苏鲁超高压变质带是当今世界上典型的陆-陆碰撞造山带。目前大多数学者普遍认为,呈北东-南西向展布的烟台-青岛-五莲断裂为苏鲁超高压变质带与华北板块的界线(Tang et al., 2007, 2008b; Zhang et al., 2014),沿该断裂带的东南侧为北苏鲁超高压变质地体,西北侧为华北板块东南缘的胶北地体。多年来的研究表明,苏鲁超高压变质地体是中-晚三叠世扬子板块向华北板块之下发生单向深俯冲-折返的产物(Cong, 1996; Liou et al., 1996, 2000, 2009; Hacker et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2000; Zheng et al., 2005)。锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和同位素综合研究结果表明,该超高压变质带主要由新元古代(850~750Ma)的花岗质片麻岩、表壳岩夹榴辉岩、超基性岩透镜体组成(Ames et al., 1996; Cong, 1996; Liou et al., 1996, 2000; Hacker et al., 1998),其主体原岩与扬子板块北缘的新元古代岩浆岩具有亲缘性(Zheng et al., 2003, 2004, 2006, 2009; Tang et al., 2008a)。以粒间柯石英和锆石中柯石英包体为代表的大量超高压矿物的发现,表明榴辉岩及其围岩组成的巨量陆壳物质普遍经历了深俯冲和超高压变质作用(Liou et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2009; Liu and Liou, 2011),超高压变质时代为中-晚三叠世(240~220Ma)(Liu et al., 2004a, b, 2005, 2006; 刘福来和薛怀民, 2007; Liu and Liou, 2011; 刘福来等, 2011)。而位于断裂带西北侧的胶北地体,是华北板块东部胶-辽-吉古元古构造带的一部分,以出露太古宙-古元古代的TTG-花岗质片麻岩、表壳岩和变基性岩等早前寒武纪变质基底为特征(Wan et al., 2006; Jahn et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2013a; Wang et al., 2014),它们普遍经历了古元古代(1950~1850Ma)麻粒岩相变质事件的改造(刘平华等, 2010; 王舫等, 2010; Tam et al., 2012a, b, c; Liu et al., 2013b, 2017b)。
随着研究工作的不断深入,部分研究者在苏鲁超高压变质带的内部及边部发现一些非超高压变质的新太古代-古元古代岩石(Liou et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2006, 2014; Tang et al., 2008b; Zhou et al., 2008a; Xiang et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2017a),有些记录了古元古代(1900~1800Ma)的变质事件(Liou et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2006; Xiang et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2017a)。然而,有关它们的原岩性质及构造属性,还存在较大争议。一种观点认为,它们是来自扬子板块的陆壳物质(Tang et al., 2008b; Xiang et al., 2014);另一种观点则认为它们与华北板块具有亲缘性(Liou et al., 2006; Zhou et al., 2008a; Zhang et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2017a)。其中,以海阳所变质杂岩为代表的非超高压变质地体,主要由TTG-花岗质片麻岩、表壳岩和变基性岩组成,其新太古代-古元古代的原岩时代及古元古代的麻粒岩相变质作用(Liou et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2006; 刘利双等, 2015; Liu et al., 2017a),明显区别于苏鲁超高压变质带,而与胶北地体具有相似性(Liu et al., 2017a)。刘利双等(2015)和Liu et al.(2017a)研究认为海阳所变质杂岩是来自于华北板块东南缘的变质基底。此外,超高压变质的榴辉岩和非超高压变质的高压基性麻粒岩在威海-午极一带均有出露,其中后者与海阳所地区变基性岩具有可比性,均记录了古元古代(1900~1800Ma)的中-高压麻粒岩相变质事件(刘利双等, 2015, 2017; Liu et al., 2017a)。由此可见,苏鲁超高压变质带内不仅发育来自扬子板块的新元古代变质基底,又出露与华北板块具有亲缘性的变质基性岩残片(刘利双等, 2017)。
然而,目前有关苏鲁超高压变质带内部是否广泛发育具有华北板块属性的变质岩系、其岩石组合类型和空间展布规律等问题,尚缺乏深入的研究。本文在以往工作基础上,以苏鲁超高压变质带内的变花岗质岩石为重点研究对象,开展深入的岩石学、锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学的综合研究,查明变花岗质岩石成因类型的多样性,限定它们的原岩性质、年代格架及构造属性,为进一步探讨华北板块与扬子板块之间的三叠纪陆-陆俯冲-折返动力学背景提供制约。
1 地质背景苏鲁-大别造山带在三叠纪时期形成后,经北北东向郯庐断裂发生“左”行走滑,其东段向北东方向错断约500km,形成北东-南西向展布的苏鲁高压-超高压变质带。其中北苏鲁超高压变质带西北缘以烟台-青岛-五莲断裂为界与华北板块东南缘的胶北地体相邻,东南缘毗邻黄海(图 1)。

|
图 1 北苏鲁超高压带和胶北地体地质简图及样品位置 Fig. 1 Simplified geological map of the North Sulu UHP belt and Jiaobei terrane with sample locations |
北苏鲁超高压变质带的主体为花岗质片麻岩,夹有表壳岩和变镁铁-超镁铁质岩石薄层或透镜体(Cong and Wang, 1999; Zheng et al., 2003; Liu and Liou, 2011)。花岗质片麻岩的原岩主要为A型花岗岩;表壳岩主要包括绿帘黑云(二云)斜长(二长)片麻岩、大理岩等;变镁铁-超镁铁质岩石以榴辉岩为代表,呈无根的透镜体、脉状和似层状产于片麻岩中,长轴方向与区域片麻理总体方向一致。这些大面积出露的花岗质片麻岩及大多数围岩,包括表壳岩、变镁铁-超镁铁质岩石的原岩物质均形成于新元古代(850~750Ma)(Ames et al., 1996; Hacker et al., 1998; Zheng et al., 2003, 2004, 2007; Liu et al., 2004a, b; 许志琴等, 2006; Tang et al., 2008a)。花岗质片麻岩与榴辉岩的原岩物质共同反映了与罗迪尼亚超大陆裂解存在密切成因关系的双峰式岩浆活动(Zheng et al., 2003, 2004, 2006, 2009; Tang et al., 2008a)。前人在榴辉岩、花岗质片麻岩、副片麻岩、大理岩和超基性岩中,识别出大量以柯石英、金刚石等为代表的超高压矿物(Ye et al., 2000a; Liu and Liou, 2011),表明榴辉岩及其围岩组成的巨量陆壳物质普遍发生了超高压变质作用,其变质演化P-T-t轨迹具有近等温减压的顺时针型式(Liou et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2009; Liu and Liou, 2011),变质演化可划分为四个阶段:高压石英榴辉岩相进变质阶段、峰期超高压柯石英/金刚石榴辉岩相变质阶段、峰后石英榴辉岩-麻粒岩相退变质阶段和晚期角闪岩相退变质阶段,其变质温压条件分别为570~690℃、17~21kbar,750~850℃、34~40kbar,600~750℃、12~24kbar和550~650℃、7~10.5kbar(Zhang et al., 1995, 2005, 2009; Liu and Liou, 2011)。大量锆石同位素年代学和矿物包体的综合研究,厘定其超高压变质的时代为中三叠世(240~225Ma),角闪岩相退变质时代为晚三叠世(220~200Ma),分别代表大陆板块发生深俯冲和快速折返的时代(Liu et al., 2004a, b, 2005, 2006; 刘福来和薛怀民, 2007; Liu and Liou, 2011; 刘福来等, 2011)。综合岩石学、矿物学、地球化学和同位素年代学等大量资料,前人建立了三叠纪时期扬子板块向华北板块发生单向深俯冲-折返的构造演化模式(Liou et al., 2000, 2009; Zhang et al., 2000)。
胶北地体位于胶-辽-吉古元古构造带的西南端,是华北板块的一部分,且记录了多期岩浆-变质事件。它主要由TTG-花岗质片麻岩、以荆山群和粉子山群为代表的表壳岩和以基性麻粒岩为代表的变镁铁-超镁铁质岩石组成(Jahn et al., 2008; Tam et al., 2011, 2012a, b, c; Liu et al., 2013a; Wang et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2014)。其中,花岗质片麻岩的原岩包括A型、碱性、钙碱性及斑状花岗岩等多种成因类型,其形成时代为太古宙-古元古代(~2900Ma、~2700Ma、~2500Ma和~1900Ma)(Jahn et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2013a; Wang et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2014)。部分古元古代花岗质岩石具有太古宙陆壳重熔的岩石地球化学和同位素特征(Liu et al., 2014)。区内基性岩的原岩形成时代为2550~2500Ma、2300~2000Ma和1950~1800Ma(刘平华等, 2015),变基性岩和变泥质岩石均记录了古元古代(1950~1850Ma)麻粒岩相变质事件(Zhou et al., 2008b; Tam et al., 2011; 刘平华等, 2011; Liu et al., 2017c),并伴随广泛的深熔作用(刘福来等, 2015)。其变质演化P-T-t轨迹具有近等温减压至近等压冷却的顺时针型式(刘平华等, 2010; 王舫等, 2010; Tam et al., 2012a, b, c; Liu et al., 2013b),表明胶-辽-吉构造带是一条古元古代碰撞造山带(Zhao et al., 2012)。
2 野外产状及样品特征变花岗质岩石是北苏鲁超高压变质带的主体,本文采样点主要位于乳山-威海一带(图 1、图 2),代表性样品的野外露头和显微结构照片分别见图 3和图 4。据目前的年代学和地球化学研究,威海地区的变花岗质岩石成因类型较单一,而乳山市午极-海阳所地区的变花岗质岩石类型相对复杂。野外产状及样品特征分别简述如下。
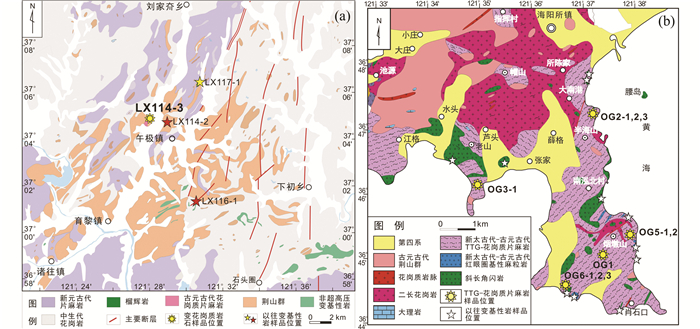
|
图 2 午极和海阳所地区地质简图及样品位置 Fig. 2 Simplified geological map of Wuji and Haiyangsuo areas with sample locations |
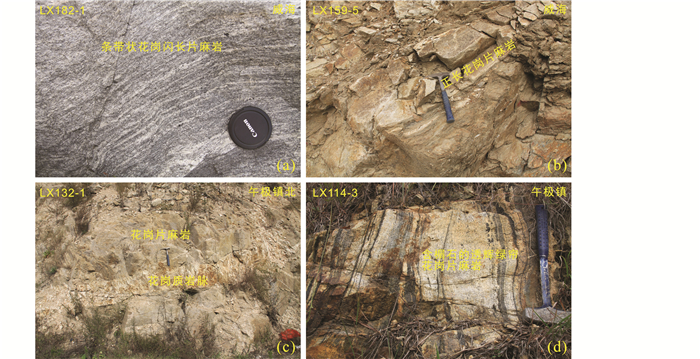
|
图 3 变花岗质岩石的野外露头照片 Fig. 3 Outcrop photographs of meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP belt |
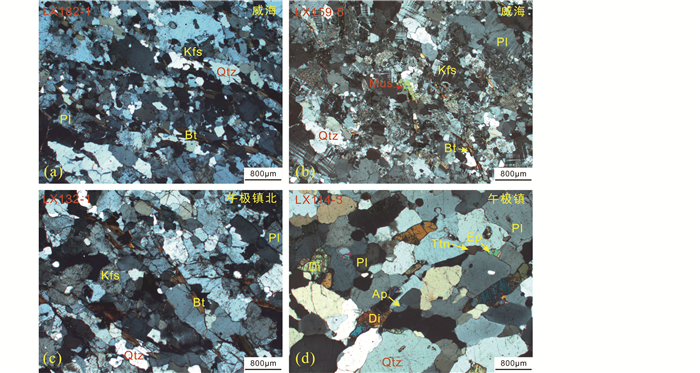
|
图 4 变花岗质岩石的显微结构照片 (a)条带状花岗闪长片麻岩LX182-1,主要由斜长石(Pl)+石英(Qtz)+黑云母(Bt)+钾长石(Kfs)组成;(b)正长花岗片麻岩LX159-5,主要由微斜长石+石英+斜长石+黑云母+白云母(Mus)等组成,可见钾长石和石英的不规则溶蚀边;(c)花岗片麻岩LX132-1,主要由钾长石+石英+黑云母+斜长石组成;(d)含榍石的透辉绿帘花岗片麻岩LX114-3,主要由石英+斜长石+透辉石(Di)+绿帘石(Ep)等组成,含少量榍石(Ttn)、磷灰石(Ap)和电气石 Fig. 4 Microphotographs of meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP belt (a) banded grandioritic gneiss, mainly composed of plagioclase+quartz+biotite+K-feldspar; (b) syenogranitic gneiss, mainly composed of microcline+quartz+biotite+muscovite; (c) granitic gneiss, mainly composed of K-feldspar+quartz+biotite+ plagioclase; (d) titanite-bearing diopside-epidote-granitic gneiss, mainly composed of quartz+plagioclase+diopside+epidote, with minor titanite, apatite and tourmaline |
威海地区出露灰色的条带状花岗闪长片麻岩和黄白色的正长花岗片麻岩,呈花岗变晶结构,片麻状-弱片麻状构造(图 3a, b)。前者肉眼可见暗色矿物定向排列,主要由钾长石、石英、斜长石和少量的黑云母组成(图 4a);后者主要由微斜长石、石英、斜长石和少量的黑云母、白云母组成(图 4b)。
此外,乳山午极地区出露新元古代和古元古代的花岗质片麻岩、古元古代的荆山群变沉积岩系,它们在空间上紧密伴生(图 2a)。午极镇北(高陵镇南)出露的黄白色花岗片麻岩(被晚期的花岗伟晶岩脉切穿(图 1、图 3c),主要由钾长石、石英和黑云母组成,暗色矿物定向排列(图 4c)。在午极镇出露的大量荆山群变沉积岩系附近,见有含榍石透辉绿帘花岗片麻岩(图 1、图 2a、图 3d),呈粒状变晶结构,主要由石英、斜长石、透辉石和绿帘石组成,次要矿物有黑云母、白云母、电气石、角闪石等,副矿物含榍石(图 4d)。
海阳所地区广泛出露新太古代-早古元古代(2700~2400Ma)的TTG-花岗质片麻岩,与之相伴生的有古元古代(2100~1900Ma)荆山群变沉积岩系,以及少量新太古代-古元古代的高压基性麻粒岩和斜长角闪岩透镜体(图 2b),它们共同发生了强烈的糜棱岩化作用(Liu et al., 2017a)。其中TTG-花岗质片麻岩呈灰白色,粒状变晶结构,片麻状构造,主要矿物包括斜长石、石英和钾长石,次要矿物为黑云母、白云母、角闪石,副矿物有钛铁矿和磁铁矿(Liu et al., 2017a)。
