目前,多智能体系统的分布式协调控制引起了众多学者的关注,并得到了广泛应用。一致性问题是多智能体系统协调控制的最简单与最基本问题之一,得到了非常深入的研究,并取得了广泛的研究成果。
近些年,一致性滤波问题[1]引起了部分学者的研究兴趣,并在分布式估计、分布式传感器网络等领域得到应用。一致性滤波问题是指基于一致性协调控制的滤波算法,使每个智能体通过和相邻智能体之间进行信息通信来达到相同的状态;如果每个智能体渐近收敛到给定输入的平均值,那么这就是平均一致性滤波问题[2]。Olfati-Saber等[3-5]分别提出了分布式低通一致性滤波和高通一致性滤波,它们通过追踪网络中所有智能体输入的平均值来实现一致性滤波,但是存在估计误差。针对文献[3-5]中算法存在的误差,涌现了一些改进算法来减少估计误差[6-9]。Freeman等[7]提出了比例积分算法(proportional-integral algorithm),证明了该算法在输入是常量的情况下收敛一致。与文献[7]相比,Bai等[8]运用内部模型原则[10]设计传递函数使每个智能体跟踪所有时变输入的平均值。Li等[11]对比例积分算法(PI)进一步研究,提出了改进的PI算法,并证明该算法收敛到定常输入的加权平均值;同时,Li等[12]也提出一种新的混杂一致性滤波协议,给出了该协议分别在固定拓扑和切换图下渐近一致的条件。
实际上,在多智能体协调控制网络中,智能体之间进行信息传输伴随着通信时延,会影响系统集体行为。目前,具有通信时延的一阶和二阶多智能体系统的一致性问题受到了学者的广泛关注[13-18]。Olfati-Saber等[19]考察了具有通信时延的一阶多智能体系统的一致性问题,给出了在相同通信时延作用下多智能体系统收敛一致的时延范围。Wang等[20]基于圆盘定理和最大模原理,给出了智能体在具有不同通信时延的一阶多智能体系统达到渐近一致的收敛条件。Lin等[21]分析了具有相同时延的二阶多智能体系统的一致性问题,给出了一致性收敛的时延相关充要条件。针对具有不同时延的二阶多智能体系统的一致性问题,Yang等[22]根据小增益稳定性原理,分别得到具有时不变和时变通信时延的系统渐近达到一致的充要条件,并把结论运用到时延高阶多智能体系统的一致性分析中。
本文研究具有定常输入的二阶多智能体系统的平均一致性滤波问题。在现有的一致性滤波算法基础上,提出了一种比例积分算法(PI),并考察多智能体系统在定常输入和对称连通拓扑结构下的收敛问题。利用Routh判据,得到二阶多智能体系统渐近达到平均一致滤波的重要条件;根据Nyquist判据,分析了二阶多智能体系统在相同通信时延约束下渐近收敛平均一致滤波的充分条件。
1 问题描述 1.1 连接拓扑图| ${l_{ij}}{\rm{ = }}\left\{ \begin{array}{l}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 1}^n {{a_{ij}}} ,\;\;\;\;i = j\\ - {a_{ij}},\;\;\;\;i \ne j\end{array} \right.$ |
在图
在本文中,
| $\left\{ \begin{array}{l}{{\dot x}_i} = {v_i}\\{{\dot v}_i} = {u_i},i \in {{\varGamma }}\end{array} \right.$ | (1) |
式中:
| ${\lim _{t \to \infty }}{x_i}(t) = \frac{1}{n}\sum\limits_{i \in {{\varGamma }}} {{\varphi _i}} $ |
则称多智能体系统式(1)解决平均一致滤波问题。
为解决二阶多智能体系统的平均一致滤波问题,本文提出了比例-积分一致性滤波算法,即
| $\left\{ \begin{array}{l}{u_i} = - k{v_i} + \gamma ({\varphi _i} - {x_i}) - {k_P}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}({x_i} - {x_j})} - {k_I}{\eta _i}\\{{\dot \eta }_i} = \sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}({x_i} - {x_j})} \end{array} \right.$ | (2) |
式中:
在式(2)作用下,系统式(1)的闭环形式为
| $\left\{ \begin{array}{l}{{\dot x}_i} = {v_i}\\{{\dot v}_i} = - k{v_i} + \gamma ({\varphi _i} - {x_i}) - {k_P}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}({x_i} - {x_j})} - {k_I}{\eta _i}\\{{\dot \eta }_i} = \sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}({x_i} - {x_j})} \end{array} \right.$ | (3) |
