文章信息
- Yao Shunbo, Liu Cang, Wang Bowen
- 姚顺波, 刘仓, 王博文
- Research on System Innovation Framework of Non-Public Forestry
- 中国非公有制林业制度创新框架
- Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2006, 42(10): 101-108.
- 林业科学, 2006, 42(10): 101-108.
-
文章历史
Received date: 2005-07-13
-
作者相关文章
2. 西安财经学院市场营销系 西安 710071
2. Department of Marketing of Xi'an Economics and Trade Institute Xi'an 710071
After the establishment of the P.R.China, it experienced the historical development stage of "from being forbidden to being limited" to the stage of "being valuable and useful to supplement social benefits" and to the stage of "an important part" to the position of non-public economy.The issue of the ownership problems discussed by the relevant forestry departments started from 1980s as so-called "three defined", i.e.the period of deepening reform of collectively-owned forestry, but it was mainly concentrated on the parts of reforms of collectively-owned ones, as separating its ownership rights and operating rights.The relevant researches of parts of non-public forestry are late than its practices.After the period of reform and opening-up, the people are eager to improve their living standards.In most of rural regions in China, it is a key approach to obtain logs and food from the forest to live a life at a subsistent level.Therefore, it is an impartible part of live for them to participate in forestryrelated activities.It also becomes an important factor to meet the need for their basic living requirements.In the first part of 1980s, in order to motivate the participating desire of the people to afforest, the central government published the policy of "whoever plants owns", in many provinces and regions started to run limit-amounted private-owned forests; at the beginning part of 1990s, with the further development of reform and opening-up, many provinces and regions in southern part of China have appeared some joint-ventured and joint-operated forests, it has formed the embryo mode of Chinese non-public forestry(Jiang, 2002).
In the initial part of the new century, the State Forestry Administration P.R.China treated the policy of "fully developing non-public forestry by introducing the attitude of letting-go" as an important guideline to realize the development by strides in thenew century for Chinese non-public forestry.It put the non-public forestry from the back stage to the great front stage of forestry ecologic construction, and also gave it a proper social position, it is reasonable to say that the non-public forestry is facing its best chance to develop since the construction of the country and it also appears its vitality and energy.According to the summed statistics of 14 provinces and regions in China, the total forest lands of non-public forestry has already occupied 23.5 of all forest lan ds, and occupied 16.11 percent of total forestry, which is 9.76 percent of forestry reserve.Several provinces develop very rapidly, the assets of non-public forestry of these provinces with rapid-developed non-public forestry have occupied 65 percent of total forestry assets, and their relevant staff reached over 85 percent(Zhou et al., 2003).
It is stated out that in "Decision on Quickening the Pace of Forestry Development" issued by the Chinese Central Committee and the State Council on Jun.25, 2003 that "let develop non-public forestry be benefited from its biggest performing stage, the nation encourages all-kind social main bodies to develop forestry in trans-ownership, trans-industries and trans-regions ways.All the farmers, urban and rural residents, scientific and technologic employees, private-owned enterprisers, foreign investors, and the staff of the enterprises and public systems with abilities are honored the right to solely or jointly participate in the forestry development activities, and be engaged in forest construction.It should be clarified that the eligible identity of the non-public forestry and it is advocated to put the policy into effect that `whoever run the forest owns it and jointly run means mutually owned', and to unify policies of the taxation, resource utilization and investment and finance, and to create a fair competitive environment for various forestry operating main bodies."
Though there is a relative satisfactory start for the non-public forestry development, with the majority of forestry stepping into their logging periods, it appears many problems such as whether one is possible to enter into market based on one's real desire supervised by the system of logging quota, which makes the forestry business operators become deeply worried and various nonpublic main economic bodies with the desire to invest also begin to take wait-and-see attitudes.As these problems are associated with the system innovation of non-public forestry, it arouses the attention of the entire society.It is the purpose of this research to eliminate the systematic obstacles for non-public forestry development to practice the systematic innovation and to establish a non-public forestry that meets the requirements of market economy.
