2. 四川省冶金地质勘查局六零六大队, 成都 611730
2. The 606 Team of Sichuan Metallurgy Geology Exploration Bureau, Chengdu 611730, China
钾质岩浆岩一般为壳-幔相互作用的产物,因此为解析深部壳-幔物质的组成提供了重要窗口(涂光炽, 1982; Rogers et al., 1998; Guo et al., 2006; 刘金宇等, 2017)。前人认为钾质岩浆岩成因主要包括:俯冲交代富集的软流圈地幔(Arnaud et al., 1992; Guo et al., 2013, 2015);富集交代的岩石圈地幔或下地壳铁镁质岩浆的部分熔融(Turner et al., 1996; Miller et al., 1999; Ding et al., 2003; Nomade et al., 2004; Chen et al., 2010, 2012; Zhou et al., 2010; Liu et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2014c)。这些研究成果进一步证实钾质或超钾质岩的形成与被俯冲的洋壳或陆壳沉积物的流体或熔融体与岩石圈地幔的交代富集作用有关(Nelson, 1992)。尤其对于陆-陆碰撞形成的钾质岩浆带,如西南三江特提斯造山中金沙江-哀牢山钾质岩浆岩带,前人通过对钾质岩浆岩研究,提出不同认识,主要包括:兰坪-思茅盆地中新生代裂谷钾质岩浆岩的形成是在裂谷反转造山的过程中形成的(何科昭等, 1996);钾质岩浆岩岩浆产于大陆内挤压、局部具有引张构造的环境(曾普胜等, 1999; 骆耀南和俞如龙, 2002; 葛良胜等, 2004);新生代的岩浆活动主要发生在后碰撞弧环境(莫宣学等, 1993)。岩浆源区为具有壳-幔混合性质的富集地幔的特征(邓万明等, 1998; 葛良胜等, 2004; 薛传东等, 2008)。此外,对本区新生代钾质岩浆岩的形成动力学机制提出了大陆俯冲模型(Spurlin et al., 2005);哀牢山剪切带走滑模型(Leloup et al., 1995; Liang et al., 2007);富集地幔交代-走滑型(Guo et al., 2005);俯冲-断离模型(Flower et al., 2013);俯冲交代的大陆岩石圈地幔拆沉减薄模型(Lu et al., 2013a, b, 2015; Yang et al., 2014)等多种岩浆成因模型。研究三江地区钾质岩浆岩形成的构造环境,对揭示其地球深部物质组成,反演深部动力学等方面有着十分重要的意义。
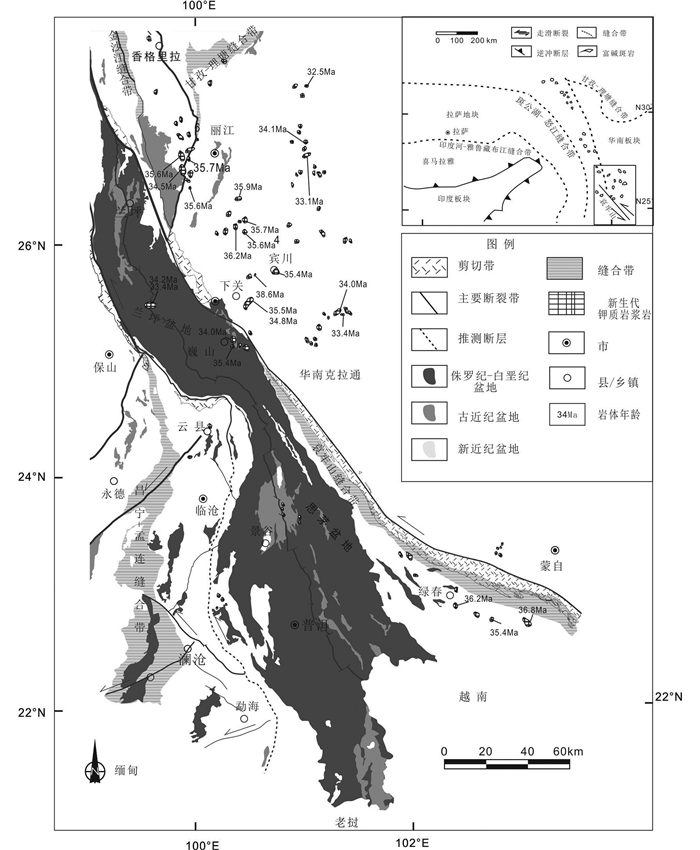
滇西钾质岩浆带沿金沙江-哀牢山断裂带及两侧分布(图 1, 曾普胜等, 2002),永平卓潘碱性杂岩体位于金沙江-哀牢山钾质岩浆带的中南部,是区内基性-中性钾质侵入岩的典型代表(李腾建等, 2017)。前人对卓潘碱性杂岩体分别在岩相学、年代学和地球化学等方面进行了研究,认为卓潘碱性杂岩体主要成分为辉石和长石(韦栋梁等,2005;李腾建等,2017),董方浏等(2005)通过黑云母测年限定卓潘碱性杂岩体的年龄为36.7Ma,董方浏等(2007)和陈喜峰等(2015)通过元素地球化学和Sr-Nd-Pb同位素的研究发现其岩浆源区具有富集地幔(EMⅡ)与下地壳共同作用的壳-幔过渡带的特征,认为该岩体形成于拉张的构造背景下。前人研究虽然确定了岩体的矿物类型、岩浆源区及构造环境,但是对兰坪盆地内卓潘碱性杂岩体的研究仍然存在争议,明添学等(2013)、陈喜峰等(2015)和李腾建等(2017)认为该区存在辉长岩。然矿相学研究表明,该地区所谓的“辉长岩”中未见斜长石,定名为辉长岩尚需斟酌;年代学方面目前报道的黑云母Ar-Ar测年,尚缺少准确的定年;岩石成因及大陆动力学背景需要进一步深入解析。鉴于该岩体处于兰坪-思茅双向弧后-陆内盆地西缘特殊的大地构造位置以及特殊的矿物组合,是其他钾质斑岩体无可替代的。因此,对卓潘岩体的深入探讨对补充完善滇西新生代钾质岩浆岩的成因有着重要的意义。本文通过对兰坪-思茅盆地的卓潘碱性杂岩体进行岩石学、岩石地球化学、锆石年代学以及Hf同位素地球化学的研究,厘定岩浆事件的年龄、物质来源、构造环境及大陆动力学背景。
|
图 1 滇西新生代富碱岩浆岩分布略图 (据Lu et al., 2012; 邓军等, 2010; Deng et al., 2014b; Wang et al., 2016修改) Fig. 1 The distribution of Cenozoic alkaline-rich porphyry in West Yunnan (after Lu et al., 2012; Deng et al., 2010, 2014b; Wang et al., 2016) |
三江特提斯造山带地质格局分为北段与南段不同的构造域。北部从西向东包括拉萨地块、西羌塘地块、东羌塘地块和中咱地块,它们被龙木错-双湖、金沙江和甘孜-理塘缝合带分隔,毗邻缝合带的火山岩-岩浆弧包括拉萨东缘岩浆带、开心岭-竹卡岩浆带、江达-维西岩浆带、义敦岛弧岩浆带;南段从西向东包括腾冲-保山地块、思茅地块,东临扬子地块,依次由昌宁-孟连和哀牢山两条缝合带分隔,毗邻缝合带的火山岩-岩浆弧包括腾冲-保山岩浆带、云县景谷岩浆带、雅轩桥岩浆带,其中龙木错-双湖和昌宁-孟连缝合带,以及金沙江和哀牢山缝合带南北贯通为统一的缝合带(邓军等, 2012; 李龚健, 2014; Deng et al., 2014a, b, 2017a, b, c; Wang et al., 2014a, 2015, 2016; Li et al., 2015, 2016; 杜斌等, 2016; 杨立飞等, 2016; Deng and Wang, 2016; 杜斌, 2017)。其中沿金沙江-哀牢山剪切带两侧分布着新生代巨型的钾质岩浆岩带,该岩带夹持于欧亚古扬子板块与古印度板块之间,向西延伸到思茅地块内部50km腹地,向东延伸到扬子板块内150km(图 1, Guo et al., 2005; 李勇等, 2011; 李龚健, 2014)。在扬子西缘主要发育太古代-元古代的变质褶皱基地和元古代的沉积盖,而且可见元古代的变质核杂岩(李龚健, 2014),且在河口群、通安群、东川群、汤丹群、大红山群、会理群及昆阳群为代表的浅变质火山-沉积岩系地层中可见中元古代的辉长-闪长岩、辉绿岩(庞维华等, 2015)。而金沙江-哀牢山缝合带则经历了二叠世-三叠世的洋壳俯冲,中三叠世,古特提斯金沙江-哀牢山洋闭合(李龚健等, 2013; Deng et al., 2014b),俯冲造山过程结束,形成了北段的江达维西火山岩浆弧和南段的雅轩桥-景谷岩浆弧(李龚健, 2014; 王长明等, 2017; Wang et al., 2014b, 2016, 2017b, 2018);60~55Ma受扬子西缘的影响,印度-欧亚板块陆陆碰撞,三江地区遭受强烈的挤压作用而发生逆冲与褶皱,地壳在原有基础上进一步增厚,形成碰撞造山带(李龚健, 2014; Liu and Hou, 2017);45~40Ma新特提斯洋岩石圈从印度大陆岩石圈断离,引发了硬碰撞(Deng et al., 2017a; Chung et al., 2005; 李龚健, 2014),三江地区挤压构造应力突然得到释放,引发金沙江-哀牢山缝合带下伏加厚的交代富集大陆岩石圈地幔的拆沉作用(李龚健, 2014; 蒋成竹, 2014; Deng et al., 2014b, 2017a);44~32Ma,三江地区进入拆沉伸展期(Deng et al., 2014b, 2017a; 李龚健,2014),沿金沙江-哀牢山缝合带形成了近一千千米的巨型钾质岩浆岩带。该钾质岩浆岩带,大致分为北部钾质岩浆带其年龄较老(49~34Ma)主要集中在玉龙地区(Hou et al., 2003; Liang et al., 2009; 伍静等, 2011; 李龚健, 2014),中部和南部钾质岩浆岩年龄较小(38~32Ma)大多分布在扬子地块西缘、兰坪盆地内部及绿春东南部(图 1, Hou et al., 2003; 毕献武等, 2005; 祝向平, 2010; 和文言等, 2014; Lu et al., 2012, 2013a, b, 2015; Deng et al., 2015a, b; Zhang et al., 2017)。
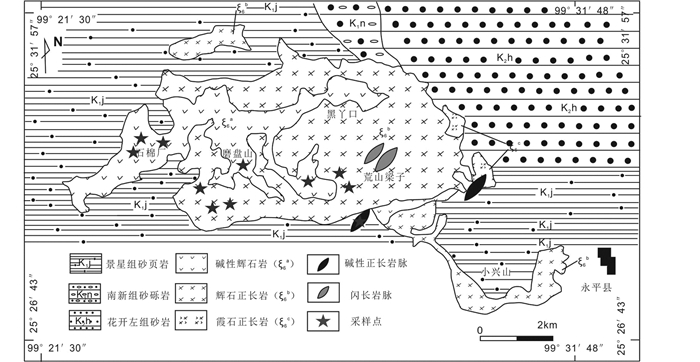
2 样品和分析方法 2.1 样品云南永平卓潘碱性杂岩体大地构造位置处于兰坪盆地西缘,是盆地内零星分布钾质岩浆岩的一部分,距永平县西北约5km。岩体呈近东西走向产出,侵入到兰坪盆地西部的白垩纪景星组砂岩,南新组砂砾岩及花开左组的砂岩中, 出露面积约40km2(李勇, 2012; 董方浏等, 2007)。岩体岩性主要由西部的碱性辉石岩(30%)和中东部的辉石正长岩(65%)组成,并有少量碱性正长岩和霞石正长岩(5%)沿岩体周围呈条带状或呈岩脉的方式分布。本次工作位置及取样点如图 2。
|
图 2 西南三江永平卓潘碱性杂岩体地质图 (据董方浏等, 2007修编) Fig. 2 Geological map of the Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping, Southwest China (after Dong et al., 2007) |
碱性辉石岩 手标本整体呈灰绿色,细粒-中粒半自形粒状结构,块状构造(图 3a)。主要矿物有透辉石(约85%)和正长石(约12%),次要矿物为极少量黑云母(约1%),副矿物(约2%)为磁铁矿等。其中透辉石为无色,粒径0.3~2.5mm,呈自形柱状和粒状,正高突起,干涉色二级蓝绿-橙黄(图 3b)。正长石为无色,粒径0.1~1.5mm,大小不等的他形粒状,可见卡式双晶,负低突起,干涉色为一级灰(图 3b);黑云母少见,褐色-深褐色,粒径0.05~0.1mm。磁铁矿为黑色,全消光,粒径0.1~0.2mm。

|
图 3 西南三江永平卓潘碱性杂岩体岩石学和岩相学特征 (a)正长辉石岩手标本照片;(b)碱性辉石岩中的柱状和粒状透辉石(+);(c)黑云辉石正长岩手标本照片;(d)黑云辉石正长岩镜下照片(+);(e)霓辉霞石正长岩手标本照片;(f)霓辉霞石正长岩镜下照片,横向裂纹的霞石,正长石发育卡式双晶,霓辉石环带周围为霓石(+).Or-正长石;Bt-黑云母;Agt-霓辉石;Aeg-霓石;Ne-霞石;Aug-普通辉石;Di-透辉石 Fig. 3 Photographs and micro-photographs of the Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping, Southwest China |
