作为造山带俯冲过程的直接产物,高压-超高压变质岩石为研究俯冲带形成环境、机制、演化历史等信息提供了直接研究对象。现今对造山带的研究总结得出,根据造山带的形成环境等要素将造山带分为阿尔卑斯型(Alpine-type或A-type)和太平洋型(B-type),即大陆型和大洋型。其中大洋型俯冲带在原岩建造上可保留完整的洋壳岩石组合特征,包括从底部的超基性岩、部分保留枕状构造的由玄武岩变质的榴辉岩及变质沉积岩等(张立飞等, 2008);如西阿尔卑斯的Zermatt-saas带(Reinecke, 1991; Bucher et al., 2005)和中国的西天山(Zhang et al., 2002a, b, 2007; 张立飞等, 2008)。而大陆型俯冲带则以大面积出露的正副片麻岩以及其中少量的呈透镜体或似层状产出的榴辉岩及超基性岩为特征;如中国的大别-苏鲁造山带(Jahn, 1999),以及本文的研究区域柴北缘(柴达木盆地北缘)超高压变质带。
柴北缘以出露大面积的花岗质片麻岩、副片麻岩以及其中少量呈透镜体产出的榴辉岩、橄榄岩等为特征。本区出露的副片麻岩及榴辉岩均发现有柯石英包裹体(Yang et al., 2001; Song et al., 2003a; Zhang et al., 2009a, b, 2010; Liu et al., 2012),且石榴橄榄岩的锆石中保留有金刚石包体(Song et al., 2005),表明柴北缘曾作为一个整体发生了大规模的深俯冲超高压变质作用。近年来又在都兰的沙柳河剖面识别出了较完整的发生过深俯冲的蛇绿岩组合及异剥钙榴岩,从而证明了柴北缘超高压变质带由早期的大洋俯冲消亡到大陆俯冲碰撞的完整过程(Zhang et al., 2013)。本区榴辉岩的地球化学特征和年代学数据等反映其来自于两个源区:1) 具有原岩年龄>750Ma,变质年龄为430Ma左右的新元古代初始洋盆或者地幔柱相关岩浆岩(Zhang et al., 2005b, 2017; 张建新, 2015; Chen et al., 2009a; Song et al., 2010; Yu et al., 2013);2) 沙柳河蛇绿岩剖面中原岩时代为520Ma左右,变质时代为440~450Ma的早古生代洋壳残余(张贵宾等, 2005; Zhang et al., 2008a, 2009b, 2016)。对于围岩变质泥质岩的年代学,之前的研究更注重于探讨其经历高压(超高压)变质作用的时代(Song et al., 2003a; Mattinson et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2008b),但缺少对其中碎屑锆石的系统定年研究工作。
由于锆石极强的抗风化、磨蚀和蚀变能力以及较高的封闭温度,其能够在沉积循环过程中不受破坏,因此碎屑锆石往往可以用于研究沉积物源区性质(Krogh and Keppie, 1990; Sircombe and Freeman, 1999; Liu et al., 2015)。其所保留的岩浆和变质事件对应的年龄和微量元素组成等可相互比对,得到源区的亲缘性。传统碎屑锆石定年工作往往选取沉积岩样品,如沉积地层样品或砂样。对于俯冲带而言,虽然其岩石往往受高压/超高压变质作用影响,锆石都经历过高压/超高压变质作用的改造,但变质泥质片麻岩(片岩)中的碎屑锆石,其核部较为古老年龄的组成及统计学结果对于揭示俯冲碰撞前的演化历史具有重要意义。
本文通过对柴北缘超高压变质带中绿梁山和都兰地区的变质泥质岩进行岩石学分析,并对其中的碎屑锆石进行U-Pb定年,以期得到较为古老的年龄,为发生在800~1000Ma与Rodinia超大陆活动相关的大陆碰撞和裂解及古祁连洋的演化提供证据。同时对碎屑锆石定年数据绘制年龄分布谱图,通过与邻近克拉通对比得到柴达木-祁连地体与邻近克拉通的亲缘性,并限定该地区的构造演化历史。
2 区域地质背景及样品描述柴北缘超高压变质带位于中国青海省境内,属青藏高原东北部的加里东期造山带,总长度约400km。如图 1,其北部为祁连地体,具有与扬子板块相似的前寒武纪结晶基底(Wan et al., 2001; Song et al., 2006)。南部为柴达木地体,同样具有前寒武纪结晶基底,但大多被中新生代沉积物所覆盖。西侧被阿尔金断裂所切,东接秦岭造山带,整体呈NWW-SEE走向展布,并与北部200km处的北祁连加里东期缝合带呈平行关系,两者分别与阿尔金山南部的早古生代超高压变质带和阿尔金山北部的蛇绿岩带相对应,为受阿尔金断裂控制的同一造山带(许志琴等, 1999)。
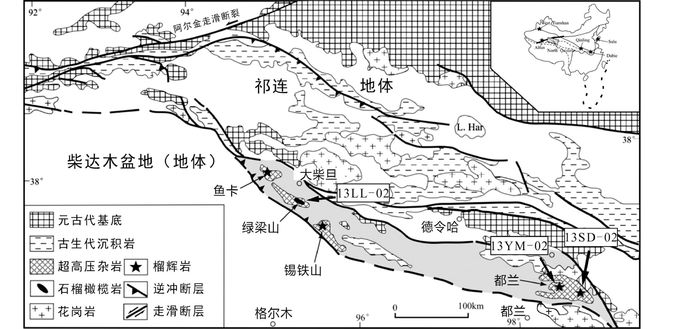
|
图 1 柴北缘-阿尔金超高压变质带及相邻地区构造分区图(据Zhang et al., 2013修改) Fig. 1 Geological sketch map showing the geological setting and major subunits in the North Qaidam-Altyn Tagh belt, China (after Zhang et al., 2013) |
柴北缘超高压变质带中的变质岩石主要出露于自西向东的鱼卡、绿梁山、锡铁山和都兰四个区域。其中鱼卡、锡铁山及都兰地区,主要以大面积的花岗质和泥质片麻岩及其中呈透镜状或似层状出露的榴辉岩为主。而绿梁山地区则主要出露片麻岩夹石榴橄榄岩和榴辉岩退变质形成的高压麻粒岩。本文所研究的副片麻岩(片岩)来自绿梁山和都兰两个地区。
绿梁山位于大柴旦镇以南约20km处,大部分地区被第四系覆盖,且其西侧侵入有志留纪花岗岩(Song et al., 2004)。岩石类型主要以花岗质片麻岩和含夕线石(蓝晶石)的副片麻岩为主,橄榄岩作为一个大块体(500~800m)出露于其中(杨建军等, 1994; Song et al., 2004, 2005, 2007)。样品13LL-02为石榴石黑云母片麻岩,主要矿物组合为石英30%,长石35%,黑云母15%,石榴石5%。石榴石多破碎且退变质程度较高,样品中长石蚀变严重,不等粒变晶结构(图 2a)。

|
图 2 样品镜下照片 (a)样品13LL-02;(b)样品13SD-09;(c)样品13YM-02 Fig. 2 Microphotographs under the microscope illustrating the mineral assemblages |
都兰地区位于柴北缘超高压变质带的最东端,青海省都兰县城北东40km的野马滩-沙柳河一带。根据榴辉岩的岩石、矿物组合、地球化学特征及不同的折返过程,都兰地区被划分为南北两带(杨经绥等, 2003; Song et al., 2003a, b)。样品13SD-09采自都兰南带,为石榴石白云母片岩,主要矿物组合为石英45%,白云母30%,斜长石10%,石榴石10%,见少量黑云母(1%),不等粒粒状变晶结构。石榴石多破裂且含有较多包体,部分出现蚀变黑云母或绿泥石共生;其中斜长石生长有聚片双晶,表面绢云母化明显(图 2b)。样品13YM-02采自都兰北带野马滩,为含石榴石二云母片岩,主要矿物组合为石英65%,白云母15%,黑云母15%,少量石榴石和钠质斜长石,偶见蓝晶石,等粒变晶结构(图 2c)。柴北缘超高压变质带中的第一个柯石英包体即发现于同一个露头的泥质片岩中(Song et al., 2003a)。
3 研究方法岩石样品清洗后被粉碎,先用重液和磁选将锆石分离出来,然后在双目镜下进行手工挑选。将挑选出的锆石颗粒和锆石标样(TEMORA, 417Ma, Black et al., 2003)分别粘到环氧树脂做成的25mm靶上,之后抛光。我们采用北京大学电镜实验室的扫描电镜(FEI PHILIPS XL30 SFEG SEM)对锆石的内部结构特征进行了阴极荧光图像拍摄,工作条件是15kV、120μA,扫描时间为2min。
锆石的原位U-Pb年龄测定分别在北京大学地球与空间科学学院造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验和中国地质大学地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室完成。北京大学地球与空间科学学院造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室的工作条件为:激光剥蚀使用的是德国相干公司(Coherent)193nm准分子激光器COMPlex Pro102;质谱为Agilent ICP-MS 7500ce。中国地质大学地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室的工作条件为:激光剥蚀系统为德国Lamda Physik公司的193nm Geolas 200M;质谱为Elan 6100DRC。分析中采用的激光束斑直径均为30μm,微量元素数据采用NIST610玻璃作为外标,29Si作为内标,数值采用Pearce et al. (1997)中的结果。U-Pb同位素比值的确定采用TEMORA锆石标样进行元素间的分馏校正。数据处理应用GLITTER软件获得微量元素含量及U-Pb同位素比值,年龄计算采用ISOPLOT(Ludwig, 2003)软件进行。
4 分析结果本次分析样品中13LL-02和13YM-02的锆石具有类似特征,这些锆石从形态上大致可分为两种:其中一种表现为无色透明,晶型较好,内部包体较少(图 3a-c, g-i);而另一种则为深棕色,内部裂隙和包体较多导致透明性降低,自形程度差,包体较多。而两种锆石的边部都呈浑圆状,显示了锆石可能受后期变质作用的改造(图 3)。CL图像下一些锆石内部均较暗,并具有极窄的亮边,其中少部分可见微弱的环带结构(图 3b);另外一些锆石内部残留有具有较好岩浆震荡环带的继承核,显示了可能的岩浆成因(图 3c)。而13SD-09样品中锆石仅一种透明浑圆状,含大量包体,CL图像下具备复杂的内部结构,部分具有生长环带的继承核(图 3d-f)。
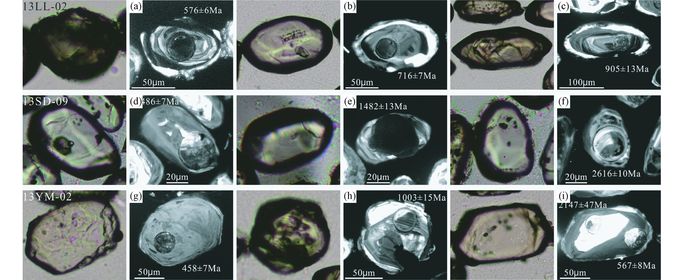
|
图 3 副片麻岩碎屑锆石阴极发光图像及对应的透射光镜下照片 Fig. 3 Cathodoluminescene (CL) images and corresponding transparent light microscope photos showing internal textures of representative zircon crystals |
到目前为止,柴北缘超高压变质带正副片麻岩中的确凿超高压变质作用证据只在都兰北带野马滩地区有发现,其对应锆石变质边的年龄为约425Ma(Song et al., 2003a)。之后其余地体的大量锆石数据表明此带的片麻岩均具有类似的变质年龄(Zhang et al., 2013)。尽管没有确凿的超高压变质矿物证据,本文选取的3个样品中的部分锆石也同样具有同时代的变质增生边,说明其也经历了可能的高压/超高压变质作用。
锆石在变质作用过程中可以在流体的参与下发生变质重结晶,变质增生等过程;同时在变质过程中也会有新生变质锆石生长(Zhang et al., 2016)。此外,变质作用导致的可能的铅丢失现象也会使得很多古老的年龄变得不再可靠,增加了选取年龄数据的难度。但考虑区内榴辉岩和片麻岩变质年龄集中在上述的430Ma左右(Song et al., 2014)。最后的数据选取我们遵循以下几点:1) 选取>500Ma;2) 谐和度大于90%;3) 激光剥蚀坑与CL图像严格比对,同时结合稀土配分曲线模式(图 4;REE数据略)排除混合年龄。在这样的原则下,本次测试共从3个样品中获得139个有效数据点作图。