1 The content of non-public forestry 1.1 The definitionThere are some different understandings in the theoretic circle in regard to non-public forestry caused by their researching perspectives.The project group of the State Forestry Administration P.R.China Research Center (2003)has regarded that "the so-called non-public forestry is referred to the sum up of all non-public main bodies that participate in the forestry activities.It embodies the performance of all non-public economy in the forestry part, and it is a combination of non-public economy and forestry economy.It is a part together with the public forestry to form the total Chinese forestry".This definition emphasizes the quality of main body' s economic characteristics deciding the characteristics of the forestry operated.Mr.Ba Lianzhu and Li Shuxin (2003)have defined it through the perspective of non-public forestry as:the non-public forestry refers to all other-formed forestry but the state-owned and collectively-owned ones.It includes individual-owned, private-operated and foreign-owned ones etc..They treat non-public forestry as a concept of property right.Mr.Zhou Shaozhou and Mr.Miao Guangping (2003)regard non-public forestry as one in regard to public forestry.It includes the economic forms of individual-owned, private-operated and foreign-owned forestry and other mixed owned forestry forms other than state-owned and collective-owned.
The non-public forestry mentioned in this paper refers to the forestry economic forms established on the part which belong to state-owned and collective-owned forests and logs run by individuals, private-owned, and foreign-owned and also benefit from it and deal with the operated forests and logs independently according to the relevant laws.
1.2 The characteristics of non-public forestry 1.2.1 Relevant clearly arranged property right relationsBased on the fact that the ownership of forestry is belonged to the state or the collective-owned organization, the operators of non-public forestry enjoy the ownership right, profit earning right and profit allocation right during the contract chartered period according to the legal regulations, it clarifies the relations of relevant rights and responsibilities and profits and makes it clear who are the operating main bodies.
1.2.2 Flexible mechanismsThe property right of the non-public forestry is clear, and its mechanisms of decision-making, human resource developing, allocating and stipulating are very flexible, and has a high adjustment ability and be capable to operate independently and to assume sole responsibility for its profits and losses, and be self-development and self-reliance.
1.2.3 Profit-cared, powerful inside self-motivating forceUnder the condition of clarified property right arrangements, the operators and the operating targets form a profit-linked relation.The forest land productivity, the quality of logs and forest products will direct affect the income of the operators, the related income motivating mechanism will produce high self-motivating force in the forestry industry.
1.2.4 Closely related to the marketsThe paramount target for non-public forestry operators is pursuing economic profits, their attention focus is technologic development and product innovation, and its industrial structure and product structure will be adjusted to meet the changes of market adequately.
1.3 The functions of non-public forestryBeing a now-formed forestry ownership, the prosperous non-public forestry will play a significant role in Chinese forestry industry development, ecologic harmonization, and formers' income increasing and rural regions' development.It is reasonable to figure the function of non-public forestry as:
1.3.1 Benefit to realize the multi-formed Chinese forestry property rightThe non-public forestry has motivated the participating desire of the investors and attracted, much social fund to participate in the construction of non-public forestry and in the end it will form a multi-formed framework which is guided by national investment.Led by counties and villages investment, it will form a new period for running forestry by the society.
1.3.2 Benefit to adjust the forestry economic structure, forest and wood structure, ownership structure and to change the forestry operating mechanism and optimize the forest resource allocationFor many years, Chinese national forestry resource has met the obvious conflicts between forest protecting and deforesting, between forestry resource raising and relevant capital shortage, between the supply and demand contradiction of logs and its finished products, it has limited the development of national economic construction and brought many difficulties to the people' s lives.And developing non-public forestry is a practical approach to break the systematic restrictions and change the operating mechanism.
1.3.3 An important approach to deal with the problems related to "Sannong"(agriculture, rural areas and farmers)Currently, there are 592 poverty counties, and 496 of them are located in the mountain areas.To those areas, the potential and advantage to solve the poverty problem is to develop forestry.Therefore, it needs to actively develop the non-public forestry.
