2. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049;
3. 新疆有色地质勘查局, 乌鲁木齐 830000
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China;
3. Xinjiang Geoexploration Bureau for Nonferrous Metals, Uramuqi 83000, China
造山型金矿为近年来国际上的研究热点,学者们共识其基本特征为:变质地体中受构造控制的脉状后生金矿床,在时间和空间上与造山作用有关(Groves et al., 1998; Kerrich et al., 2000; Chen et al., 2001, 2005; 范宏瑞等, 2003)。以比较矿床学为指导(涂光炽和李朝阳, 2006),陈衍景(2006)将造山型金矿的概念进行了拓展,系统总结了造山型矿床的识别标志,包括:常产于增生型造山带的俯冲增生楔变质地体(Kerrich et al., 2000) 和碰撞型造山带内部,矿体常呈脉状产于剪切带等断裂构造中;成矿流体系统以富CO2变质流体为主;成矿深度变化于5~20km;成矿作用发生挤压向伸展转换体制,具有三阶段性;后生成矿,成矿时间滞后于区域变质作用时间;等等。随后,在这一思想指导下,我国学者先后在秦岭造山带和兴蒙造山带等地识别出一大批造山型金、银、铅锌、铜、钼矿床,如河南铁炉坪银矿(Chen et al., 2004),银洞沟银矿(张静等, 2004, 2009),围山城银金多金属成矿带(张静等, 2008; Zhang et al., 2008, 2009, 2011),冷水北沟铅锌矿(祁进平等, 2007),纸坊钼矿(邓小华等, 2008, 2009),大湖金钼矿床(Li et al., 2011a, b; 倪智勇等, 2008; Ni et al., 2012),内蒙古白乃庙铜矿(李文博等, 2007, 2008),辽宁高家堡子银矿(王可勇等,2008),以及新疆乌拉斯沟铜矿床(Zheng et al., 2012) 等。同时,国外学者还在挪威加里东造山带内识别出了造山型钼钨矿床(Larsen and Stein, 2007)。
中亚造山带被共识为增生型造山带,经历了长期的、多个大洋板块的俯冲消减和陆壳增生,于晚石炭世-三叠纪初发生碰撞造山(Sengor and Natal’in, 1996; 陈衍景, 2000; Chen et al., 2007; Xiao et al., 2003, 2009; 肖文交等, 2008及其引文)。按照现今的造山-成矿理论(陈衍景, 2006, 2012),中亚造山带有利于发育大陆增生体制和大陆碰撞体制的造山型矿床。但是,作为中亚造山带最具代表性的北疆地区,除造山型金矿外,其他矿种的造山型矿床仍然是空白。因此,寻找和识别北疆地区代表性的造山型矿床显得尤为紧迫,并将会对北疆地区的找矿部署工作带来积极意义。
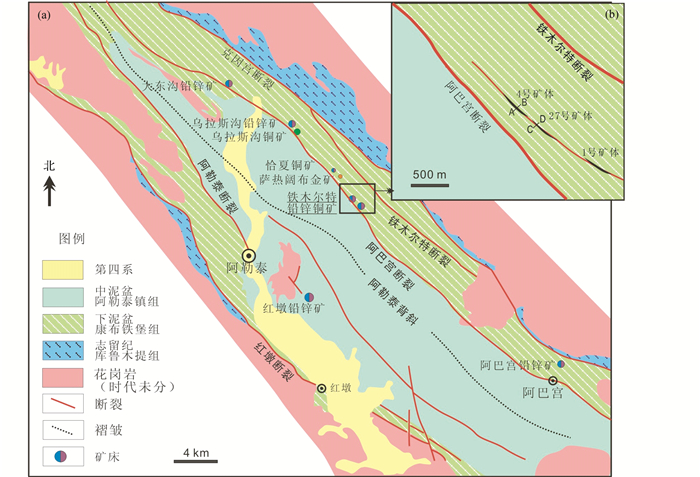
新疆铁木尔特铅锌铜矿床位于阿尔泰造山带南缘阿巴宫多金属成矿带(图 1a)。该矿床发现于1987年,Pb+Zn普查储量2.9×105t,Cu远景储量1.4×105t,为中型铅锌矿(Zhang et al., 2012)。前人对铁木尔特铅锌铜矿床进行了大量研究,但对其成因争议较大,已有观点包括:VMS型(王京彬等, 1998; 闫新军和陈维民, 2001; 尹意求等, 2005; 徐九华等, 2008; 万博和张连昌, 2006; Wan et al., 2010a, b)、VMS与SEDEX过渡类型(王书来等, 2007)、海底火山喷流沉积改造型(姜俊, 2003; 童满云, 2007) 或喷气沉积改造型(马忠美等, 2001) 以及造山型(Zhang et al., 2012) 等。野外调研表明,铁木尔特铅锌铜矿床与典型的热水沉积矿床(VMS或/和SEDEX型) 有很大的差别(Pirajno, 2009; 陈衍景等, 2007),集中表现在:条带发生强烈的变形、变质;矿体未出现典型热水沉积矿床的“双层结构”(Ohmoto, 1996),而呈现出对称蚀变的特征。镜下观察显示,溶蚀交代等热液矿化特征显著。流体包裹体研究表明,该区所谓的“VMS”型矿床脉石矿物中富含大量的碳质流体包裹体(徐九华等, 2008),其流体特征与现代大洋海底喷流沉积(Lüders et al., 2001) 和变质微弱的热水沉积矿床(日本黑矿, Ishikawa et al., 1962; 北美红狗SEDEX型铅锌矿, Kelley et al., 2004; 俄罗斯乌拉尔, Bailly et al., 1999) 的研究结果相差甚远。Zhang et al.(2012)通过对铁木尔特不同期次流体包裹体详细研究认为,铁木尔特铅锌铜矿成矿流体是以中温,低盐度,高CO2为特征,沸腾作用导致成矿物质沉淀,铁木尔特铅锌铜矿为典型的造山型矿床。
|
图 1 阿巴宫多金属成矿带及铁木尔特铅锌铜矿地质图(据Zhang et al., 2012修改) Fig. 1 Geological map of the Abagong ore belt and the Tiemurt deposit (modified after Zhang et al., 2012) |
前述各种成因观点可归为两类:同生(VMS\\SEDEX\\热水沉积) 和后生(造山型)。从时间尺度上,前者要求成岩与成矿必须近乎同时发生,而后者成矿作用则必须晚于赋矿围岩时代。显然,研究铁木尔特铅锌铜矿床的成矿时代,并与成岩时代相比较,既有助于解决铁木尔特矿床成因问题,又有助于丰富阿尔泰造山带热液矿床的成因类型和形成时代。基于上述,本文对矿区内2件赋矿火山岩样品进行了锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年,并对2个多金属硫化物-石英脉中云母样品进行40Ar/39Ar定年,以期厘定铁木尔特成岩成矿时代,探讨铁木尔特矿床成因类型及成矿的大地构造背景。
