文章信息
- 朱德宁, 韩宇, 房伟民, 陈发棣, 陈素梅, 邓波, 管志勇
- ZHU Dening, HAN Yu, FANG Weimin, CHEN Fadi, CHEN Sumei, DENG Bo, GUAN Zhiyong
- 多花型园林小菊品质评价与品种筛选
- Studies on the quality evaluation and variety selection of multi-flower garden chrysanthemum
- 南京农业大学学报, 2018, 41(2): 266-274
- Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018, 41(2): 266-274.
- http://dx.doi.org/10.7685/jnau.201705031
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2017-05-18
菊花(Chrysanthemum morifolium)是我国的十大传统名花之一, 在中国已有3 000多年的栽培历史[1]。因其花色丰富, 品种繁多, 花型多变而深受人们喜爱。菊花的栽培利用形式也丰富多彩, 独本菊、多头菊、大立菊、悬崖菊、菊艺盆景等各种产品成为菊花应用的独特现象[2]。随着菊花育种工作的深入, 多花型园林小菊品种逐渐进入人们的视野中, 这类品种花序直径不大, 但其花枝繁多, 颜色艳丽, 适合整株观赏, 成为庭院装饰, 城乡美化的新类别[3-4]。多花型园林小菊冠幅大于传统菊花, 且株形圆整、花期一致, 在园林建设中具有更加广泛的用途, 颇受市场欢迎, 也是国内外菊花育种的热点之一。目前此类品种在农业部的品种权申请件数已达50余个[5]。随着多花型园林小菊品种不断涌现, 亟待制定合理的品种评价标准, 采用科学的评价方法来对这些品种进行统一比较、评价, 以便及时筛选出优良品种进行推广, 这既是推动菊花新优品种选育也是促进菊花新品种景观应用的基础。
层次分析法(AHP)主要应用于观赏植物品种资源的筛选和评价[6-10]。不同研究者采用层次分析法已分别建立了传统盆菊[11]、标准切花菊[12]、多头切花菊[13]品种的评价体系, 并筛选出了优良品种, 推动了其产业化。此外, 在菊花引种适应性评价[14]和专用品种筛选[15]及在育种群体中选择优良株[16]等方面该方法也发挥了有效的作用。而在多花型园林小菊品种的评价方面虽然也有报道[17], 但其评价对象是国庆菊(早秋菊)品种群体。随着菊花品种的持续改良, 园林小菊品种群体构成及其观赏品质也已明显不同。此外, 已有工作在适应性评价上主要通过模拟干旱和湿涝条件来进行抗性方面的评价, 而多花型园林小菊适应性除了受制于水分因素的限制外, 还有众多不可忽视的其他环境因素[18]。本试验选取南京农业大学菊花课题组近年来选育的69个多花型园林小菊钟山系列品种进行综合评价, 旨在以此建立园林小菊综合评价体系, 并从中筛选出优良的多花型园林小菊品种, 进一步丰富菊花的园林建设形式, 为生产推广和园林建设提供优良品种素材。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验材料供试材料为69个钟山系列多花型园林小菊品种(表 1), 来自南京农业大学菊花种质资源保存中心。
| 编号 Code |
品种 Variety |
| 1 | 钟山金阳 Zhongshanjinyang |
| 2 | 钟山云桂 Zhongshanyungui |
| 3 | 钟山粉韵 Zhongshanfenyun |
| 4 | 钟山紫辰 Zhongshanzichen |
| 5 | 钟山早白 Zhongshanzaobai |
| 6 | 钟山紫薇 Zhongshanziwei |
| 7 | 钟山光辉 Zhongshanguanghui |
| 8 | 钟山紫莓 Zhongshanzimei |
| 9 | 钟山樱桂 Zhongshanyinggui |
| 10 | 钟山矮黄 Zhongshanaihuang |
| 11 | 钟山金葵 Zhongshanjinkui |
| 12 | 钟山香梨 Zhongshanxiangli |
| 13 | 钟山金莲 Zhongshanjinlian |
| 14 | 钟山星桂 Zhongshanxinggui |
| 15 | 钟山丹桂 Zhongshandangui |
| 16 | 钟山金冠 Zhongshanjinguan |
| 17 | 钟山金芒 Zhongshanjinmang |
| 18 | 钟山金维尼 Zhongshanjinweini |
| 19 | 钟山香橙 Zhongshanxiangcheng |
| 20 | 钟山蜜橘 Zhongshanmiju |
| 21 | 钟山金戎 Zhongshanjinrong |
| 22 | 钟山紫芍药 Zhongshanzishaoyao |
| 23 | 钟山紫松果 Zhongshanzisongguo |
| 24 | 钟山紫阳 Zhongshanziyang |
| 25 | 钟山嫣红 Zhongshanyanhong |
| 26 | 钟山粉蝶 Zhongshanfendie |
| 27 | 钟山紫日 Zhongshanziri |
| 28 | 钟山紫鹃 Zhongshanzijuan |
| 29 | 钟山旭紫 Zhongshanxuzi |
| 30 | 钟山紫鸢 Zhongshanziyuan |
| 31 | 钟山酒红 Zhongshanjiuhong |