1.3.4 Relieving the conflicts between Chinese forestry and ecologic construction and lacking of investment fundThere are 126 million hm2 mountain land which are suitable to be afforested, and calculated by the average afforesting investment RMB 3 000 yuan·hm-2, the project of eliminating the desert mountain lands will need the capital of RMB 380 billion yuan.And Chinese rapid forest richening project will afforest 14 million hm2 in 15 years, and it will require investment of about RMB 40 billion yuan.According to the State Council' s Construction Program on National Ecologic Environment, it will spend about 50 years to control the deterioration of ecological environment, to richen the creature diversity, to stipulate the sustainable development of social economy, and it needs over of 340 million hm2 and to recover the land losses will need about RMB 1 100 billion yuan.The cost for afforesting of desert lands needs 18 000 hm-2 and the 260 million hm2 desert land needs RMB 2 400 billion yuan (including the investment of partial hydro engineering projects for channeling water).All the above items need to invest RMB 40 000 billion yuan.Calculated by year 2001 forestry central government investment as RMB 18 billion yuan (it has already improved fundamentally comparing to the previous several decades), it will take 222 years to realize this grand macro aim (Zhou, 2002).On one hand it is lacking investment to the forestry construction, and on the other hand there is over RMB 100 billion yuan deposit leaving unused in the banks.It is practical to attract the social capital by non-public forestry' s clarified relations of rights, liabilities and benefits and economic profit, and to activate the forest operating systems and to adjust the afforesting investment structures.
2 The principles of non-public forestry system innovation 2.1 The principle of protecting the private-owned propertyIt is necessary to pay special attention to the following issues to meet the requirements of non-public forestry system innovation:
1) Protecting the right of free fluctuation of private property.From the perspective of economics, the value of property reflects itself only through the way of fluctuation and the increment of value is also through this way.Restricting the fluctuation is equal to making the property right itself no place to develop.The backward developed Chinese forestry is mainly connected with the problems of lacking of markets of forestry lands and live log, and the difficulties to fluctuate of forestry lands and live logs.
2) Clarifying distinctly the direction of protecting private property right by the government.It is forbidden to deprive or restrict the rights of private-owned property except for some legally published exceptions.The current laws have clearly stipulated only to meet the public interests could the private-owned assets be requisitioned or requisitioned.
3) Clarifying clearly that it is necessary to compensate impartially and reasonably the private-owned property when it is requisitioned or imposed by the nation.In this way, it is possible to compensate reasonably the forestry owners being requisitioned.
4) Clarifying clearly that there is a legally judicial relief approach to aid when the public rights violate the private rights.
2.2 The principle of loosened controlIn the study of economics, government regulation refers to the general regulation and special behaviors stipulated and put into effect by the government that interfere the market allocation system or indirectly affect the policy making of enterprises and consumers.Though it brings positive effects to the development of Chinese forestry economy, it also leads obvious increased cost, low efficient resource allocation and low standard social welfare.Therefore it is necessary to face these facts and modify the function of government to reach an advanced degree, and concentrate on the macro adjustments and creating a favorable market environment, loosening the government regulations, and improving the regulating efficiency.The following parts are introduced to specify it:
1) Limiting the areas of government regulation and improving the government credit.The government should return the private power to its original place.
2) Adapting the mode of government power practicing, and maximally utilizing the marketilization mode to run the public right.The government may allocate the resources according to market demands through auction to reduce the activities of rentseeking; to decrease the negative effects of rent-seeking activities to social economy; to increase the economic efficiency and social welfare of entire society.
3) Increasing the transparency of the power utilizing process and strengthening the protecting power of property right.As Mr.Zaire mentioned:"to enjoy one' s land, capital and labor steadily is the most powerful motivation to direct the people to put their producing factors into production." Property right is the motivate source to initiate people' s pioneer workings.
2.3 Principle of efficiencyEfficiency mainly refers to the ratio between input and output.The construction of new system is aimed to reduce the high trade cost caused by the old systematic framework, and to stimulate social integration process.While in the process of non-public forestry innovation, the principle of efficiency requires us to introduce the following:
1) Strengthening the "generality" of the system.It includes three rules, as firstly, the system should be characterized as be generalized.The system should be impartial whatever conditions are and whoever individuals are if there are no certain circumstance differences.Secondly, the system should be characterized as being confirmed.It is necessary to be easily understood in order to be a high efficient one.Thirdly, the system should be characterized as be both steadily and a certain degreed openness.The frequently changed rules are hard to be understood and it is bound to be low efficient to guide relevant actions.
2) Paying attention to its coordinative relations with other related systems.As each system is " embedded" in the systematic structure, it is certain that it is connected with other arrangements, therefore the efficacy of each system' s performance is bound to be affected by the completeness of others that are designed to reach their relevant individual targets.
