巍巍秦岭,中国之脊梁。中国脊梁是如何形成与演化的一直是国际地球科学关注的重要科学问题。秦岭作为分隔我国南北地理和气候的重要地质构造单元,是一个典型的碰撞型造山带(Meng and Zhang, 1999; 张国伟等, 2001)。该造山带西连祁连-昆仑造山带,东接桐柏-大别造山带,构成横贯我国东西的延伸几千千米的中央造山系。该中央造山系是研究华北板块和扬子板块这两大板块相互碰撞的时限和发展过程的重要途径(Meng and Zhang, 1999, 2000; 张国伟等, 2001)。已有研究表明秦岭造山带主要经历了三个不同的构造演化阶段:(1) 前寒武纪结晶基底形成阶段,即由新太古代的变质地体和古元古代-新元古代的沉积基底构成(Wilde and Zhao, 2005; Zhai and Santosh, 2011; Zhao and Zhai, 2013);(2) 新元古代、古生代和中生代时期,秦岭造山带强烈复杂的多期构造变形和岩浆事件记录了板块裂解与汇聚作用,为秦岭的主造山期(Wang et al., 2013a; 王晓霞等, 2015; Tang et al., 2015; Cao et al., 2016);(3) 晚中生代和新生代的陆内造山作用与构造演化阶段;最终形成了现今的构造格局(张国伟等, 1996a, b; Li et al., 2009a, 2013; Dong et al., 2016; Dong and Santosh, 2016)。其间发育的两条重要缝合带:商丹缝合带和勉略缝合带,将秦岭造山带由北至南划分为华北板块南缘、北秦岭、南秦岭和扬子板块北缘(张国伟等, 2001)。其中,商丹缝合带因涉及到秦岭古洋盆的演化,对其拼合汇聚的时间及过程的研究具有重要意义(Dong et al., 2008, 2011a, b, 2015; Liu et al., 2013)。近年来对北秦岭高压-超高压(HP-UHP)变质岩做了大量工作(杨经绥等, 2002; 陈丹玲等, 2004; 苏犁等, 2005; 刘军锋和孙勇, 2005; 李晔等, 2012; 李源等, 2012; 刘良等, 2009; 陈丹玲和刘良, 2011; Cheng et al., 2011, 2012; Wang et al., 2011, 2013a, b, c; 张建新等, 2011; Liu et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2015),证明秦岭群这些变质岩经历了500~480Ma的峰期变质作用和460~420Ma的退变质作用。但上述研究主要集中在商丹缝合带的东部,包括陕西的丹凤和商南以及河南的西峡、内乡等地。对于北秦岭的西延部分由于地理环境等因素研究较为薄弱。因此,我们选择陕西宝鸡地区作为研究对象。
宝鸡眉县鹦鸽咀一带出露有一套属于秦岭群的中高级变质岩石(图 1b, c),由南向北依次为云母石英片岩、含石墨大理岩、变中基性火山岩(斜长角闪岩)、蛇纹岩、辉长岩等(李海平等, 2001; 陈隽璐等, 2008)。尽管该套变质岩经历了造山后期构造作用的强烈改造,但可能仍然记录有秦岭早古生代俯冲-碰撞造山作用过程。遗憾的是尚未见报道有代表板块俯冲-碰撞作用形成的HP-UHP岩石。幸运的是我们在眉县营口镇南部发现了榴闪岩。对其进行岩石学,特别是其中锆石的原位年代学和Hf-O同位素地球化学分析,试图了解北秦岭西延部分变质作用时代和缝合带位置等科学问题。

|
图 1 秦岭造山带地质简图及研究区地质图 (a)秦岭-桐柏-大别-苏鲁造山带构造格架图(据Wang et al., 2013a, b);(b)北秦岭各构造单元及各岩群地质简图(据Dong et al., 2011a, b);(c)研究区地质图(据陕西省地质局, 1966①修改).图中采样位置用五角星表示 Fig. 1 Simplified geological map of Qinling orogen and tectonic framework of the studied area (a) geological sketch of the Qinling-Tongbai-Dabie-Sulu orogenic belts (modified after Wang et al., 2013a, b); (b) simplified tectonic map of the North Qinling orogenic belt showing the major tectonic division and units (modified after Dong et al., 2011a, b); (c) tectonic framework of the studied area. The star shows the sampling locality |
①陕西省地质局.1966. 1:200000陕西省地质图.图Ⅰ-48-(18) (宝鸡幅).西安
2 地质背景秦岭造山带由华北板块南缘、北秦岭、南秦岭和扬子板块北缘构成,而其中的北秦岭则由宽坪群、二郎坪群、秦岭群、丹凤群以及松树沟蛇绿岩组成(张国伟等, 2001)。其中宽坪群主要由基性火山岩、黑云母大理岩和绿片岩组成,群内石英片岩碎屑锆石年龄以及绿片岩锆石年龄限定宽坪群形成于新元古代晚期-早古生代早期(Shi et al., 2013; 第五春荣等, 2010);二郎坪群为一套经绿片岩-低角闪岩相变质的弧后盆地型火山-沉积岩建造,群内基性火山岩的锆石年龄为463~475Ma(赵姣等, 2012),主体形成时代为早古生代。
秦岭岩群由片麻岩、大理岩和斜长角闪岩组成,含少量石榴斜长角闪岩即退变榴辉岩。其形成时代较大争议,根据群内变沉积岩中碎屑锆石年代学结果将其形成时代限定为中元古代(陆松年等, 2006; 万渝生等, 2011)。丹凤岩群由低角闪岩相变质的岛弧火山-沉积岩组成,并被后期辉长岩所侵入。其形成时代大致为新元古代晚期-早古生代早期(Shi et al., 2013; 时毓, 2012)。松树沟超镁铁质岩体主要由纯橄岩以及少量的方辉橄榄岩、橄榄辉石岩、条带状铬铁矿组成,镁铁质围岩主要由榴闪岩等组成(董云鹏等, 1997; Cao et al., 2016)。该岩体的成因演化机制仍未有确切结论,松树沟超镁铁岩40Ar/39Ar快中子活化法得到高温坪年龄为833.8±2.3Ma,等时线年龄为848.2±4Ma(陈丹玲等, 2002; 陈丹玲和刘良, 2011),其Sm-Nd全岩年龄为1030±46Ma(Dong et al., 2008),表明松树沟原岩形成时代在中元古代。近期通过对其中榴闪岩进行锆石年代学研究,结果表明松树沟超镁铁质岩体的就位年龄为~500Ma(Sun et al., 2006; Dong et al., 2008; Tang et al., 2015)。
传统观点认为北秦岭隶属华北板块,由于华北板块与扬子板块碰撞而卷入其中,为华北板块南缘的古活动大陆边缘(张国伟, 1988; 张本仁, 1998)。但部分学者根据Pb同位素等地球化学特征以及岩性特征等认为其更接近扬子板块(朱炳泉等, 1998; 周炼等, 2007)。近年来更多的岩石地球化学数据表明北秦岭是独立于华北板块在洋岛的基础上形成的微陆块(欧阳建平和张本仁, 1996; 张本仁等, 1998; 董云鹏等, 2003; Liu et al., 2016; Tang et al., 2015)。宽坪群碎屑锆石中存在一期时代约1.0Ga的构造热事件,为北秦岭特有而与华北和扬子板块都无太大联系提供了有力证据(第五春荣等, 2010; Zhu et al., 2011; Shi et al., 2013)。
新元古代和早古生代期间,秦岭进入了主造山期并处于洋-陆相互作用阶段。围绕着古商丹洋,北秦岭显示了活动大陆边缘的特征。这一时期各类岩石组合暗示发生了多次洋壳的俯冲消减及碰撞事件,如新元古代时期的具有岛弧构造环境特征的丹凤群火山沉积岩(张旗等, 1995)以及受弧后盆地火山作用的二郎坪群火山岩(夏林圻等, 1998)。近年来对北秦岭东部地区出露的HP-UHP岩石(退变榴辉岩、高压麻粒岩、辉长岩等)进行了大量年代学研究后发现,这些呈面状出露的岩石记录了早古生代时期北秦岭存在着陆壳的深俯冲作用以及随后出现的折返作用(陈丹玲等, 2015; Zhang et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2016)。这些岩石被认为是秦岭群代表的微陆块向华北板块发生俯冲作用的结果(刘良等, 2013)。
北秦岭西部秦岭群在陕西宝鸡眉县鹦鸽咀地区出露有一套蛇绿混杂岩和变质火山-沉积岩系(裴先治等, 2007a; 李源等, 2012),其主要岩石组合包括蛇纹岩、变玄武岩、变辉长岩、硅质岩和云母石英片岩。从鹦鸽咀到眉县红河地区还存在一套火山杂岩和深成杂岩(李海平等, 2001),其中深成杂岩有辉长岩、辉石岩及具有地幔岩性质的蛇纹岩、变质橄榄岩。这些岩体可能记录了北秦岭西部存在着类似与北秦岭东部秦岭群的俯冲-碰撞造山作用。
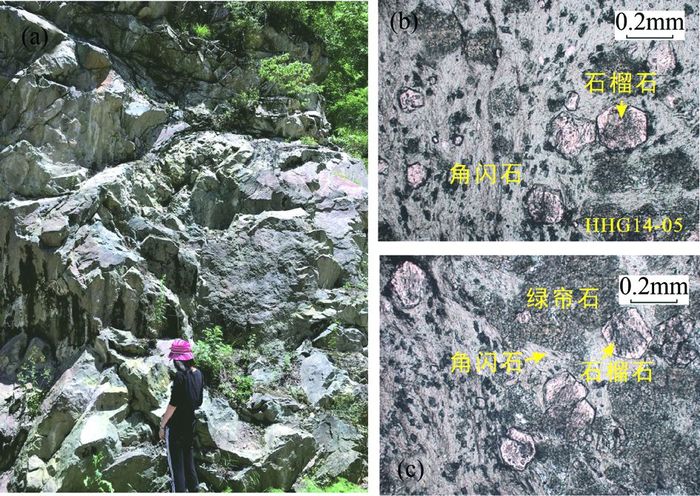
3 岩相学特征本文研究的榴闪岩样品代表的榴闪岩体出露于陕西省宝鸡眉县营口镇大理村一带,位于秦岭造山带太白岩体北缘(图 1c),采样点地理坐标为N34°8′2″、E107°44′55″,其围岩主要为石英片岩、大理岩夹角闪岩、斜长角闪岩、黑云母花岗岩(图 2)。岩体主要呈块状出露,由于流体活动强烈发生绿帘石化造成岩块颜色不均一,主体为灰黑色,夹杂绿色、淡黄色,表面呈蜡状光泽。镜下观察发现矿物颗粒较小,均小于0.2mm,主要由石榴子石、角闪石、石英、绿帘石等组成。其中石榴石粒度变化较大,直径范围为0.05~0.20mm,具有自形到半自形晶的特征,部分石榴石呈残斑状。岩石蚀变作用强烈,角闪石部分因蚀变呈现帘石形态。

|
图 2 眉县地区榴闪岩露头照片(a)和单偏光镜下照片(b、c) 自形的石榴石变斑晶分布在细小的角闪石之中 Fig. 2 Field photograph (a) and microphotographs under plane-polarized light (Sample HHG14-05) (b, c) of garnet amphibolite in Meixian Euhedral garnet porphyroclasts set in tiny amphiboles |
将采自北秦岭西部陕西省眉县营口镇大理村附近的榴闪岩一分为二,小份磨成探针薄片便于开展岩相学工作,于西北大学大陆动力国家重点实验室进行电子探针分析;另一份进行常规的重力、磁分选,最终在双目镜下挑选出锆石颗粒。为了进行锆石微区原位的年代学和同位素测试,需将样品锆石与标准锆石Penglai(Li et al., 2010a)和内标Qinghu(李献华等, 2013)一起嵌入环氧树脂样品座中,然后打磨抛光直至露出锆石颗粒的核心部分而制成样品靶。除CL图像在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室完成外,其余测试均在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所离子探针实验室(U-Pb定年和O同位素)和多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱实验室(Lu-Hf同位素)完成。
4.1 矿物的主量元素分析为了确定岩石中各主要组成矿物的化学成分,对岩石薄片中的石榴石、角闪石等进行了电子探针分析。分析是在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室的电子探针实验室进行的,使用仪器为JXA-8230型电子探针仪,工作条件:加速电压15kV,束斑电流1×10-8A,束斑直径1μm束。代表性矿物的化学成分见表 1。石榴石的成分剖面见图 3d,绿帘石成分剖面见图 4c, d。
|
|
表 1 榴闪岩中代表性矿物矿物的主量元素组成(wt%) Table 1 Major element compositions (wt%) of represent minerals from the garnet amphibolite |
|
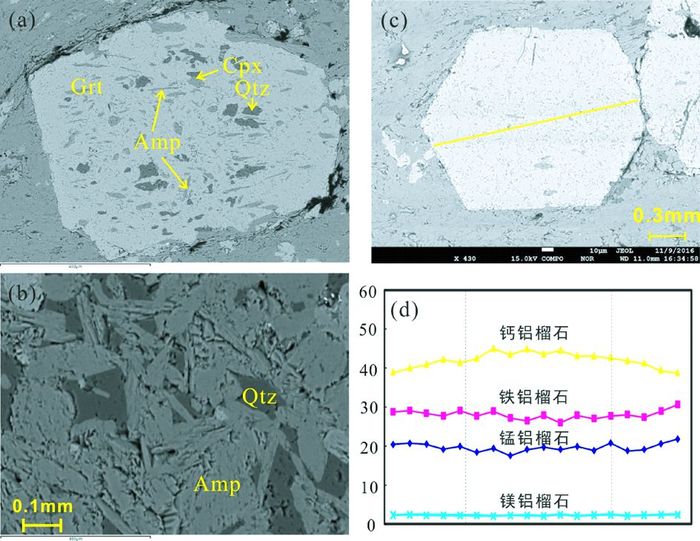
图 3 榴闪岩背散射图及石榴石斑晶成分剖面图 (a-c)榴闪岩背散射图照片:其中(a)显示了石榴石变斑晶中包裹有单斜辉石、角闪石和石英包裹体;(b)基质中角闪石及石英颗粒;(d)为根据(c)图所示石榴石变斑晶成分剖面图.矿物代号除角闪石采用Amp、石英采用Qz外,其它矿物引自Kretz (1983):Grt-石榴石;Cpx-单斜辉石 Fig. 3 Backscattered images of the garnet amphibolites and compositional profile of the porphyroblastic garnet (a-c) backscattered images of the garnet amphibolites: (a) cliniproxene, amphibole and quartz inclusions in porphyroblastic garnet; (b) amphibole and quartz in the matrix; (d) compositional profile along the line shown on (c) showing porphyroblastic garnet zoning during the retrograde metamorphism. Mineral abbreviations except amphibole (Amp) and quartz (Qz) quoted from Kretz (1983): Grt-garnet; Cpx-clinopyroxene |

|
