文章信息
- 周艳涛, 李硕, 孟昭军, 王嘉冰, 刘英胜, 张爱军, 严善春
- Zhou Yantao, Li Shuo, Meng Zhaojun, Wang Jiabing, Liu Yingsheng, Zhang Aijun, Yan Shanchun
- 光肩星天牛诱捕器颜色的改进及其引诱剂最佳缓释量的确定
- Improvement of Trap Color for Anoplophora glabripennis and Determination of the Optimus Sustained-Release Amount of Attractants
- 林业科学, 2017, 53(6): 168-174.
- Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2017, 53(6): 168-174.
- DOI: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20170620
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2016-05-23
- 修回日期:2016-12-20
-
作者相关文章
2. 国家林业局森林病虫害防治总站 沈阳 110034;
3. 衡水市林业局森林病虫害 防治检疫站 衡水 053000;
4. 美国农业部农业研究服务中心外来入侵昆虫生物防控及行为实验室 贝茨维尔 MD 20705
2. General Station of Forest Pest Management of State Forestry Administration Shenyang 110034;
3. Control and Quarantine Station of Hengshui Forestry Bureau, Hebei Province Hengshui 053000;
4. USDA-ARS, Invasive Insect Biocontrol and Behavior Laboratory, BARC-West Beltsville MD 20705
光肩星天牛(Anoplophora glabripennis),又名亚洲天牛(Asian longhorned beetle,ALB), 隶属于鞘翅目(Coleoptera)天牛科(Cerambycidae),是阔叶林重要的蛀干害虫(王伦等,2015)。该虫广泛分布在我国各个省区市,危害杨属(Populus)、榆属(Ulmus)、桑属(Morus)、槭属(Acer)和柳属(Salix)、桦木属(Betula)等多种落叶性阔叶树种。该虫频繁暴发,已经造成严重的经济和生态损失(范丽清等,2013;金幼菊等,2000;李继泉等,2003;Morewood et al., 2003)。由于该虫生活隐蔽,借助一般的防治方法很难到达预期防治效果(罗亚萍,2013;魏可等,2015),需要有效的监测手段监测其发生动态,以便做到及时发现及时防控。
在昆虫视觉线索中,颜色在昆虫寻求配偶、寄主和食物源等方面起着重要作用(Brunton et al., 1995;Jiggins et al., 2011;Harris et al., 1983;Kelber et al., 2003;Zaccardi et al., 2006)。一些鞘翅目昆虫对不同的颜色刺激能作出比较明显的行为反应(Hausmann et al., 2004;Doring et al., 2007;Campbell et al., 2006)。Strom等(2001)通过研究不同颜色诱捕器对松大小蠹(Dendroctonus frontalis)的引诱作用发现,与白色或黄色漏斗形诱捕器相比,黑色、蓝色、暗褐色、紫色、绿色和红色诱捕器能引诱更多松大小蠹成虫。失明的马铃薯甲虫(Leptinotarsa decemlineata)很难对其寄主进行定位(Jermy, 2011)。2013年,笔者在室内通过Y型嗅觉仪进行选择试验发现,与红色、绿色、黑色和黄色相比,光肩星天牛雌雄成虫对暗褐色表现出更强烈的行为反应(另文发表)。