将式(3)表示为多变量形式
| $\left\{ \begin{array}{l}{\dot{ x}} = {{v}}\\{\dot{ v}} = - k{{v}} + \gamma ({{\varphi }} - {{x}}) - {k_P}{{Lx}} - {k_I}{{\eta }}\\{\dot{ \eta }} = {{Lx}}\end{array} \right.$ | (4) |
将式(4)进行Laplace变换,可得
| $\begin{array}{c}{{x}}(s) = {{P}}(s){{\varphi }}(s) + \displaystyle\frac{{s + k}}{\gamma }{{P}}(s){{x}}(0) + \\[8pt]\displaystyle\frac{1}{\gamma }{{P}}(s){{v}}(0) - \displaystyle\frac{{{k_I}}}{\gamma }\frac{{{{P}}(s)}}{s}{{\eta }}(0)\end{array}$ | (5) |
其中
| ${{P}}(s) = \frac{{\gamma s{{I}}}}{{({s^3} + k{s^2} + \gamma s){{I}} + {k_p}{{L}}s + {k_I}{{L}}}}$ | (6) |
定理1 假设多智能体系统式(3)的连接拓扑为对称连通的,且
1)
2)
成立,其中,
证明 证明过程分两步。1) 利用Routh判据给出满足传递函数矩阵(6)特征方程的根在左半平面的条件;2) 利用传递函数的终值定理来证明多智能体系统式(3)渐近达到平均一致性。
1) 令传递函数矩阵
| $\det (({s^3} + k{s^2} + \gamma s){{I}} + {k_p}{{L}}s + {k_I}{{L}}) = 0$ | (7) |
等价于
| $\prod\limits_{i = 1}^n {{s^3} + k{s^2} + (\gamma + {k_p}{\lambda _i})s + {k_I}{\lambda _i} = 0} $ | (8) |
接下来,考察方程(9)的根的分布:
| ${s^3} + k{s^2} + (\gamma + {k_p}{\lambda _i})s + {k_I}{\lambda _i} = 0,\;i = 1, \cdots ,n$ | (9) |
当
| $s({s^2} + ks + \gamma ) = 0$ | (10) |
根据定理1的条件1)可得:特征方程式(10)有一个根
当
| $\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{s^3}}&1&{\gamma + {k_p}{\lambda _i}} \\ {{s^2}}&k&{{k_I}{\lambda _i}} \\ s&{\displaystyle\frac{{k(\gamma + {k_p}{\lambda _i}) - {k_I}{\lambda _i}}}{k}}&{} \\ {{s^0}}&{{k_I}{\lambda _i}}&{} \end{array}$ |
当且仅当定理1中的条件1)和2)都成立,Routh阵列表第一列系数为正数,特征方程式(9)的根是负实数。
因此,当且仅当定理1的条件1)和2)都成立时,多智能体系统式(3)渐近达到一致,则
2)为了证明多智能体系统式(3)渐近达到平均一致滤波,分别证明式(5)满足:
①
② 保证式(5)中
①的证明 在无向连通拓扑结构下,Laplacian矩阵
通过计算,可得
| $\begin{array}{c}{{P}}(s) = {{{Q}}^{\mathop{\rm T}\nolimits} }{{QP}}(s){{{Q}}^{\mathop{\rm T}\nolimits} }{{Q}} = \\{{{Q}}^{\mathop{\rm T}\nolimits} }\displaystyle\frac{{\gamma s{{I}}}}{{({s^3} + k{s^2} + \gamma s){{I}} + {k_p}{{QL}}{{{Q}}^{\mathop{\rm T}\nolimits} }s + {k_I}{{QL}}{{{Q}}^{\mathop{\rm T}\nolimits} }}}{{Q}} = \\[8pt]{{{Q}}^{\mathop{\rm T}\nolimits} }\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{h_1}(s)} & {{\bf{0}}_{n - 1}^{\rm{T}}}\\{{{\bf{0}}_{n - 1}}} & {{\bar{ P}}(s)}\end{array}} \right){{Q}}\end{array}$ | (11) |
式中
| ${h_1}(s) = \frac{\gamma }{{{s^2} + ks + \gamma }}$ | (12) |