图 4 榴闪岩背散射图及绿帘石斑晶成分剖面图 (a、b)榴闪岩的背散射图照片,其中(b)为(a)中黄框放大部分,显示了绿帘石颗粒环带特征;(c、d)为根据(b)图中A-B所示绿帘石变斑晶成分剖面图.矿物代号除石英采用Qz外,其它矿物引自Kretz (1983):Ep-绿帘石 Fig. 4 Backscattered images of the garnet amphibolites and compositional profile of the porphyroblastic epidote (a, b) backscattered images of the garnet amphibolite. (b) is the magnified section of the yellow box in (a), showing epidote compositional zoning; (c, d) compositional profile along the line A-B shown on (b). Mineral abbreviations except quartz (Qz) quoted from Kretz (1983): Ep-epidote |
为了便于观察锆石内部结构以及选出目标点,因而在进行氧同位素、U-Pb定年和Lu-Hf同位素测试之前,先将锆石靶镀碳,用装载有Gatan CL3+检测器和Oxford能量色散光谱系统的FEI Quanta 400 FEG型扫描电镜拍摄阴极发光(CL)图像。
4.3 锆石O同位素将样品抛光,并镀高纯金膜,在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所离子探针实验室进行O同位素测定,所用仪器为Cameca IMS-1280型双离子源多接受器二次离子质谱仪。详细分析步骤见Li et al.(2010a, b)。实验原理为:用强度为~2nA的一次133Cs+离子源,通过10kV的加速电压轰击样品,离子束束斑直径约20μm,经过-10kV加速电压提取负二次离子,用两个法拉第杯接受16O和18O。仪器的质量分馏校正使用标样Penglai δ18O=5.31(Li et al., 2010a),本次研究通过重复测量标样Penglai的外精度为0.38(2SE, n=50)。通过每十个测试样品加测一个标样Qinghu的方法来监测样品数据的可靠性,十四组Qinghu标样的δ18O加权平均值为5.45±0.36,与标准误差范围内一致(李献华等, 2013)。
4.4 锆石U-Pb年代学锆石的U、Th、Pb同位素也是在同一台Cameca IMS-1280上测试的。详细分析方法参见Li et al. (2009b)和李献华等(2009)。与测试氧同位素不同的是离子源为O2-,用强度为~10nA的一次离子源通过13kV的加速电压轰击样品,离子束为20μm×30μm大小的椭圆形束斑,二次离子束采用60eV的能量窗和~5400的质量分辨率将Pb+分离出来而不受谱峰干扰,用单接受器电子倍增器记录二次离子束峰的强度,每次测量扫描7次,分析用时12分钟。每十个样品加入内标Qinghu来监测U-Pb测试的稳定性。本次实验的样品Pb/U比值用标准锆石TEMORA 2(谐和年龄为417 Ma)校正(Black et al., 2004);Th和U含量用标准锆石91500计算(Whitehouse et al., 1997)。数据处理采用Isoplot/Ex rev. 2.49软件(Ludwig, 2003)。
|
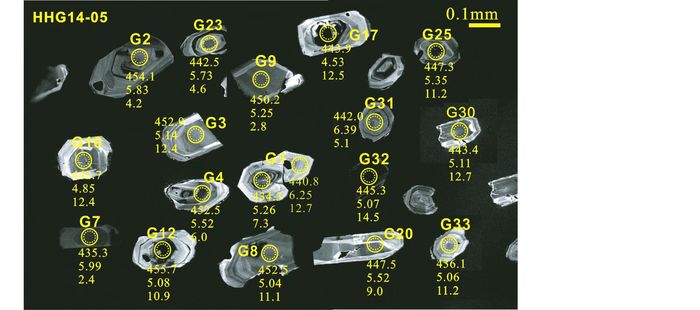
图 5 榴闪岩中典型锆石的阴极发光图像 图中颗粒G的序号与表 2相对应,虚线圈代表了利用Cameca sims-1280测试的U-Pb年龄和O同位素组成的位置,而实线圈指示了用LA-MC-ICPMS测试Hf同位素的位置). U-Pb (206Pb/238U)年龄下面依次为氧同位素和εHf(t)值 Fig. 5 Cathodoluminescence images of representative zircons for the garnet amphibolites Grain (G) numbers correspond to those in Table 2. The dashed circle shows the location of the Cameca sims-1280 U-Pb age and oxygen isotope and the solid circle indicates the location of LA-MC-ICPMS Hf isotopic analysis spot. Numbers below the U-Pb (206Pb/238U) age refer to oxygen isotope followed by εHf(t) value |
|
|
表 2 榴闪岩中锆石的U-Pb年龄和O同位素组成 Table 2 U-Pb age and O isotopic data in zircons from the garnet amphibolite |
随着近年来多接受电感耦合等离子质谱仪(MC-ICP-MS)技术的飞速发展,人们可以对单颗粒锆石进行激光剥蚀原位分析,这种方法不仅提升了测试精度,同时大大降低了样品的制备要求,提升了测试速度。更重要的是可以对具有环带结构的锆石分别进行核心和边缘原位分析,避免了全颗粒锆石溶液法获得的混合年龄,这一点对通常具有岩浆核心和变质增生边的高级变质岩中锆石的定年尤为重要。本次工作的锆石Hf同分素分析是在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所等离子体质谱实验室进行的,分析采用了Neptune型仪器并配备了Geolas-193型紫外激光剥蚀系统(LA)的多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱仪。激光剥蚀的脉冲速率为8Hz,束斑直径为40μm,能量密度为10J/cm2,剥蚀时间约为40s,详细的分析过程见Wu et al. (2006)。测定的176Hf/177Hf比值用179Hf/177Hf=0.7325校正,用标准锆石GJ-1(176Hf/177Hf=0.282020±0.000030)、Mud Tank(176Hf/177Hf=0.282500±0.000030) 与样品交叉分析对仪器进行外部监控,本次实验过程中标样测定平均值在允许误差内与文献综合结果一致(谢烈文等, 2008)。
5 分析结果 5.1 矿物化学榴闪岩主要由石榴石和角闪石两种矿物组成(图 2),其中角闪石含量约占55%、石榴石约占35%,含少量绿帘石和充填在细脉中的石英细小颗粒。石榴石颗粒大小不等,直径范围为0.05~0.20mm,这类石榴石的MnO含量大于20%,即为锰铝榴石(图 3、表 1)。角闪石呈粒状分布,粒径约0.1~0.2mm,部分后期蚀变呈现帘石的形态,呈短柱状,粒径约0.1mm(图 3b),其SiO2含量在52%~54%。石英表面干净,未受强烈变质作用的影响(图 3b)。绿帘石有两种形态,一种为角闪石退变形成的短柱状;另一种呈自形柱状,直径范围为0.1~0.3mm(图 4a)。
石榴石常含有矿物包裹体,主要有单斜辉石、角闪石以及石英(图 3a、表 1)。其中单斜辉石的成分和松树沟退变榴辉岩中透辉石后成合晶成分类似(表 1),可能为绿辉石退变形成的透辉石(陈丹玲等, 2015)。石榴石包裹体内的角闪石总量比其它角闪石的总量稍高,说明其挥发组分更少些,这与其形成时所处环境的温度压力有关,包裹体内角闪石形成于更高的温压条件。包裹体内石英颗粒较基质中分布的石英,其表面分布有裂纹,表明其可能经历过强变质作用。在超高压岩石中,柯石英常具有放射性裂纹并常以包裹体形式存在于石榴石、锆石等颗粒中(章军锋和金振民, 1999)。因该样品中的裂纹未成放射状,因而难以确定是否经历过柯石英相变质作用。
石榴石残斑具有环带结构(图 3c, d),根据电子探针线扫描结果,并采用石榴石组分的Rickwood方法计算绘制石榴石成分剖面图(图 3d),其环带的核部至边部钙铝榴石(Grs)分子含量降低了约10%,铁铝榴石(Alm)及锰铝榴石(Sps)有所升高,Ca含量的多少与压力升降相关(郭敬辉等, 1999)。这些特征反映了石榴石残斑经历后期的减压过程,为退变质扩散环带(Carswell et al., 2000)。
自形柱状绿帘石在背散射图上具有清晰的环带特征(图 4b),其化学成分相应的也有一定的变化(图 4c, d),其中XFe(XFe=Fe3+/(Al3++Cr3++Fe3++Mn3+))核部(0.3~0.4) 到边缘(0.25~0.30) 呈现降低的变化趋势,同时CaO和Al2O3含量呈现由低到高的变化趋势,这与青龙山榴辉岩中形成于榴辉岩相变质阶段形成的绿帘石有类似的成分变化特征(梁金龙等, 2006; 翟伟等, 2006)。
5.2 U-Pb年代学样品中锆石的CL图像显示,锆石的颗粒较小,多为50×60~80×150μm(图 5)。大颗粒锆石自形程度高,多为自形晶,小颗粒锆石多为浑圆状(图 5)。锆石普遍具有熔蚀现象,较小颗粒锆石的边部常出现晶棱圆化和港湾状结构,大颗粒锆石具有熔蚀坑/洞(图 5)。特别应该指出的是这些锆石具有类似“岩浆”锆石的环带结构,出现面状或带状环带。这并非特例,Liati et al. (2002)发现Rhodop岩体中减压退变作用形成的变质锆石也有震荡环带特征。尽管这些锆石具有很宽的Th(24×10-6~1959×10-6)和U(52×10-6~1236×10-6)变化范围,但大多数锆石的Th和U含量很低(Th<410×10-6; U<400×10-6; 表 2)。而且同一颗锆石的白色边缘具有更低的Th和U含量(如G1, 表 2)。同时,这些锆石具有非常高且宽的Th/U比值(0.47~1.66)(表 2)。如此高的Th/U比值说明这些锆石并非是在“干”体系下形成的变质锆石。加上上述锆石特征说明该榴闪岩中锆石是在退变质作用过程中大量流体活动形成的。已有研究证明在大量流体活动的退变质过程中形成的锆石具有很宽的Th/U比值变化范围和高的Th/U比值(吴元保和郑永飞, 2004; Hoskin and Black, 2000; 倪涛, 2006; Schaltegger et al., 2015)。
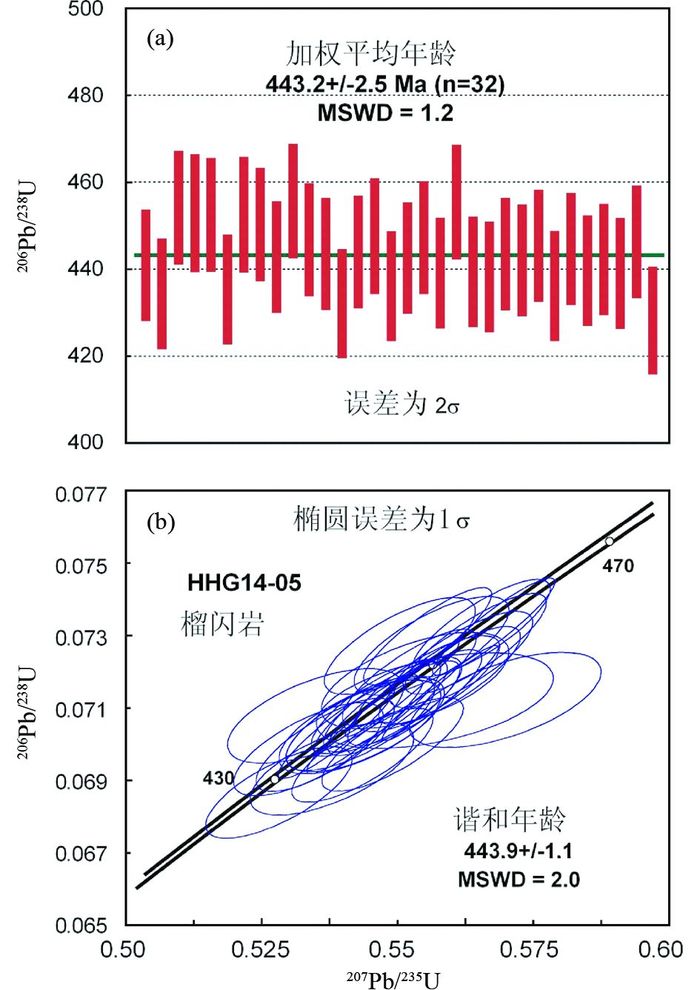
这些锆石获得了30个有效的U-Pb年龄,单个数据点误差均为1σ。尽管206Pb/238U单点年龄具有较大的变化范围(428~456Ma, 表 2),但其所有数据点都分布在谐和线上(图 6),即获得了很好的谐和年龄443.9±1.1Ma(MSWD=2.0) 和206Pb/238U的加权平均年龄443.2±2.5Ma(MSWD=1.2)。
|
图 6 榴闪岩中锆石的206Pb/238U加权平均年龄图(a)和207Pb/235U-206Pb/238U谐和图(b) 图中分析点的误差椭圆表示1σ Fig. 6 The 207Pb/235U vs. 206Pb/238U concordia (b) and the weighted mean (a) diagrams of zircons from the garnet amphibolite Data point error ellipses are 1σ |
通常情况下,高级变质岩中早期形成的锆石后期如果发生强烈的铅丢失,会造成锆石的δ18O降低,从而不能代表锆石原有的氧同位素组成(Valley et al., 2005; Wan et al., 2013)。据图 6可知,榴闪岩中锆石年龄均分布在谐和线上,说明这些锆石未发生明显的铅丢失或退变质过程中造成锆石的年龄完全重置。因此,如果是前一种情况,获得的分析结果可以代表锆石的初始氧同位素组成;如果是后一种情况,获得的锆石的氧同位素数据很可能也有退变质过程的影响。
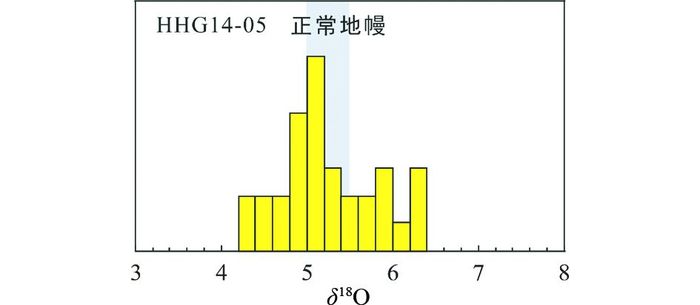
29个锆石颗粒30个氧同位素测点得到一个相对较宽的δ18O范围(4.25‰~6.39‰, 表 2和图 7),从稍低于正常地幔的氧同位素(5.3±0.6‰ (2σ), Valley et al., 2005)到稍高于正常地幔氧同位素组成。其加权平均值为5.15±0.19‰(2σ)非常接近正常地幔的氧同位素数值,即与地幔来源的岩浆结晶出来的岩浆锆石具有类似氧同位素组成。变质锆石当其达到变质平衡时,其氧同位素组成即可反映岩石体系的氧同位素组成特征(Chen et al., 2011)。因此,该榴闪岩的原岩的氧同位素总体上具有亏损地幔特征。
|
图 7 榴闪岩中锆石的氧同位素直方图 图中阴影区为正常地幔源岩石的δ18O值(5.3±0.6‰, Taylor, 1980和Valley et al., 2005) Fig. 7 Oxygen isotope histogram of zircons from the garnet amphibolite The shaded field shows the value of normal mantle (δ18O=5.3±0.6‰, taken from Taylor, 1980 and Valley et al., 2005) |
同时,应该指出的是锆石在退变质重结晶过程中,流体、温度以及时间都会影响氧同位素的保留(Gordon et al., 2009)。从CL图像以及Th、U含量变化可以发现样品中锆石形成时是有流体活动参与的,流体的存在明显增强氧同位素的扩散速率,造成δ18O值变化如增高。另外,我们发现同一颗粒锆石其边部具有更高的δ18O值(如图 5G1),外形较为浑圆的具有类似重结晶特征的锆石氧同位素较高,δ18O值可高达6.39‰(图 5G31)。这可能是这些锆石具有相对较宽的氧同位素的主要原因。
5.4 Hf同位素地球化学因锆石的Hf含量普遍较高,而Lu含量很低,造成锆石的176Lu/177Hf比值很低,大多低于0.002。这说明锆石形成后基本没有放射性成因Hf的累积,所测定的176Hf/177Hf比值基本代表了其形成时体系的Hf同位素组成(Amelin et al., 1999; Kinny and Maas, 2003)。在高级变质岩中,锆石Hf同位素主要受原岩的组成和变质过程控制。变质过程中会造成锆石Lu含量下降,Hf含量升高,因而变质锆石的Lu/Hf比值会降低(倪涛等, 2006; 陈道公等, 2007)。本研究中,锆石30个测试点的176Lu/177Hf比值分布在0.000744~0.005123范围之间,且具有很高的176Hf/177Hf比值以及宽的分布范围(0.282575~0.282934)(表 3)。其εHf(t)尽管存在很大的变化范围(2.4~14.7),但皆为正值,说明该榴闪岩的原岩来源于亏损地幔。其εHf(t)亏损地幔模式年龄即tDM为0.48~0.95Ga,暗示榴闪岩的原岩形成于新元古代。