许多学者研究发现,寄主植物挥发物在光肩星天牛对寄主选择和定位中具有重要作用(金幼菊等,2000;李继泉等,2003;李建光,2001;阎雄飞等,2008)。Zhang等(2002)发现雄性光肩星天牛产生的信息素由2种物质组成,即4-(正庚氧基)丁烷基-1-醇、4-(正庚氧基)-1-丁醛,当两者按体积比1:1的比例存在时,对光肩星天牛两性成虫都具有一定的吸引作用。Nehme等(2009)通过Y管嗅觉生测试验发现:相对于雄虫,雄性信息素对雌虫的引诱作用更大;而植物挥发物对雄虫的引诱作用较雌虫更强;且芳樟醇+雄性信息素、顺-3-己烯醇+雄性信息素诱到的雄成虫数量明显比单独雄性信息素诱到的多;通过田间诱捕试验发现,1-戊醇和2-戊醇对光肩星天牛成虫具有较强的引诱作用,但其最佳释放率尚未见报道。理想的诱芯释放量应该是,在天牛的活跃期,有效活性物质的释放速率应相对稳定并且保持长时间有效(王新花等,2015)。
本研究在林间检验颜色改进型暗褐色拦截诱捕器是否比黑色的对光肩星天牛具有更好的诱捕效果;另外,将缓释的1-戊醇和2-戊醇单独或与信息素组合后,结合颜色改进型诱捕器进行田间诱捕试验,探究对光肩星天牛的引诱效果,以期开发监测光肩星天牛的有效工具。
1 材料与方法 1.1 样地概况2014年6月中下旬,光肩星天牛田间诱捕试验在河北省衡水市北部开发区(115°19′30″-115°32′41″E, 37°20′32″-37°19′46″N)农田防护林内进行,主要树种为13年生旱柳(Salix matsudana),胸径25~35 cm。防护林的一侧为道路,另一侧为玉米(Zea mays)、大豆(Glycine max)、小麦(Triticum aestivum)等农作物。根据防护林面积的大小,将其分为3个样地,每个样地之间相距8~10 m,每个样地内至少包含40棵旱柳。
1.2 试验方法1) 颜色改进型诱捕器 根据室内生测结果得知光肩星天牛雌雄成虫更加偏好暗褐色,将美国俄勒冈州波特兰APTIV公司的黑色飞行拦截挡板式诱捕器改进为暗褐色。诱捕器颜色改进方法依据严善春等(2015a)实用新型专利进行改进。
2) 植物源引诱剂的缓释 根据室内Y型嗅觉仪生测结果,选择对光肩星天牛具有较好引诱效果的2种植物源挥发物1-戊醇(≥99%,Sigma-Aidrich)和2-戊醇(98%,Sigma-Aidrich)作为引诱剂的有效成分,并对其进行缓释处理。1-戊醇或2-戊醇的缓释率均各设为160,135,115和70 mg·d-1,其有效作用时间分别可以维持4,6,7和11天。缓释方法依据严善春等(2015b)发明专利。
3) 光肩星天牛雄性信息素及其配制 光肩星天牛雄性信息素由一种醇类物质[4-(正庚氧基)丁烷基-1-醇]和一种醛类物质[4-(正庚氧基)-1-丁醛]组成,由张爱军研究员(美国农业部农业研究中心)合成并提供。当信息素2组分体积比为1:1时,对光肩星天牛成虫具有较强的引诱作用(Zhang et al., 2002)。
诱芯制备的方法:信息素的载体橡胶垫(rubber septum),容积为50~80 μL,表面涂有抗氧化剂1076;溶剂为正己烷,纯度为97%,以上均由Sigma-Aldrich提供。取100 μg且2组分体积比为1:1的雄性信息素,将其置于载体橡胶垫中,然后加入几滴正己烷,将信息素浸入橡胶垫中。观察10 min,待正己烷挥发后,轻轻敲击橡胶垫,然后将橡胶垫装入聚氟乙烯塑料袋中,低温保存,备用。
