2. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
右江盆地是我国卡林型金矿主要集中分布区之一,产有水银洞、烂泥沟、紫木凼、戈塘、泥堡、丫他、金牙、高龙等超大、大-中型卡林型金矿床。矿床以台地相不纯碳酸盐岩和盆地相细碎屑岩为主要容矿岩石,矿体明显受断裂控制,与As、Sb、Hg(Tl)等元素密切共生,具有去碳酸盐化、粘土化、硫化物化和硅化等围岩蚀变特征,类似于美国内华达州的卡林型金矿床(Hu et al., 2002; Su et al., 2009a)。二十多年来,前人已对该类金矿形成的地质背景与成矿条件、含金硫化物矿物学与地球化学、成矿流体特征与成矿年代、成矿机制与成矿模式等方面都进行了较多的研究(胡瑞忠等, 1995, 2007, 2015;朱赖民等, 1997, 1998a, b; 朱赖民和胡瑞忠, 1999;蒋国豪等,2000;Zhu and Hu, 2000; 贾大成和胡瑞忠,2001;Hu et al., 2002; 苏文超,2002;Wang et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2003;陈懋弘等, 2006, 2007, 2009;张弘弢,2007;刘建中等,2008;Su et al., 2008, 2009a, b, 2012;夏勇等,2009;陈本金等,2010;罗刚,2010;Hu and Zhou, 2012; 张长青等,2012;代鸿章,2012;章永梅等,2013;Chen et al., 2015a, b; Tan et al., 2015;Hou et al., 2016)。
近年来的勘探实践,在右江盆地南缘发现一些金矿产于二叠纪辉绿岩体内部或辉绿岩与沉积岩接触带之中,如桂西北龙川、八渡以及滇东南安那等金矿床。这些金矿床在控矿构造、元素与矿物组合、热液蚀变以及金的赋存状态等方面,类似于盆地内以沉积岩为容矿岩石的卡林型金矿床,而在矿石品位、流体性质、成矿物质来源等方面与之存在差别(肖龙,1997;潘家永等,1998;覃文明和何志美,2003;陈新敏等,2011;寸伟才等,2011;覃少耀和颜小东,2012;Li et al., 2012;董文斗等,2013),前人对该类型金矿成矿流体性质与来源及其成矿过程等缺少系统的研究。本文通过对滇东南安那金矿床矿石显微岩相学结构、矿物学与地球化学、流体包裹体岩相学与显微测温学、激光Raman光谱以及氢氧同位素地球化学等分析,获取该类型金矿成矿流体性质和组成,探讨成矿流体的来源、演化及其成矿过程,对深入了解西南大面积低温成矿域的形成具有重要的科学意义。
1 区域地质背景与矿床地质特征安那金矿区位于右江盆地南缘的滇东南褶皱带文山-富宁断褶带东端(图 1),紧邻越北逆冲推覆褶皱带(Tran et al., 2016)。矿区主要出露泥盆系地层,主要为中下泥盆统灰黑色-灰绿色页岩、粉砂质泥岩和薄层泥灰岩夹黑色燧石条带,是矿区西南部革挡金矿床的赋矿层位。寒武系和奥陶系地层主要分布在矿区的西北部,主要为中-上寒武统灰黑色中厚层条带状白云岩和白云质灰岩,局部夹泥质粉砂岩、砂岩及透镜状燧石条带和中-下奥陶统灰白色中厚层石英砂岩、灰岩、白云岩和泥质灰岩,夹泥质粉砂岩和生物碎屑灰岩。石炭系地层零星分布,主要为浅灰色厚层状灰岩、生物碎屑灰岩和白云岩。二叠系和三叠系地层主要分布在矿区的东部,主要为灰岩、泥质粉砂岩、砂岩等。

|
图 1 安那金矿床区域地质简图 Fig. 1 Simplified geological map of the Anna gold deposit |
矿区褶皱和断裂构造十分发育,自北向南主要有东西向南劳背斜、洞波向斜和者桑背斜等褶皱构造。断裂构造主要发育北东向叭洞和龙叭断裂以及东西向岩河和者桑南断裂,其次为北西向富宁弧形断裂。矿区内岩浆活动较为强烈,主要为二叠纪偏碱性辉长辉绿岩和苏长-辉长岩(Zhou et al., 2006),其主体侵位于泥盆系地层之中,围岩广泛发育角岩化等热接触交代蚀变,并伴随有铜矿化等。
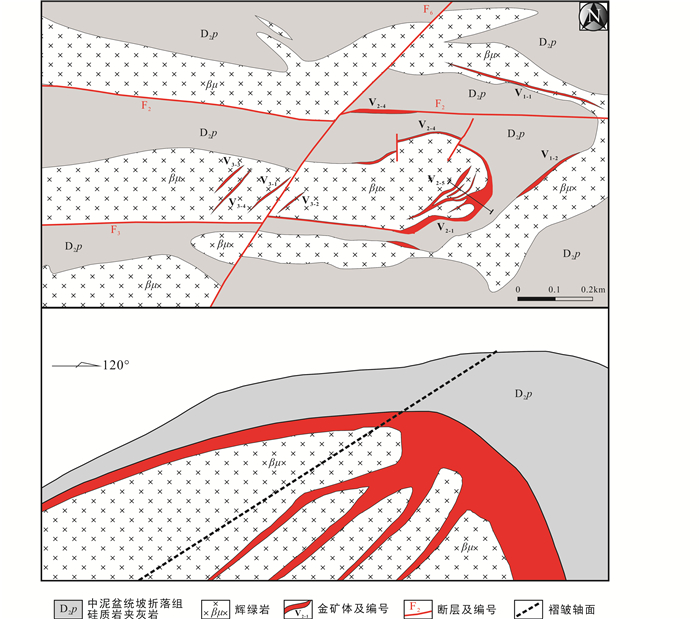
安那金矿床产于东西向安那背斜的东部倾伏段(图 2)。背斜的核部为辉绿岩侵入,两翼地层为中泥盆统坡折落组硅质岩。目前发现V1、V2和V3三个矿体群(寸伟才等,2011),其中V1和V2矿体群呈似层状,产于背斜核部或两翼的辉绿岩与硅质岩接触部位的蚀变辉绿岩内。矿体一般长280~450m,厚0.63~23.6m,Au平均品位1.04×10-6~1.27×10-6。V3矿体群均产于蚀变辉绿岩内,矿体主要由石英脉和蚀变辉绿岩组成,受北东向张性裂隙控制,呈“雁行”式脉状产出,矿体长20~100m,厚0.5~2m,Au平均品位1.22×10-6。所有矿体均广泛发育乳白色石英脉或网脉(图 3a),金矿化强度与石英脉的发育程度及围岩蚀变程度有关,含金硫化物主要分布在石英脉两侧的蚀变辉绿岩中,石英脉中很少见有硫化物。以石英脉为中心,两侧的辉绿岩通常发育褪色蚀变带,远离石英脉,热液蚀变逐渐减弱。褪色蚀变主要为硅化、伊利石化、绢云母化、绿泥石化以及碳酸盐岩化等,金主要以不可见金的形式赋存在含砷黄铁矿和毒砂之中(图 3)。矿石中矿石矿物主要有黄铁矿、毒砂等,脉石矿物主要有石英、金红石、方解石、白云石、云母、伊利石、重晶石、绿泥石等。矿石构造主要为块状构造、浸染状构造。
|
图 2 安那金矿床矿区平面图和剖面图(据寸伟才等,2011修改) Fig. 2 Simplified geological plan and cross-section of the Anna gold deposit (modified after Cun et al., 2011) |
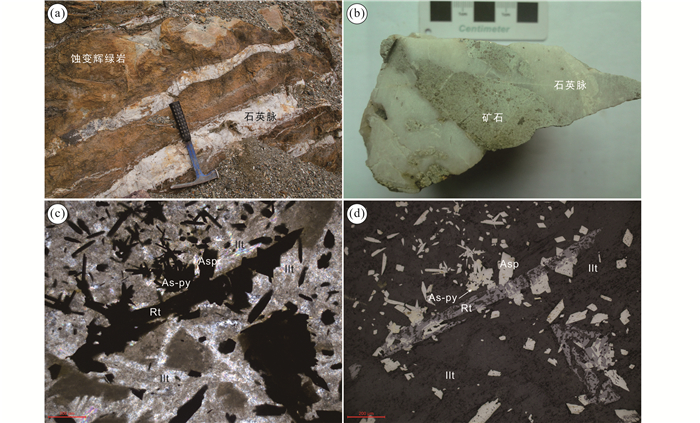

|
图 3 安那金矿床矿体与矿石显微岩相学结构 (a)蚀变辉绿岩矿体野外照片;(b)石英脉和含金硫化物的原生矿石样品照片;(c、d)原生矿石的显微镜下照片显示载金的含砷黄铁矿(As-py)和毒砂(Asp)围绕着金红石(Rt)和伊利石(Ilt)(c,透射光;d,反射光) Fig. 3 Photograph and photomicrographs of ore samples from Anna gold deposit (a) photograph of altered diabase ore with quartz veins; (b) photograph (thin section) of primary ore, showing the relationship among gold-bearing sulphides and quartz vein; (c, d) micro-photograph of gold-bearing arsenian pyrite (As-py) and arsenopyrite (Asp): surrounding of rutile (Rt) and illite (Ilt) in primary ores (transmitted light and reflected light) |
