2. 山东农业大学 农药环境毒理研究中心,山东 泰安 271018
2. Research Center of Pesticide Environmental Toxicology, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an 271018, Shandong Province, China
黄瓜在栽培过程中经常发生霜霉病、白粉病和灰霉病[1-3],目前主要通过施用各类杀菌剂控制其危害,但因黄瓜果实成熟期短和安全间隔期不足而常常导致农药残留量超标。在欧盟制定的农药最大残留限量 (MRL) 标准中,杀菌剂在黄瓜中的MRLs值多数低于0.05 mg/kg[4],中国规定黄瓜中农药的MRLs值在0.02~5 mg/kg之间[5]。随着生活水平的提高,消费者越来越重视食品安全,有必要建立高效、快速检测黄瓜中农药残留的分析方法,评估黄瓜上杀菌剂的使用风险。
目前,关于黄瓜上农药的多残留检测方法主要有气相色谱法 (GC)[6-7]、液相色谱法 (LC)[8]、气相色谱-质谱联用法 (GC-MS)[9-10]及超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法 (UPLC-MS/MS)[11-12]等。其中UPLC-MS/MS法具有灵敏、快速和准确等优点,适用于基质较复杂的痕量化合物分析,定性准确性高,可有效避免假阳性结果。随着检测设备的更新换代,样品前处理方法也变得简单高效,其中QuEChERS[13]净化方法已广泛用于农药残留分析中[14-15]。王雯等[16]利用LC-MS/MS法建立了黄瓜中5种有机磷农药的检测方法,样品经固相萃取后利用LC-MS/MS检测,但其仅涉及了有机磷类农药,且前处理步骤繁琐;褚大可等[17]利用QuEChERS-LC-MS/MS法检测了黄瓜中21种氨基甲酸酯类农药的残留,但其中杀菌剂较少;侯雪等[18]利用QuEChERS-GC-MS/MS法建立了草莓中21种杀菌剂残留的检测方法。本研究选择黄瓜上施用频率较高以及在未来黄瓜病害防治中有可能使用的29种杀菌剂,其中除霜脲氰、稻瘟灵、抑霉唑、稻瘟酰胺、腈苯唑、环氟菌胺和噻呋酰胺外,其他药剂均在黄瓜上有登记。苯醚甲环唑、吡唑醚菌酯、唑菌酮、氟吡菌胺、氟硅唑、甲霜灵、腈菌唑、咪鲜胺、嘧菌酯、嘧霉胺、氰霜唑、霜脲氰、戊唑醇、烯酰吗啉和抑霉唑在黄瓜上的MRLs值在0.05~5 mg/kg之间,而其他药剂尚无限量值规定。本研究结合基质特点,通过优化传统的QuEChERS法,采用UPLC-MS/MS建立了黄瓜中29种杀菌剂的分析方法。
1 材料与方法 1.1 药剂与试剂29种杀菌剂标准品纯度均不低于98%,购自德国Dr. Ehrenstorfer公司;甲醇和乙腈均为色谱纯,德国Dr. Ehrenstorfer公司;乙二胺-N-丙基硅烷 (PSA) ,美国Agilent公司;石墨化碳黑 (GCB) 粉末,上海安谱科学仪器有限公司;氯化钠和无水硫酸镁均为分析纯;试验用水为高温蒸馏水。