4) 田间诱捕试验 2014年6月18日,在每个样地内悬挂32个诱捕器,即4种引诱剂(2种单独或分别与信息素混合)×4种释放率×2种颜色诱捕器(暗褐色和黑色),每个诱捕器之间相距6~8 m(根据样地大小而定),用尼龙绳将诱捕器悬挂在柳树枝干上,距离地面2.5~4.5 m,3个样地共悬挂96个诱捕器(图 1)。每天检查1遍诱捕器,统计、鉴定诱捕到的光肩星天牛的雌、雄数量。在各种缓释率引诱剂达到各自维持作用时间后,更换诱芯,每次更换诱芯时,将图 1中“位置1”处的8个诱捕器悬挂到“位置2”处,“位置2”处的悬挂到“位置3”处,依次类推,“位置4”处的诱捕器悬挂到“位置1”处,以起到随机挂放的效果(Nehme et al., 2009)。
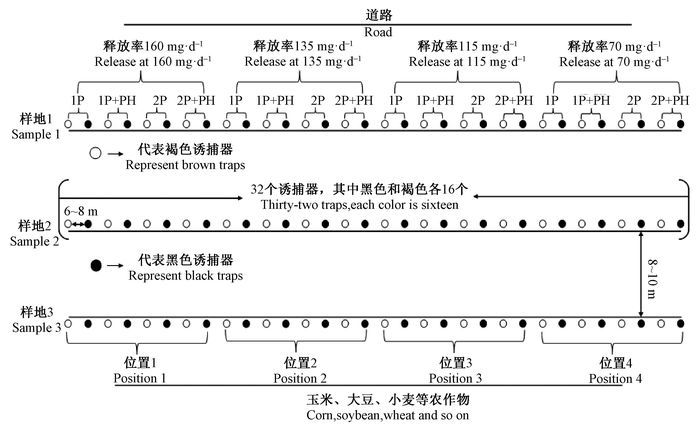
|
图 1 田间诱捕试验设计示意 Fig.1 Schematic of test design in field trapping 1P:1-戊醇1-pentanol; 2P:2-戊醇2-pentanol; PH:雄性信息素Male pheromone. |
采用Kolmogorov-Smimov法检验试验原始数据的正态性,结果显示各试验中大多数原始数据均服从正态分布,故采用原始数据进行各项统计分析。采用广义线性模型(generalized linear model)中的正交分析法分析4种引诱剂之间平均诱捕效果的差异性。采用2个独立样本t检验方法比较2种颜色诱捕器诱捕效果的差异性;比较同种引诱剂对雌雄天牛诱捕效果的差异性。所有统计分析均通过SPSS17.0软件完成。
2 结果与分析 2.1 诱捕器颜色对雌、雄天牛引诱量及雌性引诱比的影响诱捕器颜色的差异显著影响对光肩星天牛的引诱效果(图 2)。在大约8周的田间诱捕期内,与不同释放率1-戊醇或2-戊醇结合后,褐色诱捕器对天牛的诱捕总量为73头,平均诱捕量为1.521头;黑色诱捕器的诱捕总量为51头,平均诱捕量为1.063头,褐色的诱捕量显著高于黑色(t=4.854,P=0.047)。褐色诱捕器对雌性天牛的平均引诱量显著高于黑色诱捕器(t=3.647,P=0.033);2种颜色诱捕器对雄性天牛的平均诱捕量相当,差异不显著(t=2.741,P=0.236)。褐色诱捕器对雌性天牛的诱捕量为42头,显著高于雄性的诱捕量(31头),差异显著(t=2.136,P=0.039),雌性引诱比为0.58±0.23。黑色诱捕器对雌雄天牛的诱捕量相当,雌性23头,雄性28头,差异不显著(t=3.502,P=0.062),雌性的引诱比仅为0.45±0.19。

|
图 2 不同颜色诱捕器的光肩星天牛平均诱捕量 Fig.2 Mean numbers of ALB caught by different color traps 误差线表示标准误差的大小。不同字母表示在P<0.05水平下,2种颜色诱捕器对同一性别天牛的引诱效果差异显著;*表示同一颜色诱捕器对雌雄天牛引诱效果之间差异显著。 Error bars represent SEM. Letters over bars represent significantly different means at the 95% confidence level across trap colors for each sex, asterisk represents significantly different means between males and females captured by the same color trap. |
