2. 中国科学技术大学地球与空间科学学院, 合肥 230026;
3. 中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所, 北京 100037;
4. 北京大学地球与空间科学学院, 北京 100871
2. School of Earth and Space Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China;
3. Institute of Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing 100037, China;
4. School of Earth and Space Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
“高Ba-Sr花岗岩”由Tarney and Jones (1994)提出,与传统分类中的Ⅰ型、S型和A型花岗岩(统称低Ba-Sr花岗岩)相比,高Ba-Sr花岗岩具有高Ba(通常≥600×10-6)和Sr(通常≥300×10-6)含量,相对低Rb(通常≤200×10-6)和显著的低Y(通常≤30×10-6)及HREE含量,高Sr/Y和K/Rb值,无显著Eu负异常等一系列微量元素地球化学特征。目前关于高Ba-Sr花岗岩的成因具有多解性(Tarney and Jones, 1994; Fowler et al., 2001; Qian et al., 2003; Ye et al., 2008),因其具有高Sr/Y比,无显著Eu负异常,并且普遍与具有相似微量元素特征的基性岩相伴生(Fowler et al., 2001; Qian et al., 2003),多数学者认为高Ba-Sr花岗岩源区具有幔源物质参与,并且上述一系列微量元素特征继承自富集地幔组分,可以用来反演地幔源区富集机制(Ionov and Hofmann, 1995; Ionov et al., 1997; Kepezhinskas et al., 1997; La Flèche, et al., 1998; Furman and Graham, 1999; Pilet et al., 2004)。然而,花岗质岩浆作用过程复杂,幔源岩浆在演化形成高Ba-Sr花岗质岩浆过程中可能会经历分离结晶,围岩混染或者与壳源物质的混合,这些事件均会对高Ba-Sr花岗岩中的特征微量元素产生显著影响。因此,详细探讨高Ba-Sr花岗岩的演化历程对于深入理解该类花岗岩中特征微量元素的成因,同时正确限定其地幔源区富集机制具有重要意义。
由古生代至新生代,华北克拉通(NCC)由巨厚的(>180km)古老富集岩石圈地幔转变为薄的(~80km)新生大洋型岩石圈地幔(Griffin et al., 1998; Menzies and Xu, 1998; 周新华, 2006),同时在华北克拉通东部和中部地区形成大规模、多样的(基性至酸性)中生代岩浆活动(Fan et al., 2001; Zhang et al., 2014)。关于上述“华北克拉通(NCC)中生代破坏”,前人提出了不同的成因机制,包括下地壳拆沉(Gao et al., 2002, 2004, 2009; Xu et al., 2006)、热侵蚀(Menzies et al., 1993; Xu, 2001)、橄榄岩-熔体相互作用(Zhang et al., 2002, 2005; 张宏福, 2006)及岩石圈地幔水化(牛耀龄, 2005)等模型。但是,作为世界上最古老的克拉通之一,华北克拉通内各区域的演化历史存在高度差异,并且地球物理数据(Chen et al., 2009; Chen, 2009, 2010)显示现今华北克拉通岩石圈地幔由东向西逐渐增厚,西部地区仍保留巨厚的古老岩石圈地幔,表明华北克拉通中生代破坏的时空不均一性(徐义刚, 2004, 2006; 马金龙和徐义刚, 2004)。因此,针对规模较小,研究程度较低的中部带岩浆活动的研究对于比较华北克拉通东、西部破坏差异和详细刻画华北克拉通破坏机制具有重要意义。然而前人关于该区中生代岩浆活动的成因存在明显分歧:张旗等(2001, 2008)认为该区岩浆由加厚下地壳底部麻粒岩部分熔融形成或由中生代增生在华北地壳底部的年轻基性麻粒岩部分熔融形成;Xu et al.(2008a, 2010)通过对该区中生代符山岩体及其中地幔橄榄岩包体的研究,认为该岩体是拆沉下地壳物质熔融形成的熔体与周围地幔橄榄岩反应的产物;Wang et al. (2006)认为太行山地区早白垩世钾质玄武岩为NCC中部带晚中生代富集岩石圈地幔(Chen and Zhai, 2003; Chen et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2004)熔融产物;Chen et al. (2003)则强调“壳-幔岩浆混合作用”在太行山地区岩浆活动中的重要性。随着地球化学测试技术的飞速发展,近年来部分学者针对NCC内中/新生代玄武岩从不同角度(如Mg、Fe等非传统同位素)开展了更加深入的研究(Liu et al., 2015a, b; Qian et al., 2017)。Qian et al. (2017)通过对NCC东部早白垩世玄武岩中橄榄石包裹体地球化学组成,Pb同位素和氧逸度等方面的研究指出NCC破坏与岩石圈地幔多期交代弱化,太平洋板块俯冲和相关的地幔柱活动密切相关。
本文选取华北克拉通中部带具有高Ba-Sr特征的老山及狐偃山杂岩体,开展系统的年代学、全岩及Sr-Nd同位素地球化学研究,限定岩体形成时代及成因,从而探讨:(1)高Ba-Sr花岗质岩浆演化历程及其对Ba、Sr等特征元素的影响;(2)华北克拉通中部带岩石圈地幔富集机制和中生代“破坏”机制。
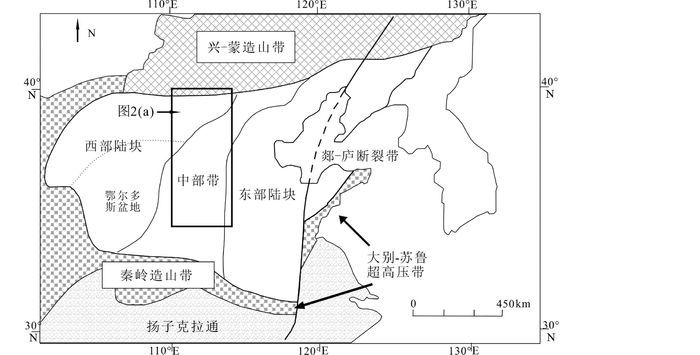
1 区域地质背景及岩体地质具有2.5~3.8Ga结晶基底(Jahn and Bai, 1983; Liu et al., 1992; Zhao et al., 2001)的华北克拉通是世界上最古老的克拉通之一(图 1),可分为东部、中部和西部陆块三部分(Zhao et al., 2001, 2005),~1.85Ga时东、西部陆块沿中部带发生碰撞拼合从而形成统一的结晶基底。之后,华北克拉通北缘在晚古生代与西伯利亚板块发生碰撞(Şengör et al., 1993),三叠纪时南缘与扬子板块发生碰撞(Li et al., 2000),扬子板块深俯冲(>200km)形成大别-苏鲁超高压带(Ye et al., 2000),中生代时太平洋板块开始沿着华北克拉通东缘俯冲(Maruyama et al., 1997; Li and Li, 2007)。
|
图 1 华北克拉通构造简图(据Zhang et al., 2004修改) Fig. 1 Simplified geological map of the North China Craton (modified after Zhang et al., 2004) |
华北克拉通中部带(图 1)中基底岩石主要由晚太古代至早元古代TTG片麻岩、表壳岩、铁镁质岩墙和同构造或构造后花岗岩组成,具有2.6~2.0Ga的原岩年龄和1.8~1.9Ga的变质年龄(赵国春, 2009)。中部带晚中生代岩浆活动主要沿着东、西缘两个大型断裂带分布(图 2a),即东部太行山地区(Chen et al., 2003, 2004, 2008; Zhang et al., 2004; Gao et al., 2012; Shen et al., 2013; Li et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2014)和西部的大同-吕梁-临汾一线(邵济安等, 2001, 2005; He and Santosh, 2014; Li et al., 2014, 2015; Ying et al., 2007, 2011; 王亚莹等, 2014)。太行山地区岩体中发现少量煌斑岩墙(Chen and Zhai, 2003)和地幔橄榄岩包体(Xu et al., 2008a, 2010)。新生代时,汉诺坝、鹤壁和繁峙等地区发育玄武质岩浆活动并包含大量下地壳麻粒岩和地幔橄榄岩捕掳体(图 2a, Zheng et al., 2001, 2007; Xu et al., 2008b)。
|
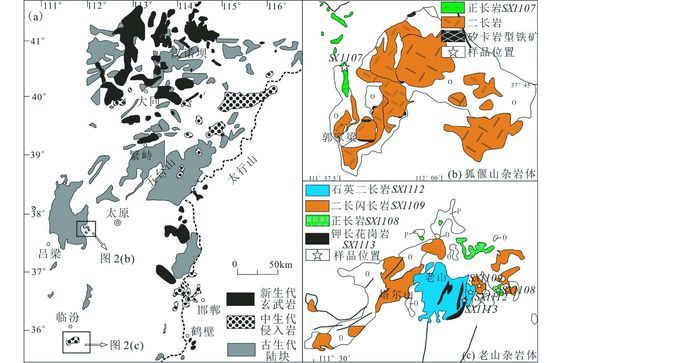
图 2 华北克拉通中部带(CNCC)地质简图(a, 据汤艳杰等, 2006)、狐偃山岩体(b)和老山岩体(c)地质简图 Fig. 2 Simplified geological map of the Central North China Cronton (a, modified after Tang et al., 2006) and simplified geological maps of the Huyanshan complex (b) and the Laoshan complex (c) |
狐偃山杂岩体位于中部带中部(图 2b),包括二长岩和少量正长岩,侵入前寒武系至二叠系地层中。老山杂岩体位于中部带南端(图 2c),周围还出露塔儿山、二峰山(Ying et al., 2011)和卧虎山等多个小岩体。老山岩体主体由石英二长岩构成,呈岩床状侵入周围的奥陶系碳酸盐地层中,内部被晚期花岗斑岩脉穿插,东北部出露少量二长闪长岩和正长岩。狐偃山和老山岩体与碳酸盐围岩接触处均发生矽卡岩化,形成小型Fe-Cu矿床。我们系统采集了老山岩体的四种岩石和狐偃山岩体中研究程度较低的正长岩,它们具有类似的主要矿物组成:钾长石+斜长石+角闪石+黑云母。其中,狐偃山正长岩中钾长石含量高(60%),暗色矿物为黑云母(10%)和少量角闪石(5%),后期流体交代形成少量方解石(图 3a)。老山主体石英二长岩中暗色矿物为黑云母(图 3b),钾长花岗斑岩中少见暗色矿物(图 3c),正长岩和二长闪长岩中暗色矿物以角闪石为主(图 3d)。老山岩体中普遍存在磷灰石,榍石和磁铁矿等副矿物。

|
图 3 狐偃山及老山岩体岩石镜下照片 (a)组1狐偃山正长岩(SX1107);(b)组1老山石英二长岩(SX1112);(c)组2老山钾长花岗斑岩(SX1113);(d)组2老山正长岩(SX1108).Kfs-钾长石;Bt-黑云母;Hbl-角闪石;Cal-方解石;Fe Oxide-含铁氧化物;Ap-磷灰石 Fig. 3 Microphotographs showing the texture and mineral assemblage of rocks from the Huyanshan and Laoshan complex (a) Huyanshan syenite from Group 1 (Sample SX1107); (b) Laoshan quartz monzonite from Group 1 (Sample SX1112); (c) Laoshan K-feldspar granite porphyry from Group 2 (Sample SX1113); (d) Laoshan syenite from Group 2 (Sample SX1108). Kfs-K-feldspar; Bt-biotite; Hbl-hornblende; Cal-calcite; Ap-apatite |
为确定老山和狐偃山岩体形成时间,分别从老山石英闪长岩(SX1112)、正长岩(SX1108)、二长闪长岩(SX1109)和钾长花岗岩(SX1113)及狐偃山正长岩(SX1107)中挑选锆石,制靶后在中国地质科学院地质研究所北京离子探针中心进行阴极发光(CL)成像(图 4),并在中国地质科学院地质研究所大陆构造与动力学重点实验室开展锆石BSE图像观察,揭示锆石内部结构,选取U-Pb测试点。锆石U-Pb同位素定年测试在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所成矿作用与资源评价重点实验室进行,所用仪器为德国Finnigan公司生产的Neptune型激光多接收等离子体质谱(LA-MC-ICP-MS),并结合美国New Wave公司生产的UP213nm激光剥蚀系统,斑束直径为25μm,频率为10Hz,能量密度约为2.5J/cm2,以He为载气。U和Th含量根据外标M127 (U=923×10-6, Th=439×10-6, Th/U=0.475)校正。每测定10个样品点前后重复测量两次锆石标样GJ-1和一次锆石标样Plesovice。分析数据的离线处理(包括对样品和空白信号的选择、仪器灵敏度漂移校正、元素含量及U-Th-Pb同位素比值和年龄计算)采用软件ICPMSDataCal完成(Liu et al., 2010),锆石年龄谐和图用Isoplot 3.0程序获得,测试结果见表 1和图 5。在下文数据描述中,锆石测点年龄大于900Ma的采用207Pb/206Pb年龄,小于900Ma的为206Pb/238U年龄。

|
图 4 老山岩体锆石CL图像 Fig. 4 Cathodoluminescence(CL)images showing the texture and respective spots for U-Pb analysis on zircon grains from Laoshan complex |
|
|
表 1 老山杂岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年数据 Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb isotopic data for rocks from Laoshan complex |
|
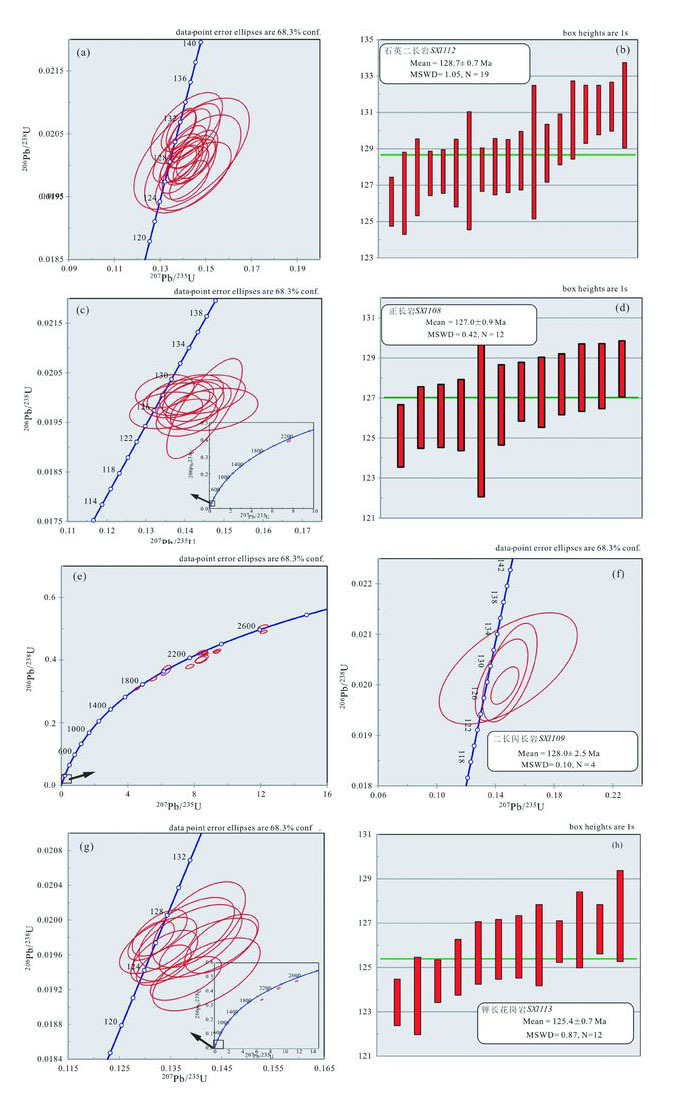
图 5 老山各类岩石锆石U-Pb定年谐和图和年龄分布图 Fig. 5 U-Pb concordia and age distribution diagrams for LA-ICP-MS analytical results of rocks from Laoshan complex |
研究样品全岩主量和微量元素成分测试在国土资源部国家地质实验测试中心进行。主量元素通过XRF(X荧光光谱仪3080E)方法测试,分析精度为5%。微量元素和稀土元素(REE)通过等离子质谱仪(ICP-MS-Excell)分析,含量大于10×10-6的元素测试精度为5%,而小于10×10-6的元素精度为10%,个别低含量的元素测试误差大于10%,分析结果列在表 2中。
|
|
表 2 老山杂岩体和狐偃山正长岩主量元素(wt%),微量元素(×10-6)和Sr-Nd同位素组成 Table 2 Whole-rock major (wt%), trace element (×10-6) and Sr-Nd isotopic data of samples from Laoshan complex and Huyanshan syenite |
代表性样品的Rb-Sr和Sm-Nd同位素比值采用同位素稀释法测定,在中国科学技术大学放射性同位素地球化学实验室热电离质谱计MAT-262上进行。样品的化学分离纯化在净化实验室完成。Sr和Nd同位素比值测定分别采用86Sr/87Sr=0.1194和146Nd/149Nd=0.7219进行质量分馏标准化校正,化学流程和同位素比值测定参见Chen et al.(2002, 2007)。根据各类岩石锆石U-Pb定年结果,分别计算初始Sr和Nd同位素比值,分析结果见表 2。
