文章信息
- 苟大平, 王曦茁, 汪来发, 田国忠, 朱天辉, 郭民伟
- Gou Daping, Wang Xizhuo, Wang Laifa, Tian Guozhong, Zhu Tianhui, Guo Minwei
- 一种适于PCR和LAMP检测的松木中松材线虫DNA快速提取方法
- A Method for Rapidly Extracting DNA of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus from the Infested Pine Wood for PCR and LAMP Detection
- 林业科学, 2015, 23(6): 100-110
- Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2015, 23(6): 100-110.
- DOI: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20150612
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2014-01-17
- 修回日期:2014-06-08
-
作者相关文章
2. 中国林业科学研究院森林生态环境与保护研究所 国家林业局森林保护学重点实验室 北京 100091
2. Key Laboratory of Forest Protection of State Forestry Administration Research Institute of Forest Ecology, Environment and Protection, CAF Beijing 100091
松材线虫病(Bursaphelenchus xylophilus)发病迅速,传播范围广,是一种毁灭性的森林病害,被多个国家列为重要森林植物检疫对象。松材线虫的检测和鉴定是松材线虫检疫的重要手段。近年来,基于PCR的分子生物学技术(王明旭,2004; 陈凤毛等,2012; 夏彦飞等,2009)的实时荧光定量PCR(葛建军等,2005; 王明旭等,2005; 陈凤毛等,2007; François et al., 2007; 郭立新等,2011; Ye et al., 2013)、环介导等温扩增技术(LAMP)(Kikuchi et al., 2009)等被越来越广泛地运用于松材线虫的检测和鉴定。获得一定数量和质量的线虫基因组是进行准确高效分子检测的前提条件。传统的方法是经贝尔曼漏斗法从感染松材线虫的木片中分离出线虫,再通过SDS法、CTAB法或蛋白酶K法提取线虫DNA(张奇等,2008; 王姝颖,2009; Francois et al., 2007),然而,这些方法较为耗时,不适于野外检测。因此,建立一种直接从病木中高效提取线虫DNA的方法极为必要。Takeuchi等(2005; 2009)、王新荣等(2009)、胡月清(2006)和Kanetani等(2011)分别运用CTAB法、SDS酚仿抽提法和蛋白酶K法直接从感病木块或松褐天牛体内提取松材线虫DNA。这些方法虽然省去了收集线虫的步骤,但仍存在一些问题:CTAB法和SDS法需要经过反复的酚仿抽提,步骤繁琐,并且DNA在转移过程中有损失并伴有大片段破碎; 而蛋白酶K法虽然避免了这一问题,却同样需要1 h以上的温育反应,比较耗时,或者需要借助昂贵的试剂盒。
Chelex-100是一种可与多价金属离子结合的螯合型离子交换树脂,其悬液在碱性环境(pH=8.0~11)和100 ℃的条件下,可导致细胞膜破裂和DNA变性并释放出来(步嵘等,1999)。Chelex-100还能够结合影响下一步分析的其他外源物质,并能通过结合金属离子而防止DNA降解(陈辉等,2004),被广泛运用于血痕(周月琴等,2003; 巴华杰等,2007; 杨电等,2008)、细菌(钱雪琴等,2008; 胡晓红等,2008)、真菌(陈吉良等,2011; 兰茗清等,2012)和放线菌(周双清等,2010)等微生物和微小动物(Musapa et al., 2013)DNA的提取。用Chelex-100法提取线虫基因组DNA,尤其直接从木块中提取松材线虫DNA尚未见报道。本文以Chelex-100 法提取或直接从病木中提取松材线虫DNA,作为rDNA-ITS序列 PCR 扩增和LAMP扩增的模板,以期得到特异性强、明亮清晰的PCR 检测条带或肉眼可直接观察的试验结果,旨在探索建立一种高效、快速的提取松材线虫DNA的方法。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验材料 1.1.1 生物材料采集18个地点松材线虫感病植株木样(表 1)。选取当年死亡的松树,在伐倒树干的基部、中部和树冠基部3个部位截取5cm左右厚度的圆盘放入采样袋中,带回实验室。样品经贝尔曼漏斗于室温(25 ℃)条件下分离24 h,进行显微镜下的形态鉴定和ITS区、18S基因测序鉴定。人工挑取纯化后接种到盘多毛孢(Pestalotiopsis microspora)马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基上,4 ℃冰箱保藏。选取木样树皮以内心材以外3~5 cm的圆环10 g,用斧头劈成1~2 mm厚度的木片,作为试验的木块。取6 g木块置于室温下采用贝尔曼漏斗法分离,24 h后,线虫悬液用线虫计数皿进行计数,每个样品重复3次,取平均值。剩余4 g木块用于DNA提取。
|
|
5%(W/V)Chelex-100; 异硫氰酸胍碱性缓冲液:3 mmol·L-1 CH5N3·HSCN,50 mmol·L-1 Tris-HCl(pH 8.0),20 mmol·L-1 EDTA(pH 8.0),1% Triton X-100; CTAB提取缓冲液:2.0%(W/V)CTAB,1.4 mmol·L-1 NaCl,100 mmol·L-1 Tris-HCl(pH 8.0),20 mmol·L-1 EDTA(pH 8.0),1%(V/V)β-巯基乙醇; ISOHAIR DNA提取试剂盒,购自日本Nippon gene。
1.2 Chelex-100法的初步建立吸取5 μL的松材线虫悬浮液(约含线虫50头,分离于安徽合肥病死马尾松),放入1.5 mL 离心管中,加入异硫氰酸胍提取缓冲液(3 mmol·L-1 CH5N3·HSCN,50 mmol·L-1 Tris-HCl(pH 8.0),20 mmol·L-1 EDTA(pH 8.0),1% Triton X-100)40 μL,枪头搅拌混匀,冰上放置10 min,沸水煮10 min,然后加入5%(W/V)Chelex-100 40 μL,枪头搅拌混匀,沸水煮10 min,吸取上清液用于PCR检测,重复3次。
1.3 Chelex-100法的优化 1.3.1 Chelex-100浓度对DNA提取的影响在1.2节的基础上,在其他条件不变的情况下,用终浓度分别为1.0%,1.5%,2.0%和2.5%(W/V)的Chelex-100提取线虫DNA。DNA提取液分别进行10,100和1 000倍的梯度稀释,稀释液进行PCR检测以确定最适的Chelex-100浓度。
1.3.2 冻融时间对DNA提取的影响采用1.3.1节中筛选出的Chelex-100最适浓度,设置不同的冻融时间,即3,4,5和6 min(冰煮时间相同),提取线虫DNA。DNA提取液分别进行10,100和1 000倍的梯度稀释,稀释液进行PCR检测以确定最佳冻融时间。
1.3.3 煮沸时间对DNA提取的影响采用之前确定的Chelex-100最适浓度、最佳冻融时间,设置不同的煮沸时间,即4,6,8和10 min,提取线虫DNA。DNA提取液分别进行10,100和1 000倍的梯度稀释,稀释液进行PCR检测以确定最佳煮沸时间。