黑色诱捕器与135 mg·d-1和160 mg·d-1的1-戊醇组合对雌性和雄性天牛引诱量相等,且显著高70 mg·d-1对雌性和雄性的诱捕量(GLM:χ2=3.76,df=1,P=0.037;χ2=2.55,df=1,P=0.041,图 3A);添加信息素后,增强了160 mg·d-1和135 mg·d-1 1-戊醇对雌性天牛的引诱量,且对雄性的引诱量均显著高于115和70 mg·d-1 1-戊醇的引诱量(GLM:χ2=5.09,df=1,P=0.044,图 3B),但4种释放率1-戊醇或1-戊醇+信息素对雌、雄天牛引诱效果之间差异不显著。黑色诱捕器与135 mg·d-1的1-戊醇组合诱捕的雌性比为0.40;添加信息素后,诱捕的雌性比为0.50。褐色诱捕器与释放量为135 mg·d-1的1-戊醇组合共诱捕到4头雌性天牛,显著高于115和70 mg·d-1的1-戊醇对雌性诱捕量(GLM:χ2=5.82,df=1,P=0.044;χ2=5.51,df=1,P=0.039,图 3C);褐色诱捕器与135 mg·d-1 1-戊醇的组合诱捕到的雄性天牛数量也为4头,显著高于释放量为70 mg·d-1的1-戊醇诱捕量(GLM:χ2=5.41,df=1,P=0.024,图 3C)。褐色诱捕器与135 mg·d-1 1-戊醇的组合诱捕到的雌性天牛数量显著高于雄性天牛的诱捕量,差异显著(t=4.133,P=0.039,图 3C);添加信息素后,增强了褐色诱捕器与1-戊醇组合对雌性天牛的引诱效果,与雄性天牛引诱效果相比,差异显著(t=5.267,P=0.034,图 3D),且与70 mg·d-1对雌性天牛引诱效果相比,差异也显著(GLM:χ2=6.22,df=1,P=0.041)。褐色诱捕器与135 mg·d-1的1-戊醇组合诱捕的雌性比为0.50;添加信息素后,诱捕的雌性比为0.55。

|
图 3 不同颜色诱捕器与1-戊醇或1-戊醇+信息素组合对雌雄天牛的平均诱捕量 Fig.3 Mean numbers of male and female ALB caught by combination of different color traps and 1-pentanol or 1-pentanol + male pheromone 误差线表示标准误差大小。不同字母表示在P<0.05水平下,不同释放率引诱剂与诱捕器组合对天牛引诱效果差异显著,大写字母代表雌性天牛,小写字母代表雄性天牛;*表示释放率相同时,引诱剂对雌雄天牛引诱效果差异显著,P<0.05;下同。 Error bars represent SEM. Different letters over bars represent significantly different means at the 95% confidence level across combination of vision traps and different release 1-pentanol for each sex, capital letters for females and lowercase letters for males. An asterisk over the bar represents significantly different means at the 95% confidence level between females and males. The same below. |
黑色诱捕器与135 mg·d-1的2-戊醇组合对雄性天牛的诱捕量显著高于115, 70 mg·d-1的雄性诱捕量(GLM:χ2=4.68,df=1,P=0.048,χ2=3.52,df=1,P=0.034),且与雌性诱捕量相比,差异也显著(t=3.662,P=0.041);添加信息素后,增强了160 mg·d-1和135 mg·d-1的2-戊醇对雌性的诱捕量,尤其增强了160 mg·d-1雌性诱捕量,且与雄性诱捕量相比,差异显著(t=4.122,P=0.046)。135 mg·d-1的2-戊醇对雌性引诱比仅为0.25,添加信息素后,引诱雌性比为0.50(图 4A、B)。与褐色诱捕器组合后,135 mg·d-1的2-戊醇对雌性天牛诱捕量最多(5头),显著高于释放量为70 mg·d-1的诱捕量(GLM:χ2=4.68,df=1,P=0.034),且与雄性诱捕量相比,差异也显著(t=3.822,P=0.044),引诱雌性比为0.63;添加信息素后,显著增强了135 mg·d-1的2-戊醇对雌性天牛的诱捕量,雌性引诱比达到0.67(图 4C、D)。