1 区域地质背景铁木尔特铅锌铜矿床位于阿尔泰山造山带南缘克兰火山-沉积盆地内。该盆地实为西伯利亚板块阿尔泰南缘晚古生代活动陆缘的弧后拉张盆地(Chen et al., 2001, 2012; 万博和张连昌, 2006; Wan et al., 2010a, b; Zhang et al., 2012),区内主要出露地层包括志留系中上统库鲁姆提组、泥盆系下统康布铁堡组、泥盆系中统阿尔泰镇组。库鲁姆提组为一套混合岩、片麻岩夹变质砂岩、片岩组合,与上覆的康布铁堡组呈断层接触;康布铁堡组为一套海相中酸性火山岩-火山碎屑岩、陆源碎屑沉积岩-碳酸盐岩建造;阿勒泰镇组为一套变质粉砂岩、变质砂岩、云母石英片岩和千枚岩组合。上述地层单元之间多为断层接触(图 1a),发生多期次变质和岩浆侵入活动,区域变质程度达到中级绿片岩相,特征变质矿物组合为黑云母-绿泥石-绿帘石-阳起石±角闪石。区内岩浆岩主要形成于泥盆纪和石炭纪,也包括一些奥陶纪、二叠纪、三叠纪和少量侏罗纪中酸性侵入岩(图 1中未区分时代)。
克兰盆地及其主构造均呈NW-SE向,以阿勒泰复式向斜为主体,轴长50km,轴面倾向NE,倾角50°~70°,NE翼倒转,SW翼正常。向斜核部主要发育中泥盆统阿勒泰镇组,向两翼依次为康布铁堡组和库鲁姆提组。次级褶皱轴线走向与主构造线一致,以紧闭的线性褶皱为主,NE翼多数次级褶皱发生倒转。盆地内NW断裂构造发育,且多沿不同地层单元之间的边界发育,显示对地层发育的控制作用。例如,克因宫断裂和红墩断裂构成志留系与泥盆系的边界,阿巴宫断裂和阿勒泰断裂总体表现为康布铁堡组与阿勒泰镇组的边界(图 1a)。尤其重要的是,断裂构造还控制了矿床的空间分布。其中,阿巴宫断裂控制着大东沟铅锌矿、乌拉斯沟铅锌矿、乌拉斯沟铜矿、恰夏铅锌矿、萨热阔布金矿和铁木尔特铅锌铜矿等(图 1a)。
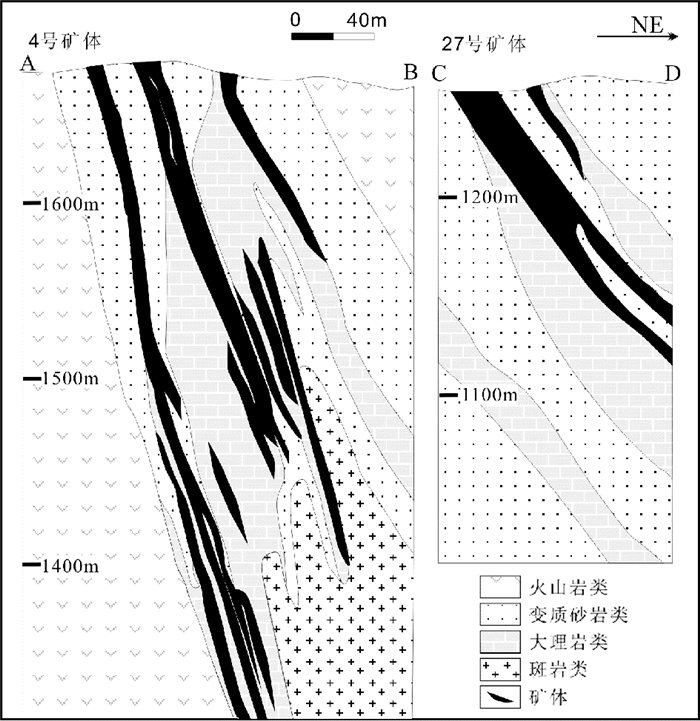
2 矿床地质特征康布铁堡组为一套变质级别达中绿片岩相的流纹质晶屑凝灰岩、火山碎屑岩夹碳酸岩建造,厚度约500~1500m,由下而上,可分为三个岩性段。铁木尔特矿床赋矿层位为康布铁堡组上亚组第二岩性段(D1k22)(图 1b)。主矿体位于第二岩性段大理岩及其上下盘的绿泥石黑云母石英片岩、铁锰质大理岩和变钙质砂岩中,直接容矿围岩为铁锰质大理岩和绿泥石黑云母石英片岩(图 2)。
|
图 2 铁木尔特4#、27#矿体剖面图(据Zhang et al., 2012修改) Fig. 2 Geological profiles of No. 4 and 27 orebodies, the Tiemurt deposit (modified after Zhang et al., 2012) |
矿区内褶皱构造比较复杂,萨拉热阔布复式向斜横贯矿区,北翼有恰夏复式背斜,另有规模不等的褶皱遍布矿区。区内断裂多分布于康布铁堡组第二岩性段内,沿铁锰钙质岩层与变流纹质晶屑凝灰岩的接触界面等处发育。
矿体呈透镜状,长n×10~>1000m,走向314°~318°,倾向44°~48°,倾角49°~60°。目前已探明的矿体有1号、4号和27号,(Pb+Zn+Cu) 平均品位为5.84%,且Pb>Zn,富含Cu,总体为含铜的铅锌多金属矿体,并发育有多个矿化层(图 2)。
矿石矿物主要有方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、黄铁矿、磁黄铁矿等;脉石矿物有石英、透闪石、阳起石、石榴石、角闪石、绿泥石、绿帘石、方解石、重晶石、萤石等。矿石结构主要为自形-半自形结构、交代残余结构、压碎结构等。矿石构造主要有条带状构造、浸染状构造、块状构造、细脉状构造等。矿石的结构构造显示,矿床经历了强烈的热液交代作用。围岩蚀变主要包括绿泥石-绿帘石化、石榴石化、硅化和黄铁矿化等。
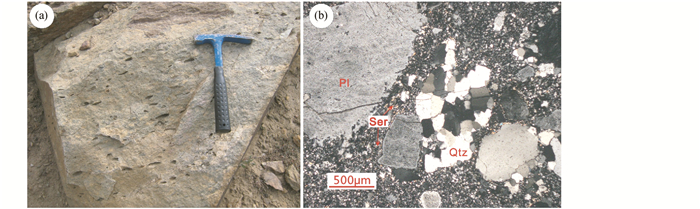
3 火山岩锆石年代学研究 3.1 样品特征用于锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年的样品采自4号矿体外接触带的变质晶屑凝灰岩。晶屑凝灰岩呈灰色,凝灰结构,微定向排列,由晶屑、岩屑和重结晶的火山灰组成。其中,晶屑由棱角状石英和长石组成,也可见石英集合体呈长条状定向排列,或呈透镜状产出,胶结物为火山灰发生重结晶并定向排列的石英、长石、绢云母集合体(图 3)。
|
图 3 铁木尔特矿区火山岩岩相学特征 (a)-晶屑凝灰岩(手标本);(b)-长石-石英斑晶,石英、长石和绢云母基质(正交偏光镜下).缩写:Qtz-石英; Fl-长石; Ser-绢云母 Fig. 3 Photograph (a) and microphotograph (b) of volcanics in Tiemurt Abbreviations: Qtz-quartz; Fl-feldspar; Ser-sericite |
首先将0.5kg左右的样品破碎成约1cm3的小块, 放入直径为20cm的不锈钢钵中,在XZW100型振动磨样机中研磨3~5s后取出,此过程反复进行直到样品全部通过0.3mm的孔径筛,洗去粉尘,经铝制淘砂盘富集重矿物,然后通过磁选和电磁选,将剩余非电磁部分再淘洗获得锆石精矿,最后在双目镜下挑选出用于定年的锆石。将锆石颗粒置于环氧树脂制成直径为1.4cm的样品靶,抛光至锆石颗粒中心。然后,进行显微镜下观察和透、反射光照相,并在中国科学院广州地球化学研究所电子探针仪上进行了CL图像分析,分析仪器为JEOL JXA-8100电子探针仪,分析流程及实验参数见Huang et al.(2007)。
锆石的U-Pb定年是在中国科学院广州地球化学研究所同位素年代学和地球化学重点实验室完成,所用仪器为美国Resonetics公司生产的RESOlutionM-50激光剥蚀系统和Aglilent 7500a型的ICP-MS联机,激光剥蚀斑束直径为31μm,频率为8Hz,采用单点剥蚀的方法。元素含量外标采用美国国家标准技术研究院人工合成的硅酸盐玻璃标准参考物质NIST610,元素内标采用29Si,锆石年龄外标采用Temora (417Ma),详细实验流程见文献(袁洪林等, 2003)。数据处理见文献(Liu et al., 2008), 锆石年龄计算采用Isoplot软件(Ludwig, 2003),普通铅校正见文献(Andersen, 2002)。单个数据点的误差均为1σ,采用206Pb /238U年龄,其加权平均值为95%的置信度。
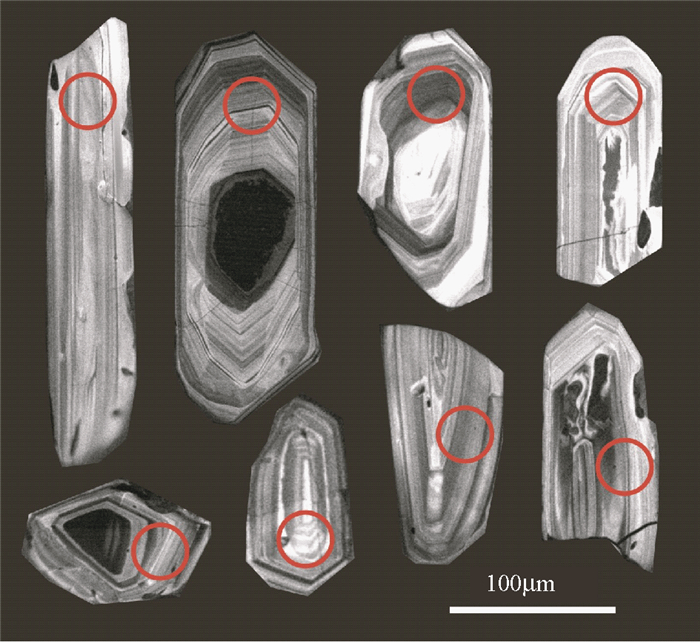
3.3 测试结果铁木尔特矿区内康布铁堡地层中的两个样品(10TM-4a和10TM-11) 所含锆石多为半自形-自形,短柱状、双锥状,大多数颗粒晶棱及晶面较为清晰,粒度80~200μm,长宽比约为1:1~10:1左右。阴极发光图像中锆石均发育韵律环带结构(图 4)。从两个靶样中各挑选晶形完整、无裂缝的锆石颗粒进行了LA-ICP-MS U-Pb分析,两个样品分析结果列于表 1。对于小于1000Ma的锆石,207Pb具有低的测试精度,故采用206Pb/238U年龄(Compston et al., 1992)。