3) Meeting the technological quality requirements of the producing process.Any systematic arrangements are formed by the conditions of certain productivity and technologic level, with the further development of productive forces and technology, it is compulsory to adjust or change relevant systematic arrangements, if not it will lead to systematic arrangements' low efficiency.
3 The value preference of non-public forestry innovation 3.1 Be favorable to the accomplishment of the target of the forestry' s sustainable developmentThe forestry sustainable development is the base of social economic sustainable development.And it is also the general developing tendency of world forestry, and the key target for Chinese forestry leaped-style development.It also stands for the development direction of forestry and the demand of advanced productive forces.As the inborn characteristics of non-public forestry of profit-seeking, diversified and small-scaled; it will inevitably arouse conflicts with the needs of sustainable development sooner or later with the rapid enlargement of vegetative cover and farmers' living standard rising, therefore, it is practical to guide the non-public forestry to the road of sustainable development.
3.2 Be favorable to the forming of running forestry by the societyFor a long time in the past, our country located constantly the forestry as a significant material-producing department, which is a typical evidence of running forestry by department.It is tightly related to the grand background of the state order economy and with significant order economy characteristic.There is a compulsory demand to change from department running to the society running.The new-era society running forestry should undoubtedly form an idea of guiding forestry developing by market economy, and in a further step, it will maximally open to the society and stipulate favorable policies to attract the social resources to accumulate to the forestry.Special attentions should be paid on developing the non-public ones and it is necessary to treat it as a key part for developing future commodity forest and put new dynamism into it.
3.3 Be favorable to establish the micro economic base for an independently operated and energetic forestryPresently, there still lacks of a dynamic operating system for ecologic and log forest construction.If it is not changed, it is hard to strengthen the ecologic construction and meet the demand of implementing the six engineering projects, therefore, it is necessary to stick to treat the state-owned system as a base and to establish an economic system maintaining multi-economic parts' developing, and while enforcedly developing the non-public forestry, it is required to work hard to search a practical form to run state-owned system efficiently, and bravely adopt new forestry producing forms to meet the social mass production, and to develop new dynamism to construct the ecologic forestry.
4 The fundamental content of non-public forestry systematic innovation 4.1 The innovational aim of non-public forestry system 4.1.1 Constructing a non-public forestry commodity forest systematic system centered on the forestry subsidiaryThe general aim of main body of non-public forestry investing on forestry is to pursue profits.Currently, some forestry economics researchers regard the main reason of the supply of commodity forest higher than its demand as the exterior characteristic of forestry, which leads its private cost is higher than its social cost and social benefits higher than private benefits, therefore it is necessary to adjust it by Pigon tax.This paper argues the exterior characteristic of forestry is just its necessary condition and is not its sufficient condition.The real reason slowing the development of non-public forestry commodity forest is the existence of current non-public forestry systematic blunders, to perform systematic innovation and establish a forestry system centered by forestry subsidiary, paying attention to and protecting non-public forestry property right, eliminating log quota system, providing lo ng-term loans, deducting or exempting forestry tax, decreasing forestry rent.The above is the key to realize the sustainable development of non-public forestry commodity forest(Yao, 2004a).
4.1.2 Establishing public interest forest system centered by government procurementPublic interest forest is a kind of public product, it should be provided by the government.For a long period, China has practiced the approach of producing by itself.The nation has invested hugely in several recent great ecological engineering constructions, and achieved some results, however its general effects are not very favorable.With the improvement of people' s living standards, the current ecological public interest forestry construction will not meet the their demands any more.It is necessary to fully utilize the fundamentally resource allocating function of market to use the private capital to run the public interest forestry construction.It is also practical to transform the need of ecological public interest forestry to part of public financial budget, and in its scope, the government will purchase the produced public interest forestry and at the same time utilize the competitive mechanism to the public interest forestry constructions to perform the public invitation for bids and invite the potential non-public forestry main body participators to enter into this business area(Yao, 2004b).
4.1.3 Establish and complete the non-public forestry property right systemForestry property right system is the core of Forestry system.It is based on the conditions of transparently arranged forestry property right and being well protected that the non-public commodity forestry and public interest forestry are established.For a long time, though the government has done relevant large amount of work and it already has made the forestry property right system relatively clear, there are still some unsolved problems in the areas of forestry property right protection, property right fluctuations.It is not the target to establish a property right system just for itself but a fluctuate one.The aim of establishing property right system is to lower the transaction cost and stipulate the fluctuation of forestry property right to stimulate it development(Yao, 2002).