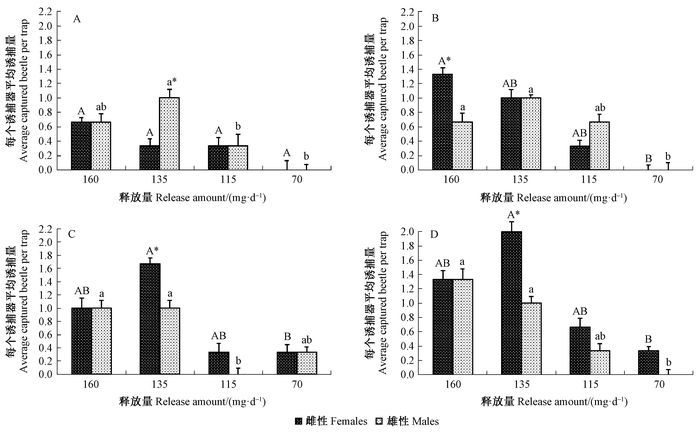
|
图 4 不同颜色诱捕器与2-戊醇或2-戊醇+信息素组合对雌雄天牛的平均诱捕量 Fig.4 Mean numbers of male and female ALB caught by combination of different color traps and 2-pentanol or 2-pentanol + male pheromone |
昆虫在寻找寄主进行取食和产卵时,视觉刺激(visual stimuli)起着一定的调节作用。Lefuleselen等(2011)在研究沟芫菁(Hycleus apicicornis)对不同颜色寄主定位选择中发现,与寄主形状相比,颜色在视觉刺激中起着更重要的作用。伍苏然等(2010)通过田间诱捕试验研究发现,褐色诱捕器对松墨天牛(Monochamus alternatus)的引诱量明显高于其他颜色诱捕器,并且对雌性天牛的引诱量最高。本研究结果表明,诱捕器颜色能显著影响对光肩星天牛的诱捕效果,褐色诱捕器与引诱剂组合能显著增强对雌性天牛的引诱效果,诱捕到的天牛雌性比为0.58,而黑色诱捕器诱捕到的天牛雌性比仅为0.45。据张宏世等(2002)报道,自然界中光肩星天牛的平均雌性比为0.49。进一步证明了该研究结果。
褐色诱捕器与135 mg·d-1的1-戊醇或2-戊醇组合对光肩星天牛的诱捕效果最佳,均为8头,诱捕到的天牛雌性比分别为0.50和0.63。释放量为135 mg·d-1的1-戊醇+雄性信息素或2-戊醇+雄性信息素与褐色诱捕器组合对天牛的诱捕量最高,均为9头,雌性比分别提高为0.55和0.67。说明控制1-戊醇或2-戊醇的释放量及添加信息素后,不同程度地增强了褐色诱捕器对光肩星天牛的诱捕效果,尤其对雌性天牛的诱捕效果。控制诱芯的释放量还可以延长其有效诱捕时间,节约害虫治理成本。如果将1-戊醇与2-戊醇混合后,使释放量控制为135 mg·d-1,单独或与雄性信息素组合作为引诱剂,能否再度增强对光肩星天牛的引诱效果,有待进一步研究验证。
4 结论添加信息素且释放率为135 mg·d-1的1-戊醇和2-戊醇引诱剂对雌雄天牛的引诱效果最好;暗褐色诱捕器也能显著增强对雌雄天牛的诱捕量。因此,可将暗褐色诱捕器与添加雄性信息素的释放量为135 mg·d-1的1-戊醇或2-戊醇组合,作为监测光肩星天牛发生动态的有效工具。
| [] |
范丽清, 严善春, 孙宗华, 等. 2013. 光肩星天牛对植物源挥发物的触角电位和行为反应. 生态学杂志, 32: 42–148.
( Fan L Q, Yan S C, Sun Z H, et al. 2013. EAG and behavioral responses of Asian longhorn beetle Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) to plant volatiles. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32: 42–148. [in Chinese] ) |
| [] |
金幼菊, 李继泉, 李建光, 等. 2000. 光肩星天牛对干旱胁迫下复叶槭挥发物的嗅觉反应. 林业科学, 40(1): 99–105.