| $\begin{array}{c}{\bar{ P}}(s) = {\mathop{\rm diag}\nolimits} \left\{ {\displaystyle\frac{{\gamma s}}{{{s^3} + k{s^2} + (\gamma + {k_p}{\lambda _2})s + {k_I}{\lambda _2}}}} \right., \cdots ,\\[8pt]\left. {\displaystyle\frac{{\gamma s}}{{{s^3} + k{s^2} + (\gamma + {k_p}{\lambda _n})s + {k_I}{\lambda _n}}}} \right\}\end{array}$ | (13) |
根据终值定理可得
| $\begin{array}{c}{\lim _{s \to 0}}s{{P}}(s)\displaystyle\frac{{{\varphi }}}{s} = {{P}}(0){{\varphi }} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{\displaystyle\frac{{{{\bf{1}}_n}}}{{\sqrt n }}} & {{S}}\end{array}} \right)\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{h_1}(0)} & {{\bf{0}}_{n - 1}^{\rm{T}}}\\{{{\bf{0}}_{n - 1}}} & {{\bar{ P}}(0)}\end{array}} \right)\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{\displaystyle\frac{{{\bf{1}}_n^{\rm{T}}}}{{\sqrt n }}}\\{{{{S}}^{\rm{T}}}}\end{array}} \right){{\varphi }} = \\[8pt]\displaystyle\frac{{{{\bf{1}}_n}{\bf{1}}_n^{\rm{T}}}}{n}{h_1}(0){{\varphi }} + {{S\bar P}}(0){{{S}}^{\mathop{\rm T}\nolimits} }{{\varphi }}\end{array}$ | (14) |
根据式(12)、(13)可得
因此,得到
②的证明 由①的证明可得:
| ${\lim _{s \to 0}}s\frac{{s + k}}{\gamma }{{P}}(s){{x}}(0) = {\lim _{s \to 0}}s\frac{{s + k}}{\gamma }s{{P}}(s)\frac{{{{x}}(0)}}{s} = {{\bf{0}}_n}$ |
| ${\lim _{s \to 0}}s\frac{1}{\gamma }{{P}}(s){{v}}(0) = {\lim _{s \to 0}}s\frac{1}{\gamma }s{{P}}(s)\frac{{{{v}}(0)}}{s} = {{\bf{0}}_n}$ |
同时,结合定理1中的假设
| $\begin{array}{c}{\lim _{s \to 0}}s\displaystyle\frac{{{k_I}}}{\gamma }\frac{{{{P}}(s)}}{s}{{\eta }}(0) = {\lim _{s \to 0}}\frac{{{k_I}}}{\gamma }s{{P}}(s)\frac{{{{\eta }}(0)}}{s} = \\\displaystyle\frac{{{k_I}}}{\gamma }\frac{{{{\bf{1}}_n}{\bf{1}}_n^{\mathop{\rm T}\nolimits} }}{n}{{\eta }}(0) = \frac{{{k_I}{{\bf{1}}_n}}}{{n\gamma }}\sum\limits_{i \in {{\Gamma }}} {{\eta _i}(0) = {{\bf{0}}_n}} \end{array}$ |
综合证明①和②,可以得到
由于通信时延在多智能体系统协调控制中不可忽略,接下来考察式(2)在相同通信时延约束下的收敛问题:
| $\begin{array}{c}{u_i}(t) = - k{v_i}(t) + \gamma ({\varphi _i} - {x_i}(t)) - \\{k_p}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}} ({x_i}(t - \tau ) - {x_j}(t - \tau )) - {k_I}{\eta _i}(t)\\[8pt]{{\dot \eta }_i}(t) = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}} ({x_i}(t - \tau ) - {x_j}(t - \tau ))\end{array}$ | (15) |
在式(15)作用下,多智能体系统式(1)的闭环形式为
