文章信息
- 高瑞桐, Wang Baode, Victor C. Mastro, Richard C. Reardon, 李国宏.
- Gao Ruitong, Wang Baode, Victor C. Mastro, Richard C. Reardon, Li Guohong.
- 树冠喷药毒杀光肩星天牛成虫效果及农药残留分析
- Efficacy of 4 Insecticides Used as Cover Spray for Controlling Adult Anoplophora glabripennis (Motsch.) and the Levels of these Insecticides Detected in Leaves and Twigs
- 林业科学, 2005, 41(3): 202-205.
- Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2005, 41(3): 202-205.
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2003-05-30
-
作者相关文章
2. US Department of Agriculture, Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service, CPHST, Otis Pest Survey, Detection, and Exclusion Laboratory Otis ANGB, MA 02542;
3. US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team Morgantown, WV 26505
2. US Department of Agriculture, Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service, CPHST, Otis Pest Survey, Detection, and Exclusion Laboratory Otis ANGB, MA 02542;
3. US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team Morgantown, WV 26505
利用杀虫剂防治害虫是一种见效快、效果好的方法; 但是, 杀虫剂的使用也带来环境污染问题, 因此杀虫剂的合理使用已成为目前关注的焦点。光肩星天牛[Anoplophora glabripennis (Motsch.)]是杨树的重要蛀干害虫, 幼虫期在树干内钻蛀危害, 而且个体分散, 加之树木高大, 防治起来十分困难。成虫期以树的小枝、叶柄和叶片作补充营养, 是进行化学防治的有利时期。以前用化学方法防治该害虫, 往往仅注意杀虫剂的防治效果(张仲信, 1964; 康青, 1981; 孙长春, 1987; 梁成杰等, 1997a; 1997b;高瑞桐等, 2001; 萧刚柔, 1992), 缺乏杀虫剂在树体内残留量问题的研究和药剂对害虫杀伤效果的系统观察。本文在1999年室内用药液浸渍法, 对7种农药不同浓度毒杀光肩星天牛成虫试验的基础上, 初步筛选出4种农药及每种农药的浓度, 于2000年在北京市海淀区中国林业科学研究院试验苗圃, 进行了毒杀光肩星天牛成虫试验, 并就每种农药在树枝内的含量随时间的变化及杀虫效果进行了研究。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验材料供试树种为1.5年生杨树(Populus sp.)。供试杀虫剂氯菊酯乳剂:ASTRO (有效成分36.8%氯菊酯)由美国FMC公司生产, 毒死蜱乳剂:AllPro DURSBAN 4E (有效成分44.9%毒死蜱)由美国Sureco Inc.公司生产, 乙酰甲胺磷可湿性粉剂:Orthene 75 S (有效成分75%乙酰甲胺磷)由美国VALENT公司生产, 甲萘威乳剂:SEVIN XLR PLUS (有效成分44.1%甲萘威)由法国罗纳普郎克农化公司(Rhone-Poulenc AG Co.)生产。供试成虫采自天津市汉古区茶店的旱柳(Salix sp.)行道树。
1.2 试验方法1) 喷药 由于未见过利用上述杀虫剂防治光肩星天牛成虫的报道, 因此, 本试验采用各种杀虫剂说明书上介绍的最高使用剂量进行试验。杀虫剂乳剂用量筒量体积、粉剂用天平称重的方法将4种杀虫剂的浓度配好:氯菊酯为920 mg·kg-1, 毒死蜱为2 245 mg·kg-1, 乙酰甲胺磷7 500 mg·kg-1, 甲萘威17 640 mg·kg-1。7月10日用背负式喷药器分别在野外4组杨树上喷药, 喷洒至树叶、小枝及树干滴液为止。2)成虫饲养于喷药后1 d开始采摘小枝饲养成虫, 以后每3 d采摘1次进行饲养, 直到采摘饲养至连续2次死亡率低于50%以下为止。成虫饲养在室内直径9.5 cm, 高30 cm的柱形铁纱笼内, 为防止树枝很快干燥, 铁纱笼内放一罐头瓶, 瓶底放吸水脱脂棉将枝条下端插入其内, 供枝条吸收水分。再把健康成虫放入笼内, 每笼1对, 每种杀虫剂饲养20笼。以不喷药树枝饲养的成虫作对照。然后每天观察1次试虫死亡情况, 连续观察3天。
