2. 青岛海洋科学与技术国家实验室海洋地质功能实验室, 青岛 266061 ;
3. 中国地质科学院地质研究所, 北京 100037 ;
4. 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 北京 100029 ;
5. 西北大学地质学系, 西安 710069 ;
6. 中国地质调查局西安地质调查中心, 西安 710054
2. Laboratory for Marine Geology, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao 266061, China ;
3. Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing 100037, China ;
4. Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029, China ;
5. Department of Geology, Northwest University, Xi'an 710069, China ;
6. Xi'an Geological Survey Center, China Geological Survey, Xi'an 710054, China
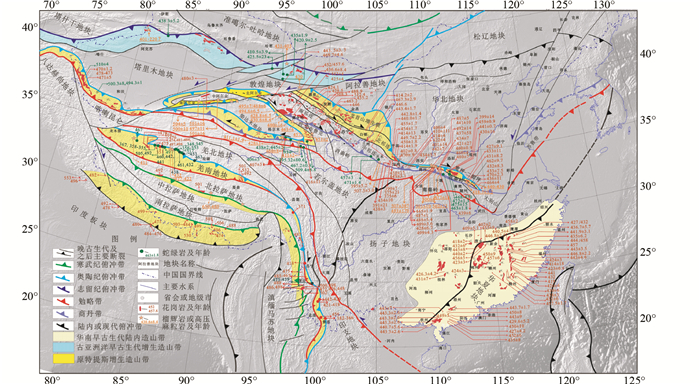
东亚早古生代一系列蛇绿岩带和高压-超高压变质带,如北祁连高压带、柴北缘超高压带、阿尔金超高压带、北秦岭超高压带、龙木措-双湖构造带、西昆仑构造带等(图 1),记录了原特提斯洋内复杂的陆块运动与结构状态。近年的研究已表明,除印支期以外,早古生代也是东亚部分陆块/微陆块间聚合的重要时期,也更为广泛地形成了一系列的蛇绿岩带、高压-超高压带和花岗岩带(图 1)。中国学者在这些构造带的岩石学、地球化学和年代学方面作了大量工作(李兴振等,1990;蔡立国等,1993;潘裕生,1994;陈智梁,1994;潘桂棠等, 1997, 2004;钟大赉,1998;陆松年, 2001;郭福祥,2001;李兴振和尹福光, 2002;肖序常等,2003;Xiao et al., 2003, 2009;高长林等, 2005;Li et al., 2008;李文昌等,2010;Dong et al., 2011a, b; Wang et al., 2011;付长垒等,2014),取得长足进展。但是迄今,关于原特提斯洋南部和北部遗迹界线、俯冲极性和古板块运动学特征均存在巨大争议(向鼎璞, 1982;郑健康, 1992;冯益民等, 1994;夏林圻等, 1996;杨经绥等, 1998, 2000, 2005;葛肖虹和刘俊来, 1999;张雪亭等,1999;李怀坤等,1999;于海峰等,1999;赵凤清等, 2000;张招崇等,2001;陆松年, 2002;王惠初等, 2001, 2005;庄儒新和李峰,2006;张建新等, 2007, 2015; 刘良等,2009;林宜慧等,2010;张贵宾和张立飞,2011),而对这些问题的准确厘定与理解不仅可以丰富原特提斯的研究内容, 而且是Pangea东亚重建的重要基础,同时可为构建Pangea东亚重建新方案和建立Pangea东亚重建动态演化模型提供科学依据。
2 东亚原特提斯洋南、北边界界定针对中国境内主要早古生代构造带,前人的研究主要集中在岩石学、地层学、生物古地理、地球化学和年代学等方面(图 1),但这些研究还没能回答:1)哪条构造带代表原特提斯洋的最北界和最南界?2)东亚原特提斯洋的具体范围如何?这两个问题是重建Pangea超大陆东亚陆块/微陆块早古生代古地理位置的重要基础,也是系统研究“Pangea东亚聚合”的第一个核心科学问题。
|
图 1 原特提斯构造域南、北边界分布(据李三忠等,2016d补充,数据来自大量文献,不一一列举) Fig. 1 Northern and southern border faults of the Proto-Tethyan Tectonic Domain(revised after Li et al., 2016d; Data from many references) |
5年来通过消化国内外已有研究成果(图 1),本文分别针对原特提斯域北部和南部边界,开展了下列深入综合集成研究:
① 原特提斯洋北界主要构造遗迹界线厘定
大多数研究表明,北秦岭构造带是中央造山带东部原特提斯洋已知的最北界,其向西延,过徽成、共和盆地,却出现北祁连、中祁连、柴北缘、昆北、昆中、昆南等有加里东期变形变质记录的构造带,因此确定北秦岭构造带与前述何者衔接是界定中央造山带西段原特提斯北界的关键。
(a)大地构造单元配置分析:确定北秦岭构造带及商丹带向西和北祁连带、中祁连带、柴北缘带的连接关系;厘定各构造带地表地质特征,确定其岩石组合类型,综合厘定其主要界线物质记录和其它对比标志(杨朝等,2015;李涛等,2015;熊莉娟,2014);分析其形成构造环境和构造属性,为大地构造单元厘定、划分、配置研究提供基础。
(b)古俯冲-拼合带深部结构:揭示地壳古俯冲带结构,结合地表野外地质考察,确定原特提斯洋内各微陆块、古老构造带深部结构或残存特征(Sun et al., 2015b),探讨原特提斯洋俯冲板块运动学。
通过对原特提斯洋北界从地表到深层结构的深入研究与确认,从而达到厘定原特提斯洋北界范围,为探讨原特提斯北部陆块/微陆块的多块体拼合动力学机制提供板块边界条件,为探讨原特提斯洋形成演化的动力学模式提供约束,为查明Pangea超大陆聚合前早古生代构造背景奠定基础。
②原特提斯洋南部地质记录
已知原特提斯洋南部广泛经历了加里东期构造变形,但蛇绿岩、相关岛弧型火山岩建造较少报道。本文在全面理解掌握和消化吸收前人资料(钟大赉,1998;许志琴等, 2007, 2013;Zhu et al., 2013; Nie et al., 2015)的基础上,进一步就前人发表的早古生代蛇绿岩出露点或蛇绿岩剖面进行深入甄别工作。由于这些蛇绿岩分布零星,所以主要研究工作侧重加里东期变形和岩石记录的寻找与研究,确定其变形期次、几何学构造样式与运动学特征,探讨其动力学演化。最终试图勾勒出加里东期变形的最南部界线(安慧婷,2014),根据变形南界的确定从而初步约束原特提斯南界。
(a)选择可能的原特提斯洋地质记录,如景洪变质岩带(团梁子岩组)和华南加里东期岩浆岩分布,进行系统的同位素年代学、岩石学、岩石地球化学集成分析,进一步寻找原特提斯洋南部地质记录,结合岩石年龄和构造拓展的空间分布规律,探讨原特提斯洋南部地质演化和块体拼合历史;
(b)针对出露于八布构造带的蛇绿岩(钟大赉,1998),开展岩石学、精细的锆石U-Pb或全岩Ar-Ar定年以及元素Sr-Nd-Pb同位素组成研究,并进行区域追踪,明确其延展;
(c)在昌都加里东造山带开展早古生代碎屑岩碎屑锆石LA-ICP-MS年代学和沉积岩元素-同位素地球化学研究,开展物源示踪;尽可能对越南马江一带蛇绿岩和高压蓝片岩(钟大赉,1998)及相关花岗岩,开展SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学研究;
(d)通过原特提斯域南部深部结构探测,揭示地壳古俯冲带结构,探讨原特提斯洋可能的南界深部构造特征,探讨原特提斯洋南部的构造属性。
但遗憾的是因种种原因,后三部分没能实现,今后将加强研究。有幸的是,近来相关工作不断报道(Zhu et al., 2013; Nie et al., 2015),为甄别和确定原特提斯南界提供了线索。
2.1 原特提斯北部边界前人研究笼统地指出,原特提斯洋的北界应该在华北-塔里木陆块以南(李兴振等,1990;陈智梁,1994;潘桂棠等,1997;陆松年, 2001;郭福祥,2001;Xiao et al., 2003, 2009;von Raumer and Stampfli, 2008;李文昌等,2010)。最近,Liu et al. (2015)依据Th/U比值,揭示出特提斯地幔域(高Th/U比)与古亚洲洋地幔域(低Th/U比)之间的界限在华北-塔里木地块北缘。然而,对于前一观点,该界限是固定的一条构造带还是不同时期变迁的构造带?具体是哪条构造带或断裂?都没有详细证明和结论。通常认为,华北-塔里木陆块以南的扬子陆块、柴达木、中祁连等微陆块是在新元古代-早古生代早期从冈瓦纳大陆北缘裂离出来的,这些陆块/微陆块之间以多岛洋分割,分散在大洋中间(高长林等, 2005;Li et al., 2008),在早古生代末可能经历了陆块/微陆块两两之间的复杂俯冲与拼合过程,并伴随多条复杂的蛇绿岩带和高压-超高压变质带的形成,如北秦岭构造带(Dong et al., 2011a, b; Wang et al., 2011)、北祁连构造带(向鼎璞, 1982;郑健康, 1992;冯益民等, 1994;许志琴等,1994;夏林圻等, 1996;葛肖虹和刘俊来, 1999;张招崇等,2001;林宜慧等,2010)、柴北缘构造带(杨经绥等, 1998, 2000;张雪亭等,1999;李怀坤等,1999;陆松年, 2002;于海峰等, 1999;赵凤清等, 2000;王惠初等, 2001, 2005;庄儒新和李峰,2006;张贵宾和张立飞,2011)、阿尔金构造带(杨经绥等,2005;张建新等,2007;刘良等,2009)等。这些蛇绿岩带和高压-超高压变质带记录了地壳物质从俯冲到构造折返的一个完整的动力学过程,是研究早古生代末陆块/微陆块拼贴及原特提斯北部边界的重要载体(张旗和周国庆, 2001)。
30多年来,前人对这些构造带开展了大量的研究,并取得了丰富的成果。但是,目前有关北秦岭构造带的西延问题仍存在多种观点,如:1)通过宝鸡-天水断裂向北和北祁连衔接(肖序常等,1978;向鼎璞,1982;张建新和许志琴,1995;冯益民等,1994;宋忠宝等,2005;林宜慧等,2010);2)通过拉脊山-青海湖-武山-宝鸡-天水断裂与中祁连相连(杨钊等,2006;董云鹏等,2007);3)与柴北缘对接(杨经绥等, 1998, 2003;许志琴等,2003;Xu et al., 2006; 张贵宾等,2005;王惠初等,2005; 张建新等,2007;刘良等,2009;宋述光等,2011;王宗起等, 2009;闫臻等,2012);4)过共和盆地与东昆仑中带对接,而昆中断裂与商丹带相连(Ren and Xie, 1991;许效松等,1996;任纪舜等,2000; 陈能松等,2008)。北秦岭构造带究竟与上述哪条构造带相连是解决早古生代洋-陆基本格局的关键。此外,这些带继续西延与阿尔金和西昆仑的交接关系存在同样争论(肖序常等, 1986; 郑健康, 1992)。澄清这些问题也是认识Pangea超大陆最终聚合位置和过程的重要基础。
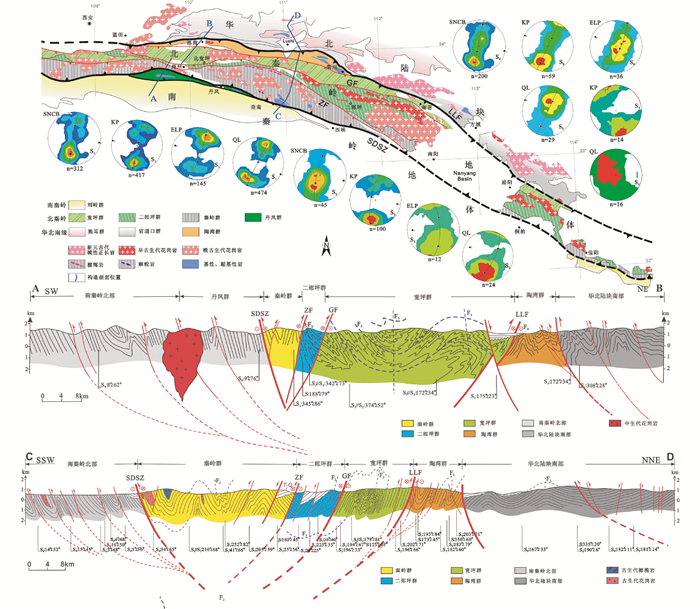
根据碎屑锆石(与其它类型锆石一同可视为地质基因(geo-gene))年龄谱(可视作地质DNA)对比(Cao et al., 2016),可以发现宽坪群碎屑岩和北祁连下古生界物源没有华北组成。由此可见,宽坪洋、北祁连洋、北阿尔金洋是个分割性的洋盆,自然也是沉积盆地物源区的分界。因而,原特提斯洋北界应当是宽坪群北界,但不是中生代洛南-栾川断裂带,而是我们称为古洛南-栾川断裂带及其西段对应的构造带(图 2;Zhao et al., 2015;李三忠等,2016b)。虽然前人研究认为,商丹洋是原特提斯洋主大洋(张国伟等,2001),最近Liu et al. (2016)提出500Ma左右变质的北秦岭榴辉岩是商丹大洋俯冲期间南秦岭微陆块中原岩年龄为800Ma左右的岩石卷入深俯冲的结果。这也与北秦岭作为商丹洋俯冲的上部板片难以发生深俯冲是一致的;而且这些观点还认为宽坪群和二郎坪群都代表其弧后盆地(Dong et al., 2011a, b; Liu et al., 2016),且南祁连下古生界与南秦岭具有可比性,因此,商丹带向西延应当对应中祁连地块南缘断裂,是一条重要分划性构造带(杨钊等,2006;董云鹏等,2007);但是本文认为商丹带也可能对应南祁连南部边界,因为南祁连下古生界主要是寒武系、奥陶系岛弧火山岩及相关蛇绿岩构成,志留系出露很少,主要是一套活动型浅海相-陆相沉积组合,与南秦岭还不一样,因此,在此段可能存在商丹俯冲带向南的跃迁,导致商丹带现今向西的分叉现象。昆中断裂带难以与商丹带直接相连,因为两者之间的西秦岭上千千米没有任何洋壳残存记录。昆中断裂带实际被后期瓦洪山断裂错移,应当与中祁连南缘断裂的西段、或者与武山断裂-青海南山断裂、或者与北宗务隆山断裂、南祁连山山前断裂衔接,这样便解决了商丹带西延的问题,但商丹洋是不是原特提斯洋主大洋还值得商榷。刘国惠等(1993)最早根据北秦岭变质岩群岩石学、岩石地球化学和年代学详细研究认为,新元古代时期北秦岭微陆块已经增生成为华北陆块南缘组成;Dong et al.(2011a, b)提出方城一带北西西向展布的碱性花岗岩(图 2)是北秦岭和华北南缘在844Ma左右(包志伟等,2008)拼合标志,进一步支持了刘国惠等(1993)的观点。但是,980~726Ma的新元古代岩体主要分布在宽坪群南侧(Dong et al., 2014)、北侧(包志伟等, 2008)两条构造带中,北带方城碱性正长岩形成年龄为844Ma左右(包志伟等,2008),包志伟等(2008)认为该碱性正长岩是北秦岭主体与Rodinia主体在890Ma拼合后转入伸展-裂解背景下就位的。实际上,这些碱性岩全部位于古洛南-栾川断裂带以北,并侵入到官道口群之中,而官道口群现被归属为华北陆块南缘(Wu et al., 2008;Liu et al., 2013),因而这些碱性岩不应当属于北秦岭构造带。南带新元古代岩体主要年代介于980~728Ma之间(图 3;陆松年等,2003; Dong et al., 2014),且空间上严格约束在北秦岭-中祁连微陆块中,即宽坪群-二郎坪群以南、商丹带以北,属S型同碰撞造山花岗岩(陆松年等,2003),这显然不同于华北南缘碱性岩和阿拉善伸展型A型花岗岩(耿元生和周喜文,2010)。特别是,介于这两条新元古代花岗岩带之间的宽坪群中没有任何新元古代花岗岩分布(图 2、图 3),因此,北侧碱性岩带和南侧花岗岩带都不应当是宽坪洋消亡导致北秦岭与华北南缘(Dong et al., 2014)或扬子北缘(包志伟等,2008)在新元古代早期碰撞拼合后转入伸展环境的标志。现今大量新的同位素年代学资料(Liu et al., 2013; Zhao et al., 2015)揭示,北秦岭新元古代原岩经历的主要变质事件是加里东期,也否定了新元古代变质事件(刘国惠等,1993)的广泛性。
|
图 2 北秦岭构造带单元划分和不同时代岩体分布(据Zhao et al., 2015) 新元古代碱性正长岩皆位于古洛南-栾川断裂以北,侵入华北南缘的官道口群,剖面揭示原特提斯洋早古生代的向南俯冲极性 Fig. 2 Tectonic units and pluton distribution with different ages of the North Qinling Belt (after Zhao et al., 2015) Neoproterozoic alkaline synites emplaced into the Guandaokou Group north of Paleo-Luonan-Luanchuan Fault. Structural profiles reveal the southward subduction polarity of the Proto-Tethyan Ocean |

|
图 3 北秦岭新元古代花岗岩及构造地层单元分布(据Dong et al., 2014) 9 80~720Ma的新元古代侵入岩不越过北秦岭-中祁连地块北界(年龄统计见Dong et al., 2014) Fig. 3 Simplified map with the principal tectonostratigraphic units within the North Qinling Belt showing the distribution of the Kuanping mélange, Paleozoic mélange of the Shangdan Suture and Erlangping Basin, as well as the Neoproterozoic plutons and their published ages (after Dong et al., 2014) 9 80~720Ma of Neoproterozoic plutons (ages seen in Dong et al., 2014) are not across the north margin of the Central Qilian-North Qinling Terrane |
前人基于北秦岭与华北南缘新元古代拼合的认识,提出了宽坪群和二郎坪群都是弧后盆地。高山(1989)根据地球化学物源示踪,提出宽坪群碎屑岩具有双向物源特征,并明确其分别为华北南缘太华群和北秦岭两个物源,这一认识似乎进一步证明了宽坪群碎屑岩代表宽坪洋消亡(或之后再打开)的一个弧后盆地。宽坪群由基性岩和碎屑岩两部分组成。其中主体基性岩形成时代为1400~1000Ma(张寿广等,1991;陆松年等,2003),但最新年代学揭示还存在611Ma(闫全人等,2008)基性岩,同时宽坪群碎屑岩中还存在540Ma左右的碎屑锆石(第五春荣等,2013),因而590Ma左右开始启动的商丹洋俯冲(Liu et al., 2004, 2013; Dong et al., 2012)不可能产生比商丹洋俯冲时间还早的宽坪弧后盆地,最多也只能导致较晚的二郎坪弧后盆地;特别是宽坪群碎屑岩中碎屑锆石年龄谱与扬子完全一样(Liu et al., 2004; Yu et al., 2015; Cao et al., 2016),这样就可能否定了宽坪群碎屑岩双向物源成因的认识,即所谓的华北太华群物源区可能不对,而是可能两种成因:1)来自崆岭群等扬子克拉通或冈瓦纳大陆某处而不是华北的太华群;2)华北属性的一些岩片后期卷入北秦岭构造带变形。
根据北秦岭-中祁连带状分布的早古生代花岗岩(图 1、图 3),可以判断早古生代宽坪洋是向南俯冲到中阿尔金-中祁连-北秦岭微陆块之下,或朝柴达木微陆块外侧的欧龙布鲁克(达肯达坂群)和昆中(金水口群)微陆块之下俯冲,宽坪洋-北祁连洋-北阿尔金洋南侧是活动大陆边缘,而北侧华北陆块南缘、塔里木陆块西南缘、柴达木微陆块内南北侧残存的下古生界都为显著的被动陆缘沉积建造。此外,从北秦岭,到陇西地区通关河东侧、中祁连还发育有低压相系变质作用(肖思云等,1988),从祁连地区的分析结果(张建新等,2015)来看,一些低压变质发生时代可能也是加里东期;而同期北祁连蓝片岩、榴辉岩等高压-超高压变质(张建新等,2015)和北秦岭中压变质相系主要分布在这条低压变质相系北侧(肖思云等,1988)。这些双变质带特征的岩石学标志也进一步指示宽坪洋向南的俯冲极性。对泥盆系不整合之下的第一幕构造解析以及北祁连志留-泥盆系沉积盆地原型恢复也表明,宽坪洋-北祁连洋皆向南俯冲(Yan et al., 2007, 2010; Xiao et al., 2009; Zhao et al., 2015; Sun et al., 2015b; Yuan and Yang, 2015);而且向西延伸,在北祁连门源(张建新等,2015)、柴北缘乌兰都发现双变质带(李秀财等,2015),再到西昆仑,构造解析也揭示早古生代是向南俯冲(Mattern and Schneider, 2000; 曹颖等,2016)。