3 实验方法 3.1 锆石U-Pb定年锆石分选在河北省廊坊市区域地质调查研究院进行。首先将每件样品破碎至适当粒级,经清洗、烘干和筛选,采用磁选和重液分选法,分选出不同粒级的锆石晶体,然后在双目镜下挑选出颗粒较好的锆石晶体制靶。阴极发光(CL)图像拍摄在北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成,采用的扫描电镜为日本电子的JSM-6510.cl,探头为gatan mini cl,操作电压为10kV。LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年在北京科荟测试技术有限公司完成,采用的激光剥蚀系统为ESI NWR 193nm,激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子质谱是Analytikjena PlasmaQuant MS Elite ICP-MS。激光剥蚀过程中采用氦气作为载气、氩气作为补偿气以调节灵敏度,二者在进入ICP之前通过一个Y型接头混合。每个时间分辨分析数据包括15~20s的空白信号和45s的样品信号。对分析数据的离线处理(包括对样品和空白信号的选择、仪器灵敏度漂移校正、元素含量及U-Th-Pb同位素比值和年龄计算)采用软件ICPMSDataCal(侯可军等, 2009; Liu et al., 2010b)完成,锆石U-Pb年龄处理采用Isoplot程序(Ludwing, 2003)。锆石微量元素含量利用SRM610作为外标、Si作内标的方法进行定量计算(Liu et al., 2010b)。玻璃中元素含量的推荐值据GeoReM数据库(http://georem.mpch-mainz.gwdg.de/)。U-Pb定年采用锆石标准GJ-1作外标进行同位素分流校正,每分析5~10个样品点,分析2次GJ-1。对于与分析时间有关的U-Th-Pb同位素比值漂移,利用GJ-1的变化采用线性内插的方式进行校正(Liu et al., 2010b)。
3.2 全岩地球化学全岩地球化学样品的粉末(200目)制备在河北省区域地质矿产调查研究所完成,主量和微量元素化学成分测试在国家地质实验测试中心完成。主量元素测试采用X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF,型号PW4400),执行GB/T 14506.28—2010标准,检测项目包括Al2O3、CaO、Fe2O3、K2O、MgO、MnO、Na2O、P2O5、SiO2、TiO2等10项;稀土和微量元素采用PE300D型电感耦合等离子质谱仪(ICP-MS)完成测试,执行DZ/T 14506.30—20010标准;H2O+按GB/T 14506.2—2010标准;CO2按GB 9835—1988标准;LOI按LY/T 1253—1999标准;FeO按GB/T 14506.14—2010标准。
4 实验结果 4.1 锆石U-Pb年代学 4.1.1 锆石阴极发光(CL)图像特征威海地区条带状花岗闪长片麻岩LX182-1的锆石呈板柱状,长、宽分别为150~300μm、70~150μm,含较多的磷灰石和斜长石等矿物包体。根据CL图像可将锆石分为两类(图 5a):第一类具有明显的核边结构,核部呈灰-灰白色,发育清晰的岩浆振荡环带,边部较窄,呈浅灰白色,发光性均匀,为变质锆石特征;第二类锆石不发育核边结构,发光性较均匀,呈浅灰-灰白色,与第一类锆石边具有相同的结构特征。
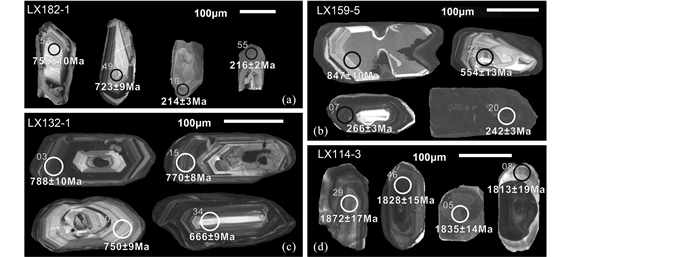
|
图 5 变花岗质岩石中的锆石阴极发光图像及U-Pb定年结果 (a)花岗闪长片麻岩LX182-1中岩浆锆石核和发光性均匀的变质锆石(边);(b)正长花岗片麻岩LX159-5中岩浆锆石核和深熔锆石(边);(c)花岗片麻岩LX132-1中岩浆锆石;(d)含榍石的透辉绿帘花岗片麻岩LX114-3中岩浆锆石核和发光性均匀的变质锆石(边) Fig. 5 Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of the zircons from meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP belt (a) inherited magmatic zircon cores with oscillatory zoning and metamorphic zircon (rim) with homogeneous gray-luminescent imaging, in sample LX182-1; (b) inherited magmatic zircon core with oscillatory zoning and anatexis zircon (rim) with weak oscillatory zoning and dark-luminescent imaging, in sample LX195-5; (c) magmatic zircon with clear oscillatory zoning, in sample LX132-1; (d) inherited magmatic zircon (core) with weak oscillatory zoning and metamorphic zircon (rim) with homogeneous gray-luminescent imaging, in sample LX114-3 |
威海地区正长花岗片麻岩LX159-5的锆石呈长柱状或短柱状,长100~300μm,宽60~150μm,不含或含少量长石和石英包体。根据CL图像可将锆石分为三类(图 5b):第一类具有明显核边结构,核部发光性较强,发育岩浆环带,为典型岩浆锆石,边部较窄,发光性较弱,呈灰黑-深黑色,发育微弱的振荡环带,为深熔锆石特征;第二类保存岩浆振荡环带,但发光性较弱,呈灰黑色,可能是岩浆锆石被后期流体改造的结果;第三类锆石特征与第一类锆石的边部特征相似。
乳山地区花岗片麻岩LX132-1的锆石呈柱状,长100~270μm,宽50~100μm,含少量长石包体。CL图像显示该样品的锆石呈灰-灰白色,发育明显的岩浆振荡环带,均为岩浆锆石(图 5c)。
含榍石的透辉绿帘花岗片麻岩LX114-3的锆石呈半自形柱状或椭圆状,长80~200μm,宽50~120μm。根据CL图像可将锆石分为两类(图 5d):第一类锆石基本不发育增生边,具有较暗的发光性和岩浆(振荡)环带,为岩浆锆石;第二类锆石呈单独的颗粒或发育在第一类锆石边部,呈灰-灰白色,发光性均匀,具有变质锆石的特征。
4.1.2 锆石微量元素及U-Pb年代学LX182-1中42颗锆石微区记录的U-Pb年龄可分为二组(见电子版附表 1)。第一组38颗继承性锆石(核)具有相对较高的Th(20×10-6~396×10-6)、U(42×10-6~529×10-6)含量和较高的Th/U比值(0.36~0.79),显示富集重稀土(HREE)、显著的负Eu异常和正Ce异常(图 6a和电子版附表 2),为典型岩浆锆石,记录的206Pb/238U表面年龄为778±10Ma~584±10Ma,不一致线上交点年龄为811±25Ma(MSWD=2.8),谐和线附近9颗岩浆锆石加权平均年龄为762±6Ma(MSWD=1.18),而其余锆石普遍位于不一致线下方(图 6b),表明这些岩浆锆石受到后期变质热事件改造而普遍发生Pb丢失,其不一致线上交点偏老,加权平均值~762Ma更接近该样品的原岩结晶年龄。第二组4颗发光性均匀的锆石(边)具有相对较低的Th(< 1×10-6)、U(53×10-6~154×10-6)含量和Th/U比值(接近0.01),并显示与岩浆锆石相当或略低的HREE和较低的中稀土(MREE),且无Eu异常(图 6a和附表 2),记录的206Pb/238U表面年龄为219±4Ma~213±3Ma,加权平均年龄为215±3Ma(MSWD=0.46)(图 6b和附表 1),应代表该样品的变质时代。

|
图 6 变花岗质岩石中锆石的球粒陨石标准化稀土配分曲线(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)和U-Pb年龄谐和图 Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) and U-Pb concordia plots of the zircons from meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP belt |
|
|
附表 1 变花岗质岩石的锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Appendix Table 1 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages of zircons fome representative meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP belt |
|
|
附表 2 变花岗质岩石中锆石稀土元素含量(×10-6) Appendix Table 2 Rare earth element compositions (×10-6) of zircons from representative meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP balt |
LX159-5中23颗锆石微区记录的U-Pb年龄可分为2组(附表 1)。第一组10颗锆石(核)的Th、U含量和Th/U比值分别为59×10-6~396×10-6、80×10-6~1173×10-6、0.10~0.94,具有富集HREE、显著的负Eu异常和正Ce异常特征(图 6c和附表 2),是典型的岩浆锆石,记录的206Pb/238U表面年龄变化于847±10Ma~255±3Ma之间,谐和线附近5颗岩浆锆石加权平均年龄为824±25Ma(MSWD=2.5),不一致线上交点年龄为749±35Ma(MSWD=5)(图 6d)。由图 6d可以看出,谐和线附近5颗锆石位于谐和曲线上方,不一致线由于受到岩浆锆石或后期变质锆石的影响而在作图过程中向上偏移,因此该样品的原岩形成时代不能单一地使用最老的加权平均年龄或不一致线上交点年龄,而应限定在824~749Ma之间。第二组11颗保留岩浆环带的锆石发光性比第一组锆石弱,具有较高的Th(63×10-6~1899×10-6)和U(533×10-6~4209×10-6)含量,Th/U比值变化大(0.02~0.80),其稀土元素仍保留岩浆锆石的特征(图 6c),记录的206Pb/238U表面年龄为282±4Ma~242±3Ma,这可能与变质过程中锆石U-Pb体系受到不同程度的影响有关;第三组2颗锆石具有高Th(87×10-6~1230×10-6)、U(754×10-6~3282×10-6)含量、低Th/U比值(0.11~0.37)、陡峭的REE配分型式和显著的负Eu异常(图 6c和附表 2),其结构特征与Th、U组成具有深熔锆石的特征(Hoskin and Schaltegger, 2003),记录的206Pb/238U年龄222±3Ma~217±2Ma,加权平均年龄为219±31Ma(图 6d),应代表该样品发生深熔作用的时代。
LX132-1中32颗锆石微区具有中等的Th(46×10-6~740×10-6)、U(51×10-6~710×10-6)含量和较高的Th/U比值(0.59~2.39)(附表 1),显示富集HREE、显著的负Eu异常和正Ce异常特征(图 6e和附表 2),均为岩浆锆石,记录的206Pb/238U表面年龄为792±9Ma~579±7Ma,谐和线附近12颗岩浆锆石加权平均年龄为770±8Ma(MSWD=2.0),与不一致线上交点年龄782±16Ma(MSWD=1.5)接近(图 6f),应代表其原岩岩浆侵位的时代。
LX114-3中48颗锆石微区记录的U-Pb年龄可分为二组(附表 1)。第一组17颗锆石(核)的Th、U含量和Th/U比值分别为51×10-6~336×10-6、125×10-6~849×10-6、0.20~0.65,显示富集HREE、显著的负Eu异常和正Ce异常特征(图 6g和附表 2),为岩浆锆石,但其稀土总量(195.7×10-6~731.7×10-6)低于上述3件样品的岩浆锆石(255×10-6~2787×10-6)(图 6g),且记录的207Pb/206Pb表面年龄为1880±17Ma~1825 ±15Ma,不一致线上交点年龄为1868±24Ma(MSWD=0.61),在误差范围内与加权平均年龄1847±7Ma(MSWD=1.3)接近(图 6h、附表 1)。第二组31颗变质锆石(边)Th、U含量和Th/U比值较第一组锆石稍有降低,分别为27×10-6~432×10-6、172×10-6~1564×10-6、0.03~0.61,一些测试点显示与继承性岩浆锆石不一致的稀土特征(图 6g),记录的207Pb/206Pb表面年龄为1876±19Ma~1813±19Ma,其中谐和线附近11颗锆石的加权平均年龄为1864±7Ma(MSWD=0.21),与不一致线上交点年龄1873±17Ma(MSWD=0.56)一致(图 6h),应代表该样品晚古元古代的变质时代。
4.2 全岩地球化学本文对威海-荣成-午极地区23件新元古代、海阳所地区1件~2700Ma(OG1-1)、3件2550~2500Ma(OG2-1、OG2-2和OG2-3)、9件~ 2400Ma(OG5-1、OG5-2、OG6-1、OG6-2和OG6-3等)和午极地区1件~1870Ma(LX114-3)的变花岗质岩石开展全岩主量、稀土和微量元素地球化学分析(部分年代结果参考Liu et al., 2017a),代表性样品的分析结果分别列于表 1和表 2。
|
|
表 1 新元古代花岗质片麻岩的主量(wt%)、微量和稀土(×10-6)元素含量 Table 1 Major element (wt%), trace and rare earth element (×10-6) compositions of representative Neoproterozoic granitic gneiss samples in the North Sulu UHP belt |
|
|
表 2 新太古代-古元古代TTG-花岗质片麻岩的主量(wt%)、微量和稀土(×10-6)元素含量 Table 2 Major element (wt%), trace and rare earth element (×10-6) compositions of representative Neoarchean to Paleoproterozoic TTG-granitic gneiss samples in the North Sulu UHP belt |
新元古代变花岗质岩石的SiO2、Al2O3含量分别为69.01%~77.13%和12.48%~16.65%,Na2O、K2O和全碱(Na2O+K2O)含量分别为3.08%~4.68%、2.97%~6.03%和7.10%~9.15%,Na2O、K2O与SiO2相关性不明显(图 7a, b),CaO含量为0.52%~2.22%(表 1)。MgO、FeO、TiO2、MnO及P2O5含量很低,分别介于0.14%~0.90%、0.13%~1.56%、0.09%~0.40%、0.01%~0.06%、0.03%~0.13%之间。主量元素Al2O3、MgO、FeOT、TiO2、CaO、P2O5与SiO2具有明显的负相关性,表明这些花岗质片麻岩可能是同源岩浆不断演化的产物(图 7c-h)。在SiO2-K2O分类图上(图 7h)(据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976; Middlemost, 1985),大部分样品落入高钾钙碱性系列区域。
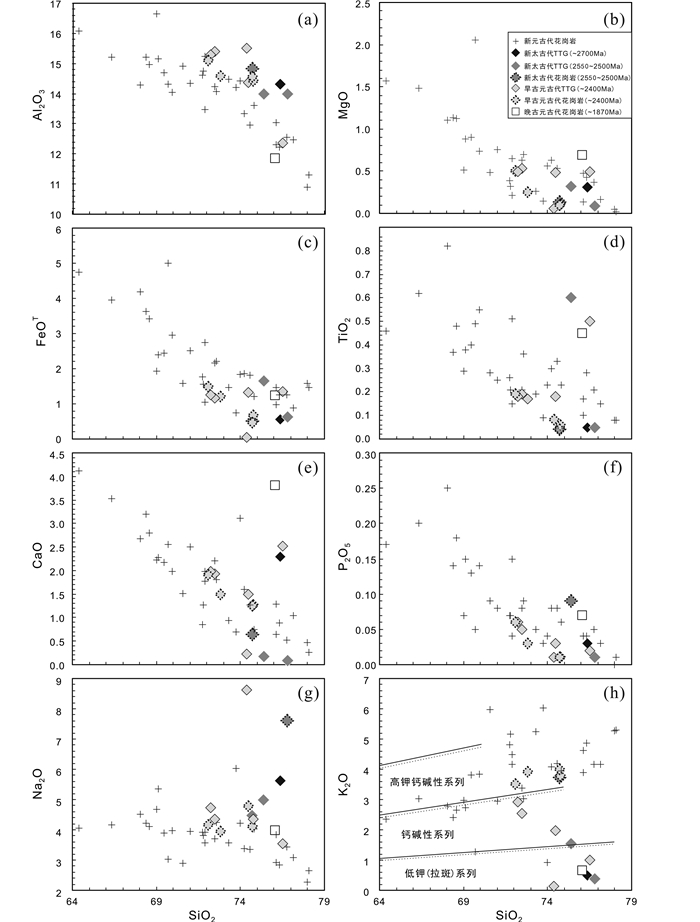
|
图 7 主量元素Al2O3、MgO、FeOT、TiO2、CaO、P2O5、Na2O、K2O与SiO2的相关性图解 图 7h中实线据Peccerillo and Taylor(1976),虚线据Middlemost(1985);图 10-图 13图例同此图 Fig. 7 SiO2 versus Al2O3, MgO, FeOT, TiO2, CaO, P2O5, Na2O and K2O diagrams for meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP belt Solid and dashed lines cited from Peccerillo and Taylor (1976) and Middlemost (1985), respectively, in Fig. 7h; The legends in Fig. 10-Fig. 13 are the same as in this figure |
|
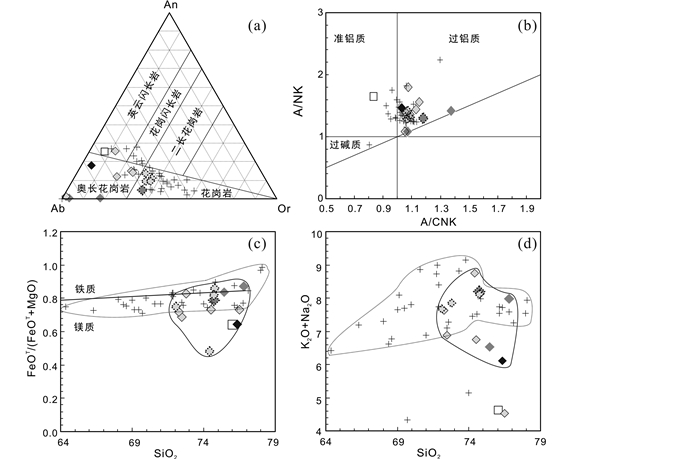
