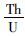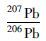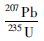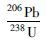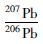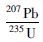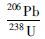华北克拉通是全球古老的克拉通之一(Liu et al., 1992; Rogers and Santosh, 2003; Zhai et al., 2005;万渝生等,2009a;翟明国,2010),由太古宙-古元古代变质基底和中、新元古代-显生宙沉积盖层组成。其中,新太古代变质岩石分布广泛,约占太古宙基底出露面积的85%,主要包括2.7~2.8Ga TTG片麻岩(Sun et al., 1994;Jahn et al., 1988,2008;Kröner et al., 1988;Liu et al., 2009;Diwu et al., 2010; Zhu et al., 2013),~2.5Ga的TTG片麻岩(劳子强和王世炎,1999;王凯怡等,2000;Guan et al., 2002;Zhao et al., 2002,2008a,b;Kröner et al., 2005b;田伟等,2005;陈斌等,2006;刘树文等, 2007,2011;郭丽爽等,2008;刘富等,2009;万渝生等,2009b;周艳艳等,2009;Diwu et al., 2011);2.5~2.6Ga同构造期花岗岩(刘建辉等,2011;刘树文等,2011;杨崇辉等,2011;张瑞英等,2012),以及各类经历~2.5Ga角闪岩相-麻粒岩相变质作用的表壳岩(Zhai et al., 2005;翟明国,2011)。关于华北克拉通的地壳生长和再造存在较大争议。早先大量研究认为~2.5Ga是华北地块最重要的大陆地壳生长时期(Windley,1995;Gao et al., 2004),并认为这是华北克拉通特殊性之所在。随着大量Nd、Hf同位素研究工作的开展,揭示华北克拉通同样发育2.7~3.0Ga的陆壳生长事件(Zhai,2004; Wu et al., 2005; Diwu et al., 2010;Jiang et al., 2010; Zhai and Santosh, 2011),即华北克拉通与全球主要的陆壳生长时期一致。Wang and Liu(2012)系统总结了华北克拉通前寒武纪下地壳岩石、沉积盖层、现代河流沉积物及新太古代同构造花岗岩等锆石Hf同位素特征,认为2.7~2.8Ga与2.5~2.6Ga的陆壳生长事件均存在于华北克拉通,2.7~2.8Ga岩浆事件和陆壳生长的范围比想象的更为广泛。一般认为,TTG成分岩石的大量出现代表了大陆地壳的生长事件,那么对华北克拉通广泛出露的TTG岩石的研究无疑会为上述争论的解决提供关键证据。此外,华北克拉通新太古代晚期~2.5Ga构造岩浆热事件广泛发育,目前对于这期岩浆热事件的性质主要有岛弧岩浆作用和板底垫托作用两种不同的认识,而二者所反映的不同构造意义对华北克拉通形成和演化的研究起着关键性的作用。
关于华北克拉通早前寒武纪陆壳生长的事件不仅在时限上存在争议(~2.7Ga与~2.5Ga两期构造-热事件),就其形成机制也存在较大争议(板块俯冲导致陆块的拼合或是地幔柱作用)。那么,对于华北克拉通~2.7Ga和~2.5Ga两期构造-热事件的时限、性质及相互间的演化关系的研究显得非常重要。TTG岩系是太古宙基底岩石的重要组成部分,在华北克拉通中部的中条山区广泛分布,包括~2.5Ga(田伟等,2005;郭丽爽等,2008)和~2.7Ga(Zhu et al., 2013)两期,但是对这两期岩浆事件的性质研究相对薄弱。因此,本研究选择位于中条地区的涑水杂岩中TTG片麻岩作为研究对象,在详细分析其主、微量元素地球化学特征和形成时代的基础上,结合Hf同位素研究来探索华北克拉通地壳形成和演化的规律,以期为探讨上述问题提供证据。
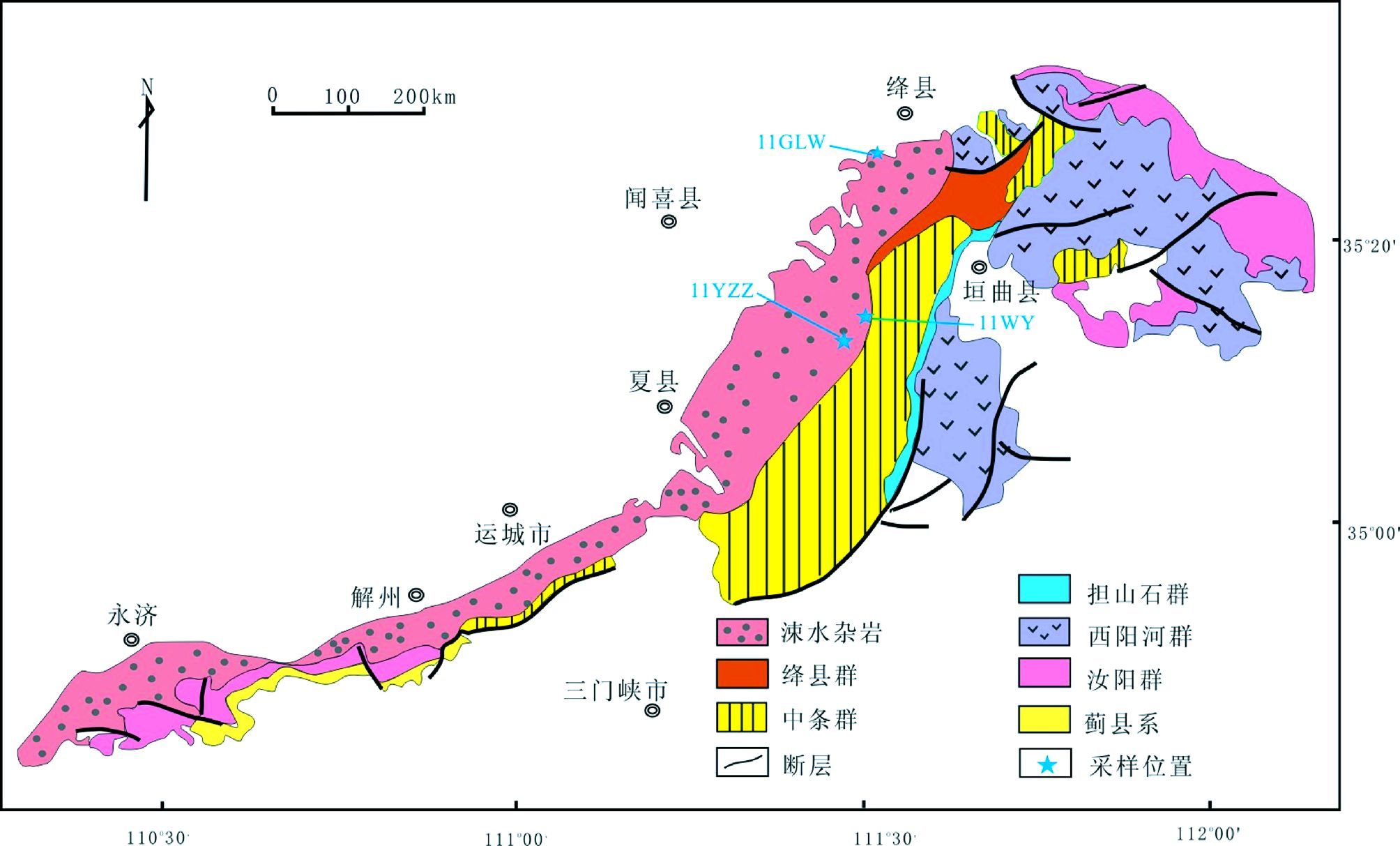
2 区域地质背景中条山前寒武纪杂岩位于华北克拉通的中南部,主要由涑水杂岩和上覆的古元古代绛县群、中条群、担山石群和中元古代西阳河群、汝阳群组成。其中涑水杂岩出露于中条山脉的西北侧,是该区最古老的岩石地质单元,分别与上覆的早、中元古界呈不整合接触关系(图 1)。涑水杂岩主要由变质的英云闪长岩-奥长花岗岩-花岗闪长岩(TTG)和钙碱性花岗质岩石组成,发育少量表壳岩和变质基性岩墙。古元古代绛县群由变泥质和变火山岩组成(李秋根等,2008);中条群主体为一套变质碳酸盐岩;担山石群则主要为一套变质碎屑岩(白瑾等,1997)。中元古代西阳河群是一套以未变质的双峰式火山岩为主体的沉积-火山岩系,与古元古代变质岩层为明显角度不整合接触(白瑾等,1997; He et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2012)。
|
图 1 中条山地区前寒武纪地质简图据(白瑾等,1997) Fig. 1 Geological sketch map of the Zhongtiao Mountain(revised after Bai et al., 1997) |
西姚和寨子TTG质片麻岩是涑水杂岩的重要组成部分。早期研究认为涑水杂岩中TTG岩系主要形成于新太古代-古元古代(孙大中和胡维兴,1993; 张兆琪等,2003)。近年来,随着锆石U-Pb年代学的广泛应用,获得了大量的年代学数据,基本确定了涑水杂岩中发育~2.7Ga和~2.5Ga两期TTG岩系。~2.5Ga TTG质片麻岩大多集中在涑水杂岩的东北部和中部,田伟等(2005)通过SHRIMP锆石U-Pb法获得寨子英云闪长质片麻岩的年龄为2560±6Ma;郭丽爽等(2008)获得西姚石英闪长质片麻岩的SHRIMP锆石207Pb/206Pb加权平均年龄为2536±8Ma。而~2.7Ga这一期TTG岩系主要发现于中条山西南段,赵斌等(2012)在中条山的西南段获得寨子-西姚片麻岩中2790±15Ma的古老继承锆石年龄;Zhu et al.(2013)获得涑水杂岩中TTG的侵位年龄为2.69~2.71Ga。除了上述两期强烈变形的TTG质片麻岩外,中条山地区还发育有新太古代的横岭关、解州花岗岩体(张瑞英等,2012)以及古元古代的北峪奥长花岗岩体(Yu et al., 2006)和烟庄钾质花岗岩体(张瑞英等,2012)等。
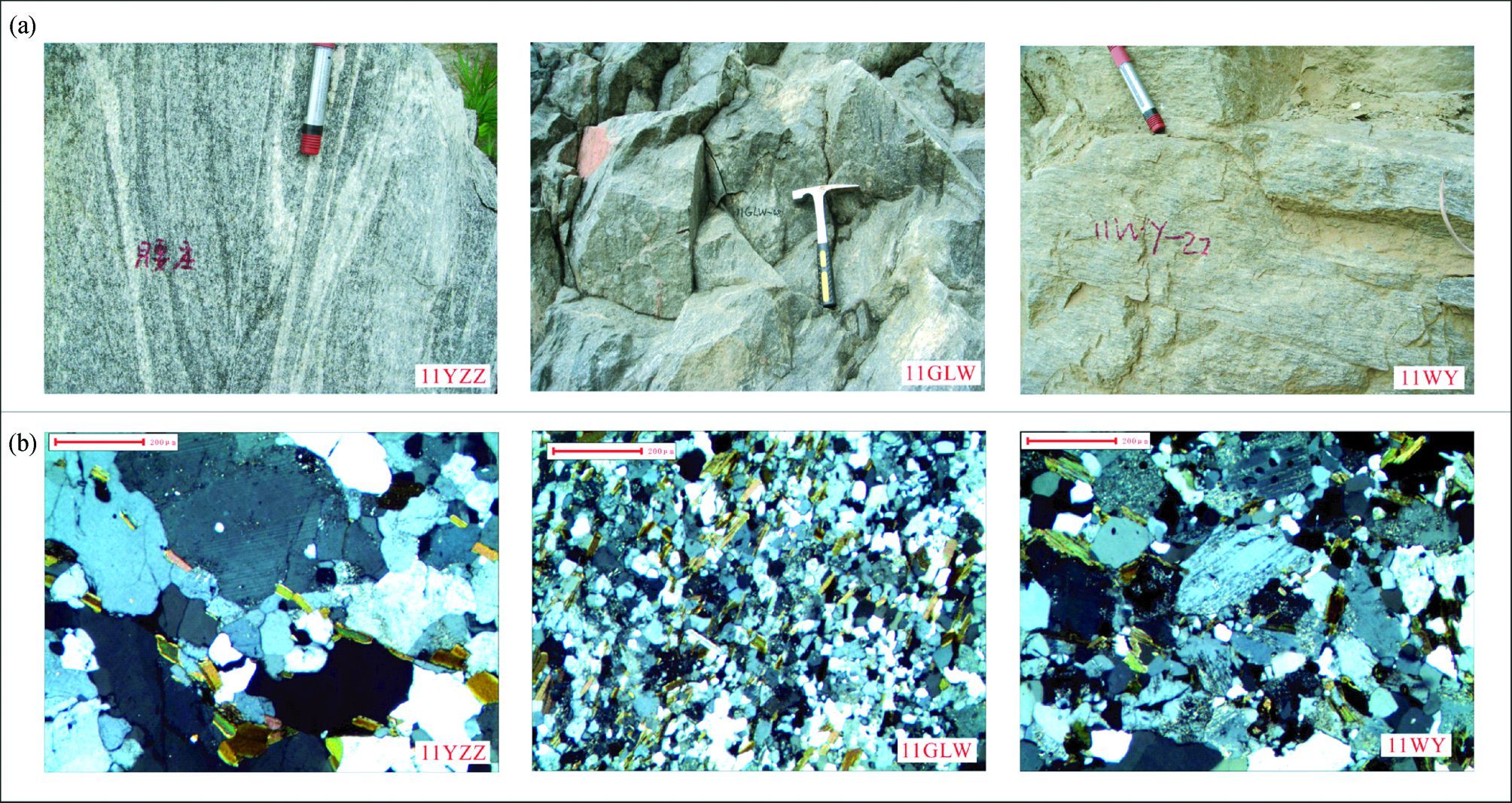
3 岩相学野外地质调查中采集了涑水杂岩中TTG质片麻岩年龄样品3件(11YZZ、11WY和11GLW),以及相应的地球化学样品6件。主要分布于涑水杂岩的东北部,具体采样位置见图 1。岩石露头(见图 2a)观察表明,寨子-西姚灰色片麻岩主体为黑云斜长片麻岩。岩石学特征:(1)样品11YZZ为西姚TTG片麻岩,取自垣曲县腰庄地区,岩石呈灰色,弱片麻状构造,局部发生混合岩化。主要矿物组合为斜长石(60%~65%)、石英(25%~30%)、黑云母(5%~10%)和少量角闪石(图 2b); 斜长石为更长石,可见聚片双晶发育,并且普遍发生绢云母化;石英呈他形粒状,可见波状消光现象,黑云母和角闪石定向排列构成片麻理,黑云母有一定程度的绿泥石化;该岩石具有鳞片粒状变晶结构。(2)样品11WY采自垣曲县瓦窑地区,属寨子TTG片麻岩。野外岩石新鲜面呈灰色或浅灰色,露头上,黑云斜长片麻岩局部具有条带状构造,与中条群呈角度不整合接触。岩石具有粒状变晶结构,主要由斜长石(55%~65%)、石英(~25%)、黑云母(10%~15%)和微量碱性长石组成(图 2b),副矿物有磁铁矿等。斜长石以半自形为主,发育聚片双晶,有微弱的绢云母化。黑云母以聚集条带状分布,呈弱定向。(3)样品11GLW取自绛县西南部的郭老凹地区,该处出露的片麻岩因表面风化成灰褐色,新鲜面为灰色。镜下观察,该岩石具有中粒花岗变晶结构,矿物组合为斜长石、石英、角闪石和黑云母。斜长石为半自形板状,聚片双晶发育,不同程度发生绢云母化,含量为60%~65%;石英均为他形粒状,含量为20%~25%;暗色矿物为黑云母和角闪石,其含量为5%~15%,多发生强烈的绿泥石化。
|
图 2 涑水杂岩中TTG质片麻岩的野外地质和镜下特征 Fig. 2 Field geological properties and photocrographs of the samples from the TTG gneisses of Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao Mountain |
选择新鲜的具有代表性的岩石样品进行地球化学分析。所有样品的主量、微量元素测试均在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室完成。主量元素测试是通过X射线荧光(Rigaku RIX 2100)玻璃熔饼法完成,分析精度优于2%。稀土和微量元素的分析是采用电感耦合等离子质谱(ICP-MS)法,在测试过程中每测10个分析样品加测一个QC标准,并在一批溶液分析中加测2个BHVO-2、AGV-2和1个BCR-2或其他国际标准物质,采用含量权重的线性拟合方式对样品进行最终的校正计算,相对误差一般小于2%~5%。
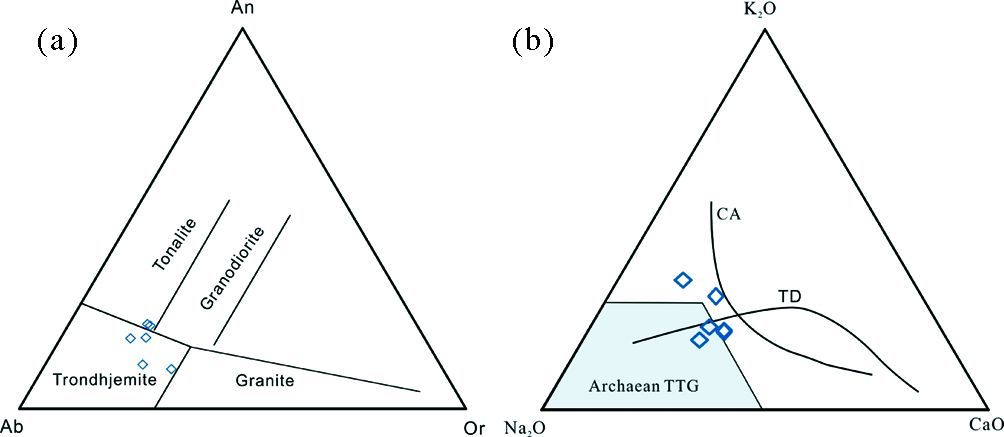
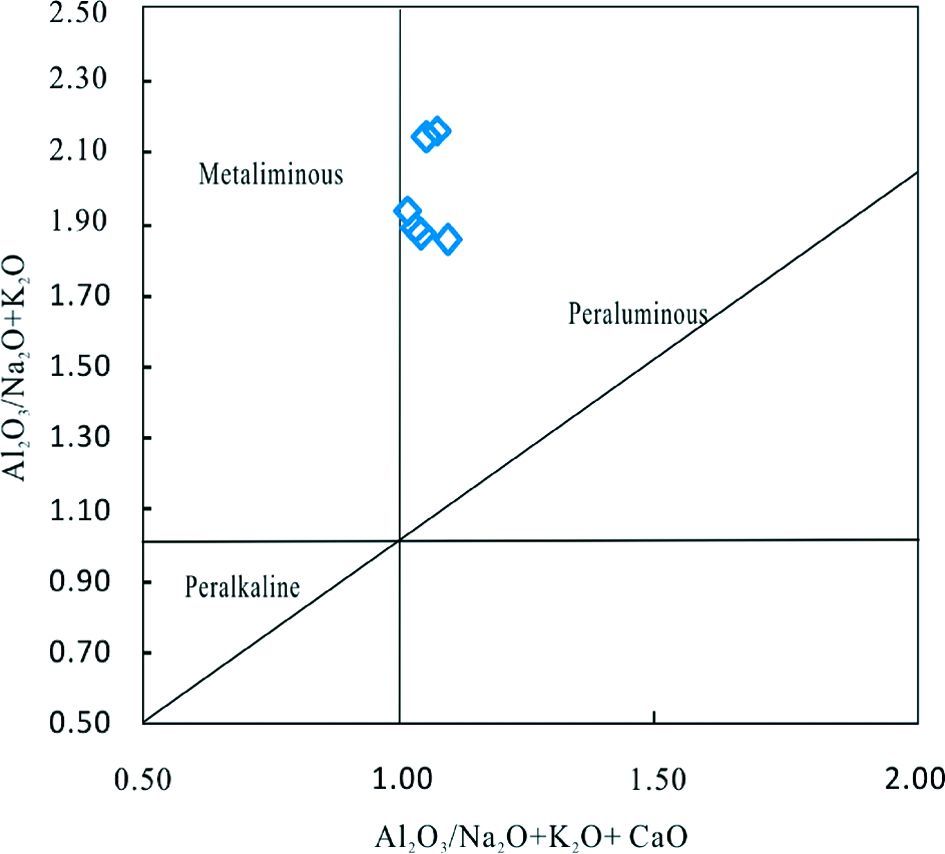
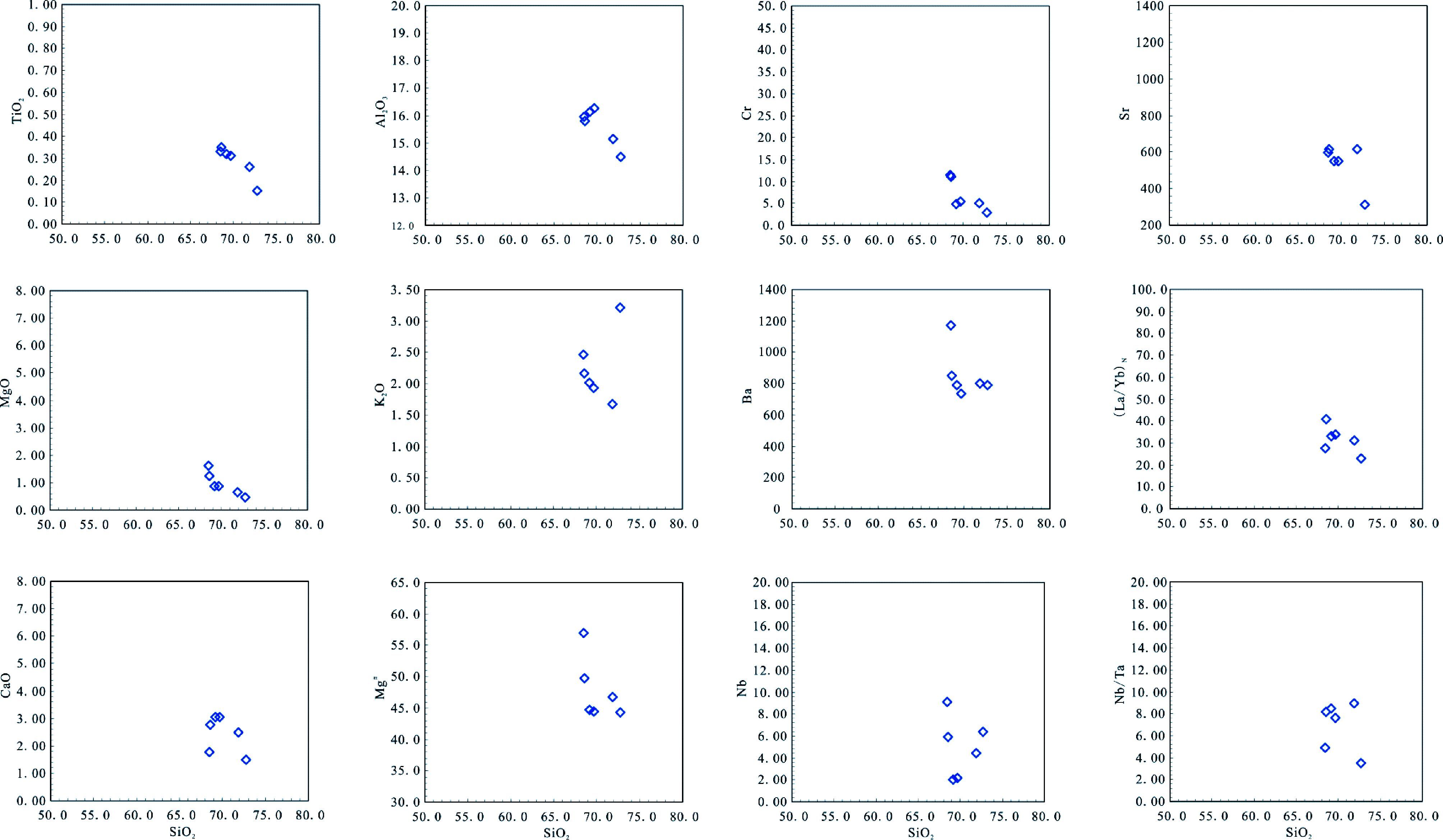
本次所采集的涑水杂岩中TTG片麻岩样品的SiO2含量均大于65%(见表 1)。根据标准矿物分子计算,样品在An-Ab-Or图解上(图 3a)基本都落在了TTG区域,并以奥长花岗质和英云闪长质片麻岩为主。在K-Na-Ca图解(图 3b)上,涑水杂岩中TTG岩石样品投点沿着奥长花岗岩趋势分布,部分样品显示钙碱性演化趋势。奥长花岗质片麻岩总体表现为高硅、富钠(SiO2=68.49%~72.73%,Na2O=4.76%~5.32%)低钾的特征,Na2O/K2O比值为1.48~2.98,均大于1。CaO含量介于1.49%~2.77%之间,Al2O3含量变化范围为14.49%~15.96%,铝饱和指数(A/CNK)为1.01~1.09,在铝饱和指数图解上(图 4)多数样品落于过铝质区域。Fe2O3/MgO比值范围是1.77~2.93,Mg#值大多数小于50,只有一个样品(11GLW-1)的Mg#稍大于50。英云闪长质片麻岩样品的SiO2含量为69.15%~69.71%,Na2O的含量为4.63%~4.64%,Na2O+K2O+CaO=9.61%~9.72%,Na2O/K2O比值都大于1,属于富钠质系列岩石;样品的Al2O3含量高(16.13%~16.25%),A/CNK=1.05~1.07,表现为过铝质的特点;Fe2O3/MgO比值范围是2.89~2.91,Mg#为44.5~44.7。另外,从TTG质片麻岩样品的Harker图解(图 5)可以看出,随着SiO2含量的增加,TiO2、Al2O3、MgO和CaO的含量相应地下降,与SiO2表现出相对较好的相关性,其符合单一母源岩浆结晶分异所产生的岩石系列的特征,说明这套岩石具有很好的亲缘性。
|
图 3 涑水杂岩中TTG质片麻岩An-Ab-Or分类图解(a,据Barker,1979)和K-Na-Ca图解(b,据Barker and Arth, 1976) Fig. 3 The classification diagram according to An-Ab-Or(a,after Barker,1979)and the K-Na-Ca diagram(b,after Barker and Arth, 1976)of the TTG gneisses of Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao Mountain |
|
|
