苯并烯氟菌唑 (benzovindiflupyr) 是瑞士先正达公司于2012年开发的吡唑酰胺类杀菌剂,化学名称为N-[9-(二氯甲基)-1,2,3,4-四氢-1, 4-亚甲基萘-5-基]-3-(二氟甲基)-1-甲基-1H-吡唑-4-羧酰胺[1],结构式见图式 1。

|
图式 1 苯并烯氟菌唑化学结构式 Scheme1 Structural formula of benzovindiflupyr |
苯并烯氟菌唑被认为是最具潜力的琥珀酸脱氢酶 (SDHI) 抑制剂[2],其对大豆、小麦、玉米、花生等常见作物的主要病害均有良好的防效[3]。虽然在中国苯并烯氟菌唑尚未被登记使用,但其多个产品已在巴西、美国等多个大豆出口大国作为防治大豆锈病的药剂登记使用[4-7]。中国是大豆进口国[8],大豆加工后的豆粕通常用作动物饲料[9],残留在饲料等产品中的苯并烯氟菌唑被动物食用后,可随着谷物及饲料的消耗转移至动物组织中[10-11],继而可能存在于肉类、牛奶、鸡蛋等动物源产品中,最终可通过食物链对人类健康产生危害[12]。为此,非常有必要针对动物源产品中苯并烯氟菌唑残留检测方法进行深入研究,对其残留进行监测,以确保消费者身体健康。
农药残留联席会议 (JMPR) 报告中显示,动物源产品中苯并烯氟菌唑的残留物包括其母体及其代谢物,但由于代谢物多以结合物的形式存在,毒性均不超过母体的十分之一,且其含量均远低于母体,故JMPR将苯并烯氟菌唑在动物源产品中的残留物仅定义为苯并烯氟菌唑母体[13]。
国际食品法典委员会 (CAC) 和欧盟规定苯并烯氟菌唑在动物源产品中的最大残留限量 (MRL值) 为0.01 mg/kg[14],而我国国家标准尚未制定其在植物源和动物源产品中的MRL值。目前,也未查询到有关该药在动物源产品中残留检测方法的报道,仅见姜宜飞等[15]应用高效液相色谱 (HPLC) 建立了苯并烯氟菌唑原药的分析检测方法。尽管JMPR报告中给出了苯并烯氟菌唑在相关动物源产品上可参考的检测方法,但其前处理过程非常复杂,且灵敏度也较低,定量限只有0.01 mg/kg[13]。
QuEChERS(Quick、Easy、Cheap、Effective、Rugged、Safe) 前处理方法具有快速、简单、廉价、有效、可靠、安全的特点,已广泛用于食品[16-17]和环境[18]样品中农药残留快速检测。本研究拟采用高效液相色谱-串联质谱法 (HPLC-MS/MS),结合QuEChERS前处理技术建立4种动物源产品 (猪肉、鸡肉、牛肉、鸡蛋) 中苯并烯氟菌唑残留的高效、准确、快速分析方法,并利用其监测中国市场上相关动物源产品中苯并烯氟菌唑的残留。
1 材料与方法 1.1 仪器与试剂高效液相色谱-三重四极杆质谱联用仪HPLC-MS/MS(TSQ QUANTUM ULTRA,美国Thermo公司);BSA323型万分之一电子天平 (瑞士赛多利斯公司);T-25 basic ULTRA-TURRAX高速植物组织捣碎机 (德国IKA公司);HYQ-3110涡旋混匀器 (美国Crystal公司);多管涡旋混合仪 (杭州奥盛仪器有限公司);3K15高速离心机 (美国Sigma公司)。
苯并烯氟菌唑 (benzovindiflupyr) 标准品 (纯度97%,购自德国Dr.E公司);无水硫酸镁、氯化钠、柠檬酸钠和柠檬酸氢二钠 (分析纯,上海国药集团化学试剂有限公司);N-丙基乙二胺 (PSA,Agela Technologies公司);甲醇 (色谱纯,德国Merck公司);乙腈 (色谱纯、分析纯);所有用水均为蒸馏水。