4.2 Fundamental content of non-public forestry innovation 4.2.1 The aim of non-public forestry system innovationIt is required to fully utilize the basic function of market resource allocation, to establish a system centered forestry subsidy and to develop coordinately with the forestry taxation system, log system, forestry land circulation system, credit system, insurance system, and to make the log and forest operators obtain the average social profit and to maintain the health sustainable development of commodity forestry.
It is required to establish the public welfare forest purchase system main bodied by the public finance by the government, and to adopt the methods as collecting public welfare forest, performing government requisition and purchasing, and project invitation etc.and to put the non-public economic factors into the public welfare forest production, and to form the competitive framework of the public welfare forest production and increase the expense efficacy of public finance.It is also required to establish a property right clarified, well protected and efficiently circulated forestry property right system.
4.2.2 The content of non-public forestry system innovationThe non-public forestry system is a complicated systematic project.Analyzed by the forestry economic process, it can be classified as systems of production, log, fluctuation, allocation etc..Analyzed by producing factors, it can be divided into systems of forest land, investment and finance, insurance, technology development and innovative etc..To make this research easier to be analyzed, the non-public forestry system innovation is classified into two kinds according to the theories of forestry operations and management in this research, i.e.the non-public commodity forestry one and non-public public welfare forestry one as in the following Fig. 1.
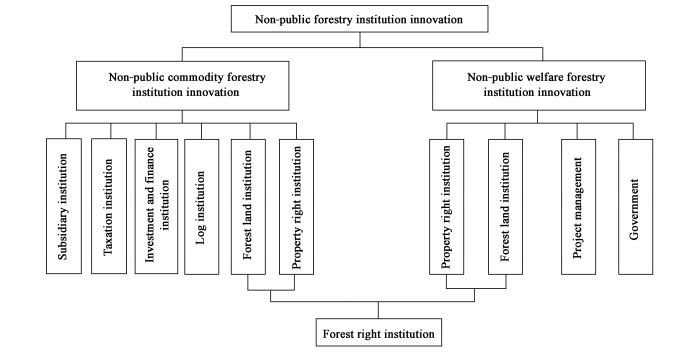
|
Fig.1 The system of non-public forestry system innovation |
1) The forest right system The forest right is the core of the forestry system; it is the power of the people dealing with forest assets.Analyzed longitudinally, it includes the forestry asset ownership and relevant derived rights as utilizing, profit collecting and allocating.While laterally, it includes the logging right of forest and logging, the collecting right related to resources above and underground forests and forests itself.It also includes the rights of landscape developing utilizing, being compensated, profit collecting, circulating, receiving loans, and warrant and breeding.It is required to establish a clarified property right system, and to clarify the forestry right main body and reflect its interest directly linked with the motivating power and dynamism of forestry development.Their guiding thinking should only be based on the Ding Xiaoping Theories and ' Three Representatives Theory' of President Jiang Zemin, and start its initial position as high raising the people' s living standards, freeing forestry productive forces and developing the mountainside and forest area economy, and based on classified operation to clarify the ownerships of forests, forest logs, and forest lands, and to further open and relax the operating rights, and to activate the operating right and make sure the profit collecting and allocating rights and fully motivate the participation of entire society, and to change the fact of forestry department running forestry to entire society running it.
2) Investment and financial system It is required to enhance government capital support to help the development of the Chinese non-public forestry adequately.It is an international recognized way to subsidize the private-owned forests.For instance, in European Union, the subsidized fund for private established forest is 70 percent of its total establishing expenses, in Japan the relevant figure is 50 percent, and in USA it has also reached 40 percent(Zhou et al., 2003).Firstly, it should be emphasized the loan support to the non-public commodity forests, and arrange some no interest loans to those who produce ecological benefits, it not only the problem of lacking staring capital, but also the loan returning pressure and stipulate the raising of high quality forests.Secondly, it is necessary to support the non-public forestry economic parts as processing industry, research, seed, intermediary services, otherwise it is impossible to link the market to the afforesting investors, and to make profits. Thirdly, the government is bound to support the ecological forest constructors.The government not only needs to subsidize them but also to enroll them into the coverage of government procurement, at the same time publish some favorable policies to protect related economic benefits as the forest travel income, the breeding logging and interval logging according to the requirements of relevant forest operating projects.