黑云辉石正长岩 手标本整体呈灰黑色,中细粒或中粗粒等粒结构,块状构造(图 3c)。主要矿物有正长石(约45%),普通辉石(约25%)和透辉石(约15%),次要矿物有黑云母(约10%),局部出现少量石榴石(3%),副矿物(约2%)为磁铁矿等。其中正长石为无色,粒径0.5~3mm,负低突起,干涉色为一级灰,部分发生较严重的泥化。普通辉石为浅绿色,多色性不明显,粒径0.5~2mm,正高突起,干涉色大多为一级暗灰到二级绿,明显发生黑云母化。透辉石为无色,粒径0.3~1mm,呈自形柱状和粒状,正高突起,干涉色一级灰到二级蓝绿,部分发生绿泥石化、黑云母化蚀变(图 3d)。黑云母多由辉石发生蚀变,因富铁而呈深褐色,多色性不明显,颗粒较大,粒径0.1~3.5mm。磁铁矿为黑色,全消光,粒径0.1~0.2mm。
霓辉霞石正长岩 手标本整体呈灰黑色,中细粒或中粗粒等粒结构,块状构造(图 3e)。主要矿物有正长石(约58%)、霞石(15%)和霓辉石(约15%)次要矿物有黑云母(约5%)和霓石(5%),局部可见少量榍石(1%)及磁铁矿(1%)。其中正长石为无色,粒径0.5~3mm,大小不等的不规则柱状,具有半定向流动构造,发育明显卡式双晶,负低突起,干涉色为一级灰白(图 3f);霞石无色,表面可见一组横向裂纹,粒径0.5~3mm,大小不等的他形柱状,负低突起,干涉色为一级灰,平行消光;霓辉石薄片中呈绿色,多色性较明显,粒径0.3~1.5mm,呈自形柱状和粒状,正高突起,干涉色从二级黄到三级蓝,部分矿物颜色呈环带状分布,自中心向边部绿色渐浓,其核部为富钙的透辉石或普通辉石,向边部渐变为富钠的霓辉石。霓石多色性明显,分布于霓辉石周围。黑云母为浅褐色-深褐色,多色性明显,粒径0.05~0.2mm,半自形片状,平行消光。磁铁矿为黑色,全消光,粒径0.05~0.1mm。
2.2 分析方法全岩粉末样品由河北廊坊宇能岩石矿物分选技术服务有限公司选择新鲜岩石,人工碎样等步骤,获得200目的新鲜全岩粉末样品,并选取部分作全岩主微量分析测试。全岩主微量测试分析在国家地质实验测试中心完成。主量元素使用X射线荧光光谱仪(PW4400)分析,采用GB/T 14506.28—2010标准。微量稀土元素在等离子质谱仪(PE300D)上分析测试,采用GB/T 14506.30—2010标准。
锆石的挑选是在河北省廊坊市宇能岩石矿物分选技术服务有限公司完成,具体挑选过程详见文献(李怀坤等, 2011)。锆石制靶及拍照工作均在北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成。锆石制靶筛选原则是挑选颗粒大、表面洁净,透明度高的锆石。挑选出的锆石在环氧树脂上制成样靶,并对锆石进行阴极发光、透射光、反射光拍照,做好分析锆石的结构特征以及定年的准备。锆石定年测试是在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室完成,同位素组成用锆石91500标样进行校正。具体LA-ICP-MS分析的方法流程及U-Th-Pb含量分析过程见Gao et al. (2002)。原位微区锆石Hf同位素比值测试在中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室(GPMR)利用激光剥蚀多接收杯等离子体质谱LA-MC-ICP-MS完成,详细的仪器操作条件和分析方法可见Hu et al. (2012)。数据的离线处理采用软件ICPMSDataCal(Liu et al., 2010)完成。
3 结果 3.1 全岩主量元素卓潘碱性杂岩体主量元素分析结果见表 1。正长辉石岩SiO2含量为50.79%,Al2O3含量为3.05%,其CaO和MgO含量明显高于其他样品值,分别为22.19%和11.63%,Mg#含量为0.78,P2O5含量2.3%,K2O+Na2O为2.04%,K2O/Na2O值为1.4,σ(里特曼指数)为0.5,为钙碱性岩。在TAS图解(图 4a)中落入辉长岩中,在SiO2-K2O图解(图 4b)中,样品落入钙碱性系区域,在SiO2-A/CNK图解(图 4d)中样品落入准铝质区域。
|
|
表 1 永平卓潘岩体主量(wt%)和微量(×10-6)元素测试结果 Table 1 The data of major elements (wt%) and trace elements (×10-6) of the Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping |

|
图 4 西南三江永平永平卓潘碱性杂岩体图解 (a) TAS(Wilson, 1989);(b) SiO2-K2O(Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976);(c) SiO2-K2O+Na2O(Wilson, 1989);(d) A/CNK-SiO2(Kemp and Hawkesworth, 2003) Fig. 4 Diagrams of the Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping, Southwest China |
辉石正长岩SiO2含量变化范围为46.72%~48.16%,Al2O3含量变化范围为10.90%~12.54%,显示出高铝的特征,TiO2含量变化范围为1.01%~1.05%,CaO(11.50%~13.24%)和MgO(6.42%~7.89%)含量相对正长辉石岩含量较低,Mg#含量变化范围0.59~0.67,P2O5含量变化范围1.11%~1.31%,K2O+Na2O为7.33%~8.53%,K2O/Na2O值范围3.04~4.64,σ(里特曼指数)为8.35~14.66,为一套碱性-过碱性岩石。在TAS图解(图 4a)中落入正长-闪长岩中,在SiO2-K2O图解(图 4b)中,样品落入钾玄岩系列,在SiO2-A/CNK图解(图 4d)中样品落入准铝质区域。
正长岩SiO2含量为56.53%,Al2O3含量为15.29%,TiO2含量为0.87%,CaO含量为5.86%,MgO含量为3.23%,Mg#含量为0.54,P2O5含量为0.56%,K2O+Na2O为10.22%,K2O/Na2O值为1.99,σ(里特曼指数)为7.36,为一套钙碱性-碱性岩石。在TAS图解(图 4a)中落入正长岩中,在SiO2-K2O图解(图 4b)中,样品落入钾玄岩系列, 在SiO2-A/CNK图解(图 4d)中样品落入准铝质区域。
霞石正长岩SiO2含量为53.85%,Al2O3含量为18.36%,显示出高铝的特征,TiO2含量为0.79%,CaO(4.38%)和MgO(2.11%)含量较其他几种岩性含量最低,Mg#含量为0.46,P2O5含量为0.28%,K2O+Na2O含量为12.82%,K2O/Na2O值为1.84,σ(里特曼指数)为14.09,为一套过碱性岩石。在TAS图解(图 4a)中正好落入霞石正长岩区域中,在SiO2-K2O图解(图 4b)中,样品落入钾玄岩系列,在SiO2-A/CNK图解(图 4d)中样品落入准铝质区域。
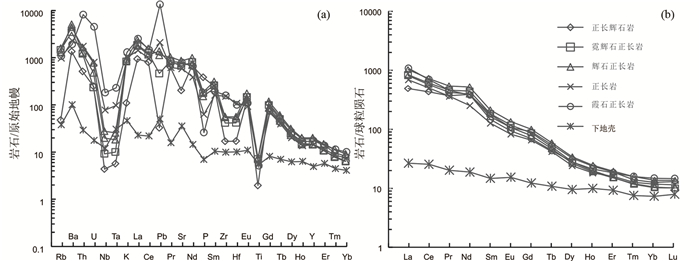
3.2 全岩稀土和微量元素卓潘碱性杂岩体稀土和微量元素分析结果见表 1。由表可知,正长辉石岩、辉石正长岩、正长岩和霞石正长岩中稀土元素总量分别为835.3×10-6、1037×10-6~1326×10-6、836.4×10-6和1192×10-6,∑LREE/∑HREE比值分别为17.7、26.5~26.6、23.8和30.7。(La/Yb)N值分别为38.2、73.0~80.3、56.7和70.5,均表现出轻稀土强烈富集、重稀土亏损的特征。经球粒陨石标准化后的稀土元素配分模式图(图 5b),为明显的右倾平滑曲线。δEu变化范围分别为0.82、0.90~0.92、0.89和0.90,显示Eu负异常不明显或无Eu负异常。
|
图 5 西南三江永平卓潘碱性杂岩体原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(a, 标准化值据McDonough et al., 1992)和球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线(b, 标准化值据Boynton, 1984) 下地壳数据组成引自Rudnick and Gao (2003) Fig. 5 Primitive mantle normalized multi-element diagrams (a, normalization values after McDonough et al., 1992) and chondrite-normalized rare earth element patterns (b, normalization values after Boynton, 1984) for Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping, Southwest China |
卓潘岩体微量元素原始地幔标准化图解中,正长辉石岩、辉石正长岩、正长岩和霞石正长岩均显示富集Rb、Pb、Th、U、Ba、Sr、K等大离子亲石元素(LILE),且富集倍数较高,而Ta、Nb、Ti、P等高场强元素(HFSE)显著亏损,其中Ti、Nb、Ta亏损尤其明显,即表现为明显的“TNT”负异常(图 5a)。
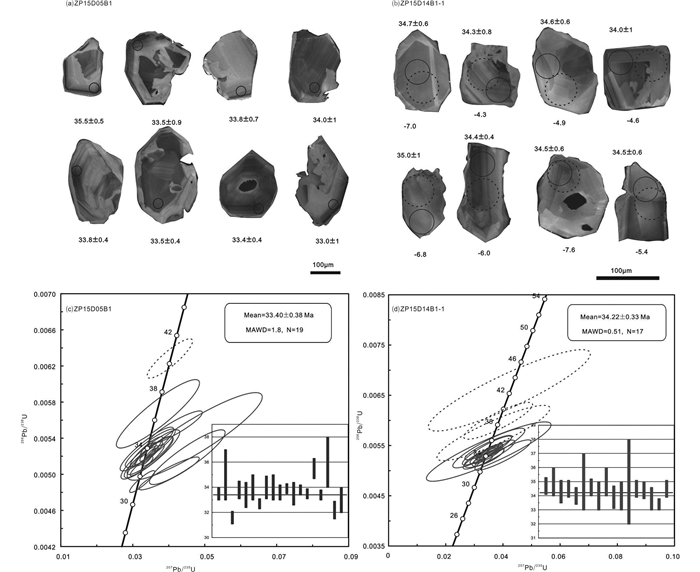
3.3 锆石U-Pb年龄本文对卓潘碱性杂岩体的正长岩(ZP15D05B1)和正长辉石岩(ZP15D14B1-1)2个样品进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年。锆石的年龄见表 2。正长岩样品中,锆石基本为自形-半自形的结构,长约110~200μm,长短轴比在1~3之间,锆石CL图像中可见振荡环带,但不明显(图 6a)。共选20个锆石颗粒进行U/Pb分析,得出锆石中Th含量变化范围较大,在53.30×10-6~3803×10-6之间,U含量在151.9×10-6~1212×10-6之间,锆石Th/U比值为0.31~3.94(表 2)均大于0.1,而且锆石的球粒陨石标准化稀土配分曲线表现为:轻稀土亏损,逐步富集重稀土元素,同时显示Ce的正异常和弱Eu的负异常(图 7a),表明它们均属于典型的岩浆成因锆石(吴元保和郑永飞, 2004; Hoskin and Schaltegger, 2003)。测定的20个点中,1个分析点存在明显Pb丢失,其余19个点的206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为33.40±0.38Ma(MSWD=1.8,图 6c)。
|
|