1.2 分析方法 1.2.1 样品前处理提取:称取均质样品 (牛肉、猪肉、鸡肉和鸡蛋)10 g于50 mL塑料离心管中,加入20 mL乙腈,于多管涡旋混合仪上振荡涡旋提取5 min,加入混合盐包 (1 g氯化钠、0.5 g柠檬酸氢二钠、4 g无水硫酸镁和1 g柠檬酸钠) 后迅速摇匀,振荡2 min,于4 000 r/min下离心5 min,待净化。
净化:取上清液1 mL于盛有150 mg无水硫酸镁和25 mg PSA的2 mL离心管中,涡旋2 min,在10 000 r/min下离心5 min后吸取上清液,经0.22 μm微膜过滤,供HPLC-MS/MS检测。
1.2.2 检测条件色谱条件:Thermo Hypersil GOLD C18色谱柱 (100 mm × 2.1 mm,3.0 μm);柱温35 ℃ ± 5 ℃;流速0.25 mL/min;进样量10 μL;流动相为乙腈和0.1%甲酸水溶液,梯度洗脱条件见表1。
|
|
表 1 流动相梯度洗脱程序 Table 1 Gradient program of mobile phase |
质谱条件:电喷雾负离子模式 (ESI-);电喷雾电压3 kV;离子源温度200 ℃;毛细管温度300 ℃;毛细管电压3.2 kV;鞘气压力344.75 kPa;辅助气压力137.90 kPa;多重反应监测 (MRM),检测条件见表2。
|
|
表 2 苯并烯氟菌唑多重反应监测条件 Table 2 The instrument conditions of benzovindiflupyr in multi-reaction monitoring mode |
1.2.3 标准曲线的制作
准确称取10 mg苯并烯氟菌唑标准品,用甲醇溶解并定容至100 mL,配制成100 mg/L的标准品储备液。再利用空白基质 (牛肉、猪肉、鸡肉和鸡蛋样品按照1.2.1节方法进行前处理所得) 将标准储备液进行稀释,配制成质量浓度分别为0.001、0.002、0.005、0.01、0.05、0.1、0.5和1 mg/L的系列标准工作溶液,按1.2.2节条件测定 (重复3次)。以进样质量浓度为横坐标,对应的峰面积为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线。
1.2.4 添加回收试验分别在空白牛肉、猪肉、鸡肉和鸡蛋样品中添加一定量的苯并烯氟菌唑标准溶液,添加水平分别为0.004、0.01和0.1 mg/kg,每个水平重复5次,按照所建立的方法进行添加回收率的检测验证。
2 结果与讨论 2.1 检测条件的选择采用高效液相色谱测定时,流动相的选择是影响色谱峰分离的重要因素。已有研究表明,向流动相乙腈-水中添加少量甲酸,不仅能够改善色谱峰的峰形,还能提高待测组分的离子化效率[19]。通过对色谱条件进行优化,最终确定采用乙腈-0.1%甲酸水溶液作为流动相。
质谱中选用电喷雾离子源 (ESI),以0.1 mg/L的苯并烯氟菌唑溶剂标准工作溶液直接进样,在m/z为50~500范围内进行全扫描,分别考察了在正离子 (ESI+) 和负离子 (ESI-) 两种模式下,苯并烯氟菌唑各碎片离子的响应值。最终确定定性及定量离子 (表2) 及相关仪器条件。