表 1 中条山涑水杂岩中TTG质片麻岩的主量(wt%)、微量及稀土元素(×10-6)分析数据 Table 1 Major elements(wt%)and trace elements(×10-6)data of TTG genisses of Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao Mountain |
|
图 4 涑水杂岩中TTG质片麻岩的A/CNK-A/NK图解 Fig. 4 Plot of A/NK vs. A/CNK for the TTG gneisses of Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao Mountain |
|
图 5 涑水杂岩中TTG质片麻岩Harker图解 Fig. 5 Harker-type diagrams for the TTG gneisses of Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao Mountain |
研究区TTG质片麻岩的稀土元素总量(∑REE=69×10-6~143×10-6)较低。 La含量为16.6×10-6~33.0×10-6,而Yb含量很低(平均值为0.53×10-6);具有较高LREE/HREE比值(16.7~21.1)和(La/Yb)N值(22.9~40.8),体现出轻重稀土强烈分异的特点。(La/Sm)N =4.3~6.4,(Gd/Yb)N=2.2~3.3,说明样品的轻稀土元素富集且分馏程度大,而重稀土分馏程度一般,球粒陨石标准化的稀土配分图表现为右倾的曲线(图 6a)。大部分样品基本上无Eu异常,δEu=0.85~1.17。微量元素普遍具有以下特点:富集Sr(311×10-6~615×10-6)、Ba(736×10-6~1171×10-6)和Rb(42×10-6~110×10-6)等大离子亲石元素,亏损Cr(2.94×10-6~11.5×10-6)、Ni(2.22×10-6~8.43×10-6)等元素。在原始地幔标准化图解上(图 6b),Nb、Ti 、Ta等高场强元素表现为负异常,大离子亲石元素Rb、Ba、Sr等正异常。高场强元素Zr和Hf基本无异常,Zr/Hf比值为33~41,平均值约为38,和大洋中脊玄武岩及球粒陨石中的Zr/Hf比值接近(37±2,Davis et al., 2000)。这套TTG岩石的Sr/Y比值高(59~108),Rb/Sr比值低(0.08~0.35)。
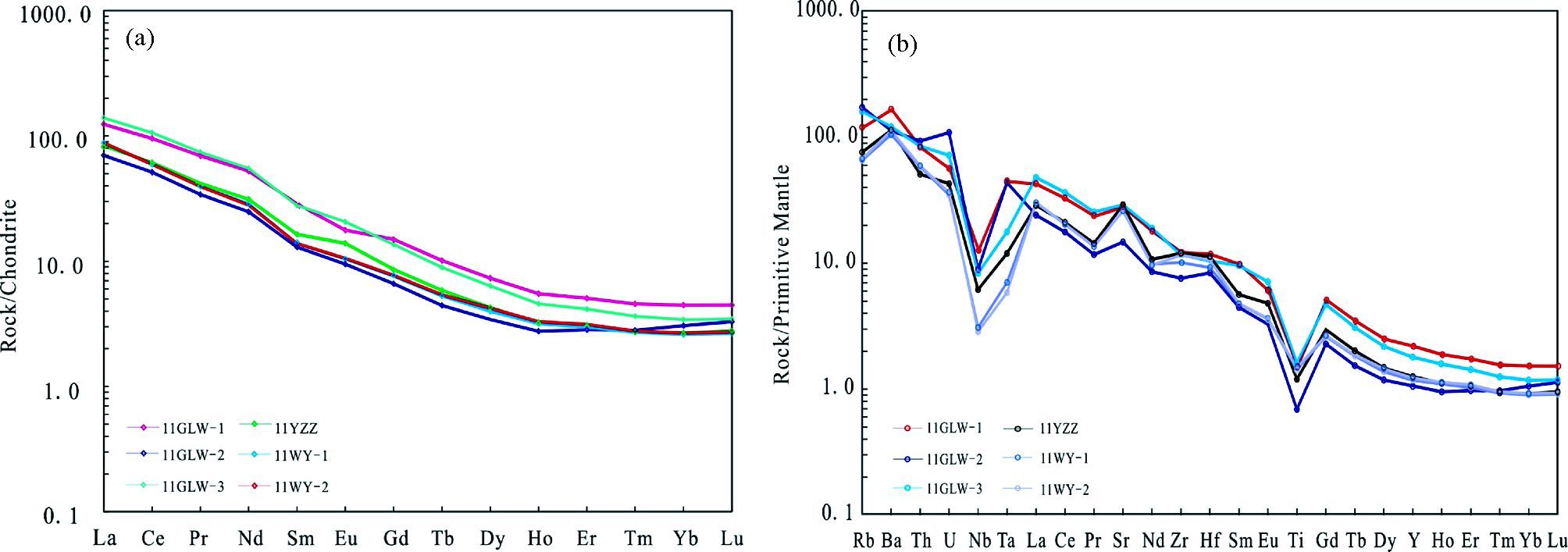
|
图 6 涑水杂岩中TTG质片麻岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图和原始地幔标准化微量元素配分图(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized trace element diagrams for the TTG gneisses of Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao Mountain(normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
锆石阴极发光(CL)图像的采集、 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年和原位Lu-Hf同位素测定都在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室完成。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年分析的详细方法、流程以及数据处理方法见参考文献(Yuan et al., 2004; 柳小明等,2007)。Lu-Hf同位素测定是采用英国Nu公司生产的Nu Plasma HR多接收器等离子体质谱仪,激光剥蚀系统为德国MicroLas公司生产的GeoLas200M;锆石原位Lu-Hf同位素测定用176Lu/175Lu=0.02669和176Yb/172Yb=0.5886进行同量异位干扰校正计算测定样品的176Lu/177Hf和176Hf/177Hf比值(Chu et al., 2002)。采用176Lu衰变常数为1.865×10-11a(Albarède et al., 2006)来计算εHf(t)值,球粒陨石现今的176Hf/177Hf=0.282772,176Lu/ 177Hf =0.0332(Bouvier et al., 2008);Hf亏损地幔模式年龄(tDM1)的计算采用现今的亏损地幔176Hf/177Hf=0.28325和176Lu/177Hf=0.0384(Vervoort et al., 1999)。单阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM)的计算是以亏损地幔为参考计算的,两阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM2)计算过程中,平均地壳的176Lu/ 177Hf比值为0.015(Rudnick and Gao, 2003)。
5.2 测试结果 5.2.1 锆石U-Pb测年结果对奥长花岗质片麻岩11YZZ和11GLW两件样品进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学研究。样品中的锆石大部分呈柱状,自形程度较好,粒度在0.1~0.2mm之间,多数锆石晶体干净透明,具有相对完整的晶形,少数锆石颗粒有裂纹。根据阴极发光(CL)图像显示,锆石基本上具有清晰的环带结构(图 7),样品11YZZ和11GLW的Th/U比值的变化范围分别为0.24~0.6和0.29~0.78,属于岩浆成因锆石(Belousova et al., 2002; Hoskin and Schaltegger, 2003)。样品11YZZ中多数锆石年龄数据点落在谐和线上,仅有几颗锆石发生轻微的铅丢失(图 8),LA-ICP-MS分析点数为24个,207Pb/206Pb年龄介于2500±33Ma~2615±34 Ma之间,其上交点年龄为2561±15Ma,加权平均年龄为2554±13Ma,二者在误差范围内一致。样品11GLW的25粒锆石LA-ICP-MS分析点207Pb/206Pb年龄在2493±33Ma~2582±33Ma之间(表 2),上交点年龄为2543±21Ma,加权平均年龄为2519±13Ma。从锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图(图 8)可以看出,该样品锆石多已发生了不同程度的铅丢失,并沿着不一致线分布。鉴于此样品铅丢失很严重,并且上交点年龄没有年龄点控制,导致年龄结果误差大。因此,采用奥长花岗质片麻岩样品11YZZ中锆石上交点年龄2561±11Ma代表岩浆的侵位年龄。
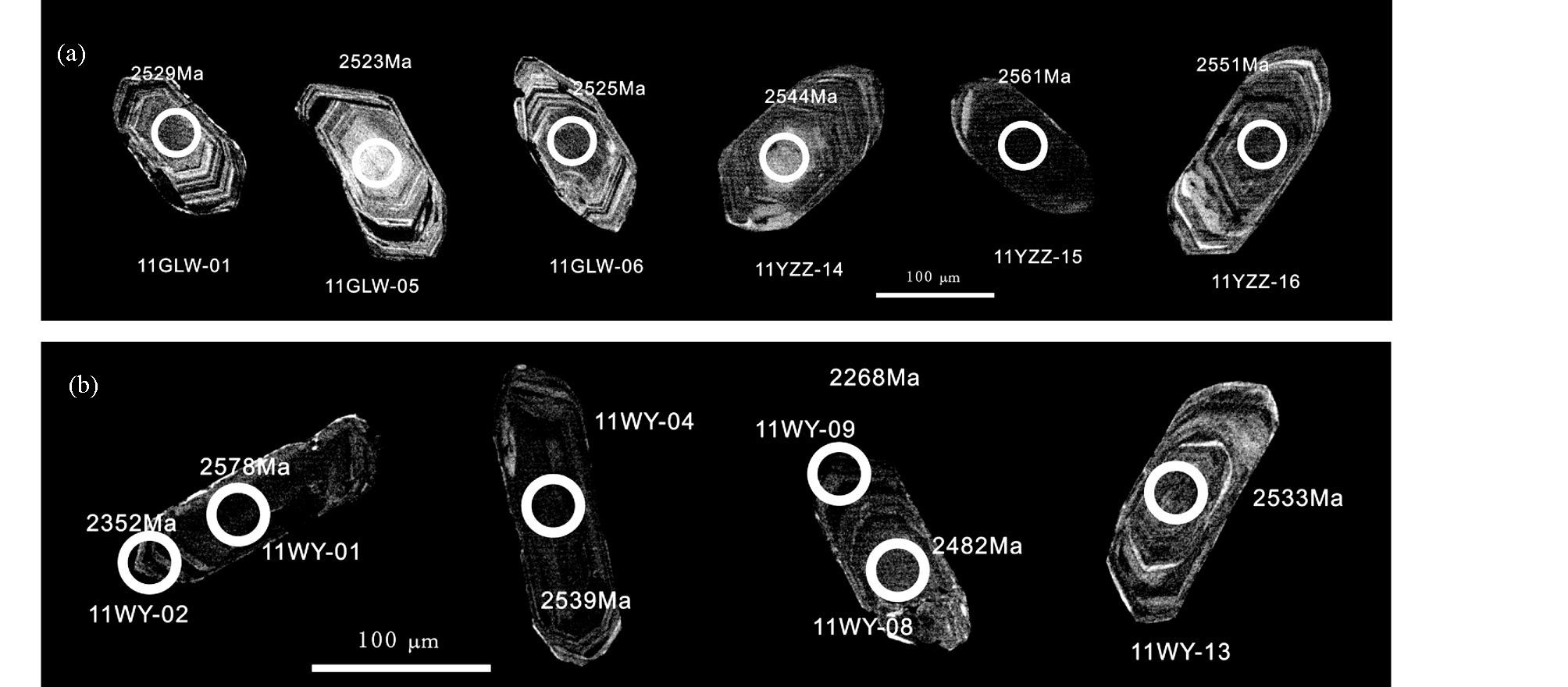
|
图 7 涑水杂岩中TTG质片麻岩锆石CL图像 (a)-奥长花岗质岩石;(b)-英云闪长质岩石.锆石年龄值为207Pb/206Pb年龄,单位为Ma;圆圈代表激光定年位置 Fig. 7 CL images of zircons from the TTG gneisses of Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao Mountain (a)-trondjemitic gneiss;(b)-tonalitic gneiss. The circles respresent the analytical spot by LA-ICPMS and corresponding 207Pb/206Pb ages |
|
|
表 2 中条山涑水杂岩中TTG质片麻岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果 Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating data of TTG genisses of Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao Mountain |
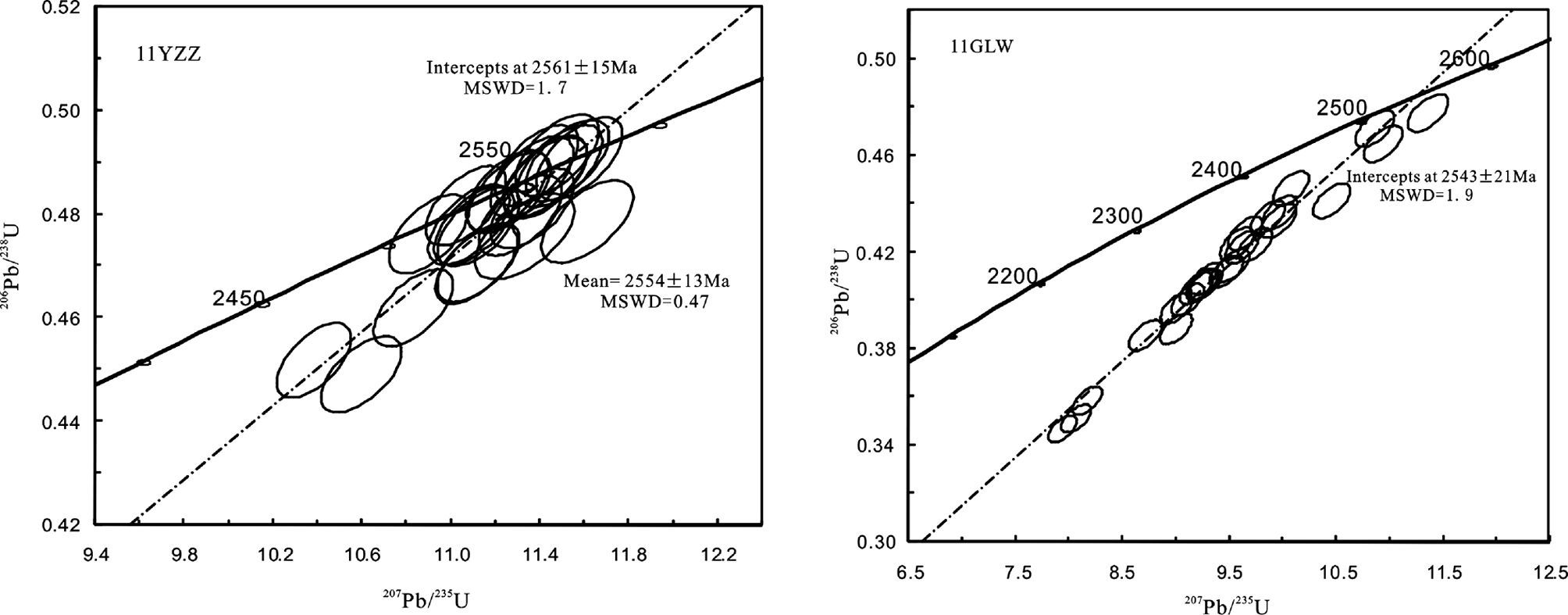
|
图 8 涑水杂岩中奥长花岗质片麻岩的锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图 Fig. 8 Concordia diagrams of LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating for samples from trondjemitic gneisses of Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao Mountain |
英云闪长质片麻岩样品11WY中多数锆石也具有清晰的韵律环带(图 7b),只有少量锆石具有核边结构(11WY-01,11WY-08);其锆石Th、U含量分别为32×10-6~462×10-6和201×10-6~1265×10-6,大部分锆石的Th/U比值大于或者接近于0.3,属于岩浆成因锆石Th/U比值范围。该样品的锆石LA-ICP-MS分析点数为20,其中有2个测试点位于锆石的边部区域,其余均位于核部。锆石U-Pb定年结果显示,207Pb/206Pb年龄分别为2268±34Ma~2352±34Ma和2460±34Ma~2589±34Ma之间(表 2)。根据锆石年龄谐和图(图 9),部分锆石U-Pb定年数据点沿着不一致线分布,选择其中位于谐和线上及其附近的16颗锆石计算所得的加权平均年龄为2537±22Ma,而上交点年龄为2553±21Ma。鉴于该岩石中锆石发生了较大程度的铅丢失,因此采用不一致线与谐和线的上交点年龄2553±21Ma代表英云闪长质片麻岩的形成时代。
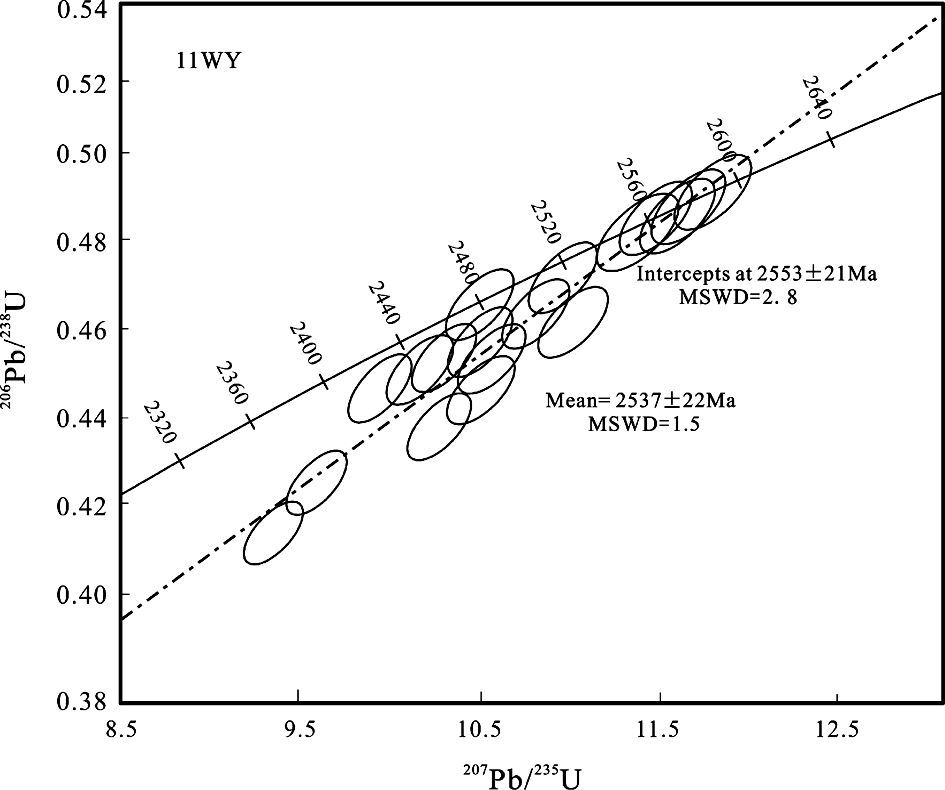
|
图 9 涑水杂岩中英云闪长质片麻岩的锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图 Fig. 9 Concordia diagrams of LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating for samples from tonalitic gneisses of Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao Mountain |
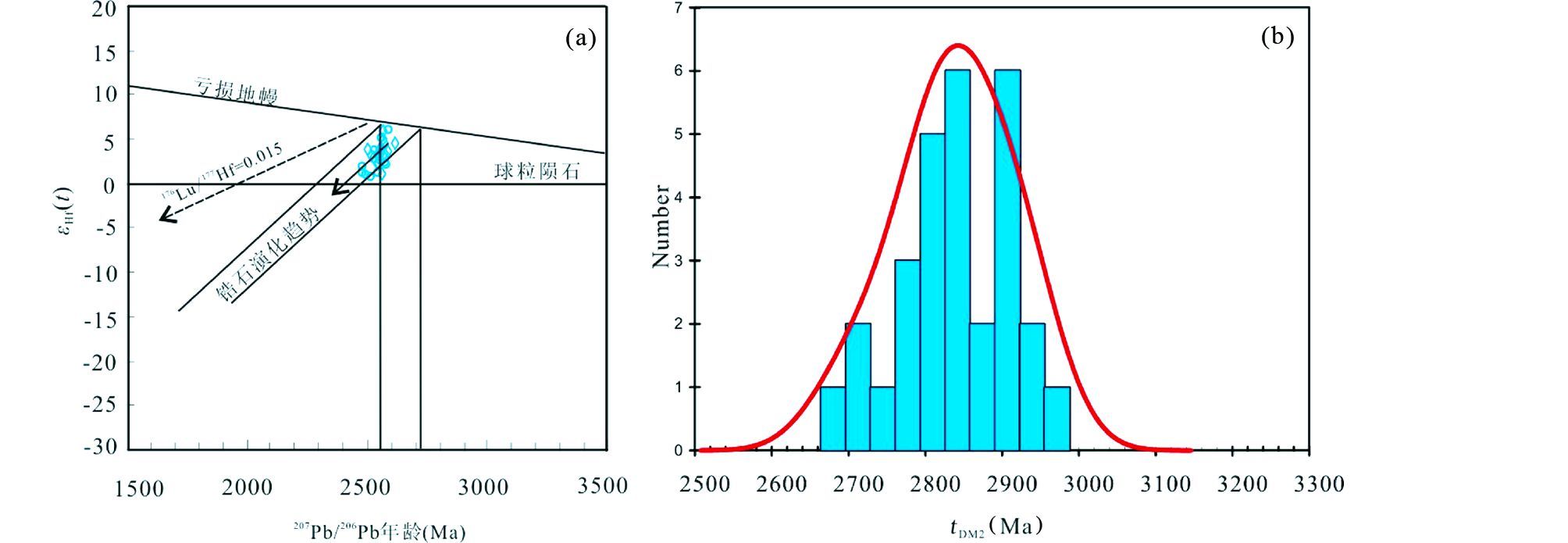
选择锆石U-Pb年龄较为谐和的TTG片麻岩样品11YZZ和11WY开展了锆石Hf同位素研究,考虑到样品中部分锆石发生了不同程度的铅丢失,故选择U-Pb年龄数据点落在谐和线上及其附近的锆石进行锆石原位Hf同位素分析。根据表 3,研究区奥长花岗岩中所有锆石的176Lu/177Hf比值均小于0.002,表明锆石在形成以后具有极低的放射性成因Hf的积累。奥长花岗质片麻岩中锆石176Hf/177Hf比值变化范围分别为0.281250~0.281343。用每个分析点锆石207Pb/206Pb年龄计算对应的εHf(t)值变化范围在+1.1~+6之间,均为正值。样品的两阶段模式年龄tDM2(CC)的变化范围是2682~2903Ma。对英云闪长质片麻岩样品11WY中10粒锆石进行Lu-Hf同位素分析,其176Hf/177Hf比值变化范围为0.281230~0.281319,同样用锆石单点207Pb/206Pb年龄计算对应的εHf(t),变化范围是 +0.9~+6.1,εHf(t)也都是正值,对应的两阶段模式年龄tDM2(CC)的变化范围是2696~2955Ma。
|
|