|
图 4 铁木尔特矿区晶屑凝灰岩锆石的阴极发光图及分析点位示意 Fig. 4 Cathode luminescence images, and locations of the points for LA-ICP-MS measurements of zircons of volcanics at the Tiemuert |
|
|
表 1 铁木尔特矿床LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄测定结果 Table 1 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating analysis of zircons from volcanics at the Tiemuert |
样品10TM-11的18个分析点的Th含量为50×10-6~518×10-6(平均246×10-6),U含量为66×10-6~868×10-6(平均315×10-6),Th/U为0.17~1.83(平均0.2)。206Pb/238U表观年龄集中在369~401Ma,分布范围集中,加权平均年龄为396±5Ma (MSWD=0.083)(图 5、表 1)。
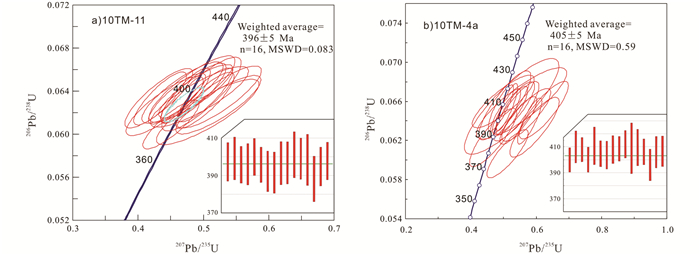
|
图 5 铁木尔特矿区晶屑凝灰岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图 Fig. 5 U-Pb concordant diagram of zircons from volcanics at the Tiemuert |
样品10TM-4a的18个分析点的Th含量为27×10-6~837×10-6(平均299×10-6),U含量51×10-6~1040×10-6(平均376×10-6),Th/U为0.41~1.42(平均0.77)。206Pb/238U表观年龄集中在379~411Ma,加权平均年龄为405±5Ma (MSWD=0.25)(图 5、表 1)。
4 黑云母Ar-Ar年代学研究 4.1 样品特征及研究方法用于云母40Ar/39Ar研究的样品分别采自4号矿体和27号矿体,为中阶段黑云母-多金属硫化物-石英脉型矿石中的大片云母,采样位置与样品描述见图 6。云母作为限定成矿年龄矿物时,必须符合以下几个条件(McDougall and Harrison, 1999; Kelley, 2002):(1) 云母与硫化物共生,即云母与共生硫化物同时形成;(2) 形成后,遭受的后期构造热事件的温度低于云母的封闭温度;(3) 过剩氩的含量可以忽略不计。本次样品符合上述条件,可以作为限定热液矿床成矿年代的理想矿物。

|
图 6 含矿石英脉中云母及其镜下照片 (a)-云母-硫化物-石英脉中大片云母;(b)-云母显微特征(正交偏光镜下).缩写:Qtz-石英; Bi-黑云母; Gn-方铅矿 Fig. 6 Photos of analyzed biotite in the mineralized quartz vein (a)-the biotite in mica-polymetallic-quartz vein; (b)-biotite under crossed polarizers. Abbreviations: Qtz-quartz; Bi-biotite; Gn-galena |
为确定云母类型和化学成分,电子探针成分分析在中国科学院广州地球化学研究所电子探针实验室进行,分析仪器为JEOL JXA-8100电子探针仪,分析流程及实验参数见Huang et al.(2007)。
将样品粉碎至20目,双目镜下挑选出纯度>98%的云母样品。经过超声波洗涤去除云母表面附着的杂质。40Ar/39Ar同位素年代分析在中国科学院广州地球化学研究所同位素地球化学和年代学实验室进行。仪器设备为英国GV Instruments 5400质谱计和深圳光大COHERENT-50W二氧化碳激光器。GV Instruments 5400质谱计和COHERENT-50W二氧化碳激光器具体的分析技术规格见Qiu and Wijbrans (2008)。实验过程中用作中子通量监测的标样是中国周口店黑云母标样ZBH-25,年龄132Ma。用于40Ar/39Ar中子活化测定年龄的样品,用铝箔包裹后,与用于标样ZBH-25一起封入石英玻璃瓶中,置于中国原子能科学研究院的49-2核反应堆B8孔道内进行中子照射,中子通量为(6.0~6.5)×1012/cm2·s。K和Ca的干扰氩的矫正因子分别为(39Ar/37Ar)Ca=8.984×10-4,(36Ar/37Ar)Ca=2.673×10-4和(40Ar/39Ar)K=5.97×10-3。高温阀规格为长210mm,半径28mm,最高温为1200℃左右。碎裂和纯化在150℃下进行大约10h,外部大约为250℃。本底值分别为36Ar=(0.002~0.004) mV,37Ar=(0.0002~0.0006) mV,38Ar=(0.0004~0.0015) mV,39Ar=(0.0025~0.0051) mV和40Ar=(0.51~1.3) mV。释气分别在管道中净化5~8min,分别在室温和450℃左右。40Ar/39Ar定年结果的计算和投点采用ArArCALC计算软件(Koppers, 2002)。
4.3 实验结果铁木尔特铅锌铜矿床硫化物石英脉中云母的电子探针化学成分分析及计算的分子式见表 2。
|
|
表 2 铁木尔特铅锌铜矿云母电子探针分析结果(wt%) 及分子式 Table 2 The electron probe analysis (wt%) and calculated molecular formula at Tiemurt Pb-Zn-Cu deposit |
本次测定两件云母样品TM-20和TM-49的分子式分别为(K1.02Na0.03)1.05(Mg1.51Fe1.22Al0.13Ti0.08Cr0.01)2.95[(Si2.82Al1.18)4O10](OH1.99Cl0.01)2和(K1.03Na0.04)1.07(Mg1.51Fe1.23Ti0.02Al0.17)2.93[(Si2.78Al1.22)4O10][OH1.99Cl0.01]2,n (Mg):n (Fe)<2,可以判断为黑云母样品。
