中国梨树种植面积和产量长期居世界首位,2017—2018年度中国梨果产量1 900万吨[1]。为了保障梨果的正常生长,不可避免地使用农药,尤其是杀虫剂,给梨果安全质量带来了隐患。螺虫乙酯 (spirotetramat) 是德国拜耳公司开发的新一代杀虫剂,属季酮酸类化合物,结构式见图式1。2011年在中国正式登记,用于防治梨木虱、柑橘红蜘蛛和苹果绵蚜等害虫[2]。该药具有双向内吸传导性能,且持效期长,已成为梨园梨木虱防治的替代品种[3-8]。
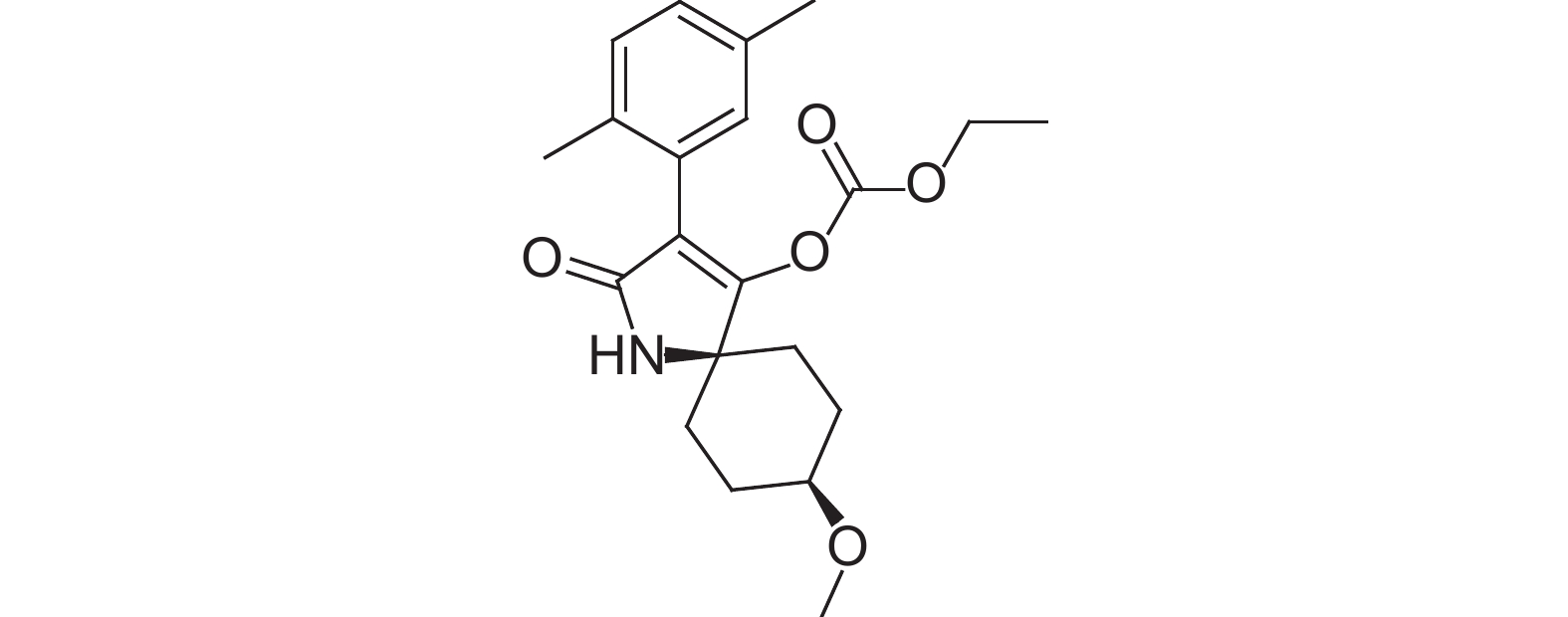
|
图式1 螺虫乙酯的结构式 Scheme1 Structural formula of spirotetramat |
螺虫乙酯在环境中的代谢物主要为螺虫乙酯-烯醇-糖苷spirotetramat-enol-glucoside (S-glu)、螺虫乙酯-酮-羟基spirotetramat-keto-hydroxy (S-keto)、螺虫乙酯-烯醇spirotetramat-enol (S-enol) 和spirotetramat-mono-hydroxy螺虫乙酯-单羟基 (S-mono)[9]。中国规定螺虫乙酯残留物定义为螺虫乙酯及其烯醇类代谢产物之和,以螺虫乙酯表示,在梨果类水果中的最大残留限量 (MRL) 标准为0.7 mg/kg[10],但没有规定其检测方法。目前,关于螺虫乙酯在农作物中残留量的检测方法已有报道。吴育佳等[11]采用液相色谱法对螺虫乙酯本体在黄瓜及土壤中的残留消解动态和最终残留量进行了研究,最低检测浓度 (LOQ) 为0.025 mg/kg;吴文涛等[12-13]采用液相色谱-串联质谱 (LC-MS/MS) 法测定了柑橘中螺虫乙酯及其4个代谢物的残留,LOQ在0.000 4–0.004 9 mg/kg;袁文悦等[14]用固相萃取柱净化土壤提取液,采用LC-MS/MS法测定了土壤中螺虫乙酯及其4个代谢物的残留,LOQ为0.027 mg/kg;孟志远等[15]采用LC-MS/MS建立了菠菜及其土壤和水体中螺虫乙酯及其代谢物的测定方法;陈慧妍等[16]采用LC-MS/MS法测定了梨中螺虫乙酯的残留量,LOQ为0.001 mg/kg,但未对4个代谢物进行鉴定和分析;兰丰等[17] 采用超高效液相色谱-串联质谱 (UPLC-MS/MS) 法建立了同时测定螺虫乙酯及其代谢物在果蔬中的残留分析方法,并对市场样品进行了检测,LOQ为0.001~0.005 mg/kg;然而,有关螺虫乙酯及其代谢物在梨果及梨园土壤中的残留动态规律和最终残留量研究尚未见报道。
自从Anastassiades等[18]和Lehotay等[19-20]在2003年创建QuEChERS (Quick,Easy,Cheap,Effective,Rugged,Safe) 样品前处理技术以来,在食品中的农药残留分析领域里已引起了人们的广泛关注[21]。目前,该方法在农药分析领域得到了广泛认可,美国分析化学家协会AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists)[22]和欧盟[23]均将QuEChERS样品前处理方法引入其相关的农作物中农药残留检测标准中。
本研究根据梨中果糖含量高、色素含量低的特点,结合空白样品色谱基线特点,采用QuEChERS法进行样品前处理,结合UPLC-MS/MS建立了梨和土壤中螺虫乙酯及其代谢物的分析测定方法,并采用该方法研究了螺虫乙酯及其代谢物在梨和土壤中的残留规律。
1 材料和方法 1.1 仪器与试剂Ulitemate 3000-TSQ ultra型超高效液相色谱-三重四极杆质谱联用仪 (赛默飞世尔科技有限公司);DV215CD电子天平 (美国奥豪斯公司);DT5-2离心机 (北京时代北利离心机有限公司);UMV-2多功能旋涡混合器 (北京优晟联合科技有限公司)。
螺虫乙酯 (纯度99.2%) 及其代谢物S-enol (纯度99.6%)、S-keto (纯度94.0%)、S-mono (纯度99.7%) 和S-glu (纯度98.6%) 标准品 (Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH,德国);N-丙基乙二胺 (PSA,天津欧姆尼基因科技有限公司)、乙腈 (色谱纯,美国Fisher公司);乙腈 (分析纯,天津康科德科技有限公司)、无水硫酸镁 (分析纯,天津市永大化学试剂有限公司);试验用水均由Milli-Q超纯水器制备。22.4%螺虫乙酯悬浮剂 (拜耳作物科学(中国)股份有限公司)。