| 32 | 钟山光芒 Zhongshanguangmang |
| 33 | 钟山红柚 Zhongshanhongyou |
| 34 | 钟山红枫 Zhongshanhongfeng |
| 35 | 钟山赤桂 Zhongshanchigui |
| 36 | 钟山红太阳 Zhongshanhongtaiyang |
| 37 | 钟山红荷 Zhongshanhonghe |
| 38 | 钟山朱玺 Zhongshanzhuxi |
| 39 | 钟山似火 Zhongshansihuo |
| 40 | 钟山赤焰 Zhongshanchiyan |
| 41 | 钟山荔红 Zhongshanlihong |
| 42 | 钟山阳红 Zhongshanyanghong |
| 43 | 钟山墨莲 Zhongshanmolian |
| 44 | 钟山红火 Zhongshanhonghuo |
| 45 | 钟山紫瑞 Zhongshanzirui |
| 46 | 钟山早樱 Zhongshanzaoying |
| 47 | 钟山小丑 Zhongshanxiaochou |
| 48 | 钟山彩虹 Zhongshancaihong |
| 49 | 钟山小香橙 Zhongshanxiaoxiangcheng |
| 50 | 钟山小红柚 Zhongshanxiaohongyou |
| 51 | 钟山粉凯蒂 Zhongshanfenkaidi |
| 52 | 钟山红鹰 Zhongshanhongying |
| 53 | 钟山桃红 Zhongshantaohong |
| 54 | 钟山墨荷 Zhongshanmohe |
| 55 | 钟山芝樱 Zhongshanzhiying |
| 56 | 钟山炫彩 Zhongshanxuancai |
| 57 | 钟山雪戎 Zhongshanxuerong |
| 58 | 钟山奶黄包 Zhongshannaihuangbao |
| 59 | 钟山红冠 Zhongshanhongguan |
| 60 | 钟山银星 Zhongshanyinxing |
| 61 | 钟山玉戎 Zhongshanyurong |
| 62 | 钟山雪桂 Zhongshanxuegui |
| 63 | 钟山银桂 Zhongshanyingui |
| 64 | 钟山霜桂 Zhongshanshuanggui |
| 65 | 钟山紫莲 Zhongshanzilian |
| 66 | 钟山紫荷 Zhongshanzihe |
| 67 | 钟山桃桂 Zhongshantaogui |
| 68 | 钟山敷粉 Zhongshanfufen |
| 69 | 钟山紫莺 Zhongshanziying |
试验于2015年3月至2016年12月在南京农业大学菊花江宁试验基地进行。于2015年5月中旬选择钟山系列园林小菊生长健壮的母株, 采取枝条充实健康、长势整齐、无病害、长6~8 cm的插穗, 用生根粉和多菌灵(80%可湿性粉剂)浸泡消毒后扦插于穴盘中。基质采用草炭和石灰岩(质量比3 : 1)混合配置。约15 d后生根完毕, 定植于露地, 种植间距为45 cm, 正常田间管理。于定植20 d后第1次摘心, 并于第1次摘心后15 d第2次摘心, 以促进侧枝的生发、快速生长。
1.3 性状测试方法花期进行植株各项指标观测。植株紧凑性:植株一级分枝与主茎靠拢程度, 目测; 植株抗倒伏能力:没有倒伏的植株所占植株总数的比例, 目测; 冠丛圆整性:盛花期冠丛的轮廓与球形的接近程度, 分为球形、近球形和其他3级; 花朵繁密度:盛花期时花序覆盖株丛表面的比例情况, 目测; 花色持久度:盛花期观察花瓣颜色保色的时间长短, 目测; 缺株数:每100株统计植株的死亡数, 计数统计。株高、冠幅、花径、花朵数量、花梗长、花期长度等性状的测试方法参照文献[19-20]。
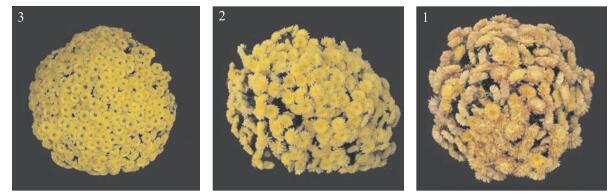
1.4 统计分析参照菊花及其他花卉的评价指标和综合评价标准[11, 13, 17, 21], 拟定了各项因素的3分制评分标准(表 2, 图 1~图 3)。根据专家的意见, 采用层次分析法进行评价打分。利用SPSS 18.0软件对69个品种进行聚类分析,然后将各个因素分为3个等级, 分别赋分值为3、2、1。根据各项评价指标进行综合评价分析。
| 因子Factor | 分值Score | ||
| 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| 株高/cm Plant height | 28~33 | < 28 | >33 |
| 冠幅/cm Crown diameter | >45 | 45~35 | < 35 |
| 分枝数 Number of branches |
分枝性强, 分枝数大于60枝 Branches are strong and they aremore than 60 branches |
分枝性适中, 分枝数小于60枝而大于40枝 Branches are moderate andthey are less than 60 branches andmore than 40 branches |
分枝性弱, 分枝数小于40枝 Branches are weak and theyare less than 40 branches |
| 植株紧凑性 Plant compactedness |
植株分枝紧凑, 各个分枝之间紧凑结合, 与主干靠拢不分散 Plant branches are not separated from the trunk, compact between thebranches of the combination |