1.4 Chelex-100法与CTAB法和蛋白酶K法的比较 1.4.1 提取方法1)CTAB法参照 Yuko Takeuchi等(2005; 2009)的方法。称取含有松材线虫的木块50 mg,置于2 mL离心管中,加入600 μL预热的CTAB提取缓冲液[2.0%(W/V)CTAB,1.4 mol·L-1 NaCl,100 mmol·L-1 Tris-HCl(pH 8.0),20 mmol·L-1 EDTA(pH 8.0),1%(V/V)β-巯基乙醇]漩涡混匀,60 ℃温育30 min,加入等体积的酚氯仿异戊醇(25:24:1)抽提,然后4 ℃下14 400 r·min-1离心15 min,吸取上清,再加入3/4体积的异丙醇,缓慢颠倒混匀,室温静置20 min,4 ℃下14 400 r·min-1离心15 min,倒掉上清,再用70%的乙醇洗涤2次,待彻底干燥后用1/10倍的TE溶解DNA,每个样品重复3次。
2)蛋白酶K法 参照日本ISOHAIR DNA提取试剂盒(购自Nippon gene)说明书以及Kanetani等(2011)的方法:首先在2 mL离心管中加入1 mL的DNA提取缓冲液 [100 mmol·L-1 NaCl、10 mmol·L-1 Tris-HCl(pH8.0)、1 mmol·L-1 EDTA]; 再添加40 μL含有蛋白酶K的Lysis buffer和50 μL Enzyme solution(ISOHAIR Nippon gene),充分搅拌混匀; 在离心管溶液中加入收集的50 mg含有松材线虫的木片,55 ℃孵育20 min,然后94 ℃孵育10 min,吸取上清液用于PCR检测,每个样品重复3次。
3)Chelex-100法 称取50 mg含有线虫的木块,放入2 mL离心管中,加入异硫氰酸胍提取缓冲液[3 mol·L-1 CH5N3·HSCN,50 mmol·L-1 Tris-HCl(pH 8.0),20 mmol·L-1 EDTA(pH 8.0),1% Triton X-100] 400 μL,枪头搅拌混匀,冰上放置5 min,沸水煮5 min,然后加入5%(W/V)Chelex-100 200 μL,枪头搅拌混匀,沸水煮8 min,吸取上清液用于PCR检测,每个样品重复3次。
1.4.2 DNA含量测定和统计分析应用核酸测定仪(紫外分光光度仪)在260和280 nm下测定DNA样本的OD260、OD280吸光度值,计算所提取样本的纯度和含量。DNA纯度以OD260/OD280值为依据; DNA含量(ng·μL-1)=OD260×50×稀释倍数。使用SPSS软件(SPSS19.0)对数据进行统计分析。数据采用平均值±标准差表示,组间差异采用方差分析检验,并采用t检验进行两两比较,P<0.05为差异显著。
1.5 PCR与LAMP验证 1.5.1 验证方法1)PCR扩增 提取的样品DNA通过普通PCR扩增进行验证。引物选用胡月清等(2006)、王姝颖(2009)设计的松材线虫特异引物,上游引物P155(5'-CTACGTGCTGTTGTTGA GTTGGC-3'),下游引物 P538(5'-TGGTGCCT AACATTGCGCGA-3')(由北京赛百盛公司合成)。25 μL的PCR反应体系为: 12.5 μL的PCR MIX(购自天根),上下游引物各1 μL,1 μL的DNA模板以及9.5 μL的ddH2O。PCR反应程序为: 94 ℃预变性3 min; 94 ℃变性1 min,53 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸45 s,35个循环; 72 ℃再延伸10 min。取4 μL PCR扩增产物在1%的琼脂糖凝胶中140 V电泳30 min,紫外灯下观察并拍照。
2)LAMP扩增 采用Chelex-100法(步骤见1.4.1节)提取病木块中的松材线虫DNA,DNA提取液稀释10倍后,取2 μL直接用于LAMP反应。引物选用Kikuchi等(2009)设计的ITS区LAMP引物组,LAMP反应方法参照荣研loopamp DNA扩增试剂盒。建立一个25 μL的反应体系,包含2.5 μL10×扩增缓冲液,2 μL dNTP(2.5 mmol·L-1),1 μL Taq酶(5U ·μL-1),2 μL Genome DNA,引物F3和B3各5 pmol,引物FIP和BIP各40 pmol,引物LoopF 20 pmol,DNA链置换酶1 μL和1 μL的荧光检测试剂(Eiken Chemical)。反应混合液63 ℃水浴60 min,最后80 ℃下温育5 min。LAMP扩增产物的检测通过反应溶液颜色变化(是否发出荧光)肉眼观察判断。
1.5.2 灵敏性、特异性和稳定性验证1)灵敏性验证 采用Chelex-100法、CTAB法和蛋白酶K法提取的DNA样品通过梯度稀释DNA提取液后,再进行PCR来分析DNA提取质量和灵敏性。称取50 mg不含松材线虫的马尾松木块,放入挑有10条松材线虫的2 mL离心管中,涡旋搅拌混匀,采用3种提取方法提取线虫DNA。提取的DNA经核酸测定仪测定后稀释到相同浓度,然后进行2n倍梯度稀释,分别稀释了2,4,8,16,32和64倍的DNA提取液作为PCR扩增模板进行PCR检测。
2)特异性验证 采用Chelex-100法提取松材线虫和拟松材线虫的感病木块(表 1)、健康马尾松(采自安徽合肥)、健康黑松(采自北京)、健康油松(采自中国林业科学研究院)木块和盘多毛孢(源自中国林业科学研究院森林生态环境与保护研究所)的DNA,DNA提取液分别进行PCR扩增验证和LAMP扩增,重复3次。
3)稳定性验证 分别称取50 mg健康马尾松、黑松和油松木块,放入挑有10条松材线虫的2 mL离心管中,涡旋搅拌混匀,采用Chelex-100法提取松材线DNA,DNA提取液分别通过PCR检测验证和LAMP扩增,重复10次。不含松材线虫的健康马尾松、黑松和油松木块DNA提取液作为阴性对照。
2 结果与分析 2.1 Chelex-100法的建立采用Chelex-100法(1.2节)提取松材线虫悬液中线虫DNA,吸取0.5 μL DNA提取液作为模板进行PCR扩增,扩增产物进行1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳。采用CTAB法(同1.4.1节)提取20 μL(约2 000头)松材线虫DNA进行PCR扩增,扩增结果作阳性对照。电泳结果显示,用Chelex-100提取的线虫DNA经PCR扩增后得到单一、特异的目的条带,并且电泳谱带清晰、均一,扩增效果稳定,而Chelex-100提取的拟松材线虫(GY1)、黑松、油松、马尾松和盘多毛孢的DNA,特异引物PCR扩增没有条带(图 1),由此表明:新方法Chelex-100法可用于松材线虫DNA的提取。
 |
图 1 Chelex-100法提取松材线虫DNA特异引物扩增结果 Fig. 1 The results of the specific PCR amplification of B. xylophilus DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method M: DNA marker Ⅲ; 1: 阴性对照 Negative control(ddH2O); 2: CTAB法提取的松材线虫(HF)DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of B. xylophilus(HF) DNA extracted by CTAB method; 3-5: Chelex-100法提取的松材线虫(HF)DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果(3个重复) The specific PCR amplification of B. xylophilus (HF) DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method(n=3); 