切(文中1.2部分描述),因此有一定的蚀变,尤其是钾长石化蚀变可能会引起K含量的带入及带出,文章中投图已对烧失量做了归一化处理,钾化的花岗闪长斑岩LOI值在2.29~2.69之间,存在一定的影响,但在误差范围内基本可以客观真实反映岩体的地球化学特征及构造地质背景。本次研究对二十一站Cu-Au矿区ZK104岩芯87~369m之间,间隔取样,岩性分别为闪长岩(1-1~1-7)和花岗闪长斑岩(2-1~2-5)。花岗闪长斑岩中部分长石斑晶有成矿热液造成的局部钾化,矿体多赋存于花岗闪长斑岩中。
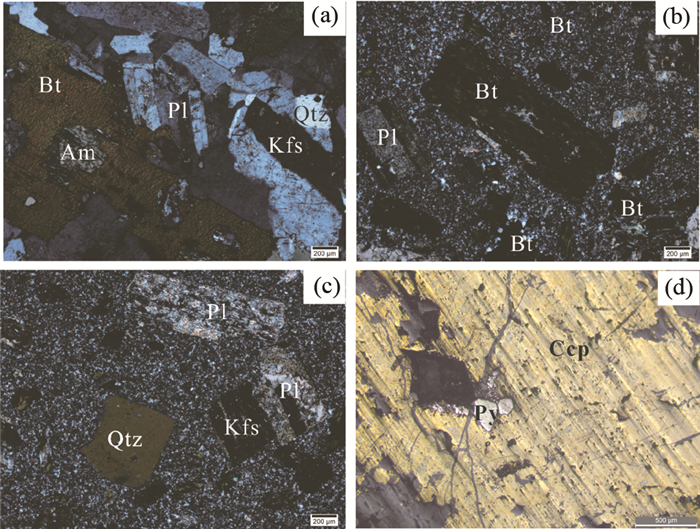
闪长岩(图 2a),岩石呈浅灰色,具不等粒花岗结构,石英(20%±)呈半自形-他形粒状,粒径(0.2~2mm);斜长石(40%±)呈自形-半自形板状,发育聚片双晶,粒径(0.5~3mm);钾长石(25%±)呈自形-半自形板状,发育卡式双晶,粒径(0.5~2mm);黑云母(10%±)呈片状,少数包裹角闪石、石英,粒径(0.2~4mm);角闪石(5%±)呈他形粒状,粒径(0.2~0.5mm)。
|
图 2 闪长岩(a)、花岗闪长斑岩(b、c)及花岗闪长斑岩中黄铜矿化(d)正交偏光下显微照片 Bt-黑云母;Kfs-钾长石;Am-角闪石;Pl-斜长石;Qtz-石英;Ccp-黄铜矿;Py-黄铁矿 Fig. 2 Microphotographs of the diorite (a), granodiorite porphyry (b, c) and chalcopyrite in granodiorite porphyry (d) Bt-biotite; Kfs-K-feldspar; Am-amphibole; Pl-plagioclase; Qtz-quartz; Ccp-chalcopyrite; Py-pyrite |
花岗闪长斑岩(图 2b, c),岩石呈浅红浅灰色,多具斑状结构,岩石受轻微绢云母化、钾长石化、绿泥石化、高岭土化,常见黄铜矿化,黄铁矿化(图 2d),斑晶约占40%,有斜长石、石英、钾长石、黑云母。斜长石,呈自形-半自形板状,粒径(1~3mm),发育聚片双晶,常成连晶,斜长石多见钾化和绢云母化、个别斜长石发育高岭土化。石英呈自形-半自形粒状,粒径(0.4~1mm),黑云母呈自形-半自形板状粒径(0.2~3mm),普遍发育绿泥石化。基质为长英质隐晶质。
3 分析方法 3.1 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年锆石挑选由河北省廊坊区域地质调查研究所实验室利用标准重矿物分离技术分选完成。锆石制靶、反射光、阴极发光以及锆石U-Pb年龄测定和痕量元素分析均在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室进行。本次测试采用的激光剥蚀束斑直径为32μm,激光剥蚀深度为20~40μm;实验中采用He作为剥蚀物质的载气。锆石年龄采用国际标准锆石91500作为外标,元素含量采用NIST SRM610作为外标,29Si作为内标元素(锆石中SiO2的质量分数为32.8%(袁洪林等, 2003),分析方法见文献(Yuan et al., 2004);普通铅校正采用Anderson推荐的方法(Andersen, 2002);样品的同位素比值及元素含量计算采用ICP-MS-DATECAL程序(Liu et al., 2008),年龄计算及谐和图的绘制采用Isoplot程序(Ludwig, 2003)。
3.2 岩石地球化学测试本次实验的主量元素和痕量元素分析样品于吉林大学地球科学学院粉碎至250目后,缩分出适量样品,由核工业北京地质研究院分析测试中心完成,主量元素的测定采用X射线荧光光谱法(XRF),实验仪器为PW2404顺序扫描型X射线荧光光谱仪,其中Al2O3、SiO2、MgO、Na2O检测限为0.015%,CaO、K2O、TiO2检测限为0.01%,Fe2O3T、MnO、P2O5检测限为0.005%;FeO用容量法完成(检测限为0.1%);微量和稀土元素测定采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪测得。对于含量大于20×10-6的元素,误差为±5%,而含量小于20×10-6的元素,误差为±10%。
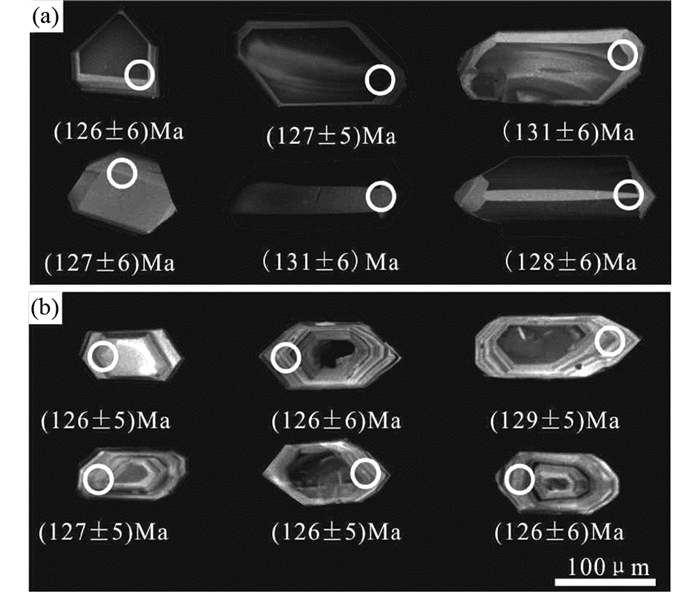
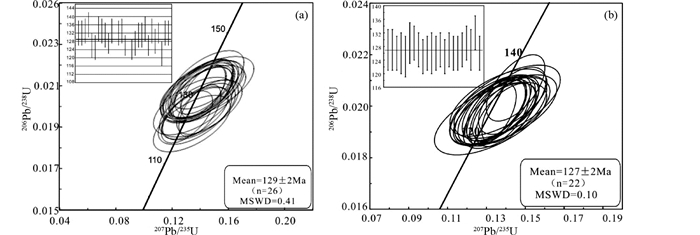
4 分析结果 4.1 锆石LA-ICP-MS年代学 4.1.1 闪长岩二十一站闪长岩锆石形态呈自形-半自形,粒径80~220μm,多呈长柱状、短柱状,CL图像显示无分带或弱分带的特征(图 3a)。本文测试的26个点Th/U比值介于0.5~1.25之间(表 1),符合岩浆锆石Th/U比值>0.4的特征(Weaver, 1991)。26个206Pb/238U分析数据的谐和年龄值为129±1Ma,MSWD=2.1;加权平均年龄为129±2Ma,MSWD=0.41(图 4a),闪长岩形成时代为早白垩世。
|
图 3 二十一站岩体锆石CL图像 (a)闪长岩;(b)花岗闪长斑岩 Fig. 3 CL images of zircons from the rocks of Ershiyizhan (a) diorite; (b) granodiorite porphyry |
|
图 4 闪长岩(a)和花岗闪长斑岩(b) U-Pb年龄协和图 Fig. 4 Zircon U-Pb concordia diagram for the rocks of diorite (a) and granodiorite porphyry (b) |
|
|
表 1 二十一站岩体锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb定年结果 Table 1 LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb analyses of the rocks from the Ershiyizhan |
研究区花岗闪长斑岩锆石形态自形-半自形,粒径60~200μm,多呈长柱状、双锥状,CL图像显示锆石颜色明亮,锆石具有清晰的震荡环带(图 3b),为典型的岩浆锆石的特征。本文测试的22个点Th/U比值介于0.33~0.93之间(表 1)。22个206Pb/238U分析数据的谐和年龄值为127±1Ma,MSWD=4.4;加权平均年龄为127±2Ma,MSWD=0.10(图 4b),确定花岗闪长斑岩形成时代为早白垩世。这说明闪长岩与花岗闪长斑岩近乎同一期岩浆时期形成。
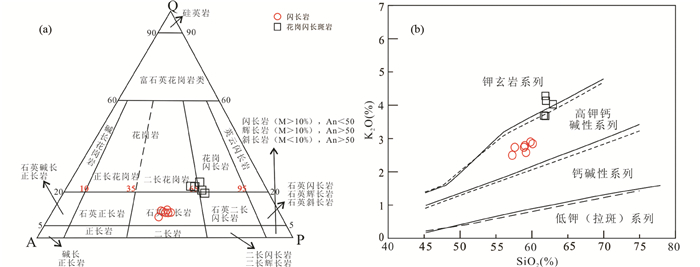