40Ar/39Ar阶段激光剥蚀分析结果见于表 3,相应的表观年龄谱、等时线和反等时线年龄见图 7。40Ar/39Ar表观坪年龄决定于:(1) > 75%的连续气体分解;(2) 至少8个阶段;(3) 表面年龄和坪年龄在不确定度1σ水平上要一致。本次测定TM-49黑云母样品19个阶段,TM-20黑云母样品19个阶段(表 3, 图 7)。样品TM-49的总气体年龄为241.04±2.29Ma,在第6-第19阶段构成的坪年龄为239.72±2.41Ma (MSWD=9.19),对应了95%的39Ar释放量,相应的39Ar/36Ar-40Ar/36Ar等时线年龄为238.07±2.63Ma (MSWD=9.32),40Ar/36Ar初始值为344.2±39.7;36Ar/40Ar-39Ar/40Ar反等时线年龄为238.94±2.58Ma (MSWD=8.09),40Ar/36Ar初始值为325.6±36.4。
|
|
表 3 黑云母39Ar/40Ar阶段激光剥蚀定年分析结果 Table 3 39Ar/40Ar stepwise laser ablation dating results of biotite |
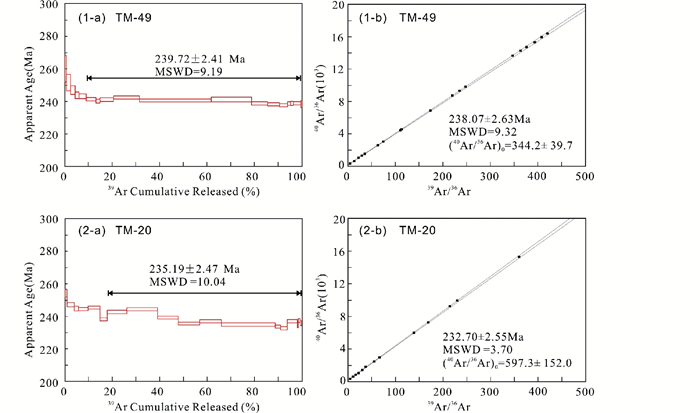
|
图 7 黑云母39Ar/40Ar阶段激光剥蚀“年龄谱”(a) 与“等时线”(b) Fig. 7 39Ar/40Ar stepwise laser ablation data of biotite (a)-spectre age; (b)-normal isochrons |
样品TM-20的总气体年龄为238.93±2.26Ma,在第7至第19阶段构成的坪年龄为235.19±2.47Ma (MSWD=10.14),对应了85%的39Ar释放量,相应的39Ar/36Ar-40Ar/36Ar等时线年龄为232.70±2.55Ma (MSWD=3.70),40Ar/36Ar初始值为597.3±152.0;36Ar/40Ar-39Ar/40Ar反等时线年龄为233.67±2.74Ma (MSWD=6.64),40Ar/36Ar初始值为519.6±179.9。
5 讨论 5.1 成岩成矿时代铁木尔特矿区内两个火山岩样品中锆石多呈柱状形态,锆石内部发育有规律的韵律环带结构(图 4),Th、U含量和Th/U比较高(>0.4),总体表现出岩浆锆石的特征(吴元保和郑永飞, 2004)。两个样品的锆石年龄协和度良好(>95%),表观年龄和加权平均年龄接近。因此,认为火山岩中锆石的加权平均年龄(396~405Ma) 可代表赋矿地层康布铁堡组形成年龄,该结果亦与前人所得结论一致(407~412Ma, Chai et al., 2009; ~400Ma, 单强等, 2012)。
铁木尔特铅锌铜矿中,中阶段多金属硫化物石英脉共生的云母充填于早期黄铁矿-石英裂隙中,并未表现出明显的变形痕迹和后期构造-热事件的影响(图 6)。前人研究表明,与云母共生的石英中所含流体包裹体的均一温度为230~374℃(Zhang et al., 2012),低于黑云母的结晶封闭温度350~400℃(朱炳泉, 1998)。因此,黑云母可以作为确定成矿年龄的理想矿物。本文获得两个云母样品(TM-49和TM-20) 表观坪年龄分别为240±2Ma和235±2Ma,相应的等时线年龄分别为238±3Ma和233±3Ma,40Ar/36Ar初始值分别为344.2±39.7和597.3±152.0,反等时线年龄分别为239±3Ma和234±3Ma,40Ar/36Ar初始值为325.6±36.4和519.6±179.9。表观坪年龄、等时线年龄和反等时线年龄接近,可代表黑云母形成的可信年龄。因此,铁木尔特铅锌铜矿成矿年龄为234~240Ma,即早三叠世。
5.2 矿床成因类型成岩成矿年龄虽然不是确定矿床成因类型的主要依据,但可作为检验矿床成因类型正确与否的试金石。不同类型的矿床形成地质条件或环境不同,与矿区地质事件或地质体的相对时间顺序不同。例如,热水沉积型矿床(VMS型或SEDEX型) 为同生矿床,其成矿时间与赋矿围岩地层时代一致;侵入体有关的岩浆热液型矿床(斑岩型或矽卡岩型) 成矿年龄同期或稍晚于成矿岩体;造山型矿床为后生矿床,成矿与造山作用有关,成矿时间同步或滞后于区域大规模变形变质作用(陈衍景, 2006; 陈衍景等, 2007, 2008)。
铁木尔特铅锌铜矿的成因争论可归结为同生矿床(热水沉积型矿床, 王京彬等, 1998; 徐九华等, 2008; Wan et al., 2010a, b) 和后生矿床(造山型矿床,Zhang et al., 2012) 之争。本文获得赋矿地层康布铁堡组的形成年龄为396~405Ma,而成矿年龄为234~240Ma;成矿年龄晚于赋矿地层约165Ma,可排除同生热水沉积型矿床的可能性。事实上,区域内额尔齐斯大断裂活动时间为246±18Ma,可代表区域大规模造山有关的变质变形时间(Briggs et al., 2009; Wan et al., 2011; Wan et al., 2012);徐学纯等(2005)获得该区变质岩中独居石的变质年龄为240~280Ma,认为区域峰期变质年龄为二叠-早三叠纪。铁木尔特铅锌铜矿成矿时间为234~240Ma,尾随峰期区域变质作用,表明该矿床可能与区域变质作用有关。考虑到铁木尔特矿床受阿巴宫断裂次级断裂和相关的韧性剪切带控制,矿体呈脉状产出;流体包裹体具有中温、低盐度、富CO2等特征(Zhang et al., 2012),与热水沉积型矿床相差甚远,却与造山型矿床完全吻合(陈衍景, 2006; 陈衍景等, 2007),认为铁木尔特属于造山型矿床。
5.3 成矿构造背景不同成因类型的矿床倾向于发育于不同的大地构造背景(Kerrich et al., 2005; Groves and Bierlein, 2007; 陈衍景等, 2008)。例如,VMS/SEDEX等类型的矿床发育在拉张背景,如洋中脊、弧后盆地或大陆边缘裂谷(Leach et al., 2005; Franklin et al., 2005);斑岩型和浅成低温型矿床发育在洋陆俯冲背景(Sillitoe, 1972; Richards, 2003) 或陆陆碰撞背景(陈衍景和富士谷,1992;陈衍景和李诺, 2009; Chen and Wang, 2011; Chen et al., 2007, 2012; Li et al., 2012a, b, c);造山型金矿发育在碰撞型或增生型造山带(Groves et al., 1998; 陈衍景, 2006)。因此,矿床成因类型可作为判断大地构造背景的探针(陈衍景等, 2008)。那么,铁木尔特铅锌铜矿形成于何种背景呢?