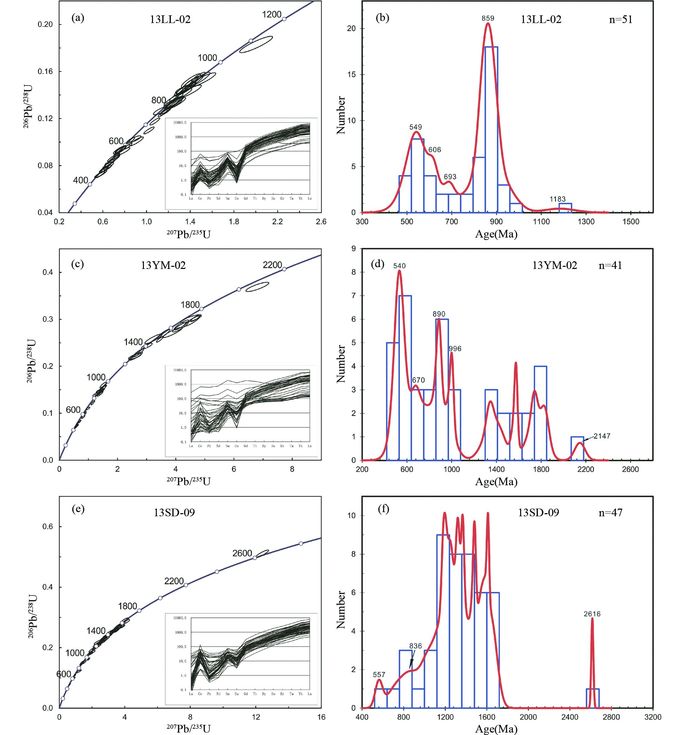
|
图 4 锆石U-Pb谐和曲线图、207Pb/206Pb年龄频率分布图以及REE图解(球粒陨石值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 4 Concordia plots for zircon ages with chondrite-normalized REE patterns (chondrite data after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
样品13LL-02的锆石207Pb/206Pb年龄除去1个最老年龄1183±70Ma之外,主要分布在978~786Ma和717~503Ma之间(图 4a、表 1)。其中978~786Ma段只有一个~859Ma的主要峰值。而717~503Ma段给出了~549Ma的主要峰值以及~605Ma和~692Ma两个次要峰值,加权平均年龄为602±34Ma(n=22)。
|
|
表 1 柴北缘变泥质岩碎屑锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄 Table 1 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages of detrital zircon from metapelite of the North Qaidam UHPM belt |
样品13YM-02的锆石207Pb/206Pb年龄除去1个最老年龄2147±47Ma之外,主要分布在1836~1321Ma、1003~770Ma和693~505Ma之间(图 4b、表 1)。其中1836~1321Ma段年龄连续分布,且数量较少无法构成峰。1003~770Ma段给出了~890Ma的主要峰值和~996Ma的次要峰值。717~503Ma段给出了~540Ma的主要峰值和~670Ma的次要峰值。
样品13SD-09的锆石207Pb/206Pb年龄除去1个最老年龄2116±10Ma之外,主要分布在1690~1105Ma之间。1100~500Ma之间年龄也有分布(图 4c、表 1),但数量太少,仅能大致给出~557Ma和~836Ma的峰值。而1690~1105Ma段间年龄连续分布,且因年龄数量较少,难以给出年龄峰值所在。
5 讨论及结论5.1 年龄分布图谱分析由于本文中的副片麻岩(片岩)都经历过高压(超高压)变质作用,相应的锆石普遍经历了榴辉岩相变质作用(Zhang et al., 2013; Song et al., 2014),导致锆石经历了普遍的铅丢失事件,使得单个样品难以获得符合统计规律的数据数量。但我们通过分析每个样品的年龄分布图谱,仍然可以将获得的年龄数据大致分为>1100Ma、1100~800Ma和800~500Ma三个组别。
5.1.1 太古代至中元古代Gehrels et al. (2003)根据对研究区内前寒武到侏罗纪地层中的大量碎屑锆石的研究,认为碎屑锆石中的太古代到中元古代的年龄(>1100Ma)来自1个具有1.6~1.4Ga的结晶岩并包括附属的1.9~1.1Ga岩石的大陆地区。但此区内少见具有这一类年龄的岩石,认为其可能的源区包括澳大利亚、华北、华南或者其他相近地块。而考虑到本次研究中样品来自大陆深俯冲带中的副片麻岩(片岩),这一部分年龄的记录说明参与俯冲的地体具有古老的结晶基底,进一步说明参与俯冲的为完整大陆而非一个年轻的大陆边缘。
5.1.2 中元古代至新元古代样品13LL-02和13YM-02中的新元古代至中元古代年龄较多且集中在1100~800Ma之间;13LL-02给出859Ma的主要峰值,13YM-02则是890Ma的主要峰值和960Ma的次要峰值(图 4)。而对区内超高压变质岩石详尽的年代学研究表明,榴辉岩的原岩年龄为870~750Ma(Zhang et al., 2005b, 2008b, 2010, 2011, 2017; 张建新, 2015; Chen et al., 2009a, b; Song et al., 2010),且Song et al. (2010)对鱼卡地区的榴辉岩的地球化学研究表明,榴辉岩原岩为大陆裂谷环境下的大陆溢流玄武岩,可能与Rodinia超大陆裂解相关。花岗质片麻岩原岩年龄为1020~900Ma(宋述光和杨经绥, 2001; Chen et al., 2009a, b; Zhang et al., 2009a, b; Song et al., 2012),区内花岗质片麻岩的地球化学特征显示为壳源同碰撞花岗岩,表明为大陆碰撞的产物(林慈銮等, 2006)。所以本次研究中所获得的新元古代至中元古代碎屑锆石年龄可能代表与Rodinia超大陆碰撞和裂解相关的一系列岩浆活动,而13YM-02中的960Ma的次要峰值和890Ma的主要峰值可能分别代表Rodinia超大陆的碰撞和裂解事件。
5.1.3 新元古代至早古生代这一部分年龄在研究区内并没有明显的岩浆岩与之对应,但在相邻的北祁连构造带中可见大量代表洋壳残余的蛇绿岩套,原岩年龄在~500Ma(Song et al., 2013)。而在柴北缘地区仅在都兰地区野马滩有疑似蛇绿岩组合(Song et al., 2003a)和沙柳河蛇绿岩组合的报道(张贵宾等, 2005; Zhang et al., 2008a),原岩年龄550~500Ma,并给出了约520Ma的平均年龄(Zhang et al., 2008a)。而本次研究中早古生代至新元古代的年龄也以~550Ma为主要峰值,可能与古祁连洋的演化有关。大洋俯冲一般会伴随岛弧岩浆作用,因此本文样品中700~500Ma的锆石年龄很可能来自于和大洋活动同时的岛弧岩浆作用。柴北缘内滩间山群的火山岩具有岛弧的地球化学特征,且年龄在550~500Ma之间(Shi et al., 2006; 李峰等, 2007),可能是作为本文副片麻岩(片岩)中锆石来源的一部分。
5.1.4 源区分析如上,作为俯冲带的产物,本文中的泥质片麻岩(片岩)随大陆作为一个整体发生深俯冲,因此确定其实际源区位置尤为困难。但通过上面的分析和样品碎屑锆石特点我们仍然可以大致恢复出每个样品不同的源区特征。其中3个样品中13LL-02年龄主要为中元古代至新元古代及新元古代至早古生代两部分,13SD-09的年龄则主要为太古代至中元古代,而13YM-02则兼具这三部分年龄(图 4)。而通过上面的分析,太古代至中元古代年龄代表古老的结晶基底,中元古代至新元古代年龄代表与Rodinia超大陆碰撞和裂解相关的岩浆活动,早古生代至新元古代年龄则代表了祁连洋的演化。由此我们可以推测:13LL-02样品沉积区域最接近Rodinia超大陆碰撞和裂解形成的大陆边缘,13SD-09样品沉积区域位于大陆内部接受结晶基底的剥蚀碎屑,13YM-02样品沉积区域则介于这两者之间,即与大陆边缘的距离13SD-09(都兰南带)>13YM-02(都兰北带)>13LL-02(绿梁山)。当然,要验证这一推测仍需要更多的沉积学等进一步的直接证据。
5.2 板块亲缘性分析之前的研究表明,柴北缘超高压变质带中的泥质片麻岩以及整个柴达木-祁连地区的(变质)沉积岩的碎屑锆石研究显示,碎屑锆石中谐和程度较高的继承核的年龄范围包括2.5~0.8Ga,其中主要峰值出现在1.0~0.8Ga以及1.8~1.5Ga,并有少部分2.5~2.2Ga的年龄。与此同时考虑古大陆的位置关系,说明柴达木-祁连地区可能与华北克拉通、扬子克拉通以及澳大利亚有板块亲缘性(Wan et al., 2001; Gehrels et al., 2003; Song et al., 2014)。Wan et al. (2006a)通过对柴北缘超高压变质带中的变质沉积岩的地球化学研究,认为其地球化学特征和Nd同位素数据与祁连造山带以及扬子克拉通类似,认为柴北缘-祁连地体是扬子克拉通的一部分。
由于碎屑锆石年龄集中的反映了区域演化历史上的部分热事件,而通过整合柴北缘超高压变质带中所有出露的变质沉积岩的碎屑锆石数据,可能代表了整体参与北向俯冲(Song et al., 2006)的柴达木板块的演化历史。因此,结合本文对柴北缘超高压变质带中选取的泥质片麻岩(片岩)中的碎屑锆石年龄数据,同时与周围可能存在联系的区域的碎屑锆石年龄数据对比,可能对其亲缘性讨论提供新的证据和思路。本文选取了西扬子、北扬子和华北南缘的碎屑锆石年龄数据用于对比(图 5)。从图 5d中我们可以看出,华北克拉通的生长主要发生在中太古代到古元古代,并具有3Ga以上的年龄。而在这之后华北克拉通广泛缺失中元古代到早古生代的热事件,尤其是本区内较为重要的Rodinia期的年龄。因此柴北缘超高压变质带与华北克拉通具备不同的演化历史。前人研究中普遍认为柴北缘—祁连地区与扬子克拉通具有成因上的联系,本文分别选取了扬子克拉通北缘和西缘的碎屑锆石数据进行对比,发现扬子克拉通北缘虽然具有类似的格林威尔期的年龄,但由于其具有更为古老的基底(ca.3.5~3.0Ga)以及缺失1.8~1.0Ga的年龄而与柴北缘超高压变质带不同(图 5c)。扬子克拉通西缘的碎屑锆石数据分布则与本文中所获得碎屑锆石数据分布类似,这与前人研究认为柴北缘-祁连地区与扬子克拉通存在成因联系吻合。并且通过与扬子克拉通北缘和西缘的对比,我们认为柴北缘超高压变质带所代表的柴达木板块与扬子克拉通的西缘具有亲缘性,可能作为扬子克拉通西缘的延伸而与扬子克拉通相连。

|
图 5 碎屑锆石年龄分布谱图 数据来源:西扬子(Li et al., 2002, 2003; Zhou et al., 2006; Zhao and Zhou, 2007; Huang et al., 2008; Zhao et al., 2008; Sun et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2012a);北扬子(Zhang et al., 2006a, b, c, 2008c; Xiao et al., 2007; Zhao and Zhou, 2008, 2009; Jiao et al., 2009; Pei et al., 2009; Xiong et al., 2009; Zhao et al., 2010; Peng et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2012b);华北南缘(Wan et al., 2006b; Diwu et al., 2008; Xu et al., 2009; Cui et al., 2011; 时毓等, 2011; Diwu et al., 2012); 北秦岭(第五春荣等, 2010; 万渝生等, 2011; Zhu et al., 2011; Shi et al., 2013);南秦岭(Shi et al., 2013).所有数据皆为谐和度大于90% Fig. 5 Zircon U-Pb age spectra |