表 2 永平卓潘岩体正长岩(ZP15D05B1)和正长辉石岩(ZP15D14B1-1)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb分析结果 Table 2 LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb analytical data of the syenites (ZP15D05B1) and pyroxenolites (ZP15D14B1-1) from the Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping |
|
图 6 西南三江永平卓潘碱性杂岩体锆石CL及U-Pb年龄 图a, b中实线代表年龄测试点位;虚线代表Hf同位素测试点 Fig. 6 Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of representative analyzed zircons from the Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping, Southwest China |
|
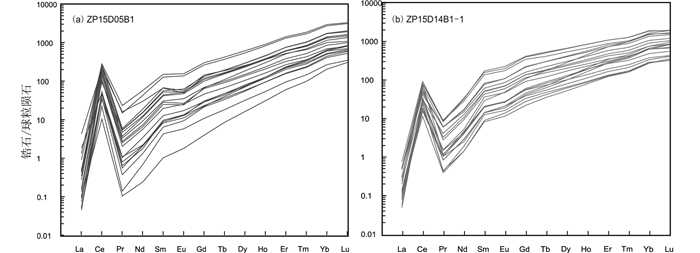
图 7 西南三江永平卓潘碱性杂岩体锆石球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线 (标准化值据Boynton, 1984) Fig. 7 Chondrite-normalized rare earth element (REE) patterns of zircons for the Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping, Southwest China (normalization values after Boynton, 1984) |
正长辉石岩锆石多为透明的自形-半自形的结构,长约110~200μm,短轴比在1~2之间,锆石CL图像可见不明显的振荡环带(图 6b)。共选20个锆石颗粒进行U/Pb分析,得出Th含量变化范围较大,54.94×10-6~4857×10-6,U含量在65.1×10-6~2027×10-6,锆石Th/U比值为0.46~4.35均大于0.1(表 2),且锆石的球粒陨石标准化稀土配分曲线表现为:轻稀土亏损,逐步富集重稀土元素,同时显示Ce的正异常和弱Eu的负异常(图 7b),表明它们均属于典型的岩浆成因锆石(吴元保和郑永飞, 2004; Hoskin and Schaltegger, 2003)。测定的20个点,其中3个分析点存在明显Pb丢失,未能获得协和年龄,其余17个点206Pb/238U加权年龄平均值为34.22±0.33Ma(MSWD=0.51,图 6d)。
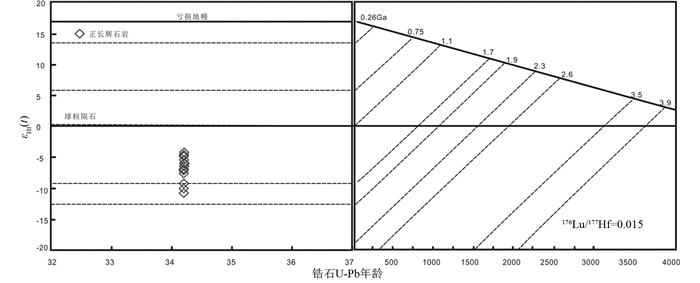
3.4 锆石Hf同位素本文对卓潘碱性杂岩体的正长辉石岩(ZP15D14B1-1)样品进行了锆石Hf同位素测试,锆石Hf同位素结果见表 3。正长辉石岩的15颗锆石的176Yb/177Hf和176Lu/177Hf比值范围分别为0.010074~0.104147和0.000240~0.002131,176Hf/177Hf值介于0.282464~0.282644之间。15颗锆石εHf(t)值介于-10.6~-4.3之间,集中于-7~-4.6,对应的Hf同位素地壳模式年龄tDMC在1356~1759Ma之间,集中于1.36~1.57Ga(图 8)。
|
|
表 3 永平卓潘碱性杂岩体正长辉石岩锆石Hf同位素 Table 3 Zircon Hf isotopic data of pyroxenolites in the Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping |
|
图 8 西南三江永平卓潘碱性杂岩体锆石εHf(t)值与U-Pb年龄图解 Fig. 8 Plots of zircon U-Pb age vs. εHf(t) for Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping, Southwest China |
两组锆石的内部结构、稀土特征以及大于0.1的Th/U比值(吴元保和郑永飞, 2004; Hoskin and Schaltegger, 2003)表明卓潘碱性杂岩体锆石均为岩浆锆石,各样品的加权平均年龄基本可以代表岩石的结晶年龄。本文获得2组卓潘碱性杂岩体锆石的加权平均年龄分别为33.40±0.38Ma(ZP15D05B1)和34.22±0.33Ma(ZP15D14B1-1),在误差范围内样品ZP15D05B1年龄与ZP15D14B1-1年龄基本一致。本文的锆石U-Pb年龄数据表明卓潘碱性杂岩体侵位时间~34Ma,这与前人40Ar/39Ar法获得该岩体36.7Ma(董方浏等, 2005)侵位年龄基本一致。卓潘碱性杂岩体属于金沙江-哀牢山钾质岩浆带的中南段,其获得的年龄与其他中南段钾质岩体,如扬子西缘的姚安(36~33Ma)、北衙(38~34Ma)、六合(~34Ma)、马厂箐(37~33Ma),盆地东缘的莲花山(~34Ma),哀牢山缝合带南部的哈播(~36Ma)等年龄基本一致(图 1, 张玉泉等, 1998; 刘金宇等, 2017; 梁华英等, 2004; 肖晓牛等, 2009; 邓军等, 2010, 2011; 李勇等, 2011; 和文言等, 2014; Lu et al., 2012, 2013a, b, 2015; Deng et al., 2014a, b, 2017a, b; 杜斌, 2017),同属于“三江”拆沉伸展期(44~32Ma)岩浆活动的产物。
4.2 岩浆岩成因与源区卓潘碱性杂岩体4种岩性的稀土配分曲线和微量元素原始地幔标准化图解基本一致,表明岩体不同类型的岩石是同源岩浆演化的产物(图 5)。岩体在SiO2-K2O+Na2O岩浆结晶分异图解中,显示岩浆具有结晶分异的特征(图 4c)。Harker图解中,正长辉石岩、辉石正长岩、正长岩、霞石正长岩的TiO2、MgO、CaO、Fe2O3T、Al2O3、P2O5等氧化物与SiO2均呈良好线性关系,暗示了这几种岩性的岩浆具有同源性(图 9)。

|
图 9 西南三江永平卓潘碱性杂岩体主量哈克图解 Fig. 9 Harker variation diagrams showing the major element compositions of the Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping, Southwest China |
研究区岩体K2O/Na2O值在1.40~4.64之间,K2O+Na2O含量除正长辉石岩外,其余K2O+Na2O含量在7.33%~12.82%之间,具有高钾富碱的特征,岩石属于钾玄岩系列;正长辉石岩在SiO2-K2O图解(图 4b)中,样品落入钙碱性系区域,这是由于岩石中的辉石主要为含Ca量较多的钙质辉石即透辉石和钙铁辉石。
岩体微量元素(图 5)显亏损高场强元素Ta、Nb、Ti,产生这种地球化学特征原因可能为:(1)源区存在俯冲带流体的交代作用(Donnelly et al., 2004; Tatsumi et al., 1986);(2)岩浆上升过程中与地壳的混染(Bernard-Griffiths et al., 1991; Huang et al., 2010; Nelson et al., 1986)。本文所有样品中Nb/La值为0.02~0.13,而原始地幔的Nb/La值接近1,地壳的Nb/La平均值为0.5(Sun and McDonough, 1989),样品的Nb/La值明显低于地壳的Nb/La值,表明样品的Ta、Nb、Ti负异常不是由地壳混染造成的。大量研究认为钾质或超钾质岩的形成与被俯冲的洋壳或陆壳沉积物的流体或熔融体与岩石圈地幔的交代富集作用有关(Nelson, 1992),因此岩体显著亏损Ta-Nb-Ti的地球化学特征反映了源区的形成可能与洋壳俯冲交代的流体有关。本文样品富集轻稀土(LREE)、大离子亲石元素(LILE)和亏损高场强元素(HFSE)的地球化学特征与岛弧岩浆的地球化学特征一致(Müller et al., 1992; Thirlwall et al., 1994; Sun and Kerrich, 1995; Lu et al., 2015),进一步证明岩浆源区的形成可能与洋壳的俯冲交代有关。岩体的Nb/U均值为2.95介于俯冲带流体(Nb/U≈0.22; Ayers, 1998)和全球俯冲沉积物(Nb/U≈5, Plank and Langmuir, 1998)之间,这进一步证明岩浆源区存在俯冲的洋壳或陆壳沉积物的流体或熔融体与岩石圈地幔的交代富集作用。
岩体岩浆锆石Hf同位素εHf(t)值介于-10.6~-4.3之间,显示了Hf同位素较富集的特征。锆石Hf同位素二阶段模式年龄在1.36~1.76Ga之间,明显早于新生代富钾岩石形成时间~34Ma,因此我们认为岩浆源区受到过地壳物质的混染或者来自于富集性地幔(吴福元等, 2007; Wang et al., 2017a)。前人对卓潘岩体的Sr-Nd-Pb的研究发现岩浆源区具有EMⅡ富集地幔端元的特征(董方浏等, 2007; 陈喜峰等, 2015),因此我们认为岩浆源区来自于富集性地幔。EMⅡ与上部的大陆地壳有一定的亲缘关系,可能代表了陆源沉积物、大陆地壳、蚀变的洋壳或者洋岛玄武岩的再循环作用(李勇, 2012),因此所测的锆石εHf(t)值具有壳源物质的属性。
结合岩石地球化学特征及锆石Hf同位素特征,我们认为卓潘碱性杂岩体钾质岩浆来源于俯冲交代富集的岩石圈地幔。富集地幔的物质可能来源于扬子西缘的太古代-元古代的变质褶皱基地和元古代的沉积盖,也可能为蚀变交代的洋壳,本文在这不作详细讨论。
金沙江-哀牢山缝合带钾质岩浆岩的形成与侵位年龄在45~32Ma,明显早于金沙江-红河断裂带的走滑断裂形成时间(32~20Ma),显然钾质岩浆岩的主体不可能受控于走滑断裂活动(李龚健, 2014; 蒋成竹, 2014; Deng et al., 2014b),因此,金沙江-哀牢山的走滑模型不足以解释岩石的成因。此外,岩体的Nb/U均值介于俯冲带流体(Nb/U≈0.22; Ayers, 1998)和全球俯冲沉积物(Nb/U≈5, Plank and Langmuir, 1998)之间,这表明岩浆源区具有洋壳交代的岩石圈地幔的特征,这与大陆俯冲模型的岩石成因形成环境相悖。因此,大陆俯冲模型不能解释研究区钾质岩浆岩的成因。本文认为研究区的成因模式为俯冲交代的大陆岩石圈地幔拆沉减薄模型,证据如下:(1)岩体具有Nb/U均值为2.95,明显低于洋中脊玄武岩和洋岛玄武岩;(2)理论依据:造山带产生岩浆作用,最有可能是岩石圈底部发生拆沉作用(Ding et al., 2003; Chung et al., 2005);(3)地球物理资料显示在新生代研究区存在软流圈地幔物质的上涌(刘建华等, 1989; 钟大赉等, 2000)。