|
|
表 3 激光多接收ICP-MS获得的榴闪岩中锆石的Lu-Hf同位素组成 Table 3 Lu-Hf isotopic data in zircons from the garnet amphibolite determined by laser MC-ICPMS |
值得注意的是在含石榴石的高级变质岩中,因Lu、Hf优先进入石榴石中,如果退变质过程中存在石榴石的溶解和重结晶,可能会在很大程度上影响锆石的Hf同位素组成(Zheng et al., 2005, 2006; Wu et al., 2006)。但如果石榴石在退变质过程中一直存在(Zheng et al., 2005; Wu et al., 2006; 郑永飞等, 2007),其共生的变质锆石即使重结晶,亦能保持高的176Hf/177Hf比值。因此,对锆石的Lu-Hf同位素影响不会太大。这完全类似于本研究中的榴闪岩,该榴闪岩在形成过成中石榴石一直存在,且锆石含有较高的176Hf/177Hf值。其较宽范围的Hf同位素组成暗示其为退变质作用影响的结果,但总体上Hf同位素尚能反映榴闪岩原岩的来源。
6 讨论 6.1 榴闪岩:退变质作用产物?根据岩相学特征和矿物化学成分分析,眉县榴闪岩中至少可以观察到两个时代的矿物组合:① 峰期变质作用阶段:特征为自形石榴石大颗粒内部以包裹体形式出现的矿物组合,即Amp+Cpx+Qtz。该矿物组合的出现说明其可能至少到达了高压麻粒岩相(卢良兆等, 2002)。但受后期退变作用的影响,其矿物组合被改造,残余物质中未找到斜长石,因而没有合适的温压计,未能直接获得峰期变质温压条件。绿帘石变斑晶显示了明显的成分环带,其核边Fe含量以及CaO、Al2O3含量变化与青龙山柯石英榴辉岩相变质阶段形成的绿帘石相一致,绿帘石核部可能记录了峰期变质时的成分特征。同时,锆石中高的176Hf/177Hf比值以及较宽的分布范围说明退变质作用发生时,石榴石一直存在。综上所述,该榴闪岩峰期变质很可能已经达到榴辉岩相。
② 退变质作用阶段:矿物组合主要为退变质作用中形成的石榴石、角闪石、绿帘石、石英等。自形石榴石颗粒退变质过程中,发生元素扩散作用形成明显的成分环带(图 3c, d),以及绿帘石的核边成分变化(图 4c, d)反映了一个降温降压的过程。退变质过程中不仅温度和压力发生了变化,还有富水流体的参与,形成了大量角闪石。这些矿物学特征都说明眉县榴闪岩为退变质作用的产物,并且在退变过程中有富水流体的加入。石榴石变斑晶中出现的峰期变质矿物的退变矿物记录暗示其可能还经历过榴辉岩相的变质作用。
6.2 榴闪岩的形成时代和原岩特征眉县榴闪岩获得一期很好的U-Pb谐和年龄(443.9±1.1Ma(MSWD=2.0),图 6)。CL图像、Th/U比值以及岩相学分析显示其榴闪岩主体是退变质过程形成的。因在退变质形成榴闪岩的过程中存在强烈的流体活动,锆石受到退变质作用的强烈改造,很可能U-Pb体系发生完全重置。部分锆石进行年龄测定时发现其核部和边部具有相同的年龄,这也说明退变质作用中U-Pb同位素体系发生了重置,因而改变了核部进变质作用的年龄。结合岩相学以及矿物化学工作,443.9±1.1Ma记录了眉县榴闪岩的退变质作用发生的时间。
因此,榴闪岩很可能是退变质的产物,而其原岩应该是玄武质岩石。榴闪岩中锆石的Hf-O研究显示尽管这些锆石具有较大的εHf(t)和δ18O变化范围(表 2和表 3、图 7和图 8),但总体上皆具有正的εHf(t)值,且δ18O总体分布在4.5‰~6.0‰,均显示了亏损地幔特征。另外,锆石的176Hf/177Hf值较高,为0.282575~0.282934,单颗粒计算得到的亏损地幔模式年龄分布在0.48~0.95Ga。在强烈的退变质作用过程中,石榴石含量的变化可能会改变锆石中的Lu、Hf含量,造成εHf(t)偏大,tDM偏低的现象(Zheng et al., 2005; 吴福元等, 2007)。因而给出的Hf同位素模式年龄应为榴闪岩原岩脱离亏损地幔的时代下限。因此,我们认为榴闪岩的原岩是新元古代时期来源于亏损地幔的玄武质岩石。

|
图 8 榴闪岩中锆石的εHf(0) 和根据单点U-Pb年龄计算所得εHf(t)值的直方图 Fig. 8 Histograms showing εHf(0) and εHf(t) values of zircons from the garnet amphibolite The εHf(t) value was calculated for the respective age from the individual zircon |
陕西省地质调查(2004①)在进行1:25万宝鸡市幅区域地质调查过程中,在岩湾、鹦鸽咀一带发现了蛇绿混杂岩,认为是古生代洋盆存在的记录(陈隽璐等, 2008; Dong et al., 2011a; 李源等, 2012)。同时在鹦鸽咀-眉县发现一条火山杂岩带,该杂岩带以块状熔岩为主,含辉长岩、辉石岩等,还含有具有地幔性质的蛇纹岩、变质橄榄岩,被认为是由于加里东期古洋盆的闭合、与丹凤岩群属同一构造体制(李海平等, 2001)。本文所研究榴闪岩体即在鹦鸽咀东北眉县营口镇以南,其经历了榴辉岩相变质作用,很可能代表秦岭造山带的一次深俯冲事件的记录。综上所述,该榴闪岩岩体的原岩为新元古代时期来自亏损地幔的玄武质岩石,大概在早古生代时期发生了深俯冲-碰撞。443.9±1.1Ma的退变质年龄是这次深俯冲事件后期的折返事件的响应。
①陕西省地质调查.2004. 1:250000西北地区区域地质调查报告.图I48C002004(宝鸡市幅).西安
6.3 进变质作用时代在北秦岭东部商南地区分布了一套HP-UHP岩体,其中也发现有榴闪岩记录(刘良等, 2013; 钱加慧等, 2013)。Yu et al. (2016)在对松树沟地区石榴斜长角闪岩进行年龄测定,得到了460Ma退变质年龄,同时在变质锆石的核部得到了峰期变质年龄为490Ma(Yu et al., 2016)。陈丹玲等(2015)对松树沟地区的榴闪岩详细岩相学研究发现其中存在绿辉石,结合石榴石环带的成分测定确定其为退变榴辉岩。同时,锆石的年代学研究获得榴辉岩的变质年龄为500±8Ma(陈丹玲等, 2015)。由此可以推测出榴辉岩的进变质作用时代大致为490~500Ma,发生榴闪岩或石榴斜长角闪岩退变质作用间隔大致为30~40Myr(图 9)。
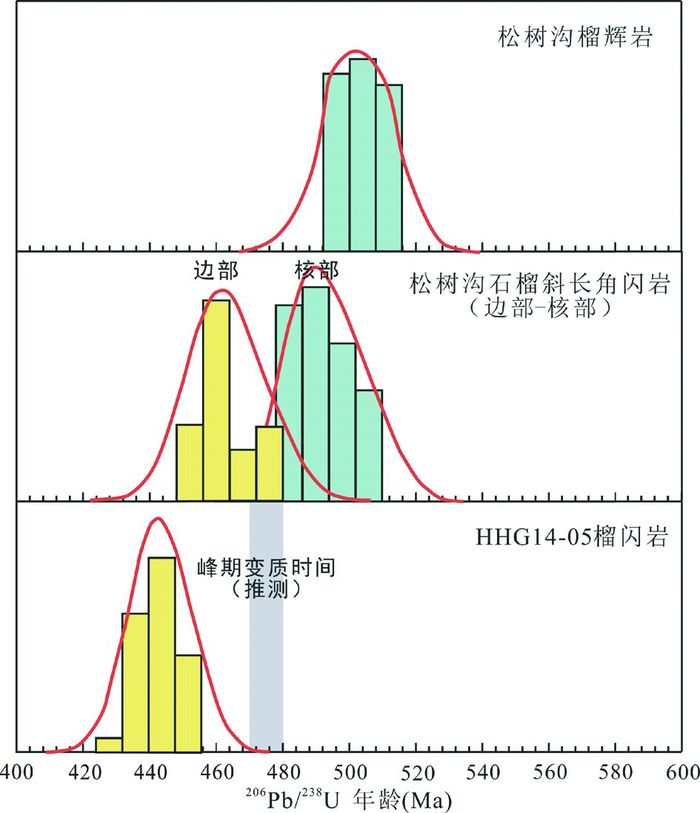
|
图 9 眉县榴闪岩、松树沟石榴斜长角闪岩和松树沟榴辉岩中锆石206Pb/238U年龄直方图 图中阴影区代表推测眉县榴闪岩峰期变质时间(470~480Ma).数据来源:松树沟榴辉岩(陈丹玲等, 2015);松树沟石榴斜长角闪岩(Yu et al., 2016) Fig. 9 The 206Pb/238U age histograms of zircons from Meixian garnet amphibolite, Songshugou garnet plagioclase amphibolite and eclogite The shaded field is the inferred peak metamorphism (470~480Ma). Date source: Songshugou eclogite (Chen et al., 2015); Songshugou garnet plagioclase amphibolite (Yu et al., 2016) |
北秦岭东部中HP-UHP岩体均成面状分布,且大面积出露,包括关坡、双槐树、清油河等,可以认为北秦岭在古生代时作为一个整体都经历了深俯冲作用(Zhang et al., 2015; 陈丹玲等, 2015)。所以我们可以通过北秦岭东部地区榴辉岩发生退变质作用时代间隔可以大致判断北秦岭西部的榴闪岩的峰期变质时代可能为470~480Ma(图 9),比东部深俯冲发生的稍晚。
6.4 北秦岭东西部俯冲-碰撞时限的差异根据商南松树沟及富水地区HP-UHP岩体中分布的退变榴辉岩和超高压麻粒岩的年代学研究得到了480~500Ma的峰期变质年龄(陈丹玲等, 2004; 刘良等, 2013; 刘军锋和孙勇, 2005; Liu et al., 2013; 陈丹玲等, 2015; Zhang et al., 2015; Yu et al., 2016; Liao et al., 2016),认为是古洋盆向北俯冲拖曳了陆壳发生了深俯冲,在这一阶段发生了超高压变质作用,榴闪岩和石榴石斜长角闪岩为发生折返时的地质记录。对比北秦岭东西部榴闪岩年龄以及峰期变质年龄可以发现,北秦岭东西部古洋盆闭合发生俯冲碰撞的时限存在差异。据此我们推测俯冲碰撞事件在商南-宝鸡一线是沿着商丹缝合带自东向西发生的。
同时,两个地区对于加里东期洋盆闭合时间也有不同。通过北秦岭东部清油河退变榴辉岩、松树沟超高压长英质片麻岩、寨根石榴辉石岩等超高压岩体得到了~500Ma的峰期变质年龄,暗示该地区拖曳陆壳发生俯冲-深俯冲的洋壳主体关闭时限应为~500Ma(Liu et al., 2013; 刘良等, 2013; Liao et al., 2016)。而在西边李子园地区发现有形成于俯冲带之上岛弧或弧前环境的玻安岩(裴先治等, 2006),并根据鹦鸽咀辉长岩474Ma的年龄,认为洋盆关闭时限应晚于474Ma,形成李子园玻安岩(李源等, 2012)。
此外,在构造特征上整个秦岭造山带沿东西向上都存在差异,其地壳剖面特征显示秦岭造山带自东向西并非同一构造层次出露:大别深部层次,东秦岭为中深、中浅层次交互出现,西秦岭为中浅层次为主(张国伟等, 1995, 1997; 张国伟, 1988)。那么,是不是也有种可能,在早古生代时期整个华北与华南板块拼合碰撞模式也是自东向西发生的,当然这还需要更多的岩石年代学、地球化学及构造学等方面的证据加以论证。
7 结论通过以上分析可以得出以下结论:北秦岭西部首次发现了一套榴闪岩。该榴闪岩是退变质作用形成的,经历过超高压变质作用,可能达到榴辉岩相变质条件。其中的锆石记录了一次与深俯冲相关的退变质事件,443Ma的年龄是退变质作用发生的时间,结合锆石的Hf-O同位素特征指示榴闪岩原岩主要是新元古代时期亏损地幔来源的玄武岩。北秦岭HP-UHP岩体研究认为北秦岭作为微陆块于早古生代整体经历了深俯冲,因此可以根据北秦岭东部的具有类似Lu-Hf同位素特征的榴闪岩中峰期变质的年龄以及榴辉岩的年龄,推测本研究区发生峰期变质时间为470~480Ma。因此,北秦岭东西部发生俯冲-碰撞作用时限上存在差异,提出俯冲-碰撞沿商丹缝合带从商南至宝鸡一线是自东向西发生的。
致谢 野外工作和实验工作得到了张娟、张雨林、于红、邹东雅、刘嘉威等的帮助,在此表示感谢!感谢主编、副主编和三位评审人对本文进行了认真和建设性的评审。| [] | Amelin Y, Lee D C, Halliday A N, Pidgeon R T. 1999. Nature of the Earth's earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons. Nature, 399(6733): 252–255. DOI:10.1038/20426 |
| [] | Black L P, Calver C R, Seymour D B, Reed A. 2004. SHRIMP U-Pb detrital zircon ages from Proterozoic and Early Palaeozoic sandstones and their bearing on the early geological evolution of Tasmania. Australian Journal of Earth Science, 51(6): 885–900. DOI:10.1111/aes.2004.51.issue-6 |
| [] | Blichert-Toft, Albarede F. 1997. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 148(1-2): 243–258. DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00040-X |
| [] | Cao H H, Li S Z, Zhao S J, Yu S, Li X Y, Somerville I D. 2016. Detrital zircon geochronology of Neoproterozoic to Early Paleozoic sedimentary rocks in the North Qinling Orogenic Belt:Implications for the tectonic evolution of the Kuanping Ocean. Precambrian Research, 279: 1–16. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2016.04.001 |
| [] | Carswell D A, Wilson R N, Zhai M. 2000. Metamorphic evolution, mineral chemistry and thermobarometry of schists and orthogneisses hosting ultra-high pressure eclogites in the Dabieshan of central China. Lithos, 52(1-4): 121–155. DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00088-2 |
| [] | Chen D G, Ni T, Xie L W. 2007. Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic compositions of ultra-high pressure metamorphic rocks from Dabie Terrain, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 331–342. |