| $\left\{ \begin{array}{l}{{\dot x}_i}(t) = {v_i}(t)\\{{\dot v}_i}(t) = - k{v_i}(t) + \gamma ({\varphi _i} - {x_i}(t)) - \\\quad\quad{k_p}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}} ({x_i}(t - \tau ) - {x_j}(t - \tau )) - {k_I}{\eta _i}(t)\\[6pt]{{\dot \eta }_i}(t) = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}} ({x_i}(t - \tau ) - {x_j}(t - \tau ))\end{array} \right.$ | (16) |
式中通信延时
| $\left\{ \begin{array}{l}\!\!\! s{x_i}(s) - {x_i}(0) = {v_i}(s)\\\!\!\! s{v_i}(s) - {v_i}(0) = - k{v_i}(s) + \gamma ({\varphi _i}(s) - {x_i}(s)) - \\\quad{k_p}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}} ({x_i}(s) - {x_j}(s)){{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }} - {k_p}{w_i}(s) - {k_I}{\eta _i}(s)\\\!\!\! s{\eta _i}(s) - {\eta _i}(0) = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}} ({x_i}(s) - {x_j}(s)){{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }} - {w_i}(s)\end{array} \right.$ | (17) |
式中
| ${w_i}(s) = \sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}} \int_{ - \tau }^0 {({x_i}(\theta ) - {x_j}(\theta ))} {{\rm{e}}^{ - s\theta }}{\rm{d}}\theta $ |
定义一个向量
| $\begin{array}{c}{{x}}(s) = {{{G}}_\tau }(s){{\varphi }}(s) + \\\displaystyle\frac{{s + k}}{\gamma }{{{G}}_\tau }(s){{x}}(0) + \frac{1}{\gamma }{{{G}}_\tau }(s){{v}}(0) - \\[6pt]\displaystyle\frac{{{k_I}}}{\gamma }\frac{{{{{G}}_\tau }(s)}}{s}{{\eta }}(0) + \frac{{{k_I} - {k_p}s}}{{\gamma s}}{{{G}}_\tau }(s){{w}}(s)\end{array}$ | (18) |
式中
| ${{{G}}_\tau }(s) = \frac{{\gamma s{{I}}}}{{({s^3} + k{s^2} + \gamma s){{I}} + {k_p}{{L}}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }}s + {k_I}{{L}}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }}}}$ | (19) |
定理2 假设多智能体系统式(16)的连接拓扑为对称连通的。参数
1)
2)
成立,其中
| ${y^3} + ({k^2} - 2\gamma ){y^2} + ({\gamma ^2} - k_p^2\lambda _i^2)y - k_I^2\lambda _i^2 = 0,i = 2,3, \cdots ,n$ | (20) |
在证明定理2之前,先给出2个有用的引理:
引理1 考察函数:
| $f(x) = \frac{{{c_1}x + {c_2}}}{{{x^3} + {c_3}{x^2} + {c_4}x}}$ |
假设满足
证明 对
| $f'(x) = \frac{{ - 2{c_1}{x^3} - ({c_1}{c_3} + 3{c_2}){x^2} - 2{c_2}{c_3}x - {c_2}{c_4}}}{{{{({x^3} + {c_3}{x^2} + {c_4}x)}^2}}}$ |
由于
引理2 考虑3次多项式:
| ${f_1}(x) = {x^3} + {d_1}{x^2} + {d_2}x + {d_3}$ |
假设满足系数
定理2证明 证明过程分两步。1)利用频域分析方法来给出使系统式(16)渐近达到平均一致滤波的通信时延
1)根据式(19)