植株分枝比较多, 但各个分枝分散不紧凑 There are more branches, but thebranches are scattered |
植株分枝少, 各个分枝之间间隙大而且分散 The plant branches are small, and the gaps between branchesare large and dispersed |
| 冠丛圆整性 Crown roundness |
盛花期冠丛圆整 The crown is round and roundin the flowering period |
冠丛稍微圆整 The crown is slightly round |
冠丛不饱满, 形状各异 The crown is not full andthe shapes are different |
| 花朵繁密度 Numerous density of flower |
盛花期花朵分布均匀, 且花朵能覆盖株丛表面 The flowers are evenly distributedand cover the surface of the plants |
盛花期花朵分布稍微均匀, 但不紧凑 The flowers are distributed slightlyeven, but not compact |
盛花时花朵分布不均匀, 相邻花之间空隙大 The flowers are not evenlydistributed, and there is a large gapbetween adjacent flowers |
| 花径/cm Flower diameter | >5 | 5~3 | < 3 |
| 花朵数量 Flower number | >400 | 400~300 | < 300 |
| 花梗长/cm Peduncle length | < 2 | 2~3 | >3 |
| 花期长度/d Flowering duration | >35 | 35~28 | < 28 |
| 花型 Flower shape | 重瓣 Double | 托桂 Anemone | 单瓣 Single |
| 花色持久度 Color persistency |
鲜艳持久或花色特殊 Bright and lasting or special |
花色鲜艳, 但色泽日渐褪色, 不持久 The color is bright, but the color fades and it doesn′t last |
花瓣色泽暗淡, 颜色不纯, 褪色快 The petals are dim, impure color, and it′s fade fast |
| 抗倒伏能力 Lodging resistance capability |
群体中没有或极少倒伏, 300株植株中少于5株 There are no or few inthe group, less than 5 in300 plants |
群体中少部分倒伏, 300株中倒伏5~20株 A few of the plants arelodged in the group, lodging 5 to 20 in 300 plants |
群体中倒伏植株多, 300株中大于20株 There are more lodging plantsin the group, more than 20 in 300 plants |
| 缺株数 Number of died plant |
群体中没有或很少死亡植株, 每100株中缺株小于5株 There are no or few deadplants in the group, and thereare fewer than 5 in 100 plants |
群体中有部分死亡植株, 每100株中缺株数为5~20株 There are partially dead plantsin the group, between 5 to 20 in 100 plants |
群体中较多植株死亡, 每100株中缺株数大于20株 More plants are died, more than 20 in 100 plants |

|
图 2 冠丛圆整性的3个等级 Figure 2 Three grades of crown roundness |

|
图 3 花朵繁密度的3个等级 Figure 3 Three grades of numerous density of flower |
参考层次分析法的层次构建的标准及前人的菊花评价体系, 结合园林小菊的性状特征, 确定各个性状指标的权重, 建立3个层次综合分析模型。第1层为目标层(A), 为优良的园林小菊品种; 第2层为约束层(C), 分别是植株的生长特性、观赏特性以及适应性; 第3层为标准层(P), 为14个具体的性状评价指标(表 3)。
| 目标层(A) Target layer(A) |
约束层(C) Constraint layer(C) |
标准层(P) Standard layer(P) |
| 优良的园林小菊 Excellent garden chrysanthemum |
植株的生长特性(C1) Plant growth characteristics |
株高Plant height(P1) 冠幅Crown diameter(P2) 分枝数Number of branches(P3) 植株紧凑性Plant compactedness(P4) 冠丛圆整性Crown roundness(P5) |