| [] | Chen D L, Liu L, Zhou D W, Luo J H, Sang H Q. 2002. Genesis and 40Ar-39Ar dating of clinopyroxene megacrysts in ultramafic terrain from Songshugou, East Qinling Mountain and its geological implication. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 18(3): 355–362. |
| [] | Chen D L, Liu L, Sun Y, Zhang A D, Liu X M, Luo J H. 2004. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating for high-pressure basic granulite from North Qinling and its geological significance. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(21): 2296–2304. DOI:10.1360/03wd0544 |
| [] | Chen D L, Liu L. 2011. New data on the chronology of eclogite and associated rock from Guanpo area, North Qinling orogeny and its constraint on nature of North Qinling HP-UHP eclogite terrane. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(2): 158–169. |
| [] | Chen D L, Ren Y F, Gong X K, Liu L, Gao S. 2015. Identification and its geological significance of eclogite in Songshugou, the North Qinling. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(7): 1841–1854. |
| [] | Chen J L, Xu X Y, Wang Z Q, Yan Q R, Wang H L, Zeng Z X, Li P. 2008. Geological features and SHRIMP U-Pb zircon age of the Yanwan-Yinggezui ophiolitic mélange in the Taibai area, West Qinling, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(4): 500–509. |
| [] | Chen Y X, Zheng Y F, Chen R X, Zhang S B, Li Q L, Dai M N, Chen L. 2011. Metamorphic growth and recrystallization of zircons in extremely 18O-depleted rocks during eclogite-facies metamorphism:Evidence from U-Pb ages, trace elements, and O-Hf isotopes. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(17): 4877–4898. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2011.06.003 |
| [] | Cheng H, Zhang C, Vervoort J D, Li X H, Li Q L, Zheng S, Cao D D. 2011. Geochronology of the transition of eclogite to amphibolite facies metamorphism in the North Qinling orogen of central China. Lithos, 125(3-4): 969–983. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.05.010 |
| [] | Cheng H, Zhang C, Vervoort J D, Li X H, Li Q L, Wu Y B, Zheng S. 2012. Timing of eclogite facies metamorphism in the North Qinling by U-Pb and Lu-Hf geochronology. Lithos, 136-139: 46–59. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.06.003 |
| [] | Diwu C R, Sun Y, Liu L, Zhang C L, Wang H L. 2010. The disintegration of Kuanping Group North Qinling orogenic belts and Neo-proterozoic N-MORB. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7): 2025–2038. |
| [] | Dong Y P, Zhou D W, Zhang G W. 1997. The emplacement mechanism and tectonic evolution of ultramafites in Songshugou area, eastern Qinling. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 32(2): 173–180. |
| [] | Dong Y P, Zhang G W, Zhu B Q. 2003. Proterozoic tectonics and evolutionary history of the North Qinling terrane. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 24(1): 3–10. |
| [] | Dong Y P, Zhou M F, Zhang G W, Zhou D W, Liu L, Zhang Q. 2008. The Grenvillian Songshugou ophiolite in the Qinling Mountains, Central China:Implications for the tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogenic belt. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 32(5-6): 325–335. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.11.010 |
| [] | Dong Y P, Zhang G W, Hauzenberger C, Neubauer F, Yang Z, Liu X M. 2011a. Palaeozoic tectonics and evolutionary history of the Qinling orogen:Evidence from geochemistry and geochronology of ophiolite and related volcanic rocks. Lithos, 122(1-2): 39–56. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.11.011 |
| [] | Dong Y P, Zhang G W, Neubauer F, Liu X M, Genser J, Hauzenberger C. 2011b. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, China:Review and synthesis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(3): 213–237. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.002 |
| [] | Dong Y P, Zhang X N, Liu X M, Li W, Chen Q, Zhang G W, Zhang H F, Yang Z, Sun S S, Zhang F F. 2015. Propagation tectonics and multiple accretionary processes of the Qinling Orogen. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 104: 84–98. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.10.007 |
| [] | Dong Y P, Santosh M. 2016. Tectonic architecture and multiple orogeny of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China. Gondwana Research, 29(1): 1–40. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.009 |
| [] | Dong Y P, Yang Z, Liu X M, Sun S S, Li W, Cheng B, Zhang F F, Zhang X N, He D F, Zhang G W. 2016. Mesozoic intracontinental orogeny in the Qinling Mountains, central China. Gondwana Research, 30: 144–158. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.05.004 |
| [] | Gordon S M, Grove M, Whitney D L, Schmitt A K, Teyssier C. 2009. Time-temperature-fluid evolution of migmatite dome crystallization:Coupled U-Pb age, Ti thermometry, and O isotopic ion microprobe depth profiling of zircon and monazite. Chemical Geology, 262(3-4): 186–201. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.01.018 |
| [] | Guo J H, Zhai M G, Li Y G, Li J H. 1999. Metamorphism, PT paths and tectonic significance of garnet amphibolite and granulite from Hengshan, North China Craton. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 34(3): 311–325. |
| [] | Griffin W L, Pearson N J, Belousova E A, Jackson S E, Achterbergh EV., O'Reilly S Y, Shee S. 2000. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle:LAM-MC-ICPMS analyses of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites-Kimberlites and related rocks. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(1): 133–147. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9 |
| [] | Hoskin PWO, Black L P. 2000. Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 18(4): 423–439. |
| [] | Kinny P D, Maas R. 2003. Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotope systems in zircon. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 327–341. DOI:10.2113/0530327 |
| [] | Kretz R. 1983. Symbols for rock-forming minerals. American Mineralogist, 68(1): 277–279. |