3 分析结果 3.1 锆石U-Pb年龄 3.1.1 老山石英二长岩(SX1112)锆石颗粒呈浑圆状,显示典型的韵律生长环带(图 4)。锆石测点U和Th含量分别为210×10-6~655×10-6和151×10-6~1370×10-6,Th/U比值为0.7~2.1,206Pb/238U年龄在126.1Ma和141.0Ma之间变化,19个测点得到128.7±0.7Ma的加权平均年龄,MSWD=1.05。典型的锆石韵律环带表明该年龄可以代表老山石英闪长岩的结晶年龄。
3.1.2 老山正长岩(SX1108)锆石颗粒分为两组:一组呈柱状或碎片状,发育典型的韵律生长环带;一组呈浑圆状,发育核-边结构,核部呈振荡环带,边部呈狭窄均一化灰白色(图 4)。前组锆石测点U和Th含量分别为212×10-6~772×10-6和393×10-6~2673×10-6,Th/U比值为1.5~3.5,206Pb/238U年龄集中于125.1Ma和143.4Ma之间,12个测点得到127.0±0.9Ma的加权平均年龄,MSWD=0.42,典型的韵律环带指示该年龄可以代表老山正长岩的结晶年龄。后组一个核部测点U和Th含量分别为253×10-6和39×10-6,Th/U比值为0.2,207Pb/206Pb年龄为2229.3Ma,可能代表源区内古老物质或者岩浆上升过程中捕获的围岩。
3.1.3 老山二长闪长岩(SX1109)锆石呈自形-半自形长柱状,显示相似的核-幔-边结构(图 4):核部呈振荡环带或均一化变质区域,幔部为均一化的灰白色,核、幔部结构特征指示变质作用,代表古老继承锆石;边部较窄(5~40μm),典型的韵律生长环带表明其为岩浆作用时在古老继承锆石外围结晶形成的増生边,其年龄指示岩浆结晶时间。针对不同微区开展U-Pb测试:边部测点Th和U含量分别为59×10-6~243×10-6和112×10-6~242×10-6,Th/U比值变化于0.5~1.0,206Pb/238U年龄集中(127.6~142.3Ma),加权平均年龄为128.0±2.5Ma(MSWD=0.10),典型的韵律环带指示该年龄代表岩体结晶年龄;核部和幔部测点特征相似,Th和U含量分别为42×10-6~765×10-6和46×10-6~1007×10-6,Th/U比值变化于0.5~4.1之间,207Pb/206Pb年龄变化于1750.0Ma和2650.3Ma。
3.1.4 老山钾长花岗岩(SX1113)与SX1108相似,该件样品中锆石可分为碎片状发育均匀韵律环带和柱状发育核-边结构的两组,后者边部为紧密的韵律生长环带。两组锆石中韵律环带和锆石边部位置测点得到Th和U含量为47×10-6~1157×10-6和94×10-6~848×10-6,Th/U比值介于0.5~1.8,206Pb/238U年龄变化于123.4Ma和127.3Ma,其中12个测点的加权平均年龄为125.4±0.7Ma(MSWD=0.87),代表岩体结晶年龄。核部测点Th和U含量分别为28×10-6~95×10-6和57×10-6~127×10-6,Th/U比值为0.4~1.0,207Pb/206Pb年龄变化于2279.9Ma和2455.6Ma之间。
在狐偃山正长岩(SX1107)中未挑选出足够数量的锆石,但Ying et al. (2011)报道了狐偃山二长岩129.9±2.3Ma的锆石U-Pb年龄,与老山四种岩石的结晶年龄在误差范围内保持一致(128.7~125.4Ma)。因此两岩体形成时间接近,均代表华北克拉通中部带早白垩世岩浆活动。普遍发育的1.7~2.7Ga古老锆石与该区基底年龄吻合(赵国春, 2009),指示源区内包含古老基底物质或者源自岩浆上升过程中捕获的围岩。
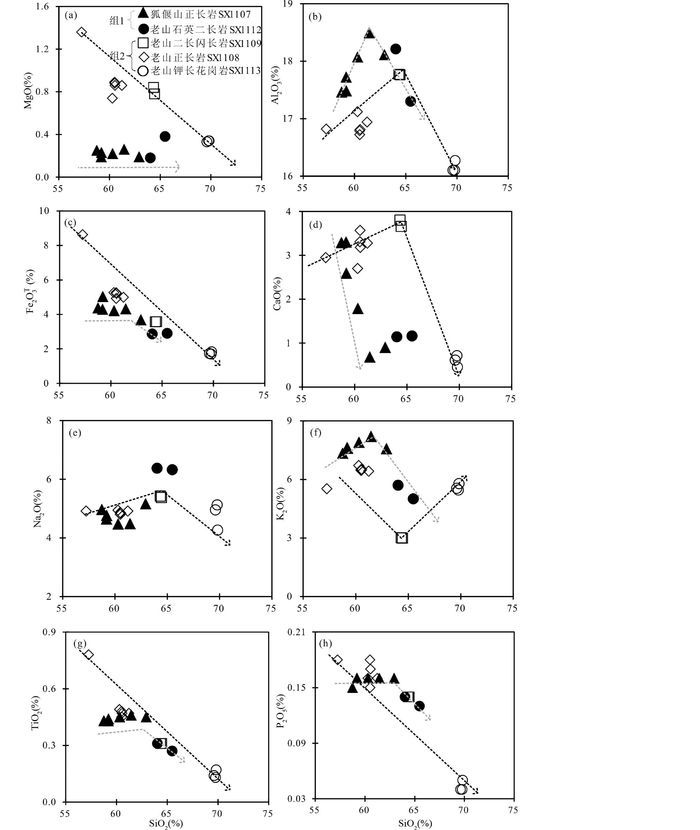
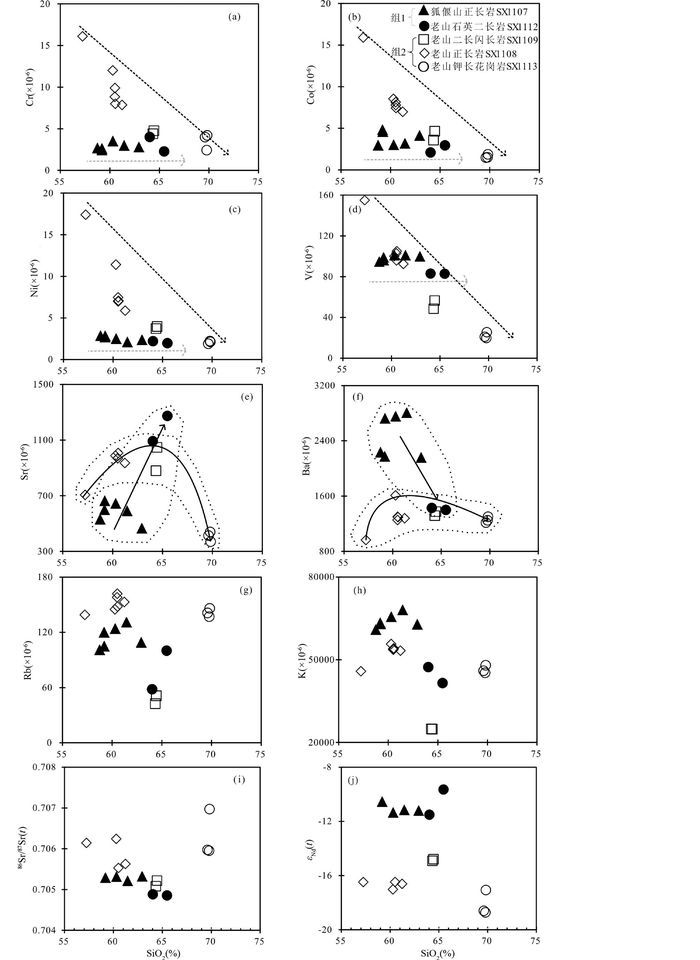
3.2 全岩地球化学特征和样品分类研究样品全岩主量元素(表 2)显示如下相似特征(图 6、图 7):(1) SiO2含量中等57.3%~69.8%,低MgO含量(0.2%~1.4%),属于中-酸性岩;(2)高K2O(3.0%~8.2%)和Na2O(4.3%~6.4%)含量,ALK(=K2O+Na2O)介于8.5%~12.9%,属于钾质至超钾质系列;(3)低CaO(0.5%~3.8%),Fe2O3T(=Fe2O3+FeO×1.1113,1.7%~8.6%),TiO2(0.1%~0.8%)和P2O5(0.04%~0.2%)含量,低烧失量(图 6,LOI=0.7%~3.0%)。此外,相容元素Cr(2×10-6~16×10-6),Co(2×10-6~16×10-6),Ni(2×10-6~17×10-6)含量低。随SiO2含量升高,主量元素和相容元素显示出两种变化趋势(图 7、图 8),据此可将本文样品分为两组:组1样品包含狐偃山正长岩和老山石英二长岩。随着SiO2含量升高,组1样品MgO和相容元素Cr、Co、Ni、V含量基本不变(图 8),CaO下降,K2O和Al2O3先升高后降低(图 7);组2样品包含老山二长闪长岩、正长岩和钾长花岗岩。随着SiO2含量升高,组2样品MgO、Fe2O3T、TiO2、P2O5和相容元素Cr、Co、Ni、V呈线性降低,CaO、Na2O和Al2O3先升高后降低,K2O先降低后升高(图 7、图 8)。

|
图 6 狐偃山正长岩和老山杂岩体微量元素(Rb、Ba、Sr)和主量元素(K2O、CaO)及同位素87Sr/86Sr(t)与烧失量LOI相关图解 Fig. 6 Covariation diagram of selected trace elements (Rb, Ba and Sr), major elements (K2O and CaO) and 87Sr/86Sr(t) vs. LOI for Laoshan complex and Huyanshan syenite |
|
图 7 狐偃山正长岩和老山杂岩体主量元素与SiO2相关图解 Fig. 7 Covariation diagram of major elements vs. SiO2 for Laoshan complex and Huyanshan syenite |
|
图 8 狐偃山正长岩和老山杂岩体微量元素和Sr-Nd同位素与SiO2相关图解 Fig. 8 Covariation diagram of trace elements and Sr-Nd isotope vs. SiO2 for Laoshan complex and Huyanshan syenite |
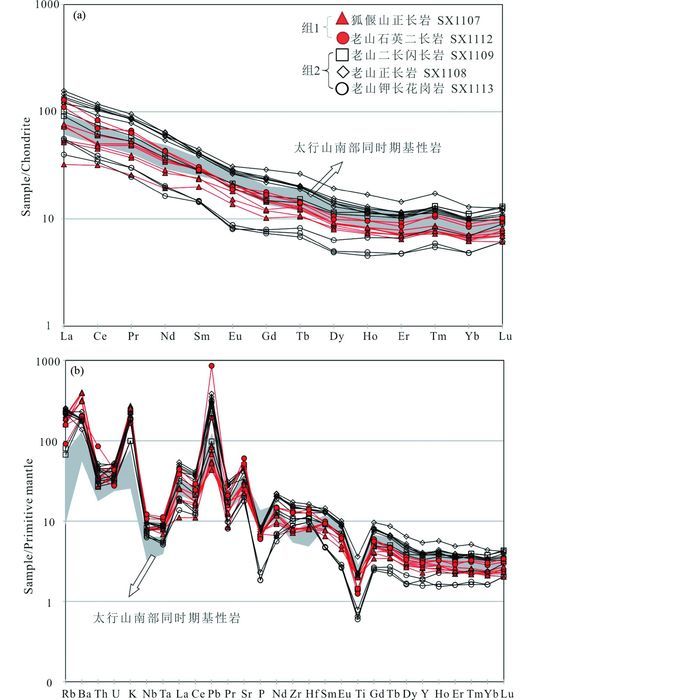
研究样品全岩微量元素(表 2)显示如下特征(图 8、图 9):(1) 2组样品稀土元素总量∑REE具有较大变化范围(49×10-6~169×10-6),但均富集轻稀土元素LREEs,亏损重稀土元素HREEs(图 9a,(La/Yb)N=4.61~15.5)。组1中Eu/Eu*=0.85~1.07,Dy/Yb=1.6~2.1;组2中Dy/Yb=1.4~2.3,Eu/Eu*=0.75~0.99,其中老山钾长花岗岩样品(SX1113)Eu/Eu*=0.75~0.83;(2)本文2组样品均富集大离子亲石元素Ba(964×10-6~2805×10-6),Sr(370×10-6~1273×10-6)和Pb(3×10-6~61×10-6),相对亏损Rb(43×10-6~162×10-6),Th(2.3×10-6~7.2×10-6),U(0.6×10-6~1.1×10-6)和高场强元素HFSEs(如Nb(4.5×10-6~8.6×10-6)、Ta(0.2×10-6~0.5×10-6)、Y(7.1×10-6~24.5×10-6))(图 9b)。组1具有高Ba特征(1399×10-6~2805×10-6),并且Ba含量随SiO2升高而降低(图 8f);组2中Ba含量相对较低(964×10-6~1610×10-6),并且随SiO2升高而微弱富集(图 8f);(3) 2组样品特征微量元素比值Nb/U(4.6~13.2)和Ce/Pb(0.7~12.2)均与岛弧岩浆接近(Hofmann et al., 1986),Zr/Hf值介于31.5~40.2。Nb/Ta(组1:16.4~20.9;组2:15.1~22.5)和Sr/Y(组1:38.5~92.9;组2:28.8~61.2)变化范围较大(图 10)。2组样品微量元素组成的差异可能指示不同的源区组分或者岩浆演化过程。
|
图 9 狐偃山岩体及老山岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素图解(a)及原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) 太行山南部同时代基性岩引自Wang et al. (2006) Fig. 9 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams (b) for Laoshan complex and Huyanshan syenite (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) The contemporary mafic rocks in South Taihang are from Wang et al. (2006) |

|
图 10 狐偃山正长岩和老山杂岩体埃达克质岩判别图解(据Defant and Drummond, 1990) Fig. 10 Discrimination diagram of adakite rocks for Laoshan complex and Huyanshan syenite (after Defant and Drummond, 1990) |
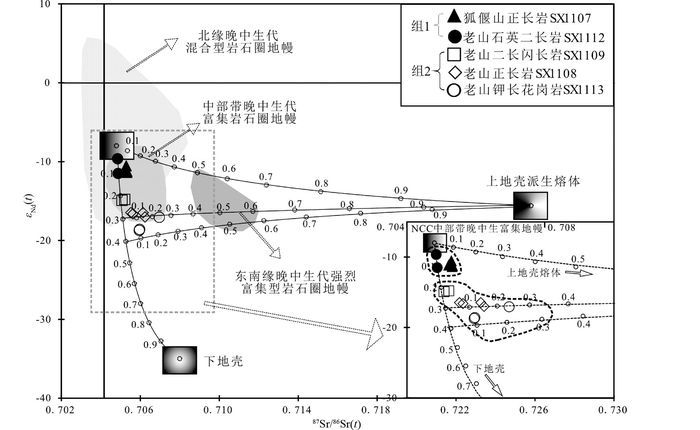
15件代表性样品的全岩Sr、Nd同位素组成见表 2和图 11,投图点的大小要大于分析误差。研究样品具有相对低Rb(43×10-6~162×10-6),高Sr(370×10-6~1273×10-6)含量和低Sm(2.1×10-6~6.4×10-6),高Nd(7.6×10-6~29.8×10-6)含量。根据锆石年龄计算的初始Sr和Nd同位素组成具有如下特征:(1)组1具有一致的低87Sr/86Sr(t)(0.7049~0.7053)和高εNd(t)(-11.5~-9.7)组成;(2)组2具有低εNd(t)值(-18.7~-14.8)和高87Sr/86Sr(t)值(0.7051~0.7070),显示更加富集特征。
|
图 11 狐偃山正长岩和老山杂岩体Sr-Nd同位素图解 NCC北缘、东南缘和中部带晚中生代岩石圈地幔数据引自Zhang et al., 2005及其中参考文献;混合模拟曲线各端元数据来源:中部带晚中生代富集岩石圈地幔引自Chen et al., 2003;华北克拉通下地壳引自Jahn et al., 1999;上地壳派生熔体引自Yang et al., 2004, 2006.模拟曲线上圆圈和数字代表端元所占比例 Fig. 11 87Sr/86Sr(t) vs. εNd(t) diagram for Laoshan complex and Huyanshan syenite The data of the SCLM from north and southeast margins and central part of NCC are after Zhang et al., 2005 and their references; The end-member of SCLM from center part of NCC is after Chen et al., 2003; The end-member of lower crust from NCC is after Jahn et al., 1999; The end-member of melts derived from upper crust of NCC is after Yang et al., 2004, 2006; circles and numbers on the modeled curve stand for end-member's proportion |
镜下观察显示,研究样品经历了不同程度的岩浆期后流体交代及低级变质作用,观察到方解石化,绢云母化和高岭土化等蚀变类型。研究样品烧失量(LOI)较低(狐偃山正长岩:1.1%~3.0%;老山岩体<1.8%),在图 6中仅狐偃山正长岩CaO与LOI呈正相关,指示岩浆期后碳酸质流体的改造,这与其镜下观察到方解石一致,其他易随流体迁移元素Rb、Ba、Sr、K2O和87Sr/86Sr(t)与LOI均无线性关系。因此,除狐偃山正长岩中CaO外,研究样品主、微量及Sr-Nd同位素组成受岩浆期后作用影响较弱,可以用于反演岩浆成因。
4.2 岩浆源区本文研究样品显示富集LILEs和LREEs,亏损HFSEs和HREEs,显著的Nb-Ta-Ti负异常和Pb的正异常等“岛弧岩浆”特征(图 9b),可能源自于:①岩浆上升过程中受围岩混染(AFC过程, DePaolo, 1981);②继承岩浆源区富集特征。前者可排除,原因如下:①研究样品中87Sr/86Sr(t)和εNd(t)与SiO2含量无线性相关(图 8i, j),多数样品εNd(t)值随着SiO2含量变化保持稳定,与分离结晶过程中发生地壳混染作用的趋势不符(DePaolo, 1981);②Ba、Rb、K等在地壳中富集的元素不随SiO2含量升高而升高(图 8f, g, h),并且相对基性样品(SX1107)具有高K、Ba、Rb含量。因此研究样品的“岛弧”特征更有可能源自深部源区。
除了传统的分类方法外(如Ⅰ型、S型和A型),Tarney and Jones (1994)提出花岗质岩石还可以分为高Ba-Sr和低Ba-Sr两种类型。高Ba-Sr花岗岩具有高Ba(≥600×10-6)和Sr(≥300×10-6)含量,相对低Rb和显著的低Y(≤30×10-6)及HREE含量,高Sr/Y和K/Rb值,无显著Eu负异常等特征。与高Ba-Sr花岗岩相比,低Ba-Sr花岗岩(即传统分类中的Ⅰ型、S型和A型花岗岩)具有相对低的Ba和Sr含量及显著的Eu负异常。上述可知,本文研究样品显示高Ba-Sr花岗岩微量元素特征。关于高Ba-Sr花岗岩的成因,前人主要提出以下几种机制:(1)加厚下地壳熔融(Ye et al., 2008; Choi et al., 2009);(2)俯冲洋岛/大洋板片熔融(Tarney and Jones, 1994);(3)交代岩石圈地幔熔融(Tarney and Jones, 1994; Qian et al., 2003; Jiang et al., 2006, 2012);(4)富集岩石圈地幔派生的钾玄质岩石分离结晶(Fowler et al., 2001; Peng et al., 2013)。加厚下地壳和俯冲大洋板片熔融会产生埃达克质熔体(Defant and Drummond, 1990),以低Mg(<3%),高Al2O3(≥15%),低Yb(<1.9×10-6)和Y(<18×10-6),高Sr(>400×10-6),富集LREE,无显著Eu负异常为特征。本文研究样品Sr/Y(28.8~92.9),(La/Yb)N比值(4.6~15.5)以及Yb(0.8×10-6~2.2×10-6)和Y含量(7.1×10-6~24.5×10-6)均显示大范围变化,相关判别图解中研究样品在埃达克质岩和经典岛弧岩石间连续分布(图 10),不显示经典埃达克质岩特征。