前人研究表明,阿尔泰造山带于晚古生代发育大量的具有岛弧特征的火山岩(单强等, 2007; 牛贺才等, 1999, 2006)、基性侵入岩(陈汉林等, 2006; Wang et al., 2006) 及相应的洋壳残片(张海祥等, 2003);同时也发育大量的同造山花岗岩,如冲乎尔盆地北岩体(曾乔松等, 2007)、塔尔浪岩体、阿舍勒岩体(Yuan et al., 2007)、铁列克岩体(童英等, 2005)、阿维滩岩体、可可托海岩体、切木尔切克岩体、库尔提岩体、蒙库岩体(杨富全等, 2008)、希勒克特哈腊苏岩体、喀腊萨依岩体等(张招崇等, 2006),表明该时期为洋陆俯冲背景,陆壳增生强烈。本文获得赋矿围岩--康布铁堡组火山岩形成年龄为396~405Ma,即同期于该期陆壳增生事件。
晚石炭-早三叠纪,阿尔泰地区发生强烈的弧陆或陆陆碰撞造山运动(Xiao et al., 2003, 2009; 肖文交等, 2008; Chen et al., 2012),诱发了大规模的变质变形作用。例如,额尔齐斯大断裂及其次级断裂活动时间为246±18Ma (Briggs et al., 2009; Wan et al., 2011, 2012);区域绿片岩相变质岩中独居石变质年龄为240~280Ma (徐学纯等, 2005)。强烈的变质变形作用导致地层发生变质脱挥发分作用,形成向上运移的富CO2的变质流体,变质流体沸腾并与浅成流体混合导致成矿物质沉淀,最终导致了铁木尔特矿床形成。
因此,尽管可能经历了泥盆纪大陆增生阶段的成矿物质预富集,但铁木尔特工业矿体总体属于三叠纪碰撞造山体制形成的造山型矿床。
6 结论(1) 获得2件赋矿地层--康布铁堡组火山岩的锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄分别为396±5Ma和405±5Ma,代表康布铁堡组的成岩年龄。
(2) 获得2件与多金属硫化物共生的黑云母的40Ar/39Ar坪年龄分别为235±2Ma和240±2Ma,代表了铁木尔特铅锌铜矿的成矿时代。
(3) 铁木尔特铅锌铜矿床为后生矿床,成矿稍滞后于区域峰期变质作用,成因类型为造山型矿床。
(4) 铁木尔特铅锌铜矿成矿构造背景为三叠纪碰撞造山体制。
致谢 研究工作在陈衍景教授指导下完成;野外工作得到国家305项目办公室和新疆有色局706队的大力支持;锆石LA-ICP-MS测试得到广州地化所孙卫东研究员和涂湘林高工帮助;Ar-Ar测试得到广州地化所邱华宁研究员和蒲志平高工指导;两位审稿人的建设性意见提高了本文质量;在此表示感谢!| [] | Andersen T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2): 59–79. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X |
| [] | Bailly L, Orgeval JJ, Tesalina S, Zaykov V and Maslennikov VV. 1999. Fluid inclusion data of Alexandrinka massive sulfide deposit, Urals. In: Stanley CJ (ed.). Mineral Deposits: Processes to Processing. Rotterdam, Netherlands: Balkema Publishers, 13-16 |
| [] | Briggs SM, Yin A, Manning CE, Chen ZL, Wang XF. 2009. Tectonic development of the southern Chinese Altai Range as determined by structural geology, thermobarometry, 40Ar/39Ar thermochronology, and Th/Pb ion-microprobe monazite geochronology. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 121: 1381–1393. DOI:10.1130/B26385.1 |
| [] | Chai FM, Mao JW, Dong LH, Yang FQ, Liu F, Geng XX, Zhang ZX. 2009. Geochronology of metarhyolites from the Kangbutiebao Formation in the Kelang basin, Altay Mountains, Xinjiang: Implications for the tectonic evolution and metallogeny. Gondwana Research, 16(2): 189–200. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2009.03.002 |
| [] | Chen HL, Yang SF, Li ZL, Yuan C, Xiao WJ, Li JY, Yu X, Lin XB. 2006. Tectonic setting of mafic rocks in southern Altay orogenic belt and its geodynamic implication. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(1): 127–134. |
| [] | Chen HY, Chen YJ, Liu YL. 2001. Metallogenesis of the Ertix gold belt, Xinjiang and its relationship to Central Asia-type orogenesis. Science in China (Series D), 44(3): 245–255. DOI:10.1007/BF02882259 |
| [] | Chen YJ, Fu SG. 1992. Gold Mineralization in West Henan. Beijing: Seismological Press: 1-234. |
| [] | Chen YJ. 2000. Progress in the study of Central Asia-type orogenesis-metallogenesis in Northwest China. Geological Journal of China Universities, 6(1): 17–22. |
| [] | Chen YJ, Pirajno F, Sui YH. 2004. Isotope geochemistry of the Tieluping silver-lead deposit, Henan, China: A case study of orogenic silver-dominated deposits and related tectonic setting. Mineralium Deposita, 39(5-6): 560–575. DOI:10.1007/s00126-004-0429-9 |
| [] | Chen YJ, Pirajno F, Qi JP. 2005. Origin of gold metallogeny and sources of ore-forming fluids, Jiaodong province, Eastern China. International Geology Review, 47(5): 530–549. DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.47.5.530 |
| [] | Chen YJ. 2006. Orogenic-type deposits and their metallogenic model and exploration potential. Geology in China, 33(6): 1181–1196. |
| [] | Chen YJ, Chen HY, Zaw K, Pirajno F, Zhang ZJ. 2007. Geodynamic settings and tectonic model of skarn gold deposits in China: An overview. Ore Geology Reviews, 31(1-4): 139–169. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.01.001 |
| [] | Chen YJ, Ni P, Fan HR, Pirajno F, Lai Y, Su WC, Zhang H. 2007. Diagnostic fluid inclusions of different types gold deposits. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(9): 2085–2108. |
| [] | Chen YJ, Xiao WJ, Zhang JJ. 2008. Ore-system as a geodynamic probe. Geology in China, 35(6): 1059–1073. |
| [] | Chen YJ, Li N. 2009. Nature of ore fluids of intracontinental intrusion related hypothermal deposits and its difference from those in island arcs. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(10): 2477–2508. |
| [] | Chen YJ, Wang Y. 2011. Fluid inclusion study of the Tangjiaping Mo deposit, Dabie Shan, Henan Province: Implications for the nature of the porbiotiteyry systems of post-collisional tectonic settings. International Geology Reviews, 53(5-6): 635–655. DOI:10.1080/00206811003783422 |
| [] | Chen YJ, Pirajno F, Wu G, Qi JP, Xiong XL. 2012. Epithermal deposits in North Xinjiang, NW China. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 101(4): 889–917. DOI:10.1007/s00531-011-0689-4 |
| [] | Compston W, Williams IS, Kirschvink JL, Zhang ZC, Ma GG. 1992. Zircon U-Pb ages for the Early Cambrian time-scale. Journal of Geological Society, 149(2): 171–184. DOI:10.1144/gsjgs.149.2.0171 |
| [] | Deng XH, Li WB, Li N, Mei M, Zhang Y. 2008. Study of fluid inclusion and genesis of the Zhifang Mo deposit in Songxian County, Henan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(9): 2133–2148. |
| [] | Deng XH, Mei M, Li WB. 2009. Study of fluid inclusions and ore genesis of the Tumen Mo-fluorite vein deposit, Henan Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 25(10): 2537–2549. |
| [] | Fan HR, Xie YH, Zhai MG, Jin CW. 2003. A three stage fluid flow model for Xiaoqinling lode gold metallogenesis in the He'nan and Shaanxi provinces, Central China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 19(2): 260–266. |
| [] | Franklin JM, Gibson HL, Jonasson I and Galley AG. 2005. Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposit. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume, 523-560 |
| [] | Groves DI, Goldfarb RJ, Gebre-Mariam M, Hagemann SG, Robert F. 1998. Orogenic gold deposits: A proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types. Ore Geology Reviews, 13(1-5): 7–27. DOI:10.1016/S0169-1368(97)00012-7 |
| [] | Groves DI, Bierlein FP. 2007. Geodynamic settings of mineral deposit systems. Journal of the Geological Society, 164(1): 19–30. DOI:10.1144/0016-76492006-065 |
| [] | Huang XL, Xu YG, Luo CH, Wang RC, Lin CY. 2007. Exsolution lamellae in a clinopyroxene megacryst aggregate from cenozoic basalt, Leizhou Peninsula, South China: Petrography and chemical evolution. Contribtions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 154(6): 691–705. DOI:10.1007/s00410-007-0218-4 |