4.2 地球化学特征 4.2.1 主量元素二十一站岩体的主量分析结果见表 2。闪长岩SiO2的含量为57.04%~59.91%,Al2O3的含量为15.5%~16.22%,Na2O的含量为4.07%~4.36%,K2O的含量为2.47%~2.86%,Mg#含量为51~61;花岗闪长斑岩的SiO2的含量为61.52%~62.77%,Al2O3的含量为13.71%~14.54%,Na2O的含量为2.93%~3.42%,K2O的含量为3.66%~4.25%,Mg#含量为52~60。在QAP图解中,样品分别落入花岗闪长岩和石英二长岩的区域(图 5a)。二十一站岩体中岩石的里特曼指数 < 3.3,在硅钾图解(图 5b)中闪长岩处于高钾钙碱性序列,花岗闪长斑岩显示由高钾钙碱性序列向钾玄岩序列过渡。
|
|
表 2 二十一站岩体主量(wt%)、稀土及微量元素(×10-6)分析结果 Table 2 The data of major (wt%), rare earth and trace element (×10-6) of the Ershiyizhan rocks |
|
图 5 二十一站岩体QAP图解(a, Streckeisen, 1976)与SiO2-K2O图解(b, 实线据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976; 虚线据Middlemost, 1985) Fig. 5 QAP diagram (a, after Streckeisen, 1976) and SiO2-K2O diagram (b, solid line after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976; dash line after Middlemost, 1985) of Ershiyizhan rocks |
二十一站闪长岩和花岗闪长斑岩的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线(图 6a)显示相类似的配分型式,表现为轻稀土元素(LREE)相对富集,重稀土元素(HREE)相对亏损的右倾曲线(LREE/HREE=11.8~14.2、(La/Yb)N=14.5~19.9),具有弱的负Eu异常(0.70~0.93),∑LREE=100×10-6~173×10-6,∑HREE=8.29×10-6~13.46×10-6,∑REE=109×10-6~186×10-6(表 2)。其中花岗闪长斑岩的稀土元素含量相对于闪长岩含量略低。这些岩石的原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(图 6b)同样显示相似的微量元素特征,富集大离子亲石元素(LILEs)(如Rb、Ba)、LREE和不相容元素(如U),强烈亏损高场强元素(HFSEs)(Nb、Ta),闪长岩相比于花岗闪长斑岩显示更明显的Zr、Hf异常,可能与源区的锆石残留有关。

|
图 6 二十一站岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a, 标准化值据Boynton, 1984)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b, 标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a, normalization values after Boynton, 1984) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams of Ershiyizhan rocks (b, normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
上黑龙江盆地区域上出露的燕山期岩体分布于隆凹过渡带部位,呈岩株或岩枝状零星出露的花岗闪长岩、正长斑岩、花岗斑岩、闪长玢岩、闪长岩、花岗岩等,与区内铜矿成矿关系密切。二十一站岩体的锆石CL图像及相对较高的Th/U比值,表现出岩浆锆石的特点,其定年结果应该代表岩浆结晶的年龄。矿化发育的闪长岩与矿体的赋存岩石花岗闪长斑岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石206Pb/238U年龄分别为127~131Ma和125~129Ma之间,其加权年龄分别为129Ma和127Ma,即它们形成的时代为早白垩世。
前人研究成果表明,上黑龙江成矿带矿化事件主要集中在早白垩世,且以金铜矿化为主,与早白垩世的浅成侵入体、次火山岩、火山岩密切伴生(李向文, 2015)。前人获得的上黑龙江盆地铜金矿成矿时代如下:虎拉林金矿床钾长石40Ar-39Ar坪年龄为136Ma(王科强等, 2010),洛古河矽卡岩型矿石的Re-Os年龄127±2Ma(孙琦等, 2015),砂宝斯金矿石英脉中原生包裹体40Ar-39Ar等时线年龄为130±1Ma、石英脉中钾长石微晶40Ar-39Ar等时线年龄为133±4Ma(刘军等, 2013),十五里桥成矿年龄为115~125Ma(孙彦峰, 2015),宝兴沟的成矿时代108~125Ma(李向文等, 2012),同时区域内相应岩体的年龄分别为三十二站花岗斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为135Ma(李向文, 2015),洛古河花岗斑岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为122±2Ma,黑云母二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为131±2Ma(孙琦等, 2015),洛古河的花岗斑岩的SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄为130±2Ma(武广等, 2009),十五里桥赋矿岩石安山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为126±1Ma(孙彦峰, 2015),宝兴沟花岗闪长斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为125±1Ma (杨言辰, 2009①),石英闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为125±1Ma(李向文等, 2012),通过对比的年龄可以清晰的看出,上黑龙江盆地的成岩、成矿时代在误差范围内较为一致,结合前人对二十一站的的K-Ar年龄(137~112Ma),与早白垩世岩体年龄较为一致,成矿时代也应处于早白垩世。
① 杨言辰. 2009.黑龙江右岸金矿床成矿地质条件、成矿规律及找矿方向.长春:吉林大学地质调查研究院
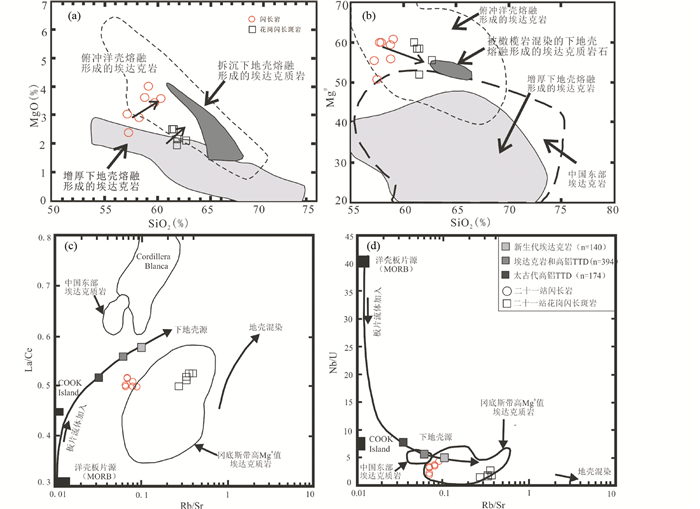