| $\det (({s^3} + k{s^2} + \gamma s){{I}} + {k_p}{{L}}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }}s + {k_I}{{L}}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }}) = 0$ |
等价于
| $\prod\limits_{i = 1}^n {{s^3} + k{s^2} + \gamma s + {k_p}{\lambda _i}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }}s + {k_I}{\lambda _i}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }} = 0} $ | (21) |
考察方程式(22)的根:
| ${s^3} + k{s^2} + \gamma s + {k_p}{\lambda _i}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }}s + {k_I}{\lambda _i}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }}{\rm{ = }}0,i = 1,2, \cdots ,n$ | (22) |
当
| ${0^3} + k{0^2} + \gamma 0 + {k_p}{\lambda _i}{{\rm{e}}^{ - 0\tau }}0 + {k_I}{\lambda _i}{{\rm{e}}^{ - 0\tau }}{\rm{ = }}0$ |
满足
当
| $1 + \frac{{{k_p}{\lambda _i}(s + \displaystyle\frac{{{k_I}}}{{{k_p}}})}}{{{s^3} + k{s^2} + \gamma s}}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }} = 0$ | (23) |
开环特征函数为
| $k(s) = \frac{{{k_p}{\lambda _i}(s + \displaystyle\frac{{{k_I}}}{{{k_p}}})}}{{{s^3} + k{s^2} + \gamma s}}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }}$ | (24) |
当
| $k({\rm{j}} w) = \frac{{{k_p}{\lambda _i}({\rm{j}} w + \displaystyle\frac{{{k_I}}}{{{k_p}}})}}{{{{({\rm{j}} w)}^3} + k{{({\rm{j}} w)}^2} + {\rm{j}} \gamma w}}{{\rm{e}} ^{ - {\rm{j}} w\tau }}$ | (25) |
根据Nyquist判据,特征方程(22)的根是负实数,等价于
| ${A_i}(w) = \frac{{{k_p}{\lambda _i}\sqrt {{w^2} + \displaystyle\frac{{k_I^2}}{{k_P^2}}} }}{{w\sqrt {{k^2}{w^2} + {{(\gamma - {w^2})}^2}} }}$ | (26) |
相频特性为
| $\beta (w) = \arctan (\frac{{{k_p}}}{{{k_I}}}w) - {\rm{arccot}} (\frac{{\gamma - {w^2}}}{{kw}}) - w\tau - \frac{\text{π}}{2}$ | (27) |
接下来,考察
| $f(y) = \frac{{k_p^2y + k_I^2}}{{{y^3} + ({k^2} - 2\gamma ){y^2} + {\gamma ^2}y}}$ | (28) |
由于
| ${y^3} + ({k^2} - 2\gamma ){y^2} + ({\gamma ^2} - k_p^2\lambda _i^2)y - k_I^2\lambda _i^2 = 0$ | (29) |
由于
| $\beta ({w_i}) = \beta (\sqrt {{y_i}} ) > - {\rm{\pi }}$ | (30) |
由式(27)得
| ${\tau _i} < \frac{{\arctan (\sqrt {{y_i}} \displaystyle\frac{{{k_p}}}{{{k_I}}}) - {\rm{arccot}} (\displaystyle\frac{{\gamma - {y_i}}}{{k\sqrt {{y_i}} }}) + \displaystyle\frac{{\rm{\pi }}}{2}}}{{\sqrt {{y_i}} }}$ | (31) |
取得的最小时延
因此,当条件1)和2)成立时,特征方程式(22)的根满足:
2)根据定理1中①的证明,可得