Qian et al. (2003)认为华北克拉通中生代时期广泛分布于东、中部的中-酸性岩石可分为高Ba-Sr花岗岩和低Ba-Sr花岗岩两种类型,前者与华北克拉通同时代基性岩具有一致的微量元素特征,为华北克拉通晚中生代富集岩石圈地幔熔融产物。此外,与本文研究区相邻的太行山地区(图 2)同时代早白垩世钾质玄武岩具有与本文样品相似的微量元素特征(图 9),Wang et al. (2006)认为这些太行山基性岩为NCC中部带晚中生代富集岩石圈地幔(Chen and Zhai, 2003; Chen et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2004)熔融产物。本文研究样品可能同样源自该富集岩石圈地幔。然而,本文两组样品中全岩Sr-Nd同位素组成存在明显差别(组2比组1更加富集),并且两组中最基性样品的Ba和Sr等特征元素含量也具有较大差别(组1中最基性样品Ba含量大于2000×10-6,而组2中小于1000×10-6,图 8f),若两者均源自该区富集岩石圈地幔,则同一地区相同时代的岩石圈地幔不可能解释如此大的地球化学差异。研究样品中大量存在与NCC基底物质年龄相近的古老锆石,上文已排除岩浆上升时围岩混染的可能,指示岩浆源区中存在壳源物质。Chen et al. (2013)提出华北克拉通中生代中-酸性岩石的壳-幔混合成因,认为这些岩石为富集岩石圈地幔派生熔体底侵至华北克拉通下地壳,烘烤下地壳并与其派生的酸性熔体混合形成,与MASH过程类似(Hildreth and Moorbath, 1988)。华北克拉通下地壳主要由中生代变质的辉长岩、镁铁质岩以及经历了强烈改造的前寒武纪下地壳麻粒岩组成,证实华北克拉通中生代幔源岩浆底侵作用(Liu et al., 2004; 翟明国等, 2005; Zhang et al., 2013)。“壳-幔”岩浆混合模型可以很好地解释本文研究样品中多变的Sr-Nd同位素特征(图 11,各端元地球化学组成见表 3):组1样品Sr-Nd同位素组成与NCC中部带晚中生代富集岩石圈地幔相近,仅需要<10%的下地壳物质参与;20%~40%下地壳物质与富集岩石圈地幔的混合可以解释组2样品更加富集的Nd同位素组成,但组2中老山正长岩和钾长花岗岩具有明显升高的Sr同位素组成,超出上述两端元的范围,并且钾长花岗岩中样品SX1113-2同时具有高εNd(t)和87Sr/86Sr(t)值,需要引入另一高87Sr/86Sr(t)端元,该端元地球化学性质与华北克拉通上地壳派生熔体相符(Yang et al., 2004, 2006)。模拟结果显示<25%的上地壳派生熔体的参与可以解释组2样品Sr-Nd同位素组成(图 11)。
|
|
表 3 各端元Sr-Nd同位素组成及本文组1、组2样品源区组分 Table 3 Sr-Nd isotopic data for end-members in Fig. 11 and source components for two group samples in this paper |
综上所述,本文研究样品源区由华北克拉通中部带富集岩石圈地幔和下地壳派生熔体不同程度混合形成,部分样品源区还存在上地壳派生熔体的参与。
4.3 分离结晶两组样品经历了不同的分离结晶作用(图 7、图 8):随着SiO2升高,组1中MgO、Cr、Co、Ni、V含量均保持稳定,指示无显著的基性矿物分离结晶。组1中由相对基性的狐偃山正长岩至老山石英二长岩,K2O、Fe2O3T和Al2O3降低(图 7),与黑云母分离结晶的趋势相符。组2样品MgO、TFe2O3、TiO2、P2O5、Cr、Co、Ni、V呈线性降低(图 7、图 8),指示基性矿物(辉石或角闪石)和含Ti、P矿物(磁铁矿,榍石,磷灰石等)的分离结晶作用;组2中钾长花岗岩SX1113系列样品具有明显降低的CaO和Na2O含量,指示斜长石分离结晶作用,这与该系列样品相对低Sr含量(图 8e)和弱负铕异常(Eu/Eu*=0.75~0.83)一致。
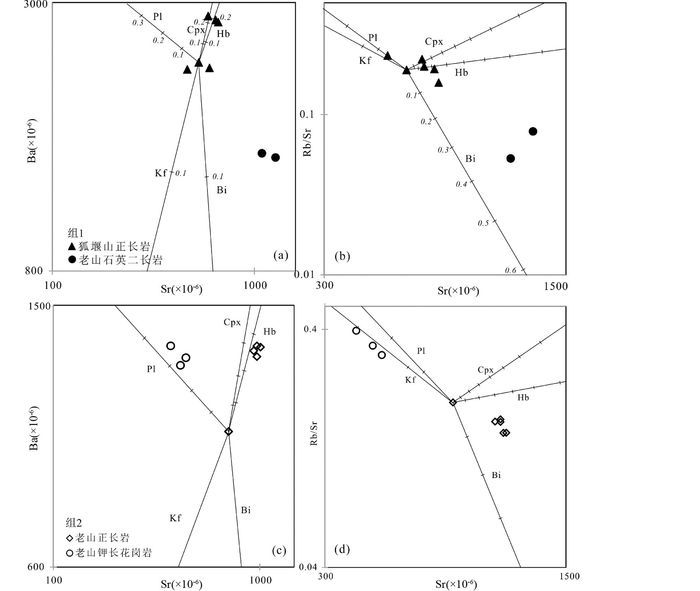
此外,根据Ba、Sr、Rb等元素在黑云母,角闪石,辉石和长石等矿物与中、酸性熔体间的分配系数(Hanson, 1978),进一步判别研究样品分离结晶趋势(图 12,以每组中最基性样品的微量元素含量为初始值):组1中老山石英二长岩由初始岩浆(以狐偃山正长岩样品SX1107-1组成为代表)经历黑云母分离结晶形成,导致Ba含量显著降低和Sr含量升高(图 12a, b);组2中老山正长岩由初始岩浆(以老山正长岩中最基性样品SX1108-6组成为代表)经历角闪石分离结晶形成,伴随Ba和Sr含量升高(图 12c),老山钾长花岗岩由初始岩浆(同样以老山正长岩中最基性样品SX1108-6组成为代表)经历斜长石分离结晶形成,导致Ba升高Sr降低(图 12d)。上述讨论可知研究样品微量与主量元素所得结论一致,进一步表明两组样品中Ba、Rb、Sr等关键元素的变化与各组中不同矿物组合的分离结晶作用有关。
|
图 12 组1和组2代表性样品微量元素分离结晶判别图解 Kf-钾长石;Pl-斜长石;Bi-黑云母;Hbl-角闪石;Cpx-单斜辉石;图中短线代表分离结晶程度 Fig. 12 Fractionation discrimination diagram using trace elements for representative samples in Group 1 and Group 2 Kfs-K-feldspar; Pl-plagiocase; Bi-biotite; Hbl-hornblende; Cpx-clinopyroxene; short lines in this figure stand for degrees of fractionation |
组2样品中一些特征微量元素比值也受到分离结晶作用的影响。角闪石的分离结晶会导致残余岩浆的中稀土亏损,重稀土变平坦(Klein et al., 1997; Bottazzi et al., 1999; Hilyard et al., 2000; Tiepolo et al., 2007),伴随Dy/Yb比值降低(Macpherson et al., 2006; Davidson et al., 2007)和Sr/Y比值升高(Castillo et al., 1999; Chiaradia et al., 2009; Gao et al., 2012),而斜长石分离结晶则会降低岩浆中Sr含量(Castillo et al., 1999),导致Sr/Y比值降低。这与组2特征相符(图 13a, b),进一步显示研究样品Sr/Y值变化与岩浆演化相关。Nb和Ta因相似的离子半径和电位,在大部分岩浆事件中保持一致的地球化学行为,但发生含Ti矿物分离(图 7g)的组2样品中Nb/Ta与TiO2呈负相关(图 13c),这与Green and Pearson (1987)提出的磁铁矿和榍石等含Ti矿物更加富集Ta而亏损Nb,它们的分离结晶会导致残余岩浆中Nb/Ta比值升高一致。发生磷灰石分离结晶(图 7h)的组2中REE含量与P2O5呈正比(图 13d),指示磷灰石是稀土元素的主要赋存矿物。

|
图 13 组2样品微量元素比值Dy/Yb、Sr/Y、Nb/Ta和REE与主量元素SiO2、TiO2和P2O5相关图解 Hbl-角闪石;Pl-斜长石;Mt-磁铁矿;Sp-榍石;Ap-磷灰石 Fig. 13 Covariation diagram of trace element ratios Dy/Yb, Sr/Y, Nb/Ta and REE vs. major elements SiO2, TiO2 and P2O5 for Group 2 samples Hbl-hornblende; Pl-plagiocase; Mt-magnetite; Sp-sphene; Ap-apatite |
综上所述,两组样品经历了不同的分离结晶作用:组1样品以黑云母分离结晶为主;组2样品则经历了角闪石和斜长石分离结晶,同时伴随榍石,磁铁矿和磷灰石等副矿物的分离结晶。不同的分离结晶矿物组合显著改变两组样品中具有指示意义的微量元素含量(Ba、Rb、Sr等)及比值(Sr/Y、Nb/Ta、Dy/Yb)。
4.4 华北克拉通中部带岩石圈地幔富集机制及其对该区中生代破坏机制的启示晚中生代时华北克拉通各区域岩石圈地幔已表现出不同的富集程度(图 11, Chen and Zhai, 2003; Chen et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2004; 周新华和张宏福, 2006; Guo et al., 2014),指示不同的演化历程(Şengör et al., 1993; Li et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2004; 周新华和张宏福, 2006),而该时期中部带岩石圈地幔的富集机制仍未明确。岩石圈地幔的富集主要有下三种机制(Menzies et al., 1987; Dawson and Smith, 1988; Harte et al., 1993; Rudnick et al., 1993; Furman, 1995; Martins et al., 2010; Gagnevin et al., 2011; O’Reilly and Griffin, 2013):(1)富碳酸盐熔体交代作用,导致地幔橄榄岩具有相对高的REE和低HFSEs含量及异常Zr/Hf值(Dupuy et al., 1992; Rudnick et al., 1993; Furman, 1995),形成低(Hf/Sm)N和(Ta/La)N值(图 14a);(2)俯冲板片派生流体交代作用,导致地幔橄榄岩富集易活动元素LILEs(Rb、Ba、K),U和Pb等,亏损相对不活动元素Th、Nb和REE等(Keppler, 1996; Hawkesworth et al., 1997; Kogiso et al., 1997; Savov et al., 2007);(3)俯冲板片派生熔体交代作用,导致地幔橄榄岩富集LILEs和LREEs等强不相容性元素,相对亏损HREEs和HFSEs(Kepezhinskas et al., 1995, 1997; Johnson and Plank, 2000; Yogodzinski et al., 2001; Bourdon et al., 2002; Gao et al., 2007)。因此,流体活动性元素Ba和流体不活动性元素La的比值(Ba/La)可指示板片派生流体交代作用程度,而熔体活动性元素Th和熔体不活动性元素Yb的比值(Th/Yb)代表板片派生熔体交代作用程度(图 14b)。本文利用含壳源物质最少,最基性的狐偃山正长岩样品(SX1107)揭示该区岩石圈地幔富集机制,可知样品远离受碳酸质熔体交代作用区域,而落入与俯冲相关熔/流体交代作用区域(图 14a),高Ba/La值和低Th/Yb值远离板片派生熔体区域,而与板片派生流体交代作用趋势相符,指示以板片派生流体交代作用为主的地幔富集机制(图 14b)。华北克拉通中部带远离板块边缘,受周边板块碰撞影响较小,最近的事件为1.8Ga时华北克拉通东、西陆块沿着中部带的碰撞拼合(Zhao et al., 2001),因此该区岩石圈地幔的富集最有可能由该时期俯冲板片派生流体交代形成。
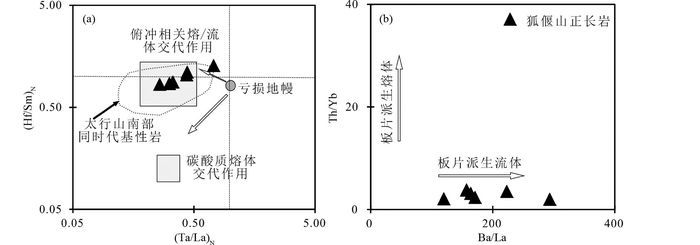
|
图 14 狐偃山正长岩样品(Ta/La)N-(Hf/Sm)N相关图解(a, 据Wang et al., 2006)和Ba/La-Th/Yb相关图解(b) Fig. 14 Covariation diagrams of (Ta/La)N vs. (Hf/Sm)N (a, after Wang et al., 2006) and Ba/La vs. Th/Yb (b) for Huyanshan syenite |
中生代时,古太平洋板块开始沿着华北克拉通东缘向下俯冲(Maruyama et al., 1997),地球物理资料显示现今太平洋板块俯冲的前缘位置与太行山区域重合(Huang and Zhao, 2006)。以太行山一线为界,华北克拉通现今岩石圈厚度具有东部薄(60~100km),中-西部厚(>200km)的特点(Chen et al., 2009; Chen, 2009, 2010; 朱日祥等, 2011),上述时空关系指示古太平洋板块俯冲对克拉通破坏事件的控制作用。此外,地震层析图像揭示华北克拉通中部带岩石圈显著减薄位置包括东部太行山和西部陕西-山西断裂带(Chen et al., 2009; Chen, 2009),与本文研究的狐偃山和老山岩体及同时期太行山基性岩区域重合,均发育在以东、西缘古老缝合带为代表的构造薄弱区域。因此,华北克拉通中部带构造薄弱区域在碰撞后伸展环境下(Müller et al., 1992; 翟明国等, 2003; 王涛等, 2007; 刘俊来等, 2008; 林伟等, 2013)发生富集岩石圈地幔减压熔融、底侵和“壳-幔”岩浆混合,这种深部岩浆抽取可能是中部带岩石圈减薄的主要机制。
5 结论华北克拉通中部带西缘老山杂岩体和狐偃山正长岩形成时间接近(128.7~125.4Ma),代表该区早白垩世岩浆作用。研究样品均属于高Ba-Sr花岗岩,形成于富集岩石圈地幔派生熔体底侵所引起的“壳-幔”岩浆混合。系统的地球化学研究显示两种岩浆演化:组1具有高Ba特征,源区中壳源组分少(<10%),经历了黑云母分离结晶作用;组2具有低Ba特征,源区中壳源组分明显升高(20%~40%),经历了角闪石,斜长石及磷灰石、磁铁矿和榍石等矿物分离结晶。2组样品不同的源区组分和分离结晶组合会显著改变岩浆中特征微量元素(Ba、Sr、Rb)含量和比值(Sr/Y、Nb/Ta、Dy/Yb)。
本文研究表明华北克拉通中部带晚中生代岩石圈地幔主要与元古代东、西陆块向中部带碰撞拼合时俯冲板块派生流体交代作用有关,该区中生代破坏机制为古太平洋板块俯冲所引起的碰撞后伸展背景下富集岩石圈地幔减压熔融、底侵和“壳-幔”岩浆相互作用所导致的深部岩浆抽取。
致谢 感谢戚学祥研究员和谢桂青研究员仔细审阅稿件,提出众多建设性修改意见。
Bottazzi P, Tiepolo M, Vanucci R, Zanetti A, Brumm R, Foley SF and Oberti R. 1999. Distinct site preferences for heavy and light REE in amphibole and the prediction of Amph/LDREE. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 137(1-2): 36-45. DOI:10.1007/s004100050580 |
Bourdon E, Eissen JP, Monzier M, Robin C, Martin H, Cotten J and Hall ML. 2002. Adakite-like lavas from Antisana Volcano (Ecuador):Evidence for slab melt metasomatism beneath Andean Northern Volcanic Zone. Journal of Petrology, 43(2): 199-217. DOI:10.1093/petrology/43.2.199 |