1.2 仪器与设备UPLC-XEVO TQ-S micro超高效液相色谱-串联四极杆质谱仪 [配电喷雾离子源 (ESI) 和Masslynx工作站]、ACQUITY UPLCTM BEH C18色谱柱 (2.1 mm × 100 mm,1.7 μm),美国Waters公司;BSA124S万分之一电子天平,德国Sartorius公司;TDL-40B高速离心机,上海安亭科学仪器厂;T-25样品匀质机,德国IKA公司;KQ-500DE数控超声波清洗器,昆山市超声仪器有限公司;QL-901涡旋混匀器,江苏海门麒麟医用仪器厂。
1.3 样品前处理供试黄瓜品种为津春1号,在日光温室内种植,未使用任何农药。实际检测样品购自山东省泰安市各大超市及蔬菜批发市场。黄瓜样品去除两头,切碎后,匀浆,于 –18 ℃密封保存,备用。
准确称取10 g (精确至0.01 g) 黄瓜样品于50 mL具塞离心管中,加入20 mL乙腈、4 g无水硫酸镁和1 g氯化钠,漩涡振荡3 min,于4 000 r/min下离心2 min;取1.5 mL上清液置于预先加有50 mg PSA和20 mg GCB的2 mL离心管中,漩涡振荡1 min,于12 000 r/min下离心2 min;取上清液经0.22 μm微孔滤膜过滤,待UPLC-MS/MS分析。
1.4 检测条件色谱条件:Waters ACQUITY UPLCTM,BEH C18色谱柱 (2.1 mm × 100 mm,1.7 μm),流动相为0.1%甲酸水溶液-甲醇;柱温35 ℃;进样体积2 μL;梯度洗脱程序见表1。
质谱条件:电喷雾离子源ESI,正离子电离模式;毛细管电压3.0 kV;脱溶剂气温度350 ℃;碰撞气氩气压力0.2 kPa;多反应监测模式 (MRM),外标法定量。
|
|
表 1 梯度洗脱程序 Table 1 Gradient elution program |
1.5 标准溶液的配制及标准曲线的绘制 1.5.1 标准储备液的配制
分别准确称取一定量的29种杀菌剂标准品,用甲醇溶解,配成一定浓度的混合标准储备液,于 –20 ℃下避光保存。
1.5.2 基质标准溶液的配制取匀浆后的黄瓜空白样品,按1.3节的方法进行前处理,制得空白黄瓜基质溶液。将1.5.1节的混合标准储备液用空白黄瓜基质溶液稀释成质量浓度为0.1、0.2、0.5、1、2、5、10、20和50 μg/L的系列混合标准溶液。按1.4节的条件测定,以标准溶液中待测农药的峰面积为纵坐标,对应的质量浓度为横坐标绘制标准曲线。
1.6 基质效应采用标准曲线斜率比值 (slope ratio) 来[19]评价基质效应 (ME)。基质校准曲线的斜率与纯溶剂标准曲线的斜率比值 (k1/k2) 在0.8~1.2[20]之间表示基质效应可以接受。比值越接近1,基质效应越弱;比值大于1时,为基质增强效应;比值小于1时,为基质抑制效应。