6: Chelex-100法提取拟松材线虫(GY1)DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of B. mucronatus(GY1) DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method; 7: Chelex-100法提取盘多毛孢DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of P. microspora DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method; 8-10: Chelex-100法提取健康黑松、马尾松、油松DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of healthy pine(P.thunbergii, P. massoniana and P. tabulaeformis) DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method. |
如图 2所示,随着Chelex-100浓度的增加,DNA提取的质量随之提高,并且当Chelex-100的浓度为 1.5%,2.0%和2.5%(W/V)时,DNA提取液稀释10,100和1 000倍后均可扩增出条带,并且由图可见,当Chelex-100的浓度达到1.5%时即可很好的提取出线虫DNA,提取出的DNA溶液稀释10倍和100倍后条带明亮清晰,在稀释 1 000倍的情况下也能扩增出较为清晰的条带,虽亮度不及浓度为2.5%(W/V)时的,但已能满足PCR扩增需求,此外,从试剂耗费经济的角度考虑,选择Chelex-100的最适浓度为1.5%(W/V)。
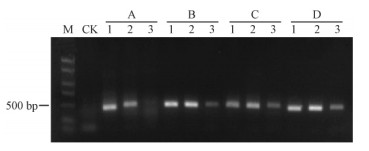 |
图 2 不同Chelex-100浓度下DNA提取液梯度稀释PCR检测结果 Fig. 2 The results of PCR amplification of DNA extraction dilution under the different Chelex-100 concentration M:BM2000+1.5K; CK:阴性对照 Negative control(ddH2O); A,B,C,D:Chelex-100浓度依次为 1%,1.5%,2.0%和2.5% The concentration of Chelex-100 was 1.0%, 1.5%, 2.0% and 2.5%,respectively; 1,2,3:线虫DNA提取液依次稀释10,100和1 000倍后特异引物PCR扩增结果 The results of the specific PCR amplification of serial 10-fold dilutions(10,100, and 1 000 times) of the nematode DNA. |
冻融时间依次为3,4,5和6 min,随着时间的增加,DNA提取含量相应的提高,扩增谱带清晰度增加。当时间达到 5 min时,采用Chelex-100法提取的线虫DNA经过10,100和1 000倍梯度稀释后均能扩增出单一的条带,并且稀释1 000倍的扩增条带亮度仅次于冻融6 min提取液的扩增条带(图 3),说明冻融时间为5 min时即可提取出高质量的线虫DNA作为普通PCR扩增的模板。因此,最佳冻融时间为5 min。
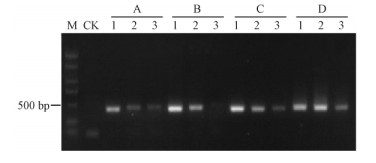 |
图 3 不同冻融时间的DNA提取液梯度稀释PCR检测结果 Fig. 3 The results of PCR amplification of DNA extraction dilution in different freezing time M:BM2000+1.5K; CK:阴性对照 Negative control(ddH2O); A,B,C,D:冻融时间依次为3,4,5和 6 min The freezing time respectively was 3, 4, 5 and 6 min; 1,2,3:线虫DNA提取液依次稀释 10,100和1 000倍后特异引物PCR扩增结果 The results of the specific PCR amplification of serial 10-fold dilutions(10,100, and 1000 times) of the nematode DNA. |
加入Chelex-100后,随着煮沸时间的增加,DNA提取质量相应提高,当煮沸时间达到8 min中时,DNA提取液梯度稀释(10,100和1 000倍)后即可扩增出均一条带,而当煮沸时间达到10 min时,虽然DNA提取液梯度稀释(10,100和1 000倍)后也能扩增出特异条带,但条带亮度却反而不如冻融8min的(图 4)。因此,对于5 μL的线虫悬液,线虫DNA的提取最经济便捷的提取方法为: 5 μL的线虫悬浮液(约含线虫50头)中,加入异硫氰酸胍提取缓冲液40 μL,枪头搅拌混匀,冰上放置5 min,沸水煮 5 min,然后加入5%(W/V)Chelex-100 20μL(即Chelex-100终浓度为 1.5%),枪头搅拌混匀,沸水煮沸8 min,吸取上清液用于PCR检测。
 |
图 4 不同煮沸时间的DNA提取液梯度稀释PCR检测结果 Fig. 4 The results of PCR amplification of DNA extraction dilution in different boiling time M:BM2000+1.5K; CK:阴性对照 Negative control(ddH2O); A,B,C,D:煮沸时间依次为4, 6,8和10 min The boiling time respectively was 4, 6, 8 and 10 min; 1,2,3:线虫DNA提取液依次稀释 10,100和1 000倍后特异引物PCR扩增结果 The results of the specific PCR amplification of serial 10-fold dilutions(10,100, and 1 000 times) of the nematode DNA。 |
来源18个不同地区的木样(表 1),木块里线虫含量不同(木块含线虫量为每10 mg 1~8头),因此提取到的DNA含量有很大的差异,但是统计分析比较后(表 2)发现,对于同一样品,新方法Chelex-100法提取的DNA产量显著高于传统的CTAB法和蛋白酶K法(P<0.05),并且Chelex-100法提取的DNA产量与CTAB法提取的DNA产量差异极显著(P<0.01)。而3种方法的OD260/OD280比值从大到小依次为CTAB法>蛋白酶K法≥Chelex-100法,Chelex-100法的OD260/OD280显著低于CTAB法的,而略低于或等同于蛋白酶K法,但这并不影响对提取的DNA进行PCR扩增。
|
|
以3种方法所提取的木块中线虫DNA为模板,采用松材线虫ITS区特异引物对P155/P538进行PCR扩增,其扩增产物进行1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,在紫外光下均可见到清晰的DNA条带(图 5,6)。
 |