| 观赏特性(C2) Ornamental characteristics |
花朵繁密度Numerous density of flower(P6) 花径Flower diameter(P7) 花朵数量Flower number(P8) 花梗长Peduncle length(P9) 花期长度Flowering duration(P10) 花型Flower shape(P11) 花色持久度Color persistency(P12) |
|
| 适应性(C3) Adaptability |
抗倒伏能力Lodging resistance capability(P13) 缺株数Number of died plant(P14) |
各个评价因素的重要性是相对的, 在2个因素之间相互比较来衡量因素的重要性。结合各因素之间的隶属关系, 根据1~9比率标度法(表 4), 园林小菊的栽培特性以及专家意见, 构造A-C, C-P之间因素两两比较矩阵, 并对其进行一致性检验(表 5)。
| 标度 Scale |
含义 Implication |
| 1 | 2个元素对某个属性具有同样重要性 Compared to the two elements, they have the same importance |
| 3 | 2个元素比较, 一元素比另一元素稍微重要 Compared to the two elements, the former is slightly important than the latter |
| 5 | 2个元素比较, 一元素比另一元素明显重要 Compared to the two elements, the former is more important than the latter obviously |
| 7 | 2个元素比较, 一元素比另一元素重要得多 Compared to the two elements, the former is more important than the latter strongly |
| 9 | 2个元素比较, 一元素比另一元素极端重要 Compared to the two elements, the former is extremely important than the latter |
| 2, 4, 6, 8 | 表示上述相邻判断的中间值 The median of above judgment |
| 1/bij | 指标i与j比较的判断值是bij, 则j与i比较的判断值是1/bij bij represents the judgment value of comparison between index i and j, then 1/bij represents the judgment value of comparison between index j and i |
| A-Ci | ||||||||
| A | C1 | C2 | C3 | Wi | ||||
| C1 | 1 | 1/2 | 2 | 0.297 | ||||
| C2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0.539 | ||||
| C3 | 1/2 | 1/3 | 1 | 0.163 | ||||
| Note: λmax=3.009, C.I.=0.005, R.I.=0.58, C.R.=0.008 < 0.10. | ||||||||
| C1-Pi | ||||||||
| C1 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | Wi | ||
| P1 | 1 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/4 | 1/8 | 0.053 | ||
| P2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1/2 | 1/4 | 0.139 | ||
| P3 | 2 | 1/3 | 1 | 1/2 | 1/6 | 0.081 | ||
| P4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1/4 | 0.189 | ||
| P5 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 0.536 | ||
| Note:λmax=5.167, C.I.=0.041, R.I.=1.12, C.R.=0.037 < 0.10. | ||||||||
| C2-Pi | ||||||||
| C2 | P6 | P7 | P8 | P9 | P10 | P11 | P12 | Wi |
| P6 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 0.301 |
| P7 | 1/6 | 1 | 1/4 | 2 | 1/6 | 1/2 | 1/5 | 0.044 |
| P8 | 1/3 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 1/2 | 0.148 |
| P9 | 1/4 | 1/2 | 1/3 | 1 | 1/5 | 2 | 1/4 | 0.051 |
| P10 | 1/2 | 6 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 1/2 | 0.192 |