| [] | Ishikawa H, Kuroda R, Sudo T. 1962. Minor elements in some altered zones of "Kuroko" (black ore) deposits in Japan. Economic Geology, 57(5): 785–798. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.57.5.785 |
| [] | Jiang J. 2003. The mineral geology of Tiemuerte. Xinjiang Nonferrous Metal, 26(2): 2–5. |
| [] | Kelley KD, Leach DL, Johnson CA, Clark JL, Fayek M, Slack JF, Anderson VM, Ayuso RA, Ridley WI. 2004. Textural, compositional, and sulfur isotope variations of sulfide minerals in the Red Dog Zn-Pb-Ag deposits, Brooks Range, Alaska: Implications for ore formation. Economic Geology, 99(7): 1509–1532. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.99.7.1509 |
| [] | Kelley S. 2002. K-Ar and Ar-Ar dating. In: Porcelli D, Ballentine CJ and Wieler R (eds.). Noble Gases in Geochemistry and Cosmochemistry. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 47(1): 785-818 |
| [] | Kerrich R, Goldfarb RJ, Groves DI, Garwin S, Jia YF. 2000. The characteristics, origins and geodynamic settings of supergiant gold metallogenic provinces. Science in China (Series D), 43(Suppl.1): 1–68. |
| [] | Kerrich R, Goldfarb DI and Richards RJ. 2005. Metallogenic provinces in an evolving geodynamic framework. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary, Volume, 799-811 |
| [] | Koppers AAP. 2002. ArArCALC-software for 40Ar/39Ar age calculations. Computers and Geosciences, 28(5): 605–619. DOI:10.1016/S0098-3004(01)00095-4 |
| [] | Larsen RB, Stein HJ. 2007. Re-Os dating of orogenic W-Mo deposits in the mid Norwegian Caledonides. Abstracts with Programs-Geological Society of America, 39(6): 276. |
| [] | Leach DL, Sangster DS, Kelley KD, Large RR, Garven G, Sllen CR, Gutzmer J and Walters SG. 2005. Sediment-hosted lead-zinc deposits: A global perspective. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume, 561-607 |
| [] | Li N, Chen YJ, Fletcher R, Zeng QT. 2011a. Triassic mineralization with Cretaceous overprint in the Dahu Au-Mo deposit, Xiaoqinling gold province: Constraints from SHRIMP monazite U-Th-Pb geochronology. Gondwana Research, 20(2-3): 543–552. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.12.013 |
| [] | Li N, Chen YJ, Santosh M, Yao JM, Sun YL, Li J. 2011b. The 1.85Ga Mo mineralization in the Xiong'er Terrane, China: Implications for metallogeny associated with assembly of the Columbia supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 186(1-4): 220–232. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2011.01.019 |
| [] | Li N, Chen YJ, Pirajno F, Ni ZY, Sun YL. 2012a. Timing of the Yuchiling giant porphyry Mo system, eastern Qinling, Central China, and implications for ore genesis. Mineralium Deposita. DOI:10.1007/s00126-012-0441-4 |
| [] | Li N, Chen YJ, Ulrich T, Lai Y. 2012b. Fluid inclusion study of the Wunugetu Cu-Mo deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Mineralium Deposita, 47(5): 467–482. DOI:10.1007/s00126-011-0384-1 |
| [] | Li N, Ulrich T, Chen YJ, Thompson TB, Peace V, Pirajno F. 2012c. Fluid evolution of the Yuchiling porphyry Mo deposit, East Qinling, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 48: 442–459. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.06.002 |
| [] | Li WB, Chen YJ, Lai Y. 2007. Fluid inclusion study of the Bainaimiao Cu-Au deposit in Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(9): 2165–2176. |
| [] | Li WB, Chen YJ, Lai Y, Ji JQ. 2008. Metallogenic time and tectonic setting of the Bainaimiao Cu-Au deposit, Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(4): 890–898. |
| [] | Liu YS, Hu ZC, Gao S, Gunther D, Xu J, Gao CG, Chen HH. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34–43. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 |
| [] | Lüders V, Pracejus B, Halbach P. 2001. Fluid inclusion and sulfur isotope studies in probable modern analogue Kuroko-type ores from the JADE Hydrothermal field (Central Okinawa Trough, Japan). Chemical Geology, 173(1-3): 45–58. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00267-9 |
| [] | Ludwig KR. 2003. ISOPLOT 3.00: A geochronology toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 4: 1–70. |
| [] | Ma ZM, Qiu YJ, Guo XJ. 2001. Sarekuobu-Tiemierte gold polymetallic metallogenetic series in Xinjiang. Geology and Prospecting, 37(4): 23–26. |
| [] | McDougall I, Harrison TM. 1999. Geochronology and Thermochronology by 40Ar/39Ar Method. Oxford: Oxford University Press: 1-269. |
| [] | Ni ZY, Li N, Guan SJ, Zhang H, Xue LW. 2008. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and ore genesis of the Dahu Au-Mo deposit in the Xiaoqinling gold field, Henan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(9): 2058–2068. |
| [] | Ni ZY, Chen YJ, Li N, Zhang H. 2012. Pb-Sr-Nd isotope constraints on the fluid source of the Dahu Au-Mo deposit in Qinling Orogen, Central China, and implication for Triassic tectonic setting. Ore Geology Reviews, 46: 60–67. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.01.004 |
| [] | Niu HC, Xu JF, Yu XY, Chen FR, Zheng ZP. 1999. Discovery of rich-Mg volcanic rock series and its geological implication. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44(9): 1002–1004. |
| [] | Niu HC, Yu XY, Xu JF, Shan Q, Chen FR, Zhang HX, Zheng ZP. 2006. Late Paleozoic Volcanismand Associated Metallogenesis in the Altay area, Xinjiang, China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-184. |
| [] | Ohmoto H. 1996. Formation of volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits: The Kuroko perspective. Ore Geology Reviews, 10(3-6): 135–177. DOI:10.1016/0169-1368(95)00021-6 |
| [] | Pirajno F. 2009. Hydrothermal Processes and Mineral System. Perth, Australia: Springer Press: 1-1250. |
| [] | Qi JP, Chen YJ, Ni P, Lai Y, Ding JY, Song YW, Tang GJ. 2007. Fluid inclusion constraints on the origin of the Lengshuibeigou Pb-Zn-Ag deposit, Henan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(9): 2119–2130. |
| [] | Qiu HN, Wijbrans JR. 2008. The Paleozoic metamorphic history of the Central Orogenic Belt of China from 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of eclogite garnet fluid inclusions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 268(3-4): 501–514. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.01.042 |
| [] | Richards JP. 2003. Tectono-magmatic precursors for porphyry Cu-(Mo-Au) deposit formation. Economic Geology, 98(8): 1515–1533. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.98.8.1515 |