图 5 3种方法提取的DNA梯度稀释后特异引物PCR扩增结果 Fig. 5 The results of specific PCR amplification of DNA extraction serial 2-fold dilution under three extraction methods M: DNA marker Ⅲ; CK:阴性对照 Negative control(ddH2O); A:Chelex-100法提取松材线虫DNA 75倍稀释液依次稀释2,4,8,16,32和64倍后特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of the serial 2-fold dilutions (2, 4, 8, 16, 32 and 64) of the 75 times dilution nematode DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method; B:蛋白酶K法提取松材线虫DNA 25倍稀释液依次稀释2,4,8,16,32和64倍后特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of the serial 2-fold dilutions (2, 4, 8, 16, 32 and 64) of the 25 times dilution nematode DNA extracted by Protein K method; C:CTAB法提取松材线虫DNA依次稀释2,4,8,16,32和64倍后特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of the serial 2-fold dilutions (2, 4, 8, 16, 32 and 64) of the nematode DNA extracted by CTAB method. |
 |
图 6 松材线虫DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 Fig. 6 The results of the specific PCR amplification of B. xylophilus DNA M: DNA marker Ⅲ; CK:阴性对照 Negative control(ddH2O); 1-9:Chelex-100法提取AQ,YX,HF,LG,AL,ZS,CP,FY和YY木片中松材线虫DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of B. xylophilus DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method directly from the infested wood sample(AQ, YX, HF, LG, AL, ZS, CP, FY and YY); 10:Chelex-100法提取GY2木片中拟松材线虫DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of B. mucronatus DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method directly from the infested wood sample(GY2); 11-13:Chelex-100法提取健康黑松、马尾松、油松木块DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of healthy pine(P.thunbergii, P. massoniana and P. tabulaeformis) DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method; 14:Chelex-100法提取盘多毛孢DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of Pestalotiopsis microspora DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method. |
在50 mg健康马尾松木样中人工挑取混入10头松材线虫,分别用Chelex-100法、蛋白酶K法和CTAB法提取线虫DNA,经核酸测定仪测定DNA含量分别为:1 516.96,514.59,20.4 ng·μL-1。分别将Chelex-100法和蛋白酶K法提取的DNA原液稀释75倍和25倍,所得稀释液与CTAB法提取液分别经2~64倍梯度稀释后进行PCR检测,均有430 bp的特异性条带出现(图 5)。
由图 5可见,Chelex-100法提取的松材线虫DNA 的75倍稀释液再稀释32倍后依然有清晰的条带,64倍时模糊,而蛋白酶K法提取的松材线虫DNA 的25倍稀释液再稀释32倍时就明显变暗,而CTAB法提取的松材线虫DNA在稀释到64倍时仍有较为明亮的条带。由此表明,Chelex-100法从木块中提取的DNA质量次于CTAB法,但略优于蛋白酶K法。此外,这也说明新方法具有极好的灵敏性,提取的DNA在稀释了接近5 000倍(75×64)时检测结果依旧呈阳性,这远远优于传统的CTAB法。
2.4.2 特异性验证采用Chelex-100法提取松材线虫和拟松材线虫的感病木块,健康马尾松、黑松、油松木块和盘多毛孢DNA, 对DNA提取液进行PCR检测验证。结果表明松材线虫感病木块均能扩增出400 bp左右单一的目的条带,而拟松材线虫感病木块、健康马尾松、黑松、油松木块和盘多毛孢DNA提取液均未扩增出条带(图 6),由此表明Chelex-100法提取的木块中松材线虫DNA用于PCR扩增时具有良好的特异性。
采用Chelex-100法提取的感病木块中的松材线虫DNA提取液稀释10倍后,用于LAMP反应。含有松材线虫的病木的LAMP结果呈阳性(图 7A1-9,B 5-8),而含有拟松材线虫的木块(图 7B 1-2)、不含有松材线虫的健康黑松木块(图 7B 3 )和盘多毛孢(图 7B4 )DNA提取液稀释10倍后进行LAMP反应,结果均呈阴性。新方法Chelex-100法提取的感病木中松材线虫DNA能够满足LAMP检测,且具有良好的特异性。
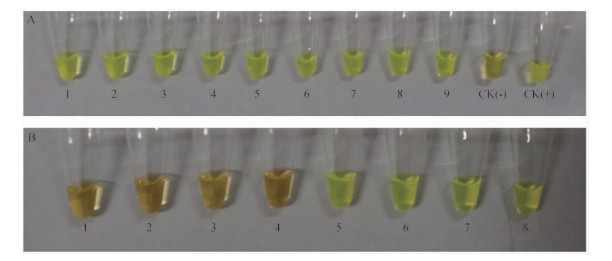 |
图 7 Chelex-100法提取的木块中线虫DNA10倍稀释液ITS区LAMP扩增结果 Fig. 7 The results of loop-mediated isothermal amplification of the 10 time dilution of the nematode DNA extracted directly from infested wood sample by Chelex-100 method A:1-9 依次为Chelex-100法提取AQ,YX,HF,LG,AL,ZS,CP,FY和YY木片中松材线虫DNA 10倍稀释液ITS区LAMP扩增结果;CK(-)(CK阴性):DNA模板为ddH2O; CK(+)(CK阳性):DNA模板为连有ITS靶序列的质粒。 