秦岭、祁连山、昆仑山共同构成了中国的中央造山带,由于其在方位上的联系,存在柴北缘-祁连构造带和秦岭-大别造山带是否有联系的疑问。在最近的研究中,Shi et al. (2013)通过将秦岭造山带分为南北两带并分别进行碎屑锆石年龄分布统计(图 5e, f),结果显示锆石U-Pb年龄分布特征与华北克拉通南缘及北扬子都无法很好的吻合,但与本文所做柴北缘及西扬子相似;而根据Gehrels et al. (2003)的研究表明祁连地体的碎屑锆石分布也具有类似的特征(未列出)。并且Shi et al. (2013)通过Lu-Hf等数据认为北秦岭是一个在中元古代到中新元古代具有独立演化历史的微陆块。因此可以推断,柴达木陆块可能作为扬子板块西缘的延伸而与扬子克拉通相连,祁连地体及北秦岭地体则作为与扬子克拉通西缘具有亲缘性的微陆块独自演化,并有可能是相连的同一地体。
5.3 构造演化历史柴北缘超高压变质带向北200km为平行的北祁连造山带,因此在讨论柴北缘的构造演化历史时通常会将北祁连造山带一起考虑进来。Yang et al.(2002a, b)认为柴北缘超高压变质带和北祁连造山带是两条向北平行俯冲的两个俯冲带。Gehrels et al. (2003)则认为整个区域形成于一次向南的俯冲,并分别形成了北祁连的高压低温变质带和柴北缘超高压变质带。Song et al. (2006)提出了一个单一的北向俯冲的模型,形成了北祁连的高压低温变质带,柴北缘超高压变质带则来自俯冲带内岩石的长距离折返并就位于现在的位置。Yin et al. (2007)认为柴北缘的变质岩与北祁连缝合带中的岛弧岩浆年龄一致,因此提出了超高压变质岩石是由于南向俯冲的祁连板片发生底辟作用上升侵位造成的。
如前所述柴北缘超高压变质带和北祁连造山带都可能具有扬子克拉通西缘的亲缘性,而前人研究认为奥陶纪时期整个秦祁昆地区均为一个多岛洋盆地,经历了Rodinia超大陆裂解及其后的裂谷系演化,并发展为多岛洋体系(Du et al., 2007; Yin et al., 2004; 姜高磊等, 2014),因此柴达木地体和祁连地体都可能为Rodinia超大陆裂解时形成的扬子克拉通的碎片。此外,祁连造山带内多岛弧岩浆活动相关的火成岩,而柴北缘超高压变质带则少见(Song et al., 2013, 2014)。祁连造山带内的低温高压变质岩石的变质年龄早于柴北缘超高压变质带的峰期变质时代(Song et al., 2013, 2014),并且形成了向北年龄变年轻的两个蛇绿岩带(Song et al., 2013)。综合上述,我们提出了一个在早古生代北祁连为主动大陆边缘,柴北缘为被动大陆边缘;在祁连地体北侧的古祁连洋闭合后柴北缘转变为主动大陆边缘的构造演化模式,如下:
第一阶段(1300~750Ma):如上述讨论,这一阶段可能发生了与Rodinia超大陆碰撞和裂解相关的构造和岩浆活动。
第二阶段(750~520Ma):Rodinia超大陆裂解后古祁连洋的张开和演化,并演化为秦祁昆的多岛洋体系。
第三阶段(520~460Ma):祁连地体北侧的古祁连洋发生了被动大陆边缘到主动大陆边缘的转化。由于祁连地区发现的最老的岛弧相关的岩浆作用的年龄大约508~516Ma(Song et al., 2013),因此洋壳的初始双向俯冲可能发生在520Ma。而祁连造山带内低温高压变质岩最年轻的年龄为460Ma(Song et al., 2013)。
第四阶段(460~420Ma):祁连地体南侧的古祁连洋由被动大陆边缘转化为主动大陆边缘,在洋壳俯冲的带动下(以沙柳河蛇绿岩剖面为代表, Zhang et al., 2008a),陆壳继续俯冲,发生了ca.435~425Ma的就位于柴北缘超高压变质带的陆壳深俯冲超高压变质作用(Song et al., 2014)。这一演化模式与现今西太平洋类似,日本西南地区的研究显示,其Sr-Nd同位素数据证明日本的俯冲-增生杂岩可能大部分由循环的古老陆壳构成,年龄可能为元古代;这一数据支持古日本可能沿着中国华南克拉通东南缘演化,之后发生分离(Jahn, 2010)。这一分离事件导致了所谓“岛弧后退”现象,即西太平洋岛弧仅在日本岛发育,而中国东南沿海少见岛弧岩浆作用;且由于增生造山作用形成了日本岛内一系列高压变质的增生杂岩。日本岛的“岛弧后退”现象和高压增生杂岩表明目前西太平洋的构造演化可与上文所述第三阶段相对应,而可以预见未来太平洋完全俯冲消减后,西太平洋可能发生与上述第四阶段相似的构造演化过程。
第五阶段(420~400Ma):发生了柴北缘超高压变质岩石的折返和抬升(Zhang et al., 2013; Song et al., 2014)。
第六阶段(400~360Ma):造山带的垮塌和后造山岩浆作用(Song et al., 2014)。
致谢 北京大学马芳博士和中国地质大学(北京)苏犁教授在锆石分析时提供了帮助; 两位审稿人及吴春明教授提出了许多建设性意见和建议; 在此一并致谢。| [] | Black LP, Kamo SL, Allen CM, Aleinikoff JN, Davis DW, Korsch RJ, Foudoulis C. 2003. TEMORA 1: A new zircon standard for Phanerozoic U-Pb geochronology. Chemical Geology, 200(1-2): 155–170. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(03)00165-7 |
| [] | Bucher K, Fazis Y, de Capitani C, Grapes R. 2005. Blueschists, eclogites, and decompression assemblages of the Zermatt-Saas ophiolite: High-pressure metamorphism of subducted Tethys lithosphere. American Mineralogist, 90(5-6): 821–835. DOI:10.2138/am.2005.1718 |
| [] | Chen DL, Liu L, Sun Y, Liou JG. 2009a. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb dating and its implications of the Yukahe HP/UHP terrane, the North Qaidam, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(3-4): 259–272. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.12.001 |
| [] | Chen NS, Gong SL, Sun M, Li XY, Xia XP, Wang QY, Wu FY, Xu P. 2009b. Precambrian evolution of the Quanji Block, northeastern margin of Tibet: Insights from zircon U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotope compositions. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(3-4): 367–376. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.10.004 |
| [] | Cui ML, Zhang BL, Zhang LC. 2011. U-Pb dating of baddeleyite and zircon from the Shizhaigou diorite in the southern margin of North China Craton: Constrains on the timing and tectonic setting of the Paleoproterozoic Xiong'er Group. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 184–193. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.01.010 |
| [] | Diwu CR, Sun Y, Yuan HL, Wang HL, Zhong XP, Liu XM. 2008. U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes for detrital zircons from quartzite in the Paleoproterozoic Songshan Group on the southwestern margin of the North China Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(18): 2828–2839. |
| [] | Diwu CR, Sun Y, Liu L, Zhang CL, Wang HL. 2010. The disintegration of Kuanping Group in North Qinling orogenic belts and Neo-Proterozoic N-MORB. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7): 2025–2038. |
| [] | Diwu CR, Sun Y, Zhang H, Wang Q, Guo AL, Fan LG. 2012. Episodic tectonothermal events of the western North China Craton and North Qinling Orogenic Belt in central China: Constraints from detrital zircon U-Pb ages. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 47: 107–122. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.07.012 |
| [] | Du YS, Zhu J, Gu SZ, Xu YJ, Yang JH. 2007. Sedimentary geochemistry of the Cambrian-Ordovician cherts: Implication on archipelagic ocean of North Qilian orogenic belt. Science in China (Series D), 50(11): 1628–1644. DOI:10.1007/s11430-007-0111-z |
| [] | Gehrels GE, Yin A, Wang XF. 2003. Detrital-zircon geochronology of the northeastern Tibetan plateau. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 115(7): 881–896. DOI:10.1130/0016-7606(2003)115<0881:DGOTNT>2.0.CO;2 |