2.2 前处理方法的确定本研究借鉴了JMPR报告中苯并烯氟菌唑在动物源基质中的样品前处理方法,采用乙腈为提取剂,PSA(primary and secondary amine exchange material) 为吸附剂进行分散固相萃取净化。所建方法前处理步骤省略了JMPR报告方法中的样品氮吹浓缩过程,节约了前处理时间。
2.3 基质效应利用基质空白配制标样的响应值与同质量浓度溶剂标样响应值的比值大小对基质效应进行评价[20]。当比值 (基质效应,matrix effect, ME) 大于1时,表现为基质增强效应;ME小于1时,表现为基质抑制效应[21]。本研究结果表明,苯并烯氟菌唑在牛肉和猪肉两种动物源基质中的ME都等于5,说明在这两种基质中存在基质增强效应,在鸡蛋中ME为0.78,即在鸡蛋基质中存在基质抑制效应 (表3)。为消除基质效应的影响,采用了基质标准曲线进行定量分析,提高了分析结果的准确度和精密度。
2.4 线性关系与检测限结果表明:在0.001~1.0 mg/L范围内,苯并烯氟菌唑在4种动物源产品中的色谱峰面积与其相应的质量浓度间呈良好的线性关系,相关系数均大于0.991 0(表3)。以最小添加浓度作为方法的定量限 (LOQ),通过添加回收试验确认,苯并烯氟菌唑在牛肉、猪肉、鸡肉和鸡蛋中的LOQ均为0.004 mg/kg,且均低于CAC及JMPR报告中建立的苯并烯氟菌唑在相应动物源产品上的MRL值 (0.01 mg/kg)。
|
|
表 3 苯并烯氟菌唑在鸡蛋、鸡肉、猪肉、牛肉中的回归方程、相关系数及基质效应 Table 3 The regression, correlation coefficient and ME of benzovindiflupyr in different animal-origin food |
2.5 添加回收率和相对标准偏差
在0.004、0.01和0.1 mg/kg 3个添加水平下,苯并烯氟菌唑在鸡蛋、鸡肉、猪肉、牛肉中的回收率分别为83%~90%、82%~96%、85%~96%和77%~97%,相对标准偏差 (RSD) 分别为6.9%~11%、5.4%~8.7%、2.6%~7.3%和7.2%~10%(表4),符合农药残留检测方法要求[22],可用于鸡蛋、鸡肉、猪肉和牛肉中苯并烯氟菌唑农药残留的检测。苯并烯氟菌唑的典型提取离子色谱图见图1。
|
|
表 4 苯并烯氟菌唑在鸡蛋、鸡肉、猪肉、牛肉中添加回收结果 Table 4 Recoveries of benzovindiflupyr in different animal-origin food |
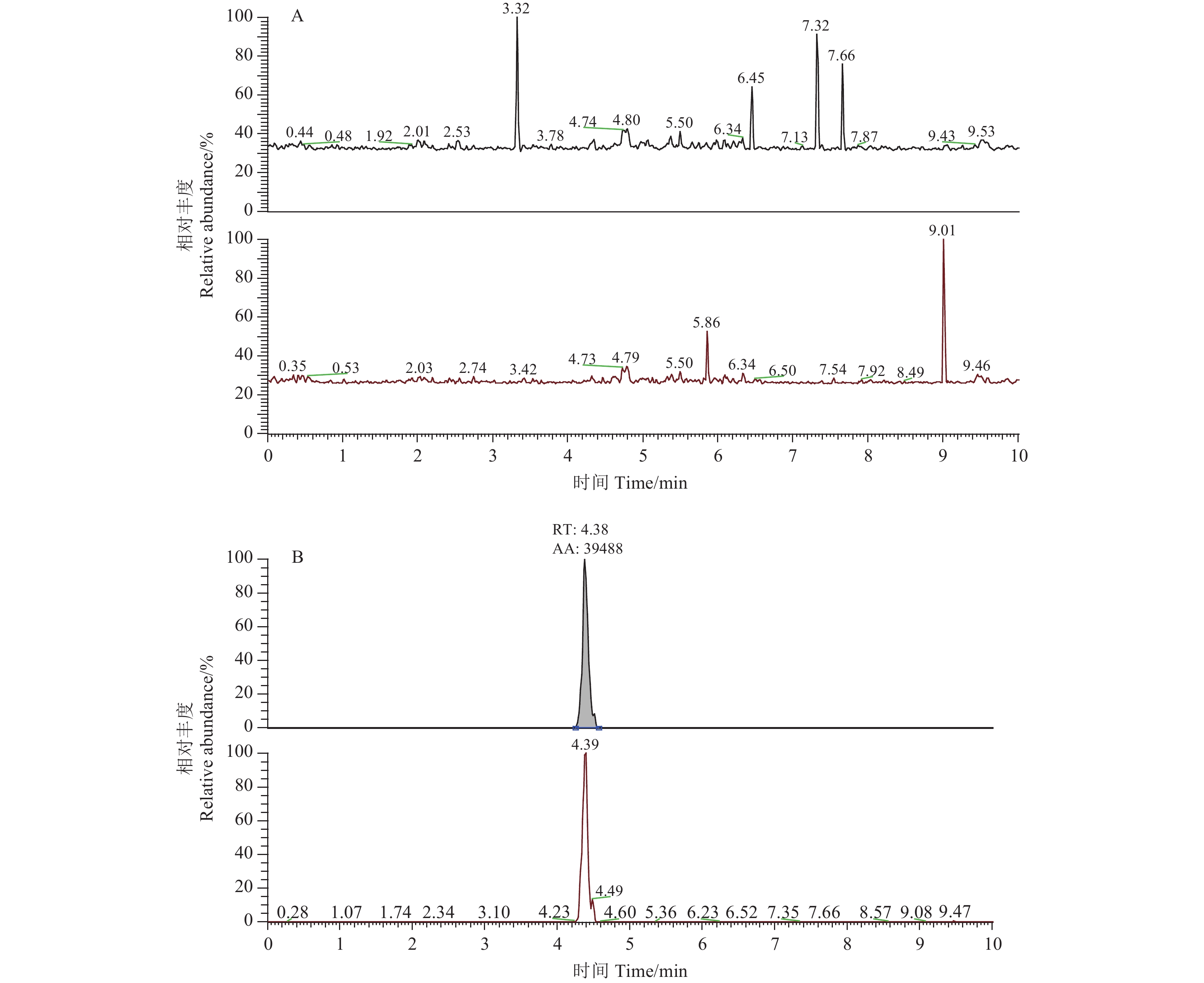
|
A. 鸡肉空白; B. 鸡肉添加样品 (0.1 mg/kg) A. Blank chicken sample; B. Chicken sample spiked at 0.1 mg/kg level 图 1 苯并烯氟菌唑典型提取离子色谱图 Fig. 1 Typical extraction ion chromatograms of benzovindiflupyr |
2.6 实际样品监测结果