本次研究样品主要采自安那金矿床露天开采的V2矿体(图 2、图 3a)。矿石主要由石英脉和蚀变辉绿岩组成(图 3b)。金矿化主要发育在蚀变辉绿岩内,并伴随黄铁矿化、毒砂化等矿化,硅化、伊利石化、绢云母化、绿泥石化以及碳酸盐岩化等褪色热液蚀变,而石英脉中很少见有黄铁矿和毒砂等硫化物。载金矿物主要为黄铁矿和毒砂(图 3d),金主要以不可见金的形式存在。电子探针波谱成分分析显示,黄铁矿含有As(0.56%~4.22%)和Au(300×10-6~1010×10-6),毒砂含有Au(300×10-6~1290×10-6)。
选取石英单晶体沿C轴切割,磨制双面抛光的流体包裹体片(厚度约200μm)进行流体包裹体观察,然后选择有代表性的包裹体开展显微测温学和激光拉曼光谱分析。流体包裹体观察和显微测温学分析在中国科学院地球化学研究所矿床地球化学国家重点实验室完成,使用仪器为英国Linkam公司THMSG 600型冷热台和配有成像分析系统的标准显微镜。实验之前,采用国际人工合成流体包裹体标样对冷热台进行了校正。在低温(<50℃)和高温(>100℃)条件下,仪器误差分别为±0.1℃,±2℃。单个流体包裹体的气相成分分析采用英国Renishaw公司的InVia Reflex型显微共聚焦激光拉曼光谱仪,氩离子激光器波长为514nm,激光功率20mw,空间分辨率为1μm,扫描时间为30~60s,扫描范围为150~4000cm-1。石英氢氧同位素分析在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所稳定同位素实验室MAT-253质谱仪上完成。氧同位素分析采用传统的BrF5分析方法(Clayton and Mayeda, 1963),即采用BrF5与石英(180目)在真空和高温条件下反应提取矿物中的氧,与电阻石墨棒燃烧转化成CO2气体用于质谱测定,氧同位素分析精度为±0.2‰。氢同位素分析则先将挑纯的石英(40~60目)在150℃下真空去气4h以上,以消除表面吸附水和次生包裹体水,然后在400℃高温下爆裂提取水,并与金属锌反应生成H2用于质谱测定,氢同位素分析精度为±2‰。
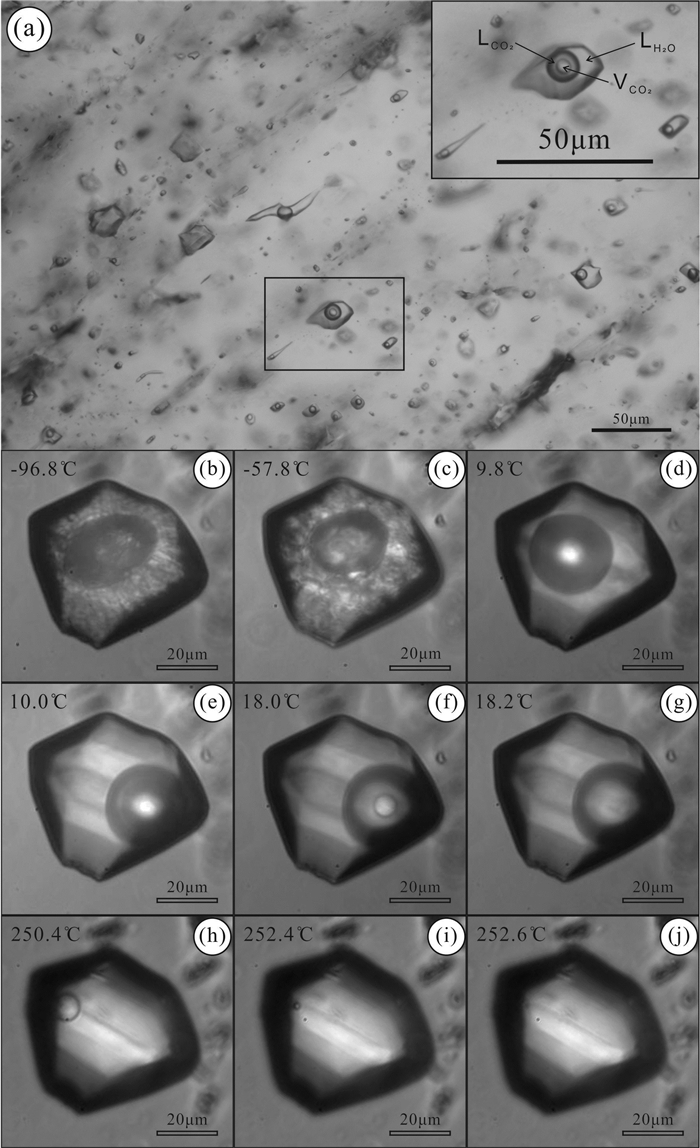
3 结果与讨论 3.1 流体包裹体岩相学对安那金矿床石英中200余个流体包裹体片进行了观察。根据流体包裹体在室温下的相态,结合降温过程中流体包裹体的相态变化和激光Raman光谱分析,发现石英中的流体包裹体均为CO2-H2O流体包裹体(图 4a)。这些流体包裹体呈负晶形,直径为5~90μm,气液比约为20%,通常沿石英的生长环带分布(图 4a),应为原生流体包裹体。室温下(25℃),该类流体包裹体通常为液态CO2(LCO2)和H2O两相(图 4a),降温时总是出现CO2气相,变为CO2-H2O三相流体包裹体(LH2O+LCO2+VCO2)。
|
图 4 安那金矿床石英中流体包裹体显微照片 (a)富CO2流体包裹体沿石英生长带分布;(b-j)富CO2流体包裹体显微测温的相变过程 Fig. 4 Photomicrographs of representative types of fluid inclusions (a) showing the distribution of aqueous-carbonic fluid inclusions in quartz growth zone from Anna gold deposit; (b-j) micro-photographs of a fluid inclusion during freezing and heating circle |
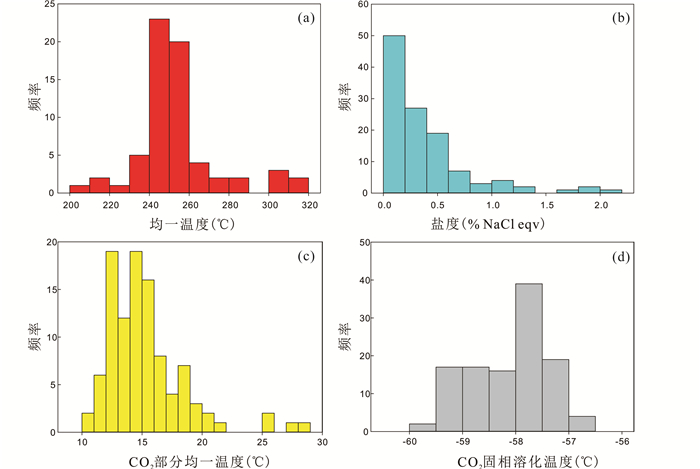
利用冷热台对安那金矿床石英中120余个包裹体的盐度和均一温度进行了测定,其结果见表 1和图 5。
|
图 5 安那金矿床石英中流体包裹体温度和盐度直方图 Fig. 5 Histograms of homogenization temperatures, salinities, CO2 part homogenization temperatures and solid CO2 melt temperatures of fluid inclusions in quartz from Anna gold deposit |
|
|
表 1 安那金矿床石英中流体包裹体显微测温结果 Table 1 Summary of microthermometric data for fluid inclusions in quartz from Anna gold deposit |
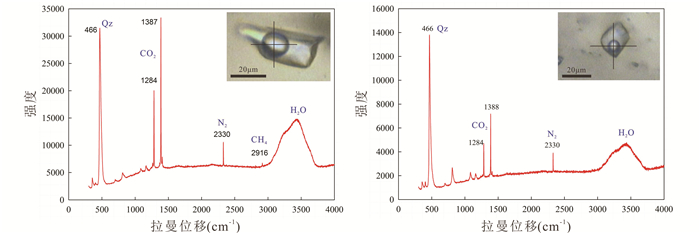
结果显示,在降温-冷冻过程中,该类流体包裹体总是出现气相CO2和固态CO2。所有包裹体CO2气相都均一到CO2液相,其均一温度(ThCO2)为10.8~28.2℃,平均15.3℃(图 4g、图 5c),计算的CO2密度为0.67~0.86 g/cm3,平均0.82 g/cm3;固态CO2的熔化温度(TmCO2)一般为-59.7~-56.8℃,平均-58.1℃,(图 4c、图 5d),低于纯CO2的三相点(-56.6℃),暗示可能含有CH4、N2等气体成分(Burruss, 1981;Shepherd et al., 1985)。激光Raman光谱分析进一步确认该类流体包裹体气相成分主要为CO2,含有少量的N2和微量的CH4(图 6)。在升温过程中,这些流体包裹体可以明显观察到CO2络合物的形成和熔化。CO2络合物的熔化温度(Tmclath)为9.0~10.3℃之间,平均为9.9℃,计算盐度为0~2.0% NaCleqv(Diamond, 1992),平均0.3% NaCleqv(图 4d、图 5b)。在加热过程中,部分流体包裹体在190~260℃之间发生了爆裂,未爆裂的流体包裹体均一到液相,其均一温度变化范围为208~312℃,主要集中在233~273℃之间,平均为254℃(表 1、图 5a),明显高于右江盆地以沉积岩为容矿岩石的卡林型金矿床(210℃)(Su et al., 2009a)。
|
图 6 安那金矿床石英中流体包裹体激光拉曼图谱 Fig. 6 Laser Raman spectra of individual fluid inclusions in quartz from Anna gold deposit |
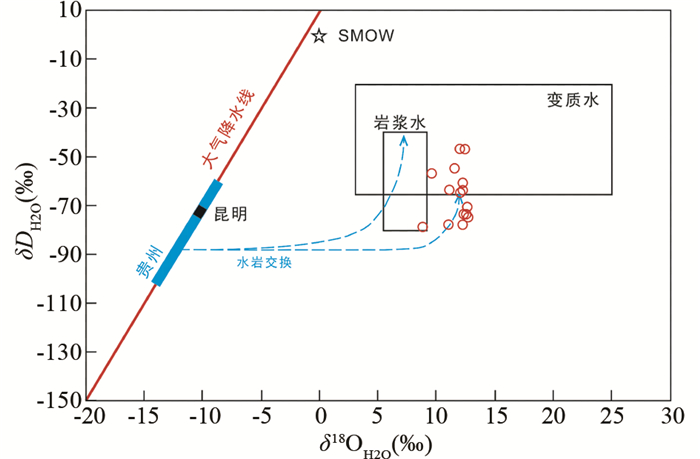
对安那金矿床矿石中15条石英脉的氢氧同位素组成进行了分析,其结果见表 2和图 7。
|
图 7 安那金矿床石英中流体包裹体δD-δ18O关系图 Fig. 7 A diagram of measured δD values versus calculated δ18O values of inclusion water in quartz veins from the Anna gold deposit The field of magmatic water is taken from Taylor (1974). The metamorphic water field combines the values of Taylor (1974) and Sheppard (1981). The meteoric water line is from Epstein et al. (1965, 1970). H and O isotopic composition of local meteoric water and the dashed arrows showing meteoric water/rock exchange are from Hofstra et al. (2005) |