| [] | Huang XL, Xu YG, Li XH, Li WX, Lan JB, Zhang HH, Liu YS, Wang YB, Li HY, Luo ZY, Yang QJ. 2008. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Neoproterozoic, highly fractionated A-type granites from Mianning, South China. Precambrian Research, 165(3-4): 190–204. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2008.06.010 |
| [] | Jahn BM. 1999. Sm-Nd isotope tracer study of UHP metamorphic rocks: Implications for continental subduction and collisional tectonics. International Geology Review, 41(10): 859–885. DOI:10.1080/00206819909465175 |
| [] | Jahn BM. 2010. Accretionary orogen and evolution of the Japanese Islands: Implications from a Sr-Nd isotopic study of the Phanerozoic granitoids from SW Japan. American Journal of Science, 310(10): 1210–1249. DOI:10.2475/10.2010.02 |
| [] | Jiang GL, Zhang SM, Liu KF, Zhang KX. 2014. Evolution of Neoproterozoic-Mesozoic sedimentary basins in Qilian-Qaidam-East Kunlun area. Earth Science, 39(8): 1000–1016. |
| [] | Jiao WF, Wu YB, Yang SH, Peng M, Wang J. 2009. The oldest basement rock in the Yangtze Craton revealed by zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope composition. Science in China (Series D), 52(9): 1393–1399. DOI:10.1007/s11430-009-0135-7 |
| [] | Krogh TE, Keppie JD. 1990. Age of detrital zircon and titanite in the Meguma Group, southern Nova Scotia, Canada: Clues to the origin of the Meguma Terrane. Tectonophysics, 177(1-3): 307–323. DOI:10.1016/0040-1951(90)90287-I |
| [] | Li F, Wu ZL, Li BZ. 2007. Recognition on formation age of the Tanjianshan Group on the northren margin of the Qaidam Basin and its geological significance. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 31(2): 226–233. |
| [] | Li XH, Li ZX, Zhou HW, Liu Y, Kinny PD. 2002. U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemistry and Nd isotopic study of Neoproterozoic bimodal volcanic rocks in the Kangdian Rift of South China: Implications for the initial rifting of Rodinia. Precambrian Research, 113(1-2): 135–154. DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(01)00207-8 |
| [] | Li ZX, Li XH, Kinny PD, Wang J, Zhang S, Zhou H. 2003. Geochronology of Neoproterozoic syn-rift magmatism in the Yangtze Craton, South China and correlations with other continents: Evidence for a mantle superplume that broke up Rodinia. Precambrian Research, 122(1-4): 85–109. DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00208-5 |
| [] | Lin CL, Sun Y, Chen DL, Diwu CR. 2006. Geochemistry and zircon LA-ICPMS dating of Iqe River granitic gneiss, northern margin of Qaidam Basin. Geochimica, 35(5): 489–505. |
| [] | Liu PJ, Li XH, Chen SM, Lan ZW, Yang B, Shang XD, Yin CY. 2015. New SIMS U-Pb zircon age and its constraint on the beginning of the Nantuo glaciation. Science Bulletin, 60(10): 958–963. DOI:10.1007/s11434-015-0790-3 |
| [] | Liu XC, Wu YB, Gao S, Liu Q, Wang H, Qin ZW, Li QL, Li XH, Gong HJ. 2012. First record and timing of UHP metamorphism from zircon in the Xitieshan terrane: Implications for the evolution of the entire North Qaidam metamorphic belt. American Mineralogist, 97(7): 1083–1093. DOI:10.2138/am.2012.4048 |
| [] | Ludwig KR. 2003. User's manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Special Publication No. 4. Berkeley CA: Berkeley Geochronology Center |
| [] | Mattinson CG, Wooden JL, Liou JG, Bird DK, Wu CL. 2006. Age and duration of eclogite-facies metamorphism, North Qaidam HP/UHP terrane, western China. American Journal of Science, 306(9): 683–711. DOI:10.2475/09.2006.01 |
| [] | Pearce NJG, Perkins WT, Westgate JA, Gorton MP, Jackson SE, Neal CR, Chenery SP. 1997. A compilation of new and published major and trace element data for NIST SRM 610 and NIST SRM 612 glass reference materials. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 21(1): 115–144. DOI:10.1111/ggr.1997.21.issue-1 |
| [] | Pei XZ, Li ZC, Ding SP, Li RB, Feng JY, Sun Y, Zhang YF, Liu ZP. 2009. Neoproterozoic Jiaoziding peraluminous granite in the northwestern margin of Yangtze Block: Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age and geochemistry and their tectonic significance. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(3): 231–249. DOI:10.1016/S1872-5791(08)60096-2 |
| [] | Peng M, Wu YB, Gao S, Zhang HF, Wang J, Liu XC, Gong HJ, Zhou L, Hu ZC, Liu YS, Yuan HL. 2012. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope compositions of Paleoproterozoic aluminous A-type granites from the Kongling terrain, Yangtze Block: Constraints on petrogenesis and geologic implications. Gondwana Research, 22(1): 140–151. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.08.012 |
| [] | Reinecke T. 1991. Very-high-pressure metamorphism and uplift of coesite-bearing metasediments from the Zermatt-Saas zone, Western Alps. European Journal of Mineralogy, 3(1): 7–18. DOI:10.1127/ejm/3/1/0007 |