| P11 | 1/5 | 2 | 1/5 | 1/2 | 1/7 | 3 | 1/3 | 0.046 |
| P12 | 1/2 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0.215 |
| Note:λmax=7.505, C.I.=0.008, R.I.=1.32, C.R.=0.062 < 0.10. | ||||||||
| C3-Pi | ||||||||
| C3 | P13 | P14 | Wi | |||||
| P13 | 1 | 1/2 | 0.333 | |||||
| P14 | 2 | 1 | 0.666 | |||||
| Note:λmax=2.000, C.I.=0, R.I.=0, C.R.=0 < 0.10. | ||||||||
根据层次分析法(APH), 结合yaahp软件的统计计算, 对各影响因素所属矩阵进行处理后, 对构造的4个矩阵进行一致性检验。以判断矩阵的随机一致性比率C.R.(< 0.10)为标准, 即判断矩阵的一般一致性指标C.I.与平均随机一致性指标R.I.的比值, 1~9阶R.I.值参见表 6。计算结果表明:上述矩阵C.R.在允许的误差范围(< 0.10)内时, 即判断矩阵具有满意的一致性, 说明各因素的权重赋值符合要求, 一致性合理。
| n | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| R.I. | 0 | 0 | 0.58 | 0.90 | 1.12 | 1.24 | 1.32 | 1.41 | 1.45 |
由层次分析法得出约束层(C)对目标层(A)的权重值以及标准层(P)对约束层(C)的权重值, 再用约束层(C)的权重值加权综合, 可算出标准层(P)对于目标层(A)的综合权重值。运用Excel 2010软件对其统计, 进行排序。由表 7可知:按优良的园林小菊的权重比例大小, 其影响效果排序依次为观赏特性、植株生长特性、适应性, 其权重值分别为0.539、0.297、0.163, 表明观赏特性对于园林小菊的综合效果影响较大; 在选取的14个指标中, 观赏特性的花朵繁密度(P6)对优良的组合盆栽(A)的权重值最大, 为0.162, 其次是植株生长特性的冠丛圆整性(P5), 其权重值为0.159, 表明对于多花型园林小菊而言, 注重品种的花朵繁密度和冠丛圆整性的选择是提高园林小菊观赏效果的关键; 而株高(P1)和花径(P7)的权重值较小, 分别为0.016、0.023, 表明株高和花径对园林小菊观赏效果的影响较小。
| 标准层(P) Standard layer(P) |
W(A-Ci) | W(C-Pi) | 标准层P对目标层 AStandard layer P to the target A |
排名 Order |
| P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 |
0.297 | 0.454 0.193 0.166 0.127 0.057 |
0.016 0.041 0.024 0.056 0.159 |
14 9 12 7 2 |
| P6 P7 P8 P9 P10 P11 P12 |
0.539 | 0.368 0.186 0.168 0.085 0.096 0.054 0.040 |
0.162 0.023 0.080 0.027 0.104 0.025 0.116 |
1 13 6 10 5 11 3 |
| P13 P14 |
0.163 | 0.750 0.250 |
0.054 0.108 |
8 4 |
参考菊花相关品质性状综合评价体系, 分别选取14个评价因素的权重值(表 7)乘以实际各项因素评价标准(表 2)的分值, 累积加成, 最后计算得出各个品种的综合评分。运用K-Means聚类方法将69个钟山系列品种进行分级, 可划分为优、良、中、差4个等级。品种综合评分和等级划分如表 8。
| 编号 Code |
分值 Score |
等级 Grade |
| 1 | 2.798 | 1 |
| 2 | 2.358 | 1 |
| 3 | 2.439 | 1 |
| 4 | 2.497 | 1 |
| 5 | 2.210 | 2 |
| 6 | 2.290 | 1 |
| 7 | 2.099 | 2 |
| 8 | 2.017 | 2 |
| 9 | 2.278 | 1 |
| 10 | 1.978 | 2 |
| 11 | 1.876 | 3 |
| 12 | 1.863 | 3 |
| 13 | 2.003 | 2 |
| 14 | 2.198 | 2 |
| 15 | 1.851 | 3 |
| 16 | 1.720 | 3 |
| 17 | 1.544 | 4 |
| 18 | 1.604 | 4 |
| 19 | 1.745 | 3 |
| 20 | 1.606 | 4 |
| 21 | 1.983 | 2 |
| 22 | 2.072 | 2 |
| 23 | 2.597 | 1 |
| 24 | 1.713 | 3 |
| 25 | 1.985 | 3 |
| 26 | 1.701 | 3 |
| 27 | 2.518 | 1 |
| 28 | 2.246 | 2 |
| 29 | 2.230 | 2 |
| 30 | 1.965 | 2 |
| 31 | 2.017 | 2 |
| 32 | 1.967 | 2 |
| 33 | 1.926 | 3 |
| 34 | 1.392 | 4 |
| 35 | 1.770 | 3 |