表 3 中条山涑水杂岩中TTG质片麻岩的锆石Hf同位素数据 Table 3 Lu-Hf isotopic compositions of TTG genisses of Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao Mountain |
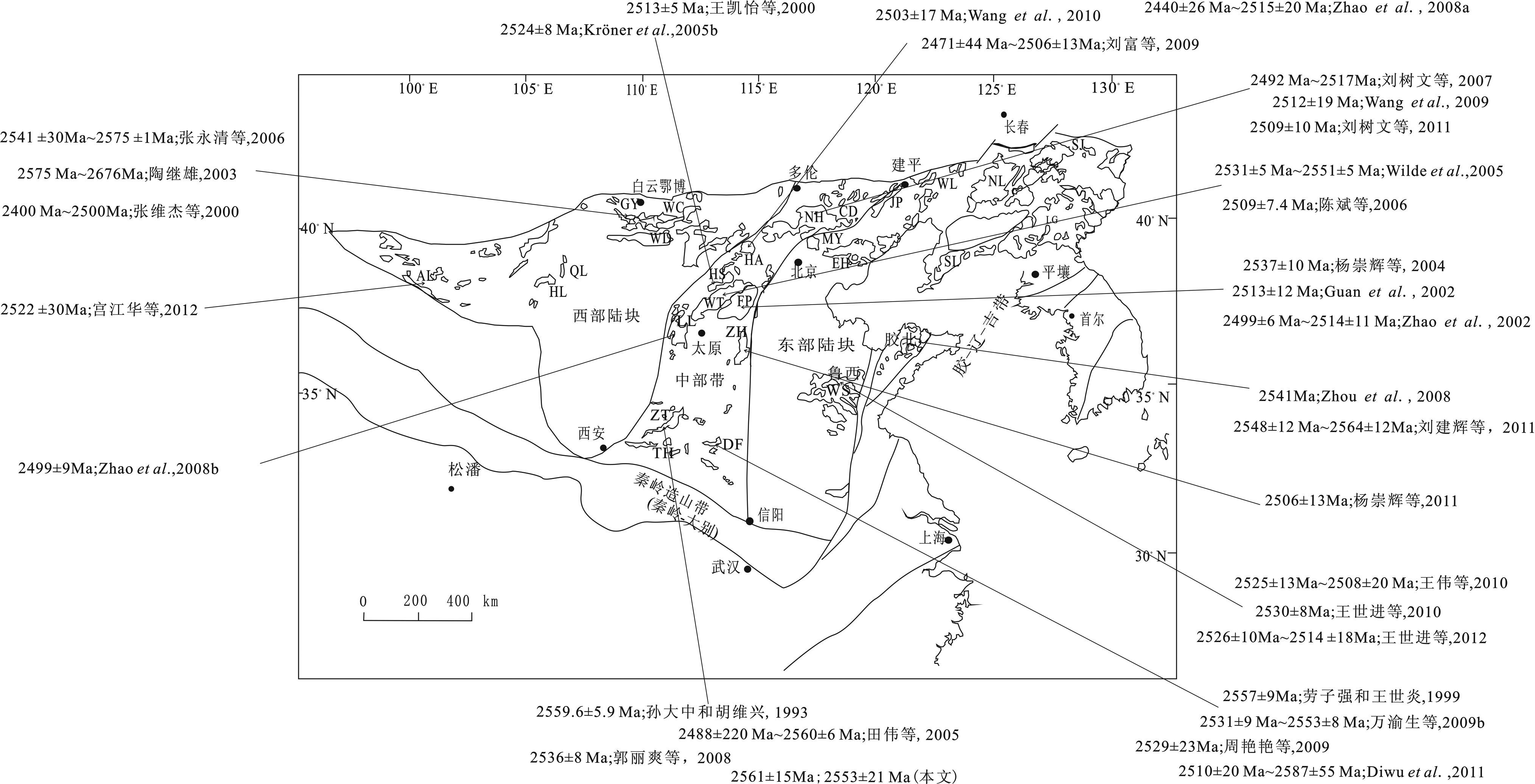
为研究华北克拉通~2.5Ga构造热事件的性质,本文总结了发育于华北~2.5Ga TTG岩石和花岗岩的代表性年龄数据。如图 10所示,华北克拉通在太古宙演化中以~2.5Ga构造岩浆热事件广泛发育为特点,其有别于其他克拉通普遍发育~2.7Ga构造热事件的特点。目前,对于这期岩浆热事件性质主要有岛弧岩浆作用和板底垫托作用两种观点。
就华北克拉通中部而言,从鲁山、嵩山、中条、赞皇、阜平-五台、恒山、怀安等地由南而北发育有大量的约2.5Ga变质侵入岩(图 10),其中TTG质片麻岩是主要的组成部分。出露于中部带南缘的太华、登封及中南部的涑水杂岩中的TTG质片麻岩,多被认为是新太古代岛弧体系下含水玄武质洋壳经部分熔融形成(田伟等,2005;林慈銮,2006;周艳艳等,2009),但登封地区早前寒武纪花岗质岩石成因解释为板底垫托作用(万渝生等,2009b)。位于中北部的恒山-五台-阜平杂岩的形成与板块俯冲有关的岛弧环境的认识基本一致(王凯怡等,2000; Zhao et al., 2000,2003; Kusky et al., 2001; Guan et al., 2002; Li et al., 2002; Kröner et al., 2005a,b; Wilde et al., 2005)。华北克拉通中部北缘的冀北、怀安、尚义等地区的前寒武纪变质杂岩中TTG岩系多被认为是形成于活动大陆边缘的构造背景(刘树文等, 2007,2011;刘富等,2009; 李孟江等,2012),而冀东新太古代表壳岩和花岗质岩石的成因也有学者认为与板底垫托作用有关(Geng et al., 2006; Yang et al., 2008)。如图 10,华北克拉通东部的鲁西、胶北等地区也出露有~2.5Ga TTG岩系。王世进等(2010)认为鲁西地区石门山TTG质花岗岩是地幔岩浆侵入混入地壳物质形成的。华北西部内蒙古地区发育~2.5Ga TTG质岩石为板块消减带之上的洋壳部分熔融的产物(张永清等,2006),而西阿拉善地区~2.5Ga TTG片麻岩被认为是来自于2.7~3.0Ga中-新太古代陆壳在新太古代末期的重熔再造(宫江华等,2012)。综上所述,可以看出,众多研究者一致肯定华北克拉通在新太古代晚期发生过广泛而强烈的构造-岩浆热事件,但其形成构造环境众说纷纭,很难达成一致。随着测试技术的进一步提升,在每个露头区深入细致的工作基础上,逐渐会使这个问题得到解决。
|
图 10 华北克拉通~2.5Ga构造岩浆热事件的分布图(据Zhao et al., 2001) Fig. 10 The distribution of ~2.5Ga tectono-magmatic hydrothermal events in North China Craton(revised after Zhao et al., 2001) |
TTG质岩系是太古宙地壳的主要组成部分,它是由含水的镁铁质岩石部分熔融形成的观点已基本得到认同。但究其构造环境,一些学者认为太古代TTG是现代埃达克岩的类似物,由俯冲的玄武质洋壳部分熔融产生,其广泛发育的根本原因是由于当时非常高的地热梯度,使得俯冲洋壳熔融更容易发生(Drummon and Defant, 1990; Drummon et al., 1996; Martin,1999; Foley et al., 2002; Martin et al., 2005)。另外一些学者主张TTG总体缺乏地幔组分贡献,与俯冲洋壳熔融无关,可能是由下地壳镁铁质岩石部分熔融产生(Smithies,2000; Condie,2005)。在中条山地区出露的涑水杂岩中2.5Ga TTG片麻岩具富Na,高Al和Sr,低Y、Cr、Ni含量的特点;稀土元素球粒陨石标准化曲线呈右倾,大部分样品基本上无Eu异常,说明残留相中并没有斜长石或者斜长石不是主要的残留矿物;根据岩石样品的微量元素配分图(图 6b),表现为富集Rb、Ba等大离子亲石元素,强烈亏损Nb、Ta等高场强元素,上述特点说明该套TTG岩系属于高铝型TTG。Mg#值大小可作为反映基性岩浆熔融过程是否受到地幔混染的标志,通常典型的大洋中脊玄武岩的Mg#<60(平均值为51),而由其部分熔融形成的熔体Mg#一般小于45(Rapp et al., 1999; Smithies,2000)。本研究区TTG片麻岩Mg#值变化范围是44.3~56.9,平均值为47.8,说明岩浆在形成或运移过程中可能有一定量的地幔组分的混染。但是这套TTG岩石所含Cr、Ni等相容元素含量均很低(Cr<11.5×10-6,Ni<8.43×10-6),并且A/CNK值较高,这与岛弧火山岩的特征不太相似,同时也说明地幔组分对该套TTG岩石的形成贡献很小,即其成因可能与俯冲洋壳熔融无关,我们认为研究区TTG片麻岩可能主要是地壳中已有镁铁质岩石发生部分熔融的产物。结合锆石的Lu-Hf同位素组成分析结果,由于部分锆石的Lu-Hf分析点接近亏损地幔演化线(图 11),说明可能也有少量地幔物质的加入。因此,推测涑水杂岩中~2.5Ga TTG岩石主要是由2.7~2.8Ga左右形成于下地壳的镁铁质岩石在新太古代末期发生分熔形成的,而非由俯冲的玄武质洋壳部分熔融所产生。
|
图 11 涑水杂岩中TTG质片麻岩锆石εHf(t)与年龄相关图和两阶段模式年龄tDM2直方图 Fig. 11 Plots of εHf(t)vs. 207Pb/206Pb ages of zircons for the TTG gneisses of Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao Mountain and corresponding relative probability plots of two-stage Hf model ages |
如图 10,TTG片麻岩并不是华北克拉通唯一记录新太古代末期岩浆热事件的岩石,华北也有大量的非TTG质花岗岩发育,如冀北地区发育2509±10Ma二长花岗岩(刘树文等,2011)和赞皇杂岩中菅等钾质花岗岩(杨崇辉等,2011)等,这里菅等钾质花岗岩具有同碰撞和后碰撞S型花岗岩的特征,是新生地壳在由挤压向伸展转换的构造背景下部分熔融所形成,标志着华北克拉通太古宙末期岩浆事件的结束以及稳定陆壳的形成(杨崇辉等,2011)。就中条山区而言,该地区不仅发育有2.7Ga和2.5Ga这两期TTG岩石,而且发育有~2.6Ga高钾钙碱性的横岭关和解州花岗岩体,其主要是由~2.7Ga TTG岩石和下地壳镁铁质岩石的部分熔融形成(张瑞英等,2012)。那么,上述在华北克拉通中部发育的一系列新太古代晚期花岗岩石和本文报道的~2.5Ga TTG质片麻岩研究结果,均表明此时华北中部并不存在大规模的俯冲作用,这或许也就说明华北克拉通在新太古代晚期已经基本成型。
6.2 华北克拉通~2.5Ga地壳再造事件全球不同克拉通的地壳生长是否呈幕式?现在依旧难于定论。Condie et al.(2005)对全球一些典型的沉积层和现代河流碎屑锆石的U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素的研究发现,在2.5Ga和1.65~1.4Ga期间大陆地壳也有显著的生长。Pietranik et al.(2008)认为全球大陆地壳在前寒武纪存在4个主要生长阶段,分别为4.4~4.5Ga、3.8Ga、3.4Ga和2.7~2.8Ga。 Iizuka et al.(2005)对密西西比河碎屑锆石的U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素研究表明,1.6~2.0Ga是年轻地壳物质形成的主要时期。
就我国华北、扬子克拉通的地壳生长特点分析,也曾有很多不同的报道。Liu et al.(2008)对扬子克拉通新元古代碎屑沉积岩中碎屑锆石的研究揭示,3.2~3.8Ga和720~910Ma是扬子克拉通地壳在前寒武纪期间的两个主要生长阶段。对于华北克拉通,根据目前报道的U-Pb年龄数据和Nd和Hf同位素资料(Zhai,2004; Wu et al., 2005; Yang et al., 2009 ; Jiang et al., 2010; 耿显雷等,2011;刘树文等,2011; Zhai and Santosh, 2011;宫江华等,2012),可以确定华北确实存在2.7~2.8Ga的地壳生长事件。但是~2.5Ga的岩浆事件的性质仍需进一步研究,即该事件代表的是地壳生长(刘富等,2009;Diwu et al., 2011;第五春荣等,2012)还是地壳再造?而对于这两期构造事件的形成机制(板块俯冲导致陆块的拼合或是地幔柱作用)也要进一步深究。
本研究区涑水杂岩中TTG片麻岩主体形成于2553~2561Ma。Lu-Hf同位素分析结果显示,锆石的εHf(t)值为正值。由于在壳幔分离过程中,最初岩浆从亏损地幔抽取形成玄武质的原始地壳时可能会有斜锆石结晶出来,而原始地壳在熔融形成长英质岩浆的过程中才可能结晶形成锆石(Wang et al., 2009),因此二阶段Hf模式年龄更能真实反映其源区物质从亏损地幔抽取的时间。本文中涑水杂岩中TTG片麻岩的两阶段模式年龄主要分布于2.7~2.8Ga之间(图 11)。锆石Hf同位素结果表明,该地区虽然并不排除具有新太古代末期新生地壳生长的可能,但结合其岩石成因,认为这套~2.5Ga TTG片麻岩可能主要是来自2.7~2.8Ga已有的下地壳镁铁质岩石在新太古代晚期的重熔再造,并不是一期主要的地壳生长事件。Zhu et al.(2013)在中条地区发现的2.7Ga TTG片麻岩中锆石Hf同位素组成表明该地区存在~2.7Ga的地壳生长事件,而本文~2.5Ga涑水杂岩中TTG片麻岩的形成反映的是初始基性地壳的熔融产生新的TTG成分岩浆岩的一期事件,我们认为,中条山区~2.5Ga岩浆事件代表着一期地壳再造事件。
7 结论(1) 涑水杂岩中TTG质片麻岩属于高铝TTG,形成于2553~2561Ma。
(2) 根据涑水杂岩中TTG质岩石地球化学证据,推测该套TTG质岩石主要是由下地壳已有古老镁铁质岩石在新太古代末期发生分熔形成的,可能有少量的地幔物质加入。结合同期发育大量花岗质岩石的事实,提出新太古代末期中条地区并不存在大规模的俯冲作用,这或许也说明华北克拉通在新太古代末期已经基本成型。
(3) 锆石Hf同位素证据表明,中条地区~2.5Ga岩浆事件代表一期重要的陆壳再造事件。
致谢 翟明国院士阅读全文并提出极富建设性的意见;三位匿名审稿人提出大量修改意见;在此一并表示诚挚的感谢。| [] | Albarède F, Scherer EE, Blichert-Toft J, et al. 2006. γ-ray irradiation in the early Solar System and the conundrum of the 176Lu decay constant. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(5): 1261–1270. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2005.09.027 |
| [] | Bai J, Yu ZX, Yan YY, et al. 1997. Precambrian Geology of Zhongtiaoshan. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Press: 1-143. |
| [] | Barker F, Arth JG. 1976. Generation of trondhjemitic-tonalitic liquids and Archean bimodal trondhjemite-basalt suites. Geology, 4(10): 596–600. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1976)4<596:GOTLAA>2.0.CO;2 |