迄今,多数人认可秦岭从北向南存在宽坪、商丹和勉略三条缝合带(Dong et al., 2014),且都认可勉略洋是晚古生代打开的洋盆,石炭纪启动俯冲,印支期闭合(Meng and Zhang, 1999)。现在存在问题的焦点是:原特提斯洋主洋盆是宽坪洋还是商丹洋,也就是原特提斯洋北界是二者中的何者,这必然涉及何者代表原特提斯洋封闭的问题。商丹带南侧分布有泥盆纪刘岭群,是一套以细碎屑岩为主夹少量碳酸盐岩、石英砂岩和(变质)火山碎屑岩组合的滨-浅海和三角洲相沉积,沉积物源来自于其北侧(杜定汉,1986;Yan et al., 2006, 2012;闫臻等,2007);吴涛等(2014)认为主要是浅海-滨海相沉积,古流向一致指示向北,基本受南侧南秦岭被动陆缘控制;Dong et al. (2014)等认为是深水复理石建造,并根据碎屑锆石认为其物源来自其南、北两侧,且南侧扬子板块是其重要的物源区之一。向西对比,对应天水以南分布的泥盆纪大草滩群,则相变为紫红色间夹杂色砂砾岩、粗砂岩、砂岩和页岩等,不整合在李子园群之上(霍福臣和李永军,1995;闫臻等,2002);再往祁连、祁漫塔格等地,泥盆系直接角度不整合在下伏地层之上,以巨厚的河流相砾岩、粗砂岩沉积为特征,标志海相沉积历史结束,被认为是造山末期的磨拉石建造(黄第藩,1966;金松桥等,1985;杜远生等, 2004)或者古岛弧隆升剥蚀沉积于其弧前盆地产物(Yan et al., 2007; Xiao et al., 2009;Yuan and Yang, 2015);东部的泥盆系被认为是古生代连续增生的沉积增生楔一部分(Ratschbacher et al., 2003; Yan et al., 2012; 陈龙耀等,2014)。这可能意味着“商丹带”西段(祁连段)加里东期曾经闭合,且后期可能再裂解,但没打开出现新的晚古生代大洋;而东段在整个古生代期间尽管有间断和角度不整合,但是个逐步关闭过程,特别是南秦岭没有任何加里东期变形记录,直到中三叠世南秦岭才卷入强烈变形,因此,商丹洋可能是原特提斯洋或古亚洲洋在东段的延续存在(图 4)。相反,宽坪洋、北祁连洋、北阿尔金洋及可比的洋盆此时则已经关闭,二郎坪群被早古生代花岗岩侵入(图 2),而且晚古生代花岗岩不仅侵入北秦岭、宽坪群,而且侵入到华北南缘,这不仅表明这个洋盆在早古生代闭合,而且表明这个洋盆在早古生代是向南俯冲的,而商丹洋晚古生代期间是向北俯冲的,且影响到华北南缘。

|
图 4 大华南陆块在早古生代450~400Ma全球构造格架最可能的状态(据李三忠等,2016c修改) ARA-阿拉瓦利-德里; CIT-印度中央地体; EDC-达瓦尔东部克拉通; EGG-高止东部麻粒岩; END-恩德比地; IC-印支地块; JL-胶-辽-吉带; KIM-金伯利; M-马来西亚半岛(西); MB-麦克阿瑟盆地; NEIT-印度东北地块; PH-普吉岛, 泰国南部; SAT-萨特布拉; SIBU-滇缅马苏地块; T-达鲁岛, 泰国南部; TNC-华北中部带; WDC-达瓦尔西部克拉通; WNC-华北西部地块; XI-熊耳 Fig. 4 The most possible state of the Greater South China Block under Early Paleozoic (450~400Ma) global tectonic framework (revised after Li et al., 2016c) ARA-Aravalli-Delhi; CIT-Central Indian Terrane; EDC-Eastern Dhawar Craton; EGG-Eastern Ghats Granulite; END-Enderby Land; IC-Indochina; JL-Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt; KIM-Kimberley; M-Peninsular Malaysia (west); MB-McArthur Basin; NEIT-North East India Terrane; PH-Phuket Island, southern Thailand; SAT-Satpura; SIBU-Sibumasu Terrane; T-Tarutao Island, southern Thailand; TNC-Trans-North China Craton Orogen; WDC-Western Dharwar Craton; WNC-Western North China; XI-Xionger |
早古生代期间,华北和华南是不是南、北向并置关系值得讨论。如果泥盆纪之前原特提斯洋是介于华北与华南陆块之间的一个大洋,那么加里东期华北、华南陆块南北向拼合期间,为什么现今南秦岭乃至华北东部没有保留任何加里东期变形和变质作用?因此,我们提出早-中泥盆世华北、华南陆块空间关系为东、西向“串联”关系,而非南、北向“并联”关系,武关岩群、刘岭群、大草滩群实际是晚泥盆世华北-北秦岭-中祁连-中阿尔金-柴达木-塔里木与冈瓦纳北缘拼合后,晚期裂离或向东平移而一同移置到南秦岭北部,与南部早-中泥盆世的舒家坝群等属于南秦岭被动陆缘的沉积建造大不相同(闫臻等, 2009, 2012),与刘岭群等相关沉积体之间也为断裂分割,且沿该断裂还分布有一系列基性-超基性岩块(郭现轻等,2014; Sun et al., 2015a),可能为增生到增生楔中的海山等建造。据此,不排除晚泥盆世华北板块向东北漂移,使得华北、华南转变为南、北关系。这在Kroner et al. (2016)的370Ma全球板块重建中也得到了体现。
2.2 原特提斯南部边界近20年来,原特提斯洋地质记录在我国青藏高原及邻区也被零星揭示(图 5),但迄今对原特提斯南界却存在模糊认识和巨大争论(李兴振等,1990;蔡立国等,1993;潘裕生,1994;钟大赉,1998;李兴振和尹福光, 2002;肖序常等,2003;潘桂棠等,2004)。目前对原特提斯洋的南界认识有4种观点:1) 沿金沙江-澜沧江-哀牢山-马江一带为古生代连续洋盆(李兴振等,1990),扬子陆块与昌都-普洱-印支陆块发育连续的早古生代加里东期褶皱带-中生代早期增生造山带,表明原特提斯洋与古特提斯洋为连续过渡关系; 2) 昌宁-孟连缝合线可能代表原特提斯洋南部的消减俯冲带(越南马江蛇绿岩等;钟大赉,1998); 3) 位于保山(-羌北)微陆块以北,但没有明确界线,且原特提斯洋盆在晚古生代并没有完全消亡,与古特提斯洋为连续被动陆缘性质过渡(徐旭辉等,2009); 4) 班公湖-怒江缝合线(蔡立国等,1993;潘桂棠等,2004)不是原特提斯洋封闭的产物,近年获得该缝合带中蛇绿岩相关岩石锆石U-Pb年龄集中在221~132Ma之间(曲晓明等, 2009, 2010; 樊帅权等, 2010; 孙立新等, 2011),证明该洋开启较晚,多数学者对该缝合线几无疑惑。总之,大多数人认为原特提斯洋南部为被动陆缘,并与古特提斯洋为连续过渡关系(高长林等,2005;徐旭辉等, 2009)。
近5年来一批更为可靠的岩石学、地球化学资料研究(Zhu et al., 2013)揭示,原特提斯南界在青藏地区并非上述四条缝合带中的任何一条,金沙江-澜沧江-哀牢山-马江一带并非为古生代连续洋盆,其打开较晚,是印支期缝合线, 甚至发育榴辉岩(Zhang et al., 1993)。大量新的蛇绿岩、早古生代花岗岩、高压变质岩分布和年代学资料表明,原特提斯南北两侧也不都是被动陆缘,羌南地块处于活动陆缘(Zhu et al., 2013),因此,原特提斯南界应是位于羌北地块与羌南地块之间,即龙木措-双湖缝合线(Zhu et al., 2013;李才等,2007;Fan et al., 2015),向南延伸可能与昌宁-孟连缝合线相连(Nie et al., 2015; 图 5),整体构成一条安第斯型活动大陆边缘(Zhu et al., 2013)。但是Zhu et al. (2013)将拉萨地块作为南羌塘地块东延部分,因而,其如何与昌宁-孟连缝合线相连又出现问题。无论如何,从龙木措-双湖-昌宁-孟连这一线,都缺乏400~380Ma洋壳、岛弧等地质记录(图 1),这一事实可能表明原特提斯洋沿该带400Ma之前已经封闭,也就是说大华南板块(含扬子、华夏、羌北、若尔盖、布列亚-佳木斯等;李三忠等,2016c)拼合到冈瓦纳北缘,直到380Ma后才重新沿该带打开,形成古特提斯洋;同期,北侧勉略洋也打开,随后才可见367Ma(三岔四方坝)、340Ma左右(德尔尼)、283Ma(略阳庄科)的岛弧型火山岩等记录,其北侧广泛出露印支期220~206Ma的姜家坪、迷坝、张家坝等多类花岗岩(张国伟等,2015),指示印支期向北俯冲关闭。因而,该带也不是前人认为的沿该带原特提斯洋和古特提斯洋是连续俯冲或连续被动陆缘。

|
图 5 可能的原特提斯域南界与古特提斯域龙木措-双湖-昌宁-孟连缝合线重合(年龄统计和底图据Xu et al., 2015) 地块或地体: NCB-华北陆块; SCB-华南陆块; TRMB-塔里木陆块; IDB-印度陆块; WQL-西秦岭地体; EKL-东昆仑地体;QDM-柴达木地体;QL-祁连地体; ALT-阿尔金地体; WKL-西昆仑地体; SPGZ-松潘-甘孜地体; NQT-QD-SM-IC-北羌塘-羌多-思茅-印支地体; SQT-BS-SBM-南羌塘-保山-滇缅马苏地体; NLS-北拉萨地体; SLS-南拉萨地体; TC-腾冲地体; TSH-甜水海地体; WB-西缅地体;HM-喜马拉雅地体. 缝合线: SDS-商丹缝合线; KZS-昆中缝合线; MLS-勉略缝合线; EKL-ANMQS-东昆仑-阿尼玛卿缝合线; WKLS-西昆仑缝合线; LTS-理塘缝合线; JSJS-ALS-SMS-金沙江-哀牢山-马江缝合线; LSS-CMS-INS-BRS-龙木措-双湖-昌宁-孟连-Inthanon-缅甸缝合线; JHS-NUS-SKS-景湖- Nan Uttaradit-Sra Kaeo缝合线; BNS-班公湖-怒江缝合线; SQH-JLS-狮泉河-嘉黎缝合线; SDS-松多缝合线; ITS-印度斯-藏布缝合线. 岛弧型地体:BHDA-Bulhanbuda岛弧地体; YD-义敦岛弧地体; LC-ST-CBA-临沧-Sukhothai-Chanthaburi岛弧地体; KA- Kohistan岛弧地体; LA- Ladakh岛弧地体.断裂:ALTF-阿尔金断裂; NQLT-北祁连逆冲断裂; LMST-龙门山逆冲断裂; RRF-红河断裂; KKF-喀喇昆仑断裂; MFT-主前缘断裂; SGF-实皆断裂; GLGF-高黎贡断裂 Fig. 5 Possible southern margin of the Proto-Tethyan Tectonic Domain overlapped by the Longmu Tso Shuanghu-Changning Menglian Suture of the Paleo-Tethyan Tectonic Domain (ages and base map from Xu et al., 2015) Blocks and terranes: NCB-North China Block; SCB-South China Block; TRMB-Tarim Block; IDB-India Block; WQL-West Qinling terrane; EKL-East Kunlun terrane; QDM-Qaidam terrane; QL-Qilian terrane; ALT-Altyn terrane; WKL-West Kunlun terrane; SPGZ-Songpan-Ganze terrane; NQT-QD-SM-IC-North Qiangtang-Qamdo-Simao-Indochina terrane; SQT-BS-SB-South Qiangtang-Baoshan-Sibumasu terrane; NLS-North Lhasa terrane; SLS-South Lhasa terrane; TC-Tengchong terrane; TSH-Tianshuihai terrane; WB-West Burma terrane; HM-Himalaya terrane. Suture zones: SDS-Shangdan Suture; KZS-Kunzhong Suture; MLS-Mianlue Suture; EKL-ANMQS-East Kunlun-A’nyemaqen Suture; WKLS-West Kunlun Suture; LTS-Litang Suture; JSJS-ALS-SMS-Jinshajiang-Ailaoshan-Song Ma Suture; LSS-CMS-INS-BRS-Longmu Tso Shuanghu-Changning Menglian-Inthanon-Burma Suture; JHS-NUS-SKS-Jinghong-Nan Uttaradit-Sra Kaeo Suture; BNS-Bangonghu-Nujiang Suture; SQH-JLS-Siquanhe-Jiali Suture; SUDS-Sumdo Suture; ITS-Indus-Tsangbo Suture. Arc terranes: BHDA-Bulhanbuda Arc terrane; YD-Yidun Arc terrane; LC-ST-CBA-Lincang-Sukhothai-Chanthaburi Arc terrane; KA-Kohistan Arc terrane; LA-Ladakh arc terrane. Faults: ALTF-Altyn Tagh Fault; NQLT-North Qilian Thrust; LMST-Longmenshan Thrust; RRF-Red River Fault; KKF-Karakurum Fault; MFT-Main Frontal Thrust; SGF-Sagaing Fault; GLGF-Gaoligong Fault |
在原特提斯洋南、北边界之间,间杂着较多的早古生代陆块/微陆块及诸类型的洋-陆边界。其遗迹除上述主要构造带以外,还有西昆仑构造带内的早古生代各种地质记录(汪玉珍和方锡廉,1987;潘裕生,1989;Yao and Hsü,1994;李永安等,1995;李兴振等,1995;王元龙等,1995;邓万明,1995;丁道桂,1996;李继亮等,1999;姜耀辉等,1999; 袁超等,2000;Xu et al., 2005; 王炬川等,2006;崔建堂等,2006;Xiao et al., 2009; Sun et al., 2011)、东昆仑构造带内(昆北、昆中和昆南)早古生代各种地质记录(郑健康, 1992; 徐强, 1996; 赖绍聪, 1997; 陈亮等, 2000; 张国伟等, 2001; 边千韬等, 2001;陈隽璐等,2002;阿成业等, 2003; 范丽琨等, 2009; 冯建赟, 2010; 孙雨, 2010)、华夏和扬子陆块间加里东期陆内造山带(刘宝珺等, 1990; 舒良树等,2008;Shu et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2010)等。现今研究揭示,西昆仑构造带内早古生代蛇绿岩为原特提斯洋向南俯冲产物(Marten and Schneider, 2000);东昆仑构造带内早古生代蛇绿岩年代学研究表明昆中洋盆在400Ma左右已经闭合,从而导致广泛发育400Ma左右变质作用(张建新等,2007),并随后转入伸展阶段(刘彬等,2012)。其南侧出现一系列类似刘岭群的建造,直到380 Ma之后再次沿昆南-阿尼玛卿-勉略构造带打开,并且石炭-二叠纪才出现洋壳,而华南陆内造山带是大华南陆块与冈瓦纳大陆拼合导致的远程效应(李三忠等,2016c)。同时,Yao and Li (2016)称该造山带为武夷-云开造山带,是奥陶纪-早志留世期间华南与冈瓦纳北缘的印度之间发生剪刀式拼合的结果。
总之,通过对原特提斯构造域南界从地表到深层结构的深入研究与确认,结合北部边界的厘定,可实现厘定原特提斯洋范围,以为探讨介于南、北边界之间的陆块/微陆块的拼合动力学机制提供板块边界条件,并为探讨原特提斯洋整体形成演化动力学模式提供约束,同时为查明Pangea超大陆聚合前的早古生代构造背景奠定基础。
3 原特提斯洋内涵前人研究表明,原特提斯洋是一个东西向古大洋,地质记录主要分布于东亚地区,因而迄今还没有形成全球概念的原特提斯洋,对于原特提斯洋的认识始终非常模糊。在Scotese全球重建方案中没有原特提斯洋的概念(Scotese, 2004),而是将古生代大洋统称为古特提斯洋,并将其与西段的亚匹特斯(Iapetus)洋相连。部分学者的全球重建方案虽然体现了原特提斯洋,但仍将亚匹特斯洋与原特提斯洋相连(von Raumer and Stampfli, 2008)。
尽管国内大多数学者认为原特提斯洋形成于震旦纪-早古生代,但对中国境内原特提斯洋的空间界定仍存在不同观点:1) 原特提斯洋由北部古中亚洋或古亚洲洋(天山-蒙古-兴安主洋盆)、中部秦-祁-昆洋和南部有深水沉积记录的未定名大洋(以滇西和桂西地区为代表)组成(Ren and Xie, 1991; 钟大赉, 1998;陆松年, 2001;郭福祥,2001)。其中古中亚洋被认为是Rodinia超大陆裂解过程产生的原特提斯主洋盆(陆松年, 2001;von Raumer and Stampfli, 2008);2) 原特提斯洋由北部具复杂多岛洋特征的古中国洋(商丹洋为其东部分支)和南部相对干净的主大洋“原特提斯洋”共同构成(高长林等,2005;徐旭辉等, 2009);3)原特提斯洋是一个位于华北-塔里木陆块以南、滇缅泰/保山地块以北的复杂大洋(李兴振等,1990;Xiao et al., 2003, 2009)。其中,第三种观点中还存在不同看法,如有人认为原特提斯洋只是指秦-祁-昆洋以南的大洋(高长林等,2005;徐旭辉等, 2009);也有人将泛华夏陆块群西南侧及其内部所有早古生代洋盆统称为原特提斯洋(陈智梁,1994;潘桂棠等,1997;许效松等,2004;李文昌等,2010)。迄今,如此众多的原特提斯洋认识必然限制对Pangea东亚聚合前早古生代构造背景理解,急需深化研究。
本文综合近10年来的研究成果发现,Rodinia裂解过程中,华北陆块可能于844Ma后(包志伟等, 2008)、阿拉善微陆块可能于950Ma后(耿元生和周喜文,2010)先裂离Rodinia超大陆或冈瓦纳大陆。随后,塔里木-柴达木、阿拉善-敦煌微陆块裂离冈瓦纳大陆北缘,向北漂移,并与从西伯利亚陆块裂离并向南迁移的华北陆块于晚奥陶世-早泥盆世之间或中奥陶世对接(李锦轶等,2012;Xu et al., 2015),形成西方学者称谓的亚洲匈奴地体群(von Raumer and Stampfli, 2008)。至此,这个地体群南部形成的小洋盆称作原特提斯洋,北部才是传统称为的古亚洲洋。由此可见,原特提斯洋应当起源于新元古代Rodinia裂解,其洋壳组成可能复杂,中国境内可分为东、西两段,东段包括一部分我们称为原亚洲洋(Proto-Asian Ocean,前人称作古中亚洋)洋壳,可能始于新元古代以前;西段才是新元古代-早古生代新形成的洋壳,并可能与欧洲亚匹特斯洋和后来的瑞克洋(Rheic)相通。随后,该洋自奥陶纪开始闭合,最终使得统一的塔里木-柴达木-敦煌-阿拉善-华北陆块群最终于400Ma前拼合于冈瓦纳北缘(李三忠等, 2016a, b, c, d)。380Ma之后,沿原特提斯南界重新打开,出现古特提斯洋。因而,南部原特提斯洋与古特提斯洋不具有连续性。
为此,本文基于前人认识和前述最新进展(李三忠等, 2016a, b, c, d)界定原特提斯洋为“起始于新元古代,闭合于早古生代末期,位于塔里木-华北陆块以南,滇缅马苏/保山微陆块以北,与Rodinia超大陆的裂解密切相关的一个古洋盆”。特别强调的是,它不是前人认为的大洋(李兴振等,1990;陈智梁,1994;潘桂棠等,1997;陆松年, 2001;郭福祥,2001;Xiao et al., 2003, 2009;von Raumer and Stampfli, 2008;李文昌等,2010),而是一个小洋盆。这个洋盆的开启、闭合及随后相关陆块/微陆块拼贴,导致了东亚乃至全球洋-陆格局的巨大转换(李文昌等,2010),这正是Pangea超大陆形成过程的一个重要环节。
4 俯冲极性前人研究表明,原特提斯洋可能存在复杂的俯冲极性。判断古大洋板块消减极性一直是造山带研究中一个难以解决的问题,甚至产生矛盾认识。这是由于可靠构造运动学证据缺乏、洋壳残片属性难于区分、缝合带两侧古陆块和增生体亲缘性难以判断、大地构造单元乱序配置等因素,导致有关洋壳俯冲极性的认识还存在分歧。这些研究差异或缺失严重阻碍了对早古生代陆块/微陆块聚合方式与过程的认识,乃至影响整个原特提斯洋演化认识和Pangea超大陆聚合前早古生代地球动力学机制探讨。由于对俯冲极性不同的判断,进而不同学者得出不同的微陆块聚合方式。如,对西昆仑的构造解释就存在开合模式和消减增生模式之争(姜春发等,1992;李向东,1995; 丁道桂, 1996;Yao and Hsü,1994; 李继亮等, 1999;潘裕生, 2000),阿尔金-柴北缘-北秦岭高压-超高压变质带就有可能代表穿时渐进拼合方式或间断式离散拼合方式(张建新等,2007;刘良等,2009)。