| [] | Li H P, Chen J L, Chen Y J, Zhang Z W, Zhao X S, Chen Y C. 2001. Foundation of the volcanic rock complex belt in Yinggezui North Qinling. Geology of Shaanxi, 19(2): 104. |
| [] | Li J H, Zhang Y Q, Dong S W, Shi W. 2013. Structural and geochronological constraints on the Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the North Dabashan zone, South Qinling, central China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 64: 99–114. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.001 |
| [] | Li S Z, Kusky T M, Liu X C, Zhang G W, Zhao G C, Wang L, Wang Y J. 2009a. Two-stage collision-related extrusion of the western Dabie HP-UHP metamorphic terranes, central China:Evidence from quartz c-axis fabrics and structures. Gondwana Research, 16(2): 294–309. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2009.03.003 |
| [] | Li X H, Liu Y, Li Q L, Guo C H, Chamberlain K R. 2009b. Precise determination of Phanerozoic zircon Pb/Pb age by multicollector SIMS without external standardization. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 10(4): Q04010. |
| [] | Li X H, Li W X, Wang X C, Li Q L, Liu Y, Tang G Q. 2009. Role of mantle-derived magma in genesis of Early Yanshanian granites in the Nanling Range, South China:In situ zircon Hf-O isotopic constraints. Science in China (Series D), 52(9): 1262–1278. DOI:10.1007/s11430-009-0117-9 |
| [] | Li X H, Long W G, Li Q L, Liu Y, Zheng Y F, Yang Y H, Chamberlain K R, Wan D F, Guo C H, Wang X C, Tao H. 2010a. Penglai zircon megacrysts:A potential new working reference material for microbeam determination of Hf-O isotopes and U-Pb age. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 34(2): 117–134. DOI:10.1111/j.1751-908X.2010.00036.x |
| [] | Li X H, Li W X, Li Q L, Wang X C, Liu Y, Yang Y H. 2010b. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the~850Ma Gangbian alkaline complex in South China:Evidence from in situ zircon U-Pb dating, Hf-O isotopes and whole-rock geochemistry. Lithos, 114(1-2): 1–15. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.07.011 |
| [] | Li X H, Tang G Q, Gong B, Yang Y H, Hou K J, Hu Z C, Li Q L, Liu Y, Li W X. 2013. Qinghu zircon:A working reference for microbeam analysis of U-Pb age and Hf and O isotopes. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(36): 4647–4654. DOI:10.1007/s11434-013-5932-x |
| [] | Li Y, Yang J S, Pei X Z, Zhang J, Chen J L, Chen S Y, Xu X Z. 2012. A model for multi-stage of the Early Palaeozoic Danfeng ophiolite in Qinling orogen belt:From arc to inter-arc basin. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(6): 1896–1914. |
| [] | Li Y, Zhou H W, Zhong Z Q, Xiang H, Zeng W, Qi D M, Zhang L. 2012. Two Eopaleozoic metamorphic events in North Qinling:Petrology and zircon U-Pb geochronology evidences from basic rocks in the Songshugou area. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 37(Suppl.): 111–124. |
| [] | Liang J L, Sun X M, Xu L, Zhai W, Tang Q, Liang Y H. 2006. Geochemistry of epidotes in HP-UHP metamorphic rocks from Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling (CCSD) Project and Qinglongshan area:An indicator of partial melting during continental slab exhumation. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(7): 1845–1854. |
| [] | Liao X Y, Liu L, Wang Y W, Cao Y T, Chen D L, Dong Y P. 2016. Multi-stage metamorphic evolution of retrograde eclogite with a granulite-facies overprint in the Zhaigen area of the North Qinling Belt, China. Gondwana Research, 30: 79–96. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.09.012 |
| [] | Liati A, Gebauer D, Wysoczanski R. 2002. U-Pb SHRIMP-dating of zircon domains from UHP garnet-rich mafic rocks and late pegmatoids in the Rhodope zone (N Greece):Evidence for Early Cretaceous crystallization and Late Cretaceous metamorphism. Chemical Geology, 184(3-4): 281–299. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00367-9 |
| [] | Liu J F, Sun Y. 2005. New data on the "Hot" emplacement age of ultramafic rocks from the Songshugou area in the eastern Qinling. Geological Review, 51(2): 189–192. |
| [] | Liu L, Chen D L, Wang C, Zhang C L. 2009. New progress on geochronology of high-pressure/ultra high-pressure metamorphic rocks from the South Altyn Tagh, the North Qaidam and the North Qinling orogenic, NW China and their geological significance. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 39(3): 472–479. |
| [] | Liu L, Zhang J F, Cao Y T, Chen D L, Yang W Q, Liao X Y. 2013. Evidence for the ultra-deep subduction (≥ 10GPa) of the continental rock from the North Qinling terrane:Constrained from the high temperature and high pressure experiment. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(Suppl.): 494–495. |
| [] | Liu L, Liao X Y, Zhang C L, Chen D L, Gong X K, Kang L. 2013. Multi-matemorphic timings of HP-UHP rocks in the North Qinling and their geological implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(5): 1634–1656. |
| [] | Liu L, Liao X Y, Wang Y W, Wang C, Santosh M, Yang M, Zhang C L, Chen D L. 2016. Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the North Qinling Orogenic Belt in Central China:Insights on continental deep subduction and multiphase exhumation. Earth-Science Reviews, 159: 58–81. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.05.005 |
| [] | Lu L Z, Dong Y S, Zhou X W. 2002. A comparative study on characteristics and origin of fluids during granulite-facies metamorphism of Jining Group and Qianxi Group. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 21(4): 387–397. |
| [] | Lu S N, Chen Z H, Xiang Z Q, Li H K, Li H M, Song B. 2006. U-Pb ages of detrital zircons from the para-metamorphic rocks of the Qinling Group and their geological significance. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(6): 303–310. |
| [] | Ludwig K R. 2003. User's Manual for Isoplot 3. 00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication, 4: 70. |
| [] | Meng Q R, Zhang G W. 1999. Timing of collision of the North and South China blocks:Controversy and reconciliation. Geology, 27(2): 123–126. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<0123:TOCOTN>2.3.CO;2 |