The loop-mediated isothermal amplification of the 10 times dilution of the B. xylophilus DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method directly from infested wood sample(AQ, YX, HF, LG, AL, ZS, CP, FY and YY);CK(-)(Negative control): The DNA sample is ddH2O;CK(+)(Positive control): The DNA sample is plasmid DNA containing the target sequence. B:1-2依次为Chelex-100法提取GY1和GY2木片中拟松材线虫DNA 10倍稀释液ITS区LAMP扩增结果 The loop-mediated isothermal amplification of the 10 times dilution of the B. mucronatus DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method directly from infected wood sample(GY1 and GY2); 3-4:依次为 Chelex-100法提取健康黑松、盘多毛孢DNA 10倍稀释液ITS区LAMP扩增结果 The loop-mediated isothermal amplification of the 10 times dilution of the healthy P.thunbergii and Pestalotiopsis microspora DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method; 5-8:依次为Chelex-100法提取TM,WZ,YC和LD木片中松材线虫DNA 10倍稀释液ITS区LAMP扩增结果 The loop-mediated isothermal amplification of the 10 times dilution of the B. xylophilus DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method directly from infested wood samples (TM, WZ, YC and LD). |
分别称取50 mg健康马尾松、黑松和油松木块,放入挑有10条松材线虫的2 mL离心管中,涡旋搅拌混匀,采用Chelex-100法提取松材线虫DNA,DNA提取液分别用于PCR检测验证和LAMP扩增。结果显示,Chelex-100法提取线虫木块混合物中线虫DNA,经PCR和LAMP扩增均为阳性,而不含松材线虫的健康马尾松、黑松和油松木块DNA提取液经PCR和LAMP扩增均显示为阴性(图 8,9)。此外,采用Chelex-100法提取新鲜木样(表 1)中松材线虫DNA进行特异引物PCR扩增,检出率为100%(表 3)。因此,Chelex-100法提取木块中线虫DNA具有良好的稳定性。
|
|
 |
图 8 Chelex-100法提取木块中松材线虫DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 Fig. 8 The results of the specific PCR amplification of B. xylophilus DNA extracted from wood sample by Chelex-100 method M: DNA marker Ⅲ; CK(-):阴性对照 Negative control(ddH2O); CK(+):Chelex-100法提取线虫悬液(HF)中线虫DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of B. xylophilus(HF) DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method; 1-5:Chelex-100法提取健康木屑中混入的松材线虫DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of B. xylophilus DNA extracted from wood tissues by Chelex-100 method; 6:Chelex-100法提取健康木屑DNA特异引物PCR扩增结果 The specific PCR amplification of the healthy pine wood DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method; A,B,C:黑松 P.thunbergii,马尾松 P. massoniana,油松 P. tabulaeformis. |
Chelex-100是一种由交联聚苯乙烯凝胶和亚胺基乙酰乙酸等组成的螯合型离子交换树脂,其成对的亚氨基二乙酸盐离子可作为螯合集团,与多价金属离子结合,阻止金属离子在高温和低离子强度条件下作为催化剂使DNA降解。Chelex-100颗粒可通过离心去除或静置沉淀,使与Chelex-100结合的物质与DNA分离,能防止结合到Chelex-100中的抑制剂或杂质带到PCR反应中而影响下游试验的DNA分析。异硫氰酸胍是一种强蛋白变性剂,能破坏蛋白质二级结构,降解核膜蛋白,并促使核蛋白与核酸分离,此外,它还能抑制核酸酶的活性,减少提取过程中核酸的降解(罗心静,2003),被广泛运用于RNA的提取分离(付月君,2003; 李想等,2004)和哺乳动物细胞中核酸的分离(Pert et al., 2000)。
本文采用异硫氰酸胍(pH 8.0)碱性蛋白质变性缓冲液结合Chelex-100,通过冻煮法建立了一个全新的从木块中快速提取松材线虫DNA的方法。首先,通过异硫氰酸胍的强变性作用,结合冻煮快速的冷热变化,使得线虫细胞破裂,释放出DNA。其次,通过加入Chelex-100后再次煮沸,进一步使DNA与蛋白质分离释放,同时,纯化提取到DNA。最后,由Chelex-100特性决定,杂质随Chelex-100沉淀去除,从而得到较好质量的DNA模板,完成DNA的提取。
新建立的Chelex-100 DNA提取法与传统的CTAB法和蛋白酶K法比较,具有以下优点:1)提取产量高、质量好。新方法通过胍盐的化学破壁结合冻煮机械破壁充分释放了细胞中的DNA,再经2次蛋白变性纯化,使得相同条件下提取的DNA含量能够达到1 516.96 ng·μL-1,远远大于常规的CTAB法和蛋白酶K法提取的20.40,514.59 ng·μL-1;同时DNA质量与CTAB法无显著差异,相同含量下,稀释32倍后仍能扩增出清晰均一的条带(图 5)。2)步骤简单,耗时少。Chelex-100法将线虫DNA的提取和纯化同时进行,免去了反复的酚仿抽提,整个提取仅需3个步骤即可完成,大大减少了提取步骤和提取耗时。 3)仪器设备简单,成本低。整个DNA提取过程只需要水浴锅、移液器等最基本的试验设备,平均一个样品的DNA提取耗费(Chelex-100、异硫氰酸胍及其余试剂1.5元+离心管、枪头耗材及水电费2.0元)约为3.5元。4)稳定性强,特异性高。多个地区的样品多次重复试验检验证明,新方法提取的DNA用于PCR检测和LAMP检测,检测结果的灵敏性高(图 5),特异性强(图 6,7)且结果稳定(图 8,9; 表 3)。
 |
图 9 Chelex-100法提取木块中松材线虫DNA ITS区LAMP扩增结果 Fig. 9 The results of loop-mediated isothermal amplification of B. xylophilus DNA extracted from wood sample by Chelex-100 method 1-5:Chelex-100法提取健康木块中混入的松材线虫DNA ITS区LAMP扩增结果 The loop-mediated isothermal amplification of the B. xylophilus DNA extracted from wood sample by Chelex-100 method; 6:Chelex-100法提取健康木块DNA ITS区LAMP扩增结果 The loop-mediated isothermal amplification of the healthy pine wood DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method; CK(+):含有ITS靶序列的质粒LAMP扩增结果 The loop-mediated isothermal amplification of plasmids containing the target sequence ITS; CK(-):阴性对照 Negative control(ddH2O); A,B,C:黑松 P.thunbergii,马尾松 P. massoniana,油松 P. tabulaeformis. |