对于华北-塔里木陆块南侧多条早古生代构造带的属性、块体拼合方式和时序同样还存在巨大争论,暗示了其复杂性。这些原特提斯域不同类型的洋-陆边界不仅记录了不同动力学背景和大地构造环境,而且经历了不同程度演化历程。如从南阿尔金经柴北缘到北秦岭的高压-超高压变质带,是否构成同一条巨型高压-超高压变质岩带?代表了早古生代时期简单的南、北两大板块简单穿时的俯冲碰撞作用(杨经绥等,2005;张建新等,2007)还是可能与多陆块或弧-陆之间的分散式对接碰撞有关(刘良等,2009)?是多个陆块或微陆块依次向北俯冲与塔里木-阿拉善-华北陆块拼贴(Song et al., 2014),还是一次性向南与冈瓦纳大陆拼贴(李三忠等,2016b)?这些问题是早古生代多微陆块拼合方式研究的核心内容,还需要开展构造地质学等方面的深入综合研究。因此,针对原特提斯北部,应集中解决复杂陆块/微陆块拼合时序、方式,这是最终重建Pangea超大陆聚合前早期演化的基础。
最新研究揭示,从南阿尔金经柴北缘到北秦岭的高压-超高压变质带并非一条几何形态简单的巨型高压-超高压变质岩带,而是北秦岭高压-超高压变质带西延与北祁连高压-超高压变质带、北阿尔金构造带相连(张建新等,2015);南阿尔金经柴北缘被瓦洪山后期断裂切割,可能转而向东昆仑-祁漫塔格延伸(李三忠等,2016b)。它们共同构成了华北-阿拉善-敦煌-塔里木-柴达木陆块群南缘的一条统一的高压-超高压构造带;第一幕构造变形分析揭示,这条构造带整体向南俯冲(Xiao et al., 2009; Zhao et al., 2015; 李三忠等,2016b),因而这些陆块群与冈瓦纳不同地段拼合方式变得非常简单。沿这个构造带不同地段可以发生陆-陆碰撞,也可能发生洋-陆俯冲-增生。只是在加里东运动后期围绕柴达木微陆块发生了弯山构造,是的祁连-柴达木-东昆仑地区,该高压超高压带变成3条。这条“S”型双弯山构造的格局完全可以和西欧华力西期造山带的对比(Shaw and Johnston, 2016)。最终,结合前文论述,确定原特提斯域多个陆块/微陆块间的拼合特征就是陆块/微陆块通过俯冲-增生向南拼合到了冈瓦纳大陆北缘(图 4),其时限总体介于450~400Ma之间。特别是,华北陆块在早古生代后期整体抬升运动,而整个中国西部和华南泥盆系与下伏地层的不整合非常普遍(李兴振等,1990;蔡立国等,1993;潘裕生,1994;钟大赉,1998;李兴振和尹福光, 2002;肖序常等,2003;潘桂棠等,2004;徐旭辉等,2009),且下-中泥盆统在中国东南大部地区广泛缺失,标志加里东期造山运动最终结束于志留纪末-泥盆纪初,至此,华南陆内造山带形成(舒良树等,2008;郝义,2010; Wang et al., 2010)。这些都可能表明加里东运动的广泛性和整体聚合性,时间上可以与劳伦古陆上的老红砂岩层角度不整合对比。
但是,也有部分研究认为,华北、华南、塔里木和印支自寒武纪至泥盆纪始终作为一个整体陆块运动(Ziegler et al., 1979), 原特提斯洋并不复杂。或认为上述陆块/微陆块实际是一个内部发育多个裂陷的独立而统一的板块,称为西域板块(葛肖虹和刘俊来,1999)。或认为,直至早古生代末, 华北、塔里木、扬子、华夏(包括黄海-东海-南海)、柴达木、(昆仑-羌北-昌都-)印支陆块等曾一度拼贴在一起,虽局部保留有坳拉槽和晚古生代连续沉积,但总体已形成具独立性和统一性的泛华夏大陆群(李兴振等,1990;蔡立国等,1993;潘裕生,1994;钟大赉,1998;李兴振和尹福光, 2002;肖序常等,2003;潘桂棠等,2004)。然而,这些结果与现今碎屑锆石年龄谱揭示的块体早古生代的亲缘性存在巨大差异(Yu et al., 2015; Cao et al., 2016)
5 结论围绕Pangea聚合过程中原特提斯洋-陆格局与微陆块早古生代聚合这一核心科学问题,本文以北秦岭、北祁连、中祁连、柴北缘及阿尔金构造带为重点研究对象,采用构造地质学、沉积学、岩石学、元素-同位素地球化学和同位素年代学等综合集成的研究手段,基于现有研究进展,对比上述构造带中已有高压-超高压变质带、蛇绿岩带研究成果和原特提斯域其它构造带特征,得出以下几点新认识:
1) 原特提斯洋北界为古洛南-栾川缝合线(或宽坪缝合线)及其西延,南界为龙木措-双湖-昌宁-孟连缝合线。
2) 原特提斯洋俯冲极性是整体向南俯冲,最终拼合于冈瓦纳大陆北缘。
致谢 近5年来,我们主要集中研究原特提斯洋的演化,本文主要介绍了研究背景、相关进展和初步认识,供专家批评指正。同时,谨以此文祝贺第一作者的导师杨振升教授85华诞。感谢舒良树教授和刘福来研究员提出的宝贵审稿意见。| [] | A CY, Wang YZ, Ren JQ, Bao GP. 2003. Disintegration of the Wanbaogou Group and discovery of Early Cambrian strata in the East Kunlun area. Geology in China , 30 (2) :199–206. |
| [] | An HT. 2014. Redefinition of the Southern Border and Oceanic and continental framework of the southern Proto-tethys Ocean. Master Degree Thesis. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 1-80 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Bao ZW, Wang Q, Bai GD, Zhao ZH, Song YW, Liu XM. 2008. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Fangcheng Neoproterozoic alkali-syenites in East Qinling orogen and its geodynamic implications. Chinese Science Bulletin , 53 (13) :2050–2061. |
| [] | Bian QT, Yin LM, Sun SF, Luo XQ, Pospelov I, Astrakhahtsev O, Chamov N. 2001. Discovery of Ordovician acritarchs in Buqingshan ophiolite complex, East Kunlun Mountains and its significance. Chinese Science Bulletin , 46 (4) :341–345. DOI:10.1007/BF03187200 |
| [] | Cai LG, Zheng B, Liu JR, Wang SD.1993. Basic Characteristics of Petroleum Geology in the Eastern Part of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press : 1 -101. |
| [] | Cao HH, Li SZ, Zhao SJ, Yu S, Li XY and Somervillec ID. 2016. Detrital zircon geochronology of Neoproterozoic to Early Paleozoic sedimentary rocks in the North Qinling Orogenic Belt: Implications for the tectonic evolution of the Kuanping Ocean. Precambrian Research, 279: 1-16 |
| [] | Cao Y, Wang J, Liu JG, Bao ZY, Song Y, Li A. 2016. Formation and significance of adakitic rocks in Datong pluton of Early Paleozoic magmatic arc of Western Kunlun Orogen. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition) , 46 (2) :425–442. |
| [] | Chen JL, Chen YC, Li HP, Zhao XS. 2002. Correlation between the Longshan rock group and the Qinling rock group at the junction of Qilian Mountain and North Qinling Mountain. Geology of Shaanxi , 20 (2) :39–49. |
| [] | Chen L, Sun Y, Liu XM, Pei XZ. 2000. Geochemistry of Derni ophiolite and its tectonic significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 16 (1) :106–110. |
| [] | Chen LY, Luo YL, Liu XC, Qu W, Hu J. 2014. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology of detrital zircons from the Liuling Group in the South Qinling tectonic belt and its tectonic significance. Geological Bulletin of China , 33 (9) :1363–1378. |
| [] | Chen NS, Sun M, Wang QY, Zhang KX, Wan YS, Chen HH. 2008. U-Pb dating of zircon from the Central Zone of the East Kunlun Orogen and its implications for tectonic evolution. Science in China (Series D) , 51 (7) :929–938. DOI:10.1007/s11430-008-0072-x |
| [] | Chen ZL. 1994. Tethyan geology for 100 years. Tethyan Geology , 18 :1–22. |
| [] | Cui JT, Wang JC, Bian XW, Zhu HP, Yang KJ. 2006. Geological characteristics of Early Paleozoic amphibolite and tonalite in northern Kangxiwar, West Kunlun, China and their zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating. Geological Bulletin of China , 25 (12) :1441–1449. |
| [] | Deng WM. 1995. Geological features of ophiolite and tectonic significance in the Karakorum-West Kunlun Mts. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 11 (Suppl.) :98–111. |
| [] | Ding DG. 1996. The formation and evolution of the southern the Tarim Basin and Western Kunlun orogenic belt. In: Ding DG, Wang DX, Liu WX and Sun SQ (eds.). West Kunlun Orogenic Belt and Basin. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 201-207 (in Chinese) |
| [] | Diwu CR, Sun Y, Gao JF, Fan LG. 2013. Early Precambrian tectonothermal events of the North China Craton: Constraints from in situ detrital zircon U-Pb, Hf and O isotopic compositions in Tietonggou Formation. Chinese Science Bulletin , 58 (31) :3760–3770. DOI:10.1007/s11434-013-5817-z |
| [] | Dong YP, Zhang GW, Yang Z, Zhao X, Ma HY, Yao AP. 2007. Geochemistry of the E-MORB type ophiolite and related volcanic rocks from the Wushan area, West Qinling. Science in China (Series D) , 50 (Suppl.2) :234–245. |
| [] | Dong YP, Zhang GW, Hauzenberger C, Neubauer F, Yang Z, Liu XM. 2011a. Palaeozoic tectonics and evolutionary history of the Qinling orogen: Evidence from geochemistry and geochronology of ophiolite and related volcanic rocks. Lithos , 122 (1-2) :39–56. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.11.011 |
| [] | Dong YP, Zhang GW, Neubauer F, Liu XM, Genser J, Hauzenberger C. 2011b. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, China: Review and synthesis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 41 (3) :213–237. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.002 |
| [] | Dong YP, Liu XM, Santosh M, Chen Q, Zhang XN, Li W, He DF, Zhang GW. 2012. Neoproterozoic accretionary tectonics along the northwestern margin of the Yangtze Block, China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry. Precambrian Research , 196-197 :247–274. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2011.12.007 |
| [] | Dong YP, Yang Z, Liu XM, Zhang XN, He DF, Li W, Zhang FF, Sun SS, Zhang HF, Zhang GW. 2014. Neoproterozoic amalgamation of the Northern Qinling terrain to the North China Craton: Constraints from geochronology and geochemistry of the Kuanping ophiolite. Precambrian Research , 255 :77–95. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2014.09.008 |
| [] | Du DH.1986. Study of the Devonian of the Qinba Area, Shaanxi Province. Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press : 1 -230. |
| [] | Du YS, Zhu J, Han X, Gu SZ. 2004. From the back-arc basin to foreland basin-Ordovician Devonian sedimentary basin and tectonic evolution in the North Qilian orogenic belt. Geological Bulletin of China , 23 (9-10) :911–917. |
| [] | Fan JJ, Li C, Xie CM, Liu YM. 2015. Depositional environment and provenance of the Upper Permian-Lower Triassic Tianquanshan Formation, northern Tibet: Implications for the Palaeozoic evolution of the Southern Qiangtang, Lhasa, and Himalayan terranes in the Tibetan Plateau. International Geology Review , 58 (2) :228–245. |
| [] | Fan LK, Cai YP, Liang HC, Li HL. 2009. Characters and evolution of the geodynamics in the Eastern Kunlun. Geological Survey and Research , 33 (3) :181–186. |
| [] | Fan SQ, Shi RD, Ding L, Liu DL, Huang QS, Wang HQ. 2010. Geochemical characteristics and zircon U-Pb age of the plagiogranite in Gaize ophiolite of central Tibet and their tectonic significance. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica , 29 (5) :467–478. |
| [] | Feng JY. 2010. The geological characteristic, age and tectonic significance of Kekesha-Kekekete mafic-ultramafic rocks in Dulan County of the East Kunlun region. Master Degree Thesis. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 1-73 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Feng YM, He SP, Yan J. 1994. The discovery and geological significance of sheeted dyke complex in the Early-Middle Ordovician ophiolite in the central section of the North Qilian Mountains, China. Geological Review , 40 (3) :252–264. |