3) Forestry governing system with stimulated characteristic Being Stimulated Forestry Governing is to refer to the regulating behavior that regulates the malfunction of the market and improves economic efficiency and through the approaches of stimulating and guiding to direct the main bodies of non-public markets according to the government aims.It is a new-styled regulating approach compared with the sole governing by the government.Current forestry governing is the compulsory control to the economic activities of market main bodies; it is with the characteristics of being passive and choice, in contrast, the forestry governing system with stimulated characteristic will introduce the stimulating instruments into the government governing and though careful designed methods, the government stimulate the interests of forestry market main bodies and provide some guiding force by introducing some stimulating regulations to let the forestry market main bodies participate in relevant activities voluntarily.The governing mode of forestry governing system with stimulated characteristic is a new-styled governing mode based on behavior science theories and the restricting and stimulating mechanism theories of administrative laws.Guided by the public administrative reforming theories, this governing mode treats to loose the forestry governing as a breakthrough to produce and develop itself.As its basic structure is based on balanced structured dualism game theory, the general governing mode appears the main body regulated by administrative legal relations, they perform the governing function according to relevant legal regulations, and implement the regulating instruments, all above reflect the openness characteristic of suiting whole regulating processes, adequately competitiveness and efficient.It mainly treats stimulating and restricting system as a link, and forms a front and back coordinated collection of four concrete and independent administrative behavior modes, which embodies themselves as:treating loosely controlled forestry governance as their basic linkup part; treating administrative-guided governing orders as profit-leading orders; treating administrative contracts as the carrier for practicing instruments of governing orders and employ governing, treating administrative award to show relevant legal consequences(Yao, 2005).
4) The public interest forest requisition system Aimed to meet the demands of the national ecological construction, the public interest forest requisition system is a compulsory legal purchasing system.To establish non-public pubic interest forest system, on one hand, it is necessary to maintain the legally practice of protecting non-public forestry property right, on the other hand, it is also necessary to consider the need to national ecological and economic construction, to utilize the forest management right suitably, and to increase social welfare and to improve social environment.The forms of forest requisition are two kinds as the requisition of forest ownership (typical requisition) and forest utilizing right requisition (leasing).The requisition of forest ownership (typical requisition)refers to the behavior of acquiring the non-public forestry with observable ecological benefits by the government; the forest ownership will be transferred after acquiring.The requisition (leasing)of forest utilizing right refers to the behavior of leasing the non-public forestry with ecological benefits by the government; the forest ownership will be not transferred after leasing, however, the utilizing right of the forest during the leasing period is belong to the government. Currently, Chinese government mainly utilizes the forest governing methods to restrict the practices of the non-public forest property right, such as logging quota system, logging license system, and this kind of action is called quasi requisition legally, i.e.as the consequence of government practicing its governing power, the relevant rights are restricted such as the rights of utilizing and benefit collecting, which leads the decreasing of forest assets.It is practical legally to adjust relevant actual losses as the consequence of government governing economy.Otherwise, the government will change the form of requisition to governing to escape relevant restricts of requisition by the constitution and relevant laws and refuse to compensate relevant property owners. It is compulsory to compensate the losses of relevant forest property owners according to the principle of equity for their sacrifice of giving up their practicing property rights to meet the demand of national ecological construction.