|
|
表 2 安那金矿床石英氢氧同位素组成 Table 2 Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions of inclusion water and quartz from the Anna gold deposit |
可以看出,石英流体包裹体中H2O的δD值变化范围为-79‰~-47‰,与邻近者桑金矿床石英流体包裹体氢同位素变化范围(-75‰~-40‰)和滇东南中生代大气降水的氢同位素组成(-75.0‰)相近(代鸿章等,2014)。石英的δ18O值变化范围为18.6‰~22.4‰,根据Friedman and O’Neil(1977)石英-水氧同位素平衡分馏方程(δ18OQz-δ18OH2O=3.38×106/T2-2.9),计算获得H2O的δ18O值变化范围为8.9‰~12.7‰,明显高于昆明和贵州地区大气降水的氧同位素组成(图 7)。在δD-δ18O图解中,除1个样品点落入岩浆水范围内之外,其余所有样品点均落在变质水范围内或附近(图 7),表明安那金矿床成矿流体主要来源于变质流体,并与围岩发生了不同程度的水-岩交换反应。
以上研究表明,安那金矿床成矿流体为低盐度(0~2% NaCleqv)、中温(233~273℃)、富含CO2的变质流体,与造山型金矿成矿流体特征相似(Ridley and Diamond, 2000),有别于右江盆地以沉积岩为容矿岩石的卡林型金矿相对低温(210℃)、中等盐度(~6% NaCleqv)、低CO2含量的成矿流体特征(Su et al., 2009a)。对安那金矿床蚀变辉绿岩矿石中伊利石的40Ar-39Ar定年表明,该矿床形成于印支期(232±5Ma)(未发表),因此,认为这种变质流体可能与印支期右江盆地南缘越北逆冲推覆造山变质事件有关(Zaw et al., 2014; Tran et al., 2016)。
3.4 金的沉淀富集机制实验研究表明,在中低温( < 250℃)、富H2S的弱酸性热液条件下,Au主要以Au(HS)2-或Au(HS)0的形式迁移(Seward, 1973, 1993),而As则主要以H3AsO3的形式存在(Heinrich and Eadington, 1986;Pokrovski et al., 2002)。Au的沉淀富集一般认为与流体-岩石相互作用、流体混合以及流体不混溶过程等有关(Seward, 1973;Naden and Shepherd, 1989;Groves and Foster, 1991;Nesbitt,1991)。
流体包裹体研究表明,安那金矿床仅发育低盐度(0.3% NaCleqv)、中温(254℃)、富含CO2-H2O流体包裹体,缺乏沸腾流体包裹体组合。成矿流体氢氧同位素组成显示变质流体来源,暗示流体不混溶或流体混合可能不是该类型金矿床金沉淀富集的关键控制因素。热力学计算表明,在中低温( < 250℃)条件下,这种富含CO2的成矿流体具有弱酸性(pH=5.07~5.21)(Hofstra and Cline, 2000)。这种弱酸性的含Au热液可以使赋矿的辉绿岩中的含Ti-Fe辉石或者钛铁矿溶解释放Fe2+,为硫化物的形成和Au的沉淀富集提供了Fe的来源,溶解Fe的硫化作用过程使含Au黄铁矿和毒砂富集在金红石的边缘(图 3d),保留钛铁矿原始晶体形态,并伴随伊利石化、绿泥石化等热液蚀变,如钛铁矿与含Au热液的化学反应:

|
通过对滇东南安那金矿床流体包裹体岩相学、显微测温学以及氢氧同位素地球化学等研究,获得以下认识:
(1)安那金矿床成矿流体具有低盐度(0~2% NaCleqv)、中温(233~273℃)、富含CO2的流体特征,与造山型金矿成矿流体特征相似,其成矿动力学背景可能与右江盆地南缘印支期越北逆冲推覆造山事件有关。
(2)成矿流体氢氧同位素组成显示变质流体成因,结合矿石显微岩相学结构,认为变质流体溶蚀交代辉绿岩中的含Ti-Fe辉石或者钛铁矿,溶解Fe的硫化作用过程是含Au黄铁矿和毒砂沉淀富集的重要机制。
致谢 野外工作得到了富宁华联矿业有限公司的大力协助;耿跃成工程师在制备流体包裹体片过程中给予了大力帮助,秦朝建工程师在流体包裹体激光拉曼测试中给予了热情指导;在此一并表示感谢。| [] | Burruss RC. 1981. Analysis of phase equilibria in C-O-H-S fluid inclusions. In:Hollister LS and Crawford ML (eds.). Short Course Handbook. Canada:Mineralogical Association of Canada, 6:39-74 |
| [] | Chen BJ, Wen CQ, Huo Y, Cao SY, Song FZ , Zhou Y. 2010. Study on fluid inclusion of the Shuiyindong gold deposit, southwestern Guizhou. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry , 29 (1) :45–51. |
| [] | Chen MH, Mao JW, Wu LL , Zheng JM. 2006. A review on the chronology of micro-disseminated gold deposits in Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi triangle area, southwestern China. Journal of Guilin University of Technology , 26 (3) :334–340. |
| [] | Chen MH, Mao JW, Qu WJ, Wu LL, Uttley PJ, Norman T, Zheng JM , Qin YZ. 2007. Re-Os dating of arsenian pyrites from the Lannigou gold deposit, Zhenfeng, Guizhou Province, and its geological significances. Geological Review , 53 (3) :371–382. |
| [] | Chen MH, Mao JW, Chen ZY , Zhang W. 2009. Mineralogy of arsenian pyrites and arsenopyrites of Carlin-type gold deposits in Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi "golden triangle" area, southwestern China. Mineral Deposits , 28 (5) :539–557. |
| [] | Chen MH, Mao JW, Li C, Zhang ZQ , Dang Y. 2015a. Re-Os isochron ages for arsenopyrite from Carlin-like gold deposits in the Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi "golden triangle", southwestern China. Ore Geology Reviews , 64 :316–327. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.07.019 |