5.2 岩石源区与岩石成因埃达克岩(adakite)是Defant and Drummond (1990)研究阿留申群岛新生代俯冲洋壳熔融产生的火山岩时提出的术语,用以概括具有特定地球化学性质的一套中酸性火山岩和侵入岩的组合,包括安山岩、英安岩、安粗岩、石英闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、石英二长岩、英云闪长岩、斜长花岗岩等。其地球化学特征是SiO2≥56%,Al2O3≥15%,MgO < 3%(少量>6%),亏损重稀土元素(HREE)与Y(Y≤18×10-6),高Sr(多数大于400×10-6)、La/Yb≥20.0、Sr/Y>40,一般具有正铕异常(少数具有弱的负铕异常)(Defant and Drummond, 1990, 1993; Drummond and Defant, 1990; Defant et al., 1991, 1992; Taylor and Mclennan, 1995; Martin, 1999; Martin et al., 2005; Richards and Kerrich, 2007)。
二十一站岩体的闪长岩、花岗闪长斑岩的主微量与埃达克岩有非常类似的特征,在Sr/Y-Y图解(图 7a)和(La/Yb)-Yb图解(图 7b)样品全落入埃达克岩区。由于埃达克岩源区部分熔融的残留相为榴辉岩或石榴角闪岩,而在角闪石、石榴石和单斜辉石中,Sr的分配系数很小(分别为0.058、0.015和0.2),而Y的较高(分别为3.2、12.5和2.0),因为导致埃达克岩岩浆亏损Y和HREE,并具有高的La/Yb和Sr/Y比值(Defant and Drummond, 1990)。

|
图 7 二十一站岩体Sr/Y-Y图解(a)和La/Yb-Yb图解(b)(底图据Richards and Kerrich, 2007) Fig. 7 Sr/Y vs. Y (a) and La/Yb vs. Yb (b) diagrams discriminating between adakitic and classic arc calc-alkaline compositions for the Ershiyizhan rocks (base map after Richards and Kerrich, 2007) |
根据Na2O/K2O比值、Sr-Nd同位素特征和产出位置将埃达克岩划分为四种成因类型:1)年轻的大洋板片俯冲发生部分熔融(O型,即原始定义类型)(Defant and Drummond, 1990);2)增厚的玄武质下地壳铁镁质岩石熔融(C型)(Atherton and Petford, 1993; 张旗等, 2001b; 熊小林等, 2001; Wang et al., 2003a, b, c; 赵振华等, 2007);3)拆沉下地壳的部分熔融(Xu et al., 2002; 王强等, 2004; Guo et al., 2004);4)富集地幔的部分熔融和地壳同化混染(Xie et al., 2008, 2011)。其中,O型埃达克岩具有富钠贫钾的特征(Na2O/K2O>2),而C型埃达克岩相对于O型具有明显富钾的特征(Na2O/K2O≈1或>1)(张旗等, 2001a; 王强等, 2001)。二十一站闪长岩Na2O/K2O=1.51~1.77、花岗闪长斑岩Na2O/K2O=0.75~0.86,同时,古亚洲洋和鄂霍茨克洋分别闭合于二叠纪和中侏罗世之前,因此,排除了二十一站岩体是受洋壳俯冲发生部分熔融成因的可能。
大洋中脊玄武岩部分熔融只产生Mg#值小于45的熔体,但熔体只要与橄榄岩发生10%的混染便可以使熔体的MgO#值从45上升到55(Rapp and Watson, 1995),典型的埃达克岩Mg#值在50左右(Martin, 1999; Martin et al., 2005; Richards and Kerrich, 2007)。而二十一站岩体Mg#值为51~61之间,多数接近60左右,反应了岩浆源区有相对富镁的物质参与,可能是受橄榄岩混染的下地壳熔融形成的(Smithies, 2000; Defant et al., 2002; Xu et al., 2002),同样也可能造成了二十一站岩体的MgO值偏高,因此在SiO2-MgO图解中样品落入了增厚下地壳熔融形成的埃达克岩区以上向拆沉下地壳形成埃达克质岩方向过渡,SiO2-Mg#图解中样品也落入了增厚下地壳熔融形成的埃达克岩和中国东部埃达克岩的区域以上的靠近被橄榄岩混染的下地壳熔融形成的埃达克质岩区;在La/Ce-Rb/Sr和Nb/U-Rb/Sr图解(图 8c, d)中,二十一站闪长岩和花岗闪长斑岩基本全部落于冈底斯高Mg#值埃达克质岩范围内,而岩石的Rb-Sr值较低,表明地壳混染微弱,岩石的形成过程中有地幔物质的加入。增厚的下地壳镁铁质岩石在转化为高密度的榴辉岩相拆沉进入到地幔后熔融,在软流圈上涌的过程中受到地幔的混染(Wu et al., 2010)。
|
图 8 二十一站岩体SiO2-MgO图解(a)、SiO2-Mg#图解(b)、La/Ce-Rb/Sr图解(c)和Nb/U-Rb/Sr图解(d) 图a中,俯冲洋壳熔融形成的埃达克岩引自Defant and Drummond (1990); Martin (1999); Smithies (2000); Defant et al. (2002);增厚下地壳熔融形成的埃达克岩引自Atherton and Petford (1993); Petford and Atherton (1996); Smithies (2000);拆沉下地壳熔融形成的埃达克质岩引自Xu et al. (2002).图b中,俯冲洋壳熔融形成的埃达克岩引自Defant and Drummond (1990); Martin (1999); Smithies (2000);中国东部埃达克质岩王焰和张旗(2001);被橄榄岩混染的下地壳熔融形成的埃达克质岩和增厚下地壳熔融形成的埃达克质岩肖龙等(2004).图c和d中,俯冲洋壳熔融形成的埃达克质岩以Cook岛埃达克质岩为代表,引自Stern and Kilian (1996);新生代埃达克岩、埃达克岩和高铝TTG及大古代高铝TTG引自Drummond et al. (1996);来自下地壳的中国东部埃达克质岩引自Xu et al. (2002)和Cordillela Blance埃达克质岩引自Petford and Atherton (1996);冈底斯带高Mg#值埃达克质岩侯增谦等(2004) Fig. 8 SiO2 vs. MgO (a), SiO2 vs. Mg# (b), La/Ce vs. Rb/Sr (c) and Nb/U vs. Rb/Sr (d) diagrams for the Ershiyizhan rocks |
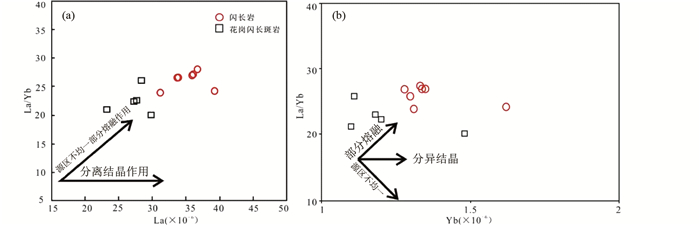
在La-La/Yb图解(图 9a)与Yb-La/Yb图解(图 9b)中,岩体均表现出部分熔融或源区不均一的特征,说明二十一站岩体不是由岩浆分离结晶作用形成的。Eu异常(Eu/Eu*)是示踪地壳演化和壳幔交换作用的重要依据(Taylor, 1985; Gao and Wedepohl, 1995),幔源岩石通常无Eu异常,地幔形成的新生地壳同样不具Eu异常,部分熔融残余的下地壳与底侵作用产生的下地壳则表现明显的正Eu异常(高山等, 1999)。二十一站岩体样品Eu负异常(0.70~0.93),且Mg#值高(51~61),可能是因为榴辉岩或高镁质麻粒岩构成的下地壳拆沉后,不仅造成大陆地壳总体成分向长英质方向演化,同时Eu异常向负异常方向演化。因此,综合地球化学和地质背景,认为二十一站早白垩世埃达克质岩石是由源区存在的榴辉岩或高镁麻粒岩构成的增厚下地壳拆沉,熔融,并受到源区橄榄岩混染而形成。