2 结果与讨论 2.1 净化剂用量的优化传统的QuEChERS前处理方法以PSA为净化剂,对于待测样品中的金属离子、脂肪酸、糖类及少量脂溶性色素具有良好的吸附作用[21],但对黄瓜中的色素净化效果差。GCB对色素具有较强的吸附能力[22-23],能有效去除黄瓜中的叶绿素、叶黄素和胡萝卜素等。但GCB具有六元环结构,会吸附一些具有平面或对称结构的农药,导致这些组分的回收率达不到要求。因此,需要对净化剂中GCB的用量进行优化,使其在起到净化作用的同时不会对农药的回收率产生较大影响。本研究考察了GCB用量分别为10、20、40、80和100 mg时对目标物回收率的影响。由图1可知:当GCB用量为10~20 mg时,回收率符合残留试验要求[24-25](虚线部分表示70%~110%),考虑到GCB的去色素能力,最终选择GCB用量为20 mg。
2.2 检测条件的优化待测的29种杀菌剂根据其水溶性强弱依次排序。首先,通过母离子全扫描谱图选择分子离子峰或相对丰度最高的特征碎片峰作为母离子,然后锁定母离子,获得子离子全扫描谱图,选择峰度较高的合理断裂碎片离子作为子离子。最后通过MRM,手动调谐确定各离子对的最佳碰撞能量 (表2)。图2 为黄瓜中MRM模式下29种杀菌剂 (0.005 mg/kg) 的选择离子对色谱图。由表2可知:29种杀菌剂的保留时间均在10 min以内,而在候雪等[18]方法中的保留时间均在15 min之后。
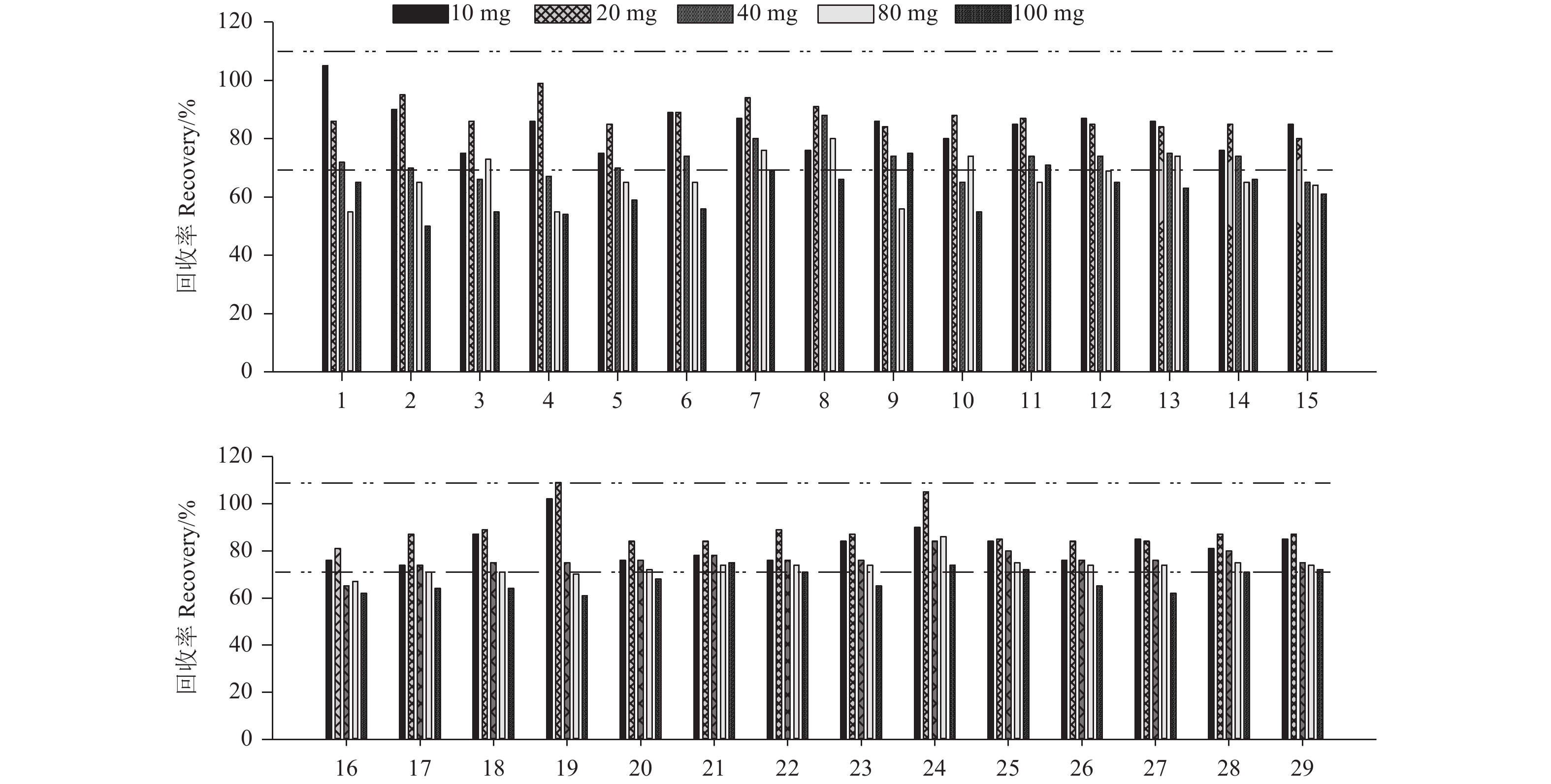
|
1:霜脲氰;2:嘧霉胺;3:乙嘧酚;4:乙霉威;5:甲霜灵;6:腈菌唑;7:稻瘟灵;8:抑霉唑;9:戊唑醇;10:己唑醇;11:氟硅唑;12:氰霜唑;13:稻瘟酰胺;14:腈苯唑;15:甲基硫菌灵;16:氟菌唑;17:吡唑萘菌胺;18:啶氧菌酯;19:四氟醚唑;20:咪鲜胺;21:氟吡菌胺;22:吡唑醚菌酯;23:烯酰吗啉;24:鰁唑菌酮;25:嘧菌酯;26:苯醚甲环唑;27:肟菌酯;28:环氟菌胺;29:噻呋酰胺。 1: cymoxanil; 2: pyrimethanil; 3: ethirimol; 4: diethofencarb; 5: metalaxyl; 6: myclobutanil; 7: isoprothiolane; 8: imazalil; 9: tebuconazole; 10: hexaconazole; 11: flusilazole; 12: cyazofamid; 13: fenoxanil; 14: fenbuconazole; 15: thiophanate-methyl; 16: triflumizole; 17: isopyrazam; 18: picoxystrobin; 19: tetraconazole; 20: prochloraz; 21: pyraclostrobin; 22: fluopicolide; 23: dimethomorph; 24: famoxadone; 25: azoxystrobin; 26: difenoconazole; 27: trifloxystrobin; 28: cyflufenamid; 29: thifluzamide. 图 1 不同GCB用量下29种杀菌剂的回收率 (n = 5) Fig. 1 Recoveries of 29 fungicides purified with different amount of GCB (n = 5) |