| [] | Fu CL, Yan Z, Guo XQ, Niu ML, Xia WJ, Wang ZQ, Li JL. 2014. Geochemistry and SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age of diabases in the Lajishankou ophiolitic melange,South Qilian terrane. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 30 (6) :1695–1706. |
| [] | Gao CL, Huang ZG, Ye DL, Liu GX, Ji RS, Qin DY. 2005. Three Paleo-Oceans in the Early Paleozoic and their control to basins in China. Petroleum Geology and Experiment , 27 (5) :439–448. |
| [] | Gao S. 1989. Structure, composition and evolution of the continental crust in the Qinling orogenic belt and its adjacent North China and Yangtze cratons. Ph. D. Dissertation. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 20-50 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Ge XH, Liu JL. 1999. Formation and tectonic background of the northern Qilian Orogenic Belt. Earth Science Frontiers , 6 (4) :223–230. |
| [] | Geng YS, Zhou XW. 2010. Early Neoproterozoic granite events in Alax area of Inner Mongolia and their geological significance: Evidence from geochronology. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica , 29 (6) :779–795. |
| [] | Guo FX. 2001. Paleozoic Tectono-Paleobiogeography of Xinjiang, China. Xinjiang Geology , 19 (1) :20–26. |
| [] | Guo XQ, Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Fu CL, Chen L. 2014. Tectonic setting of Lijiabian Ti-Fe deposit in Shanyang-Zhashui ore concentration area, Qinling Orogen. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 30 (2) :437–450. |
| [] | Hao Y. 2010. Caledonian structural characteristics and dynamics in South China. Master Degree Thesis. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 1-66 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Huang DP. 1966. Study on the Laojun Mountains in the north piedmont of eastern part of North Qilian Mountains. Geological Review , 24 (1) :1–7. |
| [] | Huo FC, Li YJ.1995. Construction and Geological Evolution of the West Qinling Orogenic Belt. Xi'an: Northwestern University Press : 1 -166. |
| [] | Jiang CF, Yang JS, Feng BG, Zhu ZZ, Zhao M, Chai YC, Shi XD, Wang HD, Hu JQ.1992. Opening-Closing Tectonics of Kunlun Mountains. Beijing: Geological Publishing House : 1 -217. |
| [] | Jiang YH, Rui XJ, Hou JR, Guo KY, Yang WZ. 1999. Tetonic type of Caledonian granitoids and tectonic significance in the West Kunlun Mts. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 15 (1) :105–115. |
| [] | Jin SQ, Zhu WY, Zuo GC. 1985. The Paleogeographic changes of Late Paleozoic in Qilianshan region. Experimental Petroleum Geology , 7 (1) :38–46. |
| [] | Kroner U, Roscher M, Romer RL. 2016. Ancient plate kinematics derived from the deformation pattern of continental crust: Paleo-and Neo-Tethys opening coeval with prolonged Gondwana-Laurussia convergence. Tectonophysics , 681 :220–233. DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2016.03.034 |
| [] | Lai SC. 1997. Geochemical features of the ultramafic rocks in Mianlue Suture Zone, Qinling orogenic belt. Northwestern Geology , 18 (3) :36–45. |
| [] | Li C, Zhai QG, Dong YS, Zeng QG, Huang XP. 2007. Lungmu Co-Shanghu plate suture in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and records of the evolution of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean in the Qiangtang area, Tibet, China. Geological Bulletin of China , 26 (1) :13–21. |
| [] | Li HK, Lu SN, Zhao FQ, Yu HF, Zheng JK. 1999. Determination and significance of the coesite eclogite on the Yuqia River on the north margin of the Qaidam Basin. Geoscience , 13 (1) :43–50. |
| [] | Li JL, Sun S, Hao J, Chen HH, Hou QL, Xiao WJ. 1999. On the classification of collision orogenic belts. Scientia Geologica Sinica , 34 (2) :129–138. |
| [] | Li JY, Zhang J, Qu JF. 2012. Amalgamation of North China craton with Alxa Block in the late of Early Paleozoic: Evidence from sedimentary sequences in the Niushou Mountain, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, NW China. Geological Review , 58 (2) :208–214. |
| [] | Li SZ, Yang Z, Zhao SJ, Li XY, Guo LL, Yu S, Liu X, Suo YH, Lan HY. 2016a. Global Early Paleozoic orogens (I): Collision-type orogeny. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition) , 46 (4) :945–967. |
| [] | Li SZ, Yang Z, Zhao SJ, Li XY, Suo YH, Guo LL, Yu S, Dai LM, Li SJ, Mu DL. 2016b. Global Early Paleozoic orogens (Ⅱ): Subduction-accretionary-type orogeny. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition) , 46 (4) :968–1004. |
| [] | Li SZ, Li XY, Zhao SJ, Yang Z, Liu X, Guo LL, Wang YM, Hao Y, Zhang J, Hu MY. 2016c. Global Early Paleozoic orogens (Ⅲ): Intracontinental orogen in South China. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition) , 46 (4) :1005–1025. |
| [] | Li SZ, Yang Z, Zhao SJ, Liu X, Yu S, Li XY, Guo LL, Suo YH, Dai LM, Guo RH, Zhang GW. 2016d. Global Early Paleozoic orogens (Ⅳ): Plate reconstruction and supercontinent Carolina. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition) , 46 (4) :1026–1041. |
| [] | Li T, Zhao SJ, Li SZ, Yu S, Lou D, Suo YH, Wang XB, Sun WJ, Yang Z, Dang LM. 2015. The features of nappe structure in the northeastern Junggar Basin. Geological Review , 61 (2) :356–366. |
| [] | Li WC, Pan GT, Hou ZQ, Mo XX, Wang LQ.2010. Multiple Island Arc Basin System in Southwest "Sanjiang": The Collisional Orogenic Metallogenic Theory and Prospecting Techniques. Beijing: Geological Publishing House : 1 -461. |
| [] | Li XC, Niu ML, Yan Z, Da LC, Han Y, Wang YS. 2015. LP/HT metamorphic rocks in Wulan County, Qinghai Province: An Early Paleozoic paired metamorphic belt on the northern Qaidam Basin?. Science Bulletin , 60 (35) :3501–3513. |
| [] | Li XD. 1995. The Kudibei tectonic belt and its tectonic significance. In: Li YA, Li XD, Sun DJ and Han YL (eds.). The Tectonic Evolution of Kangxiwa Tectonic Belt and Qiangtang Block of Southwestern Xinjiang, China. Urumqi: Xinjiang Science and Technology Health Publishing House, 39-53 (in Chinese) |
| [] | Li XZ, Pan GT and Luo JN. 1990. A boundary between Gondwanaland and Laurasia continents in Sanjiang region. In: Editing Committee of Geological Memoirs of Qinghai-Xizang (ed.). Geological Memoirs of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau (20): Geological Tectonics of "Sanjiang". Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 217-233 (in Chinese) |
| [] | Li XZ, Xu XS, Pan GT. 1995. Evolution of the Pan-Cathaysian landmass group and Eastern Tethyan tectonic domain. Sedimentary Facies and Palaeogeography , 15 (4) :1–13. |
| [] | Li XZ, Yin FG. 2002. Comparative study of the geological structure of the Eastern and West Kunlun Mountains. Geological Bulletin of China , 21 (11) :777–783. |
| [] | Li YA, Li Q, Zhang H, Sun DJ, Cao YD, Wu SZ. 1995. Palaeomagnetic study of Tarim and its adjacent area as well as the formation and evolution of Tarim Basin. Xinjiang Geology , 13 (4) :293–376. |
| [] | Li ZX, Bogdanova SV, Collins AS, Davidson A, De Waele B, Ernst RE, Fitzsimons ICW, Fuck RA, Gladkochub DP, Jacobs J, Karlstrom KE, Lu S, Natapov LM, Pease V, Pisarevsky SA, Thrane K, Vernikovsky V. 2008. Assembly, configuration, and break-up history of Rodinia: A synthesis. Precambrian Research , 160 (1-2) :179–210. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.021 |
| [] | Lin YH, Zhang LF, Ji JQ, Wang QJ, Song SG. 2010. 40Ar/39Ar isochron ages of lawsonite blueschists from Jiuquan in the northern Qilian Mountain, NW China, and their tectonic implications. Chinese Science Bulletin , 55 (19) :2021–2027. DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-3239-8 |
| [] | Liu B, Ma CQ, Zhang JY, Xiong FH, Huang J, Jiang HA. 2012. Petrogenesis of Early Devonian intrusive rocks in the east part of Eastern Kunlun Orogen and implication for Early Palaeozoic orogenic processes. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 28 (6) :1785–1807. |
| [] | Liu BJ, Zhou MK, Wang RZ. 1990. Early Palaeozoic palaeogeography and tectonic evolution of South China. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences , 20 (1) :97–98. |
| [] | Liu GH, Zhang SG, You ZD, Suo ST, Zhang GW.1993. Main Metamorphic Rocks and Metamorphic Evolution in the Qinling Orogenic Belt. Beijing: Geological Publishing House : 1 -190. |
| [] | Liu L, Chen DL, Wang C, Zhang CL. 2009. New progress on geochronology of high-pressure/ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks from the South Altyn Tagh, the North Qaidam and the North Qinling orogenic, NW China and their geological significance. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition) , 39 (3) :472–479. |
| [] | Liu L, Liao XY, Wang YW, Wang C, Santosh M, Yang M, Zhang CL and Chen DL. 2016. Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the North Qinling Orogenic Belt in Central China: Insights on continental deep subduction and multiphase exhumation. Earth-Science Reviews, 159: 58-81 |