2 试验结果 2.1 4种杀虫剂对成虫的致死效果7月10日施药后1~24 d采摘枝条饲养成虫, 观察的死亡结果如表 1。
|
|
从表 1可以看出, 氯菊酯对光肩星天牛成虫致死效果最好, 施药后15 d内致死效果都在95%以上, 而且用药浓度为毒死蜱的41.0%, 乙酰甲胺磷的12.3%, 甲萘威的5.2%, 明显较低。效果最差的是毒死蜱, 第3天致死效果即下降到65%以下。甲萘威虽然较其他2种杀虫剂的致死效果好, 但是, 其施药浓度为毒死蜱的7.9倍, 乙酰甲胺磷的2.4倍。
另外, 还可看出, 4种杀虫剂在试验的浓度下死亡率降至50%时的时间分别为:氯菊酯约18 d, 毒死蜱约9 d, 甲萘威15~18 d, 乙酰甲胺磷12~15 d。
2.2 4种杀虫剂在杨树幼树体内的残留量分析与杀虫剂有关的气温、降水量及光照等3种气象数据, 自北京市海淀区气象站获得如表 2。
|
|
甲萘威、氯菊酯、毒死蜱、乙酰甲胺磷4种杀虫剂在杨树小枝及叶片中的残留量数据由中国林业科学研究院分析中心提供。1)样本采集:于喷药后第3、6、9、20和40 d时, 分别在试验地内砍伐5株杨树, 每株在中部以上采摘枝条50 g、树叶50 g, 各分为2个样本, 共采集10个样本。2)样本的分析测定:1)将样品60 ℃烘48 h后, 粉碎过60目筛, 称取5.0 g样品于100 mL具塞三角瓶中, 加入50 mL二氯甲烷放入超声波振荡器中振荡2 h, 过夜。第2天过滤, 滤渣中再加入二氯甲烷超声振荡2 h, 过滤弃去残渣, 合并滤液。将滤液放在通风厨内, 自然风干后加入5 mL二氯甲烷溶解残渣, 经慢速定性滤纸过滤后, 清液待气相色谱检测。2)色谱条件:仪器为Shimadzu(岛津)GC7AG气相色谱, 色谱柱:SE-54 30 m×0.32 mm, 流速:20 mL5min-1, 检测器:FPD, 外标法定量进行数据处理。残留量测定结果如图 1、2。
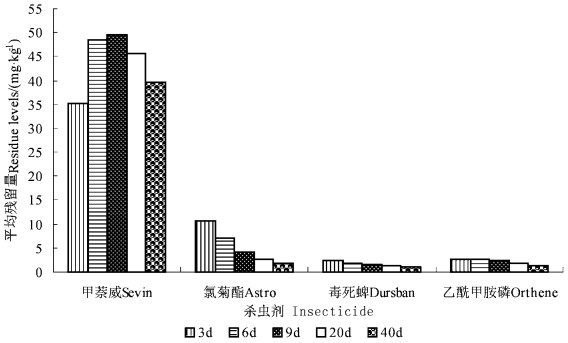
|
图 1 施药后不同天数叶内杀虫剂残留量 Fig. 1 Levels of insecticides in tree leaves at different days following application |
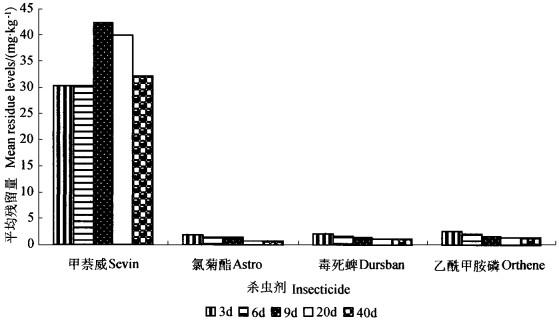
|
图 2 喷药后不同天数小枝内杀虫剂残留量 Fig. 2 Levels of insecticides in tree twigs at different days following application |
对天牛成虫致死力和残留量进行综合分析认为, 4种杀虫剂对害虫同时具有触杀和胃毒2种作用, 药剂喷于树冠后害虫靠接触或取食粘辅或吸收于枝叶内的药剂中毒死亡。氯菊酯在树叶内浓度为4 mg·kg-1左右, 枝内为1.4 mg·kg-1时致死率可达到95%以上; 乙酰甲胺磷在树叶内为2.5 mg·kg-1, 枝内为2.1 mg·kg-1时致死率可达到90%以上。毒死蜱在树叶内为2.5 mg·kg-1, 枝内为2.1 mg·kg-1时致死率仅为62.5%, 其毒力比上述2种杀虫剂低。甲萘威施药浓度和在枝叶内的残留量都比其他3种杀虫剂高很多, 但在6天内致死效果却比氯菊酯和乙酰甲胺磷稍差, 对光肩星天牛成虫的毒力小。
3 结语与讨论综上所述采用树冠喷药防治光肩星天牛成虫时, 首选杀虫剂为氯菊酯, 其次为乙酰甲胺磷。
氯菊酯为菊酯杀虫剂、毒死蜱和乙酰甲胺磷为有机磷杀虫剂、甲萘威为氨基甲酸酯杀虫剂。甲萘威杀虫剂在树叶和小枝内的残留似乎不象想象中的“随时间的增加残留降低的规律”, 另外, 该杀虫剂对光肩星天牛成虫的致死情况也有前3 d最高-随后降低-12 d后逐渐升高-18 d后又降低的趋势, 也与其他杀虫剂死亡率随时间增加逐渐降低的趋势不相符合, 因此, 该杀虫剂施药后在杨树体内外的粘辅、吸收和代谢及致死性能仍需进一步探讨。
高瑞桐, 王保德, 李国宏, 等. 2001. 锐劲特和氯菊酯毒杀两种天牛成虫研究. 林业科技通讯, (11): 17-19. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4938.2001.11.006 |
梁成杰, 李国宏, 李广武, 等. 1997a. 诱饵树施内吸和菊酯类农药防治两种天牛的研究. 林业科学研究, (2): 189-192. |
梁成杰, 李国宏, 李广武, 等. 1997b. 十种农药防治光肩星天牛的药效分析. 林业科学研究, (3): 325-328. |
康青. 1981. 注射氨水防治木蠹蛾和光肩星天牛幼虫. 林业科技通讯, (3): 23-24. |
孙长春. 1987. 光肩星天牛发生危害及防治. 宁夏林业科技, (2): 22-23. |
萧刚柔主编. 1992.中国森林昆虫(第2版).北京:中国林业出版社, 513-14
|
张仲信. 1964. 光肩星天牛生活习性及防治的研究. 山东农业科学, (3): 39-41. |
 2005, Vol. 41
2005, Vol. 41