| $\begin{array}{l}{{{G}}_\tau }(s) = {{{Q}}^{\rm{T}}}{{Q}}{{{G}}_\tau }(s){{{Q}}^{\rm{T}}}{{Q}} = \\[5pt]{{{Q}}^{\rm{T}}}\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{h_1}(s)} & {{\bf{0}}_{n - 1}^{\rm{T}}}\\[5pt]{{{\bf{0}}_{n - 1}}} & {{{{\bar{ G}}}_\tau }(s)}\end{array}} \right]{{Q}}\end{array}$ | (32) |
式中
| $\begin{array}{c}{{{\bar{ G}}}_\tau }(s) = {\mathop{\rm diag}\nolimits} \left\{ {\displaystyle\frac{{\gamma s}}{{{s^3} + k{s^2} + (\gamma + {k_p}{\lambda _2}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }})s + {k_I}{\lambda _2}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }}}}} \right. , \cdots , \\\left. {\displaystyle\frac{{\gamma s}}{{{s^3} + k{s^2} + (\gamma + {k_p}{\lambda _n}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }})s + {k_I}{\lambda _n}{{\rm{e}}^{ - s\tau }}}}} \right\}\end{array}$ | (33) |
| ${{\bar{ G}}_\tau }(0) = {{\bf{0}}_{n \times n}}$ | (34) |
根据
| ${{{G}}_\tau }(0) = {{{Q}}^{\rm{T}} }{{Q}}{{{G}}_\tau }(0){{{Q}}^{\rm{T}} }{{Q}} = \frac{{{{\bf{1}}_n}{\bf{1}}_n^{\rm{T}} }}{n}$ | (35) |
根据终值定理
| ${\lim _{s \to 0}}s{{{G}}_\tau }(s)\frac{{{\varphi }}}{s} = {{{G}}_\tau }(0){{\varphi }} = \frac{{{{\bf{1}}_n}{\bf{1}}_n^{\rm{T}}}}{n}{{\varphi }}$ | (36) |
与定理1的②的证明类似,式(18)运用终值定理,可得
| ${\lim _{s \to 0}}s\frac{{s + k}}{\gamma }{{{G}}_\tau }(s){{x}}(0) = {{\bf{0}}_n}$ | (37) |
| ${\lim _{s \to 0}}s\frac{1}{\gamma }{{{G}}_\tau }(s){{v}}(0) = {{\bf{0}}_n}$ | (38) |
同时,结合定理2中的假设
| ${\lim _{s \to 0}}s\frac{{{k_I}}}{\gamma }\frac{{{{{G}}_\tau }(s)}}{s}{{\eta }}(0) = \frac{{{k_I}{{\bf{1}}_n}}}{{\gamma n}}{\bf{1}}_n^{\rm{T}} {{\eta }}(0) = {{\bf{0}}_n}$ | (39) |
| $\begin{array}{c}{\lim _{s \to 0}}s\displaystyle\frac{{{k_I} - {k_p}s}}{{\gamma s}}{{{G}}_\tau }(s){{w}}(s) = \displaystyle\frac{{{k_I}}}{\gamma }{{{G}}_\tau }(0){{w}}(0) = \frac{{{k_I}{{\bf{1}}_n}}}{{\gamma n}}{\bf{1}}_n^{\rm{T}}{{w}}(0) = \\[10pt]\displaystyle\frac{{{k_I}{{\bf{1}}_n}}}{{\gamma n}}\sum\limits_{i \in {{\varGamma }}} {\left(\sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}} \int_{ - T}^0 {({x_i}(\tau ) - {x_j}(\tau ))} {\rm{d}}\tau \right)} \end{array}$ | (40) |
由于
| ${a_{ij}}\int_{ - T}^0 {({x_i}(\tau ) - {x_j}(\tau ))} {\rm{d}}\tau + {a_{ji}}\int_{ - T}^0 {({x_j}(\tau ) - {x_i}(\tau ))} {\rm{d}}\tau = 0$ |
因此
| $\sum\limits_{i \in {{\varGamma }}} {\left(\sum\limits_{j \in {N_i}} {{a_{ij}}} \int_{ - T}^0 {({x_i}(\tau ) - {x_j}(\tau ))} {\rm{d}}\tau \right)} = 0$ | (41) |