| [] | Liu XC, Jahn BM, Liu DY, Dong SW, Li SZ. 2004. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of a metagabbro and eclogites from western Dabieshan (Hong'an block), China, and its tectonic implications. Tectonophysics , 394 (3-4) :171–192. DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2004.08.004 |
| [] | Liu XC, Jahn BM, Li SZ, Liu YS. 2013. U-Pb zircon age and geochemical constraints on tectonic evolution of the Paleozoic accretionary orogenic system in the Tongbai orogen, central China. Tectonophysics , 559 :67–88. |
| [] | Liu XJ, Xu JF, Xiao WJ, Castillo PR, Shi Y, Wang SQ, Huo QY, Feng ZH. 2015. The boundary between the Central Asian Orogenic belt and Tethyan tectonic domain deduced from Pb isotopic data. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 113 :7–15. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.04.039 |
| [] | Lu SN. 2001. From Rodinia to Gondwanaland supercontinents: Thinking about problems of researching Neoproterozoic supercontinents. Earth Science Frontiers , 8 (4) :441–448. |
| [] | Lu SN.2002. Preliminary Study of Precambrian Geology in the North Tibet-Qinghai Plateau. Beijing: Geological Publishing House : 1 -125. |
| [] | Lu SN, Li HK, Chen ZH, et al.2003. Neoproterozoic Geological Evolution and the Response to the Rodinia Super Continent Events. Beijing: Geological Publishing House : 1 -194. |
| [] | Mattern F, Schneider W. 2000. Suturing of the Proto- and Paleo-Tethys oceans in the western Kunlun (Xinjiang, China). Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 18 (6) :637–650. DOI:10.1016/S1367-9120(00)00011-0 |
| [] | Meng QR, Zhang GW. 1999. Timing of collision of the North and South China blocks: Controversy and reconciliation. Geology , 27 (2) :123–126. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<0123:TOCOTN>2.3.CO;2 |
| [] | Nie XM, Feng QL, Qian X, Wang YJ. 2015. Magmatic record of Prototethyan evolution in SW Yunnan, China: Geochemical, zircon U-Pb geochronological and Lu-Hf isotopic evidence from the Huimin metavolcanic rocks in the southern Lancangjiang zone. Gondwana Research , 28 (2) :757–768. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2014.05.011 |
| [] | Pan GT, Chen ZL, Li XZ, Yan YJ, Xu XS, Xu Q, Jiang XS, Wu YL, Luo JN, Zhu TX, Peng YM.1997. The Geological Tectonic Formation and Evolution of the Eastern Tethys. Beijing: Geological Publishing House : 65 -128. |
| [] | Pan GT, Zhu DC, Wang LQ, Liao ZL, Geng QR, Jiang XS. 2004. Bangong Lake-Nu River suture zone-the northern boundary of Gondwanaland: Evidence from geology and geophysics. Earth Science Frontiers , 11 (4) :371–382. |
| [] | Pan YS. 1989. A preliminary study on the regionalization of the structures in the Kunlun Mountains region. Journal of Natural Resources , 4 (3) :196–203. |
| [] | Pan YS. 1994. Discovery and evidence of the fifth suture zone of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Acta Geophysica Sinica , 37 (2) :184–192. |
| [] | Pan YS.2000. The Geological Evolution of the Karakorum-Kunlun Mountains Area. Beijing: Science Press : 1 -258. |
| [] | Qu XM, Wang RJ, Xin HB, Zhao YY, Fan XT. 2009. Geochronology and geochemistry of igneous rocks related to the subduction of the Tethys oceanic plate along the Bangong Lake arc zone, the western Tibetan Plateau. Geochimica , 38 (6) :523–535. |
| [] | Qu XM, Xin HB, Zhao YY, Wang RJ, Fan XT. 2010. Opening time of Bangong Lake Middle Tethys oceanic basin of the Tibet Plateau: Constraints from petro-geochemistry and zircon U-Pb LAICPMS dating of mafic ophiolites. Earth Science Frontiers , 17 (3) :53–63. |
| [] | Ratschbacher L, Hacker BR, Calvert A, Webb LE, Grimmer JC, McWilliams MO, Ireland T, Dong SW, Hu JM. 2003. Tectonics of the Qinling (Central China): Tectonostratigraphy, geochronology, and deformation history. Tectonophysics , 366 (1-2) :1–53. DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(03)00053-2 |
| [] | Ren JS and Xie GL. 1991. Proceeding of first international symposium on Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion-Geological evolution of eastern Tethys: November 25-December 1, 1991, Kunming, China. Beijing: China University of Geosciences Press |
| [] | Ren JX, Wang ZX and Chen BW. 2000. A Tectonic Map of China and Its Adjacent Area (1:5 million). Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese) |
| [] | Scotese CR. 2004. A continental drift flipbook. The Journal of Geology , 112 (6) :729–741. DOI:10.1086/424867 |
| [] | Shaw J, Johnston ST. 2016. Terrane wrecks (coupled oroclines) and paleomagnetic inclination anomalies. Earth-Science Reviews , 154 :191–209. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.01.003 |
| [] | Shu LS, Yu JH, Jia D, Wang B, Shen WZ, Zhang YQ. 2008. Early Paleozoic orogenic belt in the eastern segment of South China. Geological Bulletin of China , 27 (10) :1581–1593. |
| [] | Shu LS, Jahn BM, Charvet J, Santosh M, Wang B, Xu XS, Jiang SY. 2014. Early Paleozoic depositional environment and intraplate tectono-magmatism in the Cathaysia block (South China): Evidence from stratigraphic, structural, geochemical and geochronological investigations. American Journal of Science , 314 (1) :154–186. DOI:10.2475/01.2014.05 |
| [] | Song SG, Zhang C, Li XH, Zhang LF. 2011. HP/UHP metamorphic time of eclogite in the Xitieshan terrane, North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 27 (4) :1191–1197. |
| [] | Song SG, Niu YL, Su L, Zhang C, Zhang LF. 2014. Continental orogenesis from ocean subduction, continent collision/subduction, to orogen collapse, and orogen recycling: The example of the North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China. Earth-Science Reviews , 129 :59–84. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.11.010 |
| [] | Song ZB, Li ZP, Ren YX, Yang JG, Li YZ, Xie CL. 2005. Chronology and geological significance of Chelugou dacite porphyry in North Qilian Mountains. Geological Science and Technology Information , 24 (3) :15–19. |
| [] | Sun LX, Bai ZD, Xu DB, Li HK, Song B. 2011. Geological characteristics and Zircon U-Pb SHRIMP dating of the plagiogranite in Amduo ophiolites, Tibet. Geological Survey and Research , 34 (1) :10–15. |
| [] | Sun MD, Xu YG, Wilde SA, Chen HL, Yang SF. 2015a. The Permian Dongfanghong island-arc gabbro of the Wandashan Orogen, NE China:Implications for Paleo-Pacific subduction. Tectonophysics , 659 :122–136. DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2015.07.034 |
| [] | Sun WJ, Li SZ, Liu X, Santosh M, Zhao SJ, Guo LL, Cao HH, Yu S, Dai LM, Zhang Y. 2015b. Deep structures and surface boundaries among Proto-Tethyan micro-blocks: Constraints from seismic tomography and aeromagnetic anomalies in the Central China Orogen. Tectonophysics , 659 :109–121. DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2015.07.033 |
| [] | Sun Y. 2010. The geological characteristics, age and tectonic environment studies about Delishitan ophiolites in Buqingshan, south of East Kunlun Mountains. Master Degree Thesis. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 1-74 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | von Raumer JF, Stampfli GM. 2008. The birth of the Rheic Ocean-Early Palaeozoic subsidence patterns and subsequent tectonic plate scenarios. Tectonophysics , 461 (1-4) :9–20. DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2008.04.012 |
| [] | Wang H, Wu YB, Gao S, Zhang HF, Liu XC, Gong HJ, Peng M, Wang J, Yuan HL. 2011. Silurian granulite-facies metamorphism, and coeval magmatism and crustal growth in the Tongbai orogen, central China. Lithos , 125 (1-2) :249–271. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.02.010 |
| [] | Wang HC, Yuan GB, Xin HT, Hao GJ, Zheng JK, Zhang BH. 2001. Occurrence of the eclogite and its genesis in the Luliangshan area, the northern margin of the Qaidam Basin. Chinese Geology , 28 (7) :22–27, 8. |
| [] | Wang HC, Lu SN, Mo XX, Li HK, Xin HT. 2005. An Early Paleozoic collisional orogen on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin, northwestern China. Geological Bulletin of China , 24 (7) :603–612. |
| [] | Wang JC, Cui JT, Luo QZ, Bian XW, Zhu HP, Yang KJ, Peng HL, Wang F, Zhang HP, Lin SY, Ge SM, Ma ZK. 2006. The discovery and tectonic significance of a small branch ocean basin in Monggubao-Pushouyuan, Tethyan ocean of northern Kangxiwa, West Kunlun Mountain. Geology of Shaanxi , 24 (2) :41–49. |
| [] | Wang YJ, Zhang AM, Fan WM, Peng TP, Zhang FF, Zhang YH, Bi XW. 2010. Petrogenesis of Late Triassic post-collisional basaltic rocks of the Lancangjiang tectonic zone, Southwest China, and tectonic implications for the evolution of the eastern Paleotethys: Geochronological and geochemical constraints. Lithos , 120 (3-4) :529–546. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.09.012 |