5) Subsiding system of commodity forest To solve the problems related to property right is just the base for attracting invests for non-public commodity forest constructions.It is the following issue to maintain its profit rate be competitive to a certain degree.The forest producing main bodies will not invest actively to a project without attractive profit rate.The aim of the subsiding system of commodity forest is to "aid", i.e.to improve its development; and its instrument is "subsidizing", i.e. making up the gap with the average social benefits to the producing main bodies.In order to encourage the afforesting business, it is necessary to inducing the economic leverage to maintain the afforesting investing factors can obtain the average social benefits, otherwise they will move to no-forestry industries which provide higher profit rates and the development of forestry will just like water without a source.One approach to increase the profit making level of forestry is to decrease its taxation.After the elimination of agricultural taxes, it is necessary to elimination of forestry taxes.It is foreseen that if its taxation rate decrease to 15 percent, the internal rate of rate of forestry will increase to 15.5 percent, the afforesting projects will be with some attractive abilities.While this rate is just the same as the rate enjoyed by the foreign afforesting investors (Chen, 2003), suppose that the domestic afforesting investors share the same low tax rate, there will appear a broad development space for forest.If the tax rate that same as low as 5 percent as the one of Indonesia, Brazil, or the New Zealand, etc, their internal rate of return will be 19.8 percent(Mao et al., 2002).Another approach of improving afforesting profit making is to decrease the forest rent or exempt it. In 19th century, in order to encourage more people emigrate to the west; the nation stipulated many flexible and favorable policies for land developing, and it accelerated the process of west development substantially.The government published consecutively during that period the stipulations as the Law for encouraging western afforesting, the desert land law, which stipulated that only if one plants tree or grass or construct irrigating channels for a certain time and to certain area, one can receive a certain amount of land as a return.Because it is possible to private American lands, so it is practical to utilize the way of giving as a gift to encourage the development of its remote and poor areas.As China practices the way of public owned, it is impossible to develop the forestry with the same approach.However it is possible to adopt the methods of exchanging land to ecology to motivate people' s desire of participation.And it is useful to transfer some land utilizing rights to the forestry construction investors and to support them in their initial development period with loans, subsidies, discounts, and medical care, and these relevant regulations will not change in several decades and the investors will enjoy adequate land utilizing, transferring, operating and profit collecting rights.The government target is invest first, then decrease its investments and encourages to people treat afforesting and land regulating as their long-time or even life-time careers; after the obvious improvement of land regulating and developing, the government will invest their profit to land regulating in a large area through all kinds of approaches and form newstyled forest producing aid system, and it will take about 20 to 50 percent of the afforesting cost in the perspective of the relevant operating of forestry industry; and it is necessary to forbid the logging during the low-interest loan years.The relevant forestry subsidiaries are referred to all sorts of economic aiding instruments (including subsidiaries, credit, taxation deduction or exemption and land rent deduction or exemption)by all leveled governments to the afforesting main bodies to improve the forestry development.
Ba Lianzhu(巴连柱), Li Shuxin(李淑新).2003.Thinking about non-public forestry in law.Forestry Economics(林业经济), (4): 44-46
|
Chen Xiaoqian(陈晓倩).2003.Talk about the margin mechanism of ecosystem forestry continuable development.Forestry Economics(林业经济), (3): 38-40
|
Mao Yushi(茅于轼), Dang Jie(唐杰).2002.The property right and taxation issues of commodity forestry development.Management World(管理世界), (7): 75-88 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GLSJ200207010.htm
|
Jiang Zehui(江泽慧).2002.Research report on Chinese forestry sustainable development: second half.Beijing : Chinese Forestry Press(北京: 中国林业出版社)
|
The project group of the National Forestry Bureau Economics Research Center(国家林业局经济研究中心课题组).2003.About the development system obstacle and solve counterplan of non-public forestry.Forestry Economics(林业经济), (4): 18-21
|
Yao Shunbo((姚顺波).2002.Framework on exchanging land to ecological forests.Ecological Economics(生态经济), (8): 47-49 http://www.cqvip.com/qk/96795X/200208/6550230.html
|
Yao Shunbo(姚顺波).2004a.Research on system of forestry government purchasing public interest forest.Green China(绿色中国).12B : 24-26
|
Yao Shunbo(姚顺波).2004b.Research on requisition and compensation of non-public forestry.Forestry Economics Issues(林业经济问题), (2): 81-84 http://www.cqvip.com/qk/96809X/200402/9775306.html
|
Yao Shunbo(姚顺波).2005.On forestry governance of stipulated forestry.Forestry Economics Issues(林业经济问题), (2): 87-90 http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=15220999
|
Zhou Shengxian(周生贤).2002.Research report on Chinese forestry sustainable development: first half.Beijing : Chinese Forestry Press(北京: 中国林业出版社)
|
Zhou Shaozhou(周少舟), Liao Guangping(缪光平).2003.Research summary of Chinese non-public forestry.Forestry Economics(林业经济), (4): 38-41
|
 2006, Vol. 42
2006, Vol. 42