| [] | Chen MH, Zhang ZQ, Santosh M, Dang Y , Zhang W. 2015b. The Carlin-type gold deposits of the "golden triangle" of SW China:Pb and S isotopic constraints for the ore genesis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 103 :115–128. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.08.022 |
| [] | Chen XM, Shi JP, Zou RR , Yang SH. 2011. On the genesis and ore guide of Naping Au deposit in Funing. Yunnan Geology , 30 (1) :15–17. |
| [] | Clayton RN , Mayeda TK. 1963. The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxides and silicates for isotopic analysis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta , 27 (1) :43–52. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(63)90071-1 |
| [] | Cun WC, Wang SM , Tu GF. 2011. An analysis of the ore control factor of Anna Au deposit in Funing, Yunnan. Yunnan Geology , 30 (3) :265–268. |
| [] | Dai HZ. 2012. Genetic mineralogy of the Zhesang gold deposit in Funing, Yunnan province. Master Degree Thesis. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology, 1-53 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Dai HZ, Chen CH, Gu XX, Li BH, Dong SY , Cheng WB. 2014. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids from Zhesang gold deposit in Funing County, Yunnan Province. Geoscience , 28 (5) :893–904. |
| [] | Diamond LW. 1992. Stability of CO2 clathrate hydrate+CO2 liquid+CO2 vapour+aqueous KCl-NaCl solutions:Experimental determination and application to salinity estimates of fluid inclusions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta , 56 (1) :273–280. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(92)90132-3 |
| [] | Dong WD, Su WC, Shen NP, Zhu LY , Cai JL. 2013. Mineralogy and geochemistry of gold-bearing sulfides from the Badu Carlin-type gold deposit, Guangxi, China. Acta Mineralogica Sinica , 33 (Suppl.) :431–432. |
| [] | Epstein S, Sharp RP , Gow AJ. 1965. Six-year record of oxygen and hydrogen isotope variations in South Pole firn. Journal of Geophysical Research , 70 (8) :1809–1814. DOI:10.1029/JZ070i008p01809 |
| [] | Epstein S, Sharp RP , Gow AJ. 1970. Antarctic ice sheet:Stable isotope analyses of Byrd station cores and interhemispheric climatic implications. Science , 168 (3939) :1570–1572. DOI:10.1126/science.168.3939.1570 |
| [] | Friedman I and O'Neil JR. 1977. Compilation of stable isotope fractionation factors of geochemical interest. Professional Paper 440-KK. US:U.S. Geological Survey, 1-12 |
| [] | Groves DI and Foster RP. 1991. Archaean lode gold deposits. In:Foster RP (ed.). Gold Metallogeny and Exploration. US:Springer, 63-103 |
| [] | Heinrich CA , Eadington PJ. 1986. Thermodynamic predictions of the hydrothermal chemistry of arsenic, and their significance for the paragenetic sequence of some cassiterite-arsenopyrite-base metal sulfide deposits. Economic Geology , 81 (3) :511–529. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.81.3.511 |
| [] | Hofstra AH , Cline JS. 2000. Characteristics and models for Carlin-type gold deposits. Reviews in Economic Geology , 13 :163–220. |