根据式(41),式(40)可以进一步表述为
| ${\lim _{s \to 0}}s\frac{{{k_I} - {k_p}s}}{{\gamma s}}{{{G}}_\tau }(s){{w}}(s) = {{\bf{0}}_n}$ | (42) |
根据式(36)~(39)、(42),得到
根据定理2的证明,如果条件1)成立,
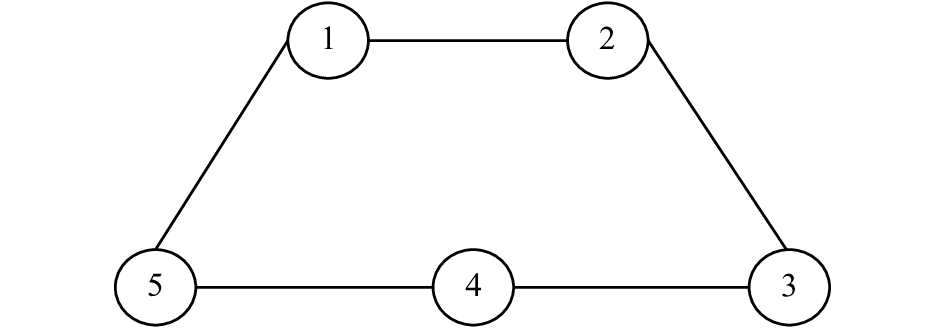
考察由5个智能体构成的多智能体系统,其拓扑结构是无向连通的(见图1)。在连接拓扑中,智能体之间的连接权值是对称的,分别为:
|
Download:
|
| 图 1 包含4个多智能连接拓扑G Fig. 1 Graphical topology of four agents | |
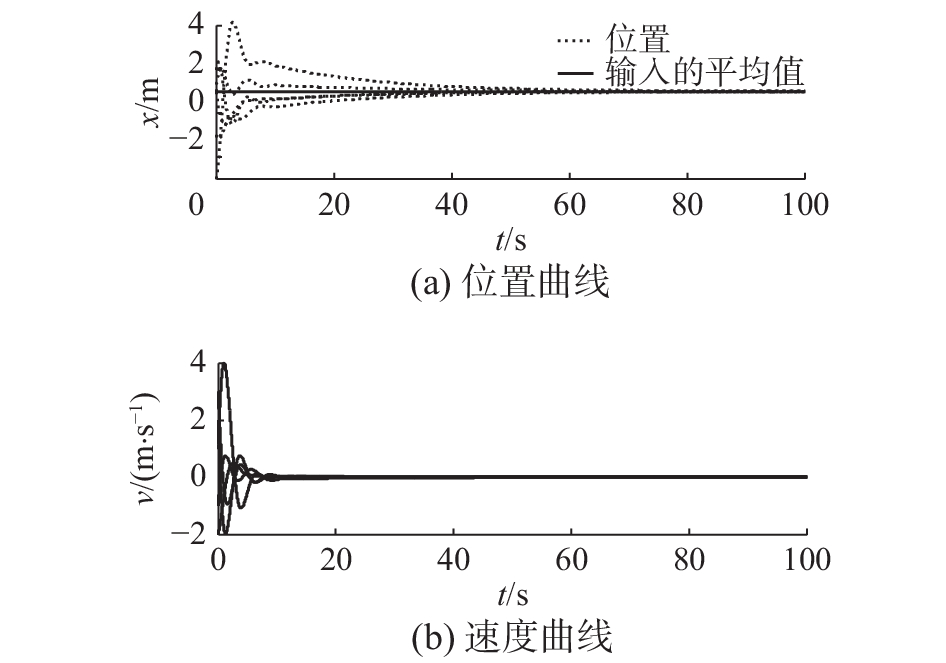
随机设定智能体初始位置和初始速度,且内部状态的初始值设为
|
Download:
|
|
图 2 智能体的位置和速度(
|
|
|
Download:
|
|
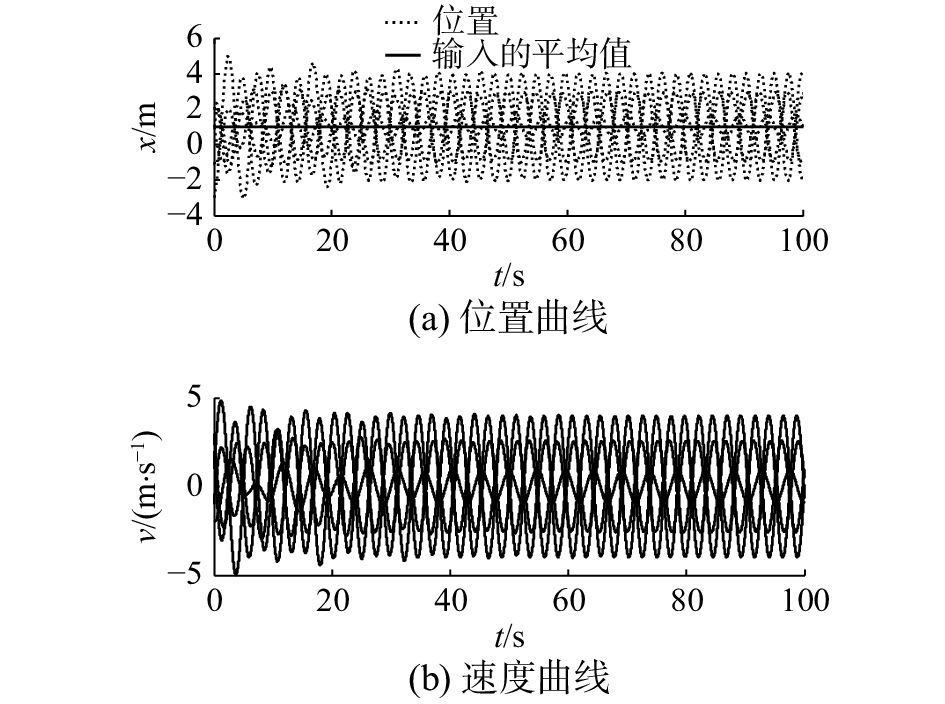
图 3 智能体的位置和速度(
|
|

|
Download:
|
|
图 4 智能体的位置和速度(
|
|
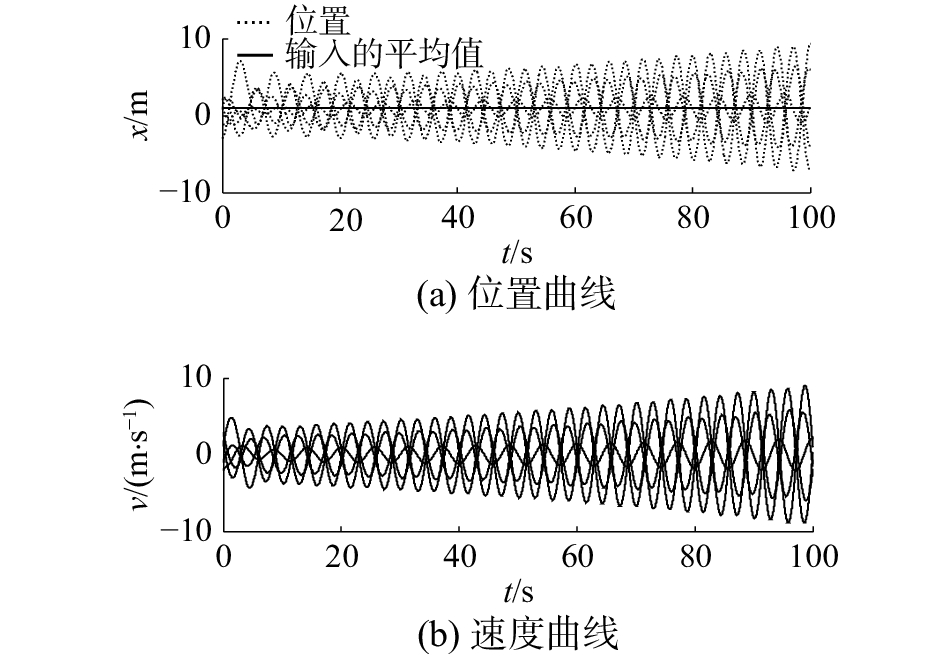
针对具有通信时延的多智能体系统式(16),选择和3.1小节中的相同连接拓扑、连接权重以及控制参数:
| $\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle\frac{{{\rm{d}}\varphi (w)}}{{{\rm{d}}w}} = - T + \displaystyle\frac{1}{{\left[ {1 + {{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{{{k_p}}}{{{k_I}}}} \right)}^2}{w^2}} \right][{k^2}{w^2} + {{(\gamma - {w^2})}^2}]}} \times \\\left\{ \! {\displaystyle\frac{{{k_p}}}{{{k_I}}}(1 - k\frac{{{k_p}}}{{{k_I}}}){w^4} \!+\! [\frac{{{k_p}}}{{{k_I}}}({k^2} \!-\! 2\gamma ) - k - k{{(\displaystyle\frac{{{k_p}}}{{{k_I}}})}^2}\gamma ]{w^2} \!+\! \displaystyle\frac{{{k_p}}}{{{k_I}}}{\gamma ^2} \!-\! k\gamma } \! \right\} \!\!= \\ - T + \displaystyle\frac{{ - 164{w^4} - 49{w^2} + 0.9}}{{(1 + 177.8{w^2})({w^4} + 0.4{w^2} + 0.09)}}\end{array}$ |
显然,
给定任意选择智能体的初始状态,且选择

|
Download:
|
|
图 5 智能体的位置和速度(
|
|
|
Download:
|
|
图 6 智能体的位置和速度(
|
|
针对具有定常输入的二阶多智能体系统的平均一致性滤波问题,本文研究对称连通拓扑结构下的一致性算法的设计与分析。本文设计一种PI型一致性滤波算法。利用Routh判据,分析二阶多智能体系统实现渐近平均一致滤波的充要条件。当系统存在通信时延的情况下,采用同步匹配的一致性算法形式,并利用Nyquist稳定判据得到二阶多智能体系统渐近收敛平均一致滤波的时延相关收敛条件,在特定参数条件下,该时延条件也是充要条件。
| [1] |
BATTISTELLI G, CHISCI L, FANTACCI C, et al. Consensus-based multiple-model Bayesian filtering for distributed tracking[J]. IET radar, sonar and navigation, 2015, 9(4): 401-410. DOI:10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0071 ( 0) 0)
|
| [2] |
TINATI M A, REZAII T Y. Multi-target tracking in wireless sensor networks using distributed joint probabilistic data association and average consensus filter[C]//Proceedings of 2009 International Conference on Advanced Computer Control. Singapore, 2009: 51–56.