| [] | Sengor AMC and Natal'in BA. 1996. Paleotectonics of Asia: Frangments of synthesis. In: Yin A and Harrison TM (eds.). The Tectonic Evolution of Asia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 480-640 |
| [] | Shan Q, Niu HC, Yu XY, Zeng QS. 2007. Geochemical characteristics, magmtic genesis and tectonic background of the Late Paleozoic high potassium and high silicon ignimbrite on the southern margin of Altaid, North Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(7): 1721–1729. |
| [] | Shan Q, Zeng QS, Li NB, Yang WB, Luo Y, Jiang YH, Yu XY. 2012. Zircon U-Pb ages and geochemistry of the potassic and sodic rhyolites of the Kangbutiebao Formation in the southern margin of Altay, Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(7): 2132–2144. |
| [] | Sillitoe RH. 1972. A plate tectonic model for the origin of porphyry copper deposits. Economic Geology, 67(2): 184–197. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.67.2.184 |
| [] | Tong MY. 2007. Geological characteristics and genesis of Tiemuerte Pb-Zn deposit. Xinjiang Nonferrous Metal, 30(Suppl.): 42–44. |
| [] | Tong Y, Wang T, Hong DW, Liu XM, Han BF. 2005. Zircon U-Pb age of syn-orogenic Tielieke pluton in the western part of Altay orogenic belt and its structural implications. Acta Geoscientic Sinica, 26(Suppl.1): 74–77. |
| [] | Tu GC, Li CY. 2006. Brief remarks on comparative metallogeny. Geochimica, 35(1): 1–5. |
| [] | Wan B, Zhang LC. 2006. Sr-Nd-Pb isotope geochemistry and tectonic setting of Devonian polymetallic metallogenic belt on the southern margin of Altaids, Xingjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(1): 145–152. |
| [] | Wan B, Zhang LC, Xiao WJ. 2010a. Geological and geochemical characteristics and ore genesis of the Keketale VMS Pb-Zn deposit, southern Altay metallogenic belt, NW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 37(2): 114–126. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2010.01.002 |
| [] | Wan B, Zhang LC, Xiang P. 2010b. The Ashele VMS-type Cu-Zn deposit in Xinjiang, NW China formed in a rifted arc setting. Resource Geology, 60(2): 150–164. DOI:10.1111/(ISSN)1751-3928 |
| [] | Wan B, Xiao W, Zhang L, Windley BF, Han C, Quinn CD. 2011. Contrasting styles of mineralization in the Chinese Altai and East Junggar, NW China: Implications for the accretionary history of the southern Altaids. Journal of the Geological Society, 168(6): 1311–1321. DOI:10.1144/0016-76492011-021 |
| [] | Wan B, Xiao WJ, Zhang LC, Han CM. 2012. Iron mineralization associated with a major strike-slip shear zone: Radiometric and oxygen isotope evidence from the Mengku deposit, NW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 44: 136–147. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.09.011 |
| [] | Wang JB, Qin KZ, Wu ZL, Hu JH, Deng JN. 1998. Volcanic-exhalative-sedimentary Lead Zinc Deposit in the Southern Margin of the Altai, Xinjiang. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-210. |
| [] | Wang KY, Wang L, Liu ZH. 2008. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and origin of Gaojiapuzi silver deposit, Liaoning Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(9): 2085–2093. |
| [] | Wang SL, Chen KQ, Kang JC, Guo Q. 2007. Stable isotope of Pb-Zn deposits occurred in the Maizi Devolnian volcanic-sedimentary basin in the south margin of Altay Mountain, Xinjiang. Geology and Prospecting, 43(6): 25–31. |
| [] | Wang T, Hong DW, Jahn BM, Tong Y, Wang YB, Han BF, Wang XX. 2006. Timing, petrogenesis, and setting of Paleozoic synorogenic intrusions from the Altai Mountains, Northwest China: Implications for the tectonic evolution of an accretionary orogen. Journal of Geology, 114(6): 735–751. DOI:10.1086/507617 |
| [] | Wu YB, Zheng YF. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(16): 1589–1604. |
| [] | Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Hao J. 2003. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the Central Asian orogenic belt. Tectonics, 22(6): 1069–1080. |
| [] | Xiao WJ, Shu LS, Gao J, Xiong XL, Wang JB, Guo ZJ, Li JY, Sun M. 2008. Continental dynamics of the Central Asian orogenic belt and its metallogeny. Xinjiang Geology, 26(1): 4–7. |
| [] | Xiao WJ, Kusky T. 2009. Geodynamic processes and metallogenesis of the Central Asian and related orogenic belts, introduction. Gondwana Research, 16(2): 167–169. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2009.05.001 |
| [] | Xu JH, Shan LH, Ding RF, Hart C, Wang LL, Wei XF. 2008. Carbonic fluid inclusion assemblages and their geological significance at the Tiemurte lead-zinc deposit, Altay. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(9): 2094–2104. |
| [] | Xu XC, Zheng CQ, Zhao QY. 2005. Metamorphic types and crustal evolution of hercynian orogenic belt in Altai Region, Xinjiang. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 23(1): 7–11. |
| [] | Yan XJ, Chen WM. 2001. Geological and geochemical study on Tiemierte-Qiaxia-Sarekuobu polymetallic gold deposit series. Mineral Resources and Geology, 85(15): 366–370. |
| [] | Yang FQ, Mao JW, Yan SH, Liu F, Chai FM, Zhou G., Liu GR, He LX, Geng XX, Dai JZ. 2008. Geochronology, geochemistry and geological implications of the Mengku synorogenic plagiogranite pluton in Altay, Xinjiang. Acta Geologica Sinica, 82(4): 485–499. |
| [] | Yin YQ, Yang YM, Li JX, Guo ZL, Guo XJ. 2005. Sediment-structural evolution and lead-zinc mineralization in the Devonian volcanic-sedimentary Kelan Basin in southern Altay, Xinjiang. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 29(4): 53–59. |
| [] | Yuan C, Sun M, Xiao WJ, Li XH, Chen HL, Lin SF, Xi XP, Long XP. 2007. Accretionary orogenesis of the Chinese Altai: Insights from Paleozoic granitoids. Chemical Geology, 242(1-2): 22–39. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.02.013 |
| [] | Yuan HL, Wu FY, Gao S, Liu XM, Xu P, Sun DY. 2003. Determination of U-Pb age and rare earth element concentrations of zircons from Cenozoic intrusions in northern China by laser ablation ICP-MS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(22): 2411–2421. |
| [] | Zeng QS, Chen GH, Wang H, Shan Q. 2007. Geochemical characteristics, SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating and tectonic implication for granitoids in Chonghuer basin, Altai, Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(8): 1921–1932. |
| [] | Zhang HX, Niu HC, Terada K. 2003. SHRIMP zircon age of the plagiogranite in Kuerti ophiolite of the North Altai area, Xinjiang, China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(12): 1350–1354. |