|
图 9 二十一站岩体La-La/Yb图解(a)与Yb-La/Yb图解(b)(据蔡宏明等, 2010) Fig. 9 La vs. La/Yb (a) and Yb vs. La/Yb (b) diagrams for the Ershiyizhan rocks (after Cai et al., 2010) |
二十一站岩体在Rb-(Y+Nb)判别图解中(图 10a),投影点全部落入火山弧和后碰撞花岗岩的过渡区;在R1-R2判别图解中(图 10b),投影点基本全部落入后碰撞隆升区(Ⅲ区)。花岗岩类构造判别图解表明研究区花岗岩形成于后碰撞隆升的构造背景下。

|
图 10 Rb-Y+Nb判别图解(a, 据Pearce, 1996)和R1-R2判别图解(b, 据Batchelor and Bowden, 1985) Fig. 10 The diagram of Rb vs. Y+Nb (a, after Pearce, 1996) and R1 vs. R2 (b, after Batchelor and Bowden, 1985) |
区域构造演化分析表明,晚古生代-早中生代期间,位于蒙古-中朝大陆和西伯利亚大陆之间的蒙古鄂霍茨克洋自西向东剪刀式闭合,形成蒙古-鄂霍次克造山带(Zhao et al., 1990; Zonenshain et al., 1990; Zorin, 1999; Parfenov et al., 2001; 李锦轶等, 2004);中侏罗世末-晚侏罗世早期在上黑龙江盆地形成漠河推覆构造和大量北倾的逆冲断层,使泥盆系灰岩推覆至下-中侏罗统陆相碎屑岩之上,并造成了上黑龙江前陆盆地沉积物褶皱,地壳缩短、增厚。根据大兴安岭满洲里地区出现的早侏罗世玄武岩-玄武安山岩-安山岩钙碱性火山岩组合(陈志广等, 2006; 许文良等, 2013),反映了活动陆缘的特征,而非被动陆缘的构造环境(Zorin, 1999),证明了蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋向南俯冲到了额尔古纳陆块之下。同时大兴安岭火山岩的地球化学表明,它们源于被俯冲流体交代的富集岩石圈地幔(陈志广等, 2006; 张连昌等, 2007; Zhang et al.2008b, ),早白垩世后火山岩形成于造山后伸展的环境,而非太平洋板块俯冲引起的弧后伸展(Fan et al., 2003),因此排除了上黑龙江盆地岩体受太平洋板块俯冲形成的可能性。
早白垩世晚期(131~110Ma),大兴安岭地区北部以上库力组流纹岩和伊列克得组玄武岩为代表,它们形成于131~114Ma之间(Zhang et al., 2008a; Ying et al., 2010; 孟恩等, 2011)。该期的火山事件为典型的双峰式火山岩组合,结合该区早白垩世晚期广泛发育的变质核杂岩、A型花岗岩,表明该时期区域处于伸展的构造环境(Davis et al., 2001; Wu et al., 2002),可能与蒙古-鄂霍茨克缝合带闭合后加厚陆壳的拆沉过程相联系(Xu et al., 2013)。
鉴于以上原因,研究区的早白垩世岩体的形成与古亚洲洋闭合后造山、环太平洋的俯冲过程无关,而与蒙古-鄂霍茨克造山带具有一致的时空关系。因此,上黑龙江盆地二十一站早白垩世岩体形成于蒙古-中朝大陆与西伯利亚大陆碰撞后局部隆升的构造环境,可能是蒙古-鄂霍茨克造山带陆陆碰撞期间加厚下地壳发生拆沉,熔融,并受到幔源物质混染的产物。
5.4 二十一站Cu(Au)成矿意义斑岩型矿床是大兴安岭北段重要的矿床类型,如岔路口、乌奴格吐山等大型-超大型铜钼矿床,同时在与本区相邻的俄罗斯境内,已经查明了鲁戈康矿结、上奥列克明、嘎兹穆尔-扎沃达瓦3个超大型-大型斑岩型铜(金)矿床(柴璐等, 2013),而上黑龙江盆地发现的铜金矿床规模较小(如二十一站、龙沟河等)。在成矿背景及时代方面,上述斑岩型铜金矿床多与燕山期中酸性岩浆活动有关,成矿上受控于复背斜、基底隆带上多组断裂的交汇部位(王召林等, 2012),构造背景多与蒙古鄂霍茨克洋闭合后的活动有关。二十一站铜金矿床所处的上黑龙江盆地广泛发育燕山期岩浆活动,受控于腰站断陷、十八站隆起、深大断裂带和一些次级断裂的影响,本区也具备邻区大型斑岩型矿床成矿相似的地质条件,因此,研究区同样具备与蒙古鄂霍茨克洋闭合后有关的燕山期中酸性岩体中寻找大型斑岩型铜、钼、金矿床的潜力(武广等, 2006, 2014)。
埃达克质岩与矽卡岩铜铁矿(谢桂青等, 2008)、浅成低温热液和斑岩型铜-金成矿系统关系密切(Thiéblemont et al., 1997; 张旗等, 2002; 张炯飞等, 2004; 熊小林等, 2005; 赵振华等, 2006)。张旗等(2001b)指出,中国中新生代的斑岩型铜(钼)、金矿床(如:江西德兴铜矿、安徽沙溪铜矿、西藏玉龙铜矿等)的含矿花岗岩均具埃达克岩的特征,研究区二十一站、龙沟河等斑岩型矿床的成矿岩体也具有埃达克质岩石的特征,板块俯冲过程中产生的高氧逸度可以氧化地幔楔中的金、铜硫化物,从而释放铜金到板片熔体或岛弧岩浆中,提高熔体的铜金含量(曾键年和许继峰, 2008);埃达克质岩浆富流体可以携带大量的金属物质和一些金属的络合物,利于金属元素的萃取和富集成矿(Wang et al., 2006b)。
二十一站岩体地球化学特征与与中国东部多数埃达克质岩石相比(张旗等, 2001a),二十一站岩体具有更高的Mg#值和Cr、Ni含量,表明其形成过程中受到了地幔物质(橄榄岩)的混染(肖龙等, 2004),从深源获得了大量的铜、金、硫等成矿物质。因此,相对于中国东部由下地壳直接熔融形成的埃达克岩,研究区的埃达克岩更有利于斑岩型铜金矿床的形成(武广等, 2008)。此外,二十一站矿床的矿化发生于该花岗闪长斑岩中,以细网脉不规则线状产出,该岩体应为二十一站铜金矿床的成矿母岩,矿化发生的时间应稍晚于闪长岩与花岗闪长斑岩的成岩年龄。因此,上黑龙江地区应加强对同时期的该类型岩体的含矿性评价和找矿工作。
6 结论(1) 二十一站闪长岩锆石和花岗闪长斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果分别为129±2Ma(MSWD=0.74)和127±2Ma(MSWD=0.10),显示二者均形成于早白垩世。
(2) 矿区的闪长岩、花岗闪长斑岩属于高钾钙碱性序列,主微量特征与埃达克质岩石一致,但岩体受到了地幔物质的混染;岩体可能是蒙古-鄂霍茨克造山带陆陆碰撞期间加厚下地壳拆沉、熔融的产物,形成于蒙古-中朝大陆与西伯利亚大陆碰撞后隆升的构造环境。
(3) 上黑龙江盆地具有良好的斑岩型铜金矿床的成矿背景,可加强寻找与埃达克岩有关的斑岩型铜金矿床。
致谢 野外及论文撰写过程中得到了中国地质调查局发展中心于晓飞研究员,吉林大学王琳琳博士、李良博士,天津地质调查中心曾乐硕士,及黑龙江省齐齐哈尔矿产勘查开发总院的帮助与支持。两位审稿专家及编辑部俞良军老师对论文提出了诸多宝贵意见和建议。在此一并致以衷心的感谢!