( Jin Y J, Li J Q, Li J G, et al. 2000. Olfactory response of Anoplophora glabripennis to volatile compounds from Ash-leaf Maple (Acer negundo) under drought stress. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 40(1): 99–105. [in Chinese] ) |
| [] |
李继泉, 樊慧, 金幼菊. 2003. 光肩星天牛对损伤后复叶槭植株的行为反应. 北京林业大学学报, 25(5): 42–46.
( Li J Q, Fan H, Jin Y J. 2003. Behavior response of Anoplophora glabripennis to the mechanical-wounded and herbivore-fed ashleaf maples. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 25(5): 42–46. [in Chinese] ) |
| [] |
李建光. 2001. 光肩星天牛对寄主植物挥发性物质的行为反应及作用机理的研究. 北京: 北京林业大学博士学位论文. ( Li J G. 2001. Research of the response of Anoplophora glabripennis to plant host volatiles and mechanism of action. Beijing: PhD thesis of Beijing Forestry University. [in Chinese]) |
| [] |
罗亚萍. 2013. 光肩星天牛的寄主选择行为和植物源引诱剂研究. 杭州: 浙江农业大学硕士学位论文. ( Luo Y P. 2013.The host choice behavior of Anoplophora glabripenn and the research of lure from host. Hanzhou: MS thesis of Zhejiang Agricultural University. [in Chinese]) |
| [] |
王伦, 李创. 2015. 印楝提取物对光肩星天牛成虫体内保护酶的影响. 煤炭与化工, 38(2): 66–68.
( Wang L, Li C. 2015. Effects of the neem extracts on protective enzyme of Anoplophra glabripennis. Coal and Chemical Industry, 38(2): 66–68. [in Chinese] ) |
| [] |
王新花, 庞献伟, 李冬梅, 等. 2015. 一种缓释型双条杉天牛引诱剂缓释效果的研究. 中国生物防治学报, 31(3): 416–422.
( Wang X H, Pang X W, Li D M, et al. 2015. Effect of slow-releasing attractants on the Semanotus bifsaciatus. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 31(3): 416–422. [in Chinese] ) |
| [] |
魏可, 张翌楠, 杨忠岐, 等. 2015. 花绒寄甲在甘肃地区越冬情况和耐寒能力调查. 林业科学研究, 28(4): 588–592.
( Wei K, Zhang Y N, Yang Z Q, et al. 2015. Overwintering and cold tolerance of a parasitic natural enemy, Dastarcus helophoroides (Coleoptera: Bothrideridae), in Gansu Province. Forest Reaearch, 28(4): 588–592. [in Chinese] ) |
| [] |
伍苏然, 王凯, 袁素蓉, 等. 2010. 诱捕器形状及颜色对松墨天牛诱捕效果的影响. 中国森林病虫, 29(1): 5–7.
( Wu S R, Wang K, Yuan S R, et al. 2010. Influence of traps of different shapes and colors on the trapping effect on Monochamus altematus Hope. Forest Pest and Disease, 29(1): 5–7. [in Chinese] ) |
| [] |
严善春, 周艳涛, 孟昭军, 等. 2015a. 光肩星天牛视觉效果改进型拦截挡板式诱捕器. 黑龙江: CN104542528A, 2015-04-29. ( Yan S C, Zhou Y T, Meng Z J, et al. 2015a. improved vision effect of interceptpanel trap for Anoplophra glabripennis. Heilongjiang Province: CN104542528A, 2015-04-29.) |
| [] |
严善春, 周艳涛, 孟昭军, 等. 2015b. 光肩星天牛缓释诱芯的研制方法. 黑龙江: CN104542524A, 2015-04-29. ( Yan S C, Zhou Y T, Meng Z J, et al. 2015b. Method of production for slow-releasing attractants on Anoplophra glabripennis. Heilongjiang Province: CN104542528A, 2015-04-29.) |
| [] |
阎雄飞, 李晓娟, 骆有庆, 等. 2008. 光肩星天牛成虫对原寄主枝条挥发物趋向的测定. 北京林业大学学报, 30(3): 80–84.