| [] | Hofstra AH, Emsbo P, Christiansen WD, Theodorakos P, Zhang XC, Hu RZ, Su WC and Fu SH. 2005. Source of ore fluids in Carlin-type gold deposits, China:Implications for genetic models. In:Mao JW and Bierlein FP (eds.). Mineral Deposit Research:Meeting the Global Challenge. Berlin Heidelberg:Springer, 533-536 |
| [] | Hou L, Peng HJ, Ding J, Zhang JR, Zhu SB, Wu SY, Wu Y , Ouyang HG. 2016. Textures and in situ chemical and isotopic analyses of pyrite, Huijiabao trend, Youjiang basin, China:Implications for paragenesis and source of sulfur. Economic Geology , 111 (2) :331–353. DOI:10.2113/econgeo.111.2.331 |
| [] | Hu RZ, Su WC, Bi XW , Li ZQ. 1995. A possible evolution way of ore-forming hydrothermal fluid for the Carlin-type gold deposits in the Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi triangle area. Acta Mineralogica Sinica , 15 (2) :144–149. |
| [] | Hu RZ, Su WC, Bi XW, Tu GZ , Hofstra AH. 2002. Geology and geochemistry of Carlin-type gold deposits in China. Mineralium Deposita , 37 (3-4) :378–392. DOI:10.1007/s00126-001-0242-7 |
| [] | Hu RZ, Peng JT, Ma DS, Su WC, Shi CH, Bi XW , Tu GC. 2007. Epoch of large-scale low-temperature mineralizations in southwestern Yangtze massif. Mineral Deposits , 26 (6) :583–596. |
| [] | Hu RZ , Zhou MF. 2012. Multiple Mesozoic mineralization events in South China:An introduction to the thematic issue. Mineralium Deposita , 47 (6) :579–588. DOI:10.1007/s00126-012-0431-6 |
| [] | Hu RZ, Mao JW, Hua RM , Fan WM.2015. Intra-continental Mineralization of South China Craton. Beijing: Science Press : 1 -903. |
| [] | Jia DC , Hu RZ. 2001. Analysis of genesis of Carlin-type gold deposits in Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi triangle area. Mineral Deposits , 20 (4) :378–384. |
| [] | Jiang GH, Hu RZ , Fang WX. 2000. The primary metallogenic thermal mechanism of Carlin-type gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry , 19 (4) :290–292. |
| [] | Li ZY, Lan TL, Ran RD , Cheng GF. 2012. A new type of micro-disseminated gold deposits in association with diabase found in Yunnan and Guizhou provinces and Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region:Their geological characteristics and metallogenic conditions. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry , 31 (4) :449–456. DOI:10.1007/s11631-012-0596-9 |
| [] | Liu JZ, Xia Y, Zhang XC, Deng YM, Su WC , Tao Y. 2008. Model of strata Karlin-type gold deposit:The Shuiyindong super-scale gold deposit. Gold Science and Technology , 16 (3) :1–5. |
| [] | Luo G. 2010. Study for the Micro-disseminate gold deposit, geological and metallogenic in southeastern Yunnan area. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-83 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Naden J , Shepherd TJ. 1989. Role of methane and carbon dioxide in gold deposition. Nature , 342 (6251) :793–795. DOI:10.1038/342793a0 |
| [] | Nesbitt BE. 1991. Phanerozoic gold deposits in tectonically active continental margins. In:Foster RP (ed.). Gold Metallogeny and Exploration. US:Springer, 104-132 |
| [] | Pan JY, Zhang Q , Shao SX. 1998. A new type of fine disseminated gold deposits found in Northwest Guangxi, China. Gold , 19 (7) :3–5. |