| 36 | 1.602 | 4 |
| 37 | 1.766 | 3 |
| 38 | 1.702 | 3 |
| 39 | 1.592 | 4 |
| 40 | 2.200 | 2 |
| 41 | 1.962 | 2 |
| 42 | 1.655 | 3 |
| 43 | 1.808 | 3 |
| 44 | 1.800 | 3 |
| 45 | 2.101 | 2 |
| 46 | 1.805 | 3 |
| 47 | 1.831 | 3 |
| 48 | 2.460 | 1 |
| 49 | 1.907 | 3 |
| 50 | 1.580 | 4 |
| 51 | 1.530 | 4 |
| 52 | 2.369 | 1 |
| 53 | 1.765 | 3 |
| 54 | 1.607 | 4 |
| 55 | 1.927 | 3 |
| 56 | 1.735 | 3 |
| 57 | 1.436 | 4 |
| 58 | 1.693 | 3 |
| 59 | 1.635 | 4 |
| 60 | 2.203 | 2 |
| 61 | 1.754 | 3 |
| 62 | 2.108 | 2 |
| 63 | 2.601 | 1 |
| 64 | 1.974 | 2 |
| 65 | 2.373 | 1 |
| 66 | 1.501 | 4 |
| 67 | 2.048 | 2 |
| 68 | 2.045 | 2 |
| 69 | 1.771 | 3 |
由表 8可知:69个钟山系列品种按优、良、中、差4个等级划分的比例为17.39%、31.88%、33.33%和17.39%, 良等级和中等级所占的比例比较大, 优等级和差等级的比例相同, 均为12个品种。优等级的品种有‘钟山金阳’‘钟山粉韵’‘钟山紫辰’‘钟山紫日’和‘钟山彩虹’等, 其综合分值分别为2.798、2.439、2.497、2.518、2.544;而‘钟山红枫’‘钟山小红柚’‘钟山粉凯蒂’‘钟山墨荷’等品种的综合品质比较差, 为差等级别, 其综合分值分别为1.392、1.580、1.530、1.607, 在生产过程中, 可利用良等级丰富的品种资源, 充分发挥品种多样化的作用。
从各个性状的权重值可以看出, 观赏指标的权重值最高, 以花朵繁密度最为重要, 其次是花期长度和花朵数量, 而花直径和花型重要性程度在花朵性状中最低。植株生长性状指标中冠丛圆整性最重要, 其次是植株紧凑性和冠幅大小, 最后是分枝数和株高。而植株适应性指标中缺株数较植株的抗倒伏能力更为重要。
综上所述, 综合性状表现优的有12个品种, 分别为‘钟山金阳’‘钟山光辉’‘钟山赤焰’‘钟山早白’‘钟山银桂’‘钟山敷粉’‘钟山紫瑞’‘钟山樱桂’‘钟山紫鹃’‘钟山紫松果’‘钟山紫辰’‘钟山紫日’, 其在花朵繁密度、冠丛圆整性、花色持久度、群体存活率、花期、花朵数量、植株紧凑性等这些权重较大的指标上表现都比较突出, 符合筛选要求, 观赏性状优良。
3 讨论与结论层次分析法是将定性分析与定量分析有机结合的科学决策方法, 既包含了主观的逻辑判断和分析, 又发挥了定量分析的优势[22]。在制定评价标准和数据统计过程中, 由于测量方法和个人操作存在误差, 综合评价的得分必然会有所差异[23], 但层次分析法作为观赏植物评价的方法之一, 可以将复杂的问题运用分层方法简化, 从而得出最佳的方案。通过确立各评价对象的权重, 从而得出综合的得分情况。在不同观赏植物的品种评价中, 采用层次分析法为指标权重赋值时, 应根据具体的品种评价目标在选择指标和矩阵赋值上灵活变动, 建立合适的评价体系[9]。
适应性往往成为品种推广及应用中的限制因子, 而植物在不同生育阶段受到的胁迫对其影响差异较大[24]。不同于在苗期基于胁迫模拟的适应性评价, 本研究以群体在盛花期的存活率为适应性评价的“终极”指标, 评价指标直观, 评价工作效率高, 更符合生产与绿化实践。
不同于传统菊花的观赏品质评价较注重对个体的欣赏, 多花型园林小菊强调群体效果的展示。本研究新采用的与园林小菊整株观赏品质相关的3个指标:冠丛圆整性、花朵(序)繁密度、花色持久度, 是在本试验评价指标体系中权重最大, 在前人的研究中未有报道。观赏品质方面的花期长度、花朵数量、植株紧凑性的权重紧随3个指标其后, 均位于花朵局部性状之前, 说明园林小菊品种的评价上整体观赏品质优于局部性状, 这与翟丽丽等[17]的研究结果基本一致。而花径和花型在评价体系中的权重较低, 与参试品种群体内的两性状差异不大有关, 这种性状上的接近是育种上长期定向选择造成的[25]。而花梗长等其他更为局部性的花朵性状的权重更低, 反映这一评价体系注重群体效果的合理性。因此, 利用层次分析法筛选品种也适用于多花型园林的小菊品种, 可以为生产实践和园林应用提供指导。
优良的多花型园林小菊品种的筛选目标是植株株丛圆整、花朵繁密、开花持久、花朵数量多、适应性强[5]。因此, 在这个基础上参考其他观赏植物的评价标准, 并结合专家意见, 选出了14个与筛选目标关系密切的性状因子, 用层次分析法将其量化。采取3分制法对这14个性状因子进行打分, 进行综合评价能够获得理想的评价结果。
从钟山系列园林小菊品质性状的众多影响因子中筛选出对品质性状影响较大的14个因子, 建立了钟山系列园林小菊品质评价体系; 对69个钟山系列园林小菊品种进行综合评价, 从中筛选出12个优等级品种, 占17.39%;而其中良等级品种16个, 作为补充品种, 占31.88%。本研究的品种评价结果与近年课题组在各地推广试验的表现相符合, 筛选出的优良品种可直接用于大面积推广应用。
| [1] |
李鸿渐, 邵健文. 中国菊花品种资源的调查收集与分类[J].
