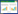扩展功能
文章信息
- 肖靖芳, 李俊, 孟飞燕, 王建军, 徐伟江, 范丽仙
- Lancang River, XIAO Jingfang, LI Jun, MENG Feiyan, WANG Jianjun, XU Weijiang
- 澜沧江奇额墨头鱼寄生指环虫属单殖吸虫一新种记述
- Description of A New Species of Genus Dactylogyrus (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) Parasitizing Gills of Host Fish Garra mirofrontis from Lancang River, Yunnan Province
- 四川动物, 2015, 34: 403-406
- Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 2015, 34: 403-406
- 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7083.2015.03.014
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2014-09-03
- 接受日期:2014-12-26
2. 云南农业大学农学与生物技术学院, 昆明650201;
3. 西双版纳州环境监测站, 云南景洪666100
2. College of Agronomy and Biological Technology, Yunnan Agricultural University, Kunming 650201, China;
3. Station of Environmental Monitor of Xishuangbanna, Jinghong, Yunnan Province 666100, China
指环虫属Dactylogyrus Diesing隶属扁形动物门Platyhelminthes吸虫纲Trematoda单殖亚纲Monogenea指环虫目Dactylogyridae,1937指环虫科Dactylogyridae,1933,全世界已报道600种以上,其中,我国记载了369余种(吴宝华等,2000;Cribb et al.,2002;Chiary et al.,2014)。指环虫属物种的分类依据主要包括后吸器、肠管分支、生殖系统等的形态结构,尤其以后吸器几丁质结构和雄性交接器形态,如中央大钩、边缘小钩的形态结构及其量度,联结片和辅助片的形态大小、交接器的形态结构及其量度等作为稳定的形态分类性状(Gusev,1985;Lim et al.,2010)。同时,有证据表明不同属的鲤科鱼类能够感染不同指环虫属种类,即指环虫属种类对宿主具有属水平上的宿主特异性(Lamber & Gharbi,1995;Simkov et al.,2004)。
奇额墨头鱼Garra mirofrontis属鲤形目Cypriniformes鲤科Cyprinidae野鯪亚科Labeoninae墨头鱼属Garra Hamilton,在中国仅分布于澜沧江水系(褚新洛,崔桂华,1987;褚新洛等,1989)。2013年10月,作者对采自澜沧江云南省西双版纳景洪流域段的奇额墨头鱼鳃进行剖检时,检获一种指环虫属单殖吸虫,并对其形态进行了观察。与指环虫属其他种类进行形态比较后,认为其是一未记录新种,命名为澜沧江指环虫Dactylogyrus lancangjiangensis。 1 材料与方法 1.1 采集地点与采集方式
宿主鱼类奇额墨头鱼从澜沧江景洪流域段(海拔576 m,22°00.288'N,100°47.430'E)支流中捕获或从当地渔民、集市购买获得。 1.2 标本处理
取下宿主鱼类的鳃片,于生理盐水中挑取虫体。用波恩氏液固定虫体,硼砂洋红染色,酸酒精分色,70%、80%、90%和100%酒精逐级脱水,丁香油或二甲苯透明,用中性树胶封片,在显微镜Olympus CX-41下绘制及测量其形态结构。 2 结果 2.1 澜沧江指环虫新种Dactylogyrus lancangjiangensis sp. nov.