Andersen T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2): 59-79. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X |
Atherton MP and Petford N. 1993. Generation of sodium-rich magmas from newly underplated basaltic crust. Nature, 362(6416): 144-146. DOI:10.1038/362144a0 |
Batchelor RA and Bowden P. 1985. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters. Chemical Geology, 48(1-4): 43-55. DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(85)90034-8 |
Boynton WV. 1984. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies. In: Henderson P (ed.). Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 63-114
|
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Heilongjiang Province. 1993. Regional Geology of Heilongjiang Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-941. |
Cai HM, Zhang HF, Xu WC, Shi ZL and Yuan HL. 2010. Petrogenesis of Indosinian volcanic rocks in Songpan-Garze fold belt of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau: New evidence for lithospheric delamination. Science China (Earth Sciences), 53(9): 1316-1328. DOI:10.1007/s11430-010-4033-9 |
Chai L, Zhu Q and Zhou YH. 2013. Distribution of significant metal mineral resources the in adjacent areas of China, Russia and Mongolia. Geology and Resources, 22(5): 397-402. |
Chen YJ, Chen HY, Zaw K, Pirajno F and Zhang ZJ. 2007. Geodynamic settings and tectonic model of skarn gold deposits in China: An overview. Ore Geology Reviews, 31(1-4): 139-169. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.01.001 |
Chen ZG, Zhang LC, Zhou XH, Wan B, Ying JF and Wang F. 2006. Geochronology and geochemical characteristics of volcanic rocks section in Manzhouli Xinyouqi, Inner-Mongolia. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(12): 2971-2986. |
Davis GA, Zheng YD, Wang C, Darby BJ, Zhang CH and Gehrels G. 2001. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Yanshan fold and thrust belt, with emphasis on Hebei and Liaoning provinces, northern China. In: Hendrix MS and Davis GA (eds.). Paleozoic and Mesozoic Tectonic Evolution of Central Asia: From Continental Assembly to Intra-continental Deformation. Boulder, Colorado: Geological Society of America Memoir, 194: 171-197
|
Defant MJ and Drummond MS. 1990. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature, 347(6294): 662-665. DOI:10.1038/347662a0 |
Defant MJ, Maury RC, Ripley EM, Feigenson MD and Jacques D. 1991. An example of island-arc petrogenesis: Geochemistry and petrology of the southern Luzon arc, Philippines. Journal of Petrology, 32(3): 455-500. DOI:10.1093/petrology/32.3.455 |
Defant MJ, Jackson TE, Drummond MS, De Boer JZ, Bellon H, Feigenson MD, Maury RC and Stewart RH. 1992. The geochemistry of young volcanism throughout western Panama and southeastern Costa Rica: An overview. Journal of the Geological Society, 149(4): 569-579. DOI:10.1144/gsjgs.149.4.0569 |
Defant MJ and Drummond MS. 1993. Mount St. Helens: Potential example of the partial melting of the subducted lithosphere in a volcanic arc. Geology, 21(6): 547-550. |
Defant MJ, Xu JF, Kepezhinskas P, Wang Q, Zhang Q and Xiao L. 2002. Adakites: Some variations on a theme. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 18(2): 129-142. |
Drummond MS and Defant MJ. 1990. A model for trondhjemite-tonalite-dacite genesis and crustal growth via slab melting: Archean to modern comparisons. Journal of Geophysical Research, 95(B13): 21503-21521. DOI:10.1029/JB095iB13p21503 |
Drummond MS, Defant MJ and Kepezhinskas PK. 1996. Petrogenesis of slab-derived trondhjemite-tonalite-dacite/adakite magmas. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh-Earth Sciences, 87(1-2): 205-215. DOI:10.1017/S0263593300006611 |
Fan WM, Guo F, Wang YJ and Lin G. 2003. Late Mesozoic calc-alkaline volcanism of post-orogenic extension in the northern Da Hinggan Mountains, northeastern China. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 121(1-2): 115-135. DOI:10.1016/S0377-0273(02)00415-8 |
Gao S and Wedepohl KH. 1995. The negative Eu anomaly in Archean sedimentary rocks: Implications for decomposition, age and importance of their granitic sources. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 133(1-2): 81-94. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(95)00077-P |
Gao S, Zhang BR, Jin ZM and Kern H. 1999. Lower crust delamination in the Qinling-Dabie orogenic belt. Science in China (Series D), 42(4): 423-433. DOI:10.1007/BF02874262 |
Ge WC, Lin Q, Sun DY, Wu FY, Won C, Lee M, Jin M and Yun S. 1999. Geochemical characteristics of the Mesozoic basalts in Da Hinggan Ling: Evidence of the mantle-crust interaction. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(3): 396-407. |
Guo F, Fan WM, Wang YJ and Lin G. 2001. Petrogenesis of the late Mesozoic bimodal volcanic rocks in the southern Da Hinggan Mts, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(1): 161-168. |
Guo F, Fan WM, Wang YJ and Zhang M. 2004. Origin of Early Cretaceous calc-alkaline lamprophyres from the Sulu orogen in eastern China: Implications for enrichment processes beneath continental collisional belt. Lithos, 78(3): 291-305. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.05.001 |
Hou ZQ, Gao YF, Meng XJ, Qu XM and Huang W. 2004. Genesis of adakitc porphyry and tectonic controls on the Gangdese Miocene porphyry copper belt in the Tibetan orogen. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(2): 239-248. |
Li CZ. 1999. Metallogenic series of the Erguna polymetallic ore belt and its metallogenic conditions. Geological Exploration for Non-Ferrous Metals, 8(6): 329-332. |
Li JY, He ZJ, Mo SG and Sorokin AA. 2004. The age of conglomerates in the lower part of the Xiufeng Formation in the northern Da Hinggan Mountains, NE China, and their tectonic implications. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(2): 120-129. |
Li L, Sun FY, Li BL, Qian Y and Xu QL. 2015. Ore-forming fluid features and genesis of Shabaosi gold deposit in Mohe Country, Heilongjiang Province. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 40(7): 1163-1176. DOI:10.3799/dqkx.2015.097 |
Li XM. 2016. Geological characteristic and metallogenic prognosis of copper and gold deposit in Twenty-one Station, Tahe, Heilongjiang Province. Master Degree Thesis. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-56 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Li XW. 2012. Geologic characteristics and metallogenic tectonic environment of the Baoxinggou gold deposit in Tahe, Heilongjiang Province. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 42(6): 1700-1710. |
Li XW. 2015. Metallogenic regularities of gold deposits in upper Heilongjiang metallogenic belt and its prospecting. Ph. D. Dissertation. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-78 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Lin Q, Ge WC, Sun DY, Wu FY, Chong KW, Kyung DM, Myung SJ, Moon W, Chi SK and Sung HY. 1998. Tectonic significance of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in northeastern China. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 33(2): 129-139. |
Liu J, Wu G, Qiu HN, Gao DZ and Yang XS. 2013. 40Ar/39Ar dating of gold-bearing quartz vein from the Shabaosi gold deposit at the northern end of the Great Xing'an Range and its tectonic significance. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(10): 1570-1579. |
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Gao S, Günther D, Xu J, Gao CG and Chen HH. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34-43. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 |
Ludwig KR. 2003. User's manual for Isoplot 3.00: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 4: 1-70. |
Mao JW, Zhou ZH, Wu G, Jiang SH, Liu CL, Li HM, Ouyang HG and Liu J. 2013. Metallogenic regularity and minerogenetic series of ore deposits in Inner Mongolia and adjacent areas. Mineral Deposits, 32(4): 715-729. |
Martin H. 1999. Adakitic magmas: Modern analogues of Archaean granitoids. Lithos, 46(3): 411-429. DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00076-0 |
Martin H, Smithies RH, Rapp R. Moyen JF and Champion D. 2005. An overview of adakite, tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG), and sanukitoid: Relationships and some implications for crustal evolution. Lithos, 79(1-2): 1-24. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.04.048 |
Meng E, Xu WL, Yang DB, Qiu KF, Li CH and Zhu HT. 2011. Zircon U-Pb chronology, geochemistry of Mesozoic volcanic rocks from the Lingquan basin in Manzhouli area, and its tectonic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(4): 1209-1226. |