图 10 变花岗质岩石的原岩性质判别图解 (a)标准矿物An-Ab-Or图解(Barker, 1979);(b)A/CNK-A/NK图解(Maniar and Piccoli, 1989);(c)SiO2-FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)分类图解(Frost et al., 2001);(d)SiO2-(K2O+Na2O)图解 Fig. 10 The discrimination diagrams for the protolith natures of meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP belt (a) An-Ab-Or diagram (Barker, 1979); (b) A/CNK vs. A/NK diagram (Maniar and Piccoli, 1989); (c) SiO2 vs. FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) diagram (Frost et al., 2001); (d) SiO2 vs. (K2O+Na2O) diagram |

|
图 11 变花岗质岩石的原岩成因类型判别图解 A型花岗岩与I & S型花岗岩的界线引自Whalen et al. (1987) Fig. 11 The discrimination diagrams for the protolith petrogenetic types of meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP belt The boundary between A-type granite and I & S-type granite is cited from Whalen et al. (1987) |
|
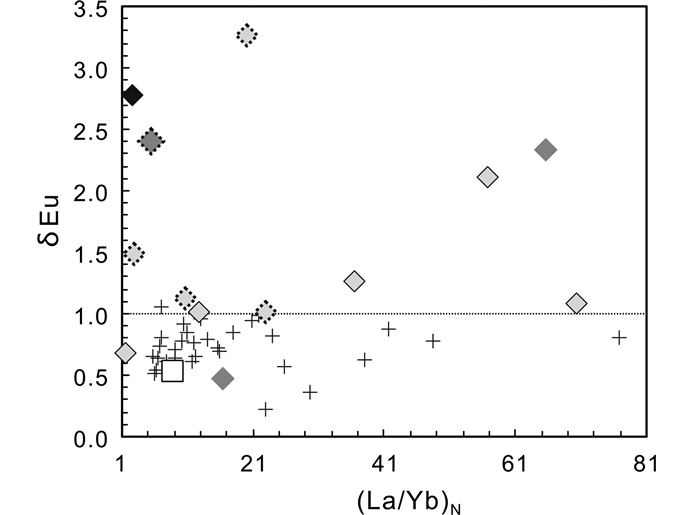
图 12 变花岗质岩石稀土元素(La/Yb)N-δEu关系图解 Fig. 12 (La/Yb)N vs. δEu diagram for meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP belt |

|
图 13 变花岗质岩石构造环境判别图解 (a)埃达克岩和经典岛弧岩石的Y-Sr/Y判别图解(Defant and Drummond, 1990);(b-c)Y-Nb、(Y + Nb)-Rb判别图解(Pearce et al., 1984) Fig. 13 The discrimination diagrams for the structural environment of meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP belt (a) Y vs. Sr/Y diagram (Defant and Drummond, 1990); Y vs. Nb (b) and (Y+Nb) vs. Rb (c) diagrams (Pearce et al., 1984) |
新元古代变花岗质岩石的稀土总量(ΣREE)介于60.11×10-6~208.8×10-6之间(平均值为130.1×10-6),富集轻稀土(LREE)(53.77×10-6~202.0×10-6,平均值为120.4×10-6),相对亏损HREE(5.55×10-6~18.18×10-6,平均值为9.70×10-6)(表 1)。在球粒陨石标准化稀土配分模式图解上(图 8a),所有新元古代花岗质片麻岩均具有明显的LREE、HREE分馏特征,(La/Yb)N=6.59~41.7,且LREE分异比HREE分异明显,(La/Gd)N=4.45~15.6,(Gd/Yb)N=0.68~2.68,并显示不同程度的负Eu异常(δEu=0.57~0.95,平均值为0.87),重稀土配分曲线一致且平坦,但总体含量变化范围较大(图 8a和表 1)。
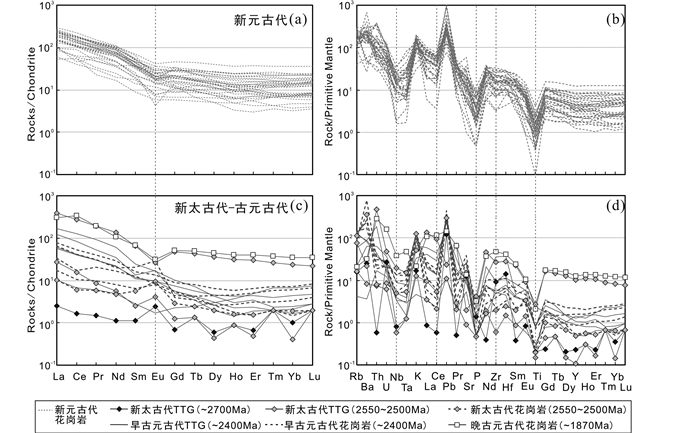
|
图 8 变花岗质岩石的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线和原始地幔均一化微量元素蛛网图(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 8 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized spider diagrams for meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP belt (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
在原始地幔均一化的微量元素蛛网图解中(图 8b),所有新元古代变花岗质岩石表现为富集Rb、Ba、K等大离子亲石元素,强烈亏损Nb、Ta、P和Ti等高场强元素,但Zr、Hf不亏损或弱亏损。
4.2.2 新太古代-古元古代变花岗质岩石北苏鲁地区新太古代-古元古代变花岗质岩石的原岩具有多期次特点,时代分别为:~2700Ma、2550~2500Ma、~2400Ma(Liu et al., 2017a)和~1870Ma。它们的地球化学特征与新元古代花岗质片麻岩存在明显差异(图 7、图 8和表 2)。不同时代的TTG-花岗质片麻岩具有相近的主量元素含量。SiO2(72.25%~76.82%)和Na2O(3.54%~7.60%)含量相对集中在较高范围,Al2O3含量(12.36%~15.40%)与新元古代花岗质片麻岩相当,K2O(0.38%~3.91%)、MgO(0.09%~0.53%)、FeOT(0.52%~1.65%)和P2O5(0.01%~0.09%)的含量明显偏低,绝大多数样品的TiO2(0.04%~0.60%)、CaO(0.08%~2.52%)的含量也偏低(图 7)。各主量元素与SiO2的无明显相关性(图 7)。在SiO2-K2O分类图上(图 7h)(据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976; Middlemost, 1985),早古元古代的变花岗质岩石具有从低钾(拉斑)系列向高钾钙碱性系列演化的趋势。
大部分新太古代-古元古代花岗质片麻岩的ΣREE集中在较低范围内(3.36×10-6~164.6×10-6)变化(OG2-2和LX114-3除外),平均值(126.9×10-6)略低于新元古代变花岗质岩石(130.1×10-6)。在球粒陨石标准化稀土配分模式图解上(图 8c),1件新太古代(~2700Ma)样品(OG1-1)的ΣREE极低(3.36×10-6),且具有平坦的稀土配分模式,其较低的稀土含量可能与母岩部分熔融过程中高流体引起的低温条件有关,该条件下形成的花岗质熔体很难与富稀土的副矿物平衡,这也与岩相学观察相吻合。3件新太古代(2550~2500Ma)样品(OG2-1、OG2-2和OG2-3)显示不一致的稀土特征(图 8c),其中,OG2-1和OG2-3具有较低的ΣREE(12.26×10-6~20.77×10-6),而OG2-2具有较高的ΣREE(385.5×10-6),但它们均显示微弱的轻、重稀土分异特征,(La/Yb)N=5.38~16.3,(La/Gd)N=3.53~8.26,(Gd/Yb)N=1.53~1.97(OG2-1除外)。5件早古元古代(~2400Ma)花岗质片麻岩(G5-1、OG5-2、OG6-1、OG6-2和OG6-3)的ΣREE为57.81×10-6~164.6×10-6,多数样品的轻、重稀土分馏特征比新元古代花岗质片麻岩略弱(图 8a, c),(La/Yb)N=12.6~70.3,(La/Gd)N=7.58~24.0,(Gd/Yb)N=1.21~4.22,呈无Eu异常或正Eu异常(δEu=1.01~3.27)(图 8c和表 2)。仅有的1件古元古代(~1870Ma)花岗质片麻岩(LX114-3)与OG2-2具有一致的稀土配分特征(图 8c)。
在原始地幔均一化的微量元素蛛网图解上(图 8b, d),绝大多数新元古代-古元古代变花岗质岩石与新元古代花岗质片麻岩均具有相似的“右倾型”配分曲线,并富集Rb、Ba、Th、U、K等大离子亲石元素、亏损Nb、Ta、P、Zr、Ti等高场强元素,呈显著的正Pb异常。它们以较低的Tb-Lu微量元素含量区别于新元古代花岗质片麻岩(图 8b, d和表 1、表 2)。
5 讨论 5.1 原岩时代和变质(深熔)时代 5.1.1 原岩时代威海地区2件样品(LX182-1和LX159-5)在锆石U-Pb不一致线的上交点年龄分别为811±25Ma和749±35Ma,LX182-1中最谐和岩浆锆石具有比上交点更年轻的加权平均年龄(762±6Ma),而LX159-5中谐和锆石的的加权平均年龄(824±25Ma)大于上交点年龄(图 6b, d)。引起这种差别的原因可能是分析误差、后期高级变质作用的改造使岩浆锆石发生Pb丢失或其U-Pb同位素体系被重置,因此作者在上文小心对两件样品进行了分析并合理选择限定它们的原岩形成时代(824~749Ma)。乳山市午极北LX132-1中岩浆锆石记录了较接近的不一致线上交点年龄(782±16Ma)和加权平均年龄(770±8Ma),应代表其原岩形成时代。由锆石年龄分布直方图(图 9a-c)和附表 1可以看出,威海、午极镇地区3件花岗质片麻岩的继承性岩浆锆石206Pb/238U表面年龄变化于847±10Ma~255±3Ma之间,其年龄主峰分布在810~745Ma之间,与上文对3件样品的原岩时代分析结果一致,同时考虑到后期变质作用的影响,745~255Ma的年龄数据无代表性意义。因此,午极-威海地区变花岗质岩石的原岩形成时代可限定在820~750Ma之间。这与以往对苏鲁超高压变质带内大量花岗质片麻岩和榴辉岩等超高压变质岩石中锆石U-Pb年代学研究结果(850~750Ma)十分吻合(Ames et al., 1996; Hacker et al., 1998, 2000; Zheng et al., 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006),表明威海-午极地区普遍存在原岩形成于新元古代的变花岗质岩石,它们与扬子板块北缘新元古代岩浆岩具有一致的原岩时代和地球化学特征,其原岩应来自于扬子板块北缘的变质基底,与罗迪尼亚超大陆裂解存在密切成因关系有关(Zheng et al., 2003; Tang et al., 2008a; Liu and Liou, 2011)。
|
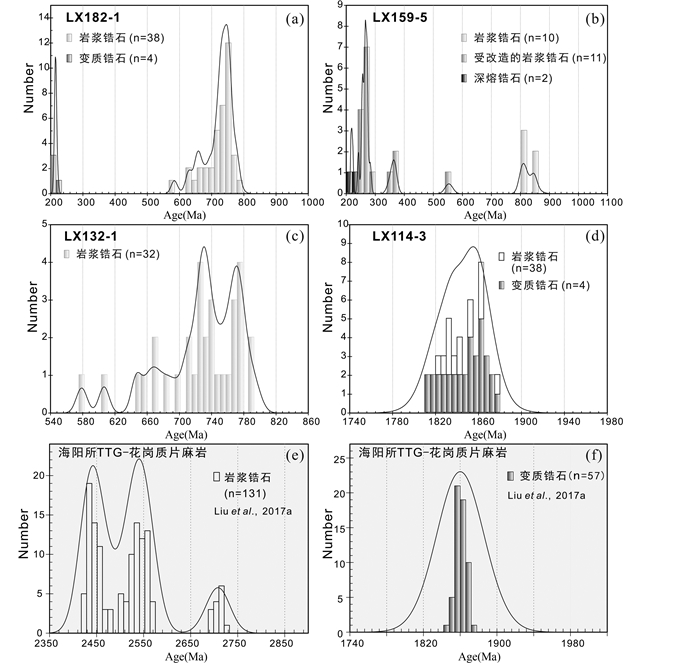
图 9 北苏鲁超高压变质带内变花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb年龄直方图 (a-c)3件新元古代花质片麻岩样品(LX182-1、LX159-5和LX132-1)中锆石U-Pb年龄直方图;(d)古元古代花岗片麻岩样品LX114-3中锆石U-Pb年龄直方图;(e)海阳所地区TTG-花岗质片麻岩中继承性岩浆锆石U-Pb年龄直方图(Liu et al., 2017a);(f)海阳所地区TTG-花岗质片麻岩中变质锆石U-Pb年龄直方图(Liu et al., 2017a) Fig. 9 Histograms of U-Pb ages for zircons from meta-granitic rocks in the North Sulu UHP belt (a-c) histogram of U-Pb ages for zircons from the Neoproterozoic granitic gneiss LX182-1, LX159-5 and LX132-1; (d) histogram of U-Pb ages for zircons from the Paleoproterozoic granitic gneiss LX114-3; (e) histogram od U-Pb ages for inherited magmatic zircons from the Neoarchean to Early Paleoproterozoic TTG-granitc samples in the Haiyangsuo area (Liu et al., 2017a); (f) histogram of U-Pb ages for Paleoproterozoic metamorphic zircons from the Neoarchean to Paleoproterozoic TTG-granitc samples in the Haiyangsuo area (Liu et al. 2017a) |
午极地区花岗片麻岩样品LX114-3与新元古代花岗质片麻岩的野外及岩相学特征难以明确区分,但锆石U-Pb年代学研究发现,LX114-3中具有岩浆振荡环带的17颗锆石记录的207Pb/206Pb表面年龄变化于1880±17Ma~1825±15Ma之间(图 9d和附表 1),不一致线上交点年龄为1868±24Ma,其加权平均年龄(1847±7Ma)较年轻(图 6h),这可能与原岩侵位后随即发生的变质事件或三叠纪变质改造有关,使其锆石普遍发生Pb丢失,因此不一致线上交点年龄可能更接近其原岩形成时代,这也与Zhang et al.(2014)在乳山北获得的2件花岗质片麻岩样品的原岩时代(1858~1827Ma)相接近。这些北苏鲁超高压变质带内的古元古代岩浆成因锆石,与胶北地区部分古元古代花岗质片麻岩中的岩浆锆石记录了一致的原岩时代(~1850Ma)(Tang et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2014)。此外,海阳所镇附近存在一套由TTG-花岗质片麻岩、变基性岩和变沉积岩组成的非超高压变质基底(Liou et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2017a)。Liu et al.(2017a)在该区识别出TTG-花岗质片麻岩的原岩侵位具有多期次(~2700Ma、2550~2500Ma和~2400Ma)的特点(图 9e),与胶北地体内新太古代-古元古代的多期酸性岩浆侵位时代(董春艳等, 2011; 刘建辉等, 2011, 2015; Liu et al., 2013a; 谢士稳等, 2015)基本吻合。
上述研究结果进一步表明,北苏鲁超高压变质带内不仅存在大量传统意义上的新元古代(820~750Ma)花岗质片麻岩,而且广泛发育与华北板块、胶北地体存在密切联系的2700~1870Ma TTG-花岗质片麻岩(图 9a-e)。
5.1.2 变质(深熔)时代研究区样品LX182-1中的变质锆石,记录的206Pb/238U表面年龄为219±4Ma~213±3Ma(附表 1),与超高压变质岩石的晚期角闪岩相退变质时代(220~200Ma)相一致(Liu et al., 2004a, b, 2005, 2006, 2007; Liu and Liou, 2011)。正长花岗片麻岩样品LX159-5中2颗记录晚三叠世年龄222±4Ma~217±3Ma的锆石在CL图像、Th-U体系方面明显不同于LX182-1的变质锆石,它们发光性极弱,发育微弱的岩浆环带,且Th、U含量极高而Th/U比值低,是典型深熔锆石(边),其时代与以往对苏鲁造山带深熔锆石的研究结果(224~210Ma)一致(Wallis et al., 2005; 刘福来等, 2009; Liu et al., 2010a, 2012; 曾令森等, 2011; Chen et al., 2013a, b),上述两组年龄均晚于超高压变质时限(245~225Ma)(Liu et al., 2004a, b, 2005, 2006, 2007; Liu and Liou, 2011),而与角闪岩相退变质时代相当。结合以往研究结果,北苏鲁威海、南苏鲁中国大陆科学钻探及大别地区广泛发育的新元古代花岗质片麻岩中含柯石英的变质锆石记录的时代为中三叠世,从而表明它们经历了中三叠世超高压变质作用(Ye et al., 2000b; Liu et al., 2001; Liu and Liou, 2011),而且明显受到晚三叠世角闪岩相退变质作用的改造(Liu et al., 2012; Chen et al., 2013a, b; 刘福来等, 2009)。