| [] | Shi RD, Yang JS, Wu CL, Tsuyoshi I, Takafumi H. 2006. Island arc volcanic rocks in the North Qaidam UHP belt, northern Tibet Plateau: Evidence for ocean-continent subduction preceding continent-continent subduction. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 28(2-3): 151–159. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.019 |
| [] | Shi Y, Yu JH, Xu XS, Tang HF, Qiu JS, Chen LH. 2011. U-Pb ages and Hf isotope compositions of zircons of Taihua Group in Xiaoqinling area, Shaanxi Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(10): 3095–3108. |
| [] | Shi Y, Yu JH, Santosh M. 2013. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogenic belt, Central China: New evidence from geochemical, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes. Precambrian Research, 231: 19–60. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2013.03.001 |
| [] | Sircombe KN, Freeman MJ. 1999. Provenance of detrital zircons on the Western Australia coastline: Implications for the geologic history of the Perth basin and denudation of the Yilgarn craton. Geology, 27(10): 879–882. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<0879:PODZOT>2.3.CO;2 |
| [] | Song SG, Yang JS. 2001. Sanidine+quartz inclusions in Dulan eclogites: Evidence for UHP metamorphism on the north margin of the Qaidam basin, NW China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 75(2): 180–185. |
| [] | Song SG, Yang JS, Xu ZQ, Liou JG, Shi RD. 2003a. Metamorphic evolution of the coesite-bearing ultrahigh-pressure terrane in the North Qaidam, Northern Tibet, NW China. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 21(6): 631–644. DOI:10.1046/j.1525-1314.2003.00469.x |
| [] | Song SG, Yang JS, Liou JG, Wu CL, Shi RD, Xu ZQ. 2003b. Petrology, geochemistry and isotopic ages of eclogites from the Dulan UHPM terrane, the North Qaidam, NW China. Lithos, 70(3-4): 195–211. DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(03)00099-9 |
| [] | Song SG, Zhang LF, Niu YL. 2004. Ultra-deep origin of garnet peridotite from the North Qaidam ultrahigh-pressure belt, Northern Tibetan Plateau, NW China. American Mineralogist, 89(8-9): 1330–1336. DOI:10.2138/am-2004-8-922 |
| [] | Song SG, Zhang LF, Niu YL, Su L, Jian P, Liu DY. 2005. Geochronology of diamond-bearing zircons from garnet peridotite in the North Qaidam UHPM belt, Northern Tibetan Plateau: A record of complex histories from oceanic lithosphere subduction to continental collision. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 234(1-2): 99–118. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.036 |
| [] | Song SG, Zhang LF, Niu YL, Su L, Song B, Liu DY. 2006. Evolution from oceanic subduction to continental collision: A case study from the Northern Tibetan Plateau based on geochemical and geochronological data. Journal of Petrology, 47(3): 435–455. |
| [] | Song SG, Su L, Niu Y, Zhang LF, Zhang GB. 2007. Petrological and geochemical constraints on the origin of garnet peridotite in the North Qaidam ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt, northwestern China. Lithos, 96(1-2): 243–265. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.09.017 |
| [] | Song SG, Su L, Li XH, Zhang GB, Niu YL, Zhan LF. 2010. Tracing the 850Ma continental flood basalts from a piece of subducted continental crust in the North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China. Precambrian Research, 183(4): 805–816. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2010.09.008 |
| [] | Song SG, Su L, Li XH, Niu YL, Zhang LF. 2012. Grenville-age orogenesis in the Qaidam-Qilian block: The link between South China and Tarim. Precambrian Research, 220-221: 9–22. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2012.07.007 |
| [] | Song SG, Niu YL, Su L, Xia XH. 2013. Tectonics of the North Qilian orogen, NW China. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1378–1401. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.004 |
| [] | Song SG, Niu YL, Su L, Zhang C, Zhang LF. 2014. Continental orogenesis from ocean subduction, continent collision/subduction, to orogen collapse, and orogen recycling: The example of the North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China. Earth-Science Reviews, 129: 59–84. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.11.010 |
| [] | Sun SS, McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313–345. DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 |
| [] | Sun WH, Zhou MF, Gao JF, Yang YH, Zhao XF, Zhao JH. 2009. Detrital zircon U-Pb geochronological and Lu-Hf isotopic constraints on the Precambrian magmatic and crustal evolution of the western Yangtze Block, SW China. Precambrian Research, 172(1-2): 99–126. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2009.03.010 |
| [] | Wan YS, Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Zhang JX. 2001. Ages and compositions of the Precambrian high-grade basement of the Qilian Terrane and its adjacent areas. Acta Geologica Sinica, 75(4): 375–384. |