Castillo PR, Janney PE and Solidum RU. 1999. Petrology and geochemistry of Camiguin island, southern Philippines:Insights to the source of adakites and other lavas in a complex arc setting. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 134(1): 33-51. DOI:10.1007/s004100050467 |
Chen B and Zhai M. 2003. Geochemistry of Late Mesozoic lamprophyre dykes from the Taihang Mountains, North China, and implications for the sub-continental lithospheric mantle. Geological Magazine, 140(1): 87-93. DOI:10.1017/S0016756802007124 |
Chen B, Jahn BM and Zhai MG. 2003. Sr-Nd isotopic characteristics of the Mesozoic magmatism in the Taihang-Yanshan orogen, North China craton, and implications for Archean lithosphere thinning. Journal of the Geological Society, 160(6): 963-970. DOI:10.1144/0016-764902-129 |
Chen B, Jahn BM, Arakawa Y and Zhai MG. 2004. Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic intrusive complexes from the southern Taihang orogen, North China craton:Elemental and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic constraints. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 148(4): 489-501. DOI:10.1007/s00410-004-0620-0 |
Chen B, Tian W, Jahn BM and Chen ZC. 2008. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb ages and in-situ Hf isotopic analysis for the Mesozoic intrusions in South Taihang, North China Craton:Evidence for hybridization between mantle-derived magmas and crustal components. Lithos, 102(1-2): 118-137. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.06.012 |
Chen B, Jahn BM and Suzuki K. 2013. Petrological and Nd-Sr-Os isotopic constraints on the origin of high-Mg adakitic rocks from the North China Craton:Tectonic implications. Geology, 41(1): 91-94. DOI:10.1130/G33472.1 |
Chen F, Siebel W, Satir M, Terzioǧlu M and Saka K. 2002. Geochronology of the Karadere basement (NW Turkey) and implications for the geological evolution of the Istanbul zone. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 91(3): 469-481. DOI:10.1007/s00531-001-0239-6 |
Chen F, Li XH, Wang XL, Li QL and Siebel W. 2007. Zircon age and Nd-Hf isotopic composition of the Yunan Tethyan belt, southwestern China. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 96(6): 1179-1194. DOI:10.1007/s00531-006-0146-y |
Chen L. 2009. Lithospheric structure variations between the eastern and central North China Craton from S-and P-receiver function migration. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 173(3-4): 216-227. DOI:10.1016/j.pepi.2008.11.011 |
Chen L, Cheng C and Wei ZG. 2009. Seismic evidence for significant lateral variations in lithospheric thickness beneath the central and western North China Craton. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 286(1-2): 171-183. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2009.06.022 |
Chen L. 2010. Concordant structural variations from the surface to the base of the upper mantle in the North China Craton and its tectonic implications. Lithos, 120(1-2): 96-115. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.12.007 |
Chiaradia M, Müntener O, Beate B and Fontignite D. 2009. Adakite-like volcanism of Ecuador:Lower crust magmatic evolution and recycling. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 158(5): 563-588. DOI:10.1007/s00410-009-0397-2 |
Choi SG, Rajesh VJ, Seo J, Park JW, Oh CW, Pak SJ and Kim SW. 2009. Petrology, geochronology and tectonic implications of Mesozoic high Ba-Sr granites in the Haemi area, Hongseong Belt, South Korea. Island Arc, 18(2): 266-281. |
Davidson J, Turner S, Handley H, Macpherson C and Dosseto A. 2007. Amphibole "sponge" in arc crust. Geology, 35(9): 787-790. DOI:10.1130/G23637A.1 |
Dawson JB and Smith JV. 1988. Metasomatised and veined upper-mantle xenoliths from Pello Hill, Tanzania:Evidence for anomalously-light mantle beneath the Tanzanian sector of the East African Rift Valley. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 100(4): 510-527. DOI:10.1007/BF00371380 |
Defant MJ and Drummond MS. 1990. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature, 347(6294): 662-665. DOI:10.1038/347662a0 |
DePaolo DJ. 1981. Trace element and isotopic effects of combined wallrock assimilation and fractional crystallization. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 53(2): 189-202. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(81)90153-9 |
Dupuy C, Liotard JM and Dostal J. 1992. Zr/Hf fractionation in intraplate basaltic rocks:Carbonate metasomatism in the mantle source. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 56(6): 2417-2424. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(92)90198-R |
Fan WM, Guo F, Wang YJ, Lin G and Zhang M. 2001. Post-orogenic bimodal volcanism along the Sulu Orogenic Belt in eastern China. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A:Solid Earth and Geodesy, 26(9-10): 733-746. DOI:10.1016/S1464-1895(01)00123-5 |
Fowler MB, Henney PJ, Darbyshire DPF and Greenwood PB. 2001. Petrogenesis of high Ba-Sr granites:The Rogart pluton, Sutherland. Journal of the Geological Society, 158(3): 521-534. DOI:10.1144/jgs.158.3.521 |
Furman T. 1995. Melting of metasomatized subcontinental lithosphere:Undersaturated mafic lavas from Rungwe, Tanzania. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 122(1-2): 97-115. DOI:10.1007/s004100050115 |
Furman T and Graham D. 1999. Erosion of lithospheric mantle beneath the East African Rift system:Geochemical evidence from the Kivu volcanic province. Lithos, 48(1-4): 237-262. DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00031-6 |
Gagnevin D, Daly JS, Horstwood MSA and Whitehouse MJ. 2011. In-situ zircon U-Pb, oxygen and hafnium isotopic evidence for magma mixing and mantle metasomatism in the Tuscan Magmatic Province, Italy. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 305(1-2): 45-56. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2011.02.039 |
Gao S, Rudnick RL, Carlson RW, McDonough WF and Liu YS. 2002. Re-Os evidence for replacement of ancient mantle lithosphere beneath the North China Craton. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 198(3-4): 307-322. DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00489-2 |
Gao S, Rudnick RL, Yuan HL, Liu XM, Liu YS, Xu WL, Ling WL, Ayers J, Wang XC and Wang QH. 2004. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China craton. Nature, 432(7019): 892-897. DOI:10.1038/nature03162 |
Gao S, Zhang JF, Xu WL and Liu YS. 2009. Delamination and destruction of the North China Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(19): 3367-3378. |
Gao YF, Hou ZQ, Kamber BS, Wei RH, Meng XJ and Zhao RS. 2007. Adakite-like porphyries from the southern Tibetan continental collision zones:Evidence for slab melt metasomatism. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 153(1): 105-120. DOI:10.1007/s00410-006-0137-9 |