| [] | Meng Q R, Zhang G W. 2000. Geologic framework and tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, central China. Tectonophysics, 323(3-4): 183–196. DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00106-2 |
| [] | Ni T, Chen D G, Jin P. 2006. Zircon REE and Th, U characteristics of metamorphic rocks from the Dabie Mountains. Geological Journal of China Universities, 12(2): 249–258. |
| [] | Ouyang J P, Zhang B R. 1996. Geochemical evidence for the formation and evolution of North Qinling microcontinent. Science in China (Series D), 39. |
| [] | Pei X Z, Liu H B, Ding S P, Li Z C, Hu B B, Sun R Q, Hou Y H. 2006. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic significance of the meta-volcanic rocks in the Liziyuan Group from Tianshui area, western Qinling orogen. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 30(2): 193–205. |
| [] | Pei X Z, Ding S P, Li Z C, Liu Z P, Li G Y, Li R B, Wang F, Li F J. 2007a. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of the gabbro from the Guanzizhen ophiolite in the northern margin of the western Qinling and its geological significance. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(11): 1550–1561. |
| [] | Pei X Z, Ding S P, Zhang G W, Liu H B, Li Z C, Li W Y, Liu Z Q, Meng Y. 2007b. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of Neoproterozoic granitoid gneisses in the north margin of West Qinling and geological implication. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(6): 772–786. |
| [] | Qian J H, Yang X Q, Liu L, Cao Y T, Chen D L, Yang W Q. 2013. Zircon U-Pb dating, mineral inclusions, Lu-Hf isotopic data and their geological significance of garnet amphibolite from Songshugou, North Qinling. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(9): 3087–3098. |
| [] | Schaltegger U, Schmitt A K, Horstwood MSA. 2015. U-Th-Pb zircon geochronology by ID-TIMS, SIMS, and laser ablation ICP-MS:Recipes, interpretations, and opportunities. Chemical Geology, 402: 89–110. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.02.028 |
| [] | Shi Y. 2012. Formation and evolution of the eastern Qinling Orogenic belt in Central China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Nanjing:Nanjing University, 1-86 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Shi Y, Yu J H, Santosh M. 2013. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogenic belt, Central China:New evidence from geochemical, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes. Precambrian Research, 231: 19–60. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2013.03.001 |
| [] | Söderlund U, Patchett P J, Vervoort J D, Isachsen C E. 2004. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of precambrian mafic intrusions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 219(3-4). |
| [] | Su L, Song S G, Zhou D W. 2005. Petrogenesis of Songshugou dunite body in the Qinling orogenic belt, Central China:Constraints from geochemistry and melt inclusions. Science in China (Series D), 48(8): 1146–1157. DOI:10.1360/03yd0037 |
| [] | Sun W D, Sun Y, Zhou B, Liu J F. 2006. The emplacement age of the Songshugou ultramafic massif:LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon dating. VM Goldschmidt Conference, 70(18): A628. |
| [] | Tang L, Santosh M, Dong Y P. 2015. Tectonic evolution of a complex orogenic system:Evidence from the northern Qinling belt, Central China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113: 544–559. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.03.033 |
| [] | Taylor Jr HP. 1980. The effects of assimilation of country rocks by magmas on 18O/16O and 87Sr/86Sr systematics in igneous rocks. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 47(2): 243–254. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(80)90040-0 |
| [] | Valley J W, Lackey J S, Cavosie A J, Clechenko C C, Spicuzza M J, Basei MAS, Bindeman I N, Ferreira V P, Sial A N, King E M, Peck W H, Sinha A K, Wei C S. 2005. 4. 4 billion years of crustal maturation:Oxygen isotope ratios of magmatic zircon. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 150(6): 561–580. |
| [] | Wan Y S, Liu D Y, Dong C Y, Yin X Y. 2011. SHRIMP zircon dating of meta-sedimentary rock from the Qinling Group in the north of Xixia, North Qinling Orogenic Belt:Constraints on complex histories of source region and timing of deposition and metamorphism. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(4): 1172–1178. |
| [] | Wan Y S, Zhang Y H, Williams I S, Liu D Y, Dong C Y, Fan R L, Shi Y R, Ma M Z. 2013. Extreme zircon O isotopic compositions from 3. 8 to 2.5Ga magmatic rocks from the Anshan area, North China Craton. Chemical Geology, 352: 108–124. |
| [] | Wang H, Wu Y B, Gao S, Liu X C, Gong H J, Li Q L, Li X H, Yuan H L. 2011. Eclogite origin and timings in the North Qinling terrane, and their bearing on the amalgamation of the South and North China blocks. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 29(9): 1019–1031. DOI:10.1111/jmg.2011.29.issue-9 |
| [] | Wang H, Wu Y B, Gao S, Liu X C, Liu Q, Qin Z W, Xie S W, Zhou L, Yang S H. 2013a. Continental origin of eclogites in the North Qinling terrane and its tectonic implications. Precambrian Research, 230: 13–30. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2012.12.010 |
| [] | Wang H, Wu Y B, Qin Z W, Zhu L Q, Liu Q, Liu X C, Gao S, Wijbrans J R, Zhou L, Gong H J, Yuan H L. 2013b. Age and geochemistry of Silurian gabbroic rocks in the Tongbai orogen, central China:Implications for the geodynamic evolution of the North Qinling arc-back-arc system. Lithos, 179: 1–15. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.07.021 |
| [] | Wang X X, Wang T, Zhang C L. 2013c. Neoproterozoic, Paleozoic, and Mesozoic granitoid magmatism in the Qinling Orogen, China:Constraints on orogenic process. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 72: 129–151. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.037 |
| [] | Wang X X, Wang T, Zhang C L. 2015. Granitoid magmatism in the Qinling orogen, central China and its bearing on orogenic evolution. Science China (Earth Sciences), 58(9): 1497–1512. DOI:10.1007/s11430-015-5150-2 |