与之相比,古元古代花岗片麻岩样品LX114-3中变质锆石,记录的207Pb/206Pb表面年龄为1876±19Ma~1813±19Ma(图 9d和附表 1),完全不同于新元古代花岗质片麻岩(图 9a-c)。该样品最谐和变质锆石的加权平均年龄(1864±7Ma)(图 6h),应代表其变质时代。此外,海阳所地区大量TTG-花岗片麻岩也记录了1870~1860Ma的麻粒岩相变质时代(图 9f)(Liu et al., 2017a),这进一步充分表明,研究区新太古代-古元古代TTG-花岗质片麻岩曾共同经历古元古代构造热事件,应归属华北板块或胶北地体的变质基底,且与超高压带内新元古代岩石具有完全不同的成因机理和构造背景。
5.2 岩石地球化学特征对比 5.2.1 新元古代花岗质片麻岩全岩地球化学结果显示,北苏鲁超高压变质带内新元古代变花岗质岩石在CIPW标准矿物An-Ab-Or分类图解上主要落入花岗岩区域内,少数向奥长花岗岩-花岗闪长岩-英云闪长岩区域过渡(图 10a)。铝饱和指数A/CNK集中在1.02~1.13之间,A/NK集中在1.22~1.53之间,为准铝质-弱过铝质系列(图 10b)。在SiO2-FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)分类图解上,绝大部分样品落入镁质系列区域(图 10c),且基本不随SiO2含量的变化而变化,结合主量元素与SiO2明显的负相关关系可知,这些新元古代花岗岩是同源岩浆不断演化的产物。在微量元素(Zr、Nb、Y和Ce)与10000Ga/Al相关性图解中(图 11),大部分新元古代花岗质片麻岩落入I & S型与A型花岗岩区域的交界位置,有从I & S型花岗岩向A型花岗岩演化的趋势。而以往对苏鲁超高压变质带内新元古代花岗质片麻岩的研究表明,其原岩多为A型花岗岩(刘福来等, 2004)。结合同位素的研究结果,这些新元古代花岗质片麻岩应为形成于伸展背景下的裂谷岩浆岩(Zheng et al., 2003; Tang et al., 2008a)。它们显示一定程度的负Eu异常、中、重稀土分异较低的特征(图 8a, b和图 12),表明其源区为斜长石稳定域,而没有石榴石或角闪石的残留。在构造环境判别图解上,它们显示与岛弧岩浆岩相似的高Y、低Sr/Y比值特征(图 13a),有向板内岩浆岩演化的趋势(图 13b, c)。结合前人有关新元古代花岗质片麻岩大量的地球化学研究结果,表明这些新元古代花岗质岩石是中-基性地壳物质在压力较低的中-上地壳层次发生部分熔融的产物,应来源于扬子板块北缘的变质基底,且与Rodinia超大陆裂解有关(Zheng et al., 2003; Tang et al., 2007; 郑永飞等, 2007)。
5.2.2 新太古代-古元古代TTG-花岗质片麻岩全岩主量地球化学结果显示,新太古代-早古元古代(2700~2400Ma)TTG-花岗质片麻岩在CIPW标准矿物An-Ab-Or分类图解上大部分落入奥长花岗岩-英云闪长岩-花岗岩区域,少数包括1件2550~2500 Ma和4件~2400 Ma样品落入花岗岩区域(图 10a和表 2),表明大部分原岩具有TTG岩系的主量元素特征,而少数原岩为花岗岩。TTG质原岩与花岗岩相比具有较低的K2O含量,而其他主量元素特征相似(图 7、图 10和表 2)。它们的铝饱和指数A/CNK变化于1.03~1.37之间,A/NK变化于1.22~1.53之间,均具有过铝质系列的特征(图 10b)。在SiO2-FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)分类图解上(图 10c),绝大部分样品比新元古代花岗质片麻岩更富MgO,表明基性或超基性组分对其源区的贡献比新元古代花岗岩更大。SiO2-(K2O+Na2O)图解显示,TTG片麻岩比新元古代花岗质片麻岩具有较低的全碱(Na2O+K2O)含量(图 10d)。在SiO2-K2O分类图解上(图 7h),它们的原岩具有从低钾(拉斑)系列向钙碱性系列演化的趋势,明显不同于新元古代的高钾系列(图 7h)。而新太古代-早古元古代的花岗岩为高钾钙碱性系列,与新元古代岩石相比仍具有较低的K2O含量。由此可见,新太古代-古元古代的TTG和花岗质岩石均表现出与新元古代花岗质片麻岩有明显区别的主量元素特征,而与胶北地区不同期次TTG片麻岩具有明显的亲缘性(刘建辉等, 2015; 谢士稳等, 2015)。
在微量元素方面,新太古代-早古元古代TTG片麻岩和花岗岩片麻岩并无明显差异(图 10-图 13)。在(Zr、Nb、Y和Ce)与10000Ga/Al相关性图解中(图 11),它们均落入I & S型花岗岩区域,在Sr/Y与Y相关图解中以较高的Sr/Y比值区别于新元古代花岗质片麻岩,与埃达克岩具有类似的地球化学特征(图 13a),可与胶北地区太古宙TTG片麻岩进行对比,但它们又以较低的Mg#指数以及Sr、Cr、Ni含量区别于埃达克质岩石(图 13)(刘建辉等, 2015)。正Eu或无Eu异常及重稀土亏损的特征(图 8c、图 12)表明,其源区无斜长石而可能有角闪石的残留。由此看来,新太古代-早古元古代TTG-花岗质片麻岩与新元古代花岗质片麻岩在主量元素和微量元素方面均存在本质上的区别。
此外,午极地区晚古元古代样品LX114-3与海阳所地区部分新太古代-古元古代TTG-片麻岩具有相似的主量元素特征,而在微量元素方面存在显著差异。在原岩性质判别图解上,LX114-3落入英云闪长岩区域(图 10a)(据Barker, 1979),具有相对较低的全碱、Al2O3、K2O和较高的MgO、TiO2、FeOT和P2O5含量(图 10d),属于准铝质系列(图 10b),结合岩相学观察表明其原岩物质中具有比新太古代-早古元古代TTG岩石更多的基性组分。该样品较高的稀土和微量元素含量(图 8c, d)与岩石中较多的副矿物如榍石、钛铁矿等存在直接关系。在Zr、Nb、Ce与10000Ga/Al相关图解中均落入A型花岗岩区域(图 11a, b, d),但其较低的K2O含量(0.65%)、K2O/Na2O比值(0.84)和较高的CaO含量与I型花岗岩具有可比性。在Y-Sr/Y图解(图 13a)上,LX114-3显示与经典岛弧岩浆岩相近的特征。在Y-Nb和(Y+Nb)-Rb判别图解上(图 13b, c),LX114-3比古老的TTG-花岗片麻岩更富Nb、Y。通过对比研究发现,样品LX114-3的原岩与北苏鲁地区新元古代花岗岩、新太古代-早古元古代TTG-花岗岩均存在差异。根据目前数据分析,晚古元古代花岗质片麻岩LX114-3更趋近于I型花岗岩,是典型的造山型花岗岩。而扬子板块北缘发现的古元古代花岗质岩石均为非造山的A型花岗岩(熊庆等, 2008; 张丽娟等, 2011),与之相邻的华北板块东南缘胶-辽-吉带中存在多种成因类型的古元古代花岗岩,包括造山的S型、I型和非造山的A型花岗岩(Liu et al., 2014, 2017b; Zhang et al., 2014; 王鹏森等, 2017; 王祥俭等, 2017)。此外,Zhang et al.(2014)通过对午极地区两件古元古代花岗质片麻岩的研究,发现它们的继承性岩浆锆石(1858~1827Ma)具有正的δ18O值(7.5‰~9.8‰)、负的εHf(t)(-7.9~-3.5 at 1850Ma),Hf模式年龄为~2855Ma,这与胶北古元古代相似岩石也具有可比性(Liu et al., 2014)。因此,午极地区~1.87Ga的花岗岩很可能与胶北地区麻粒岩记录的1.95~1.85Ga的碰撞造山事件(Tam et al., 2011, 2012a, b, c; 刘平华等, 2010, 2011; 王舫等, 2010)有关,它们来自于太古宙基底岩石的重熔和再造(Liu et al., 2014)。
5.3 地质意义苏鲁-大别超高压变质带是典型的陆-陆俯冲-碰撞造山带,多数研究者认为它是三叠纪时期扬子板块向华北板块发生单向深俯冲-快速折返形成的(Liou et al., 2000, 2009; Zhang et al., 2009; Zheng et al., 2009, 2011; Liu and Liou, 2011),而华北板块的变质基底并未参与三叠纪的造山过程。地球化学和同位素年代学研究结果表明,苏鲁超高压变质带广泛出露的新元古代花岗质片麻岩和榴辉岩的原岩共同反映了与罗迪尼亚超大陆的裂解有关的双峰式岩浆活动,它们经历了中三叠世的超高压变质作用和晚三叠世角闪岩相退变质作用的改造(图 14)(Ames et al., 1996; Li et al., 2003a, b; Zheng et al., 2003; 唐俊等, 2004; Tang et al., 2007, 2008b; 郑永飞等, 2007; 刘福来等, 2009; Liu et al., 2010a, 2012; He et al., 2016)。而位于烟台-青岛-五莲断裂西北侧的胶北地区,其变质基底以太古代-古元古代TTG-花岗质片麻岩、基性麻粒岩和泥质麻粒岩为主(唐俊等, 2004; Wan et al., 2006; Jahn et al., 2008; Zhou et al., 2008b; Liu et al., 2013a; Wang et al., 2014),它们共同经历了古元古代麻粒岩相变质事件的改造(刘平华等, 2010; 王舫等, 2010; Tam et al., 2012a, b, c; Liu et al., 2013b, 2017b),是华北板块、胶-辽-吉古元古代构造带变质基底的重要组成部分。
|
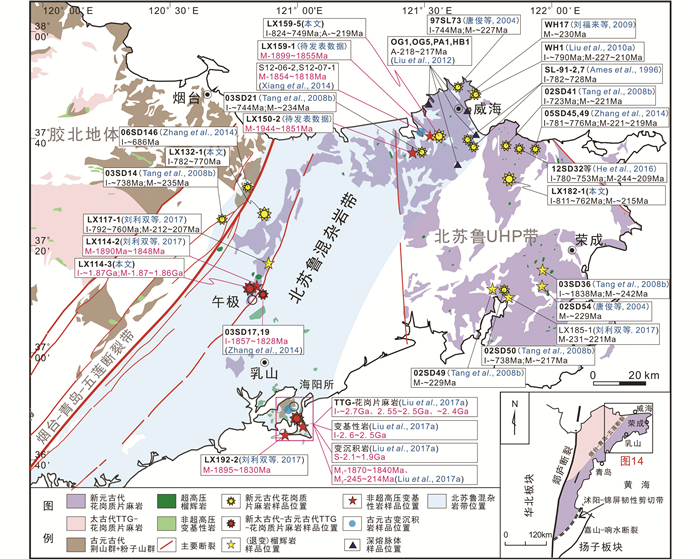
图 14 北苏鲁混杂岩带的位置及变花岗质岩石、变基性岩、变沉积岩年龄分布图 Fig. 14 The North Sulu mélange belt identified in the North Sulu UHP belt, with zircon U-Pb age data as in present and previous studies |
值得注意的是,以往和现今研究发现,苏鲁超高压变质带不是由单一新元古代变质岩系所组成的,带内存在大量新太古代-古元古代的变质岩系(图 14)(Liou et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2006, 2014; Tang et al., 2008b; Zhou et al., 2008a; Xiang et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2017a; 刘利双等, 2017),其中,部分具有扬子板块属性,而另一部分与华北板块具有亲缘性。Yang et al.(2003)和Tang et al.(2008b)在荣成地区发现形成于晚古元古代(1.85~1.75Ga)的榴辉岩和片麻岩,其变质锆石中柯石英包体的存在表明它们经历了三叠纪的超高压变质作用,且进一步的锆石O同位素表明,它们具有扬子板块的属性。而Liou et al.(2006)和Zhang et al.(2006)在海阳所地区发现一套古老的(>2500Ma)、记录麻粒岩相变质的外来地体。Zhou et al.(2008a)在石桥-坪上地区发现一套古元古代(2100~1900Ma)、与华北板块具有亲缘性的浅变质沉积地层,且经历了晚二叠世-早三叠世变质事件的改造。Xiang et al.(2014)在威海地区识别出一套古元古代(~1850Ma)变质的泥质岩系(图 14)。Zhang et al.(2014)通过锆石氧和铪同位素研究,发现午极地区古元古代花岗质片麻岩与胶北地古元古代相似岩石具有一致的特征,认为它们应归属于胶北地体(图 14)。刘利双等(2015)发现海阳所变基性岩记录两期中-高压麻粒岩相变质作用,限定两期变质作用P-T轨迹均具有顺时针型式。Liu et al.(2017a)进一步厘定区内TTG-花岗质片麻岩、变基性岩以及变沉积岩两期变质作用的时代分别为古元古代(1870~1840Ma)和三叠纪(245~214Ma)(图 14)。此外,午极和威海地区的变基性岩普遍记录了古元古代(1900~1800Ma)和中-晚三叠世(235~200Ma)的变质事件(图 14)(刘利双等, 2017及待发表数据),它们和海阳所基性麻粒岩的原岩,均与胶北地体的高压基性麻粒岩具有亲缘性。这些与华北板块具有亲缘性的古老变质基底区别于来自扬子板块基底物质的重要特征是,普遍记录晚古元古代(1.95~1.80Ga)的麻粒岩相变质作用,但无任何超高压变质作用的迹象。本文对变花岗质岩石的研究进一步表明,苏鲁超高压变质带北缘的海阳所-午极-威海一带,不仅存在来自于扬子板块的变质基底,而且广泛发育与华北板块变质基底存在密切成因联系的新太古代-古元古代变质岩系,它们共同构成一条在空间上呈北东-南西向展布的北苏鲁混杂岩带(图 14)。这些新太古代-古元古代岩系,不仅经历了胶-辽-吉带古元古代的碰撞造山事件,而且也卷入了中-晚三叠世扬子板块与华北板块俯冲-碰撞的造山过程中。这一新成果对于重新厘定苏鲁超高压带内的物质组成、多期变质事件的性质、原岩性质和构造归属,以及重新建立苏鲁超高压变质带的动力学模式均具有重要的科学意义。
6 结论通过对北苏鲁超高压变质带内不同类型变花岗质岩石的岩石学、同位素年代学和全岩地球化学的综合研究,得出结论如下:
(1) 北苏鲁超高压变质带内变花岗质岩石具有多种成因类型:一类为广泛发育的新元古代(820~750Ma)花岗质片麻岩,另一类为新太古代-古元古代(~2700Ma、2550~2500Ma、~2400Ma和~1870Ma)的TTG-花岗质片麻岩。
(2) 新元古代花岗质片麻岩经历了晚三叠世(222~213Ma)的变质和深熔事件;而新太古代-古元古代TTG-花岗质片麻岩记录了古元古代(~1864Ma)和中-晚三叠世(235~200Ma)两期变质事件,分别与胶-辽-吉造山带和苏鲁超高压变质带的形成存在密切成因关系。
(3) 新元古代花岗质片麻岩的原岩趋近于A型花岗岩,属于过铝质-准铝质的高钾钙碱性系列,可能来自于中上地壳物质的部分熔融;新太古代-早古元古TTG-花岗质片麻岩的原岩为TTG和I & S型花岗岩,属于低钾-钙碱性系列,与新元古代花岗质片麻岩的成因特点存在本质差异;晚古元古代花岗质片麻岩的原岩为I型花岗岩,属于准铝质的低钾系列,应来自于太古宙基底岩石的重熔与再造。
(4) 新元古代花岗质片麻岩的原岩应为源自于扬子板块北缘的变质基底,与罗迪尼亚超大陆裂解存在密切成因关系;而新太古代-晚古元古代TTG-花岗质片麻岩的原岩应源于胶北地体,与华北板块变质基底、胶-辽-吉古元古构造带具有亲缘性。
(5) 在苏鲁超高压变质带内的威海-乳山一带,由具有扬子板块属性和具有华北板块属性的变质基底,沿北东-南西向共同组成了一条北苏鲁混杂岩带。华北板块东南缘和扬子板块北缘的陆壳物质,在中-晚三叠世发生了相向(双向)俯冲-折返的造山过程。
致谢 本文在野外采样、室内分析测试以及成文过程中,得到项目组刘建辉研究员、刘超辉研究员、田忠华副研究员、杨红助理研究员和许王博士的大力帮助。两位审稿人对本文提出了十分宝贵的修改意见。在此一并表示衷心的感谢!适逢沈其韩院士九十六华诞暨从事地质事业和科研教育工作七十五周年,谨以此文敬贺,衷心祝愿先生健康长寿!
Ames L, Zhou GZ and Xiong BC. 1996. Geochronology and isotopic character of ultrahigh‐pressure metamorphism with implications for collision of the Sino‐Korean and Yangtze cratons, central China. Tectonics, 15(2): 472-489. DOI:10.1029/95TC02552 |
Barker F. 1979. Trondhjemite: Definition, environment and hypotheses of origin. In: Barker F (ed. ). Trondhjemites, Dacites, and Related Rocks. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1-12
|