| [] | Pokrovski GS, Kara S , Roux J. 2002. Stability and solubility of arsenopyrite, FeAsS, in crustal fluids. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta , 66 (13) :2361–2378. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00836-0 |
| [] | Qin SY , Yan XD. 2012. Geological mineralization characteristics and genesis study of Badu gold deposit in Tianlin County, Guangxi Province. Guangdong Science & Technology (19) :140–141, 172. |
| [] | Qin WM , He ZM. 2003. Geological features of gold deposits that have relationship with diabase in the northwest of Guangxi:Taking example of the Longchuan gold deposit in Baise. Gold Geology , 9 (3) :49–54. |
| [] | Ridley JR , Diamond LW. 2000. Fluid chemistry of orogenic lode gold deposits and implications for genetic models. Reviews in Economic Geology , 13 :141–162. |
| [] | Seward TM. 1973. Thio complexes of gold and the transport of gold in hydrothermal ore solutions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta , 37 (3) :370–399. |
| [] | Seward TM. 1993. The hydrothermal geochemistry of gold. In:Foster RP (eds.). Gold Metallogeny and Exploration. Netherlands:Springer, 37-62 |
| [] | Shepherd TJ, Rankin AH and Alderton DHM. 1985. A Practical Guide to Fluid Inclusion Studies. Glasgow:Blackie Sons Ltd., 1-293 |
| [] | Sheppard SMF. 1981. Stable isotope geochemistry of fluids. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth , 13-14 :419–445. DOI:10.1016/0079-1946(81)90021-5 |
| [] | Su WC. 2002. The hydrothermal fluid geochemistry of the Carlin-type gold deposits in the southwestern Yangtze Craton, China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Guiyang:Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Su WC, Xia B, Zhang HT, Zhang XC , Hu RZ. 2008. Visible gold in arsenian pyrite at the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China:Implications for the environment and processes of ore formation. Ore Geology Reviews , 33 (3-4) :667–679. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.10.002 |
| [] | Su WC, Heinrich CA, Pettke T, Zhang XC, Hu RZ , Xia B. 2009a. Sediment-hosted gold deposits in Guizhou, China:Products of wall-rock sulfidation by deep crustal fluids. Economic Geology , 104 (1) :73–93. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.104.1.73 |
| [] | Su WC, Hu RZ, Xia B, Xia Y , Liu YP. 2009b. Calcite Sm-Nd isochron age of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China. Chemical Geology , 258 (3-4) :269–274. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.10.030 |
| [] | Su WC, Zhang HT, Hu RZ, Ge X, Xia B, Chen YY , Zhu C. 2012. Mineralogy and geochemistry of gold-bearing arsenian pyrite from the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China:Implications for gold depositional processes. Mineralium Deposita , 47 (6) :653–662. DOI:10.1007/s00126-011-0328-9 |
| [] | Tan QP, Xia Y, Xie ZJ, Yan J , Wei DT. 2015. S, C, O, H, and Pb isotopic studies for the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Southwest Guizhou, China:Constraints for ore genesis. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry , 34 (4) :525–539. DOI:10.1007/s11631-015-0063-5 |