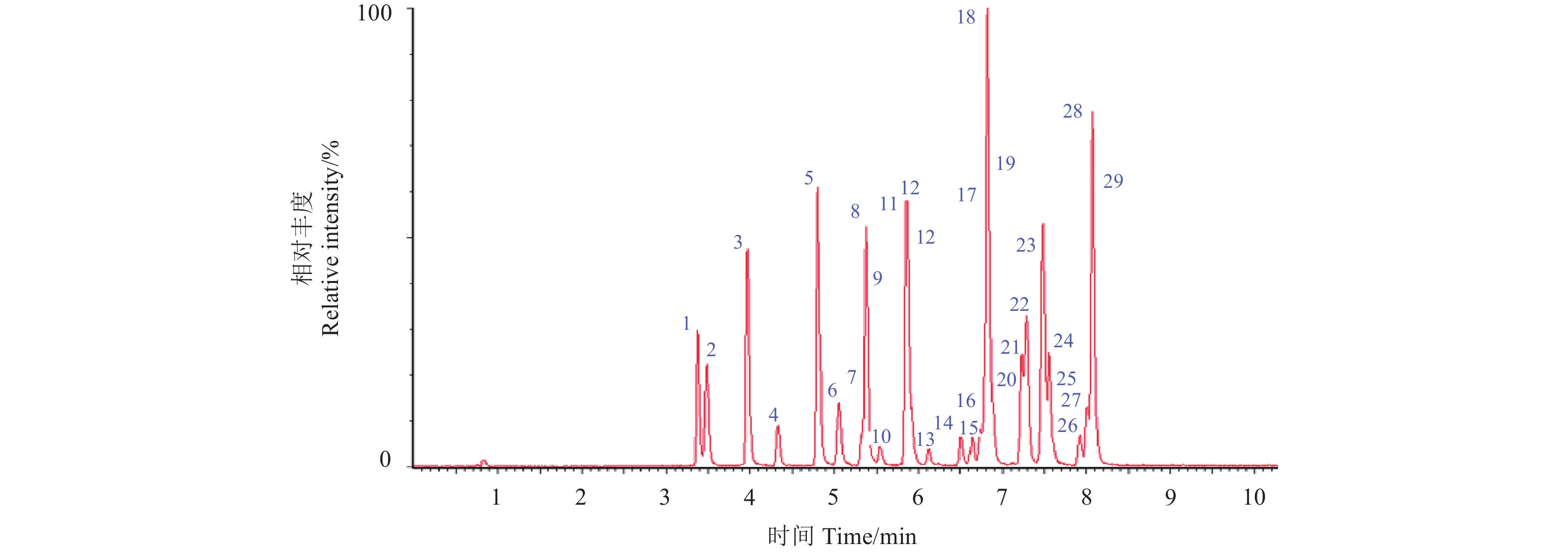
|
1:霜脲氰;2:乙嘧酚;3:甲基硫菌灵;4:抑霉唑;5:甲霜灵;6:嘧霉胺;7:嘧菌酯;8:乙霉威;9:烯酰吗啉;10:稻瘟灵;11:氟吡菌胺;12:腈菌唑;13:四氟醚唑;14:氰霜唑;15:噻呋酰胺;16:腈苯唑;17:稻瘟酰胺;18:啶氧菌酯;19:氟硅唑;20:戊唑醇;21:咪鲜胺;22:鰁唑菌酮;23:吡唑醚菌酯;24:环氟菌胺;25:己唑醇;26:苯醚甲环唑;27:吡唑萘菌胺;28:肟菌酯;29:氟菌唑。 1: cymoxanil; 2: ethirimol; 3: thiophanate-methyl; 4: imazalil; 5: metalaxyl; 6: pyrimethanil; 7: azoxystrobin; 8: diethofencarb; 9: dimethomorph; 10: isoprothiolane; 11: fluopicolide; 12: myclobutanil; 13: tetraconazole; 14: cyazofamid; 15: thifluzamide; 16: fenbuconazole; 17: fenoxanil; 18: picoxystrobin; 19: flusilazole; 20: tebuconazole; 21: prochloraz; 22: famoxadone; 23: pyraclostrobin; 24: cyflufenamid; 25: hexaconazole; 26: difenoconazole; 27: isopyrazam; 28: trifloxystrobin; 29: thiflumizole. 图 2 黄瓜中29种杀菌剂在多反应监测模式的色谱图 (0.005 mg/kg) Fig. 2 Ion chromatogram of 29 fungicides (0.005 mg/kg) using MRM mode in cucumber |
|
|
表 2 29种杀菌剂在UPLC-MS/MS多反应监测模式下的检测条件 Table 2 Multiple reaction monitoring conditions for the determination of 29 fungicides using UPLC-MS/MS |
|
|
表 2 (续表) Table 2 (Continued) |
2.3 方法的线性范围和定量限
在0.000 1~0.05 mg/kg内,29种杀菌剂的质量浓度与对应的峰面积间呈良好线性关系,相关系数均大于0.996 (表3)。依照欧盟标准333/2007[26],以10倍信噪比 (S/N=10) 计算定量限 (LOQ);依次类推,29种杀菌剂的线性关系和定量限见表3。由表3可知:29种杀菌剂的定量限在0.000 1~0.01 mg/kg之间。