南京农业大学学报, 1990, 13(1): 30-36.
Li H J, Shao J W. The investigation and collection of chrysanthemum variety resources in China[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 1990, 13(1): 30-36. DOI: 10.7685/j.issn.1000-2030.1990.01.006 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [2] |
李鸿渐.
中国菊花[M]. 南京: 江苏科学技术出版社, 1992.
Li H J. Chinese Chrysanthemum[M]. Nanjing: Jiangsu Science and Technology Press, 1992. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] |
陈俊愉, 崔娇鹏.
地被菊培育与造景[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2006, 6-36.
Chen J Y, Cui J P. Cultivation and Scape Creation of Ground-cover Chrysanthemum[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2006, 6-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] |
曾海祥. 广州地区引种栽培国庆小菊——金陵红莲初报[J].
现代园艺, 2016(4): 48-49.
Zeng H X. Initial report of introduction and cultivation of guoqing chrysanthemum with small inflorescences in Guangzhou area:Jinlinghonglian[J]. Modern Horticulture, 2016(4): 48-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] |
张树林, 戴思兰.
中国菊花全书[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2013.
Zhang S L, Dai S L. Chinese Chrysanthemum Book[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] |
董航, 张杰, 孙红梅. 亚洲百合新品种引进与筛选[J].
沈阳农业大学学报, 2013, 44(6): 816-819.
Dong H, Zhang J, Sun H M. Introduction and screening of new varieties of asiatic hybrid lily[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2013, 44(6): 816-819. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] |
李振芳, 张新叶, 陈慧玲, 等. 紫薇品种性状综合评价选择体系[J].
东北林业大学学报, 2017, 45(3): 39-44.
Li Z F, Zhang X Y, Chen H L, et al. Comprehensive evaluation and selection system of Lagerstroemia variety characters[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2017, 45(3): 39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] |
王业社, 陈立军, 杨贤均, 等. 湖南云山野生地被植物资源及其综合评价分析[J].
草业学报, 2015, 24(7): 30-40.
Wang Y S, Chen L J, Yang X J, et al. A comprehensive evaluation of the wild ground cover plants resources in Yunshan, Hunan[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(7): 30-40. DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2014344 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] |
熊亚运, 夏文通, 王晶, 等. 基于观赏价值和种球再利用的郁金香品种综合评价与筛选[J].
北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(1): 107-114.
Xiong Y Y, Xia W T, Wang J, et al. Comprehensive evaluation and screening of tulip cultivars based on their ornamental value and reuse of bulbs[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2015, 37(1): 107-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] |
陈和明, 江南, 朱根发, 等. 层次分析法在大花蕙兰品种选择上的应用[J].
亚热带植物科学, 2009, 38(2): 30-32.
Chen H M, Jiang N, Zhu G F, et al. Application of AHP in selection of cymbidium hybridum cultivars[J]. Subtropical Plant Science, 2009, 38(2): 30-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] |
张亚琼, 张伟, 戴思兰, 等. 基于AHP的中国传统盆栽菊花产业化品种筛选[J].
中国农业科学, 2011, 44(21): 4438-4446.
Zhang Y Q, Zhang W, Dai S L, et al. AHP-based screening of traditional potted chrysanthemum for industrialized production[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(21): 4438-4446. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] |
韩勇, 陈发棣, 房伟民, 等. 单头切花菊品质性状综合评价体系构建[J].
南京农业大学学报, 2011, 34(5): 32-36.
Han Y, Chen F D, Fang W M, et al. A synthetic system established for assessing the quality of standard cut chrysanthemum[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011, 34(5): 32-36. DOI: 10.7685/j.issn.1000-2030.2011.05.006 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] |
韩勇, 叶燕萍, 陈发棣, 等. 多头切花菊品质性状综合评价体系构建[J].