Chen YX, Zheng YF and Hu Z. 2013a. Petrological and zircon evidence for anatexis of UHP quartzite during continental collision in the Sulu orogen. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 31(4): 389-413. DOI:10.1111/jmg.2013.31.issue-4 |
Chen YX, Zheng YF and Hu ZC. 2013b. Synexhumation anatexis of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks: Petrological evidence from granitic gneiss in the Sulu orogen. Lithos, 156-159: 69-96. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.10.008 |
Cong BL. 1996. Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphic Rocks in the Dabieshan-Sulu Region of China. Beijing: Science Press: 19-9224.
|
Cong BL and Wang QC. 1999. The Dabie-Sulu UHP rocks belt: Review and prospect. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44(12): 1074-1086. DOI:10.1007/BF02886130 |
Defant MJ and Drummond MS. 1990. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature, 347(6294): 662-665. DOI:10.1038/347662a0 |
Dong CY, Wang SJ, Liu DY, Wang JG, Xie HQ, Wang W, Song ZY and Wan YS. 2011. Late Palaeoproterozoic crustal evolution of the North China Craton and formation time of the Jingshan Group: Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of meta-intermediate-basic intrusive rocks in eastern Shandong Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(6): 1699-1706. |
Frost BR, Barnes CG, Collins WJ, Arculus RJ, Ellis DJ and Frost CD. 2001. A geochemical classification for granitic rocks. Journal of Petrology, 42(11): 2033-2048. DOI:10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033 |
Hacker BR, Ratschbacher L, Webb L, Ireland T, Walker D and Dong SW. 1998. U/Pb zircon ages constrain the architecture of the ultrahigh-pressure Qinling-Dabie Orogen, China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 161(1-4): 215-230. DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00152-6 |
Hacker BR, Ratschbacher L, Webb L, McWilliams MO, Ireland T, Calvert A, Dong SW, Wenk HR and Chateigner D. 2000. Exhumation of ultrahigh‐pressure continental crust in east central China: Late Triassic-Early Jurassic tectonic unroofing. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 105(B6): 13339-13364. DOI:10.1029/2000JB900039 |
He Q, Zhang SB and Zheng YF. 2016. High temperature glacial meltwater-rock reaction in the Neoproterozoic: Evidence from zircon in-situ oxygen isotopes in granitic gneiss from the Sulu orogen. Precambrian Research, 284: 1-13. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2016.07.012 |
Hoskin PWO and Schaltegger U. 2003. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. In: Hanchar JM and Hoskin PWO (eds. ). Zircon. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, Vol 53. Washington: Mineralogical Society of America, 27-62
|
Hou KJ, Li YH and Tian YR. 2009. In situ U-Pb zircon dating using laser ablation-multi ion counting-ICP-MS. Mineral Deposits, 28(4): 481-492. |
Jahn BM, Liu DY, Wan YS, Song B and Wu JS. 2008. Archean crustal evolution of the Jiaodong Peninsula, China, as revealed by zircon SHRIMP geochronology, elemental and Nd-isotope geochemistry. American Journal of Science, 308(3): 232-269. DOI:10.2475/03.2008.03 |
Li XH, Li ZX, Ge WC, Zhou HW, Li WX, Liu Y and Wingate MTD. 2003a. Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China: Crustal melting above a mantle plume at ca.825 Ma? . Precambrian Research, 122(1-4): 45-83. DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00207-3 |
Li ZX, Li XH, Kinny PD, Wang J, Zhang S and Zhou H. 2003b. Geochronology of neoproterozoic syn-rift magmatism in the Yangtze Craton, South China and correlations with other continents: Evidence for a mantle superplume that broke up Rodinia. Precambrian Research, 122(1-4): 85-109. DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00208-5 |
Liou JG, Zhang RY, Eide EA, Maruyama S, Wang X and Ernst WG. 1996. Metamorphism and tectonics of high-P and ultrahigh-P belts in Dabie-Sulu Regions, eastern central China. In: Yin A and Harrison TM (eds. ). The Tectonic Evolution of Asia. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, 300-343
|
Liou JG, Hacker BR and Zhang RY. 2000. Geophysics: Into the forbidden zone. Science, 287(5456): 1215-1216. DOI:10.1126/science.287.5456.1215 |
Liou JG, Tsujimori T, Chu W, Zhang RY and Wooden JL. 2006. Protolith and metamorphic ages of the Haiyangsuo Complex, eastern China: A non-UHP exotic tectonic slab in the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure terrane. Mineralogy and Petrology, 88(1-2): 207-226. DOI:10.1007/s00710-006-0156-2 |
Liou JG, Ernst WG, Zhang RY, Tsujimori T and Jahn BM. 2009. Ultrahigh-pressure minerals and metamorphic terranes-the view from China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(3-4): 199-231. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.10.012 |
Liu FL, Xu ZQ, Liou JG and Song B. 2004a. SHRIMP U-Pb ages of ultrahigh-pressure and retrograde metamorphism of gneisses, south-western Sulu terrane, eastern China. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 22(4): 315-326. DOI:10.1111/j.1525-1314.2004.00516.x |
Liu FL, Xu ZQ and Xue HM. 2004b. Tracing the protolith, UHP metamorphism, and exhumation ages of orthogneiss from the SW Sulu terrane (eastern China): SHRIMP U-Pb dating of mineral inclusion-bearing zircons. Lithos, 78(4): 411-429. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.08.001 |
Liu FL, Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Zhang ZM, Xue HM and Li TF. 2004. Geochemical characteristics and UHP metamorphism of granitic gneisses in the main drilling hole of Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling Project and its adjacent area. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(1): 9-26. |
Liu FL, Liou JG and Xu ZQ. 2005. U-Pb SHRIMP ages recorded in the coesite-bearing zircon domains of paragneisses in the southwestern Sulu terrane, eastern China: New interpretation. American Mineralogist, 90(5-6): 790-800. DOI:10.2138/am.2005.1677 |
Liu FL, Gerdes A, Liou JG, Xue HM and Liang FH. 2006. SHRIMP U‐Pb zircon dating from Sulu‐Dabie dolomitic marble, eastern China: Constraints on prograde, ultrahigh‐pressure and retrograde metamorphic ages. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 24(7): 569-589. DOI:10.1111/jmg.2006.24.issue-7 |
Liu FL and Xue HM. 2007. Review and prospect of SHRIMP U-Pb dating on zircons from Sulu-Dabie UHP metamorphic rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(11): 2737-2756. |
Liu FL, Xue HM and Liu PH. 2009. Partial melting time of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in the Sulu UHP terrane: Constrained by zircon U-Pb ages, trace elements and Lu-Hf isotope compositions of biotite-bearing granite. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(5): 1039-1055. |
Liu FL, Robinson PT, Gerdes A, Xue HM, Liu PH and Liou JG. 2010a. Zircon U-Pb ages, REE concentrations and Hf isotope compositions of granitic leucosome and pegmatite from the North Sulu UHP terrane in China: Constraints on the timing and nature of partial melting. Lithos, 117(1-4): 247-268. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.03.002 |