| [] | Barker F. 1979. Trondhjemites: Definition, environment and hypotheses of origin. In: Barker F (ed.). Thondhiemites, Dacites and Related Rocks. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1-11 |
| [] | Belousova EA, Griffin WL, Suzanne Y, et al. 2002. Igneous zircon: Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 143(5): 602–622. DOI:10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7 |
| [] | Bouvier A, Vervoort JD, Patchett PJ. 2008. The Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotopic composition of CHUR: Constraints from unequilibrated chondrites and implications for the bulk composition of terrestrial planets. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 273(1-2): 48–57. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.06.010 |
| [] | Chen B, Liu SW, Geng YS, et al. 2006. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf isotopes and significance of the Late Archean-Paleoproterozoic granitoids from the Wutai-Luliang terrain, North China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(2): 296–304. |
| [] | Chu NC, Taylor RN, Chavagnac V, et al. 2002. Hf isotope ratio analysis using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: An evaluation of isobaric interference corrections. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 17(12): 1567–1574. DOI:10.1039/b206707b |
| [] | Condie KC. 2005. TTGs and adakites: Are they both slab melts?. Lithos, 80(1-4): 33–44. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2003.11.001 |
| [] | Condie KC, Beyer E, Belousova E, et al. 2005. U-Pb isotopic ages and Hf isotopic composition of single zircons: The search for juvenile Precambrian continental crust. Precambrian Research, 139(1-2): 42–100. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2005.04.006 |
| [] | Davis W, Hanmer S, Aspler L et al. 2000. Regional differences in the Neoarchean crustal evolution of the Western Churchill Province: Can we make sense of it? Geological Association of Canada Mineralogical Association of Canada Joint Annual Meeting, Calgaru |
| [] | Diwu CR, Sun Y, Lin CL, et al. 2010. LA-(MC)-ICPMS U-Pb zircon geochronology and Lu-Hf isotope compositions of the Taihua Complex on the southern margin of the North China Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(23): 2557–2571. DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-3273-6 |
| [] | Diwu CR, Sun Y, Guo AL, et al. 2011. Crustal growth in the North China Craton at ~2.5Ga: Evidence from in situ zircon U-Pb ages, Hf isotopes and whole-rock geochemistry of the Dengfeng complex. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 149–170. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.01.011 |
| [] | Diwu CR, Sun Y, Wang Q. 2012. The crustal growth and evolution of North China Craton: Revealed by Hf isotopes in detrital zircons from modern rivers. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(11): 3520–3530. |
| [] | Drummon MS, Defant MJ. 1990. A model for trondhjemite-tonalite-dacite genesis and crustal growth via slab melting: Archean to modern comparisons. Journal of Geophysical Research, 95(B13): 21503–21521. DOI:10.1029/JB095iB13p21503 |
| [] | Drummon MS, Defant MJ, Kepezhinskas PK. 1996. Petrogenesis of slab-derived trondhjemite-tonalite-dacite/adakite magmas. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences, 87(1-2): 205–215. DOI:10.1017/S0263593300006611 |
| [] | Foley S, Tiepolo M, Vannucci R. 2002. Growth of early continental crust controlled by melting of amphibolite in subduction zones. Nature, 417(6891): 837–840. DOI:10.1038/nature00799 |
| [] | Gao S, Rudnick RL, Yuan HL, et al. 2004. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China Craton. Nature, 432(7019): 892–897. DOI:10.1038/nature03162 |
| [] | Geng XL, Gao S, Chen C. 2011. Crustal growth of the eastern north China craton and Sulu orogen as revealed by U-Pb dating and Hf isotopes of detrital zircons from modern rivers. Earth Science, 36(3): 487–489. |
| [] | Geng YS, Liu FL, Yang CH. 2006. Magmatic event at the end of the Archean in eastern Hebei Province and its geological implication. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(6): 819–833. |
| [] | Gong JH, Zhang JX, Yu SY, et al. 2012. ~2.5Ga TTG rock in the Western Alashan massif and its geological significance. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(28-29): 2715–2728. |
| [] | Guan H, Sun M, Wilde SA, et al. 2002. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Fuping complex: Implications for formation and assembly of the North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 113(1-2): 1–18. DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(01)00197-8 |
| [] | Guo LS, Liu SW, Liu YL, et al. 2008. Zircon Hf isotopic features of TTG gneisses and formation environment of Precambrian Sushui complex in Zhongtiao mountains. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(1): 139–148. |
| [] | He YH, Zhao GC, Sun M, et al. 2008. Geochemistry, isotope systematics and petrogenesis of the volcanic rocks in the Zhongtiao Mountain: An alternative interpretation for the evolution of the southern margin of the North China Craton. Lithos, 102(1-2): 158–178. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.09.004 |