Meng QR. 2003. What drove Late Mesozoic extension of the northern China-Mongolia tract?. Tectonophysics, 369(3-4): 155-174. DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(03)00195-1 |
Middlemost EAK. 1985. Magmas and Magmatic Rocks: An Introduction to Igneous Petrology. London: Longman: 1-266. |
Ouyang HG, Mao JW, Santosh M, Zhou J, Zhou ZH, Wu Y and Hou L. 2013. Geodynamic setting of Mesozoic magmatism in ne china and surrounding regions: Perspectives from spatio-temporal distribution patterns of ore deposits. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 78: 222-236. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.07.011 |
Ouyang HG, Mao JW, Zhou ZH and Su HM. 2015. Late mesozoic metallogeny and intracontinental magmatism, southern great Xing'an range, northeastern China. Gondwana Research, 27(3): 1153-1172. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2014.08.010 |
Parfenov LM, Popeko LI and Tomurtogoo O. 2001. Problems of tectonics of the Mongol-Okhotsk orogenic belt. Geology of the Pacific Ocean, 16(5): 797-830. |
Pearce JA. 1996. Sources and Settings of granitic rocks. Episodes, 19(4): 120-125. |
Peccerillo R and Taylor SR. 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1): 63-81. DOI:10.1007/BF00384745 |
Petford N and Atherton M. 1996. Na-rich partial melts from newly underplated basaltic crust: The cordillera Blanca batholith, Peru. Journal of Petrology, 37(6): 1491-1521. DOI:10.1093/petrology/37.6.1491 |
Qi JP, Chen YJ and Pirajno F. 2005. Geological characteristics and tectonic setting of the epithermal deposits in the Northeast China. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 25(2): 47-59. |
Rapp RP and Watson EB. 1995. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8~32kbar: Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling. Journal of Petrology, 36(4): 891-931. DOI:10.1093/petrology/36.4.891 |
Richards JP and Kerrich R. 2007. Special paper: Adakite-like rocks: Their diverse origins and questionable role in metallogenesis. Economic Geology, 102(4): 537-576. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.102.4.537 |
Sengor AMC and Natal'in BA. 1996. Paleotectonics of Asia: Fragments of a synthesis. In: Yin A and Harrison TM (eds. ). The Tectonic Evolution of Asia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 486-640
|
Shao JA, Zang SX, Mu BL, Li XB and Wang B. 1995. Extension of orogenic belts and upwelling of asthenosphere: The example of Hinggan-Mongolian orogenic belt. Chinese Science Bulletin, 40(1): 50-56. |
Shao JA, Zhang FQ and Mu BL. 1998. Tectono-thermal evolution of middle-south section of the Da Hinggan Mountains. Science in China (Series D), 41(6): 570-579. DOI:10.1007/BF02878738 |
Smithies RH. 2000. The Archaean tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG) series is not an analogue of Cenozoic adakite. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 182(1): 115-125. DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00236-3 |
Stern CR and Kilian R. 1996. Role of the subducted slab, mantle wedge and continental crust in the generation of adakites from the Andean Austral volcanic zone. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 123(3): 263-281. DOI:10.1007/s004100050155 |
Streckeisen AL. 1976. Classification of the common igneous rocks by means of their chemical composition: A provisional attempt. Neues Jahrbuch fur Mineralogie, Monatshefte, 1: 1-15. |
Sun Q, Ren YS, Yang Q, Duan MX and Hao YJ. 2015. Ore genesis and metallogenic age of Luoguhe polymetallic deposit in Mohe area, Heilongjiang Province. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 35(3): 20-28. |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implication for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunder AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42: 313-345
|
Sun YF. 2015. Geological characteristics and metallogenesis of the Shiwuliqiao gold deposit in Tahe, Heilongjiang Province. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: Chinese University of Geosciences, 1-68 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Taylor SR and McLennan SM. 1985. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution. Oxford: Blackwell. |
Taylor SR and McLennan SM. 1995. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(2): 241-265. DOI:10.1029/95RG00262 |
Thiéblemont D, Stein G and Lescuyer JL. 1997. Gisements epithermaux et porphyriques: La connexion adakite. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences-Series ⅡA-Earth and Planetary Science, 325(2): 103-109. |
Wang F, Zhou XH, Zhang LC, Ying JF, Zhang YT, Wu FY and Zhu RX. 2006a. Late Mesozoic volcanism in the Great Xing'an Range (NE China): Timing and implications for the dynamic setting of NE Asia. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 251(1-2): 179-198. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.09.007 |
Wang KQ, Huang H, Wang ZH, Zhang Y, Song GB and Liu ZT. 2010. 39Ar-40Ar age of potassium feldspar of Hulin gold ore deposit and its geological significance in Erguna, Inner Mongolia. Mineral Deposits, 29(Suppl.1): 41-46. |
Wang PJ, Liu WZ, Wang SX and Song WH. 2002. 40Ar/39Ar and K/Ar dating on the volcanic rocks in the Songliao Basin, NE China: Constraints on stratigraphy and basin dynamics. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 91(2): 331-340. DOI:10.1007/s005310100219 |
Wang Q, Xu JF and Zhao ZH. 2001. The summary and comment on research on a new kind of igneous rock: Adakite. Advance in Earth Science, 16(2): 201-208. |
Wang Q, Xu JF, Zhao ZH, Xiong XL and Bao ZW. 2003a. Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Tongling area, Anhui Province, China and their constraint on geodynamic process. Science in China (Series D), 46(8): 801-815. DOI:10.1007/BF02879524 |
Wang Q, Zhao ZH, Xu JF, Li XH, Bao ZW, Xiong XL and Liu YM. 2003b. Petrogenesis and metallogenesis of the Yanshanian adakite-like rocks in the eastern Yangtze block. Science in China (Series D), 46(S1): 164-176. |
Wang Q, Zhao ZH, Bai ZH, Bao ZW, Xiong XL, Mei HJ, Xu JF and Wang YX. 2003c. Carboniferous adakites and Nb-enriched arc basaltic rocks association in the Alataw Mountains, North Xinjiang: Interactions between slab melt and mantle peridotite and implications for crustal growth. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(19): 2108-2115. DOI:10.1007/BF03037015 |
Wang Q, Zhao ZH, Xu JF, Bai ZH, Wang JX and Liu CX. 2004. The geochemical comparison between the Tongshankou and Yinzu adakitic intrusive rocks in southeastern Hubei: (Delaminated) lower crustal melting and the genesis of porphyry copper deposit. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(2): 351-360. |
Wang Q, Xu JF, Jian P, Bao ZW, Zhao ZH, Li CF, Xiong XL and Ma JL. 2006b. Petrogenesis of adakitic porphyries in an extensional tectonic setting, Dexing, South China: Implications for the genesis of porphyry copper mineralization. Journal of Petrology, 47(1): 119-144. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egi070 |
Wang Y and Zhang Q. 2001. A granitoid complex from Badaling area, North China: Composition, geochemical characteristics and its implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(4): 533-540. |
Wang ZL, Jin J and She HQ. 2012. The time-space distribution characteristics of porphyry deposits of northern Greater Hinggan Mountains. Advances in Earth Science, 27(Suppl.1): 277. |
Weaver BL. 1991. The origin of ocean island basalt end-member compositions: Trace element and isotopic constraints. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 104(2-4): 381-397. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(91)90217-6 |
Wu FY, Sun DY, Li HM, Jahn BM and Wilde S. 2002. A-type granites in northeastern China: Age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis. Chemical Geology, 187(1-2): 143-173. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00018-9 |
Wu G, Zhu Q and Zhao CS. 2002. Types and geological characteristics of gold-copper deposits in upper Heilongjiang depression, North Daxinganling. Mineral Deposits, 21(S1): 261-264. |
Wu G. 2006. Metallogenic setting and metallogenesis of nonferrous-precious metals in northern Da Hinggan Moutain. Ph. D. Dissertation. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-221 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Wu G, Sun FY, Zhu Q, Li ZT, Ding QF, Li GY, Pang QB and Wang HB. 2006. Geological characteristics and genesis of gold deposits in upper Heilongjiang basin. Mineral Deposits, 25(3): 215-230 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wu G, Chen YJ, Sun FY, Li JC, Li ZT and Wang XJ. 2008. Geochemistry of the Late Jurassic granitoids in the northern end area of Da Hinggan Mountains and their geological and prospecting implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(4): 899-910. |