1.2 田间试验按照文献[24]方法进行。试验地设在河北省石家庄市新华区东营村果园,位于东经114°47′,北纬38°05′,年均降水量569.8 mm,年均温12.9 ℃。土壤质地为壤土,梨树品种为黄冠,树龄15 a。选择长势均匀、挂果充足、近2 a内没有施用过螺虫乙酯的不套袋梨树作为试验小区,每个试验处理设3个重复小区,每小区2棵梨树。另设不喷药对照小区。各小区之间至少隔开1棵树作为保护行。试验用药为22.4%螺虫乙酯悬浮剂。
1.2.1 梨果中螺虫乙酯的消解动态试验于梨果实长至直径3 cm时施药,保证小区内所有梨果实均匀着药。施药剂量为有效成分112 mg/kg,施药1次。分别于施药后2 h及1、3、7、14、21、30和45 d按文献[25]方法,随机在梨树上中下及前后左右多点采集生长正常、无病害的果实,采集量不少于2 kg,去除果梗将整个果实粉碎,于 –20 ℃冰柜中保存待测。
1.2.2 梨园土壤中螺虫乙酯消解动态试验选一块30 m2梨园空地,单独施药,施药剂量为有效成分112 mg/kg,喷雾量为3 000 L/hm2。分别于施药后0 (2 h)、1、3、5、7、10、15、30、45和60 d按文献 [25] 方法随机取点5~10 个。采集0~15 cm深度土壤1~2 kg,除去碎石等杂物,粉碎,过1 mm孔径筛,待测。
1.2.3 最终残留试验设2个施药剂量,分别为有效成分75和112 mg/kg,各设2次和3次施药。在梨果长至直径3 cm时开始施药,施药间隔为7 d。2次施药处理的时间晚于3次施药处理7 d后开始施药。分别距最后一次施药7、14和21 d采集梨果样品和土壤样品。梨果样品采集和处理按1.2.1节进行,土壤样品采集和处理按1.2.2节进行。
1.3 分析方法 1.3.1 样品前处理采用AOAC推荐的QuEChERs方法[22]进行样品前处理。取5 g样品 (精确至0.01 g) 于50 mL离心管中,加入5 mL蒸馏水和10 mL含体积分数为1%乙酸的乙腈溶液,涡旋混匀2 min,加入4 g无水硫酸镁和1 g乙酸钠,涡旋混匀2 min,于3 500 r/min下离心5 min;取2 mL上清液,转移至装有300 mg无水硫酸镁、50 mg PSA的具塞离心管中,涡旋混匀2 min,于3 500 r/min下离心5 min;取上清液,过0.22 μm有机滤膜,供UPLC-MS/MS测定。
1.3.2 仪器条件Luna C18(2)-HST (100 mm × 2 mm,2.5 μm)色谱柱;柱温30 ℃,进样量5 μL;流动相为乙腈-0.5%甲酸水 (V/V) 溶液,采用梯度洗脱:0 min,5%乙腈;8 min,95%乙腈;15 min,5%乙腈;18 min,5% 乙腈。
质谱检测器:ESI离子源,离子源温度350 ℃,毛细管温度350 ℃,雾化电压3 800 V,雾化气体氮气,雾化气体压力:鞘气241 Pa,辅助气103 Pa;碰撞气体氩气,碰撞气体压力 2 Pa。正离子扫描,选择反应监测模式 (SRM)。
1.3.3 方法的线性关系试验分别取适量的螺虫乙酯及其4个代谢物标准品于100 mL容量瓶中,用乙腈定容,配制成10 mg/L的混合标准溶液,再用乙腈依次稀释成0.5、0.1、0.05、0.01、0.005和0.000 5 µg/mL系列标准溶液,采用1.3.2节条件测定,以进样质量浓度对峰面积作图,绘制标准工作曲线。
1.3.4 添加回收试验分别称取5 g梨果空白样品或土壤空白样品于50 mL离心管中,加入螺虫乙酯及4种代谢物标准品,添加水平分别为0.005、0.02、0.1和0.7 mg/kg,按本研究所选条件进行前处理及检测。每个处理重复6次。计算添加平均回收率及RSD。
2 结果与分析 2.1 定性离子和定量离子选择在电喷雾正离子模式下,根据螺虫乙酯及其4个代谢物的相对分子质量,确定其母离子,进行分子离子全扫描。每种目标化合物选择2个响应信号较稳定的子离子,以SRM扫描方式进行监测,选择子离子响应信号最强时的碰撞能量作为质谱条件。每个母离子选择2个子离子进行定性,一个丰度较强的子离子进行定量。螺虫乙酯及代谢物的UPLC-MS/MS检测参数见表1。检测总离子流图见图1。
|
|
表 1 螺虫乙酯及4种代谢物的UPLC-MS/MS检测参数 Table 1 The UPLC-MS/MS parameters for spirotetramat and its 4 metabolites |