宿主:奇额墨头鱼
寄生部位:鳃丝。
自然感染率:奇额墨头鱼28尾,其中19尾感染,自然感染率为68%,每片鳃上感染4~8枚虫体。
采集地点:2013年10月,采自云南省澜沧江西双版纳景洪流域段(22°00.288'N,100°47.430'E)。
保存地点:新种模式标本经过制片保存于云南师范大学生命科学学院动物学教研室,正模编号K20131017-1,副模编号K20131017-2。宿主标本经95%酒精带回后保存于遗传学教研室-40 ℃冰箱。
通过对8枚染色标本的形态学分类研究,结构测量数值见表 1(单位μm)。虫体中小型,眼点2对,阴道管1个,开口于虫体右侧,体长289~366(平均317),体宽93~109(平均101)。咽球形明显,大小19×21。后吸器(图 1)位于虫体末端,具1对中央大钩、7对边缘小钩、联结片和副联结片。边缘小钩雏形,不具明显的柄、柄轴和钩尖基突,形态较为一致,全长16~29;中央大钩全长44~46,基部长33~35,钩尖长9~11,内突长17~18,外突长4~6。联结片中部略狭窄,两端圆钝、较宽,大小(3~4)×(28~31),副联结片小,呈月牙形,中间微凸,大小2×14。交接器由交接管和支持器组成,交接管长据弯度254~263,基部膨大呈球形,基径7~9,后部缢缩形成细管,管径15,盘曲成螺旋形,3~5圈不等,螺旋直径27,支持器呈复杂棒状,交接管端部从中穿过,支持器全长23(图 2)。
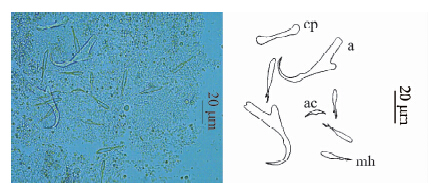
|
| 图 1 澜沧江指环虫Dactylogyrus lancangjiangensis sp. nov.后吸器 Fig. 1 Opisthohapter elements of Dactylogyrus lancangjiangensis sp. nov. a. 中央大钩anchor,ac. 副联结片accessory connection piece,cp. 联结片connection piece,mh. 边缘小钩marginal hook. |
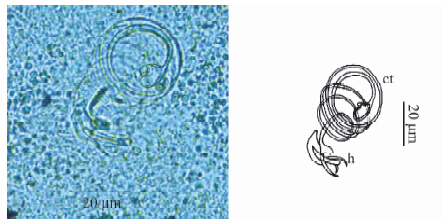
|
| 图 2 澜沧江指环虫Dactylogyrus lancangjiangensis sp. nov.交接器 Fig. 2 Copulatory complex of Dactylogyrus lancangjiangensis sp. nov. ct. 交接管copulatory tube,h. 支持器hander. |
词源:新种依宿主采集地命名为澜沧江指环虫Dactylogyrus lancangjiangensis sp. nov.。 3 讨论
本新种在形态结构上与寄生于无须墨头鱼G. pingi的墨头指环虫D. garrae最为相似(吴宝华等,2000),但它们在边缘小钩、副联结片和交接器上存在明显差异。墨头指环虫的小钩发育完全,柄、柄轴和钩尖基突均显著,副联结片棒形,交接管呈线型螺旋,支持器呈树叉形;而本种后吸器较大,且小钩结构简单,部分雏形,副联结片月牙形,交接管呈管状螺旋,基部膨大呈球形,支持器呈复杂棒形。鉴于以上区别,认为本种为一科学上的未记录种,以采集地将其命名为澜沧江指环虫Dactylogyrus lancangjiangensis sp. nov.。
在单殖吸虫的形态分类鉴定过程中,虽然虫体的体长、体宽会随生长周期而改变,但中央大钩、联结片和边缘小钩等几丁质结构的形状及大小具有一定的稳定性,在区分种时仍然可靠(Matejusová et al.,2001; Milne & Avenant-Oldewage,2012)。一般认为,鱼类单殖吸虫雄性生殖系统的结构,尤其是交接器的多样性显著,其形态结构具有种的特异性,而且交接器在同种不同成体间非常稳定,因此,一般也将交接器作为属内定种的重要依据(Pariselle & Euzet,2009;Rehulková et al.,2013)。
大部分单殖吸虫的寄生表现出较高的宿主特异性,且不同种类的特异性存在差异。郎所(1964)和夏晓勤等(2000)认为单殖吸虫具有较强的宿主特异性,其中指环虫属在宿主属阶元、种阶元层次上显示出较强的宿主特异性。据统计,60%以上的单殖吸虫只有1种宿主,约75%的单殖吸虫的宿主仅为1属,超过97%的单殖吸虫的宿主在1科之内,目前还没有1种单殖吸虫可寄生在超过3个科的宿主上。Rohde(1979)的研究证实了单殖吸虫宿主特异性的不同程度,在调查的435种单殖吸虫中,有78%只寄生在1种宿主上,89%的宿主为1个属,占已知单殖吸虫种类74%~78%的虫种只寄生于各自单一的宿主上。因此在单殖吸虫的物种鉴定中,宿主鱼类的分类学地位和分布也可作为分类的重要依据之一。本实验采集到的奇额墨头鱼是澜沧江特有鱼类。目前的调查表明,在澜沧江采集到的其他鱼类如马口鱼Opsariichthys bidens、长臀鲃Mystacoleucus marginatus、短吻鱼Sikukia gudgeri、宽额鳢Channa gachua、叉尾斗鱼Macropodus opercularis、黄颡鱼Pelteobagrus fulvidraco、棒花鱼Abbottina rivularis等鳃上并未发现本种单殖吸虫。基于单殖吸虫形态学上的鉴别特征和宿主特异性,将寄生于奇额墨头鱼鳃上的该指环虫认定为指环虫属Dactylogyrus科学上一未记录种。
我国鱼类单殖吸虫中,指环虫属记录370余种,是我国淡水鱼类单殖吸虫中种类组成的优势类群(吴宝华等,2000;赵江山等,2011)。由于流经区域具有独特的气候特点和地理条件,澜沧江水系孕育了世界上最丰富的淡水鱼类生态系统。本次发现指环虫寄生的鱼类宿主奇额墨头鱼就是澜沧江特有鱼类。对这样的地方性鱼类单殖吸虫进行研究,就有可能发现不同于我国内陆其他水体鱼类单殖吸虫的特点,为我国不同地域鱼类单殖吸虫的区系组成和病原分布相关研究提供科学资料,对于揭示寄生虫和宿主鱼类的协同进化具有不同于我国其他区系的优势(郎所,1964;马成伦,李远培,1991;吴宝华,李远培,2000;吴相云等,2007)。
致谢:衷心感谢云南大学陈自明教授在宿主鱼类分类鉴定上的周详指导。感谢沈剑峰、白俊萍同学给予的帮助。| 褚新洛, 陈银瑞, 等.1989.云南鱼类志(上册)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 269-278. |