|
|
表 3 29种杀菌剂的线性回归方程、相关系数、基质效应和定量限 (线性范围:0.000 1~0.05 mg/kg) Table 3 Linear regression equations, correlation coefficients, matrix effects and LOQs of 29 fungicides (Linear range: 0.000 1-0.05 mg/kg) |
|
|
表 3 (续表) Table 3 (Continued) |
2.4 方法的准确度和精密度
由表4可知:在0.01、0.05和0.5 mg/kg添加水平下,29种杀菌剂的回收率在 74%~112% 之间,相对标准偏差在 1.1%~17% 之间。表明所建立方法有良好的准确度和精密度, 能满足黄瓜中29种杀菌剂的检测要求。
|
|
表 4 29种杀菌剂添加回收率和相对标准偏差 (n = 5) Table 4 Recoveries and RSDs of 29 fungicides at three spiked levels (n = 5) |
2.5 基质效应
由表3可知:29种杀菌剂的基质效应在0.86~1.10之间,表现为较弱基质效应。为最大程度消除基质效应干扰,所有样品均采用基质匹配标准曲线定量。
2.6 实际样品的检测采用本研究建立的分析方法,对市场上随机抽取的7份黄瓜样品进行分析,共检出8种杀菌剂。其中1份样品中检出嘧霉胺0.133 mg/kg、乙霉威0.028 mg/kg、氟吡菌胺0.038 mg/kg、氟硅唑0.021 mg/kg和氰霜唑0.028 mg/kg;2份样品中检出甲霜灵,含量分别为0.08和0.016 mg/kg;3份样品中检出甲基硫菌灵,含量分别为0.012、0.173和0.014 mg/kg。同时分别对检测出的农药进行了PICs子离子确证扫描,确定了结果的可靠性。根据GB 2763–2016中对黄瓜残留限量值的规定[5],7批购自市场的黄瓜中杀菌剂残留量均未超标。
3 结论本研究在QuEChERS方法的基础上,通过优化GCB用量,建立的dSPE净化方法切实可行。样品前处理操作简便、溶剂消耗少,分析时间短。结合UPLC-MS/MS建立的黄瓜中29种杀菌剂残留的快速检测方法具有良好的灵敏度、准确度和精密度,能够满足目前黄瓜中常用杀菌剂多残留的检测需要。
| [1] | LEBEDA A, COHEN Y. Cucurbit downy mildew (Pseudoperonospora cubensis)—biology, ecology, epidemiology, host-pathogen interaction and control [J]. Eur J Plant Pathol, 2011, 129(2): 157–192. doi:10.1007/s10658-010-9658-1 |
| [2] |
于春雷, 李素霞, 张斌, 等. 四氟醚唑对黄瓜的安全性及其对黄瓜白粉病的防治效果[J]. 植物保护学报, 2012, 39(3): 265–270.