Liu FL and Liou JG. 2011. Zircon as the best mineral for P-T-time history of UHP metamorphism: A review on mineral inclusions and U-Pb SHRIMP ages of zircons from the Dabie-Sulu UHP rocks. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(1): 1-39. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.08.007 |
Liu FL, Shi JR, Liu JH, Ye JG, Liu PH and Wang F. 2011. Protolith and ultranhigh-pressure (UHP) metamorphic ages of ultramafic rocks in Weihai area, North Sulu UHP terrane. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(4): 1075-1084. |
Liu FL, Robinson PT and Liu PH. 2012. Multiple partial melting events in the Sulu UHP terrane: Zircon U-Pb dating of granitic leucosomes within amphibolite and gneiss. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 30(8): 887-906. DOI:10.1111/jmg.2012.30.issue-8 |
Liu FL, Liu PH, Wang F, Liu CH and Cai J. 2015. Progresses and overviews of voluminous meta-sedimentary series within the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji orogenic/mobile belt, North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(10): 2816-2846. |
Liu FL, Liu LS, Liu PH, Wang F, Cai J, Liu JH, Wang W and Ji L. 2017a. A relic slice of archean-early Paleoproterozoic basement of Jiaobei Terrane identified within the Sulu UHP belt: Evidence from protolith and metamorphic ages from meta-mafic rocks, TTG-granitic gneisses, and metasedimentary rocks in the Haiyangsuo region. Precambrian Research, 303: 117-152. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2017.03.014 |
Liu FL, Liu CH, Itano K, Iizuka T, Cai J and Wang F. 2017b. Geochemistry, U-Pb dating, and Lu-Hf isotopes of zircon and monazite of porphyritic granites within the Jiao-Liao-Ji orogenic belt: Implications for petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Precambrian Research, 300: 78-106. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2017.08.007 |
Liu JB, Ye K, Maruyama S, Cong BL and Fan HR. 2001. Mineral inclusions in zircon from gneisses in the ultrahigh-Pressure zone of the Dabie Mountains, China. The Journal of Geology, 109(4): 523-535. DOI:10.1086/320796 |
Liu JH, Liu FL, Liu PH, Wang F and Ding ZJ. 2011. Polyphase magmatic and metamorphic events from Early Precambrian metamorphic basement in Jiaobei area: Evidences from the zircon U-Pb dating of TTG and granitic gneisses. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(4): 943-960. |
Liu JH, Liu FL, Ding ZJ, Liu CH, Yang H, Liu PH, Wang F and Meng E. 2013a. The growth, reworking and metamorphism of early Precambrian crust in the Jiaobei terrane, the North China Craton: Constraints from U-Th-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopic systematics, and REE concentrations of zircon from Archean granitoid gneisses. Precambrian Research, 224: 287-303. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2012.10.003 |
Liu JH, Liu FL, Ding ZJ, Liu PH, Guo CL and Wang F. 2014. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Paleoproterozoic granitoid rocks in the Jiaobei Terrane, North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 255: 685-698. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2013.12.004 |
Liu JH, Liu FL, Ding ZJ, Liu PH and Wang F. 2015. Early Precambrian major magmatic events, and growth and evolution of continental crust in the Jiaobei terrane, North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(10): 2942-2958. |
Liu LS, Liu FL, Liu PH, Cai J, Shi JR and Liu CH. 2015. Geochemical characteristics and metamorphic evolution of meta-mafic rocks from Haiyangsuo area, Sulu ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(10): 2863-2888. |
Liu LS, Liu FL and Wang W. 2017. The polygenetic meta-mafic rocks from the northeast of Sulu ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt: Insight from petrology, isotope geochronology and geochemistry. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(9): 2899-2924. |
Liu PH, Liu FL, Wang F and Liu JH. 2010. Genetic mineralogy and metamorphic evolution of mafic high-pressure (HP) granulites from the Shandong Peninsula, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7): 2039-2056. |
Liu PH, Liu FL, Wang F and Liu JH. 2011. U-Pb dating of zircons from Al-rich paragneisses of Jingshan Group in Shandong peninsula and its geological significance. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 30(5): 829-843. |
Liu PH, Liu FL, Liu CH, Wang F, Liu JH, Yang H, Cai J and Shi JR. 2013b. Petrogenesis, P-T-t path, and tectonic significance of high-pressure mafic granulites from the Jiaobei terrane, North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 233: 237-258. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2013.05.003 |
Liu PH, Liu FL, Wang F, Liu CH, Yang H, Liu JH, Cai J and Shi JR. 2015. P-T-t paths of the multiple metamorphic events of the Jiaobei terrane in the southeastern segment of the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt (JLJB), in the North China Craton: Impication for formation and evolution of the JLJB. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(10): 2889-2941. |
Liu PH, Liu FL, Cai J, Wang F, Liu CH, Liu JH, Yang H, Shi JR and Liu LS. 2017c. Discovery and geological significance of high-pressure mafic granulites in the Pingdu-Anqiu area of the Jiaobei Terrane, the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, the North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 303: 445-469. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2017.05.022 |
Liu YS, Gao S, Hu ZC, Gao CG, Zong KQ and Wang DB. 2010b. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced Melt-peridotite interactions in the trans-North China orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2): 537-571. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egp082 |
Ludwing KR. 2003. ISOPLOT 3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley, CA: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 4: 1-70. |
Maniar PD and Piccoli PM. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101(5): 635-643. DOI:10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2 |
Middlemost EAK. 1985. Magmas and Magmatic Rocks: An Introduction to Igneous Petrology. London: Addison-Wesley Longman Ltd: 1-266.
|
Pearce JA, Harris NBW and Tindle AG. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983. DOI:10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 |
Peccerillo A and Taylor SR. 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1): 63-81. DOI:10.1007/BF00384745 |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publicaion, 42(1): 313-345
|
Tam PY, Zhao GC, Liu FL, Zhou XW, Sun M and Li SZ. 2011. Timing of metamorphism in the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt: New SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of granulites, gneisses and marbles of the Jiaobei massif in the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 19(1): 150-162. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.05.007 |