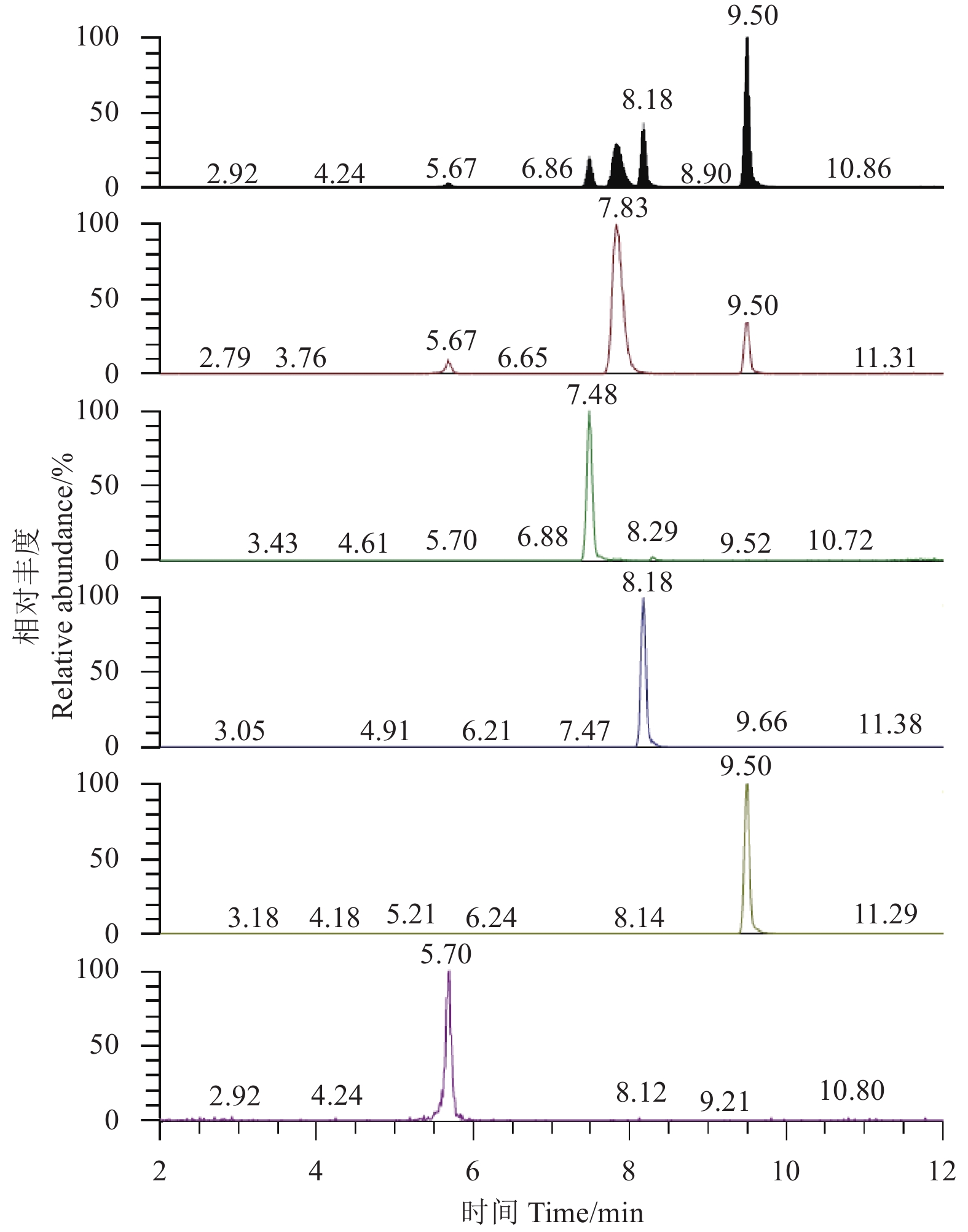
|
图 1 螺虫乙酯及4种代谢物总离子流色谱图(0.05 mg/L) Fig. 1 Total ion chromatogram of spirotetramat and its four metabolites (0.05 mg/L) |
2.2 方法的线性关系
结果 (表2) 表明:螺虫乙酯在0.000 5~0.1 mg/L范围内,S-glu在0.005~0.5 mg/L范围内,S-keto、S-enol和S-mono在0.000 5~0.5 mg/L范围内,各化合物的质量浓度与质谱峰面积间均具有良好的线性关系 (R2 ≥ 0.999)。
|
|
表 2 方法的线性方程和决定系数 Table 2 Linear equations and correlation coefficients |
2.3 分析方法的准确度和精密度
结果 (表3) 表明:在0.005~0.7 mg/kg添加水平内,螺虫乙酯及其代谢物在梨果中平均回收率为84%~109%,RSD为1.2%~3.3%;在土壤中平均回收率为86%~102%,RSD为1.1%~3.6%。最低检测浓度 (LOQ) 为0.005 mg/kg
|
|
表 3 螺虫乙酯及其代谢物在梨果及梨园土壤中的添加回收率及相对标准偏差 (n = 6) Table 3 The recoveries of spirotetramat and its metabolites from pear and soil samples (n = 6) |
2.4 螺虫乙酯及其代谢物在梨果及梨园土壤中的消解动态
结果 (表4) 表明:螺虫乙酯在梨果和梨园土壤中的消解动态均符合一级反应动力学方程ct = c0e–kt,半衰期分别为12.4 d和7.1 d。
|
|
表 4 螺虫乙酯及其代谢物在梨及土壤中的消解动态 Table 4 Dissipation dynamic of spirotetramat and its metabolites in pear and soil |
2.5 螺虫乙酯及其代谢物在梨果及栽培土壤中的最终残留量
测定结果 (表5和表6) 表明:螺虫乙酯及其代谢物在梨中的最终残留量在0.020~0.057 mg/kg之间。各处理最终残留量均低于MRL值 (0.7 mg/kg);在土壤中的最终残留量在 < LOD~0.015 mg/kg之间。
|
|
表 5 螺虫乙酯及其代谢物在梨果中的最终残留量 Table 5 Final residues of spirotetramat and its metabolites in pear fruit |
|
|
表 6 螺虫乙酯及其代谢物在梨园土壤中的最终残留量 Table 6 Final residues of spirotetramat and its metabolites in pear orchard soils |
3 结论与讨论
采用体积分数为1%的乙酸乙腈为提取剂,以PSA和无水硫酸镁为分散净化剂的QuEChERS方法净化梨果和土壤样品,利用超高效液相色谱-串联质谱 (UPLC-MS/MS) 在选择反应监测模式 (SRM) 下进行检测,外标法定量,对梨果及土壤中的螺虫乙酯及其代谢物进行了定性定量分析,方法的线性关系、准确度及精密度均可满足农药残留分析的要求[24]。
农药登记资料显示,22.4%螺虫乙酯悬浮剂在梨树上使用,推荐使用安全间隔期为21 d,最多使用2次[2]。本研究表明,按照推荐最高剂量 (有效成分) 112 mg/kg施药,螺虫乙酯在梨果中的半衰期为12.4 d,在土壤中的半衰期为7.1 d。在设定的不同施药剂量、不同施药次数 (2次和3次) 和不同间隔期 (7、14、21 d) 的条件下采摘梨果样品,螺虫乙酯及其代谢物最终残留量检测结果均不超过中国规定的螺虫乙酯在仁果类水果中MRL值 (0.7 mg/kg)[10],说明22.4%螺虫乙酯悬浮剂在试验地气候条件下按推荐剂量使用,用于防治梨树害虫是安全的。
粮农组织/世界卫生组织农药残留联合专家会议报告显示:螺虫乙酯在动植物组织中的代谢非常复杂,在不同农作物中的代谢途径也不尽相同,产生代谢物的相对含量也有所区别[26]。在本研究的梨果样品中,检出的主要代谢物为螺虫乙酯本体,其代谢物S-enol、S-keto和S-mono也有少量检出,而S-glu未检出。这可能与气候条件和基质酸碱度有关。