YU C L, LI S X, ZHANG B, et al. Safety of tetraconazole to cucumber and its efficacy against cucumber powdery mildew[J]. J Plant Prot, 2012, 39(3): 265–270. |
| [3] | YUNIS H, ELAD Y, MAHRER Y. Influence of fungicidal control of cucumber and tomato grey mould (Botrytis cinerea) on fruit yield [J]. Pest Manage Sci, 2010, 31(3): 325–335. |
| [4] | MRLs formerly defined under Directives 86/362/EEC, 86/363/EEC and 90/642/EEC, referred to in Article 21(1): Commission Regulation (EC) No 149/2008[S]. Rue Froissart: European Commission, 2008. |
| [5] |
食品中农药最大残留限量: GB 2763—2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014.
National food safety standard-maximum residue limits for pesticides in food: GB 2763—2014[S]. Beijing: Standard Press of China 2014. |
| [6] |
周凤霞, 陈存. 气相色谱法同时测定蔬菜中醚菌酯和肟菌酯残留量的方法研究[J]. 农业环境与发展, 2009, 26(4): 81–84.
ZHOU F X, CHEN C. Determination of kresoxim-methyl and trifloxystrobin residues in vegetables[J]. Agro-Environ Dev, 2009, 26(4): 81–84. |
| [7] | SINGH G, SINGH B, BATTU R S, et al. Persistence of ethion residues on cucumber, Cucumis sativus (Linn.) using gas chromatography with nitrogen phosphorus detector [J]. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol, 2007, 79(4): 437–439. doi:10.1007/s00128-007-9251-2 |
| [8] |
金叶舟, 柯建赛, 蒋武毅. 离心法测定黄瓜中多种农药残留[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2013(6): 720–722.
JIN Y Z, KE J S, JIANG W Y. Determination of pesticide residues in cucumber by centrifugal method[J]. J Zhejiang Agric Sci, 2013(6): 720–722. |
| [9] | NASIRI A, AMIRAHMADI M, MOUSAVI Z, et al. A multi residue GC-MS mmethod for determination of 12 pesticides in cucumber[J]. Iran J Pharm Res, 2016, 15(4): 809–816. |
| [10] |
周鸿, 康长安, 何娟, 等. 气质联用法测定黄瓜中多农药残留及其动态降解研究[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2009, 19(6): 1259–1261.
ZHOU H, KANG C A, HE J, et al. Determination of multi-residues in cucumber by GC-MSD and degradation of pesticides[J]. Chin J Health Lab Technol, 2009, 19(6): 1259–1261. |
| [11] |
李蓉, 储大可, 张朋杰, 等. QuEChERS/HPLC-MS/MS法测定黄瓜、菜心、葡萄、香蕉中127种农药残留[J]. 分析测试学报, 2015, 34(5): 502–511.
LI R, CHU D K, ZHANG P J, et al. Determination of 127 pesticide residues in cucumber, flowering cabbage, grape and banana by QuEChERS method coupled with high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry[J]. J Instrum Anal, 2015, 34(5): 502–511. |
| [12] | LEHOTAY S J, DE KOK A, HIEMSTRA M, et al. Validation of a fast and easy method for the determination of residues from 229 pesticides in fruits and vegetables using gas and liquid chromatography and mass spectrometric detection[J]. J AOAC Int, 2005, 88(2): 595–614. |
| [13] | ANASTASSIADES M, LEHOTAY S J, STAJNBAHER D, et al. Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and "dispersive solid-phase extraction" for the determination of pesticide residues in produce[J]. J AOAC Int, 2003, 86(2): 412–431. |
| [14] |
李娜, 张玉婷, 刘磊, 等. QuEChERS-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定动物源食品中4类29种禁限用兽药残留[J]. 色谱, 2014, 32(12): 1313–1319.