Wu G, Chen YJ, Zhao ZH, Zhao TP, Li ZT and Zhang Z. 2009. Geochemistry, zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age and petrogenesis of the East Luoguhe granites at the northern end of the Great Hinggan Range. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(2): 233-247. |
Wu G, Chen YJ, Sun FY, Zhang Z, Liu AK and Li ZT. 2010. Geochemistry and genesis of the Late Jurassic granitoids at northern Great Hinggan Range: Implications for exploration. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(2): 321-332. DOI:10.1111/acgs.2010.84.issue-2 |
Wu G, Wang GR, Liu J, Zhou ZH, Li TG and Wu H. 2014. Metallogenic series and ore-forming pedigree of main ore deposits in northern Great Xing'an Range. Mineral Deposits, 33(6): 1127-1150. |
Xiao L, Rapp PR and Xu JF. 2004. The role of deep processes controls on variation of compositions of adakitic rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(2): 219-228. |
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Li RL and Bierlein FP. 2008. Geochemistry and Nd-Sr isotopic studies of Late Mesozoic granitoids in the southeastern Hubei Province, Middle-Lower Yangtze River belt, eastern China: Petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Lithos, 104(1-4): 216-230. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.12.008 |
Xie GQ, Li RL, Jiang GH, Zhao CS and Hou KJ. 2008. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic granitoids in southeastern Hubei Province and constrains on the timing of lithospheric thinning, Middle-Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River, eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8): 1703-1714. |
Xie GQ, Mao JW and Zhao HJ. 2011. Zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic intrusions in the Southeast Hubei Province, Middle-Lower Yangtze River Belt (MLYRB), East China. Lithos, 125(1-2): 693-710. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.04.001 |
Xiong XL, Zhao ZH, Bai ZH, Mei HJ, Xu JF and Wang Q. 2001. Origin of Awulale adakitic sodium-rich rocks in western Tianshan: Constraints for Nd and Sr isotopic compositions. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(4): 514-522. |
Xiong XL, Cai ZY, Niu HC, Chen YB, Wang Q, Zhao ZH and Wu JH. 2005. The Late Paleozoic adakites in eastern Tianshan area and their metallogenetic significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(3): 967-976. |
Xu GZ, Bian QT and Wang YF. 1998. Tectonic evolution and metallization of the Erguna orogenic belt. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 33(1): 84-92. |
Xu JF, Shinjo R, Defant MJ, Wang Q and Rapp RP. 2002. Origin of Mesozoic adakitc intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of East China: Partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust?. Geology, 30(12): 1111-1114. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<1111:OOMAIR>2.0.CO;2 |
Xu WL, Pei FP, Wang F, Meng E, Ji WQ, Yang DB and Wang W. 2013. Spatial-temporal relationships of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in NE China: Constraints on tectonic overprinting and transformations between multiple tectonic regimes. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 74: 167-193. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.003 |
Xu WL, Wang F, Pei FP, Meng E, Tang J, Xu MJ and Wang W. 2013. Mesozoic tectonic regimes and regional ore-forming background in NE China: Constraints from spatial and temporal variations of Mesozoic volcanic rock associations. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(2): 339-353. |
Ying JF, Zhou XH, Zhang LC, Wang F and Zhang YT. 2010. Geochronological and geochemical investigation of the Late Mesozoic volcanic rocks from the northern Great Xing'an Range and their tectonic implications. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 99(2): 357-378. DOI:10.1007/s00531-008-0395-z |
Yuan HL, Wu FY, Gao S, Liu XM, Xu P and Sun DY. 2003. Determination of U-Pb age and rare earth element concentrations of zircons from Cenozoic intrusions in northeastern China by laser ablation ICP-MS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(22): 2411-2421. |
Yuan HL, Gao S, Liu XM, Li HM, Günther D and Wu FY. 2004. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 28(3): 353-370. DOI:10.1111/ggr.2004.28.issue-3 |
Zeng JN and Xu JF. 2008. Adakite-like rocks and mineralization: Confusion and inquiry. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(6): 278-292. |
Zhang JF, Zhu Q, Wu G, Shao J, Zhu HC and Jin CZ. 2002. Binary determined classification of the gold deposits genetic type: Taking example of the gold deposits in northern Great Xing'anling. Gold Geology, 8(3): 27-32. |
Zhang JF, Li ZT and Jin CZ. 2004. Adakites in northeastern China and their mineralized implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(2): 361-368. |
Zhang JH, Ge WC, Wu FY, Wilde SA, Yang JH and Liu XM. 2008a. Large-scale Early Cretaceous volcanic events in the northern Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China. Lithos, 102(1-2): 138-157. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.08.011 |
Zhang JH. 2009. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 1-116 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zhang LC, Chen ZG, Zhou XH, Ying JF, Wang F and Zhang YT. 2007. Characteristics of deep sources and tectonic-magmatic evolution of the Early Cretaceous voleanics in Genhe area, Da-Hinggan Mountains: Constraints of Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic geochemistries. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(11): 2823-2835. |
Zhang LC, Zhou XH, Ying JF, Wang F, Guo F, Wan B and Chen ZG. 2008b. Geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes of Early Cretaceous basalts from the Great Xinggan Range, NE China: Implications for their origin and mantle source characteristics. Chemical Geology, 256(1-2): 12-23. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.07.004 |
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Qian Q, Yang JH, Wang YL, Zhao TP and Guo GJ. 2001a. The characteristics and tectonic-metallogenic significances of the adakites in Yanshan period from eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinice, 17(2): 236-244. |
Zhang Q, Qian Q, Wang EQ, Wang Y, Zhao TP, Hao J and Guo GJ. 2001b. An East China plateau in Mid-Late Yanshanian Period: Implication from adakites. Chinese Journal of Geology, 36(2): 248-225. |
Zhang Q, Wang YL, Zhang FQ, Wang Q and Wang Y. 2002. Adakite and porphyry copper deposit. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, (3): 85-90. |
Zhao XX, Coe RS, Zhou YX, Wu HR and Wang J. 1990. New paleomagnatic result from North and South China. In: Hillhouse JW (ed. ). Deep Structure and Past Kinematics of Accreted Terrances. American Geophysical Union, Geophysics. Monoger. IUGC, 5: 278-293
|
Zhao YM and Zhang DQ. 1997. Metallogeny and Prospective Evaluation of Copper-Polymetallic Deposits in the Da Hinggan Mountains and Its Adjacent Region. Beijing: Seismological Press: 8-156.
|
Zhao ZH, Wang Q, Xiong XL, Zhang HX, Niu HC, Xu JF, Bai ZH and Qiao YL. 2006. Two types of adakites in North Xinjiang, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5): 1249-1265. |
Zhao ZH, Xiong XL, Wang Q, Bai ZH and Qian YL. 2007. Underplating during Late Paleozoic in North Xinjiang: Evidence from shoshonitic series volcanic rocks and adakite. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(5): 606-619. |
Zonenshain LP, Kuzmin MI, Natapov LM and Page BM. 1990. Geology of the USSR: A Plate-tectonic Synthesis. Washington DC: AGU. |
Zorin YA. 1999. Geodynamics of the western part of the Mongolia-Okhotsk collisional belt, Trans-Baikal region (Russia) and Mongolia. Tectonophysics, 306(1): 33-56. DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00042-6 |
蔡宏明, 张宏飞, 徐旺春, 时章亮, 袁洪林. 2010. 松潘带印支期岩石圈拆沉作用新证据:来自火山岩岩石成因的研究. 中国科学(地球科学), 40(11): 1518-1532. |
柴璐, 朱群, 周永恒. 2013. 中俄蒙毗邻地区主要金属矿产分布特征. 地质与资源, 22(5): 397-402. |
陈志广, 张连昌, 周新华, 万博, 英基丰, 王菲. 2006. 满洲里新右旗火山岩剖面年代学和地球化学特征. 岩石学报, 22(12): 2971-2986. |
高山, 张本仁, 金振民, Kern H. 1999. 秦岭-大别造山带下地壳拆沉作用. 中国科学(D辑), 29(6): 532-541. |
葛文春, 林强, 孙德有, 吴福元, 元钟宽, 李文远, 陈明植, 尹成孝. 1999. 大兴安岭中生代玄武岩的地球化学特征:壳幔相互作用的证据. 岩石学报, 15(3): 396-407. |
郭锋, 范蔚茗, 王岳军, 林舸. 2001. 大兴安岭南段晚中生代双峰式火山作用. 岩石学报, 17(1): 161-168. |
黑龙江省地质矿产局. 1993. 黑龙江省区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-941.