| [] | Whitehouse M J, Claesson S, Sunde T, Vestin J. 1997. Ion microprobe U-Pb zircon geochronology and correlation of Archaean gneisses from the Lewisian Complex of Gruinard Bay, northwestern Scotland. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61(20): 4429–4438. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00251-2 |
| [] | Wilde S A, Zhao G C. 2005. Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 519–522. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.06.004 |
| [] | Wu F Y, Yang Y H, Xie L W, Yang J H, Xu P. 2006. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology. Chemical Geology, 234(1-2): 105–126. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.003 |
| [] | Wu F Y, Li X H, Zheng Y F, Gao S. 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185–220. |
| [] | Wu Y B, Zheng Y F. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(15): 1554–1569. DOI:10.1007/BF03184122 |
| [] | Xia L Q, Xia Z C, Xu X Y. 1998. Early Palaeozoic Mid-ocean ridge-ocean island and back-arc basin volcanism in the North Qilian Mountains. Acta Geologica Sinica, 72(4): 301–312. |
| [] | Xie L W, Zhang Y B, Zhang H H, Sun J F, Wu F Y. 2008. In situ simultaneous determination of trace elements, U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopes in zircon and baddeleyite. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(10): 1565–1573. |
| [] | Yang J S, Xu Z Q, Pei X Z, Shi R D, Wu C L, Zhang J X, Li H B, Meng F C, Rong H. 2002. Discovery of diamond in North Qinling:Evidence for a giant UHPM belt across Central China and recognition of Paleozoic and Mesozoic dual deep subduction between North China and Yangtze plates. Acta Geologica Sinica, 76(4): 484–495. |
| [] | Yu H, Zhang H F, Li X H, Zhang J, Santosh M, Yang Y H, Zhou D W. 2016. Tectonic evolution of the North Qinling Orogen from subduction to collision and exhumation:Evidence from zircons in metamorphic rocks of the Qinling Group. Gondwana Research, 30: 65–78. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.07.003 |
| [] | Zhai M G, Santosh M. 2011. The Early Precambrian odyssey of the North China Craton:A synoptic overview. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 6–25. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.02.005 |
| [] | Zhai W, Sun X M, Liang J L, Xu L, Tang Q, Liang Y H, Su L W. 2006. Chemical compositions and fluid inclusions of epidotes in Qinglongshan ultrahigh pressure metamorphic eclogite, North Jiangsu Province, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(7): 2029–2038. |
| [] | Zhang B R, Han Y W, Xu J X, Ouyang J P. 1998. Geochemical evidence for North Qinling being a part of Yangtze plate prior to the Neoproterozoic. Geological Journal of China Universities, 4(4): 369–381. |
| [] | Zhang G W. 1988. The composition and evolution of the Early Precambrian crust in the southern part of the North China block and the formation and evolution of the Qinling Mountains orogenic belt. Journal of Northwest University, 18(1): 21–23. |
| [] | Zhang G W, Meng Q R, Lai S C. 1995. Structure and tectonic of Qinling orogenic belt. Science in China (Series B), 25(9): 994–1003. |
| [] | Zhang G W, Meng Q R, Yu Z P, Sun Y, Zhou D W, Guo A L. 1996a. Orogenesis and dynamics of the Qinling Orogen. Science in China (Series D), 39(3): 225–234. |
| [] | Zhang G W, Guo A L, Liu F T, Xiao Q H, Meng Q R. 1996b. Three-dimentional architecture and dynamic analysis of the Qinling Orogenic Belt. Science in China (Series D), 26(Suppl.): 3–11. |
| [] | Zhang G W, Meng Q R, Liu S F, Yao A P. 1997. Huge intracontinental subduction zone at south margin of North China Block. Geological Journal of China University, 3(2): 129–143. |
| [] | Zhang G W, Dong Y P, Yao A P. 2001. Review on the development of studies on the tectonic and orogen process of orogenic belt, and discussing on some new key problems. Northwestern Geology, 34(1): 1–9. |
| [] | Zhang H F, Yu H, Zhou D W, Zhang J, Dong Y P, Zhang G W. 2015. The meta-gabbroic complex of Fushui in North Qinling orogen:A case of syn-subduction mafic magmatism. Gondwana Research, 28(1): 262–275. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2014.04.010 |
| [] | Zhang J F, Jin Z M. 1999. Review on phase transformation of coesite-quartz from ultra-high pressure metamorphic rocks. Geological Science and Technology Information, 18(3): 6–10. |
| [] | Zhang J X, Yu S Y, Meng F C. 2011a. Ployphase Early Paleozoic metamorphism in the northern Qinling orogenic belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(4): 1179–1190. |
| [] | Zhang Q, Zhang Z Q, Sun Y, Han S. 1995. Trace element and isotopic geochemistry of metabasalts from Danfeng Group (DFG) in Shangxian-Danfeng area, Shaanxi Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 11(1): 43–54. |
| [] | Zhao G C, Zhai M G. 2013. Lithotectonic elements of Precambrian basement in the North China Craton:Review and tectonic implications. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1207–1240. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.08.016 |
| [] | Zhao J, Chen D L, Tan Q H, Chen M, Zhu X H, Guo C L, Liu L. 2012. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of basic volcanics from Erlangping Group of the North Qinling, eastern Qinling Mountains and its geological implications. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(4): 118–125. |
| [] | Zheng Y F, Wu Y B, Zhao Z F, Zhang S B, Xu P, Wu F Y. 2005. Metamorphic effect on zircon Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systems in ultrahigh-pressure eclogite-facies metagranite and metabasite. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 240(2): 378–400. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.09.025 |
| [] | Zheng Y F, Zhao Z F, Wu Y B, Zhang S B, Liu X M, Wu F Y. 2006. Zircon U-Pb age, Hf and O isotope constraints on protolith origin of ultrahigh-pressure eclogite and gneiss in the Dabie orogen. Chemical Geology, 231(1-2): 135–138. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.01.005 |
| [] | Zheng Y F, Chen R X, Zhang S B, Tang J, Zhao Z F, Wu Y B. 2007. Zircon Lu-Hf isotope study of ultrahigh-pressure eclogite and granitic gneiss in the Dabie orogen. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 317–330. |