DNA提取是许多分子检测技术的第一步,许多试验失败的原因可追溯到该步骤,该阶段提取的DNA产量不足、DNA质量差、干扰物质多或DNA部分降解等可直接影响检测的结果(Yaxsier et al., 2011)。因此,本文探索建立了一种简便高效的提取松材线虫悬液和木块中线虫DNA的方法即Chelex-100法,运用该方法提取的线虫DNA用于PCR和LAMP等检测时灵敏度高,特异性强,结果稳定可靠,充分满足普通PCR和LAMP等分子检测需求。此外,本方法所需实验设备简单,试剂药品的保藏使用对温度也无特殊要求,无需操作人员具有特别的专业知识,极适合于现场检测以及基层检测推广。
| [1] |
巴华杰, 刘冰泉, 马骏, 等. 2007. Chelex-100法提取滤纸血痕DNA影响因素的比较. 法医学杂志, 23(5): 347-348. (Ba H J, Liu B Q, Ma J, et al. 2007. Comparative research of the influence factors of DNA extraction of bloodstain on the filter paper with Chelex-100 method. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 23(5): 347-348[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [2] |
步嵘, 王耀平, 叶元康. 1999. 以Chelex 100为介质抽提DNA. 中华病理学杂志, 28(5): 379-380. (Bu R, Wang Y P, Ye Y K. 1999. Extraction of DNA by Chelex-100 method. Chinese Journal of Pathology, 28(5): 379-380[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [3] |
陈凤毛, 叶建仁, 吴小芹. 2007. 松材线虫实时PCR检测技术. 南京林业大学学报:自然科学版, 31(4): 121-124. (Chen F M, Ye J R, Wu X Q. 2007. Detection technique of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus using real time PCR. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University:Natural Sciences Edition, 31(4): 121-124[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [4] |
陈凤毛, 叶建仁, 吴小芹, 等. 2012. 松材线虫SCAR标记与检测技术. 林业科学, 48(3): 88-94. (Chen F M, Ye J R, Wu X Q, et al. 2012. SCAR Marker and Detection Technique of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 48(3): 88-94[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [5] |
陈辉, 刘永波, 谢庆瑞, 等. 2004. 有机酚法和Chelex 100法提取不同组织微量DNA效果比较. 郑州大学学报:医学版, 39(6): 988- 991. (Chen H, Liu Y B, Xie Q R, et al. 2004. Comparison the effect of phenol/ chloro form method and Chelex-100 method on micro DNA extraction using different tissues. Journal of Zhengzhou University:Medical Sciences, 39(6): 988- 991[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [6] |
陈吉良, 黄小龙, 吴安迪, 等. 2011. 一种快速高效提取病原真菌DNA作为PCR模板的方法. 菌物学报, 30(1): 147-149. (Chen J L, Hang X L, Wu A D, et al. 2011. An efficient extraction method of pathogenic fungus DNA for PCR. Mycosystema, 30(1): 147-149[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [7] |
付月君, 张志云, 柴宝峰. 2003. 从棉铃虫体中提取总RNA的一种有效方法. 生物技术通报, (5): 40-42. (Fu Y J, Zhang Z Y, Chai B F. 2003. An efficient method of total RNA isolation from Helicoverpa armigera. Biotechnology Bulletin, (5): 40-42[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [8] |
葛建军, 曹爱新, 刘先宝, 等. 2005. 应用TaqMan-MGB探针进行松材线虫的实时荧光定量检测技术研究. 植物病理学报, 35(6): 52-58. (Ge J J, Cao A X, Liu X B, et al. 2005. Quantity assay of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus with TaqMan-MGB probe. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 35(6): 52-58[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [9] |
郭立新, 段维军, 顾建锋. 2011. 木质包装中松材线虫的实时荧光PCR检测. 植物保护, 37(5): 129-134. (Guo L X, Duan W J, Gu J F. 2011. Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus from woods packaging using real-time PCR. Plant Protection, 37(5): 129-134[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [10] |