| 褚新洛, 崔桂华. 1987. 中国鲤科鱼类墨头鱼属分类的整理[J]. 动物分类学报, 12(1): 93-99. |
| 郎所. 1964. 太湖鱼类寄生蠕虫单殖吸虫Ⅳ. 鲌鱼的寄生指环虫, 包括四新种的描述并论及其系谱分类上的意义[J]. 动物学报, 16(1): 21-23. |
| 马成伦, 李远培. 1991. 四川省鱼类寄生单殖吸虫[J]. 重庆师范学院学报, 8(4): 1-16. |
| 吴宝华, 郎所, 王伟俊. 2000. 中国动物志(扁形动物门: 单殖吸虫纲)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 617-622. |
| 吴相云, 谢明权, 李安心. 2007. 指环虫属的早期辐射及其与宿主鲤科鱼类的协同进化关系[J]. 动物学报, 53(4): 651-658. |
| 夏晓勤, 王伟俊, 姚卫建. 2000. 中国内陆水体单殖吸虫的宿主特异性分析[J]. 生态学报, 20(4): 594-597. |
| 肖衡, 叶辉 等. 2012. 动物学野外实习指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社: 141. |
| 赵江山, 姚卫建, 等. 2011. 额尔齐斯河高体雅罗鱼单殖吸虫中国二新记录种[J]. 水生生物学报, 35(4): 713-716. |
| Cribb TH, Chisholm LA, Bray RA. 2002. Diversity in the Monogenea and Digenea: does lifestyle matter?[J]. International Journal for Parasitology, 32: 321-328. |
| Chiary HR, Chaud hary A, Singh HS. 2014. Morphological redescription and molecular characterization of Dactylogyrus labei (Monogenea, Doctylogyridae) from Catla catla: a new host record in India [J]. Vestnik Zoologii, 48(5): 451-456. |
| Gusev AV. 1985. Keys to parasites of freshwater fish of the USSR Volame 2 [M]. Leningrad: Science publishing house: 1-425. |
| Lamber A, Gharbi SE. 1995. Monogenean host specificity as biological and taxonomic indicator for fish[J]. Biological Conservation, 72: 227-235. |
| Lim HS, Tan WB, Gibson DI. 2010. Description of Sinodiplectanotrema malayanum n. sp. (Monogenea: Diplectanidae), with comments on the taxonomic position of the genus [J]. Syst Parasitol, 76: 145-157. |
| Matejusová I, Koubková B, D'amelio S, et al. 2001. Genetic characterization of six species of diplozoids(Monogenea: Diplozodiae)[J]. Parasitology, 123(5): 465-474. |
| Milne SJ, Avenant-Oldewage A. 2012. Seasonal growth of the attachment clamps of a Paradiplozoon sp. as depicted by statistical shap analysis[J]. African Journal of Biotechnology, 11(9): 2333-2339. |
| Pariselle A, Euzet L. 2009. Systematic revision of dactylogyridean parasites (Monogenea) from cichlid fishes in Africa, the Levant and Madagascar[J]. Zoosystema, 31: 849-898. |
| Rehulková E, Mendlová M, Simková A. 2013. Two new species of Cichlidogyrus (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) parasitizing the gills of African cichlid fishes (Perciformes) from Senegal: morphometric and molecular characterization[J]. Parasitol Res, 112: 1399-1410. |
| Rohde K. 1979. A critical evaluation of intrinsic and extrinsic factors responsible for niche restriction in parasites[J]. America Nature, 114: 648-667. |
| Simkov A, Morand S, Jobet E, et al. 2004. Molecular phylogeny of congeneric monogenean parasites (Dactylogyrus): a case of intrahost speciation[J]. Evolution, 58: 1001-1018. |
 2015, Vol. 34
2015, Vol. 34