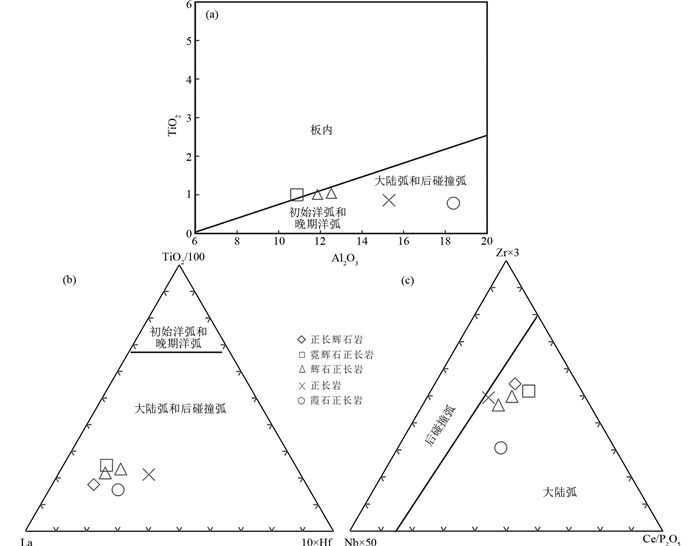
4.3 构造环境及大陆动力学背景卓潘碱性杂岩体SiO2含量为46.72%~56.53%,K2O含量在1.19%~8.30%之间,Na2O含量为0.85%~4.52%,K2O/Na2O值范围1.40~4.64均属于钾质火成岩范畴(Müller et al., 1992; 赵振华, 2007)。由于钾质火成岩显著富钾,亏损Ti、Nb、Ta等高场强元素,使用原已建立的玄武岩和花岗岩图解容易误判岩浆产生的构造环境,因此需要使用特殊类型的构造环境判别图解(Eby, 1992; Müller et al., 1992)。首先在TiO2-Al2O3(图 10a)卓潘碱性杂岩体落在弧与板内交界处,甚至有一个点跨入板内区域。其次在TiO2/100-La-Hf×10图解中(图 10b),岩体均落入大陆弧和后碰撞弧环境。最后在Zr×3-Nb×50-Ce/P2O5图解中(图 10c),岩体样品点全部落入大陆弧环境。需要指出的是:(1)研究区的岩浆活动正处于喜山运动晚期碰撞期(后碰撞初期),印度板块以一定角度向扬子板块斜向碰撞俯冲,导致显示大陆弧的构造环境(王建等, 2003);(2)源区受到过古特提斯大洋俯冲板片的富集交代作用,使Ce/P2O5含量相对较大,造成了样品投点由后碰撞弧环境跨越大陆弧环境(王建等, 2003; 胡晓佳, 2012)。本文测得岩体的年龄~34Ma,此时滇西地区正处于印度板块向欧亚大陆的俯冲和碰撞的后碰撞早期(40~26Ma)(王成善等, 2003),使得滇西地区受到持续的挤压,地壳和岩石圈均发生增厚(Wang et al., 2001; 莫宣学, 2011; 侯增谦, 2010)基于。以上原因,我们认为卓潘碱性杂岩体形成的构造环境更接近后碰撞弧,同时兼有大陆弧特征。
|
图 10 西南三江永平卓潘碱性杂岩体岩浆源区及构造判别图解 (据Müller et al., 1992) Fig. 10 Diagrams of discrimination for tectonic setting for Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping, Southwest China (after Müller et al., 1992) |
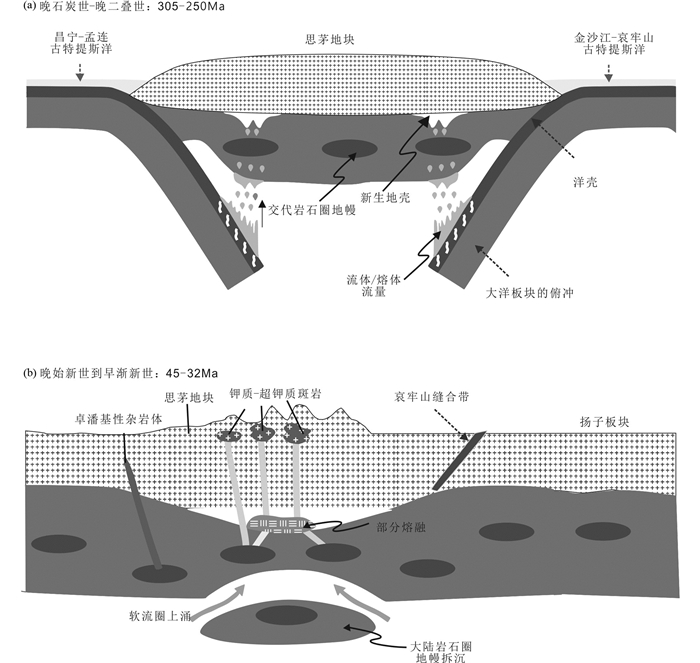
晚石炭世-晚二叠世(305~250Ma),古特提斯昌宁-孟连洋和古特提斯金沙江-哀牢山洋分别向东、西俯冲于思茅地块之下(Jian et al., 2009; Deng et al., 2014a, b; Wang et al., 2015; 王长明等, 2017),大洋板片及俯冲的沉积物发生脱水熔融,形成的熔体/流体向上运移交代上部地幔楔,形成交代富集的地幔。古近世-始渐新世,印度-欧亚陆陆碰撞使三江地区遭受强烈的挤压作用发生逆冲与褶皱,同时地壳在原有特提斯造山作用的基础上进一步增厚(李龚健, 2014; Chung et al., 2005);45~40Ma新特提斯洋岩石圈从印度大陆岩石圈断离,引发了硬碰撞(李龚健, 2014; Chung et al., 2005; Deng et al., 2017a)三江地区挤压构造应力突然得到释放,引发金沙江-哀牢山缝合带下伏加厚的交代富集大陆岩石圈地幔的拆沉作用(李龚健, 2014; 蒋成竹, 2014; Deng et al., 2014b, 2017a)。44~32Ma,三江地区进入拆沉伸展期(Deng et al., 2014b; 李龚健, 2014),热的软流圈上涌,熔融残留下来富钾的岩石圈地幔,岩浆侵位分异形成卓潘岩体。
基于以上讨论我们建立卓潘碱性杂岩体的岩浆作用模型(图 11)。在晚石炭世-晚二叠世古特提斯洋昌宁-孟连洋和古特提斯金沙江-哀牢山洋开始分别向东、向西俯冲于思茅地块之下,受俯冲板片的影响,思茅地块的岩石圈地幔发生富集作用。45~40Ma新特提斯洋岩石圈从印度大陆岩石圈断离,引发了硬碰撞使得金沙江-哀牢山缝合带下伏加厚的交代富集岩石圈地幔发生拆沉作用。在44~32Ma,拆沉作用导致热的软流圈上涌,熔融富集交代的岩石圈地幔,岩浆侵位分异形成卓潘岩体。
|
图 11 西南三江永平卓潘碱性杂岩体岩浆作用模式图 (据Deng et al., 2014b修改) Fig. 11 Schematic illustration of the petrogenesis of Zhuopan intrusion in Yongping, Southwest China (after Deng et al., 2014b) |
(1) 卓潘碱性杂岩体具有富碱高钾,准铝质-铝质特征,富集大离子亲石元素和轻稀土元素,高Pb的正异常,显著亏损高场强元素(HFSE),Eu负异常不明显,εHf(t)值介于-10.6~-4.3之间,Hf的模式年龄1.36~1.76Ga之间。
(2) 卓潘碱性杂岩体的正长岩和正长辉石岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年,年龄分别为33.40±0.38Ma和34.22±0.33Ma,厘定卓潘碱性杂岩体侵位时间为~34Ma。
(3) 岩体不同岩性的稀土配分曲线和微量元素原始地幔标准化图解基本一致,表明卓潘碱性杂岩体不同类型的岩石是同源岩浆演化的产物。Nb/U值和亏损Ti、Nb、Ta高场强元素以及Hf同位素特征暗示岩浆源区来源于俯冲交代富集的岩石圈地幔。
(4) 建立了卓潘碱性杂岩体的岩浆模式:晚石炭世-晚二叠世古特提斯洋东西向双向俯冲,形成富集岩石圈地幔;在新生代,印度板块与欧亚大陆的碰撞,导致富集岩石圈地幔拆沉,热的软流圈熔融交代富集的岩石圈地幔,岩浆侵位分异形成卓潘碱性杂岩体。
致谢 论文的完成得益于邓军教授等老师的指导。实验过程中得到了国家地质实验测试中心、西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室和中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室帮助。在此一并感谢。
Arnaud NO, Vidal P, Tapponnier P, Matte P and Deng WM. 1992. The high K2O volcanism of northwestern Tibet:Geochemistry and tectonic implications. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 111(2-4): 351-367. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(92)90189-3 |
Ayers J. 1998. Trace element modeling of aqueous fluid-peridotite interaction in the mantle wedge of subduction zones. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 132(4): 390-404. DOI:10.1007/s004100050431 |
Bernard-Griffiths J, Fourcade S and Dupuy C. 1991. Isotopic study (Sr, Nd, O and C) of lamprophyres and associated dykes from TAMazert (Morroco):Crustal contamination processes and source characteristics. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 103(1-4): 190-199. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(91)90160-J |
Bi XW, Hu RZ, Peng JT, Wu KX, Su WC and Zhan XZ. 2005. Geochemical characteristics of the Yao'an and Machangqing alkaline-rich intrusions. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(1): 113-124. |
Boynton WV. 1984. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies. In: Henderson P (ed. ). Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 63-114
|
Chen JL, Xu JF, Wang BD, Kang ZQ and Jie L. 2010. Origin of Cenozoic alkaline potassic volcanic rocks at Konglongxiang, Lhasa terrane, Tibetan Plateau:Products of partial melting of a mafic lower-crustal source?. Chemical Geology, 372(3-4286): 299. |
Chen JL, Zhao WX, Xu JF, Wang BD and Kang ZQ. 2012. Geochemistry of miocene trachytes in Bugasi, Lhasa block, Tibetan Plateau:Mixing products between mantle-and crust-derived melts?. Gondwana Research, 21(1): 112-122. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.06.008 |
Chen XF, Zeng PS, Zhang XT, Xu WR and Wan DF. 2015. Petrology and geochemistry of the Zhuopan alkaline complex in Yongping, Yunnan Province:Constraints on petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(9): 2597-2608. |