消解动态试验表明,在第2天采集的土壤样品中已检测不出螺虫乙酯本体,而在最终残留试验中,除在距离最后一次施药7 d后采集的样品中能检出少量螺虫乙酯本体外,14 d和21 d样品均未检出。这说明螺虫乙酯在土壤中的消解较快。该结果与联合国报告的结果 (螺虫乙酯在土壤中的好氧降解较快,1 d内降解90%以上)[26] 相一致。
| [1] |
Statista: Export volume of pears worldwide in 2017/2018, by leading countries (in 1,000 metric tons)[DB/OL]. (2018-09-29). https://www.statista.com/statistics/756511/global-top-pear-exporter-worldwide/
|
| [2] |
中华人民共和国农业农村部农药检定所. 农药登记数据[EB/OL]. (2016-03-16)[3019-04-29]. http://www.icama.org.cn/hysj/index.jhtml Pesticide testing institute of the ministry of agriculture and village of the People's Republic of China. Pesticide registration data. (2016-03-16)[3019-04-29]. http://www.icama.org.cn/hysj/index.jhtml |
| [3] |
宫亚军, 王泽华, 康总江, 等. 新型双向传导杀虫剂-螺虫乙酯对Q型烟粉虱的防治效果[J]. 植物保护, 2012, 38(6): 157-160. GONG Y J, WANG Z H, KANG Z J, et al. Control efficacy of a new two-way systemic insecticide spirotetramat on the whitefly Bemisia tabaci [J]. Plant Prot, 2012, 38(6): 157-160. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2012.06.036 |
| [4] |
LABANOWSKA, BARBARA H, PIOTROWSKI W, et al. Usefulness of spirotetramat (Movento 100 SC) to control spider mites on apple, blackcurrant and raspberry in Poland[J]. IOBC/WPRS Bulletin, 2017, 123: 115-119. |
| [5] |
ŁABANOWSKA B H, KORZENIOWSKI M, GASPARSKI T. Efficacy of spirotetramat in the control of the currant-sowthistle (Hyperomyzus lactucae L.) on blackcurrant plantations in Poland[J]. J Hortic Res, 2013, 21(2): 73-78. DOI:10.2478/johr-2013-0024 |
| [6] |
JAWORSKA K, OLSZAK R W, ŁABANOWSKA B H, et al. Efficacy of spirotetramat in the control of pear psylla (Cacopsylla pyri L.) on pear trees in Poland
[J]. J Fruit Ornam Plant Res, 2012, 20(2): 91-106. DOI:10.2478/v10290-012-0019-3 |
| [7] |
张传州. 22.4%螺虫乙酯悬浮剂防治梨木虱的田间药效试验[J]. 落叶果树, 2015, 47(3): 30-31. ZHANG C Z. Field efficacy trials of 22.4% spiro ethyl ester suspension against pear-leaf sucker[J]. Deciduous Fruits, 2015, 47(3): 30-31. |