| [] | Wan YS, Zhang JX, Yang JS, Xu ZQ. 2006a. Geochemistry of high-grade metamorphic rocks of the North Qaidam Mountains and their geological significance. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 28(2-3): 174–184. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.018 |
| [] | Wan YS, Wilde SA, Liu DY, Yang CX, Song B, Yin XY. 2006b. Further evidence for ~1. 85Ga metamorphism in the Central Zone of the North China Craton: SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircon from metamorphic rocks in the Lushan area, Henan Province. Gondwana Research, 9(1-2): 189–197. |
| [] | Wan YS, Liu DY, Dong CY, Yin XY. 2011. SHRIMP zircon dating of meta-sedimentary rock from the Qinling Group in the north of Xixia, North Qinling Orogenic Belt: Constraints on complex histories of source region and timing of deposition and metamorphism. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(4): 1172–1178. |
| [] | Wang LJ, Yu JH, Griffin WL, O'Reilly SY. 2012a. Early crustal evolution in the western Yangtze Block: Evidence from U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopes on detrital zircons from sedimentary rocks. Precambrian Research, 222-223: 368–385. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2011.08.001 |
| [] | Wang W, Liu SW, Feng YG, Li QG, Wu FH, Wang ZQ, Wang RT, Yang PT. 2012b. Chronology, petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Neoproterozoic Tongchang dioritic pluton at the northwestern margin of the Yangtze Block: Constraints from geochemistry and zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopic systematics. Gondwana Research, 22(2): 699–716. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.11.015 |
| [] | Xiao L, Zhang HF, Ni PZ, Xiang H, Liu XM. 2007. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology of Early Neoproterozoic mafic-intermediat intrusions from NW margin of the Yangtze Block, South China: Implication for tectonic evolution. Precambrian Research, 154(3-4): 221–235. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.12.013 |
| [] | Xiong Q, Zheng JP, Yu CM, Su YP, Tang HY, Zhang ZH. 2009. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope of Quanyishang A-type granite in Yichang: Signification for the Yangtze continental cratonization in Paleoproterozoic. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(3): 436–446. |
| [] | Xu XS, Griffin WL, Ma X, O'Reilly SY, He ZY, Zhang CL. 2009. The Taihua Group on the southern margin of the North China craton: Further insights from U-Pb ages and Hf isotope compositions of zircons. Mineralogy and Petrology, 97(1-2): 43–59. DOI:10.1007/s00710-009-0062-5 |
| [] | Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Zhang JX, Jiang M, Li HB, Cui XW. 1999. A comparison between the tectonic units on the sides of the Altun sinistral strike-slip fault and the mechanism of lithospheric shearing. Acta Geologica Sinica, 73(3): 193–205. |
| [] | Yang JJ, Zhu H, Deng JF, Zhou TZ, Lai SC. 1994. Discovery of garnet-peridotite at the northern margin of the Qaidam Basin and its significance. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 13(2): 97–105. |
| [] | Yang JS, Xu ZQ, Song SG, Zhang JX, Wu CL, Shi RD, Li HB, Brunel M. 2001. Discovery of coesite in the North Qaidam Early Palaeozoic ultrahigh pressure (UHP) metamorphic belt, NW China. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences-Series ⅡA-Earth and Planetary Science, 333(11): 719–724. |
| [] | Yang JS, Xu ZQ, Song SG, Zhang JX, Wu CL, Shi RD, Li HB, Brunel M, Tapponnier P. 2002a. Subduction of continental crust in the Early Palaeozoic North Qaidam ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt, NW China: Evidence from the discovery of coesite in the belt. Acta Geologica Sinica, 76(1): 63–68. |
| [] | Yang JS, Xu ZQ, Zhang JX, Song SG, Wu CL, Shi RD, Li HB, Brunel M. 2002b. Early Palaeozoic North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt on the north-eastern Tibetan plateau and a paired subduction model. Terra Nova, 14(5): 397–404. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-3121.2002.00438.x |
| [] | Yang JS, Liu FL, Wu CL, Wan YS, Zhang JX, Shi RD, Chen SY. 2003. Two ultrahigh pressure metamorphic events recognized in the Central Orogenic Belt of China: Evidence from the U-Pb dating of coesite-bearing zircons. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77(4): 463–477. |
| [] | Yin A, Manning CE, Lovera O, Menold CA, Chen XH, Gehrels GE. 2007. Early Paleozoic tectonic and thermomechanical evolution of ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks in the northern Tibetan Plateau, northwest China. International Geology Review, 49(8): 681–716. DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.49.8.681 |