Chung SL, Chu MF, Zhang YQ, Xie YW, Lo CH, Lee TY, Lan CY, Li XH, Zhang Q and Wang YZ. 2005. Tibetan tectonic evolution inferred from spatial and temporal variations in post-collisional magmatism. Earth-Science Reviews, 68(3-4): 173-196. |
Deng J, Yang LQ, Ge LS, Yuan SS, Wang QF, Zhang J, Gong QJ and Wang CM. 2010. Character and post-ore changes, modifications and preservation of Cenozoic alkali-rich porphyry gold metallogenic system in western Yunnan, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(6): 1633-1645. |
Deng J, Yang LQ and Wang CM. 2011. Research advances of superimposed orogenesis and metallogenesis in the Sanjiang Tethys. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2501-2509. |
Deng J, Wang CM and Li GJ. 2012. Style, process of the superimposed mineralization in the Sanjiang Tethys. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(5): 1349-1361. |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ, Li CS and Wang CM. 2014a. Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region, SW China. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 419-437. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.08.002 |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ and Santosh M. 2014b. Cenozoic tectono-magmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China. Earth-Science Reviews, 138: 268-299. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.05.015 |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ, Hou ZQ, Jiang CZ and Danyushevsky L. 2015a. Geology and genesis of the giant Beiya porphyry-skarn gold deposit, northwestern Yangtze Block, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 70: 457-485. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.02.015 |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ and Zhao Y. 2015b. Structural control and genesis of the Oligocene Zhenyuan orogenic gold deposit, SW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 42-54. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.08.002 |
Deng J and Wang QF. 2016. Gold mineralization in China:Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Research, 36: 219-274. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.003 |
Deng J, Wang QF and Li GJ. 2017a. Tectonic evolution, superimposed orogeny, and composite metallogenic system in China. Gondwana Research, 50: 216-266. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.02.005 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Selvaraja V, Jeon H, Wu B and Yang LF. 2017b. Insights into ore genesis of the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan Province, China:Evidence from Zn and in-situ S isotopes. Ore Geology Reviews, 90: 943-957. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.036 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Zi JW, Xia R and Li Q. 2017c. Constraining subduction-collision processes of the Paleo-Tethys along the Changning-Menglian Suture:New zircon U-Pb ages and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf-O isotopes of the Lincang Batholith. Gondwana Research. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.10.008 |
Deng WM, Huang X and Zhong DL. 1998. Alkali-rich porphyry and its relation with intraplate deformation of north part of Jinsha River belt in western Yunnan, China. Science in China (Seies D), 41(3): 297-305. DOI:10.1007/BF02973119 |
Ding L, Kapp P, Zhong DL and Deng WM. 2003. Cenozoic volcanism in Tibet:Evidence for a transition from oceanic to continental subduction. Journal of Petrology, 44(10): 1833-1865. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egg061 |
Dong FL, Mo XX, Hou ZQ, Wang Y, Bi XM and Zhou X. 2005. 40Ar/39Ar ages of Himalayan alkaline rocks in Lanping Basin, Yunnan Province, and their geological implications. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 24(2): 103-109. |
Dong FL, Mo XX, Yu XH, Hou ZQ and Wang Y. 2007. Trace elements geochemical and Nd-Sr-Pb isotopes characteristics of the Zhuopan alkaline complex in Yongping, Yunnan Province and its geological significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(5): 986-994. |
Donnelly KE, Goldstein SL, Langmuir CH and Spiegelman M. 2004. Origin of enriched ocean ridge basalts and implications for mantle dynamics. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 226(3-4): 347-366. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2004.07.019 |
Du B, Wang CM, He XY, Yang LF, Chen JY, Shi KX, Luo Z and Xia JS. 2016. Advances in research of bulk-rock Nd and zircon Hf isotopic mappings:Case study of the Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2555-2570. |
Du B. 2017. Magma source, formation mechanism and tectonic significance of the Dalianhuashan and Zhuopan plutons, Yunnan Province. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences: 1-78.