| [] | Zhang J, Chen YJ, Li GP, Li ZL, Wang ZG. 2004. Characteristics of ore geology and fluid inclusion of the Yindonggou silver deposit, Neixiang County, Henan Province: Implication for metallogenic type. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 24(3): 55–64. |
| [] | Zhang J, Chen YJ, Chen HY, Zhang G, Yang Y. 2008. Isotope geochemistry of the Weishancheng stratabound gold-silver ore belt, Tongbai County, Henan Province, China. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(4): 108–124. DOI:10.1016/S1872-5791(08)60043-3 |
| [] | Zhang J, Yang Y, Lu YH, Chen YJ, Wan SQ, Ma HW. 2008. Geological and geochemical characteristics and genesis of the Poshan silver deposit, Henan Province. Geology in China, 35(6): 1220–1229. |
| [] | Zhang J, Chen YJ, Qi JP, Ge J. 2009. Comparison of the typical metallogenic systems in the north slope of the Tongbai-East Qinling Mountains and its geologic implications. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(2): 396–410. DOI:10.1111/acgs.2009.83.issue-2 |
| [] | Zhang J, Yang Y, Hu HZ, Wang ZG, Li GP, Li ZL. 2009. C-S-Pb isotope geochemistry of the Yindonggou orogenic-type silver deposit in Neixiang County, Henan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11): 2833–2842. |
| [] | Zhang J, Chen YJ, Yang Y, Deng J. 2011. Lead isotope systematics of the Weishancheng Au-Ag belt, Tongbai Mountains, Central China: Implication for ore genesis. International Geology Review, 53(5-6): 656–676. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2010.496196 |
| [] | Zhang L, Zheng Y, Chen YJ. 2012. Ore geology and fluid inclusion geochemistry of the Tiemurt Pb-Zn-Cu deposit, Altay, Xinjiang, China: A case study of orogenic-type Pb-Zn systems. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 49: 69–79. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.11.019 |
| [] | Zhang ZC, Yan SH, Chen BL, Zhou G, He YK, Chai FM, He LX, Wan YS. 2006. The SHRIMP zircon age of the granites in northeastern Junggar, Xinjiang. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51(13): 1565–1574. |
| [] | Zheng Y, Zhang L, Chen YJ, Qin YJ, Liu CF. 2012. Geology, fluid inclusion geochemistry, and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Wulasigou Cu deposit, and their implications for ore genesis, Altay, Xinjiang, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 49: 128–140. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.09.005 |
| [] | Zhu BQ. 1998. The Theory and Application of Isotope System in Earth Science Field-and the Continental Crustal and Mantle Evolutions. Beijing: Science Press: 1-330. |
| [] | 陈汉林, 杨树锋, 厉子龙, 袁超, 肖文交, 李继亮, 余星, 林秀斌. 2006. 阿尔泰造山带南缘基性杂岩的形成背景及其动力学含义. 岩石学报, 22(1): 127–134. |
| [] | 陈衍景, 富士谷. 1992. 豫西金矿成矿规律. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-234. |
| [] | 陈衍景. 2000. 中国西北地区中亚型造山-成矿作用的研究意义和进展. 高校地质学报, 6(1): 17–22. |
| [] | 陈衍景. 2006. 造山型矿床、成矿模式及找矿潜力. 中国地质, 33(6): 1181–1196. |
| [] | 陈衍景, 倪培, 范宏瑞, PirajnoF, 赖勇, 苏文超, 张辉. 2007. 不同类型热液金矿系统的流体包裹体特征. 岩石学报, 23(9): 2085–2108. |
| [] | 陈衍景, 肖文交, 张进江. 2008. 成矿系统:地球动力学的有效探针. 中国地质, 35(6): 1059–1073. |
| [] | 陈衍景, 李诺. 2009. 大陆内部浆控高温热液矿床成矿流体性质及其与岛弧区同类矿床的差异. 岩石学报, 25(10): 2477–2508. |
| [] | 单强, 牛贺才, 于学元, 曾乔松. 2007. 新疆北部阿尔泰南缘晚古生代高钾高硅熔结凝灰岩的地球化学、岩浆成因及构造背景. 岩石学报, 23(7): 1721–1729. |
| [] | 单强, 曾乔松, 李宁波, 杨武斌, 罗勇, 姜玉航, 于学元. 2012. 新疆阿尔泰南缘康布铁堡组钾-钠质流纹岩锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学. 岩石学报, 28(7): 2132–2144. |
| [] | 邓小华, 李文博, 李诺, 糜梅, 张颖. 2008. 河南嵩县纸房钼矿床流体包裹体研究及矿床成因. 岩石学报, 24(9): 2133–2148. |
| [] | 邓小华, 糜梅, 李文博. 2009. 河南土门萤石脉型钼矿床流体包裹体研究及成因探讨. 岩石学报, 25(10): 2537–2549. |
| [] | 范宏瑞, 谢奕汉, 翟明国, 金成伟. 2003. 豫陕小秦岭脉状金矿床三期流体运移成矿作用. 岩石学报, 19(2): 260–266. |
| [] | 姜俊. 2003. 铁米尔特多金属矿床地质特征及成因探讨. 新疆有色地质, 26(2): 2–5. |
| [] | 李文博, 赖勇, 孙希文, 王宝国. 2007. 内蒙古白乃庙铜金矿床流体包裹体研究. 岩石学报, 23(9): 2165–2176. |
| [] | 李文博, 陈衍景, 赖勇, 季建清. 2008. 内蒙古白乃庙铜金矿床的成矿时代和成矿构造背景. 岩石学报, 24(4): 890–898. |
| [] | 马忠美, 仇银江, 郭旭吉. 2001. 萨热阔布-铁米尔特矿区金铅锌成矿系列. 地质与勘探, 37(4): 23–26. |
| [] | 倪智勇, 李诺, 管申进, 张辉, 薛良伟. 2008. 河南小秦岭金矿田大湖金-钼矿床流体包裹体特征及矿床成因. 岩石学报, 24(9): 2058–2068. |
| [] | 牛贺才, 许继峰, 于学元, 陈繁荣, 郑作平. 1999. 新疆阿尔泰富镁火山岩系的发现及其地质意义. 科学通报, 44(9): 1002–1004. |
| [] | 牛贺才, 于学元, 许继峰, 单强, 陈繁荣, 张海祥, 郑作平. 2006. 中国新疆阿尔泰晚古生代火山作用及成矿. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-184. |
| [] | 祁进平, 陈衍景, 倪培, 赖勇, 丁俊英, 宋要武, 唐国军. 2007. 河南冷水北沟铅锌银矿床流体包裹体研究及矿床成因. 岩石学报, 23(9): 2119–2130. |
| [] | 童满云. 2007. 铁米尔特铁矿地质特征及矿床成因浅析. 新疆有色地质, 30(增刊): 42–44. |
| [] | 童英, 王涛, 洪大卫, 柳晓明, 韩宝福. 2005. 阿尔泰造山带西段同造山铁列克花岗岩体锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义. 地球学报, 26(增刊): 74–77. |
| [] | 涂光炽, 李朝阳. 2006. 比较矿床学. 地球化学, 35(1): 1–5. |
| [] | 万博, 张连昌. 2006. 新疆阿尔泰南缘泥盆纪多金属成矿带Sr-Nd-Pb同位素地球化学与构造背景探讨. 岩石学报, 22(1): 145–152. |
| [] | 王京彬, 秦克章, 吴志亮, 胡剑辉, 邓吉牛. 1998. 阿尔泰山南缘火山喷流沉积型铅锌矿床. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-210. |
| [] | 王可勇, 王力, 刘正宏, 汪建宇. 2008. 辽宁高家堡子大型银矿床流体包裹体特征及矿床成因. 岩石学报, 24(9): 2085–2093. |
| [] | 王书来, 陈克强, 康吉昌, 郭全. 2007. 新疆阿尔泰山南缘产于麦兹泥盆纪火山-沉积盆地铅锌矿床稳定同位素特征. 地质与勘探, 43(6): 25–31. |
| [] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约. 科学通报, 49(16): 1589–1604. |
| [] | 肖文交, 舒良树, 高俊, 熊小林, 王京彬, 郭召杰, 李锦轶, 孙敏. 2008. 中亚造山带大陆动力学过程与成矿作用. 新疆地质, 26(1): 4–7. |
| [] | 徐九华, 单立华, 丁汝福, HartC, 王琳琳, 卫晓锋. 2008. 阿尔泰铁木尔特铅锌矿床的碳质流体组合及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 24(9): 2094–2104. |
| [] | 徐学纯, 郑常青, 赵庆英. 2005. 阿尔泰海西造山带区域变质作用类型与地壳演化. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 23(1): 7–11. |
| [] | 闫新军, 陈维民. 2001. 铁米尔特-恰夏-萨热阔布多金属金矿床系列矿床地质地球化学研究. 矿床与地质, 85(15): 366–370. |
| [] | 杨富全, 毛景文, 闫升好, 刘锋, 柴凤梅, 周刚, 刘国仁, 何立新, 耿新霞, 代军治. 2008. 新疆阿尔泰蒙库同造山斜长花岗岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义. 地质学报, 82(4): 485–499. |
| [] | 尹意求, 杨有明, 李嘉兴, 郭正林, 郭旭吉. 2005. 新疆阿尔泰山南缘克兰盆地沉积构造演化与铅锌成矿. 大地构造与成矿学, 29(4): 53–59. |
| [] | 袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 柳小明, 徐平, 孙德有. 2003. 东北地区新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析. 科学通报, 48(14): 1511–1520. |
| [] | 曾乔松, 陈广浩, 王核, 单强. 2007. 阿尔泰冲乎尔盆地花岗质岩类的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其构造意义. 岩石学报, 23(8): 1921–1932. |
| [] | 张海祥, 牛贺才, TeradaK. 2003. 新疆北部阿尔泰地区库尔提蛇绿岩中斜长花岗岩的SHRIMP年代学研究. 科学通报, 48(12): 1350–1354. |
| [] | 张静, 陈衍景, 李国平, 李忠烈, 王志光. 2004. 河南内乡县银洞沟银矿地质和流体包裹体特征及成因类型. 矿物岩石, 24(3): 55–64. |
| [] | 张静, 杨艳, 鲁颖淮, 陈衍景, 万守全, 马宏卫. 2008. 河南破山银矿床地质地球化学特征及成因研究. 中国地质, 35(6): 1220–1229. |
| [] | 张静, 杨艳, 胡海珠, 王志光, 李国平, 李忠烈. 2009. 河南银洞沟造山型银矿床硫碳铅同位素地球化学. 岩石学报, 25(11): 2833–2842. |
| [] | 张招崇, 闫升好, 陈柏林, 等. 2006. 新疆东准噶尔北部俯冲花岗岩的SHRIMP U-Pb锆石定年. 科学通报, 5l(13): 1561–1574. |
| [] | 朱炳泉. 1998. 地球科学中同位素体系理论与应用--兼论中国大陆壳幔演化. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-330. |
 2013, Vol. 29
2013, Vol. 29