| [8] |
陈金翠, 王泽华, 曹利军, 等. 三种新型杀虫剂对中国梨木虱的田间防效[J]. 北方园艺, 2017(17): 72-76. CHEN J C, WANG Z H, CAO L J, et al. Control efficacy of three new insecticides to pear psylla Psylla chinensis (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) [J]. North Hortic, 2017(17): 72-76. |
| [9] |
LIU Y Y, SU X S, JIAN Q, et al. Behaviour of spirotetramat residues and its four metabolites in Citrus marmalade during home processing
[J]. Food Addit Contam Part, 2016, 33(3): 452-459. DOI:10.1080/19440049.2015.1137638 |
| [10] |
食品中农药最大残留限量: GB 2763—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. Maximum residue limits for pestcides in food: GB 2763—2016[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2017. |
| [11] |
吴育佳, 杨仁斌, 聂红英. 螺虫乙酯在黄瓜及其土壤中残留量检测方法及残留规律研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(35): 110-115. WU Y J, YANG R B, NIE H Y. Study on residual detection method and residue rule of spirotetramat in cucumber and soil[J]. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2015, 31(35): 110-115. DOI:10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb15070108 |
| [12] |
吴文铸, 李菊颖, 何健, 等. 螺虫乙酯在柑橘中的残留消减动态[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2016, 32(6): 1003-1007. WU W Z, LI J Y, HE J, et al. Degradation dynamics of spirotetramat residue in citrus[J]. J Ecol Rural Environ, 2016, 32(6): 1003-1007. |
| [13] |
李菊颖, 吴文铸, 孔德洋, 等. 超高效液相色谱-质谱法测定柑橘和土壤中螺虫乙酯及4种代谢产物[J]. 农药, 2016, 55(1): 45-47. LI J Y, WU W Z, KONG D Y, et al. Determination of spirotetramat and its 4 metabolites in citrus and soil by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Agrochemicals, 2016, 55(1): 45-47. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-5480.2016.01.011 |
| [14] |
袁文悦, 庄惠生. 高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定土壤中螺虫乙酯及其4种代谢产物[J]. 世界农药, 2017, 39(4): 59-63. YUAN W Y, ZHUANG H S. Determination of spirotetramat and its four metabolites residues in soil by UPLC-MS/MS[J]. World Pestic, 2017, 39(4): 59-63. |