| [] | Taylor HP. 1974. The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition. Economic Geology , 69 (6) :843–883. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.843 |
| [] | Tran TH, Nevolko PA, Ngo TP, Svetlitskaya TV, Vu HL, Redin YO, Tran TA, Pham TD , Ngo TH. 2016. Geology, geochemistry and sulphur isotopes of the Hat Han gold-antimony deposit, NE Vietnam. Ore Geology Reviews , 78 :69–84. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.03.021 |
| [] | Wang GZ, Hu RZ, Su WC , Zhu LM. 2003. Fluid flow and mineralization of Youjiang Basin in the Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi area, China. Science in China (Series D) , 46 (Suppl.1) :99–109. |
| [] | Xia Y, Zhang Y, Su WC, Tao Y, Zhang XC, Liu JZ , Deng YM. 2009. Metallogenic model and prognosis of the Shuiyindong super-large stratabound Carlin-type gold deposit, southwestern Guizhou Province, China. Acta Geologica Sinica , 83 (10) :1473–1482. |
| [] | Xiao L. 1997. A new type of micro-disseminated gold deposit-the geological characteristics an ore-finding signal of micro-disseminated gold deposits exposed in diabase. Geology and Prospecting , 33 (6) :1–6. |
| [] | Zaw K, Meffre S, Lai CK, Burrett C, Santosh M, Graham I, Manaka T, Salam A, Kamvong T , Cromie P. 2014. Tectonics and metallogeny of mainland Southeast Asia:A review and contribution. Gondwana Research , 26 (1) :5–30. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.10.010 |
| [] | Zhang CQ, Wang DH, Wang YL, Wang CH , Qiu XP. 2012. Discuss on the metallogenic model for Gaolong gold deposit in Tianlin County, Guangxi, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 28 (1) :213–224. |
| [] | Zhang HT. 2007. Geochemistry of gold-bearing sulfides and the occurrence of gold at Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China. Master Degree Thesis. Guiyang:Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Zhang XC, Spiro B, Halls C, Stanley CJ , Yang KY. 2003. Sediment-hosted disseminated gold deposits in Southwest Guizhou, PRC:Their geological setting and origin in relation to mineralogical, fluid inclusion, and stable-isotope characteristics. International Geology Review , 45 (5) :407–470. DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.45.5.407 |
| [] | Zhang YM, Gu XX, Bai X, Liu RP, Zheng L, Wu CY , Peng YW. 2013. Sulfur and lead isotopic composition characteristics of the Zhesang gold deposit in Funing County, Yunnan. Earth Science Frontiers , 20 (1) :32–39. |
| [] | Zhou MF, Zhao JH, Qi L, Su WC , Hu RZ. 2006. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and elemental and Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of Permian mafic rocks in the Funing area, SW China. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology , 151 (1) :1–19. DOI:10.1007/s00410-005-0030-y |
| [] | Zhu LM, Jin JF, He MY, Liu XF , Hu RZ. 1997. On the possibility of the participation of juvenile fluids in the gold deposit formation in southwestern Guizhou. Geological Review , 43 (6) :586–592. |
| [] | Zhu LM, He MY, Jin JF , Hu RZ. 1998a. Mechanism of paragenesis and separation for As and Au in the finely-disseminated gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou Province. Geology and Prospecting , 34 (4) :29–33. |