LI N, ZHANG Y T, LIU L, et al. Simultaneous determination of 4 kinds of 29 banned and restricted veterinary drugs in animal-derived foods by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and modified QuEChERS for sample preparation[J]. Chin J Chromatogr, 2014, 32(12): 1313–1319. |
| [15] |
黄何何, 张缙, 徐敦明, 等. QuEChERS-高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定水果中21种植物生长调节剂的残留量[J]. 色谱, 2014, 32(7): 707–716.
HUANG H H, ZHANG J, XU D M, et al. Determination of 21 plant growth regulator residues in fruits by QuEChERS-high performance Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chin J Chromatogr, 2014, 32(7): 707–716. |
| [16] |
王雯, 梁颖, 沈燕, 等. 液相色谱-串联质谱法检测黄瓜中5种有机磷农药残留[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2012, 35(1): 45–50.
WANG W, LIANG Y, SHEN Y, et al. Simultaneous determination of five organophosphorus pesticide residues in cucumber by LC-MS/MS[J]. J Nanjing Agric Univ, 2012, 35(1): 45–50. |
| [17] |
储大可, 李蓉, 张朋杰, 等. 分散固相萃取-液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定果蔬中21种氨基甲酸酯类农药残留[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2015, 25(8): 1162–1165.
CHU D K, LI R, ZHANG P J, et al. Simultaneous determination of 21 carbamate pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables by dispersive-solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chin J Health Lab Technol, 2015, 25(8): 1162–1165. |
| [18] |
侯雪, 韩梅, 邱世婷. 改进的QuEChERS气相色谱-串联质谱法测定草莓中21种杀菌剂残留[J]. 农药学学报, 2017, 19(1): 46–52.
HOU X, HAN M, QIU S T, et al. Residues of 21 fungicides in Fragaria ananassa by modified QuEChERS and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chin J Pestic Sci, 2017, 19(1): 46–52. |
| [19] | DU X D, WU Y L, YANG H J, et al. Simultaneous determination of 10 β2-agonists in swine urine using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and multi-walled carbon nanotubes as a reversed dispersive solid phase extraction sorbent [J]. J Chromatogr A, 2012, 1260: 25–32. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.08.066 |
| [20] | FRENICH A G, ROMERO-GONZÁLEZ R, GÓMEZ-PÉREZ M L, et al. Multi-mycotoxin analysis in eggs using a QuEChERS-based extraction procedure and ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2011, 1218(28): 4349–4356. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2011.05.005 |
| [21] | LEHOTAY S J, SON K A, KWON H, et al. Comparison of QuEChERS sample preparation methods for the analysis of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2010, 1217(16): 2548–2560. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2010.01.044 |
| [22] | LAMBROPOULOU D A, ALBANIS T A. Methods of sample preparation for determination of pesticide residues in food matrices by chromatography-mass spectrometry-based techniques: a review[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2007, 389(6): 1663–1683. doi:10.1007/s00216-007-1348-2 |
| [23] | KOESUKWIWAT U, SANGUANKAEW K, LEEPIPATPIBOON N. Rapid determination of phenoxy acid residues in rice by modified QuEChERS extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Anal Chim Acta, 2008, 626(1): 10–20. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2008.07.034 |
| [24] | Amending annexes II, III and IV to regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European parliament and of the council as regards maximum residue levels for certain pesticides in or on certain products: Commission Regulation (EU) No 459/2010[S]. Rue Froissart: European Commission, 2010. |
| [25] | Amending annexes II, III and V to regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European parliament and of the council as regards maximum residue levels for carbaryl, procymidone and profenofos in or on certain products: Commission Regulation (EU) No 1096/2014[S]. Rue Froissart: European Commission, 2014. |
| [26] | Laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of the levels of lead, cadmium, mercury, inorganic tin, 3-MCPD and benzo(a)pyrene in foodstuffs: Commission Regulation (EC) 333/2007[S]. Brussels: EU, 2007. |
 2017, Vol. 19
2017, Vol. 19