| [15] |
孟志远, 任莉, 宋玥颐, 等. 液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定菠菜、土壤及水体中螺虫乙酯及4种代谢物残留[J]. 农药学学报, 2017, 19(4): 482-490. MENG Z Y, REN L, SONG Y Y, et al. Simultaneous determination of spirotetramat and its four metabolites in Spinacia oleracea L., soil and water using liquid chromatographytandem mass spectrometry [J]. Chin J Pestic Sci, 2017, 19(4): 482-490. |
| [16] |
陈慧妍, 季祥. 液相色谱: 串联质谱法测定梨果中螺虫乙酯残留量[J]. 现代园艺, 2018(10): 11. CHEN H Y, JI X. Determination of spiro ethyl acetate residues in pears by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Xiandai Hortic, 2018(10): 11. |
| [17] |
兰丰, 姚杰, 周先学, 等. QuEChERS-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定果蔬中螺虫乙酯、丁醚脲及代谢物残留[J]. 农药学学报, 2019, 21(2): 219-226. LAN F, YAO J, ZHOU X X, et al. Residue of spirotetramat, diafenthiuron and their metabolites in fruits and vegetables by QuEChERS-ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chin Pestic Sci, 2019, 21(2): 219-226. |
| [18] |
PAYÁ P, ANASTASSIADES M, MACK D, et al. Analysis of pesticide residues using the Quick Easy Cheap Effective Rugged and Safe (QuEChERS) pesticide multiresidue method in combination with gas and liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometric detection[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2007, 389(6): 1697-1714. DOI:10.1007/s00216-007-1610-7 |
| [19] |
LEHOTAY S J, DE KOK A, HIEMSTRA M, et al. Validation of a fast and easy method for the determination of residues from 229 pesticides in fruits and vegetables using gas and liquid chromatography and mass spectrometric detection[J]. J AOAC Int, 2005, 88(2): 595-614. |
| [20] |
LEHOTAY S J, MASTOVSKÁ K, LIGHTFIELD A R. Use of buffering and other means to improve results of problematic pesticides in a fast and easy method for residue analysis of fruits and vegetables[J]. J AOAC Int, 2005, 88(2): 615-629. |