| [] | Zhu LM, Jin JF, He MY, Hu RZ , Liu XF. 1998b. A study of isotopic geochemistry on plutonic material source for the fine-disseminated gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou Province. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology , 28 (1) :37–42. |
| [] | Zhu LM , Hu RZ. 1999. A preliminary study on the mechanisms of paragensis and separation for As and Au in the Zimudang As-bearing fine-disseminated gold deposit in southwestern Guizhou Province. Acta Mineralogica Sinica , 19 (1) :83–89. |
| [] | Zhu LM , Hu RZ. 2000. Au-Sb association and fractionation in micro-disseminated gold deposits, southwestern Guizhou:Geochemistry and thermodynamics. Science in China (Series D) , 43 (2) :208–216. |
| [] | 陈本金, 温春齐, 霍艳, 曹盛远, 宋发治, 周玉.2010. 黔西南水银洞金矿床流体包裹体研究. 矿物岩石地球化学通报 , 29 (1) :45–51. |
| [] | 陈懋弘, 毛景文, 吴六灵, 郑建民.2006. 滇黔桂矿集区微细浸染型金矿成矿年代学研究. 桂林工学院学报 , 26 (3) :334–340. |
| [] | 陈懋弘, 毛景文, 屈文俊, 吴六灵, UttleyPJ, NormanT, 郑建民, 秦运忠.2007. 贵州贞丰烂泥沟卡林型金矿床含砷黄铁矿Re-Os同位素测年及地质意义. 地质论评 , 53 (3) :371–382. |
| [] | 陈懋弘, 毛景文, 陈振宇, 章伟.2009. 滇黔桂"金三角"卡林型金矿含砷黄铁矿和毒砂的矿物学研究. 矿床地质 , 28 (5) :539–557. |
| [] | 陈新敏, 施建萍, 邹蓉蓉, 杨苏焕.2011. 富宁那坪金矿成因及找矿标志. 云南地质 , 30 (1) :15–17. |
| [] | 寸伟才, 王绍明, 涂国府.2011. 云南富宁安那金矿控矿因素分析. 云南地质 , 30 (3) :265–268. |
| [] | 代鸿章. 2012.云南省富宁县者桑金矿床成因矿物学研究.硕士学位论文.成都:成都理工大学, 1-53 |
| [] | 代鸿章, 陈翠华, 顾雪祥, 李保华, 董树义, 程文斌.2014. 云南省富宁县者桑金矿床成矿流体特征. 现代地质 , 28 (5) :893–904. |
| [] | 董文斗, 苏文超, 沈能平, 朱路艳, 蔡佳丽.2013. 广西八渡卡林型金矿床含金硫化物矿物学与地球化学研究. 矿物学报 , 33 (增) :431–432. |
| [] | 胡瑞忠, 苏文超, 毕献武, 李泽琴.1995. 滇黔桂三角区微细浸染型金矿床成矿热液一种可能的演化途径:年代学证据. 矿物学报 , 15 (2) :144–149. |
| [] | 胡瑞忠, 彭建堂, 马东升, 苏文超, 施春华, 毕献武, 涂光炽.2007. 扬子地块西南缘大面积低温成矿时代. 矿床地质 , 26 (6) :583–596. |
| [] | 胡瑞忠, 毛景文, 华仁民, 范蔚茗. 2015. 华南陆块陆内成矿作用. 北京: 科学出版社 : 1 -903. |
| [] | 贾大成, 胡瑞忠.2001. 滇黔桂地区卡林型金矿床成因探讨. 矿床地质 , 20 (4) :378–384. |
| [] | 蒋国豪, 胡瑞忠, 方维萱.2000. 黔西南卡林型金矿成矿热机制初探. 矿物岩石地球化学通报 , 19 (4) :290–292. |
| [] | 刘建中, 夏勇, 张兴春, 邓一明, 苏文超, 陶琰.2008. 层控卡林型金矿床矿床模型——贵州水银洞超大型金矿. 黄金科学技术 , 16 (3) :1–5. |
| [] | 罗刚. 2010.滇东南地区微细粒浸染型金矿床地质特征和成矿规律研究.博士学位论文.北京:中国地质大学, 1-83 |
| [] | 潘家永, 张乾, 邵树勋.1998. 桂西北发现一类新的微细浸染型金矿. 黄金 , 19 (7) :3–5. |
| [] | 覃少耀, 颜小东.2012. 广西田林县八渡金矿地质矿化特征及成因研究. 广东科技 (19) :140–141, 172. |
| [] | 覃文明, 何志美.2003. 桂西北与辉绿岩类岩石有关的金矿地质特征——以百色龙川金矿为例. 黄金地质 , 9 (3) :49–54. |
| [] | 苏文超. 2002.扬子地块西南缘卡林型金矿床成矿流体地球化学研究.博士学位论文.贵阳:中国科学院地球化学研究所 |
| [] | 夏勇, 张瑜, 苏文超, 陶琰, 张兴春, 刘建中, 邓一明.2009. 黔西南水银洞层控超大型卡林型金矿床成矿模式及成矿预测研究. 地质学报 , 83 (10) :1473–1482. |
| [] | 肖龙.1997. 一种新的微细浸染型金矿——产于辉绿岩中的微细浸染型金矿特征及找矿标志. 地质与勘探 , 33 (6) :1–6. |
| [] | 张长青, 王登红, 王永磊, 王成辉, 邱小平.2012. 广西田林县高龙金矿成矿模式探讨. 岩石学报 , 28 (1) :213–224. |
| [] | 张弘弢. 2007.贵州水银洞卡林型金矿床含金硫化物地球化学与金的赋存状态研究.硕士学位论文.贵阳:中国科学院地球化学研究所 |
| [] | 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 摆祥, 刘瑞萍, 郑硌, 吴程赟, 彭义伟.2013. 云南富宁者桑金矿床硫铅同位素地球化学特征与成矿物质来源. 地学前缘 , 20 (1) :32–39. |
| [] | 朱赖民, 金景福, 何明友, 刘显凡, 胡瑞忠.1997. 论深源流体参与黔西南金矿床成矿的可能性. 地质论评 , 43 (6) :586–592. |
| [] | 朱赖民, 何明友, 金景福, 胡瑞忠.1998a. 黔西南微细浸染型金矿床金、砷共生分异机制初步研究. 地质与勘探 , 34 (4) :29–33. |
| [] | 朱赖民, 金景福, 何明友, 胡瑞忠, 刘显凡.1998b. 黔西南微细浸染型金矿床深部物质来源的同位素地球化学研究. 长春科技大学学报 , 28 (1) :37–42. |
| [] | 朱赖民, 胡瑞忠.1999. 紫木凼含砷微细浸染型金矿床金砷成矿过程初步研究. 矿物学报 , 19 (1) :83–89. |
 2016, Vol. 32
2016, Vol. 32