|
侯增谦, 高永丰, 孟祥金, 曲晓明, 黄卫. 2004. 西藏冈底斯中新世斑岩铜矿带:埃达克质斑岩成因与构造控制. 岩石学报, 20(2): 239-248. |
李长珠. 1999. 额尔古纳成矿带金铜多金属矿成矿条件和成矿系列. 有色金属矿产与勘查, 8(6): 329-332. |
李锦轶, 和政军, 莫申国, Sorokin AA. 2004. 大兴安岭北部绣峰组下部砾岩的形成时代及其大地构造意义. 地质通报, 23(2): 120-129. |
李良, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 钱烨, 许庆林. 2015. 黑龙江省漠河县砂宝斯金矿床流体特征及矿床成因. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 40(7): 1163-1176. |
李孝敏. 2016. 黑龙江省塔河县二十一站河铜、金矿床地质特征及成矿预测. 硕士学位论文. 长春: 吉林大学, 1-56 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-1016089631.htm
|
李向文, 杨言辰, 王献忠, 刘智杰, 公维国. 2012. 黑龙江省塔河县宝兴沟金矿床地质特征及成矿构造环境. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 42(6): 1700-1710. |
李向文. 2015. 上黑龙江成矿带金矿床成矿规律与找矿预测研究. 博士学位论文. 长春: 吉林大学, 1-78 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-1015593148.htm
|
林强, 葛文春, 孙德有, 吴福元, 元钟宽, 闵庚德, 陈明植, 李文远, 权致纯, 尹成孝. 1998. 中国东北地区中生代火山岩的大地构造意义. 地质科学, 33(2): 129-139. |
刘军, 武广, 邱华宁, 高德柱, 杨鑫生. 2013. 大兴安岭北部砂宝斯金矿床含金石英脉40Ar/39Ar年龄及其构造意义. 地质学报, 87(10): 1570-1579. |
毛景文, 周振华, 武广, 江思宏, 刘成林, 李厚民, 欧阳荷根, 刘军. 2013. 内蒙古及邻区矿床成矿规律与成矿系列. 矿床地质, 32(4): 715-729. |
孟恩, 许文良, 杨德彬, 邱昆峰, 李长华, 祝洪涛. 2011. 满洲里地区灵泉盆地中生代火山岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 27(4): 1209-1226. |
祁进平, 陈衍景, Pirajno F. 2005. 东北地区浅成低温热液矿床的地质特征和构造背景. 矿物岩石, 25(2): 47-59. |
邵济安, 张履桥, 牟保磊. 1998. 大兴安岭中南段中生代的构造热演化. 中国科学(D辑), 28(3): 193-200. |
孙琦, 任云生, 杨群, 段明新, 郝宇杰. 2015. 黑龙江省漠河县洛古河多金属矿床成因与成矿时代. 矿物岩石, 35(3): 20-28. |
孙彦峰. 2015. 黑龙江省塔河县十五里桥金矿床地质特征及矿床成因探讨. 硕士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-68 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1015391377.htm
|
王科强, 黄辉, 王治华, 张勇, 宋贵斌, 刘忠田. 2010. 内蒙古额尔古纳虎拉林金矿床钾长石39Ar-40Ar年龄及其意义. 矿床地质, 29(增1): 41-46. |
王强, 许继锋, 赵振华. 2001. 一种新的火成岩——埃达克岩的研究综述. 地球科学进展, 16(2): 201-208. |
王强, 赵振华, 许继峰, 白正华, 王建新, 刘成新. 2004. 鄂东南铜山口、殷祖埃达克质(adakitic)侵入岩的地球化学特征对比: (拆沉)下地壳熔融与斑岩铜矿的成因. 岩石学报, 20(2): 351-360. |
王焰, 张旗. 2001. 八达岭花岗杂岩的组成、地球化学特征及其意义. 岩石学报, 17(4): 533-540. |
王召林, 金浚, 佘宏全. 2012. 大兴安岭北段斑岩型矿床的时空分布特征. 地球科学进展, 27(增1): 277. |
武广, 朱群, 赵财胜. 2002. 大兴安岭北部上黑龙江拗陷区金铜矿床类型及地质特征. 矿床地质, 21(S1): 261-264. |
武广. 2006. 大兴安岭北部区域成矿背景与有色、贵金属矿床成矿作用. 博士学位论文. 长春: 吉林大学, 1-221 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-2006094308.htm
|
武广, 孙丰月, 朱群, 李之彤, 丁清峰, 李广远, 庞庆帮, 王宏博. 2006. 上黑龙江盆地金矿床地质特征及成因探讨. 矿床地质, 25(3): 215-230. |
武广, 陈衍景, 孙丰月, 李景春, 李之彤, 王希今. 2008. 大兴安岭北端晚侏罗世花岗岩类地球化学及其地质和找矿意义. 岩石学报, 24(4): 899-910. |
武广, 陈衍景, 赵振华, 赵太平, 李之彤, 张哲. 2009. 大兴安岭北端洛古河东花岗岩的地球化学、SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石成因. 岩石学报, 25(2): 233-247. |
武广, 王国瑞, 刘军, 周振华, 李铁刚, 吴昊. 2014. 大兴安岭北部主要金属矿床成矿系列和区域矿床成矿谱系. 矿床地质, 33(6): 1127-1150. |
肖龙, Rapp PR, 许继峰. 2004. 深部过程对埃达克质岩石成分的制约. 岩石学报, 20(2): 219-228. |
谢桂青, 李瑞玲, 蒋国豪, 赵财胜, 侯可军. 2008. 鄂东南地区晚中生代侵入岩的地球化学和成因及对岩石圈减薄时限的制约. 岩石学报, 24(8): 1703-1714. |
熊小林, 赵振华, 白正华, 梅厚钧, 许继峰, 王强. 2001. 西天山阿吾拉勒埃达克质岩石成因: Nd和Sr同位素组成的限制. 岩石学报, 17(4): 514-522. |
熊小林, 蔡志勇, 牛贺才, 陈义兵, 王强, 赵振华, 吴金花. 2005. 东天山晚古生代埃达克岩成因及铜金成矿意义. 岩石学报, 21(3): 967-976. |
徐贵忠, 边千韬, 王艺芬. 1998. 额尔古纳造山带构造演化与成矿作用. 地质科学, 33(1): 84-92. |
许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 孟恩, 唐杰, 徐美君, 王伟. 2013. 中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约. 岩石学报, 29(2): 339-353. |
袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 柳小明, 徐平, 孙德有. 2003. 东北地区新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析. 科学通报, 48(14): 1511-1520. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.14.008 |
曾键年, 许继峰. 2008. 埃达克质岩与成矿:困惑与探索. 地学前缘, 15(6): 278-292. |
张炯飞, 朱群, 武广, 邵军, 祝洪臣, 金成洙. 2002. 金矿成因类型的二重限定性分类——以大兴安岭北部金矿为例. 黄金地质, 8(3): 27-32. |
张炯飞, 李之彤, 金成洙. 2004. 中国东北部地区埃达克岩及其成矿意义. 岩石学报, 20(2): 361-368. |
张吉衡. 2009. 大兴安岭中生代火山岩年代学及地球化学研究. 博士学位论文. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 1-116 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-2009153771.htm
|
张连昌, 陈志广, 周新华, 英基丰, 王非, 张玉涛. 2007. 大兴安岭根河地区早白垩世火山岩深部源区与构造-岩浆演化: Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf同位素地球化学制约. 岩石学报, 23(11): 2823-2835. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.013 |
张旗, 钱青, 王二七, 王焰, 赵太平, 郝杰, 郭光军. 2001a. 燕山中晚期的中国东部高原:埃达克岩的启示. 地质科学, 36(2): 248-255. |
张旗, 王焰, 钱青, 杨进辉, 王元龙, 赵太平, 郭光军. 2001b. 中国东部燕山期埃达克岩的特征及其构造-成矿意义. 岩石学报, 17(2): 236-244. |
张旗, 王元龙, 张福勤, 王强, 王焰. 2002. 埃达克岩与斑岩铜矿. 华南地质与矿产, (3): 85-90. |
赵一鸣, 张德全. 1997. 大兴安岭及其邻区铜多金属矿床成矿规律与远景评价. 北京: 地震出版社: 8-156.
|
赵振华, 王强, 熊小林, 张海洋, 牛贺才, 许继峰, 白正华, 乔玉楼. 2006. 新疆北部的两类埃达克岩. 岩石学报, 22(5): 1249-1265. |
赵振华, 熊小林, 王强, 白正华, 乔玉楼. 2007. 新疆北部晚古生代的底侵作用——来自橄榄玄粗岩与埃达克岩的证据. 地质学报, 81(5): 606-619. |
 2018, Vol. 34
2018, Vol. 34