| [21] |
刘满满, 康澍, 姚成. QuEChERS 方法在农药多残留检测中的应用研究进展[J]. 农药学学报, 2013, 15(1): 8-22. LIU M M, KANG S, YAO C. Research progress of QuEChERS method in pesticide mult-residue analysis[J]. Chin J Pestic Sci, 2013, 15(1): 8-22. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-7303.2013.01.02 |
| [22] |
AOAC. Official Method 2007.01. Pesticide residues in foods by acetonitrile extraction and partitioning with magnesium sulfate[S/OL]. http://www.eoma.aoac.org/methods/info.asp?ID=48938
|
| [23] |
European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Standard method EN 15662: foods of plant origin-multimethod for the determination of pesticide residues using GC- and LC-based analysis following acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and clean-up by dispersive SPE - Modular QuEChERS-method[S/OL]. (2018-05-23)[2018-09-30]. https://standards.cen.eu/dyn/www/f?p=204:110:0::::FSP_PROJECT, FSP_ORG_ID:61387, 6256&cs=10DBAB7C706FAC8588AB8D2285F35AF89
|
| [24] |
农作物中农药残留试验准则: NY/T 788—2018[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2018. Guideline for the testing of pesticide residues in crops: NY/T 788—2018[S]. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Press, 2018. |
| [25] |
农药残留分析样本的采样方法: NY/T 789—2004[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2004. Guideline on sampling residue analysis:NY/T 789—2004[S]. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Press, 2004. |
| [26] |
Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nation (2008). Evaluation of spirotetramat by the joint FAO/WHO meeting on pesticide residues (JMPR) and the joint FAO/WHO meeting on pesticide specifications (JMPS)[R/OL]. Retrieved March 2, 2019 from FAO of UN.https://www.fao.org/agriculture/crops/thematic-sitemap/theme/pests/lpe/lpe-s/ir/
|
 2019, Vol. 21
2019, Vol. 21