|
Eby GN. 1992. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:Petrogenetic and tectonic implications. Geology, 20(7): 641-644. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2 |
Flower MFJ, Hoàng N, Lo CH, Chí CT, Cu'ò'ng NQ, Liu FT, Deng JF and Mo XX. 2013. Potassic magma genesis and the Ailao Shan-Red River fault. Journal of Geodynamics, 69: 84-105. DOI:10.1016/j.jog.2012.06.008 |
Gao S, Liu XM, Yuan HL, Hattendorf B, Günther D, Chen L and Hu SH. 2002. Determination of forty two major and trace elements in USGS and NIST SRM glasses by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 26(2): 181-196. DOI:10.1111/ggr.2002.26.issue-2 |
Ge LS, Zou YL, Xing JB, Wang ZH and Guo XD. 2004. Gold mineralization system related to alkali-rich porphyries in Himalayan, the northwestern part of Yunnan. Gold Geology, 10(1): 39-47. |
Guo ZF, Hertogen J, Liu JQ, Pasteels P, Boven A, Punzalan L, He HY, Luo XJ and Zhang WH. 2005. Potassic magmatism in western Sichuan and Yunnan provinces, SE Tibet, China:Petrological and geochemical constraints on petrogenesis. Journal of Petrology, 46(1): 33-78. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egh061 |
Guo ZF, Wilson M, Liu JQ and Mao Q. 2006. Post-collisional, potassic and ultrapotassic magmatism of the Northern Tibetan Plateau:Constraints on characteristics of the mantle source, geodynamic setting and uplift mechanisms. Journal of Petrology, 47(6): 1177-1220. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egl007 |
Guo ZF, Wilson M, Zhang ML, Cheng ZH and Zhang LH. 2013. Post-collisional, K-rich mafic magmatism in South Tibet:Constraints on Indian slab-to-wedge transport processes and plateau uplift. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 165(6): 1311-1340. DOI:10.1007/s00410-013-0860-y |
Guo ZF, Wilson M, Zhang ML, Cheng ZH and Zhang LH. 2015. Post-collisional ultrapotassic mafic magmatism in South Tibet:Products of partial melting of pyroxenite in the mantle wedge induced by roll-back and delamination of the subducted Indian continental lithosphere slab. Journal of Petrology, 56(7): 1365-1406. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egv040 |
He KZ, He HS and Cai HB. 1996. Formation and evolution of the western Yunnan orogenic belt. Geological Review, 42(2): 97-106. |
He WY, Mo XX, Yu XH, Dong GC, He ZH, Huang XF, Li XW and Jiang LL. 2014. Genesis and geodynamic settings of lamprophyres from Beiya, western Yunnan:Constraints from geochemistry, geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(11): 3287-3300. |
Hoskin PWO and Schaltegger U. 2003. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 27-62. DOI:10.2113/0530027 |
Hou ZQ, Ma HW, Zaw K, Zhang YQ, Wang MJ, Wang Z, Pan GT and Tang RL. 2003. The Himalayan Yulong porphyry copper belt:Product of large-scale strike-slip faulting in eastern Tibet. Economic Geology, 98(1): 125-145. |
Hou ZQ. 2010. Metallogensis of continental collision. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(1): 30-58. |
Hu XJ. 2012. Petrogenesis and geological significance of Cenozoic K-rich intermediate-acid plutons along Ailao Shan-Red River fault Zone. Master Degree Thesis. Xi'an: Northwest University: 1-87.
|
Hu ZC, Liu YS, Gao S, Liu WG, Zhang W, Tong XR, Lin L, Zong KQ, Li M, Chen HH, Zhou L and Yang L. 2012. Improved in situ Hf isotope ratio analysis of zircon using newly designed X skimmer cone and jet sample cone in combination with the addition of nitrogen by laser ablation multiple collector ICP-MS. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 27(9): 1391-1399. DOI:10.1039/c2ja30078h |
Huang XL, Niu YL, Xu YG, Chen LL and Yang QJ. 2010. Mineralogical and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of post-collisional potassic and ultrapotassic rocks from western Yunnan, SW China. Journal of Petrology, 51(8): 1617-1654. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egq032 |
Jian P, Liu DY, Kröner A, Zhang Q, Wang YZ, Sun XM and Zhang W. 2009. Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in southwest China (Ⅱ):Insights from zircon ages of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks and generation of the Emeishan CFB province. Lithos, 113(3-4): 767-784. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.006 |
Jiang CZ. 2014. Potassic magmatism and ore-forming processes of the Beiya gold deposit in western Yunnan. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences: 1-158.
|
Kemp AIS and Hawkesworth CJ. 2003. Granitic perspectives on the generation and secular evolution of the continental crust. Treatise on Geochemistry, 3: 349-410. |
Leloup PH, Lacassin R, Tapponnier P, Schärer U, Zhong DL, Liu XH, Zhang LC, Ji SC and Trinh PT. 1995. The Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone (Yunnan, China), Tertiary transform boundary of Indochina. Tectonophysics, 251(1-4): 3-10, 13-84. DOI:10.1016/0040-1951(95)00070-4 |
Li GJ, Wang QF, Yu L, Hu ZC, Ma N and Huang YH. 2013. Closure time of the Ailaoshan Paleo-Tethys Ocean:Constraints from the zircon U-Pb dating and geochemistry of the Late Permian granitoids. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(11): 3883-3900. |
Li GJ. 2014. Tethys tectonic evolution and metallogenesis of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang Region, SW China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosiences: 1-179.
|
Li GJ, Wang QF, Huang YH, Chen FC and Dong P. 2015. Discovery of Hadean-mesoarchean crustal materials in the northern Sibumasu block and its significance for Gondwana reconstruction. Precambrian Research, 271: 118-137. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2015.10.003 |
Li GJ, Wang QF, Huang YH, Gao L and Yu L. 2016. Petrogenesis of middle ordovician peraluminous granites in the Baoshan block:Implications for the Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution along East Gondwana. Lithos, 245: 76-92. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.10.012 |
Li HK, Su WB, Zhou HY, Geng JZ, Xiang ZQ, Cui YR, Liu WC and Lu SN. 2011. The base age of the Changchengian System at the northern North China Craton should be younger than 1670Ma:Constraints from zircon U-Pb LA-MC-ICPMS dating of a granite-porphyry dike in Miyun County, Beijing. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(3): 108-120. |
Li TJ, Zhang J, Tong ZD and Pan ZW. 2017. Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of the Zhuopan alkaline complex in Yunnan Province and their geological significance. Geoscience, 31(3): 474-485. |
Li Y, Mo XX, Yu XH, Huang XK and He WY. 2011. Zircon U-Pb Dating of several selected alkali-rich porphyries from the Jinshajiang-Ailaoshan fault zone and geological significance. Geoscience, 25(2): 189-200. |
Li Y. 2012. Geochronology, petrogenesis and geological significance of the Cenozic potassic magmatic rocks in Sanjiang area, western Yunnan. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences: 1-119.
|
Liang HY, Xie YW and Zhang YQ. 2004. Influence of formation and evolution of potassium-rich alkaline rocks on copper mineralization:Case study of the Machangjing. Progress in Natural Science, 14(1): 118-120. |
Liang HY, Campbell IH, Allen CM, Sun WD, Yu HX, Xie YW and Zhang YQ. 2007. The age of the potassic alkaline igneous rocks along the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone:Implications for the onset age of left-lateral shearing. The Journal of Geology, 115(2): 231-242. DOI:10.1086/510801 |
Liang HY, Sun WD, Su WC and Zartman RE. 2009. Porphyry copper-gold mineralization at Yulong, China, promoted by decreasing redox potential during magnetite alteration. Economic Geology, 104(4): 587-596. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.104.4.587 |
Liu CZ, Wu FY, Chung SL and Zhao ZD. 2011. Fragments of hot and metasomatized mantle lithosphere in Middle Miocene ultrapotassic lavas, southern Tibet. Geology, 39(10): 923-926. DOI:10.1130/G32172.1 |
Liu JH, Liu FT, Wu H, Li Q and Hu G. 1989. Three dimensional velocity images of the crust and upper mantle beneath north-south zone in China. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 32(2): 143-152. |
Liu JY, Deng J, Li GJ, Xiao CH, Meng FJ, Chen FC, Wu W and Zhang QW. 2017. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the Lianhuashan intrusion in the Lanping Basin, western Yunnan:Constraints from bulk element composition, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(7): 2115-2128. |
Liu Y and Hou ZQ. 2017. A synthesis of mineralization styles with an integrated genetic model of carbonatite-syenite-hosted REE deposits in the Cenozoic Mianning-Dechang REE metallogenic belt, the eastern Tibetan Plateau, southwestern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 137: 35-79. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.01.010 |
Liu YS, Gao S, Hu ZC, Gao CG, Zong KQ and Wang DB. 2010. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2): 537-571. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egp082 |
Lu YJ, Kerrich R, Cawood PA, McCuaig TC, Hart CJR, Li ZX, Hou ZQ and Bagas L. 2012. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of potassic felsic intrusions in western Yunnan, SW China:Constraints on the relationship of magmatism to the Jinsha suture. Gondwana Research, 22(2): 737-747. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.11.016 |
Lu YJ, Kerrich R, Kemp AIS, McCuaig TC, Hou ZQ, Hart CJR, Li ZX, Cawood PA, Bagasi L, Yang ZM, Cliff J, Belousov EA, Jourdan F and Evans NJ. 2013a. Intracontinental Eocene-Oligocene porphyry Cu mineral systems of Yunnan, western Yangtze craton, China:Compositional characteristics, sources, and implications for continental collision metallogeny. Economic Geology, 108(7): 1541-1576. DOI:10.2113/econgeo.108.7.1541 |
Lu YJ, Kerrich R, McCuaig TC, Li ZX, Hart CJR, Cawood PA, Hou ZQ, Bagas L, Cliff J, Belousova EA and Tang SH. 2013b. Geochemical, Sr-Nd-Pb, and zircon Hf-O isotopic compositions of Eocene-Oligocene shoshonitic and potassic adakite-like felsic intrusions in western Yunnan, SW China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Journal of Petrology, 54(7): 1309-1348. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egt013 |
Lu YJ, McCuaig TC, Li ZX, Jourdan F, Hart CJR, Hou ZQ and Tang SH. 2015. Paleogene post-collisional lamprophyres in western Yunnan, western Yangtze Craton:Mantle source and tectonic implications. Lithos, 233: 139-161. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.02.003 |
Luo YN and Yu RL. 2002. Orogenic evolution and metallogenic time-space dis-tribution in Jinshajiang-Lancangjiang-Nujiang Region, Southwest China. Journal of mineralogy and Petrology, 21(3): 153-159. |
McDonough WF, Sun SS, Ringwood AE, Jagoutz E and Hofmann AW. 1992. Potassium, rubidium, and cesium in the Earth and Moon and the evolution of the mantle of the Earth. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 56(3): 1001-1012. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(92)90043-I |
Miller C, Schuster R, Klötzli U, Frank W and Purtscheller F. 1999. Post-collisional potassic and ultrapotassic magmatism in SW Tibet:Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-O isotopic constraints for mantle source characteristics and petrogenesis. Journal of Petrology, 40(9): 1399-1424. DOI:10.1093/petroj/40.9.1399 |
Ming TX, Zhu DL, Hou SG, Feng WJ, Zhu YZ and Tang Z. 2013. Characteristics of REE in the Zhuopan alkaline rockmass complex and prospecting, Yongping, Yunnan. Mineral Exploration, 4(6): 609-615. |
Mo XX, Lu FX, Shen SY, Zhu QW, Hou ZQ, Yang KH, Deng JF, Liu XP and He CX. 1993. Sanjiang Tethyan Volcanism and Related Mineralization. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-267.