为了解中国市场上动物源产品中苯并烯氟菌唑残留的基本情况,为评估中国消费者经动物源产品摄入苯并烯氟菌唑风险提供参考数据,2016年从河北、四川、湖南、江苏、湖北、山东、河南、广东、云南和安徽10省的批发市场及大型超市,随机抽检了猪肉、牛肉、鸡肉和鸡蛋样品,每种产品抽检30个批次,采用本研究所建立的方法进行检测。结果显示,所有抽检的样品中苯并烯氟菌唑的残留量均低于LOQ(0.004 mg/kg),检出率及超标率均为0。
3 结论本研究采用QuEChERS前处理与HPLC–MS/MS相结合,建立了4种动物源产品中苯并烯氟菌唑残留量的检测方法。在0.004、0.01和0.1 mg/kg 3个添加水平下,苯并烯氟菌唑的回收率在77%~97%之间 (RSD 2.6%~11%),方法定量限为0.004 mg/kg,低于CAC及JMPR报告中推荐的苯并烯氟菌唑在动物源产品中0.01 mg/kg的限量值。该方法具有操作简单、灵敏度高等特点,适用于动物源产品中苯并烯氟菌唑的检测和确证,为中国检测动物源产品中苯并烯氟菌唑的残留量提供了可参考的方法。
| [1] |
张翼翾. 广谱、持效期长的杀菌剂——苯并烯氟菌唑[J]. 世界农药, 2015, 37(5): 58–59.
ZHANG Y X. Broad spectrum, long duration of the fungicide-benzovindiflupyr[J]. World Pestic, 2015, 37(5): 58–59. |
| [2] |
王廷廷, 汤怀武. 苯并烯氟菌唑专利技术探析[J]. 农药市场信息, 2016(21): 28–30.
WANG T T, TANG H W. Analysis of patent technology of benzovindiflupyr[J]. Pestic Market News, 2016(21): 28–30. |
| [3] |
顾林玲. 先正达新有效成分苯并烯氟菌唑拟在巴西登记[J]. 现代农药, 2014, 13(2): 53.
GU L L. Syngenta has a new active ingredient (benzovindiflupyr) to be registered in Brazil[J]. Mod Agrochemicals, 2014, 13(2): 53. |
| [4] |
顾林玲. 先正达杀菌剂Elatus Plus (苯并烯氟菌唑)在法国登记[J]. 现代农药, 2016, 15(5): 56.
GU L L. Syngenta fungicide Elatus Plus (benzovindiflupyr) is registered in France[J]. Mod Agrochemicals, 2016, 15(5): 56. |
| [5] | Canadaapproves Syngenta benzovindiflupyr and several kinds of compound preparation registration[J]. Canada approves Syngenta benzovindiflupyr and several kinds of compound preparation registration[J]. Agrochemicals, 2015(12): 936. |
| [6] |
刘松松. 欧盟批准先正达杀菌剂SolatenolTM[J]. 农药市场信息, 2016(3): 49.