| [] | Hoskin PWO, Schaltegger U. 2003. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 27–62. DOI:10.2113/0530027 |
| [] | Iizuka T, Hirata T, Komiya T, et al. 2005. U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotope systematics of zircons from the Mississippi River sand: Implications for reworking and growth of continental crust. Geology, 33(6): 485–488. DOI:10.1130/G21427.1 |
| [] | Jahn BM, Auvray B, Shen QH, et al. 1988. Archean crustal evolution in China: The Taishan Complex, and evidence for juvenile crustal addition from long-term depleted mantle. Precambrian Research, 38(4): 381–403. DOI:10.1016/0301-9268(88)90035-6 |
| [] | Jahn BM, Liu DY, Wan YS, et al. 2008. Archean crustal evolution of the Jiaodong Peninsula, China, as revealed by zircon SHRIMP geochronology, elemental and Nd-isotope geochemistry. American Journal of Science, 308(3): 232–269. DOI:10.2475/03.2008.03 |
| [] | Jiang N, Guo JH, Zhai MG, et al. 2010. 2.7Ga crust growth in the North China craton. Precambrian Research, 179(1-4): 37–49. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2010.02.010 |
| [] | Kröner A, Compston W, Zhang GW, et al. 1988. Age and tectonic setting of Late Archean greenstone-gneiss terrain in Henan Province, China, as revealed by single-grain zircon dating. Geology, 16(3): 211–215. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0211:AATSOL>2.3.CO;2 |
| [] | Kröner A, Wilde SA, O’Brien PJ. 2005a. Field relationships, geochemistry, zircon ages and evolution of a Late Archaean to Palaeoproterozoic lower crustal section in the Hengshan Terrain of Northern China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(5): 605–629. |
| [] | Kröner A, Wilde S A, Li JH, et al. 2005b. Age and evolution of a Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic upper to lower crustal section in the Wutaishan/Hengshan/Fuping terrain of northern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 577–595. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.01.001 |
| [] | Kusky TM, Li JH, Tucker RT. 2001. The Archean Dongwanzi ophiolite complex, North China craton: 2.505-billion-year-old oceanic crust and mantle. Science, 292(5519): 1142–1145. DOI:10.1126/science.1059426 |
| [] | Lao ZQ, Wang SY. 1999. New advances in the study of the Dengfeng complex in the Songshan region, Henan Province. Regional Geology of China, 18(1): 9–16. |
| [] | Li JH, Kusky TM, Huang XN. 2002. Archaean podiform chromitites and mantle tectonites in ophiolitic melange, NCC: A record of early oceanic mantle processes. GSA Today, 12: 4–11. |
| [] | Li MJ, Wang RM, Zhang L. 2012. The genesis of Neoarchean TTG in the Shangyi area of the northern margin of North China Craton: Melt from basalt of oceanic crust at varying depth. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(5): 686–695. |
| [] | Li QG, Liu SW, Wang ZQ, et al. 2008. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology of the detrital zircons from the Jiangxian Group in the Zhongtiao Mountain and its tectonic significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(6): 1359–1368. |
| [] | Lin CL. 2006. Geochemistry, geochronology and tectonic settings of Archean gneisses in Lushan, Henan Province. Master Degree Thesis. Xi’an: Northwest University, 1-82(in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Liu CH, Zhao GC, Sun M, et al. 2012. U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotope geochemistry of detrital zircons from the Zhongtiao Complex: Constraints on the tectonic evolution of the Trans-North China Orogen. Precambrian Research, 222-223: 159–172. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2011.08.007 |
| [] | Liu DY, Nutman AP, Compston W, et al. 1992. Remnants of ≥3800Ma crust in the Chinese part of the Sino-Korean craton. Geology, 20(4): 339–342. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0339:ROMCIT>2.3.CO;2 |
| [] | Liu DY, Wilde SA, Wan SY, et al. 2009. Combined U-Pb, hafnium and oxygen isotope analysis of zircons from meta-igneous rocks in the southern North China Craton reveal multiple events in the Late Mesoarchean-Early Neoarchean. Chemical Geology, 261(1-2): 140–154. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.10.041 |
| [] | LiuF F, Guo JH, Lu XP, et al. 2009. Crustal growth at ~2.5Ga in the North China Craton: Evidence from whole-rock Nd and zircon Hf isotopes in the Huai’an gneiss terrane. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(17): 2517–2526. |
| [] | Liu JH, Liu FL, Liu PH, et al. 2011. Polyphase magmatic and metamorphic events from Early Precambrian metamorphic basement in Jiaobei area: Evidences from the zircon U-Pb dating of TTG and granitic gneisses. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(4): 943–960. |
| [] | Liu SW, Lü YJ, Feng YG, et al. 2007. Geology and zircon U-Pb isotopic chronology of Dantazi complex, northern Hebei Province. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13(3): 484–497. |
| [] | LiuS SW, Lü YJ, Wang W, et al. 2011. Petrogenesis of the Neoarchean granitoid gneisses in northern Hebei Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(4): 909–921. |
| [] | Liu XM, Gao S, Diwu CR, et al. 2007. In situ LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and trace element determination of the single grain zircon with 20μm beam diameter. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(2): 228–235. |