| [] | Wang YL, Wang ZG, Li XD, Huang ZL. 1995. Geologica features of the Caledonian granite zone in the West Kunlun area. Acta Mineralogica Sinica , 15 (4) :457–461. |
| [] | Wang YZ, Fang XL. 1987. Priliminary study on granite distribution of time and space in West Kunlun-Karakorun Mountains of Xinjiang. Xinjiang Geology , 5 (1) :9–24. |
| [] | Wang ZQ, Yan QR, Yan Z, Wang T, Jiang CF, Gao LD, Li QG, Chen JL, Zhang YL, Liu P, Xie CL, Xiang ZJ. 2009. New Division of the main tectonic units of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China. Acta Geologica Sinica , 83 (11) :1527–1546. |
| [] | Wu T, Jiang XJ, Zhou H. 2014. Sedimentary structure and paleo-flow characteristics of the Devonian in "Liu Lingqun" of the Shanyang-Zhashui basin, Eastern Qinling Mountains. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition) , 11 (10) :42–44. |
| [] | Wu YB, Zheng YF, Gao S, Jiao WF, Liu YS. 2008. Zircon U-Pb age and trace element evidence for Paleoproterozoic granulite-facies metamorphism and Archean crustal rocks in the Dabie Orogen. Lithos , 101 (3-4) :308–322. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.07.008 |
| [] | Xia LQ, Xia ZC, Xu XY.1996. Origin of Marine Volcanic Rocks in Northern Qilian Mountains. Beijing: Geological Publishing House : 1 -15. |
| [] | Xiang DP. 1982. The characteristics of geological structures in the Chilienshan region, China. Scientia Geologica Sinica (4) :364–370. |
| [] | Xiao SY, Zhang WJ, Song ZJ.1988. Metamorphic Strata in Northern Qinling Mountains. Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press : 1 -337. |
| [] | Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Hao J, Zhai MG. 2003. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt. Tectonics , 22 (6) :1069. |
| [] | Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Yong Y, Yan Z, Yuan C, Liu CZ, Li JL. 2009. Early Paleozoic to Devonian multiple-accretionary model for the Qilian Shan, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 35 (3-4) :323–333. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.10.001 |
| [] | Xiao XC, Chen GM, Zhu ZZ. 1978. A preliminary study on the tectonics of ancient ophiolites in the Qilian Mountain, Northwest China. Acta Geologica Sinica (4) :281–295. |
| [] | Xiao XC, Tang YQ, Gao YL. 1986. Reexposition on plate tectonics of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (14) :7–19. |
| [] | Xiao XC, Wang J, Su L, Song SG. 2003. A further discussion of the Küda ophiolite, West Kunlun, and its tectonic significance. Geological Bulletin of China , 22 (10) :745–750. |
| [] | Xiong LJ. 2014. Tectonic evolution and processes in the west segement of the Northern Proto-Tethys Tectonic Domain. Master Degree Thesis. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 1-97 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Xu Q. 1996. Early Palaeozoic sedimentary environments and basin evolution in East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Qinghai. Tethyan Geology, (20) :85–101. |
| [] | Xu XH, Gao CL, Jiang XG, Huang ZG, Zhu JH, Fan XL, Liu GX, Ji RS.2009. An Outline of Dynamic Analysis of Petroliferous Basins of China. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press : 1 -194. |
| [] | Xu XS, Xu Q, Pan GT, Liu QH, Fan YN, He YX.1996. Paleogeography of the South China Continent (SCC) and Its Contrast with Pangea. Beijing: Geological Publishing House : 1 -161. |
| [] | Xu XS, Liu BJ, Mu CL, Wang ZJ, Qiu DZ.2004. Marine Basin Analysis of Central-western China and Petroleum Resources. Beijing: Geological Publishing House : 1 -230. |
| [] | Xu ZQ, Xu HF, Zhang JX, Li HB, Zhu ZZ, Qu JC, Chen DZ, Chen JL, Yang KC. 1994. The Zhoulangnanshan Caledonian subductive complex in the Northern Qilian Mountains and its dynamics. Acta Geologica Sinica , 68 (1) :1–15. |
| [] | Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Wu CL, Li HB, Zhang JX, Qi XX, Song SG, Wan YS, Chen W, Qiu HJ. 2003. Timing and machanism of formation and exhumation of the Qaidam Ultra-Pressure Metamorphic Belt. Acta Geologica Sinica , 77 (2) :163–176. |
| [] | Xu ZQ, Qi XX, Liu FL, Yang JS, Zeng LS, Wu CL. 2005. A new Caledonian Khondalite series in West Kunlun, China: Age constraints and tectonic significance. International Geology Review , 47 (9) :986–998. DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.47.9.986 |
| [] | Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Wu CL, Li HB, Zhang JX, Qi XX, Song SG, Qiu HJ. 2006. Timing and mechanism of formation and exhumation of the northern Qaidam ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 28 (2-3) :160–173. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.016 |
| [] | Xu ZQ, Qi XX, Yang JS, Ji SC, Li HB, Chen FY. 2007. Senses and timings of two kinds of shear in the Kangxiwar strike-slip shear zone, West Kunlun, and their tectonic significance. Geological Bulletin of China , 26 (10) :1252–1261. |
| [] | Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Li WC, Li HQ, Cai ZH, Yan Z, Ma CQ. 2013. Paleo-Tethys system and accretionary orogen in the Tibet Plateau. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 29 (6) :1847–1860. |
| [] | Xu ZQ, Dilek Y, Cao H, Yang JS, Robinson P, Ma CQ, Li HQ, Jolivet M, Roger F, Chen XJ. 2015. Paleo-Tethyan evolution of Tibet as recorded in the East Cimmerides and West Cathaysides. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 105 :320–337. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.01.021 |
| [] | Yan QR, Wang ZQ, Yan Z, Wang T, Chen JL, Xiang ZJ, Zhang ZQ, Jiang CF. 2008. Origin, age and tectonic implications of metamafic rocks in the Kuanping Group of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, China. Geological Bulletin of China , 27 (9) :1475–1492. |
| [] | Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Wang T, Yan QR. 2002. Sedimentary environment and tectonic significane of the Dacaotan Group of the Western Qinling Mountains. Geological Bulletin of China , 21 (8-9) :505–515. |
| [] | Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Yan QR, Wang T, Xiao WJ, Li JL, Han FL, Chen JL, Yang YC. 2006. Devonian sedimentary environments and provenance of the Qinling orogen: Constraints on Late Paleozoic southward accretionary tectonics of the North China craton. International Geology Review , 48 (7) :585–618. DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.48.7.585 |
| [] | Yan Z, Xiao WJ, Wang ZQ, Li JL. 2007. Integrated analyses constraining the provenance of sandstones, mudstones, and conglomerates, a case study: The Laojunshan Conglomerate, Qilian orogen, Northwest China. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences , 44 (7) :961–986. DOI:10.1139/e07-010 |
| [] | Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Wang T, Yan QR, Xiao WJ, Li JL, Han FL, Chen JL. 2007. Tectonic setting of Devonian sediments in the Qinling Orogen: Constrains from detrital modes and geochemistry of clastic rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 23 (5) :1023–1042. |
| [] | Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Chen JL, Yan QR, Wang T, Zhang YL. 2009. Geochemistry and SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of amphibolites from the Danfeng Group in the Wuguan area, North Qinling terrane and their tectonic significance. Acta Geologica Sinica , 83 (11) :1633–1646. |
| [] | Yan Z, Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Wang ZQ, Li JL. 2010. Silurian clastic sediments in the North Qilian Shan, NW China: Chemical and isotopic constraints on their forearc provenance with implications for the Paleozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Sedimentary Geology , 231 (3-4) :98–134. DOI:10.1016/j.sedgeo.2010.09.001 |
| [] | Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Yan QR, Wang T, Guo XQ. 2012. Geochemical constraints on the provenance and depositional setting of the Devonian Liuling Group, East Qinling Mountains, central China: Implications for the tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogenic belt. Journal of Sedimentary Research , 82 (1) :9–20. DOI:10.2110/jsr.2012.4 |
| [] | Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Li JL, Xu ZQ, Deng JF. 2012. Tectonic settings and accretionary orogenesis of the West Qinling Terrane, northeastern margin of the Tibet Plateau. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 28 (6) :1808–1828. |
| [] | Yang JS, Xu ZQ, Li HB, Wu CL, Cui JW, Zhang JX, Chen W. 1998. Discovery of eclogite at northern margin of Qaidam Basin, NW China. Chinese Science Bulletin , 43 (20) :1755–1760. DOI:10.1007/BF02883981 |
| [] | Yang JS, Xu ZQ, Song SG, Wu CL, Shi RD, Zhang JX, Wan YS, Li HB, Jin XC, Jolivet M. 2000. Discovery of eclogite in Dulan, Qinghai province and its significance for studying the HP-UHP metamorphic belt along the Central Orogenic Belt of China. Acta Geologica Sinica , 74 (2) :156–168. |