( 0) 0)
|
| [3] |
OLFATI-SABER R. Distributed Kalman filtering and sensor fusion in sensor networks[C]//ANTSAKLIS P, TABUADA P. Networked Embedded Sensing and Control. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2006: 157–167.
( 0) 0)
|
| [4] |
OLFATI-SABER R, SHAMMA J S. Consensus filters for sensor networks and distributed sensor fusion[C]//Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Seville, Spain, 2005: 6698–6703.
( 0) 0)
|
| [5] |
OLFATI-SABER R. Distributed Kalman filtering for sensor networks[C]//Proceedings of the 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. New Orleans, LA, USA, 2007: 5492–5498.
( 0) 0)
|
| [6] |
YANG Peng, FREEMAN R A, LYNCH K M. Multi-agent coordination by decentralized estimation and control[J]. IEEE transactions on automatic control, 2008, 53(11): 2480-2496. DOI:10.1109/TAC.2008.2006925 ( 0) 0)
|
| [7] |
FREEMAN R A, YANG Peng, LYNCH K M. Stability and convergence properties of dynamic average consensus estimators[C]//Proceedings of the 45th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. San Diego, CA, USA, 2006: 338–343.
( 0) 0)
|
| [8] |
BAI He, FREEMAN R A, LYNCH K M. Robust dynamic average consensus of time-varying inputs[C]//Proceedings of the 49th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Atlanta, GA, USA, 2011: 3104–3109.
( 0) 0)
|
| [9] |
ELWIN M L, FREEMAN R A, LYNCH K M. A systematic design process for internal model average consensus estimators[C]//Proceedings of the 52nd IEEE Annual Conference on Decision and Control. Florence, Italy, 2013: 5878–5883.
( 0) 0)
|
| [10] |
FRANCIS B A, WONHAM W M. The internal model principle of control theory[J]. Automatica, 1976, 12(5): 457-465. DOI:10.1016/0005-1098(76)90006-6 ( 0) 0)
|
| [11] |
LI Shuai, GUO Yi. Dynamic consensus estimation of weighted average on directed graphs[J]. International journal of systems science, 2015, 46(10): 1839-1853. DOI:10.1080/00207721.2013.837541 ( 0) 0)
|
| [12] |
LI Shuai, GUO Yi. Distributed consensus filter on directed graphs with switching topologies[C]//Proceedings of 2013 American Control Conference. Washington, DC, USA, 2013: 6151–6156.
( 0) 0)
|
| [13] |
SUN Yuangong, WANG Long, XIE Guangming. Average consensus in networks of dynamic agents with switching topologies and multiple time-varying delays[J]. Systems & control letters, 2008, 57(2): 175-183. ( 0) 0)
|
| [14] |
WANG Wei, SLOTINE J J E. Contraction analysis of time-delayed communications and group cooperation[J]. IEEE transactions on automatic control, 2006, 51(4): 712-717. DOI:10.1109/TAC.2006.872761 ( 0) 0)
|
| [15] |
LIU Chenglin, LIU Fei. Consensus Problem of Delayed Linear Multi-Agent Systems: Analysis and Design[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2017.
( 0) 0)
|
| [16] |
YANUMULA V K, KAR I, MAJHI S. Consensus of second-order multi-agents with actuator saturation and asynchronous time-delays[J]. IET control theory and applications, 2017, 11(17): 3201-3210. DOI:10.1049/iet-cta.2017.0578 ( 0) 0)
|
| [17] |
LIU Xiaoyu, DOU Lihua, SUN Jian. Consensus for networked multi-agent systems with unknown communication delays[J]. Journal of the franklin institute, 2016, 353(16): 4176-4190. DOI:10.1016/j.jfranklin.2016.08.005 ( 0) 0)
|
| [18] |
XU Xiang, LIU Lu, FENG Gang. Consensus of single integrator multi-agent systems with directed topology and communication delays[J]. Control theory and technology, 2016, 14(1): 21-27. DOI:10.1007/s11768-016-5122-x ( 0) 0)
|
| [19] |
OLFATI-SABER R, MURRAY R M. Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays[J]. IEEE transactions on automatic control, 2004, 49(9): 1520-1533. DOI:10.1109/TAC.2004.834113 ( 0) 0)
|
| [20] |
WANG Jing, ELIA N. Consensus over networks with dynamic channels[C]//Proceedings of 2008 American Control Conference. Seattle, WA, USA, 2008: 2637–2642.
( 0) 0)
|
| [21] |
LIN Peng, JIA Yingmin, DU Junping, et al. Distributed consensus control for second-order agents with fixed topology and time-delay[C]//Proceedings of 2007 Chinese Control Conference. Hunan, China, 2007: 577–581.
( 0) 0)
|
| [22] |
YANG Wen, BERTOZZI A L, WANG Xiaofan. Stability of a second order consensus algorithm with time delay[C]//Proceedings of the 47th IEEE conference on Decision and Control. Cancun, Mexico, 2009: 2926–2931.
( 0) 0)
|
 2018, Vol. 13
2018, Vol. 13