| [] | Zhou L, Gao S, Liu Y S, Ling W L, Zhang L. 2007. Geochemistry and implications of clastic sedimentary rocks from the northern margin of Yangtze Craton. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 32(1): 29–38. |
| [] | Zhu B Q, Chang X Y, Qiu H N, Sun D Z. 1998. Characteristics of Proterozoic basements on the geochemical steep zones in the continent of China and their implications for setting of superlarge deposits. Science in China (Series D), 41(Suppl.): 54–64. |
| [] | Zhu X Y, Chen F K, Li S Q, Yang Y Z, Nie H, Siebel W, Zhai M G. 2011. Crustal evolution of the North Qinling terrain of the Qinling Orogen, China:Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopic composition. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 194–204. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.12.009 |
| [] | 陈道公, 倪涛, 谢烈文. 2007. 大别地体超高压变质岩石锆石Lu-Hf同位素研究. 岩石学报, 23(2): 331–342. |
| [] | 陈丹玲, 刘良, 周鼎武, 罗金海, 桑海清. 2002. 东秦岭松树沟超镁铁质岩中辉石巨晶的成因和40Ar-39Ar定年及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 18(3): 355–362. |
| [] | 陈丹玲, 刘良, 孙勇, 张安达, 柳小明, 罗金海. 2004. 北秦岭松树沟高压基性麻粒岩锆石的LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及其地质意义. 科学通报, 49(18): 1901–1908. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.18.014 |
| [] | 陈丹玲, 刘良. 2011. 北秦岭榴辉岩及相关岩石年代学的进一步确定及其对板片俯冲属性的约束. 地学前缘, 18(2): 158–169. |
| [] | 陈丹玲, 任云飞, 宫相宽, 刘良, 高胜. 2015. 北秦岭松树沟榴辉岩的确定及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 31(7): 1841–1854. |
| [] | 陈隽璐, 徐学义, 王宗起, 闫全人, 王洪亮, 曾佐勋, 李平. 2008. 西秦岭太白地区岩湾-鹦鸽咀蛇绿混杂岩的地质特征及形成时代. 地质通报, 27(4): 500–509. |
| [] | 第五春荣, 孙勇, 刘良, 张成立, 王洪亮. 2010. 北秦岭宽坪岩群的解体及新元古代N-MORB. 岩石学报, 26(7): 2025–2038. |
| [] | 董云鹏, 周鼎武, 张国伟. 1997. 东秦岭松树沟超镁铁岩侵位机制及其构造演化. 地质科学, 32(2): 173–180. |
| [] | 董云鹏, 张国伟, 朱炳泉. 2003. 北秦岭构造属性与元古代构造演化. 地球学报, 24(1): 3–10. |
| [] | 郭敬辉, 翟明国, 李永刚, 李江海. 1999. 恒山西段石榴石角闪岩和麻粒岩的变质作用、PT轨迹及构造意义. 地质科学, 34(3): 311–325. |
| [] | 李海平, 陈隽璐, 陈永杰, 张占武, 赵选社, 陈有仓. 2001. 北秦岭鹦鸽咀发现火山杂岩带. 陕西地质, 19(2): 104. |
| [] | 李献华, 李武显, 王选策, 李秋立, 刘宇, 唐国强. 2009. 幔源岩浆在南岭燕山早期花岗岩形成中的作用:锆石原位Hf-O同位素制约. 中国科学(D辑), 39(7): 872–887. |
| [] | 李献华, 唐国强, 龚冰, 杨岳衡, 侯可军, 胡兆初, 李秋立, 刘宇, 李武显. 2013. Qinghu (清湖)锆石:一个新的U-Pb年龄和O、Hf同位素微区分析工作标样. 科学通报, 58(20): 1954–1961. |
| [] | 李源, 杨经绥, 裴先治, 张建, 陈隽璐, 陈松永, 徐向珍. 2012. 秦岭造山带早古生代蛇绿岩的多阶段演化:从岛弧到弧间盆地. 岩石学报, 28(6): 1896–1914. |
| [] | 李晔, 周汉文, 钟增球, 向华, 曾雯, 祁冬梅, 张利. 2012. 北秦岭早古生代两期变质作用:来自松树沟基性岩岩石学及锆石U-Pb年代学的记录. 地球科学, 37(增): 111–124. |
| [] | 梁金龙, 孙晓明, 徐莉, 翟伟, 汤倩, 梁业恒. 2006. CCSD及青龙山HP-UHP变质岩中绿帘石地球化学及其对板块折返过程的示踪. 岩石学报, 22(7): 1845–1854. |
| [] | 刘军锋, 孙勇. 2005. 东秦岭松树沟超基性岩体"热"侵位时代新知. 地质论评, 51(2): 189–192. |
| [] | 刘良, 陈丹玲, 王超, 张成立. 2009. 阿尔金、柴北缘与北秦岭高压-超高压岩石年代学研究进展及其构造地质意义. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 39(3): 472–479. |
| [] | 刘良, 廖小莹, 张成立, 陈丹玲, 宫相宽, 康磊. 2013. 北秦岭高压-超高压岩石的多期变质时代及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 29(5): 1634–1656. |
| [] | 卢良兆, 董永胜, 周喜文. 2002. 集宁群和迁西群麻粒岩相变质流体的特征和成因. 岩石矿物学杂志, 21(4): 387–397. |
| [] | 陆松年, 陈志宏, 相振群, 李怀坤, 李惠民, 宋彪. 2006. 秦岭岩群副变质岩碎屑锆石年龄谱及其地质意义探讨. 地学前缘, 13(6): 303–310. |
| [] | 倪涛, 陈道公, 靳平. 2006. 大别山变质岩锆石微区稀土元素和Th、U特征. 高校地质学报, 12(2): 249–258. |
| [] | 欧阳建平, 张本仁. 1996. 北秦岭微古陆形成与演化的地球化学证据. 中国科学(D辑), 26(增): 42–48. |
| [] | 裴先治, 刘会彬, 丁仨平, 李佐臣, 胡波, 孙仁奇, 侯育红. 2006. 西秦岭天水地区李子园群变质火山岩的地球化学特征及其地质意义. 大地构造与成矿学, 30(2): 193–205. |
| [] | 裴先治, 丁仨平, 李佐臣, 刘战庆, 李高阳, 李瑞保, 王飞, 李夫杰. 2007a. 西秦岭北缘关子镇蛇绿岩的形成时代:来自辉长岩中LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄的证据. 地质学报, 81(11): 1550–1561. |
| [] | 裴先治, 丁仨平, 张国伟, 刘会彬, 李佐臣, 李王晔, 刘战庆, 孟勇. 2007b. 西秦岭北缘新元古代花岗质片麻岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义. 地质学报, 81(6): 772–786. |
| [] | 钱加慧, 杨秀清, 刘良, 曹玉亭, 陈丹玲, 杨文强. 2013. 北秦岭松树沟榴闪岩锆石U-Pb定年、矿物包裹体和Lu-Hf同位素特征及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 29(9): 3087–3098. |
| [] | 时毓. 2012. 中国中部东秦岭造山带的形成和演化. 博士学位论文. 南京: 南京大学, 1-86 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10284-1015575738.htm |
| [] | 苏犁, 宋述光, 周鼎武. 2005. 秦岭造山带松树沟纯橄岩体成因:地球化学和岩浆包裹体的制约. 中国科学(D辑), 35(1): 38–47. |
| [] | 万渝生, 刘敦一, 董春艳, 殷小艳. 2011. 西峡北部秦岭群变质沉积岩锆石SHRIMP定年:物源区复杂演化历史和沉积、变质时代确定. 岩石学报, 27(4): 1172–1178. |
| [] | 王晓霞, 王涛, 张成立. 2015. 秦岭造山带花岗质岩浆作用与造山带演化. 中国科学(地球科学), 45(8): 1109–1125. |
| [] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约. 科学通报, 49(16): 1589–1604. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 |
| [] | 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及岩石学应用. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185–220. |
| [] | 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义. 1998. 北祁连山早古生代洋脊-洋岛和弧后盆地火山作用. 地质学报, 72(4): 301–312. |
| [] | 谢烈文, 张艳斌, 张辉煌, 孙金凤, 吴福元. 2008. 锆石/斜锆石U-Pb和Lu-Hf同位素以及微量元素成分的同时原位测定. 科学通报, 53(2): 220–228. |
| [] | 杨经绥, 许志琴, 裴先治, 史仁灯, 吴才来, 张建新, 李海兵, 孟繁聪, 戎合. 2002. 秦岭发现金刚石:横贯中国中部巨型超高压变质带新证据及古生代和中生代两期深俯冲作用的识别. 地质学报, 76(4): 484–495. |
| [] | 翟伟, 孙晓明, 梁金龙, 徐莉, 汤倩, 梁业恒, 苏丽薇. 2006. 青龙山超高压变质榴辉岩绿帘石化学成分与流体包裹体特征. 岩石学报, 22(7): 2029–2038. |
| [] | 张本仁, 韩吟文, 许继锋, 欧阳建平. 1998. 北秦岭新元古代前属于扬子板块的地球化学证据. 高校地质学报, 4(4): 369–381. |
| [] | 张国伟. 1988. 华北地块南部早前寒武纪地壳的组成及其演化和秦岭造山带的形成及其演化. 西北大学学报, 18(1): 21–23. |
| [] | 张国伟, 孟庆任, 赖绍聪. 1995. 秦岭造山带的结构构造. 中国科学(B辑), 25(9): 994–1003. |
| [] | 张国伟, 孟庆任, 于在平, 孙勇, 周鼎武, 郭安林. 1996a. 秦岭造山带的造山过程及其动力学特征. 中国科学(D辑), 26(3): 193–200. |
| [] | 张国伟, 郭安林, 刘福田, 肖庆辉, 孟庆任. 1996b. 秦岭造山带三维结构及其动力学分析. 中国科学(D辑), 26(增): 1–6. |
| [] | 张国伟, 孟庆任, 刘少峰, 姚安平. 1997. 华北地块南部巨型陆内俯冲带与秦岭造山带岩石圈现今三维结构. 高校地质学报, 3(2): 129–143. |
| [] | 张国伟, 董云鹏, 姚安平. 2001. 造山带与造山作用及其研究的新起点. 西北地质, 34(1): 1–9. |
| [] | 章军锋, 金振民. 1999. 超高压变质岩中柯石英-石英相变动力学研究的评述. 地质科技情报, 18(3): 6–10. |
| [] | 张建新, 于胜尧, 孟繁聪. 2011. 北秦岭造山带的早古生代多期变质作用. 岩石学报, 27(4): 1179–1190. |
| [] | 张旗, 张宗清, 孙勇, 韩松. 1995. 陕西商县-丹凤地区丹凤群变质玄武岩的微量元素和同位素地球化学. 岩石学报, 11(1): 43–54. |
| [] | 赵姣, 陈丹玲, 谭清海, 陈淼, 朱小辉, 郭彩莲, 刘良. 2012. 北秦岭东段二郎坪群火山岩锆石的LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及其地质意义. 地学前缘, 19(4): 118–125. |
| [] | 郑永飞, 陈仁旭, 张少兵, 唐俊, 赵子福, 吴元保. 2007. 大别山超高压榴辉岩和花岗片麻岩中锆石Lu-Hf同位素研究. 岩石学报, 23(2): 317–330. |
| [] | 周炼, 高山, 刘勇胜, 凌文黎, 张利. 2007. 扬子克拉通北缘碎屑沉积岩地球化学特征及意义. 地球科学, 32(1): 29–38. |
| [] | 朱炳泉, 常向阳, 邱华宁, 孙大中. 1998. 地球化学急变带的元古宙基底特征及其与超大型矿床产出的关系. 中国科学(D辑), 28(增): 63–70. |
 2017, Vol. 33
2017, Vol. 33