Gao YF, Santosh M, Hou ZQ, Wei RH, Ma GX, Chen ZK and Wu JL. 2012. High Sr/Y magmas generated through crystal fractionation:Evidence from Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the northern Taihang orogeny, North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 22(1): 152-168. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.11.002 |
Green TH and Pearson NJ. 1987. An experimental study of Nb and Ta partitioning between Ti-rich minerals and silicate liquids at high pressure and temperature. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 51(1): 55-62. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(87)90006-8 |
Griffin WL, Zhang AD, O'Reilly SY and Ryan CG. 1998. Phanerozoic evolution of the lithosphere beneath the Sino-Korean Craton. In:Fowler MFJ, Chung SL, Lo CH and Lee TY (eds.). Mantle Dynamics and Plate Interactions in East Asia. Washington:American Geophysical Union, 107-126
|
Guo PY, Niu YL, Ye L, Liu JJ, Sun P, Cui HX, Zhang Y, Gao JP, Su L, Zhao JX and Feng YX. 2014. Lithosphere thinning beneath west North China Craton:Evidence from geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotope compositions of Jining basalts. Lithos, 202-203: 37-54. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.04.024 |
Hanson GN. 1978. The application of trace elements to the petrogenesis of igneous rocks of granitic composition. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 38(1): 26-43. |
Harte B, Hunter RH and Kinney PD. 1993. Melt geometry, movement and crystallization, in relation to mantle dykes, veins and metasomatism. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A:Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 342(1663): 1-21. DOI:10.1098/rsta.1993.0001 |
Hawkesworth CJ, Turner SP, McDermott F, Peate DW and Van Calsteren P. 1997. U-Th isotopes in arc magmas:Implications for element transfer from the subducted crust. Science, 276(5312): 551-555. DOI:10.1126/science.276.5312.551 |
He XF and Santosh M. 2014. Crustal recycling through intraplate magmatism:Evidence from the Trans-North China Orogen. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 95: 147-163. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.02.011 |
Hildreth W and Moorbath S. 1988. Crustal contributions to arc magmatism in the Andes of central Chile. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 98(4): 455-489. DOI:10.1007/BF00372365 |
Hilyard M, Nielsen RL, Beard JS, Patinõ-Douce A and Blencoe J. 2000. Experimental determination of the partitioning behavior of rare earth and high field strength elements between pargasitic amphibole and natural silicate melts. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(6): 1103-1120. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00379-8 |
Hofmann AW, Jochum KP, Seufert M and White WM. 1986. Nb and Pb in oceanic basalts:New constraints on mantle evolution. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 79(1-2): 33-45. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(86)90038-5 |
Huang JL and Zhao DP. 2006. High-resolution mantle tomography of China and surrounding regions. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 111(B9). DOI:10.1029/2005JB004066 |
Ionov DA and Hofmann AW. 1995. Nb-Ta-rich mantle amphiboles and micas:Implications for subduction-related metasomatic trace element fractionations. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 131(3-4): 341-356. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(95)00037-D |
Ionov DA, Griffin WL and O'Reilly SY. 1997. Volatile-bearing minerals and lithophile trace elements in the upper mantle. Chemical Geology, 141(3-4): 153-184. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00061-2 |
Jahn BM and Bai YL. 1983. Early Archean (3.5Ga) metabasic rocks from the Tsao Zhuang Group, E Hebei, China:Sm-Nd common Pb and Rb-Sr isotopic ages. Beijing:Symposium "Precambrain Crustal Evolution"
|
Jahn BM, Wu FY, Lo CH and Tsai CH. 1999. Crust-mantle interaction induced by deep subduction of the continental crust:Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from post-collisional mafic-ultramafic intrusions of the northern Dabie complex, central China. Chemical Geology, 157(1-2): 119-146. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00197-1 |
Jiang YH, Jiang SY, Ling HF and Dai BZ. 2006. Low-degree melting of a metasomatized lithospheric mantle for the origin of Cenozoic Yulong monzogranite-porphyry, east Tibet:Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic constraints. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 241(3-4): 617-633. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.11.023 |
Jiang YH, Liu Z, Jia RY, Liao SY, Zhou Q and Zhao P. 2012. Miocene potassic granite-syenite association in western Tibetan Plateau:Implications for shoshonitic and high Ba-Sr granite genesis. Lithos, 134-135: 146-162. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.12.012 |
Johnson MC and Plank T. 2000. Dehydration and melting experiments constrain the fate of subducted sediments. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 1(12). DOI:10.1029/1999GC000014 |
Kepezhinskas PK, Defant MJ and Drummond MS. 1995. Na metasomatism in the island-arc mantle by slab melt-peridotite interaction:Evidence from mantle xenoliths in the North Kamchatka Arc. Journal of Petrology, 36(6): 1505-1527. |
Kepezhinskas P, McDermott F, Defant MJ, Hochstaedter A, Drummond MS, Hawkesworth CJ, Koloskov A, Maury RC and Bellon H. 1997. Trace element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic constraints on a three-component model of Kamchatka Arc petrogenesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61(3): 577-600. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00349-3 |
Keppler H. 1996. Constraints from partitioning experiments on the composition of subduction-zone fluids. Nature, 380(6571): 237-240. DOI:10.1038/380237a0 |
Klein M, Stosch HG and Seck HA. 1997. Partitioning of high field-strength and rare-earth elements between amphibole and quartz-dioritic to tonalitic melts:An experimental study. Chemical Geology, 138(3-4): 257-271. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00019-3 |
Kogiso T, Tatsumi Y and Nakano S. 1997. Trace element transport during dehydration processes in the subducted oceanic crust:1. Experiments and implications for the origin of ocean island basalts. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 148(1-2): 193-205. |
La Flèche MR, Camiré G and Jenner GA. 1998. Geochemistry of post-Acadian, Carboniferous continental intraplate basalts from the Maritimes Basin, Magdalen Islands, Québec, Canada. Chemical Geology, 148(3-4): 115-136. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00002-3 |