| [] | Liu XM, Gao S, Diwu CR, et al. 2008. Precambrian crustal growth of Yangtze craton as revealed by detrital zircon studies. American Journal of Science, 308(4): 421–468. DOI:10.2475/04.2008.02 |
| [] | Martin H. 1999. Adakitic magmas: Modern analogues of Archaean granitoids. Lithos, 46(3): 411–429. DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00076-0 |
| [] | Martin H, Smithies RH, Rapp R, et al. 2005. An overview of adakite, tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG) and sanukitoid: Relationships and some implications for crustal evolution. Lithos, 79(1-2): 1–24. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.04.048 |
| [] | Pietranik AB, Hawkesworth CJ, Storey CD, et al. 2008. Episodic, mafic crust formation from 4.5 to 2.8 Ga: New evidence from detrital zircons, Slave craton, Canada. Geology, 36(11): 875–878. DOI:10.1130/G24861A.1 |
| [] | Rapp RP, Shimizu N, Norman MD, et al. 1999. Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge: Experimental constraints at 3.8Gpa. Chemical Geology, 160(4): 335–356. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00106-0 |
| [] | Rogers JJW, Santosh M. 2003. Supercontinents in Earth history. Gondwana Research, 6(3): 357–368. DOI:10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70993-X |
| [] | Rudnick RL and Gao S. 2003. Composition of the Continental Crust. In: Holland HD and Turekian KK (eds.), Treatise on Geochemistry. Oxford: Pergamon, 1-64 |
| [] | Smithies RH. 2000. The Archean tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG) series is not an analogue of Cenozoic adakite. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 182(1): 115–125. DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00236-3 |
| [] | Sun DZ, Hu WX. 1993. The Geochronological Framework and Crustal Structures of Precambrian Basement in the Zhongtiao Area. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-107. |
| [] | Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345 |
| [] | Sun Y, Yu ZP, Kröner A. 1994. Geochemistry and single zircon geochronology of Archaean TTG gneisses in the Taihua high-grade terrain, Lushan area, central China. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 10(3-4): 227–233. DOI:10.1016/0743-9547(94)90022-1 |
| [] | Tao JX. 2003. Characteristics of Neoarchean metamorphic intrusives and the relationship with the mineralization of gold in Guyang region, Inner Mongolia. Geological Survey and Research, 26(1): 21–25. |
| [] | Tian W, Liu SW, Liu CH, et al. 2005. Zircon SHRIMP geochronology and geochemical of TTG rocks in Shushui Complex from Zhongtiao Mountains with its geological implication. Progress in Natural Science, 15(12): 1476–1484. |
| [] | Vervoort JD, Patchett PJ, Blichert-Toft J, et al. 1999. Relationships between Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotopic systems in the global sedimentary system. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 168(1-2): 79–99. DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00047-3 |
| [] | Wan YS, Liu DY, Dong CY, et al. 2009a. The oldest rocks and zircons in China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(8): 1793–1807. |
| [] | Wan YS, Liu DY, Wang SY, et al. 2009b. Early Precambrian crustal evolution in the Dengfeng area, Henan Province (eastern China): Constraints from geochemistry and SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(7): 982–999. |
| [] | Wang AD, Liu YC. 2012. Neoarchean (2.5~2.8Ga) crustal growth of the North China Craton revealed by zircon Hf isotope: A synthesis. Geosci. Front., 3(2): 147–173. DOI:10.1016/j.gsf.2011.10.006 |
| [] | Wang CY, Campbell IH, Allen CM, et al. 2009. Rate of growth of the preserved North American continental crust: Evidence from Hf and O isotopes in Mississippi detrital zircons. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(3): 712–728. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2008.10.037 |
| [] | Wang J, Wu YB, Gao S, et al. 2010. Zircon U-Pb and trace element data from rocks of the Huai’an Complex: New insights into the late Paleoproterozoic collision between the Eastern and Western Blocks of the North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 178(1-4): 59–71. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2010.01.007 |
| [] | Wang KY, Hao J, Wilde S, et al. 2000. Reconsideration of some key geological problems of Late Archaean-Early Proterozoic in the Wutaishan-Hengshan area: Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon data. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 35(2): 175–184. |
| [] | Wang RM, Wan YS, Cheng SH, et al. 2009. Modern-style subduction processes in the Archean: Evidence from the Shangyi complex in North China Craton. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(3): 535–543. DOI:10.1111/j.1755-6724.2009.00055.x |
| [] | Wang SJ, Wan YS, Wang W, et al. 2010. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating and the forming age of Shimenshan-Fengxianshan rock in western Shandong. Land and Resources in Shandong Province, 26(9): 1–6. |