( Yan X F, Li X J, Lio Y Q, et al. 2008. Taxis response of Anoplophora glabripennis adults to volatiles emanating from their larval host twigs. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 30(3): 80–84. [in Chinese] ) |
| [] |
张宏世, 李平平. 2002. 光肩星天牛成虫雌雄性比及其对种群消长的影响研究. 内蒙古林业科技(S1): 25–26.
( Zhang H S, Li P P. 2002. Research of female-male ratio and its influence on growth and decline of Anoplophora glabripennis population. Inner Mongolia Forestry Science Technology(S1): 25–26. [in Chinese] ) |
| [] | Brunton C F A, Majerus M E N. 1995. Ultraviolet colours in butterflies: intra-or inter-specific communication?. Biological Sciences, 260(1358): 199–204. |
| [] | Campbell S A, Borden J. 2006. Integration of visual and olfactory cues of hosts and non-hosts by three bark beetles (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Ecological Entomology, 31(5): 437–449. DOI:10.1111/een.2006.31.issue-5 |
| [] | Doring T F, Skorupski P. 2007. Host and non-host leaves in the color space of the Colorado potato beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Entomologia Generalis, 29: 81–95. DOI:10.1127/entom.gen/29/2007/81 |
| [] | Harris M O, Miller J R. 1983. Color stimuli and oviposition behavior of the onion fly, Delia antique (Meigen) (Diptera:Anthomyiidae). Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 76(4): 766–771. DOI:10.1093/aesa/76.4.766 |
| [] | Hausmann C, Samietz J, Dorn S. 2004. Visual orientation of over wintered Anthonomus pomorum (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environmental Entomology, 33(5): 1410–1415. DOI:10.1603/0046-225X-33.5.1410 |
| [] | Jermy T. 2011. Untersuchungen über Auffinden und Wahl Der Nahrung beim Kartoffelkäfer, Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say). Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 1(3): 197–208. |
| [] | Jiggins C D, Naisbit R E, Coe R L, et al. 2011. Reproductive isolation caused by color pattern mimicry. Nature, 411(6835): 302–305. |
| [] | Kelber A, Vorobyev M, Osorio D. 2003. Animal color vision-behavioral tests and physiological concepts. Biological Reviews, 78(1): 81–118. DOI:10.1017/S1464793102005985 |
| [] | Lefuleselen L, Zeyaurr K, Ahmed H, et al. 2011. Responses of the blister beetle Hycleus apicicornis to visual stimuli. Physiological Entomology, 36(3): 220–229. DOI:10.1111/pen.2011.36.issue-3 |
| [] | Morewood W D, Neiner P R, Mcneil J R. 2003. Oviposition preference and larval performance of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in four Eastern North American hardwood tree species. Environmental Entomology, 32(5): 1028–1034. DOI:10.1603/0046-225X-32.5.1028 |
| [] | Nehme M E, Keena M A, Zhang A, et al. 2009. Attraction of Anoplophora glabripennis to male-produced pheromone and plant volatiles. Environmental Entomology, 38(6): 1745–1755. DOI:10.1603/022.038.0628 |
| [] | Strom B L, Goyer R A. 2001. Effect of silhouette color on trap catches of Dendroctonus frontalis (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 94(6): 948–953. DOI:10.1603/0013-8746(2001)094[0948:EOSCOT]2.0.CO;2 |
| [] | Zaccardi G, Kelber A, Sison M, et al. 2006. Color discrimination in the red range with only one long-wavelength sensitive opsin. Journal of Experimental Biology, 209(10): 1944–1955. DOI:10.1242/jeb.02207 |
| [] | Zhang A J, Oliver E, Aldrich J R, et al. 2002. Stimulatory beetle volatiles for the Asian longhorned beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis (Motschulsky). Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung C, 57(5/6): 553–558. |
 2017, Vol. 53
2017, Vol. 53