Li Q, Santosh M, Li SR and Zhang JQ. 2015. Petrology, geochemistry and zircon U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopes of the Cretaceous dykes in the central North China Craton:Implications for magma genesis and gold metallogeny. Ore Geology Reviews, 67: 57-77. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.11.015 |
Li SG, Jagoutz E, Chen YZ and Li QL. 2000. Sm-Nd and Rb-Sr isotopic chronology and cooling history of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks and their country rocks at Shuanghe in the Dabie Mountains, Central China. Geochimica et Cosmochimca Acta, 64(6): 1077-1093. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00319-1 |
Li SR, Santosh M, Zhang HF, Shen JF, Dong GC, Wang JZ and Zhang JQ. 2013. Inhomogeneous lithospheric thinning in the central North China Craton:Zircon U-Pb and S-He-Ar isotopic record from magmatism and metallogeny in the Taihang Mountains. Gondwana Research, 23(1): 141-160. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.006 |
Li SR, Santosh M, Zhang HF, Luo JY, Zhang JQ, Li CL, Song JY and Zhang XB. 2014. Metallogeny in response to lithospheric thinning and craton destruction:Geochemistry and U-Pb zircon chronology of the Yixingzhai gold deposit, central North China Craton. Ore Geology Reviews, 56: 457-471. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.10.008 |
Li ZX and Li XH. 2007. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China:A flat-slab subduction model. Geology, 35(2): 179-182. DOI:10.1130/G23193A.1 |
Lin W, Wang J, Liu F, Ji WB and Wang QC. 2013. Late Mesozoic extension structures on the North China Craton and adjacent regions and its geodynamics. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(5): 1791-1810. |
Liu DY, Nutman AP, Compston W, Wu JS and Shen QH. 1992. Remmants of ≥ 3800Ma crust in the Chinese part of the Sino-Korean Craton. Geology, 20(4): 339-342. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0339:ROMCIT>2.3.CO;2 |
Liu J, Xia QK, Deloule E, Ingrin J, Chen H and Feng M. 2015a. Water content and oxygen isotopic composition of alkali basalts from the Taihang Mountains, China:Recycled oceanic components in the mantle source. Journal of Petrology, 56(4): 681-702. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egv013 |
Liu J, Xia QK, Deloule E, Chen H and Feng M. 2015b. Recycled oceanic crust and marine sediment in the source of alkali basalts in Shandong, eastern China:Evidence from magma water content and oxygen isotopes. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 120(12): 8281-8303. DOI:10.1002/2015JB012476 |
Liu JL, Davis GA, Ji Mo, Guan HM and Bai XD. 2008. Crustal detachment and destruction of the North China craton:Constraints from Late Mesozoic extensional structures. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(3): 72-81. DOI:10.1016/S1872-5791(08)60063-9 |
Liu YS, Gao S, Yuan HL, Zhou L, Liu XM, Wang XC, Hu ZC and Wang LS. 2004. U-Pb zircon ages and Nd, Sr, and Pb isotopes of lower crustal xenoliths from North China Craton:Insights on evolution of lower continental crust. Chemical Geology, 211(1-2): 87-109. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.06.023 |
Liu YS, Gao S, Hu ZC, Gao CG, Zong KQ and Wang DB. 2010. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2): 537-571. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egp082 |
Ma JL and Xu YG. 2004. Petrology and geochemistry of the Cenozoic basalts from Yangyuan of Hebei Province and Datong of Shanxi Province:Implications for the deep process in the western North China Craton. Geochimica, 33(1): 75-88. |
Macpherson CG, Dreher ST and Thirlwall MF. 2006. Adakites without slab melting:High pressure differentiation of island arc magma, Mindanao, the Philippines. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 243(3-4): 581-593. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.12.034 |
Martins S, Mata J, Munhá J, Mendes MH, Maerschalk C, Caldeira R and Mattielli N. 2010. Chemical and mineralogical evidence of the occurrence of mantle metasomatism by carbonate-rich melts in an oceanic environment (Santiago Island, Cape Verde). Mineralogy and Petrology, 99(1-2): 43-65. DOI:10.1007/s00710-009-0078-x |
Maruyama S, Isozaki Y, Kimura G and Terabayashi M. 1997. Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands:Plate tectonic synthesis from 750Ma to the present. Island Arcs, 6(1): 121-142. DOI:10.1111/iar.1997.6.issue-1 |
Menzies MA, Rogers N, Tindle A and Hawkesworth CJ. 1987. Metasomatic and enrichment processes in lithospheric peridotites, an affect of asthenosphere-lithosphere interaction. In:Menzies MA and Hawkesworth CJ (eds.). Mantle Metasomatism. London:Academic Press, 313-361
|
Menzies MA, Fan WM and Zhang M. 1993. Palaeozoic and Cenozoic lithoprobes and the loss of >120km of Archean lithosphere, Sino-Korean craton, China. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 76(1): 71-81. DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1993.076.01.04 |
Menzies MA and Xu YG. 1998. Geodynamics of the North China craton. In:Fowler MFJ, Chung SL, Lo CH and Lee TY (eds.). Mantle Dynamics and Plate Interactions in East Asia. Washington:American Geophysical Union, 155-165
|
Müller D, Rock NMS and Groves DI. 1992. Geochemical discrimination between shoshonitic and potassic volcanic rocks in different tectonic settings:A pilot study. Mineralogy and Petrology, 46(4): 259-289. DOI:10.1007/BF01173568 |
Niu YL. 2005. Generation and evolution of basaltic magmas:Some basic concepts and a new view on the origin of Mesozoic-Cenozoic basaltic volcanism in eastern China. Geological Journal of China Universities, 11(1): 9-46. |
O'Reilly SY and Griffin WL. 2013. Mantle metasomatism. In:Harlov DE and Austrheim H (eds.). Metasomatism and the Chemical Transformation of Rock. Berlin Heidelberg:Springer, 471-533
|
Peng TP, Wilde SA, Fan WM and Peng BX. 2013. Late Neoarchean potassic high Ba-Sr granites in the Taishan granite-greenstone terrane:Petrogenesis and implications for continental crustal evolution. Chemical Geology, 344: 23-41. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.02.012 |
Pilet S, Hemandez J, Bussy F and Sylvester PJ. 2004. Short-term metasomatic control of Nb/Th ratios in the mantle sources of intraplate basalts. Geology, 32(2): 113-116. DOI:10.1130/G19953.1 |
Qian Q, Chung SL, Lee TY and Wen DJ. 2003. Mesozoic high-Ba-Sr granitoids from North China:Geochemical characteristics and geological implications. Terra Nova, 15(4): 272-278. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-3121.2003.00491.x |
Qian SP, Ren ZY, Richard W, Zhang L, Zhang YH, Hong LB, Ding XL and Wu YD. 2017. Petrogenesis of Early Cretaceous basaltic lavas from the North China Craton:Implications for cratonic destruction. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 122(3): 1900-1918. |