| [] | Yang JS, Zhang JX, Meng FC, Shi RD, Wu CL, Xu ZQ, Li HB, Chen SY. 2003. Ultrahigh pressure eclogites of the North Qaidam and Altun Mountains, NW China and their protoliths. Earth Science Frontiers , 10 (3) :291–314. |
| [] | Yang JS, Wu CL, Zhang JX, Xu ZQ. 2005. Chronology evidence of central giant UHPM belt and two UHP metamorphism. Scientific Chinese (8) :47–52. |
| [] | Yang Z, Dong YP, Liu XM, Zhang JH. 2006. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of gabbro in the Guanzizhen ophiolite, Tianshui, West Qinling, China. Geological Bulletin of China , 25 (11) :1321–1325. |
| [] | Yang Z, Zhao SJ, Li SZ, Yu S, Sun WJ, Xu LQ, Liu X, Lou D, Wang XB, Li T. 2015. Structural constrain to hydrocarbon accumulation in the Wulungu depression of the Junggar Basin. Chinese Journal of Geology , 50 (2) :536–552. |
| [] | Yao WH, Li ZX. 2016. Tectonostratigraphic history of the Ediacaran-Silurian Nanhua foreland basin in South China. Tectonophysics , 674 :31–51. DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2016.02.012 |
| [] | Yao YG, Hsü KJ. 1994. Origin of the Kunlun Mountains by arc-arc and arc-continent collisions. The Island Arc , 3 (2) :75–89. DOI:10.1111/iar.1994.3.issue-2 |
| [] | Yu HF, Lu SN, Mei HL, Zhao FQ, Li HK, Li HM. 1999. Characteristics of Neoproterozoic eclogite-granite zones and deep level ductile shear zone in western China and their significance for continental reconstruction. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 15 (4) :532–538. |
| [] | Yu S, Li SZ, Zhao SJ, Cao HH, Suo YH. 2015. Long history of a Grenville Orogen relic-the North Qinling Terrane: Evolution of the Qinling Orogenic Belt from Rodinia to Gondwana. Precambrian Research , 271 :98–117. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2015.09.020 |
| [] | Yuan C, Zhou H, Sun M, Li JL, Hou QL. 2000. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic implications of North Kuda Pluton, West Kunlun Mountains. Geochimica , 29 (2) :101–107. |
| [] | Yuan W, Yang ZY. 2015. Late Devonian closure of the North Qilian Ocean: Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes in the eastern North Qilian Orogenic Belt. International Geology Review , 57 (2) :182–198. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2014.999357 |
| [] | Zhang GW, Zhang BR, Yuan XC, Xiao QH.2001. Qinling Mountains Orogenic Belt and Continental Dynamics. Beijing: Science Press : 1 -854. |
| [] | Zhang GB, Song SG, Zhang LF, Niu YL, Shu GM. 2005. Ophiolite-type mantle Peridotite from Shaliuhe, North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China and its tectonic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 21 (4) :1049–1058. |
| [] | Zhang GB, Zhang LF. 2011. Rodingite from oceanic lithology of Shaliuhe terrane in North Qaidam UHPM belt and its geological implication. Earth Science Frontiers , 18 (2) :151–157. |
| [] | Zhang GW, Dong YP, Li SZ, et al.2015. The Mianlue Tectonic Zone of the Qinling Orogen and China Continental Tectonics. Beijing: Science Press : 1 -501. |
| [] | Zhang JX, Xu ZQ. 1995. Caledonian subduction-accretionary complex/volcanic arc zone and its deformation features in the middle sector of North Qilian Mountains. Acta Geoscientia Sinica (2) :153–163. |
| [] | Zhang JX, Meng FC, Mattinson CG. 2007. Progress, controversies and challenge of studies on South Altyn Tagh-North Qaidam HP/UHP metamorphic belt. Geological Journal of China Universities , 13 (3) :526–545. |
| [] | Zhang JX, Yu SY, Li YS, Yu XX, Lin YH, Mao XH. 2015. Subduction, accretion and closure of Proto-Tethyan Ocean: Early Paleozoic accretion/collision orogeny in the Altun-Qilian-North Qaidam orogenic system. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 31 (12) :3531–3554. |
| [] | Zhang Q, Zhou GQ.2001. Chinese Ophiolite. Beijing: Science Press : 1 -182. |
| [] | Zhang RY, Cong BL, Maruyama S, Liou JG. 1993. Metamorphism and tectonic evolution of the Lancang paired metamorphic belts, south-western China. Journal of Metamorphic Geology , 11 (4) :605–619. DOI:10.1111/jmg.1993.11.issue-4 |
| [] | Zhang SG, Wan YS, Liu GH, Cong RX, Zhao ZR.1991. Metamorphic Geology of the Kuanping Group in the Northern Qinling Mountains. Beijing: Beijing Science and Technology Press : 1 -119. |
| [] | Zhang XT, Lv HQ, Chen ZX, Zhang BH, Li FX, Zhu YS, Li CL, Wang Y. 1999. Discovery of high-pressure metamorphic rocks of eclogite facies in Shaliuhe area of the north margin orogenic belt of Qaidam Basin and its preliminary study. Geology of Qinghai , 8 (2) :1–13. |
| [] | Zhang ZC, Zhou MF, Robinson PT, Mao JW, Yang JM, Zuo GC. 2001. SHRIMP dating of the Aoyougou ophiolite in the west sector of the North Qilian Mountains and its geological significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 17 (2) :222–226. |
| [] | Zhao FQ, Lu SN and Li HK. 2000. The geochemical characteristics of the Meso-Neoproterozoic granite belt in the Dakendaban complex rocks of the Qaidam Block. In: Abstracts of the Second Cross Strait: Qilian Mountains and Its Adjacent Areas. Beijing: 95-97 (in Chinese) |
| [] | Zhao SJ, Li SZ, Liu X, Santosh M, Somervillec ID, Cao HH, Yu S, Zhang Z, Guo LL. 2015. The northern boundary of the Proto-Tethys Ocean: Constraints from structural analysis and U-Pb zircon geochronology of the North Qinling Terrane. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 113 :560–574. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.09.005 |
| [] | Zheng JK. 1992. Regional tectonic evolution of East Kunlun. Geology of Qinghai (1) :15–25. |
| [] | Zhong DL.1998. Paleotethysides in West Yunnan and Sichuan, China. Beijing: Science Press : 1 -231. |
| [] | Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Niu YL, Dilek Y, Hou ZQ, Mo XX. 2013. The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Gondwana Research , 23 (4) :1429–1454. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.002 |
| [] | Zhuang RX, Li F. 2006. The characteristics and formation environment of Tanjianshan group volcanic rock of north margin of Chaidamu basin. Yunnan Geology , 25 (2) :209–217. |
| [] | Ziegler AM, Scotese CR, McKerrow WS, Johnson ME, Bambach RK. 1979. Paleozoic Paleogeography. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences , 7 (4) :473–502. |
| [] | 阿成业, 王毅智, 任晋祁, 保光谱.2003. 东昆仑地区万保沟群的解体及早寒武世地层的新发现. 中国地质 , 30 (2) :199–206. |
| [] | 安慧婷. 2014. 原特提斯南界的厘定及其洋-陆格局. 硕士学位论文. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 1-80 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10674-1015641707.htm |
| [] | 包志伟, 王强, 白国典, 赵振华, 宋要武, 柳小明.2008. 东秦岭方城新元古代碱性正长岩形成时代及其动力学意义. 科学通报 , 53 (6) :684–694. |
| [] | 边千韬, 尹磊明, 孙淑芬, 罗小全, PospelovI, AstrakhahtsevO, ChamovN.2001. 东昆仑布青山蛇绿混杂岩中发现奥陶纪疑源类. 科学通报 , 46 (2) :167–171. |
| [] | 蔡立国, 郑冰, 刘建荣, 王守德. 1993. 青藏高原东部石油地质基本特征. 南京: 南京大学出版社 : 1 -101. |
| [] | 曹颖, 王建, 刘建国, 包真艳, 宋樾, 李爱.2016. 西昆仑早古生代岩浆弧大同岩体中埃达克质岩石的成因及地质意义. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版) , 46 (2) :425–442. |
| [] | 陈隽璐, 陈有仓, 李海平, 赵选社.2002. 祁连与北秦岭结合部位陇山岩群与秦岭岩群对比讨论. 陕西地质 , 20 (2) :39–49. |
| [] | 陈亮, 孙勇, 柳小明, 裴先治.2000. 青海省德尔尼蛇绿岩的地球化学特征及其大地构造意义. 岩石学报 , 16 (1) :106–110. |
| [] | 陈龙耀, 罗玉凌, 刘晓春, 曲玮, 胡娟.2014. 南秦岭刘岭群砂岩碎屑锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄及其构造意义. 地质通报 , 33 (9) :1363–1378. |
| [] | 陈能松, 孙敏, 王勤燕, 张克信, 万渝生, 陈海红.2008. 东昆仑造山带中带的锆石U-Pb定年与构造演化启示. 中国科学(D辑) , 38 (6) :657–666. |
| [] | 陈智梁.1994. 特提斯地质一百年. 特提斯地质 , 18 :1–22. |
| [] | 崔建堂, 王炬川, 边小卫, 朱海平, 杨克俭.2006. 西昆仑康西瓦北侧早古生代角闪闪长岩、英云闪长岩的地质特征及其锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测试. 地质通报 , 25 (12) :1441–1449. |
| [] | 邓万明.1995. 喀喇昆仑-西昆仑地区蛇绿岩的地质特征及其大地构造意义. 岩石学报 , 11 (增) :98–111. |
| [] | 第五春荣, 孙勇, 高剑峰, 樊龙刚.2013. 华北克拉通早前寒武纪构造-热事件性质探索: 铁铜沟组石英岩中碎屑锆石U-Pb-Hf-O同位素组成. 科学通报 , 58 (28-29) :2946–2957. |
| [] | 丁道桂. 1996. 塔里木盆地南部与西昆仑造山带的形成与演化. 见: 丁道桂, 王道轩, 刘伟新, 孙世群编. 西昆仑造山带与盆地. 北京: 地质出版社, 201-207 |
| [] | 董云鹏, 张国伟, 杨钊, 赵霞, 马海勇, 姚安平.2007. 西秦岭武山E-MORB型蛇绿岩及相关火山岩地球化学. 中国科学(D辑) , 37 (增刊Ⅰ) :199–208. |
| [] | 杜定汉. 1986. 陕西秦巴地区泥盆系研究. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社 : 1 -230. |
| [] | 杜远生, 朱杰, 韩欣, 顾松竹.2004. 从弧后盆地到前陆盆地——北祁连造山带奥陶纪-泥盆纪的沉积盆地与构造演化. 地质通报 , 23 (9-10) :911–917. |
| [] | 樊帅权, 史仁灯, 丁林, 刘德亮, 黄启帅, 王厚起.2010. 西藏改则蛇绿岩中斜长花岗岩地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及构造意义. 岩石矿物学杂志 , 29 (5) :467–478. |
| [] | 范丽琨, 蔡岩萍, 梁海川, 李宏录.2009. 东昆仑地质构造及地球动力学演化特征. 地质与调查 , 33 (3) :181–186. |
| [] | 冯建赟. 2010. 东昆仑都兰可可沙-科科可特镁铁-超镁铁质岩的地质特征、形成时代及构造意义. 硕士学位论文. 西安: 长安大学, 1-73 |
| [] | 冯益民, 何世平, 阎军.1994. 北祁连山中段早中奥陶世蛇绿岩中席状岩墙杂岩的发现及其地质意义. 地质论评 , 40 (3) :252–264. |
| [] | 付长垒, 闫臻, 郭现轻, 牛漫兰, 夏文静, 王宗起, 李继亮.2014. 拉脊山口蛇绿混杂岩中辉绿岩的地球化学特征及SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄. 岩石学报 , 30 (6) :1695–1706. |
| [] | 高山. 1989. 秦岭造山带及其邻区大陆地壳结构、成分与演化的地球化学研究. 博士学位论文. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 20-50 |
| [] | 高长林, 黄泽光, 叶德燎, 刘光祥, 吉让寿, 秦德余.2005. 中国早古生代三大古海洋及其对盆地的控制. 石油实验地质 , 27 (5) :439–448. |
| [] | 葛肖虹, 刘俊来.1999. 北祁连造山带的形成与背景. 地学前缘 , 6 (4) :223–230. |