Tam PY, Zhao GC, Sun M, Li SZ, Iizuka Y, Ma GSKI, Yin CQ, He YH and Wu ML. 2012a. Metamorphic P-T path and tectonic implications of medium-pressure pelitic granulites from the Jiaobei massif in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 220. |
Tam PY, Zhao GC, Sun M, Li SZ, Wu ML and Yin CQ. 2012b. Petrology and metamorphic P-T path of high-pressure mafic granulites from the Jiaobei massif in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, North China Craton. Lithos, 155: 94-109. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.08.018 |
Tam PY, Zhao GC, Zhou XW, Sun M, Guo JH, Li SZ, Yin CQ, Wu ML and He YH. 2012c. Metamorphic P-T path and implications of high-pressure pelitic granulites from the Jiaobei massif in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 22(1): 104-117. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.09.006 |
Tang J, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Zha XP and Zhou JB. 2004. Zircon U-Pb ages and oxygen isotopes of metamorphic rocks in the western part of the Shandong Peninsula. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(5): 1063-1086. |
Tang J, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Gong B and Liu XM. 2007. Geochronology and geochemistry of metamorphic rocks in the Jiaobei terrane: Constraints on its tectonic affinity in the Sulu orogen. Precambrian Research, 152(1-2): 48-82. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.09.001 |
Tang J, Zheng YF, Gong B, Wu YB, Gao TS, Yuan HL and Wu FY. 2008a. Extreme oxygen isotope signature of meteoric water in magmatic zircon from metagranite in the Sulu orogen, China: Implications for Neoproterozoic rift magmatism. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72(13): 3139-3169. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2008.04.017 |
Tang J, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Gong B, Zha XQ and Liu XM. 2008b. Zircon U-Pb age and geochemical constraints on the tectonic affinity of the Jiaodong terrane in the Sulu orogen, China. Precambrian Research, 161(3-4): 389-418. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.09.008 |
Wallis S, Tsuboi M, Suzuki K, Fanning M, Jiang LL and Tanaka T. 2005. Role of partial melting in the evolution of the Sulu (eastern China) ultrahigh-pressure terrane. Geology, 33(2): 129-132. DOI:10.1130/G20991.1 |
Wan YS, Song B, Liu DY, Wilde SA, Wu JS, Shi YR, Yin XY and Zhou HY. 2006. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of Palaeoproterozoic metasedimentary rocks in the North China Craton: Evidence for a major Late Palaeoproterozoic tectonothermal event. Precambrian Research, 149(3-4): 249-271. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.06.006 |
Wang F, Liu FL, Liu PH and Liu CH. 2010. Metamorphic evolution of Early Precambrian khondalite series in North Shandong Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7): 2057-2072. |
Wang PS, Dong YS, Li FQ, Gao BS, Gan YC, Chen MS and Xu W. 2017. Paleoproterozoic granitic magmatism and geological significance in Huanghuadian area, eastern Liaoning Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(9): 2708-2724. |
Wang W, Zhai MG, Li TS, Santosh M, Zhao L and Wang HZ. 2014. Archean-Paleoproterozoic crustal evolution in the eastern North China Craton: Zircon U-Th-Pb and Lu-Hf evidence from the Jiaobei terrane. Precambrian Research, 241: 146-160. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2013.11.011 |
Wang XJ, Liu JH and Ji L. 2017. Zircon U-Pb chronology, geochemistry and their petrogenesis of Paleoproterozoic monzogranitic gneisses in Kuandian area, eastern Liaoning Province, Jiao-Liao-Ji belt, North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(9): 2689-2707. |
Whalen JB, Currie KL and Chappell BW. 1987. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407-419. DOI:10.1007/BF00402202 |
Wu ML, Zhao GC, Sun M, Li SZ, Bao ZA, Tam PY, Eizenhöefer PR and He YH. 2014. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes of major lithologies from the Jiaodong Terrane: Implications for the crustal evolution of the Eastern Block of the North China Craton. Lithos, 190-191: 71-84. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.12.004 |
Xiang H, Zhang ZM, Lei HC, Qi M, Dong X, Wang W and Lin YH. 2014. Paleoproterozoic ultrahigh-temperature pelitic granulites in the northern Sulu orogen: Constraints from petrology and geochronology. Precambrian Research, 254: 273-289. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2014.09.004 |
Xie SW, Wang SJ, Xie HQ, Liu SJ, Dong CY, Ma MZ, Ren P and Liu DY. 2015. Petrogenesis of ca.2.7Ga TTG rocks in the Jiaodong terrane, North China craton and its geological implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(10): 2974-2990. |
Xiong Q, Zheng JP, Yu CM, Su YP, Tang HY and Zhang ZH. 2009. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope of Quanyishang A-type granite in Yichang: Signification for the Yangtze continental cratonization in Paleoproterozoic. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(3): 436-446. |
Xu ZQ, Liu FL, Qi XX, Zhang ZM, Yang JS, Zeng LS and Liang FH. 2006. Record for rodinia supercontinent breakup event in the South Sulu ultra-high pressure metamorphic terrane. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(7): 1745-1760. |
Yang JS, Wooden JL, Wu CL, Liu FL, Xu ZQ, Shi RD, Katayama I, Liou JG and Maruyama M. 2003. SHRIMP U-Pb dating of coesite-bearing zircon from the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks, Sulu terrane, East China. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 21(6): 551-560. DOI:10.1046/j.1525-1314.2003.00463.x |
Ye K, Cong BL and Ye DN. 2000a. The possible subduction of continental material to depths greater than 200 km. Nature, 407(6805): 734-736. DOI:10.1038/35037566 |
Ye K, Yao YP, Katayama I, Cong BL, Wang QC and Maruyama S. 2000b. Large areal extent of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure terrane of East China: New implications from coesite and omphacite inclusions in zircon of granitic gneiss. Lithos, 52(1-4): 157-164. DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00089-4 |
Zeng LS, Gao LE, Yu JJ and Hu GY. 2011. SHRIMP zircon U/Pb dating on ultrahigh pressure rocks from Yangkou: Implications for the timing of partial melting in the Sulu UHP metamorphic belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(4): 1085-1094. |
Zhang LJ, Ma CQ, Wang LX, She ZB and Wang SM. 2011. Discovery of paleoproterozoic rapakivi granite on the northern margin of the Yangtze Block and its geological significance. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56(3): 306-318. DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-4236-7 |
Zhang RY, Liou JG and Ernst WG. 1995. Ultrahigh‐pressure metamorphism and decompressional P-T paths of eclogites and country rocks from Weihai, eastern China. Island Arc, 4(4): 293-309. DOI:10.1111/iar.1995.4.issue-4 |
Zhang RY, Liou JG, Yang JS and Yui TF. 2000. Petrochemical constraints for dual origin of garnet peridotites from the Dabie-Sulu UHP terrane, eastern-central China. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 18(2): 149-166. DOI:10.1046/j.1525-1314.2000.00248.x |