Rudnick RL, McDonough MF and Chappell BW. 1993. Carbonatite metasomatism in the northern Tanzanian mantle:Petrographic and geochemical characteristics. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 114(4): 463-475. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(93)90076-L |
Savov IP, Ryan JG, D'Antonio M and Fryer P. 2007. Shallow slab fluid release across and along the Mariana arc-basin system:Insights from geochemistry of serpentinized peridotites from the Mariana fore arc. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 112(B9). DOI:10.1029/2006JB004749 |
Şengör AMC, Natal'In BA and Burtman VS. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia. Nature, 364(6435): 299-307. DOI:10.1038/364299a0 |
Shao JA, Li XH, Zhang FQ, Mou BL and Liu YL. 2001. Geochemical condition for genetic mechanism of the Mesozoic bimodal dike swarms in Nankou Guyaju. Geochimica, 30(6): 517-524. |
Shao JA, Zhai MG, Zhang LQ and Li DM. 2005. Identification of 5 Time-Groups of dike swarms in Shanxi-Hebei-Inner Mongulia border area and its tectonic implications. Acta Gelogica Sinica, 79(1): 56-67. |
Shen JF, Santosh M, Li SR, Zhang HF, Yin N, Dong GC, Wang YJ, Ma GG and Yu HJ. 2013. The Beiminghe skarn iron deposit, eastern China:Geochronology, isotope geochemistry and implications for the destruction of the North China Craton. Lithos, 156-159: 218-229. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.11.003 |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes. In:Sanders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345. DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 |
Tang YJ, Zhang HF, Ying JF and Zhang J. 2006. Source characteristics and temporal-spatial evolution of Mesozoic and Cenozoic basaltic magmatism in the Taihang Mountains. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(6): 1657-1664. |
Tarney J and Jones CE. 1994. Trace element geochemistry of orogenic igneous rocks and crustal growth models. Journal of the Geological Society, 151(5): 855-868. DOI:10.1144/gsjgs.151.5.0855 |
Tiepolo M, Oberti R, Zanetti A, Vannucci R and Foley SF. 2007. Trace-element partitioning between amphibole and silicate melt. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 67(1): 417-452. DOI:10.2138/rmg.2007.67.11 |
Wang T, Zheng YD, Zhang JJ, Wang XS, Zeng LS and Tong Y. 2007. Some problems in the study of Mesozoic extensional structure in the North China craton and its significance for the study of lithospheric thinning. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(9): 1154-1166. |
Wang YJ, Fan WM, Zhang HF and Peng TP. 2006. Early Cretaceous gabbroic rocks from the Taihang Mountains:Implications for a paleosubduction-related lithospheric mantle beneath the central North China Craton. Lithos, 86(3-4): 281-302. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2005.07.001 |
Wang YY, Cai YH, Yan GH, Zhou WW and Yan ZJ. 2014. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic characteristics of the Zijinshan alkaline complex in Linxian County, Shanxi Province. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 33(6): 1052-1072. |
Xu WL, Gao S, Wang QH, Wang DY and Liu YS. 2006. Mesozoic crustal thickening of the eastern North China craton:Evidence from eclogite xenoliths and petrologic implications. Geology, 34(9): 721-724. DOI:10.1130/G22551.1 |
Xu WL, Hergt JM, Gao S, Pei FP, Wang W and Yang DB. 2008a. Interaction of adakitic melt-peridotite:Implications for the high-Mg# signature of Mesozoic adakitic rocks in the eastern North China Craton. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 265(1-2): 123-137. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.09.041 |
Xu WL, Yang DB, Gao S, Pei FP and Yu Y. 2010. Geochemistry of peridotite xenoliths in Early Cretaceous high-Mg# diorites from the Central Orogenic Block of the North China Craton:The nature of Mesozoic lithospheric mantle and constraints on lithospheric thinning. Chemical Geology, 270(1-4): 257-273. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.12.006 |
Xu YG. 2001. Thermo-tectonic destruction of the Archaean lithospheric keel beneath the Sino-Korean Craton in China:Evidence, timing and mechanism. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A:Solid Earth and Geodesy, 26(9-10): 747-757. DOI:10.1016/S1464-1895(01)00124-7 |
Xu YG. 2004. Lithospheric thinning beneath North China:A temporal and spatial perspective. Geological Journal of China Universities, 10(3): 324-331. |
Xu YG. 2006. Formation of the Taihangshan gravity lineament by the diachronous lithospheric thinning of the North China Craton. Earth Science (Jounal of China University of Geosciences), 31(1): 14-22. |
Xu YG, Blusztajn J, Ma JL, Suauki K, Liu JF and Hart SR. 2008b. Late Archean to Early Proterozoic lithospheric mantle beneath the western North China craton:Sr-Nd-Os isotopes of peridotite xenoliths from Yangyuan and Fansi. Lithos, 102(1-2): 25-42. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.04.005 |
Yang JH, Wu FY, Chung SL, Wilde SA and Chu MF. 2004. Multiple sources for the origin of granites:Geochemical and Nd/Sr isotopic evidence from the Gudaoling granite and its mafic enclaves, Northeast China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(21): 4469-4483. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2004.04.015 |
Yang JH, Wu FY, Chung SL, Wilde SA and Chu MF. 2006. A hybrid origin for the Qianshan A-type granite, Northeast China:Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence. Lithos, 89(1-2): 89-106. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2005.10.002 |
Ye HM, Li XH, Li ZX and Zhang CL. 2008. Age and origin of high Ba-Sr appinite-granites at the northwestern margin of the Tibet Plateau:Implications for Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Western Kunlun orogenic belt. Gondwana Research, 13(1): 126-138. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2007.08.005 |
Ye K, Cong BL and Ye DN. 2000. The possible subduction of continental material to depths greater than 200km. Nature, 407(6805): 734-736. DOI:10.1038/35037566 |
Ying JF, Zhang HF, Sun M, Tang YJ, Zhou XH and Liu XM. 2007. Petrology and geochemistry of Zijinshan alkaline intrusive complex in Shanxi Province, western North China Craton:Implication for magma mixing of different sources in an extensional regime. Lithos, 98(1-4): 45-66. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.02.001 |
Ying JF, Zhang HF and Tang YJ. 2011. Crust-mantle interaction in the central North China Craton during the Mesozoic:Evidence from zircon U-Pb chronology, Hf isotope and geochemistry of syenitic-monzonitic intrusions from Shanxi province. Lithos, 125(1-2): 449-462. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.03.004 |