| [] | 耿元生, 周喜文.2010. 阿拉善地区新元古代岩浆事件及其地质意义. 岩石矿物学杂志 , 29 (6) :779–795. |
| [] | 郭福祥.2001. 新疆古生代构造-生物古地理. 新疆地质 , 19 (1) :20–26. |
| [] | 郭现轻, 闫臻, 王宗起, 付长垒, 陈雷.2014. 山阳-柞水矿集区李家砭Ti-Fe矿床成矿构造背景研究. 岩石学报 , 30 (2) :437–450. |
| [] | 郝义. 2010. 华南加里东期构造变形特征和动力学机制. 硕士学位论文. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 1-66 |
| [] | 黄第藩.1966. 北祁连山东段北麓老君山群的研究. 地质论评 , 24 (1) :1–7. |
| [] | 霍福臣, 李永军. 1995. 西秦岭造山带的建造与地质演化. 西安: 西北大学出版社 : 1 -166. |
| [] | 姜春发, 杨经绥, 冯秉贵, 朱志直, 赵民, 柴耀楚, 施希德, 王怀达, 胡金庆. 1992. 昆仑开合构造. 北京: 地质出版社 : 1 -217. |
| [] | 姜耀辉, 芮行健, 贺菊瑞, 郭坤一, 杨万志.1999. 西昆仑山加里东期花岗岩类构造的类型及其大地构造意义. 岩石学报 , 15 (1) :105–115. |
| [] | 金松桥, 朱伟元, 左国朝.1985. 祁连山区晚古生代古地理变迁. 石油实验地质 , 7 (1) :38–46. |
| [] | 赖绍聪.1997. 秦岭造山带勉略缝合带超镁铁质岩的地球化学特征. 西北地质 , 18 (3) :36–45. |
| [] | 李才, 翟庆国, 董永胜, 曾庆高, 黄小鹏.2007. 青藏高原龙木错-双湖板块缝合带与羌塘古特提斯洋演化记录. 地质通报 , 26 (1) :13–21. |
| [] | 李怀坤, 陆松年, 赵风清, 于海峰, 郑健康.1999. 柴达木盆地北缘鱼卡河含柯石英榴辉岩的确定及其意义. 现代地质 , 13 (1) :43–50. |
| [] | 李继亮, 孙枢, 郝杰, 陈海泓, 侯泉林, 肖文交.1999. 论碰撞造山带的分类. 地质科学 , 34 (2) :129–138. |
| [] | 李锦轶, 张进, 曲军峰.2012. 华北与阿拉善两个古陆在早古生代晚期拼合——来自宁夏牛首山沉积岩系的证据. 地质论评 , 58 (2) :208–214. |
| [] | 李三忠, 杨朝, 赵淑娟, 李玺瑶, 郭玲莉, 余珊, 刘鑫, 索艳慧, 兰浩圆.2016a. 全球早古生代造山带(I): 碰撞型造山. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版) , 46 (4) :945–967. |
| [] | 李三忠, 杨朝, 赵淑娟, 李玺瑶, 索艳慧, 郭玲莉, 余珊, 戴黎明, 李少俊, 牟墩玲.2016b. 全球早古生代造山带(Ⅱ): 俯冲-增生型造山. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版) , 46 (4) :968–1004. |
| [] | 李三忠, 李玺瑶, 赵淑娟, 杨朝, 刘鑫, 郭玲莉, 王永明, 郝义, 张剑, 胡梦颖.2016c. 全球早古生代造山带(Ⅲ): 华南陆内造山. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版) , 46 (4) :1005–1025. |
| [] | 李三忠, 杨朝, 赵淑娟, 刘鑫, 余珊, 李玺瑶, 郭玲莉, 索艳慧, 戴黎明, 郭润华, 张国伟.2016d. 全球早古生代造山带(Ⅳ): 板块重建与Carolina超大陆. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版) , 46 (4) :1026–1041. |
| [] | 李涛, 赵淑娟, 李三忠, 余珊, 楼达, 索艳慧, 王学斌, 孙文军, 杨朝, 戴黎明.2015. 准噶尔盆地东北部逆冲推覆构造特征. 地质论评 , 61 (2) :356–366. |
| [] | 李文昌, 潘桂棠, 侯增谦, 莫宣学, 王立全. 2010. 西南"三江"多岛弧盆——碰撞造山成矿理论与勘查技术. 北京: 地质出版社 : 1 -461. |
| [] | 李向东. 1995. 库地北构造带及大地构造意义. 见: 李永安, 李向东, 孙东江, 韩玉玲编. 中国新疆西南部喀喇昆仑羌塘地块及康西瓦构造带构造演化. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆科技卫生出版社, 39-53 |
| [] | 李兴振, 潘桂棠, 罗建宁. 1990. 论三江地区冈瓦纳和劳亚大陆的分界. 见: 青藏高原地质文集编委会编. 青藏高原地质文集(20)——"三江"论文专辑. 北京: 地质出版社, 217-233 |
| [] | 李兴振, 许效松, 潘桂棠.1995. 泛华夏大陆群与东特提斯构造域演化. 岩相古地理 , 15 (4) :1–13. |
| [] | 李兴振, 尹福光.2002. 东昆仑与西昆仑地质构造对比研究之刍议. 地质通报 , 21 (11) :777–783. |
| [] | 李秀财, 牛漫兰, 闫臻, 笪梁超, 韩雨, 王玉.2015. 青海省乌兰县早古生代低压高温变质岩: 柴北缘存在双变质带?. 科学通报 , 60 (35) :3501–3513. |
| [] | 李永安, 李强, 张慧, 孙东江, 曹运动, 吴绍祖.1995. 塔里木及其周边古地磁研究与盆地形成演化. 新疆地质 , 13 (4) :293–378. |
| [] | 林宜慧, 张立飞, 季建清, 王乾杰, 宋述光.2010. 北祁连山九个泉硬柱石蓝片岩40Ar-39Ar年龄及其地质意义. 科学通报 , 55 (17) :1710–1716. |
| [] | 刘宝珺, 周名魁, 王汝植.1990. 中国南方早古生代古地理轮廓及构造演化. 中国地质科学院院报 , 20 (1) :97–98. |
| [] | 刘彬, 马昌前, 张金阳, 熊富浩, 黄坚, 蒋红安.2012. 东昆仑造山带东段早泥盆世侵入岩的成因及其对早古生代造山作用的指示. 岩石学报 , 28 (6) :1785–1807. |
| [] | 刘国惠, 张寿广, 游振东, 索书田, 张国伟. 1993. 秦岭造山带主要变质岩群及变质演化. 北京: 地质出版社 : 1 -190. |
| [] | 刘良, 陈丹玲, 王超, 张成立.2009. 阿尔金、柴北缘与北秦岭高压-超高压岩石年代学研究进展及其构造地质意义. 西北大学学报(自然科学版) , 39 (3) :472–479. |
| [] | 陆松年.2001. 从罗迪尼亚到冈瓦纳超大陆——对新元古代超大陆研究几个问题的思考. 地学前缘 , 8 (4) :441–448. |
| [] | 陆松年. 2002. 青藏高原北部前寒武纪地质初探. 北京: 地质出版社 : 1 -125. |
| [] | 陆松年, 李怀坤, 陈志宏, 等. 2003. 秦岭中-新元古代地质演化及对Rodinia超级大陆事件的响应. 北京: 地质出版社 : 1 -194. |
| [] | 潘桂棠, 陈智梁, 李兴振, 颜仰基, 许效松, 徐强, 江新胜, 吴应林, 罗建宁, 朱同兴, 彭勇民. 1997. 东特提斯地质构造形成演化. 北京: 地质出版社 : 65 -128. |
| [] | 潘桂棠, 朱弟成, 王立全, 廖忠礼, 耿全如, 江新胜.2004. 班公湖-怒江缝合带作为冈瓦纳大陆北界的地质地球物理证据. 地学前缘 , 11 (4) :371–382. |
| [] | 潘裕生.1989. 昆仑山区构造区划初探. 自然资源学报 , 4 (3) :196–203. |
| [] | 潘裕生.1994. 青藏高原第五缝合带的发现与论证. 地球物理学报 , 37 (2) :184–192. |
| [] | 潘裕生. 2000. 喀喇昆仑山-昆仑山地区地质演化. 北京: 科学出版社 : 1 -258. |
| [] | 曲晓明, 王瑞江, 辛洪波, 赵元艺, 樊兴涛.2009. 西藏西部与班公湖特提斯洋盆俯冲相关的火成岩年代学和地球化学. 地球化学 , 38 (6) :523–535. |
| [] | 曲晓明, 辛洪波, 赵元艺, 王瑞江, 樊兴涛.2010. 西藏班公湖中特提斯洋盆的打开时间: 镁铁质蛇绿岩地球化学与锆石U-Pb LAICPMS定年结果. 地学前缘 , 17 (3) :53–63. |
| [] | 任纪舜, 王作勋, 陈炳蔚. 2000. 1︰500万中国及邻区大地构造图. 北京: 地质出版社 . |
| [] | 舒良树, 于津海, 贾东, 王博, 沈渭洲, 张岳桥.2008. 华南东段早古生代造山带研究. 地质通报 , 27 (10) :1581–1593. |
| [] | 宋述光, 张聪, 李献华, 张立飞.2011. 柴北缘超高压带中锡铁山榴辉岩的变质时代. 岩石学报 , 27 (4) :1191–1197. |
| [] | 宋忠宝, 李智佩, 任有祥, 杨建国, 栗亚芝, 谢春林.2005. 北祁连山车路沟英安斑岩的年代学及地质意义. 地质科技情报 , 24 (3) :15–19. |
| [] | 孙立新, 白志达, 徐德斌, 李怀坤, 宋彪.2011. 西藏安多蛇绿岩中斜长花岗岩地球化学特征及锆石U-Pb SHRIMP年龄. 地质调查与研究 , 34 (1) :10–15. |
| [] | 孙雨. 2010. 东昆仑南缘布青山得力斯坦蛇绿岩地质特征、形成时代及构造环境研究. 硕士学位论文. 西安: 长安大学, 1-74 |
| [] | 汪玉珍, 方锡廉.1987. 西昆仑山、喀喇昆仑山花岗岩类时空分布规律的初步探讨. 新疆地质 , 5 (1) :9–24. |
| [] | 王惠初, 袁桂邦, 辛后田, 郝国杰, 郑健康, 张宝华.2001. 柴北缘绿梁山地区榴辉岩的产状及其成因意义初探. 中国地质 , 28 (7) :22–27. |
| [] | 王惠初, 陆松年, 莫宣学, 李怀坤, 辛后田.2005. 柴达木盆地北缘早古生代碰撞造山系统. 地质通报 , 24 (7) :603–612. |
| [] | 王炬川, 崔建堂, 罗乾周, 边小卫, 朱海平, 杨克俭, 彭海练, 王峰, 张汉甫, 林仕元, 葛双民, 马宗科.2006. 西昆仑康西瓦北侧蒙古包-普守原特提斯洋一分支小洋盆的发现及构造意义. 陕西地质 , 24 (2) :41–49. |
| [] | 王元龙, 王中刚, 李向东, 黄智龙.1995. 西昆仑加里东期花岗岩带的地质特征. 矿物学报 , 15 (4) :457–461. |
| [] | 王宗起, 闫全人, 闫臻, 王涛, 姜春发, 高联达, 李秋根, 陈隽璐, 张英利, 刘平, 谢春林, 向忠金.2009. 秦岭造山带主要大地构造单元的新划分. 地质学报 , 83 (11) :1527–1546. |
| [] | 吴涛, 江小均, 周海.2014. 东秦岭山阳-柞水盆地泥盆系"刘岭群"沉积构造及古流向特征研究. 长江大学学报(自然科学版) , 11 (10) :42–44. |
| [] | 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义. 1996. 北祁连山海相火山岩岩石成因. 北京: 地质出版社 : 1 -15. |
| [] | 向鼎璞.1982. 祁连山地质构造特征. 地质科学 (4) :364–370. |
| [] | 肖思云, 张维吉, 宋子季. 1988. 北秦岭变质地层. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社 : 1 -337. |
| [] | 肖序常, 陈国铭, 朱志直.1978. 祁连山古蛇绿岩带的地质构造意义. 地质学报 (4) :281–295. |
| [] | 肖序常, 汤耀庆, 高延林.1986. 再论青藏高原的板块构造. 中国地质科学院院报 (14) :7–19. |
| [] | 肖序常, 王军, 苏犁, 宋述光.2003. 再论西昆仑库地蛇绿岩及其构造意义. 地质通报 , 22 (10) :745–750. |
| [] | 熊莉娟. 2014. 原特提斯北界西段构造演化与拼合方式. 硕士学位论文. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 1-97 |
| [] | 徐强.1996. 东昆仑造山带早古生代沉积环境和盆地演化. 特提斯地质 (20) :85–101. |
| [] | 徐旭辉, 高长林, 江兴歌, 黄泽光, 朱建辉, 范小林, 刘光祥, 吉让寿. 2009. 中国含油气盆地动态分析概论. 北京: 石油工业出版社 : 1 -194. |
| [] | 许效松, 徐强, 潘桂棠, 刘巧红, 范影年, 何原相. 1996. 中国南大陆演化与全球古地理对比. 北京: 地质出版社 : 1 -161. |
| [] | 许效松, 刘宝珺, 牟传龙, 汪正江, 丘东洲. 2004. 中国中西部海相盆地分析与油气资源. 北京: 地质出版社 : 1 -230. |
| [] | 许志琴, 徐惠芬, 张建新, 李海兵, 朱志直, 曲景川, 陈代璋, 陈金禄, 杨开春.1994. 北祁连走廊南山加里东俯冲杂岩增生地体及其动力学. 地质学报 , 68 (1) :1–15. |
| [] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 吴才来, 李海兵, 张建新, 戚学祥, 宋述光, 万渝生, 陈文, 邱海峻.2003. 柴达木北缘超高压变质带形成与折返的时限及机制. 地质学报 , 77 (2) :163–176. |
| [] | 许志琴, 戚学祥, 杨经绥, 嵇少丞, 李海兵, 陈方远.2007. 西昆仑康西瓦韧性走滑剪切带的两类剪切指向、形成时限及其构造意义. 地质通报 , 26 (10) :1252–1261. |
| [] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李文昌, 李化启, 蔡志慧, 闫臻, 马昌前.2013. 青藏高原中的古特提斯体制与增生造山作用. 岩石学报 , 29 (6) :1847–1860. |
| [] | 闫全人, 王宗起, 闫臻, 王涛, 陈隽璐, 向忠金, 张宗清, 姜春发.2008. 秦岭造山带宽坪群中的变铁镁质岩的成因、时代及其构造意义. 地质通报 , 27 (9) :1475–1492. |
| [] | 闫臻, 王宗起, 王涛, 闫全人.2002. 西秦岭大草滩群的沉积环境及构造意义. 地质通报 , 21 (8-9) :505–515. |
| [] | 闫臻, 王宗起, 王涛, 闫全人, 肖文交, 李继亮, 韩芳林, 陈隽璐.2007. 秦岭造山带泥盆系形成构造环境:来自碎屑岩组成及地球化学方面的约束. 岩石学报 , 23 (5) :1023–1042. |
| [] | 闫臻, 王宗起, 陈隽璐, 闫全人, 王涛, 张英利.2009. 北秦岭武关地区丹凤群斜长角闪岩地球化学特征、锆石SHRIMP测年及其构造意义. 地质学报 , 83 (11) :1633–1646. |
| [] | 闫臻, 王宗起, 李继亮, 许志琴, 邓晋福.2012. 西秦岭楔的构造属性及其增生造山过程. 岩石学报 , 28 (6) :1808–1828. |
| [] | 杨朝, 赵淑娟, 李三忠, 余珊, 孙文军, 许立青, 刘鑫, 楼达, 王学斌, 李涛.2015. 准噶尔盆地东北缘乌伦古坳陷油气成藏的构造制约. 地质科学 , 50 (2) :536–552. |
| [] | 杨经绥, 许志琴, 李海兵, 吴才来, 崔军文, 张建新, 陈文.1998. 我国西部柴北缘地区发现榴辉岩. 科学通报 , 43 (14) :1544–1548. |
| [] | 杨经绥, 许志琴, 宋述光, 吴才来, 史仁灯, 张建新, 万渝生, 李海兵, 金小赤, JolivetM.2000. 青海都兰榴辉岩的发现及对中国中央造山带内高压-超高压变质带研究的意义. 地质学报 , 74 (2) :156–168. |
| [] | 杨经绥, 张建新, 孟繁聪, 史仁灯, 吴才来, 许志琴, 李海兵, 陈松永.2003. 中国西部柴北缘-阿尔金的超高压变质榴辉岩及其原岩性质探讨. 地学前缘 , 10 (3) :291–314. |
| [] | 杨经绥, 吴才来, 张建新, 许志琴.2005. 中央巨型超高压变质带和两期超高压变质作用的年代学证据. 科学中国人 (8) :47–52. |
| [] | 杨钊, 董云鹏, 柳小明, 张津海.2006. 西秦岭天水地区关子镇蛇绿岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年. 地质通报 , 25 (11) :1321–1325. |
| [] | 于海峰, 陆松年, 梅华林, 赵风清, 李怀坤, 李惠民.1999. 中国西部新元古代榴辉岩-花岗岩带和深层次韧性剪切带特征及其大陆再造意义. 岩石学报 , 15 (4) :532–538. |
| [] | 袁超, 周辉, 孙敏, 李继亮, 侯泉林.2000. 西昆仑山库地北岩体的地球化学特征及构造意义. 地球化学 , 29 (2) :101–107. |
| [] | 张贵宾, 宋述光, 张立飞, 牛耀龄, 舒桂明.2005. 柴北缘超高压变质带沙柳河蛇绿岩型地幔橄榄岩及其意义. 岩石学报 , 21 (4) :1049–1058. |
| [] | 张贵宾, 张立飞.2011. 柴北缘沙柳河地区洋壳超高压变质单元中异剥钙榴岩的发现及其地质意义. 地学前缘 , 18 (2) :151–157. |
| [] | 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 肖庆辉. 2001. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学. 北京: 科学出版社 : 1 -854. |
| [] | 张国伟, 董云鹏, 李三忠, 等. 2015. 秦岭勉略构造带与中国大陆构造. 北京: 科学出版社 : 1 -501. |
| [] | 张建新, 孟繁聪, MattinsonCG.2007. 南阿尔金-柴北缘高压-超高压变质带研究进展、问题及挑战. 高校地质学报 , 13 (3) :526–545. |
| [] | 张建新, 许志琴.1995. 北祁连中段加里东俯冲-增生杂岩/火山弧带及其变形特征. 地球学报 (2) :153–163. |
| [] | 张建新, 于胜尧, 李云帅, 喻星星, 林宜慧, 毛小红.2015. 原特提斯洋的俯冲、增生及闭合: 阿尔金-祁连-柴北缘造山系早古生代增生/碰撞造山作用. 岩石学报 , 31 (12) :3531–3554. |
| [] | 张旗, 周国庆. 2001. 中国蛇绿岩. 北京: 科学出版社 : 1 -182. |
| [] | 张寿广, 万渝生, 刘国惠, 丛日祥, 赵子然. 1991. 北秦岭宽坪群变质地质. 北京: 北京科学技术出版社 : 1 -119. |
| [] | 张雪亭, 吕惠庆, 陈正兴, 张宝华, 李福祥, 朱跃升, 李朝兰, 王彦.1999. 柴北缘造山带沙柳河地区榴辉岩相高压变质岩石的发现及初步研究. 青海地质 , 8 (2) :1–13. |
| [] | 张招崇, 周美付, RobinsonPT, 毛景文, 杨建民, 左国朝.2001. 北祁连山西段熬油沟蛇绿岩SHRIMP分析结果及其地质意义. 岩石学报 , 17 (2) :222–226. |
| [] | 赵凤清, 陆松年, 李怀坤. 2000. 柴达木地块达肯大坂杂岩中-新元古代花岗岩带的地球化学特征. 见: 第二届海峡两岸祁连山及邻区地学研讨会论文摘要. 北京: 95-97 |
| [] | 郑健康.1992. 东昆仑区域构造的发展演化. 青海地质 (1) :15–25. |
| [] | 钟大赉. 1998. 滇川西部古特提斯造山带. 北京: 科学出版社 : 1 -231. |
| [] | 庄儒新, 李峰.2006. 柴达木盆地北缘滩间山群火山岩及形成环境. 云南地质 , 25 (2) :209–217. |
 2016, Vol. 32
2016, Vol. 32