中国农业科学, 2011, 44(20): 4265-4271.
Han Y, Ye Y P, Chen F D, et al. Establishment of synthetic assessing system for the quality of spray cut chrysanthemum[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(20): 4265-4271. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] |
张冬菊, 张晓, 吴鹏夫, 等. 基于层次分析法的切花菊引种适应性评价[J].
北方园艺, 2013(22): 82-85.
Zhang D J, Zhang X, Wu P F, et al. Introduction adaptability evaluation of cut chrysanthemum based on Analytic Hierarchy Process[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2013(22): 82-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] |
邱民得, 胡振阳, 李宇辉, 等. 切花菊矮化盆栽品种评价[J].
安徽农业科学, 2017, 45(1): 49-51.
Qiu M D, Hu Z Y, Li Y H, et al. Evaluation of dwarf potted cultivars of cut chrysanthemum[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(1): 49-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] |
李娜娜, 张德平, 朱珺, 等. 利用层次分析法初选单头切花菊杂种F1代优良单株的研究[J].
西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 40(2): 129-135.
Li N N, Zhang D P, Zhu J, et al. A study on the primary selection of single flower cutting chrysanthemum hybrid F1using Analytic Hierchy Process[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(2): 129-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] |
翟丽丽, 房伟民, 陈发棣, 等. 国庆小菊观赏性和耐旱、涝性的综合评价[J].
中国农业科学, 2012, 45(4): 734-742.
Zhai L L, Fang W M, Chen F D, et al. Comprehensive appraisal of the ornamental value and drought and flooding resistance of Guoqing chrysanthemum with small inflorescences[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(4): 734-742. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] |
贾思振, 房伟民, 陈发棣, 等. 高温下5个夏菊品种开花特性、叶片组织结构与光合特性的比较[J].
南京农业大学学报, 2009, 32(3): 151-156.
Jia S Z, Fang W M, Chen F D, et al. Comparison of blooming traits, leaf tissue structure and photosynthetic characteristics of five summer chrysanthemum varieties under high temperature[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2009, 32(3): 151-156. DOI: 10.7685/j.issn.1000-2030.2009.03.028 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] |
中华人民共和国农业部. 植物新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南菊花: NY/T 2228-2012[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2012.
Ministry of Agriculture of Peoples Republic of China. Guidelines for the conduct of tests for distinctness, uniformity and stability: chrysanthemum NY/T 2228-2012[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2012(in Chinese). |
| [20] |
郝京辉, 游捷, 秦贺兰, 等. 菊花品种的特异性、一致性和稳定性的研究[J].
中南林业科技大学学报, 2003, 23(5): 14-18.
Hao J H, You J, Qin H L, et al. Study of the distinctness, uniformity and stability of chrysanthemum cultivars[J]. Journal of Central South Forestry University, 2003, 23(5): 14-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] |
陈莉, 孙兆法, 李梅, 等. 切花品质评价标准及采前生长条件对切花影响[J].
北方园艺, 2000(1): 40-42.
Chen L, Sun Z F, Li M, et al. Quality evaluation criteria and pregrowth conditions for cutting flowers[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2000(1): 40-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] |
赵焕臣.
层次分析法:一种简易的新决策方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986, 10-30.
Zhao H C. The Analytic Hierarchy Process:A New Simple Decision Method[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1986, 10-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] |
郭金玉, 张忠彬, 孙庆云. 层次分析法的研究与应用[J].
中国安全科学学报, 2008, 18(5): 148-153.
Guo J Y, Zhang Z B, Sun Q Y. Study and applications of Analytic Hierarchy Process[J]. Chinese Safety Science Journal, 2008, 18(5): 148-153. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] |
江学海, 李刚华, 王绍华, 等. 不同生育阶段干旱胁迫对杂交稻产量的影响[J].
南京农业大学学报, 2015, 38(2): 173-181.
Jiang X H, Li G H, Wang S H, et al. Effect of drought stress at different growth stages on grain yield of indica hybrid rice[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015, 38(2): 173-181. DOI: 10.7685/j.issn.1000-2030.2015.02.001 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] |
张飞, 房伟民, 陈发棣, 等. 菊花观赏性状的配合力分析[J].
园艺学报, 2010, 37(4): 589-596.
Zhang F, Fang W M, Chen F D, et al. Combining ability analysis on ornamental characters of chrysanthemum[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2010, 37(4): 589-596. (in Chinese with English abstract) |