Yogodzinski GM, Lees JM, Churikova TG, Dorendorf F, Wöerner G and Volynets ON. 2001. Geochemical evidence for the melting of subducting oceanic lithosphere at plate edges. Nature, 409(6819): 500-504. DOI:10.1038/35054039 |
Zhai MG, Zhu RX, Liu JM, Meng QR, Hou QL, Hu SB, Li Z, Zhang HF and Liu W. 2003. The key time of eastern North China Craton tectonic regime transformation during Mesozoic. Science in China (Series D), 33(10): 913-920. |
Zhai MG, Fan QC, Zhang HF and Sui JL. 2005. Lower crust processes during the lithosphere thinning in eastern China:Magma underplating, replacement and delamination. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(6): 1509-1526. |
Zhang HF, Sun M, Zhou XH, Fan WM, Zhai MG and Yin JF. 2002. Mesozoic lithosphere destruction beneath the North China Craton:Evidence from major-, trace-element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotope studies of Fangcheng basalts. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 144(2): 241-253. DOI:10.1007/s00410-002-0395-0 |
Zhang HF, Sun M, Zhou MF, Fan WM, Zhou XH and Zhai MG. 2004. Highly heterogeneous Late Mesozoic lithospheric mantle beneath the North China Craton:Evidence from Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic systematics of mafic igneous rocks. Geological Magazine, 141(1): 55-62. DOI:10.1017/S0016756803008331 |
Zhang HF, Sun M, Zhou XH and Ying JF. 2005. Geochemical constraints on the origin of Mesozoic alkaline intrusive complexes from the North China Craton and tectonic implications. Lithos, 81(1-4): 297-317. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.12.015 |
Zhang HF. 2006. Peridotitie-melt interaction:an important mechanism for the compositional transformation of lithospheric mantle. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(2): 65-75. |
Zhang HF, Zhu RX, Santosh M, Ying JF, Su BX and Hu Y. 2013. Episodic widespread magma underplating beneath the North China Craton in the Phanerozoic:Implications for craton destruction. Gondwana Research, 23(1): 95-107. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.12.006 |
Zhang Q, Wang Y and Wang YL. 2001. Preliminary study on the components of the lower crust in east China Plateau during Yanshanian Period:Constraints on Sr and Nd isotopic compositions of adakite-like rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinca, 17(4): 505-513. |
Zhang Q, Wang YL, Jin WJ and Li CD. 2008. Eastern China Plateau during the Late Mesozoic:Evidence, problems and implication. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(9): 1404-1430. |
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Davis GA, Ye H and Wu F. 2014. Temporal and spatial variations of Mesozoic magmatism and deformation in the North China Craton:Implications for lithospheric thinning and decratonization. Earth-Science Reviews, 131: 49-87. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.12.004 |
Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Cawood PA and Sun M. 2001. Archean blocks and their boundaries in the North China Craton:Lithological, geochemical, structural and P-T path constraints and tectonic evolution. Precambrian Research, 107(1-2): 45-73. DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00154-6 |
Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA and Li SZ. 2005. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton:Key issues revisited. Precambrian Research, 136(2): 177-202. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002 |
Zhao GC. 2009. Metamorphic evolution of major tectonic units in the basement of the North China Craton:Key issues and discussion. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(8): 1772-1792. |
Zheng JP, O'Reilly SY, Griffin WL, Lu FX, Zhang M and Pearson NJ. 2001. Relict refractory mantle beneath the eastern North China block:Significance for lithosphere evolution. Lithos, 57(1): 43-66. DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00073-6 |
Zheng JP, Griffin WL, O'Reilly SY, Yu CM, Zhang HF, Pearson N and Zhang M. 2007. Mechanism and timing of lithospheric modification and replacement beneath the eastern North China Craton:Peridotitic xenoliths from the 100Ma Fuxin basalts and a regional synthesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(21): 5203-5225. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2007.07.028 |
Zhou XH. 2006. Major transformation of subcontinental lithosphere beneath eastern China in the Cenozoic-Mesozoic:Review and prospect. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(2): 50-64. |
Zhou XH and Zhang HF. 2006. Highly chemical heterogeneity of subcontinental lithosphere mantle beneath North China and its major transformation. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 31(1): 8-13. |
Zhu RX, Chen L, Wu FY and Liu JL. 2011. Timing, scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton. Science China (Earth Sciences), 54(6): 789-797. DOI:10.1007/s11430-011-4203-4 |
林伟, 王军, 刘飞, 冀文斌, 王清晨. 2013. 华北克拉通及邻区晚中生代伸展构造及其动力学背景的讨论. 岩石学报, 29(5): 1791-1810. |
刘俊来, Davis GA, 纪沫, 关会梅, 白相东. 2008. 地壳的拆离作用与华北克拉通破坏:晚中生代伸展构造约束. 地学前缘, 15(3): 72-81. |
马金龙, 徐义刚. 2004. 河北阳原和山西大同新生代玄武岩的岩石地球化学特征:华北克拉通西部深部地质过程初探. 地球化学, 33(1): 75-88. |
牛耀龄. 2005. 玄武岩浆起源和演化的一些基本概念以及对中国东部中-新生代基性火山岩成因的新思路. 高校地质学报, 11(1): 9-46. |
邵济安, 李献华, 张履桥, 牟保磊, 刘玉琳. 2001. 南口-古崖居中生代双峰式岩墙群形成机制的地球化学制约. 地球化学, 30(6): 517-524. |
邵济安, 翟明国, 张履桥, 李大明. 2005. 晋冀蒙交界地区五期岩墙群的界定及其构造意义. 地质学报, 79(1): 56-67. |
汤艳杰, 张宏福, 英基丰, 张瑾. 2006. 太行山地区中、新生代玄武质岩浆的源区特征与时空演化. 岩石学报, 22(6): 1657-1664. |
王涛, 郑亚东, 张进江, 王新社, 曾令森, 童英. 2007. 华北克拉通中生代伸展构造研究的几个问题及其在岩石圈减薄研究中的意义. 地质通报, 26(9): 1154-1166. |
王亚莹, 蔡剑辉, 阎国翰, 周伟伟, 闫志娇. 2014. 山西临县紫金山碱性杂岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素研究. 岩石矿物学杂志, 33(6): 1052-1072. |
徐义刚. 2004. 华北岩石圈减薄的时空不均一特征. 高校地质学报, 10(3): 324-331. |
徐义刚. 2006. 太行山重力梯度带的形成与华北岩石圈减薄的时空差异性有关. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 31(1): 14-22. |
翟明国, 朱日祥, 刘建明, 孟庆任, 侯泉林, 胡圣标, 李忠, 张宏福, 刘伟. 2003. 华北东部中生代构造体制转折的关键时限. 中国科学(D辑), 33(10): 913-920. |
翟明国, 樊祺诚, 张宏福, 隋建立. 2005. 华北东部岩石圈减薄中的下地壳过程:岩浆底侵、置换与拆沉作用. 岩石学报, 21(6): 1509-1526. |
张宏福. 2006. 橄榄岩-熔体的相互作用:岩石圈地幔组成转变的重要方式. 地学前缘, 13(2): 65-75. |
张旗, 王焰, 王元龙. 2001. 燕山期中国东部高原下地壳组成初探:埃达克质岩Sr、Nd同位素制约. 岩石学报, 17(4): 505-513. |
张旗, 王元龙, 金惟俊, 李承东. 2008. 晚中生代的中国东部高原:证据、问题和启示. 地质通报, 27(9): 1404-1430. |
赵国春. 2009. 华北克拉通基底主要构造单元变质作用演化及其若干问题讨论. 岩石学报, 25(8): 1772-1792. |
周新华. 2006. 中国东部中、新生代岩石圈转型与减薄研究若干问题. 地学前缘, 13(2): 50-64. |
周新华, 张宏福. 2006. 中生代华北岩石圈地幔高度化学不均一性与大陆岩石圈转型. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 31(1): 8-13. |
朱日祥, 陈凌, 吴福元, 刘俊来. 2011. 华北克拉通破坏的时间、范围与机制. 中国科学(地球科学), 41(5): 583-592. |
 2017, Vol. 33
2017, Vol. 33