| [] | Wang SJ, Wan YS, Yang EX, et al. 2012. Mid-Neoarchean magmatism in western Shandong Province: Evidence of zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating in Xinfushan and Shanggang rock. Shandong Land and Resources, 28(4): 1–7. |
| [] | Wang W, Wang SJ, Dong CY, et al. 2010. SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircons from Neoarchean crustal derived granites in the Lushan area, Shandong, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(7): 993–1000. |
| [] | Wilde SA, Cawood PA, Wang KY, et al. 2005. Granitoid evolution in the Late Archean Wutai Complex, North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 597–613. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.11.006 |
| [] | Windley BF. 1995. The Evolving Continents. 3rd Edition. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons: 1–526. |
| [] | Wu FY, Zhao GC, Wilde SA, et al. 2005. Nd isotopic constraints on crustal formation in the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 523–545. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.10.011 |
| [] | Yang CH, Du LL, Wan YS, et al. 2004. SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb chronology of tonalitic gneiss in Banqiaogou Area, Pingshan County, Hebei Province. Geological Journal of China Universities, 10(4): 514–522. |
| [] | Yang CH, Du LL, Ren LD, et al. 2011. Petrogenesis and geodynamic setting of Jiandeng potassic granite at the end of the Neoarchean in Zanhuang Complex, North China Craton. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(2): 62–78. |
| [] | Yang J, Gao S, Chen C, et al. 2009. Episodic crustal growth of North China as revealed by U-Pb age and Hf isotopes of detrital zircons from modern rivers. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(9): 2660–2673. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2009.02.007 |
| [] | Yang JH, Wu FY, Wilde SA, et al. 2008. Petrogenesis and geodynamics of Late Archean magmatism in eastern Hebei, eastern North China Craton: Geochronological, geochemical and Nd-Hf isotopic evidence. Precambrian Research, 167(1-2): 125–149. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2008.07.004 |
| [] | Yu SQ, Liu SW, Tian W, et al. 2006. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb chronology and geochemistry of the Henglingguan and Beiyu granitoids in the Zhongtiao Mountains, Shanxi Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(6): 912–924. |
| [] | Yuan HL, Gao S, Liu XM, et al. 2004. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 28(3): 353–370. DOI:10.1111/ggr.2004.28.issue-3 |
| [] | Zhai MG. 2004. Precambrian tectonic evolution of the North China Craton. In:[D] Malpas J, Fletcher CJN, Ali JR et al. (eds.). Tectonic Evolution of China. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 226: 57–72. |
| [] | Zhai MG, Guo JH, Liu WJ. 2005. Neoarchean to Paleoproterozoic continental evolution and tectonic history of the North China Craton: A review. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 547–561. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.01.018 |
| [] | Zhai MG. 2010. Tectonic evolution and metallogenesis of North China Craton. Mineral Deposits, 29(1): 24–36. |
| [] | Zhai MG. 2011. Cratonization and the Ancient North China Continent: A summary and review. Science China (Earth Sciences), 54(8): 1110–1120. DOI:10.1007/s11430-011-4250-x |
| [] | Zhai MG, Santosh M. 2011. The Early Precambrian odyssey of the North China Craton: A synoptic overview. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 6–25. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.02.005 |
| [] | Zhang WJ, Li L, Geng MS. 2000. Petrology and dating of Neo-archaean intrusive rocks from Guyang area, Inner Mongolia. Earth Science, 25(3): 221–226. |
| [] | Zhang RY, Zhang CL, Diwu CR, et al. 2012. Zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and its geological implications for the Precambrian granitoids in Zhongtiao Mountains, Shanxi Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(11): 3559–3573. |
| [] | Zhang YQ, Zhang YK, Zheng BJ, et al. 2006. Geological character and significance of adakite and TTG in Xiaonangou-Mingxinggou district in central of inner Mongolia. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(11): 2762–2768. |
| [] | Zhang ZQ, Xue WY, Chai JZ, et al. 2003. Features of the basement rocks in south-western part of Zhongtiao Mountains. Geological Survey and Research, 26(4): 193–199. |
| [] | Zhao B, Wang DH, Hou KJ, et al. 2012. Isochronology study on Sushui Complex in Zhongtiao Mountains and its geological significance. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 34(1): 1–8. |