|
Mo XX. 2011. Magmatism, evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Geological Journal of China Universities, 17(3): 351-367. |
Müller D, Rock NMS and Groves DI. 1992. Geochemical discrimination between shoshonitic and potassic volcanic rocks in different tectonic settings:A pilot study. Mineralogy and Petrology, 46(4): 259-289. DOI:10.1007/BF01173568 |
Nelson DR, McCulloch MT and Sun SS. 1986. The origins of ultrapotassic rocks as inferred from Sr, Nd and Pb isotopes. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 50(2): 231-245. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(86)90172-9 |
Nelson DR. 1992. Isotopic characteristics of potassic rocks:Evidence for the involvement of subducted sediments in magma genesis. Lithos, 28(3-6): 403-420. DOI:10.1016/0024-4937(92)90016-R |
Nomade S, Renne PR, Mo XX, Zhao ZD and Zhou S. 2004. Miocene volcanism in the Lhasa block, Tibet:Spatial trends and geodynamic implications. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 221(1-4): 227-243. DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00072-X |
Pang WH, Ren GM, Sun ZM and Yin FG. 2015. Division and correlation of Paleo-Mesoproterozoic strata on the western margin of Yangtze block:Evidence from the U-Pb age of tuff zircon in the Tongan Formation. Geology in China, 42(4): 921-936. |
Peccerillo A and Taylor SR. 1976. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1): 63-81. DOI:10.1007/BF00384745 |
Plank T and Langmuir CH. 1998. The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle. Chemical Geology, 145(3-4): 325-394. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00150-2 |
Rogers NW, James D, Kelley SP and De Mulder M. 1998. The generation of potassic lavas from the eastern Virunga Province, Rwanda. Journal of Petrology, 39(6): 1223-1247. DOI:10.1093/petroj/39.6.1223 |
Rudnick RL and Gao S. 2003. The composition of the continental crust. Treatise on Geochemistry, 3: 1-64. |
Spurlin MS, Yin A, Horton BK, Zhou JY and Wang JH. 2005. Structural evolution of the Yushu-Nangqian region and its relationship to syncollisional igneous activity, east-central Tibet. Geological Society of America, 117(9-10): 1293-1317. |
Sun M and Kerrich R. 1995. Rare earth element and high field strength element characteristics of whole rocks and mineral separates of ultramafic nodules in Cenozoic volcanic vents of southeastern British Columbia, Canada. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(23): 4863-4879. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(95)00341-X |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for Mantle composition and processes. In:Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1):313-345
|
Tatsumi Y, Hamilton DL and Nesbitt RW. 1986. Chemical characteristics of fluid phase released from a subducted lithosphere and origin of arc magmas:Evidence from high-pressure experiments and natural rocks. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 29(1-4): 293-309. DOI:10.1016/0377-0273(86)90049-1 |
Thirlwall MF, Smith TE, Graham AM, Theodorou N, Hollings P, Davidson JP and Arculus RJ. 1994. High field strength element anomalies in arc lavas:Source or process?. Journal of Petrology, 35(3): 819-828. DOI:10.1093/petrology/35.3.819 |
Tu GC. 1982. The Preliminary Study on Two Alkali Rich Intrusive Rocks Zones. uiyang: Guizhou People's Publishing House.
|
Turner S, Arnaud N, Liu J, Rogers N, Hawkesworth C, Harris N, Kelley S, Van Calsteren P and Deng W. 1996. Post-collision, shoshonitic volcanism on the Tibetan Plateau:Implications for convective thinning of the lithosphere and the source of ocean island basalts. Journal of Petrology, 37(1): 45-71. DOI:10.1093/petrology/37.1.45 |
Wang BD, Chen JL, Xu JF and Wang LQ. 2014c. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-Os isotopic compositions of Miocene ultrapotassic rocks in southern Tibet:Petrogenesis and implications for the regional tectonic history. Lithos, 208-209: 237-250. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.09.008 |
Wang CM, Deng J, Carranza EJM and Lai XR. 2014a. Nature, diversity and temporal-spatial distributions of sediment-hosted Pb-Zn deposits in China. Ore Geology Reviews, 56: 327-351. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.06.004 |
Wang CM, Deng J, Carranza EJM and Santosh M. 2014b. Tin metallogenesis associated with granitoids in the southwestern Sanjiang Tethyan Domain:Nature, deposit types, and tectonic setting. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 576-593. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.005 |
Wang CM, Deng J, Lu YJ, Bagas L, Kemp AIS and McCuaig TC. 2015. Age, nature, and origin of Ordovician Zhibenshan granite from the Baoshan terrane in the Sanjiang region and its significance for understanding Proto-Tethys evolution. International Geology Review, 57(15): 1922-1939. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2015.1043358 |
Wang CM, Bagas L, Lu YJ, Santosh M, Du B and McCuaig TC. 2016. Terrane boundary and spatio-temporal distribution of ore deposits in the Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen:Insights from zircon Hf-isotopic mapping. Earth-Science Reviews, 156: 39-65. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.02.008 |
Wang CM, Deng J, Bagas L and Wang Q. 2017a. Zircon Hf-isotopic mapping for understanding crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the Eastern Qinling Orogen. Gondwana Research, 50: 293-310. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.04.008 |
Wang CM, Yang LF, Bagas L, Evans NJ, Chen JY and Du B. 2017b. Mineralization processes at the giant Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Lanping Basin, Sanjiang Tethys Orogen:Evidence from in situ trace element analysis of pyrite and marcasite. Geological Journal. DOI:10.1002/gj.2956 |
Wang CM, Chen JY, Yang LF, Zhang D, Du B and Shi KX. 2017. Tectonic-fluid-mineral system in the Lanping basin, Sanjiang Tethys. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(7): 1975-1977. |
Wang CM, Bagas L, Chen JY, Yang LF, Zhang D, Du B and Shi KX. 2018. The genesis of the Liancheng Cu-Mo deposit in the Lanping Basin of SW China:Constraints from geology, fluid inclusions, and Cu-S-H-O isotopes. Ore Geology Reviews, 92: 113-128. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.11.012 |
Wang CS, Li XH and Hu XM. 2003. Age of initial collision of India with Asia:Review and constraints from sediments in Southern Tibet. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77(1): 16-24. |
Wang J, Li JP and Wang JH. 2003. Shoshonitic magmatism in Dali-Jianchuan area, western Yunnan:A geochemical study of arc magmatism in a post-collisional strike-slip extensional setting. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 19(1): 61-70. |
Wang JH, Yin A, Harrison TM, Grove M, Zhang YQ and Xie GH. 2001. A tectonic model for Cenozoic igneous activities in the eastern Indo-Asian collision zone. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 188(1-2): 123-133. DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00315-6 |
Wei DL, Xia B, Zhang YQ, Wang R and Wan XK. 2005. The pyroxenes composition and petrochmical characteristics of Zhuopan-Liuhe alkali rock bodies in western Yunnan Province, China. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 25(2): 15-19. |
Wilson M. 1989. Igneous Petrogenesis. London: Unwin Hyman: 489-532.
|
Wu FY, Li XH, Zheng YF and Gao S. 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185-220. |
Wu J, Liang HY, Mo JH, Zhang YQ and Hu GQ. 2011. Petrochemistry and zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb age of the Mangzong porphyry associated with Cu-Mo mineralization in the Yulong ore belt. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 35(2): 300-306. |
Wu YB and Zheng YF. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(15): 1554-1569. DOI:10.1007/BF03184122 |
Xiao XN, Yu XH, Mo XX, Yang GL, Li Y and Huang XK. 2009. Geochemistry, zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating and origin of alkali-rich porphyries in Beiya area, north Erhai Lake, western Yunnan, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(12): 1786-1803. |
Xue CD, Hou ZQ, Liu X, Yang ZM, Liu YQ and Hao BW. 2008. Petrogenesis and metallogenesis of the Beiya-goldpolymetallic ore district, northwestern Yunnan Province, China:Responses to the Indo-Asian collisional processes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(3): 457-472. |
Yang LF, Shi KX, Wang CM, Wu B, Du B, Chen JY, Xia JS and Chen J. 2016. Ore genesis of the Jinman copper deposit in the Lanping Basin, Sanjiang Orogen:Constraints by copper and sulfur isotopes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2392-2406. |
Yang ZM, Hou ZQ, Xu JF, Bian XF, Wang GR, Yang ZS, Tian SH, Liu YC and Wang ZL. 2014. Geology and origin of the post-collisional Narigongma porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, southern Qinghai, Tibet. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 536-556. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.07.012 |
Zeng PS, Yang WG and Yu XH. 1999. Alkali porphyry zone and the relationship between the porphyry and gold metallization in the western Yunnan. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 20(Suppl.): 367-372. |
Zeng PS, Mo XX and Yu XH. 2002. Nd, Sr and Pb isotopic characteristics of the alkaline-rich porphyries in western Yunnan and its compression strike-slip setting. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 21(3): 231-241. |
Zhang J, Wang H, Li SH and Li TJ. 2017. Paleogene magmatism and gold metallogeny of the Jinping terrane in the Ailaoshan ore belt, Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen (SW China):Geology, deposit type and tectonic setting. Ore Geology Reviews, 91: 620-637. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.08.032 |
Zhang YQ, Xie YW, Qiu HN, Li XH and Zhong SL. 1998. Shoshonitic series:Geochemical characteristics of elements for ore-bearing porphyry from Yulong copper ore belt in eastern Tibet. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 23(6): 557-561. |
Zhao ZH. 2007. How to use the trace element diagrams to discriminate tectonic settings. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 31(1): 92-103. |
Zhong DL, Ding L, Liu FT, Liu JH, Zhang JJ, Ji JQ and Chen H. 2000. Multi-oriented and layered structures of lithosphere in erogenic belt and their effects on Cenozoic magmatism:A case study of western Yunnan and Sichuan, China. Science in China (Series D), 43(Suppl.1): 122-133. |
Zhou S, Mo XX, Zhao ZD, Qiu RZ, Niu YL, Guo TY and Zhang SQ. 2010. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of post-collisional volcanism in the middle Gangdese Belt, southern Tibet. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 37(3): 246-258. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.08.011 |
Zhu XP. 2010. Geological characteristics and metallogenesis in Habo porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposit, Yunnan, China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences: 1-150.