胡月清. 2006. 枯萎松树线虫种类鉴定及松材线虫检测技术. 广州:华南农业大学硕士学位论文. (Hu Y Q. 2006. Investigation and identification of nematodes in dead or dying Pinus massoniana and the detection technique of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Guangzhou:MS thesis of South China Agricultural University[in Chinese]).(  2) 2)
|
| [11] |
胡晓红, 彭惠民, 刘昕, 等. 2008. PCR及Real-time PCR评价细菌DNA提取方法. 重庆医科大学学报, 33(2): 155-159. (Hu X H, Peng H M, Liu X, et al.2008. Methods of DNA extraction from bacteria for PCR and Real-time PCR. Journal of Chongqing Medical University, 33(2): 155-159[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [12] |
兰茗清, 刘林, 杨静, 等. 2012. 直接、快速地从罹病小麦叶片中提取条锈菌基因组DNA的方法. 云南农业大学学报, 27(6): 798-801,813. (Lan M Q, Liu L, Yang J, et al. 2012. Direct DNA extraction method of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici from infected wheat leaves. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 27(6): 798-801,813[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [13] |
李想, 杨奇志, 张飞雄. 2004. 一种小量提取植物总RNA的有效方法. 生物技术通报, (2): 49-51. (Li X, Yang Q Z, Zhang F X. 2004. An effective method for plant total RNA isolation. Biotechnology Bulletin, (2): 49-51[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [14] |
罗心静. 2003. 全血基因组DNA的快速提取及其应用. 长沙:中南大学硕士学位论文. (Luo X J. 2003. Research on application of rapid extraction human genomic DNA from whole blood. Changsha:MS thesis of Central South University[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [15] |
钱雪琴, 张军, 沈芳. 2008. Chelex-100法和碱性裂解法提取细菌DNA的比较. 中国卫生检验杂志, 18(8): 1565-1566. (Qian X Q, Zhang J, Shen F. 2008. Comparison of methods for extraction of DNA by Chelex-100 and alkali split. Chinses Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 18(8): 1565-1566[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [16] |
王明旭. 2004. 松材线虫分子生物学检测技术研究进展. 湖南林业科技, 31(2): 1-3. (Wang M X. 2004. Study progress of identification techniques of molecular biology on pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Hunan Forestry Science & Technology, 31(2): 1-3[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [17] |
王明旭, 朱水芳, 罗宽. 2005. 松材线虫rDNA-ITS2的TaqMan探针实时荧光PCR检测. 林业科学, 41(2): 82-85. (Wang M X, Zu S F, Luo K. 2005. Studies on real-time fluorescent PCR with TaqMan probe for rDNA-ITS2 of Pine Wood Nematode(Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 41(2): 82-85[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [18] |
王永, 张莉, 兰青阔, 等. 2008. Chelex-100快速提取用于转基因检测DNA模板的研究. 生物技术通报, (2): 143-146. (Wang Y, Zhang L, Lan Q K, et al. 2008. Study on rapid method for extracting DNA from transgenic crops by Chelex-100. Biotechnology Bulletin, (2): 143-146[in Chinese]). |
| [19] |
王姝颖. 2009. 几种松树寄生线虫的致病性及其ITS序列分析. 南京:南京林业大学硕士学位论文. (Wang S Y. 2009. Study on Pathogenicity of several pine parasitic nematodes and their ITS sequence analysis. Nanjing:MS thesis of Nanjing Forestry University[in Chinese]).(  2) 2)
|
| [20] |
王新荣,朱孝伟,胡月清, 等. 2009. 松墨天牛携带的松材线虫PCR检测技术. 林业科学, 45(7): 70-75. (Wang X R, Zhu X W, Hu Y Q, et al. 2009. A PCR-based method for detecting Bursaphelenchus xylophilus from Monochamus alternatus. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 45(7): 70-75.[in Chinese])(  1) 1)
|
| [21] |
夏彦飞, 李红梅, 王暄, 等. 2009. 病木样本松材线虫DNA检测方法研究. 江苏农业科学, (1): 35-38. (Xia Y F, Li H M, Wang X, et al. 2009. PCR method for detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in disease pine wood samples. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, (1): 35-38[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [22] |