| [] | Zhao GC, Cawood PA, Wilde SA, et al. 2000. Metamorphism of basement rocks in the central zone of the North China Craton: Implications for Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution. Precambrian Research, 103(1-2): 55–88. DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00076-0 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Cawood PA, et al. 2001. Archean blocks and their boundaries in the North China Craton: Lithological, geochemical, structural and P-T path constraints and tectonic evolution. Precambrian Research, 107(1-2): 45–73. DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00154-6 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Cawood PA, et al. 2002. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages of the Fuping complex: Implications for late archean to paleoproterozoic accretion and assembly of the North China Craton. Am. J. Sci., 302(3): 191–226. DOI:10.2475/ajs.302.3.191 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA. 2003. Major tectonic units of the North China Craton and their Paleoproterozoic assembly. Science in China (Series D), 46(1): 23–38. DOI:10.1360/03yd9003 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Sun M, et al. 2008a. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Huai’an complex: Constraints on late Archean to Paleoproterozoic magmatic and metamorphic events in the Trans-North China Orogen. American Journal of Science, 308(3): 270–303. DOI:10.2475/03.2008.04 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Sun M, et al. 2008b. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages of granitoid rocks in the Lüliang Complex: Implications for the accretion and evolution of the Trans-North China Orogen. Precambrian Research, 160(3-4): 213–226. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.07.004 |
| [] | Zhou JB, Wilde SA, Zhao GC, et al. 2008. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of the Neoproterozoic Penglai Group and Archean gneisses from the Jiaobei Terrane, North China, and their tectonic implications. Precambrian Research, 160(3-4): 323–340. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.08.004 |
| [] | Zhou YY, Zhao TP, Xue LW, et al. 2009. Petrological, geochemical and chronological constraints for the origin and geological significance of Neoarchean TTG gneiss in the Songshan area, North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(2): 331–347. |
| [] | Zhu XY, Zhai MG, Chen FK, et al. 2013. ~2.7Ga crustal growth in the North China Craton: Evidence from zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of the Sushui Complex in the Zhongtiao terrane. The Journal of Geology, 121(3): 239–254. DOI:10.1086/669977 |
| [] | 白瑾, 余致信, 颜耀阳, 等. 1997. 中条山前寒武纪地质. 天津: 天津科学技术出版社: 1-143. |
| [] | 陈斌, 刘树文, 耿元生, 等. 2006. 吕梁-五台地区晚太古宙-古元古代花岗质岩石锆石U-Pb年代学和Hf同位素性质及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 22(2): 296–304. |
| [] | 第五春荣, 孙勇, 王倩. 2012. 华北克拉通地壳生长和演化: 来自现代河流碎屑锆石Hf同位素组成的启示. 岩石学报, 28(11): 3520–3530. |
| [] | 耿显雷, 高山, 陈晨. 2011. 华北克拉通东部及苏鲁造山带的地壳生长: 来自现代河流碎屑锆石的U-Pb定年和Hf同位素证据. 地球科学, 36(3): 487–489. |
| [] | 宫江华, 张建新, 于胜尧, 等. 2012. 西阿拉善地块~2. 5Ga TTG岩石及地质意义. 科学通报, 57(28-29): 2715–2728. |
| [] | 郭丽爽, 刘树文, 刘玉琳, 等. 2008. 中条山涑水杂岩中TTG片麻岩的锆石Hf同位素特征及其形成环境. 岩石学报, 24(1): 139–148. |
| [] | 劳子强, 王世炎. 1999. 河南省嵩山地区登封群研究的新进展. 中国区域地质, 18(1): 9–16. |
| [] | 李孟江, 王仁民, 张莉. 2012. 华北克拉通北缘尚义地区新太古代TTG成因分析: 洋壳玄武岩不同深度下熔融的产物. 地质通报, 31(5): 686–695. |
| [] | 李秋根, 刘树文, 王宗起, 等. 2008. 中条山绛县群碎屑锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 24(6): 1359–1368. |
| [] | 林慈銮. 2006. 河南鲁山地区太古代片麻岩系的地球化学、锆石年代学及其构造环境. 硕士学位论文. 西安: 西北大学, 1-82 |
| [] | 刘富, 郭敬辉, 路孝平, 等. 2009. 华北克拉通2.5Ga地壳生长事件的Nd-Hf同位素证据: 以怀安片麻岩地体为例. 科学通报, 54(17): 2517–2526. |
| [] | 刘建辉, 刘福来, 刘平华, 等. 2011. 胶北早前寒武纪变质基底多期岩浆-变质热事件: 来自TTG 片麻岩和花岗质片麻岩中的锆石U-Pb定年的证据. 岩石学报, 27(4): 943–960. |
| [] | 刘树文, 吕勇军, 凤永刚, 等. 2007. 冀北单塔子杂岩的地质学和锆石U-Pb年代学. 高校地质学报, 13(3): 484–497. |
| [] | 刘树文, 吕勇军, 王伟, 等. 2011. 冀北太古代花岗质片麻岩的成因. 岩石学报, 27(4): 909–921. |
| [] | 柳小明, 高山, 第五春荣, 等. 2007. 单颗粒锆石的20μm小斑束原位微区LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄和微量元素的同时测定. 科学通报, 52(2): 228–235. |
| [] | 孙大中, 胡维兴. 1993. 中条山前寒武纪年代构造格架和年代地壳结构. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-107. |
| [] | 陶继雄. 2003. 内蒙固阳地区新太古代变质侵入岩特征及与成矿关系. 地质调查与研究, 26(1): 21–25. |
| [] | 田伟, 刘树文, 刘超辉, 等. 2005. 中条山涑水杂岩中TTG系列岩石的锆石SHRIMP年代学和地球化学及其地质意义. 自然科学进展, 15(12): 1476–1484. |
| [] | 万渝生, 刘敦一, 董春燕, 等. 2009a. 中国最老岩石和锆石. 岩石学报, 25(8): 1793–1807. |
| [] | 万渝生, 刘敦一, 王世炎, 等. 2009b. 登封地区早前寒武纪地壳演化——地球化学和锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学制约. 地质学报, 83(7): 982–999. |
| [] | 王凯怡, 郝杰, WildeS, 等. 2000. 山西五台山-恒山地区晚太古-早元古代若干关键地质问题的再认识: 单颗粒锆石离子探针质谱年龄提出的地质制约. 地质科学, 35(2): 175–184. |
| [] | 王世进, 万渝生, 王伟, 等. 2010. 鲁西地区石门山-凤仙山岩体的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及形成时代. 山东国土资源, 26(9): 1–6. |
| [] | 王世进, 万渝生, 杨恩秀, 等. 2012. 鲁西地区新太古代中期岩浆活动——新甫山与上港等岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年的证据. 山东国土资源, 28(4): 1–7. |
| [] | 王伟, 王世进, 董春艳, 等. 2010. 山东鲁山地区新太古代壳源花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年. 地质通报, 29(7): 993–1000. |
| [] | 杨崇辉, 杜利林, 万渝生, 等. 2004. 河北平山英云闪长质片麻岩锆石SHRIMP年代学. 高校地质学报, 10(4): 514–522. |
| [] | 杨崇辉, 杜利林, 任留东, 等. 2011. 赞皇杂岩中太古宙末期菅等钾质花岗岩的成因及动力学背景. 地学前缘, 18(2): 62–78. |
| [] | 翟明国. 2010. 华北克拉通的形成演化与成矿作用. 矿床地质, 29(1): 24–36. |
| [] | 翟明国. 2011. 克拉通化与华北陆块的形成. 中国科学(地球科学), 41(8): 1037–1046. |
| [] | 张维杰, 李龙, 耿明山. 2000. 内蒙古固阳地区新太古代侵入岩的岩石特征及时代. 地球科学, 25(3): 221–226. |
| [] | 张瑞英, 张成立, 第五春荣, 等. 2012. 中条山前寒武纪花岗岩地球化学、年代学及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 28(11): 3559–3573. |
| [] | 张永清, 张有宽, 郑宝军, 等. 2006. 内蒙古中部小南沟-明星沟地区新太古代TTG岩系及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 22(11): 2762–2768. |
| [] | 张兆琪, 薛文彦, 柴金钟, 等. 2003. 中条山西南段基底岩系的地质特征. 地质调查与研究, 26(4): 193–199. |
| [] | 赵斌, 王登红, 侯可军, 等. 2012. 中条山涑水杂岩的同位素年代学研究及其地质意义. 地球科学与环境学报, 34(1): 1–8. |
| [] | 周艳艳, 赵太平, 薛良伟, 等. 2009. 河南嵩山地区新太古代TTG质片麻岩的成因及其地质意义: 来自岩石学、地球化学及同位素年代学的制约. 岩石学报, 25(2): 331–347. |
 2013, Vol. 29
2013, Vol. 29