LIU S S. EU approval of syngenta fungicide SolatenolTM[J]. Pestic Market News, 2016(3): 49. |
| [7] | DuPontVessarya fungicide registered in Brazil can effectively control Asian rust[J]. DuPont Vessarya fungicide registered in Brazil can effectively control Asian rust[J]. Agrochemicals, 2016(12): 926. |
| [8] |
高颖, 郑志浩, 吕明霞. 中国大豆进口需求实证研究[J]. 农业技术经济, 2012(12): 82–87.
GAO Y, ZHENG Z H, LV M X. An empirical study of soybean import demand in China[J]. J Agrotechnical Econ, 2012(12): 82–87. |
| [9] | China’ssoybean import demand is on the rise[J]. China’s soybean import demand is on the rise[J]. Mar China, 2016(7): 48. |
| [10] | HATCHER J M, PENNELL K D, MILLER G W. Parkinson’s disease and pesticides: a toxicological perspective[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2008, 29(6): 322–329. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2008.03.007 |
| [11] | LIU H, YAO G J, LIU X K, et al. Approach for pesticide residue analysis for metabolite prothioconazole-desthio in animal origin food[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2017, 65(11): 2481–2487. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00062 |
| [12] | JEONG I S, KWAK B M, AHN J H, et al. Determination of pesticide residues in milk using a QuEChERS-based method developed by response surface methodology[J]. Food Chem, 2012, 133(2): 473–481. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.01.004 |
| [13] | JMPR. Benzovindiflupyr[EB/OL]. [2017-06-28]. http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/agphome/documents/Pests_Pesticides/JMPR/Evaluation14/Benzovindiflupyr.pdf. |
| [14] | Codex Tnternational Food Standards. Pesticide residues in food and feed pesticides database. 261-Benzovindiflupyr[DB/OL]. [2017-06-28]. http://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/standards/ pestres/pesticide-detail/zh/?p_id=261. |
| [15] |
姜宜飞, 黄伟, 宋俊华. 苯并烯氟菌唑原药高效液相色谱分析方法研究[J]. 农药科学与管理, 2015, 36(2): 35–37.
JIANG Y F, HUANG W, SONG J H. Analytical method of benzovindiflupyr TC by HPLC[J]. Pestic Sci Adm, 2015, 36(2): 35–37. |
| [16] | LEHOTAY S J, SON K A, KWON H, et al. Comparison of QuEChERS sample preparation methods for the analysis of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2010, 1217(16): 2548–2560. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2010.01.044 |
| [17] | WILKOWSKA A, BIZIUK M. Determination of pesticide residues in food matrices using the QuEChERS methodology[J]. Food Chem, 2011, 125(3): 803–812. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.09.094 |
| [18] | SHI C H, GUI W J, CHEN J, et al. Determination of oxadiargyl residues in environmental samples and rice samples[J]. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol, 2010, 84(2): 236–239. doi:10.1007/s00128-009-9881-7 |
| [19] |
侯帆, 薛佳莹, 刘丰茂, 等. 分散固相萃取与高效液相色谱-质谱联用测定小米及土壤中咪唑乙烟酸残留[J]. 农药, 2014, 53(11): 829–831.
HOU F, XUE J Y, LIU F M, et al. Determination of Imazethapyr residues in millet and soil using HPLC-MS[J]. Agrochemicals, 2014, 53(11): 829–831. |
| [20] |
陈姣姣, 张静, 吴思卓, 等. 气相色谱法测定苹果和土壤中的高效氯氟氰菊酯[J]. 色谱, 2016, 34(10): 1005–1010.
CHEN J J, ZHANG J, WU S Z, et al. Determination of lambda-cyhalothrin in apples and soil by gas chromatography[J]. Chin J Chromatogr, 2016, 34(10): 1005–1010. |
| [21] |
李福琴, 石丽红, 王飞, 等. QuEChERS-液相色谱-串联质谱法同时检测土壤和柑橘中吡唑醚菌酯、甲基硫菌灵及其代谢物多菌灵的残留[J]. 色谱, 2017, 35(6): 620–626.
LI F Q, SHI L H, WANG F, et al. Simultaneous determination of pyraclostrobin and thiophanate-methyl and its metabolite carbendazim residues in soil and citrus by QuEChERS-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chin J Chromatogr, 2017, 35(6): 620–626. |
| [22] | European Commission. Guidance document on analytical quality control and validation procedures for pesticide residues analysis in food and feed[R]. SANCO/12571/2013, 2013. |
 2017, Vol. 19
2017, Vol. 19