杨电, 刘超, 李越, 等. 2008. Chelex-100提取生物检材DNA实时PCR定量研究. 中国法医学杂志, 23(1): 29-31. (Yang D, Liu C, Li Y, et al. 2008. Real time PCR quantificational study of DNA extracted by Chelex-100 method. Chinese Journal of Forensic Medicine, 23(1): 29-31[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [23] |
张奇,孙丹,张楚菁, 等. 2008. 松材线虫鉴定方法的研究与比较. 南开大学学报:自然科学版, 41(5): 43-49. (Zhang Q, Sun D, Zhang C J, et al. Comparative studies on identification methods of Bursaphelenchu xylophilus. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium University Nankaiensis:Natural Sciences Edition, 41(5): 43-49[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [24] |
周月琴, 朱伟, 刘志萍, 等. 2003. 用Chelex-100快速提取微量血痕中的DNA. 复旦学报:医学版, 30(4): 379-380. (Zhou Y Q, Zhu W, Liu Z P, et al. 2003. A quick method of extraction of DNA by Chelex-100 from trace bloodstains. Fudan University Journal of Medical Sciences, 30(4): 379-380[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [25] |
周双清, 黄小龙, 黄东益, 等. 2010. Chelex-100快速提取放线菌DNA作为PCR扩增模板. 生物技术通报, 2: 123. (Zhou S Q, Huang X L, Huang D Y, et al. 2010. A rapid method for extracting DNA from actinomycetes by Chelex-100. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2: 123[in Chinese]).(  1) 1)
|
| [26] |
Francois C, Castagnone C, Boonham N, et al. 2007. Satellite DNA as a target for TaqMan real-time PCR detection of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Molecular Plant Pathology, 8(6): 803-809.( 2) 2)
|
| [27] |
Kanetani S, Kikuchi T, Akiba M, et al. 2011. Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus from old discs of dead Pinus armandii var. amamiana trees using a new detection kit. Forest Pathology, 41(5): 387-391.( 2) 2)
|
| [28] |
Kikuchi T, Aikawa T, Oeda Y, et al. 2009. A rapid and precise diagnostic method for detecting the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Phytopatholog, 99(12): 1365-1369.( 2) 2)
|
| [29] |
Musapa M, Kumwenda T, Mkulama M, et al. 2013.A simple chelex protocol for DNA extraction from Anopheles spp. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 9(71):3791-3281.( 1) 1)
|
| [30] |
Pert B, Sekizawa A, Samura O, et al. 2000. Detection of male and female fetal in maternal plasma by multiplex fluorescent polymerase chain reaction amplification of short tandem repeat. Human Genetics, 106(1): 45-49.( 1) 1)
|
| [31] |
Takeuchi Y, Kanzaki N, Futai K. 2005. A nested PCR-based method for detecting the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, from pine wood. Nematology, 7(5): 775-782.( 2) 2)
|
| [32] |
Takeuchi Y, Futai K. 2009. Diagnosis and quantification of the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhner), in wood of Pinus thunbergii with real-time PCR. Nematological Research, 39(1): 9-16.( 2) 2)
|
| [33] | Walsh P S, Metzger D A, Higuchi R. 1991. Chelex 100 as a medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material. Biotechniques, 10(4): 506-513. |
| [34] |
Yaxsier D A, Virginia C, Ledy X L, et al. 2011. Comparison of three methods for DNA extraction from paraffin-embedded tissues. Biotecnología Aplicada, 28(1): 44-47.( 1) 1)
|
| [35] |
Ye W M, Giblin-Davis R M. 2013. Molecular characterization and development of real-time PCR assay for pine-wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Parasitaphelenchidae). Plos One, 8(11): e78804. 1-14.( 1) 1)
|
 2015, Vol. 23
2015, Vol. 23