| [] | Yin HF, Zhang KX, Feng QL. 2004. The archipelagic ocean system of the eastern Eurasian Tethys. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78(1): 230–236. |
| [] | Yu SY, Zhang JX, Li HK, Hou KJ, Mattinson CG, Gong JH. 2013. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Lu-Hf isotopic composition of eclogites and their host gneisses in the Dulan area, North Qaidam UHP terrane: New evidence for deep continental subduction. Gondwana Research, 23(3): 901–919. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.07.018 |
| [] | Zhang C, Zhang LF, Van Roermund H, Song SG, Zhang GB. 2011. Petrology and SHRIMP U-Pb dating of Xitieshan eclogite, North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 42(4): 752–767. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.04.002 |
| [] | Zhang GB, Song SG, Zhang LF, Niu YL, Shu GM. 2005. Ophiolite-type mantle peridotite from Shaliuhe, North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China and its tectonic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(4): 1049–1058. |
| [] | Zhang GB, Song SG, Zhang LF, Niu YL. 2008a. The subducted oceanic crust within continental-type UHP metamorphic belt in the North Qaidam, NW China: Evidence from petrology, geochemistry and geochronology. Lithos, 104(1-4): 99–118. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.12.001 |
| [] | Zhang GB, Ellis DJ, Christy AG, Zhang LF, Niu YL, Song SG. 2009a. UHP metamorphic evolution of coesite-bearing eclogite from the Yuka terrane, North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China. European Journal of Mineralogy, 21(6): 1287–1300. DOI:10.1127/0935-1221/2009/0021-1989 |
| [] | Zhang GB, Zhang LF, Song SG, Niu YL. 2009b. UHP metamorphic evolution and SHRIMP geochronology of a coesite-bearing meta-ophiolitic gabbro in the North Qaidam, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(3-4): 310–322. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.11.013 |
| [] | Zhang GB, Zhang LF, Christy AG. 2013. From oceanic subduction to continental collision: An overview of HP-UHP metamorphic rocks in the North Qaidam UHP belt, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 63: 98–111. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.07.014 |
| [] | Zhang GB, Ireland T, Zhang LF, Gao Z, Song SG. 2016. Zircon geochemistry of two contrasting types of eclogite: Implications for the tectonic evolution of the North Qaidam UHPM belt, northern Tibet. Gondwana Research, 35: 27–39. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.04.002 |
| [] | Zhang JX, Yang JS, Mattinson CG, Xu ZQ, Meng FC, Shi RD. 2005. Two contrasting eclogite cooling histories, North Qaidam HP/UHP terrane, western China: Petrological and isotopic constraints. Lithos, 84(1-2): 51–76. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2005.02.002 |
| [] | Zhang JX, Mattinson CG, Meng FC, Wan YS, Tung K. 2008b. Polyphase tectonothermal history recorded in granulitized gneisses from the north Qaidam HP/UHP metamorphic terrane, western China: Evidence from zircon U-Pb geochronology. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 120(5-6): 732–749. DOI:10.1130/B26093.1 |
| [] | Zhang JX, Mattinson CG, Yu SY, Li JP, Meng FC. 2010. U-Pb zircon geochronology of coesite-bearing eclogites from the southern Dulan area of the North Qaidam UHP terrane, northwestern China: Spatially and temporally extensive UHP metamorphism during continental subduction. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 28(9): 955–978. DOI:10.1111/jmg.2010.28.issue-9 |
| [] | Zhang JX, Yu SY, Li YS, Yu XX, Lin YH, Mao XH. 2015. Subduction, accretion and closure of Proto-Tethyan Ocean: Early Paleozoic accretion/collision orogeny in the Altun-Qilian-North Qaidam orogenic system. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(12): 3531–3554. |
| [] | Zhang JX, Yu SY, Mattinson CG. 2017. Early Paleozoic polyphase metamorphism in northern Tibet, China. Gondwana Research, 41: 267–389. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.11.009 |
| [] | Zhang LF, Ellis DJ, Jiang WB. 2002a. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in western Tianshan, China: Part Ⅰ. Evidence from inclusions of coesite pseudomorphs in garnet and from quartz exsolution lamellae in omphacite in eclogites. American Mineralogist, 87(7): 853–860. |
| [] | Zhang LF, Ellis DJ, Williams S, Jiang WB. 2002b. Ultra-high pressure metamorphism in western Tianshan, China: Part Ⅱ. Evidence from magnesite in eclogite. American Mineralogist, 87(7): 861–866. |
| [] | Zhang LF, Ai YL, Li XP, Rubatto D, Song B, Williams S, Song SG, Ellis D, Liou JG. 2007. Triassic collision of western Tianshan orogenic belt, China: Evidence from SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircon from HP/UHP eclogitic rocks. Lithos, 96(1-2): 266–280. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.09.012 |