Zhang RY, Liou JG, Tsujimori T and Maruyama S. 2006. Non-ultrahigh-pressure unit bordering the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure terrane, eastern China: Transformation of Proterozoic granulite and gabbro to garnet amphibolite. In: Hacker BR, McClelland WC and Liou JG (eds. ). Ultrahigh-Pressure Meta-Morphism: Deep Continental Subduction. Geological Society of America Special Papers, 403: 169-206
|
Zhang RY, Liou JG and Ernst WG. 2009. The Dabie-Sulu continental collision zone: A comprehensive review. Gondwana Research, 16(1): 1-26. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2009.03.008 |
Zhang SB, Tang J and Zheng YF. 2014. Contrasting Lu-Hf isotopes in zircon from Precambrian metamorphic rocks in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Constraints on the tectonic suture between North China and South China. Precambrian Research, 245: 29-50. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2014.01.006 |
Zhang ZM, Xiao YL, Liu FL, Liou JG and Hoefs J. 2005. Petrogenesis of UHP metamorphic rocks from Qinglongshan, southern Sulu, east-central China. Lithos, 81(1-4): 189-207. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.10.002 |
Zhao GC, Cawood PA, Li SZ, Wilde SA, Sun M, Zhang J, He YH and Yin CQ. 2012. Amalgamation of the North China Craton: Key issues and discussion. Precambrian Research, 222-223: 55-76. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2012.09.016 |
Zheng YF, Fu B, Gong B and Li L. 2003. Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie-Sulu orogen in China: Implications for geodynamics and fluid regime. Earth-Science Reviews, 62(1-2): 105-161. DOI:10.1016/S0012-8252(02)00133-2 |
Zheng YF, Wu YB, Chen FK, Gong B, Li L and Zhao ZF. 2004. Zircon U-Pb and oxygen isotope evidence for a large-scale 18O depletion event in igneous rocks during the Neoproterozoic. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(20): 4145-4165. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2004.01.007 |
Zheng YF, Zhou JB, Wu YB and Xie Z. 2005. Low-grade metamorphic rocks in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt: A passive-margin accretionary wedge deformed during continent subduction. International Geology Review, 47(8): 851-871. DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.47.8.851 |
Zheng YF, Zhao ZF, Wu YB, Zhang SB, Liu XM and Wu FY. 2006. Zircon U-Pb age, Hf and O isotope constraints on protolith origin of ultrahigh-pressure eclogite and gneiss in the Dabie orogen. Chemical Geology, 231(1-2): 135-158. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.01.005 |
Zheng YF, Gao TS, Wu YB, Gong B and Liu XM. 2007. Fluid flow during exhumation of deeply subducted continental crust: Zircon U-Pb age and O-isotope studies of a quartz vein within ultrahigh‐pressure eclogite. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 25(2): 267-283. DOI:10.1111/jmg.2007.25.issue-2 |
Zheng YF, Zhao ZF and Chen RX. 2007. Geodynamics of continental collision and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism: Constraints from Chinese continental scientific drilling project. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(12): 3078-3094. |
Zheng YF, Chen RX and Zhao ZF. 2009. Chemical geodynamics of continental subduction-zone metamorphism: Insights from studies of the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling (CCSD) core samples. Tectonophysics, 475(2): 327-358. DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2008.09.014 |
Zheng YF, Xia QX, Chen RX and Gao XY. 2011. Partial melting, fluid supercriticality and element mobility in ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks during continental collision. Earth-Science Reviews, 107(3-4): 342-374. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.04.004 |
Zhou JB, Wilde SA, Zhao GC, Zheng CQ, Jin W, Zhang XZ and Cheng H. 2008a. Detrital zircon U-Pb dating of low-grade metamorphic rocks in the Sulu UHP belt: Evidence for overthrusting of the North China Craton onto the South China Craton during continental subduction. Journal of the Geological Society, 165(1): 423-433. DOI:10.1144/0016-76492007-040 |
Zhou XW, Zhao GC, Wei CJ, Geng YS and Sun M. 2008b. EPMA U-Th-Pb monazite and SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of high-pressure pelitic granulites in the Jiaobei massif of the north China Craton. American Journal of Science, 308(3): 328-350. DOI:10.2475/03.2008.06 |
董春艳, 王世进, 刘敦一, 王金光, 颉颃强, 王伟, 宋志勇, 万渝生. 2011. 华北克拉通古元古代晚期地壳演化和荆山群形成时代制约——胶东地区变质中-基性侵入岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年. 岩石学报, 27(6): 1699-1706. |
侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. 2009. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位U-Pb定年技术. 矿床地质, 28(4): 481-492. |
刘福来, 许志琴, 杨经绥, 张泽明, 薛怀民, 李天福. 2004. 中国大陆科学钻探工程主孔及周边地区花岗质片麻岩的地球化学性质和超高压变质作用标志的识别. 岩石学报, 20(1): 9-26. |
刘福来, 薛怀民. 2007. 苏鲁-大别超高压岩石中锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年研究――综述和最新进展. 岩石学报, 23(11): 2737-2756. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.006 |
刘福来, 薛怀民, 刘平华. 2009. 苏鲁超高压岩石部分熔融时间的准确限定:来自含黑云母花岗岩中锆石U-Pb定年、REE和Lu-Hf同位素的证据. 岩石学报, 25(5): 1039-1055. |
刘福来, 施建荣, 刘建辉, 叶建国, 刘平华, 王舫. 2011. 北苏鲁威海地区超基性岩的原岩形成时代和超高压变质时代. 岩石学报, 27(4): 1075-1084. |
刘福来, 刘平华, 王舫, 刘超辉, 蔡佳. 2015. 胶-辽-吉古元古代造山/活动带巨量变沉积岩系的研究进展. 岩石学报, 30(10): 2816-2846. |
刘建辉, 刘福来, 刘平华, 王舫, 丁正江. 2011. 胶北早前寒武纪变质基底多期岩浆-变质热事件:来自TTG片麻岩和花岗质片麻岩中锆石U-Pb定年的证据. 岩石学报, 27(4): 943-960. |
刘建辉, 刘福来, 丁正江, 刘平华, 王舫. 2015. 胶北地体早前寒武纪重大岩浆事件、陆壳增生及演化. 岩石学报, 31(10): 2942-2958. |
刘利双, 刘福来, 刘平华, 蔡佳, 施建荣, 刘超辉. 2015. 苏鲁超高压变质带中海阳所地区变基性岩的地球化学性质及变质演化特征. 岩石学报, 31(10): 2863-2888. |
刘利双, 刘福来, 王伟. 2017. 苏鲁超高压变质带东北端多种成因类型变基性岩:来自岩石学、同位素年代学及地球化学属性的制约. 岩石学报, 33(9): 2899-2924. |
刘平华, 刘福来, 王舫, 刘建辉. 2010. 山东半岛基性高压麻粒岩的成因矿物学及变质演化. 岩石学报, 26(7): 2039-2056. |
刘平华, 刘福来, 王舫, 刘建辉. 2011. 山东半岛荆山群富铝片麻岩锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 30(5): 829-843. |
刘平华, 刘福来, 王舫, 刘超辉, 杨红, 刘建辉, 蔡佳, 施建荣. 2015. 胶北地体多期变质事件的P-T-t轨迹及其对胶-辽-吉带形成与演化的制约. 岩石学报, 31(10): 2889-2941. |
唐俊, 郑永飞, 吴元保, 查向平, 周建波. 2004. 胶东地块西部变质岩锆石U-Pb定年和氧同位素研究. 岩石学报, 20(5): 1063-1086. |
王舫, 刘福来, 刘平华, 刘建辉. 2010. 胶北地区早前寒武纪孔兹岩系的变质演化. 岩石学报, 26(7): 2057-2072. |
王鹏森, 董永胜, 李富强, 高铂森, 甘宜成, 陈木森, 许王. 2017. 辽东黄花甸地区古元古代花岗质岩浆作用及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 2017. |
王祥俭, 刘建辉, 冀磊. 2017. 胶-辽-吉带辽东宽甸地区古元古代二长(正长)花岗质片麻岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及成因. 岩石学报, 33(9): 2689-2707. |
谢士稳, 王世进, 颉颃强, 刘守偈, 董春艳, 马铭株, 任鹏, 刘敦一. 2015. 华北克拉通胶东地区~2.7Ga TTG岩石的成因及地质意义. 岩石学报, 31(10): 2974-2990. |
熊庆, 郑建平, 余淳梅, 苏玉平, 汤华云, 张志海. 2008. 宜昌圈椅埫A型花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素与扬子大陆古元古代克拉通化作用. 科学通报, 53(22): 2782-2792. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.22.017 |
许志琴, 刘福来, 戚学祥, 张泽明, 杨经绥, 曾令森, 梁凤华. 2006. 南苏鲁超高压变质地体中罗迪尼亚超大陆裂解事件的记录. 岩石学报, 22(7): 1745-1760. |
曾令森, 高利娥, 于俊杰, 胡古月. 2011. 苏鲁仰口超高压岩石SHRIMP锆石U/Pb定年与部分熔融时限. 岩石学报, 27(4): 1085-1094. |
张丽娟, 马昌前, 王连训, 佘振兵, 王世明. 2011. 扬子地块北缘古元古代环斑花岗岩的发现及其意义. 科学通报, 56(1): 44-57. |
郑永飞, 赵子福, 陈仁旭. 2007. 大陆碰撞和超高压变质的化学地球动力学:来自中国大陆科学钻探的结果. 岩石学报, 23(12): 3078-3094. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.12.004 |
 2018, Vol. 34
2018, Vol. 34