|
毕献武, 胡瑞忠, 彭建堂, 吴开兴, 苏文超, 战新志. 2005. 姚安和马厂箐富碱侵入岩体的地球化学特征. 岩石学报, 21(1): 113-124. |
陈喜峰, 曾普胜, 张雪亭, 徐文荣, 万大幅. 2015. 云南永平卓潘碱性杂岩体岩石学和地球化学特征及成因研究. 岩石学报, 31(9): 2597-2608. |
邓军, 杨立强, 葛良胜, 袁士松, 王庆飞, 张静, 龚庆杰, 王长明. 2010. 滇西富碱斑岩型金成矿系统特征与变化保存. 岩石学报, 26(6): 1633-1645. |
邓军, 杨立强, 王长明. 2011. 三江特提斯复合造山与成矿作用研究进展. 岩石学报, 27(9): 2501-2509. |
邓军, 王长明, 李龚健. 2012. 三江特提斯叠加成矿作用样式及过程. 岩石学报, 28(5): 1349-1361. |
邓万明, 黄萱, 钟大赉. 1998. 滇西金沙江带北段的富碱斑岩及其与板内变形的关系. 中国科学(D辑), 28(2): 111-117. |
董方浏, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 王勇, 毕先梅, 周肃. 2005. 云南兰坪盆地喜马拉雅期碱性岩40Ar/39Ar年龄及地质意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 24(2): 103-109. |
董方浏, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 侯增谦, 王勇. 2007. 云南永平卓潘新生代碱性杂岩体的元素地球化学和Nd-Sr-Pb同位素特征及地质意义. 岩石学报, 23(5): 986-994. |
杜斌, 王长明, 贺昕宇, 杨立飞, 陈晶源, 石康兴, 罗政, 夏锦胜. 2016. 锆石Hf和全岩Nd同位素填图研究进展:以三江特提斯造山带为例. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2555-2570. |
杜斌. 2017. 云南大莲花山和卓潘岩体岩浆源区及形成机制.硕士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学: 1-78.
|
葛良胜, 邹依林, 邢俊兵, 王治华, 郭晓东. 2004. 滇西北与喜马拉雅期富碱斑岩有关的金矿成矿系统. 黄金地质, 10(1): 39-47. |
何科昭, 何浩生, 蔡红飙. 1996. 滇西造山带的形成与演化. 地质论评, 42(2): 97-106. |
和文言, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 董国臣, 和中华, 黄雄飞, 李小伟, 姜丽莉. 2014. 滇西北衙煌斑岩的岩石成因及动力学背景:年代学、地球化学及Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf同位素约束. 岩石学报, 30(11): 3287-3300. |
侯增谦. 2010. 大陆碰撞成矿论. 地质学报, 84(1): 30-58. |
胡晓佳. 2012. 哀牢山-红河断裂带新生代富钾中酸性侵入岩的成因研究及其地质意义.硕士学位论文. 西安: 西北大学: 1-87.
|
蒋成竹. 2014. 滇西北衙金多金属矿床钾质岩浆活动与成矿作用.博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学: 1-158.
|
李龚健, 王庆飞, 禹丽, 胡兆初, 马楠, 黄钰涵. 2013. 哀牢山古特提斯洋缝合时限:晚二叠世花岗岩类锆石U-Pb年代学与地球化学制约. 岩石学报, 29(11): 3883-3900. |
李龚健. 2014. 三江特提斯复合造山带构造演化与典型矿床成矿过程研究.博士学位论. 北京: 中国地质大学: 1-179.
|
李怀坤, 苏文博, 周红英, 耿建珍, 相振群, 崔玉荣, 刘文灿, 陆松年. 2011. 华北克拉通北部长城系底界年龄小于1670Ma:来自北京密云花岗斑岩岩脉锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb年龄的约束. 地学前缘, 18(3): 108-120. |
李腾建, 张静, 佟子达, 潘泽伟. 2017. 云南省卓潘碱性杂岩体矿物学、地球化学特征及其地质意义. 现代地质, 31(3): 474-485. |
李勇, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 黄行凯, 和文言. 2011. 金沙江-哀牢山断裂带几个富碱斑岩体的锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义. 现代地质, 25(2): 189-200. |
李勇. 2012. 滇西"三江"地区新生代钾质岩浆岩年代学特征、岩石成因及其地质意义.博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学: 1-119.
|
梁华英, 谢应雯, 张玉泉. 2004. 富钾碱性岩体形成演化对铜矿成矿制约——以马厂箐铜矿为例. 自然科学进展, 14(1): 118-120. |
刘建华, 刘福田, 吴华, 李强, 胡戈. 1989. 中国南北带地壳和上地幔的三维速度图像. 地球物理学报, 32(2): 143-152. |
刘金宇, 邓军, 李龚健, 肖昌浩, 孟富军, 陈福川, 吴伟, 张琦玮. 2017. 滇西兰坪盆地莲花山岩体成因与构造意义:岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束. 岩石学报, 33(7): 2115-2128. |
骆耀南, 俞如龙. 2002. 西南三江地区造山演化过程及成矿时空分布. 矿物岩石, 21(3): 153-159. |
明添学, 朱多录, 侯蜀光, 冯文杰, 朱悦彰, 唐忠. 2013. 云南卓潘碱性杂岩体稀土元素特征及找矿远景分析. 矿产勘查, 4(6): 609-615. |
莫宣学, 路凤香, 沈上越, 朱勤文, 侯增谦, 杨开辉, 邓晋福, 刘祥品, 何昌祥. 1993. 三江特提斯火山作用与成矿. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-267.
|
莫宣学. 2011. 岩浆作用与青藏高原演化. 高校地质学报, 17(3): 351-367. |
庞维华, 任光明, 孙志明, 尹福光. 2015. 扬子地块西缘古-中元古代地层划分对比研究:来自通安组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄的证据. 中国地质, 42(4): 921-936. |
涂光炽. 1982. 华南两个富碱侵入岩带的初步研究. 贵阳: 贵州人民出版社.
|
王长明, 陈晶源, 杨立飞, 张端, 杜斌, 石康兴. 2017. 三江特提斯兰坪盆地构造-流体-成矿系统. 岩石学报, 33(7): 1957-1977. |
王成善, 李祥辉, 胡修棉. 2003. 再论印度-亚洲大陆碰撞的启动时间. 地质学报, 77(1): 16-24. |
王建, 李建平, 王江海. 2003. 滇西大理-剑川地区钾玄质岩浆作用:后碰撞走滑拉伸环境岛弧型岩浆作用的地球化学研究. 岩石学报, 19(1): 61-70. |
韦栋梁, 夏斌, 张玉泉, 王冉, 万哨凯. 2005. 滇西卓潘-六合碱性岩的辉石成分及其岩石化学特征. 矿物岩石, 25(2): 15-19. |
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185-220. |
伍静, 梁华英, 莫济海, 张玉泉, 胡光黔. 2011. 玉龙斑岩铜矿带莽总含矿斑岩体岩石学特征及锆石U-Pb年龄研究. 大地构造与成矿学, 35(2): 300-306. |
吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约. 科学通报, 49(16): 1589-1604. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 |
肖晓牛, 喻学惠, 莫宣学, 杨贵来, 李勇, 黄行凯. 2009. 滇西洱海北部北衙地区富碱斑岩的地球化学、锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及成因. 地质通报, 28(12): 1786-1803. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.12.012 |
薛传东, 侯增谦, 刘星, 杨志明, 刘勇强, 郝百武. 2008. 滇西北北衙金多金属矿田的成岩成矿作用:对印-亚碰撞造山过程的响应. 岩石学报, 24(3): 457-472. |
杨立飞, 石康兴, 王长明, 吴彬, 杜斌, 陈晶源, 夏锦胜, 陈晶. 2016. 西南三江兰坪盆地金满铜矿床成因研究:来自铜和硫同位素的联合约束. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2392-2406. |
曾普胜, 杨伟光, 喻学惠. 1999. 滇西富碱斑岩带及其与金矿化的关系. 地球学报, 20(增刊): 367-372. |
曾普胜, 莫宣学, 喻学惠. 2002. 滇西富碱斑岩带的Nd、Sr、Pb同位素特征及其挤压走滑背景. 岩石矿物学杂志, 21(3): 231-241. |
张玉泉, 谢应雯, 邱华宁, 李献华, 钟孙霖. 1998. 钾玄岩系列:藏东玉龙铜矿带含矿斑岩元素地球化学特征. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 23(6): 557-561. |
赵振华. 2007. 关于岩石微量元素构造环境判别图解使用的有关问题. 大地构造与成矿学, 31(1): 92-103. |
钟大赉, 丁林, 刘福田, 刘建华, 张进江, 季建清, 陈辉. 2000. 造山带岩石层多向层架构造及其对新生代岩浆活动制约——以三江及邻区为例. 中国科学(D辑), 30(增1): 1-8. |
祝向平. 2010. 云南哈播斑岩型铜(-钼-金)矿床地质特征与成矿作用研究.博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学: 1-150.
|
 2018, Vol. 34
2018, Vol. 34