| [] | Zhang LF, Lu Z, Zhang GB, Song SG. 2008. The geological characteristics of oceanic-type UHP metamorphic belts and their tectonic implications: Case studies from Southwest Tianshan and North Qaidam in NW China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(18): 2166–2175. |
| [] | Zhang SB, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Zhao ZF, Gao S, Wu FY. 2006a. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope evidence for 3. 8Ga crustal remnant and episodic reworking of Archean crust in South China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 252(1-2): 56–71. |
| [] | Zhang SB, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Zhao ZF, Gao S, Wu FY. 2006b. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf-O isotope evidence for Paleoproterozoic metamorphic event in South China. Precambrian Research, 151(3-4): 265–288. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.08.009 |
| [] | Zhang SB, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Zhao ZF, Gao S, Wu FY. 2006c. Zircon isotope evidence for ≥3. 5Ga continental crust in the Yangtze craton of China. Precambrian Research, 146(1-2): 16–34. |
| [] | Zhang SB, Zheng YF, Zhao ZF, Wu YB, Yuan HL, Wu FY. 2008c. Neoproterozoic anatexis of Archean lithosphere: Geochemical evidence from felsic to mafic intrusions at Xiaofeng in the Yangtze Gorge, South China. Precambrian Research, 163(3-4): 210–238. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.12.003 |
| [] | Zhao JH, Zhou MF. 2007. Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic mafic intrusions in the Panzhihua district (Sichuan Province, SW China): Implications for subduction-related metasomatism in the upper mantle. Precambrian Research, 152(1-2): 27–47. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.09.002 |
| [] | Zhao JH, Zhou MF. 2008. Neoproterozoic adakitic plutons in the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, China: Partial melting of a thickened lower crust and implications for secular crustal evolution. Lithos, 104(1-4): 231–248. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.12.009 |
| [] | Zhao JH, Zhou MF. 2009. Secular evolution of the Neoproterozoic lithospheric mantle underneath the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, South China. Lithos, 107(3-4): 152–168. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2008.09.017 |
| [] | Zhao JH, Zhou MF, Zheng JP, Fang SM. 2010. Neoproterozoic crustal growth and reworking of the northwestern Yangtze Block: Constraints from the Xixiang dioritic intrusion, South China. Lithos, 120(3-4): 439–452. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.09.005 |
| [] | Zhao XF, Zhou MF, Li JW, Wu FY. 2008. Association of Neoproterozoic A-and I-type granites in South China: Implications for generation of A-type granites in a subduction-related environment. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 1–15. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.07.018 |
| [] | Zhou MF, Ma YX, Yan DP, Xia XP, Zhao JH, Sun M. 2006. The Yanbian terrane (southern Sichuan Province, SW China): A Neoproterozoic arc assemblage in the western margin of the Yangtze block. Precambrian Research, 144(1-2): 19–38. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2005.11.002 |
| [] | Zhu XY, Chen FK, Li SQ, Yang YZ, Nie H, Siebel W, Zhai MG. 2011. Crustal evolution of the North Qinling terrain of the Qinling Orogen, China: Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopic composition. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 194–204. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.12.009 |
| [] | 第五春荣, 孙勇, 刘良, 张成立, 王洪亮. 2010. 北秦岭宽坪岩群的解体及新元古代N-MORB. 岩石学报, 26(7): 2025–2038. |
| [] | 姜高磊, 张思敏, 柳坤峰, 张克信. 2014. 祁连-柴达木-东昆仑新元古-中生代沉积盆地演化. 地球科学, 39(8): 1000–1016. |
| [] | 李峰, 吴志亮, 李保珠. 2007. 柴达木北缘滩间山群时代及其地质意义. 大地构造与成矿学, 31(2): 226–233. |
| [] | 林慈銮, 孙勇, 陈丹玲, 第五春荣. 2006. 柴北缘鱼卡河花岗质片麻岩的地球化学特征和锆石LA-ICPMS定年. 地球化学, 35(5): 489–505. |
| [] | 时毓, 于津海, 徐夕生, 唐红峰, 邱检生, 陈立辉. 2011. 陕西小秦岭地区太华群的锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成. 岩石学报, 27(10): 3095–3108. |
| [] | 宋述光, 杨经绥. 2001. 柴达木盆地北缘都兰地区榴辉岩中透长石+石英包裹体:超高压变质作用的证据. 地质学报, 75(2): 180–185. |
| [] | 万渝生, 刘敦一, 董春艳, 殷小艳. 2011. 西峡北部秦岭群变质沉积岩锆石SHRIMP定年:物源区复杂演化历史和沉积、变质时代确定. 岩石学报, 27(4): 1172–1178. |
| [] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 张建新, 姜枚, 李海兵, 崔军文. 1999. 阿尔金断裂两侧构造单元的对比及岩石圈剪切机制. 地质学报, 73(3): 193–205. |
| [] | 杨建军, 朱红, 邓晋福, 周天祯, 赖绍聪. 1994. 柴达木北缘石榴石橄榄岩的发现及其意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 13(2): 97–105. |
| [] | 杨经绥, 刘福来, 吴才来, 万渝生, 张建新, 史仁灯, 陈松永. 2003. 中央碰撞造山带中两期超高压变质作用:来自含柯石英锆石的定年证据. 地质学报, 77(4): 463–477. |
| [] | 张贵宾, 宋述光, 张立飞, 牛耀龄, 舒桂明. 2005. 柴北缘超高压变质带沙柳河蛇绿岩型地幔橄榄岩及其意义. 岩石学报, 21(4): 1049–1058. |
| [] | 张建新, 于胜尧, 李云帅, 喻星星, 林宜慧, 毛小红. 2015. 原特提斯洋的俯冲、增生及闭合:阿尔金-祁连-柴北缘造山系早古生代增生/碰撞造山作用. 岩石学报, 31(12): 3531–3554. |
| [] | 张立飞, 吕增, 张贵宾, 宋述光. 2008. 大洋型超高压变质带的地质特征及其研究意义:以西南天山、柴北缘超高压变质带为例. 科学通报, 53(18): 2166–2175. |
 2017, Vol. 33
2017, Vol. 33



