复合材料加筋/夹层板壳结构由于具有比刚度高、比强度大、耐腐蚀以及具有高度可设计性等诸多优点,已在航空航天、船舶、高速列车、建筑等工程领域中得到广泛应用。目前针对此类结构的研究广泛而深入,从理论建模分析,到特定结构优化设计,再到制造工艺探讨,各环节都有大量的文献涉及。根据应用背景的不同,复合材料加筋/夹层结构的研究又通常涉及力学、声学、材料科学、控制科学等不同学科,通常较为复杂。
复合材料加筋/夹层结构声振特性研究是建立在普通板壳结构研究基础上的,从普通板壳到复合材料加筋/夹层板壳,研究所考虑的因素逐渐增多,研究方法也在继承和发展。基于由简入繁的思路,本文首先介绍普通板壳结构的声振特性研究,再逐步过渡到复合材料加筋/夹层板壳的声振特性研究。其后介绍新材料的应用给结构声振特性研究带来了新特点。最后,由于工程结构的应用离不开一定的边界条件,探讨复合材料加筋/夹层板壳在任意边界条件下的声振特性研究。通过归纳和梳理相关文献,对复合材料加筋/夹层板壳声振特性研究以及研究所采用的各种方法进行总结,并指出相关研究的发展趋势,为相关研究者提供参考。
1 结构声振特性研究现状 1.1 研究内容结构的声振特性是指考虑结构-流体耦合作用的声振耦合特性,包含振动特性和声学特性2个部分,其研究的内容包括耦合系统中的结构振动,结构声辐射,结构声传递。在声振耦合系统中,结构振动通常由外部激励引起,用均方振速、振动加速度级等指标表征;结构声辐射由结构振动引起的声场变化造成,特征指标有辐射声压、辐射声功率和声辐射效率等;结构声传递特性是指声波通过结构后发生反射、折射、衰减从而呈现出的不同特性,通常用传递损失(TL)表征。归纳目前研究结构声振特性的文献可以发现,当结构所受外部激励为各种入射声波时,关注点通常是结构的声传递特性[1-7],而当外部激励为外力激励时,关注点是结构的振声响应[8-11]。不论结构受外力激励还是声波激励,都是外部激励作功使结构振动,结构振动又引起结构周围声场的声压变化,从而将动能转化成声能辐射出去,在这个过程中结构振动和声压变化相互影响,从而形成声振耦合系统[12]。
1.2 研究方法研究结构声振特性的方法有解析法、半解析法、数值法。解析法适用于简单结构如板壳结构、圆柱结构等,主要包括空间谐波法[2,13-15]、傅里叶变化法[16-19]、模态分析法[11,20-21]、行波法[22]、传递矩阵法[23]等,其中空间谐波法和傅里叶变化法适用于无限大周期结构,二者在本质上都是无限大代数方程组截断求解问题[24];模态分析法能利用模态正交性简化理论分析,但要实现模态解耦对结构的边界条件有所要求,主要用于有限大简支结构在中低频的声振分析;行波法采用波动形式的解来求解结构的声振耦合控制方程,可以对结构弯曲波的传播过程进行细致的机理分析。
半解析法是解析与数值相结合的求解方法。在求解结构声振特性时,计算涉及结构和声场2个域,当面对复杂结构或复杂边界时,难以获得解析解,利用离散化求解可以简化分析,将解析解和离散解组合起来的半解析法,可以兼具灵活性和计算效率,因而在研究中广泛应用[25-28]。
对于数值方法,有限元/边界元方法可以很好地求解复杂结构的振声响应,但限于网格数量和分析频率相关[29]而不适用于高频计算。统计能量法[30-32]从统计学的角度求解结构的振声响应,要求模型有足够大的振动和声模态密度,适用于中高频计算,而对模态密度不够的中低频段则存在统计学上的不确定性。用统计能量法分析结构振声响应主要取决与3个参数的估计[29]:1)单个子系统的模态密度;2)单个子系统的内部损耗因子(阻尼);3)各个子系统间的耦合损耗因子(耦合程度)。
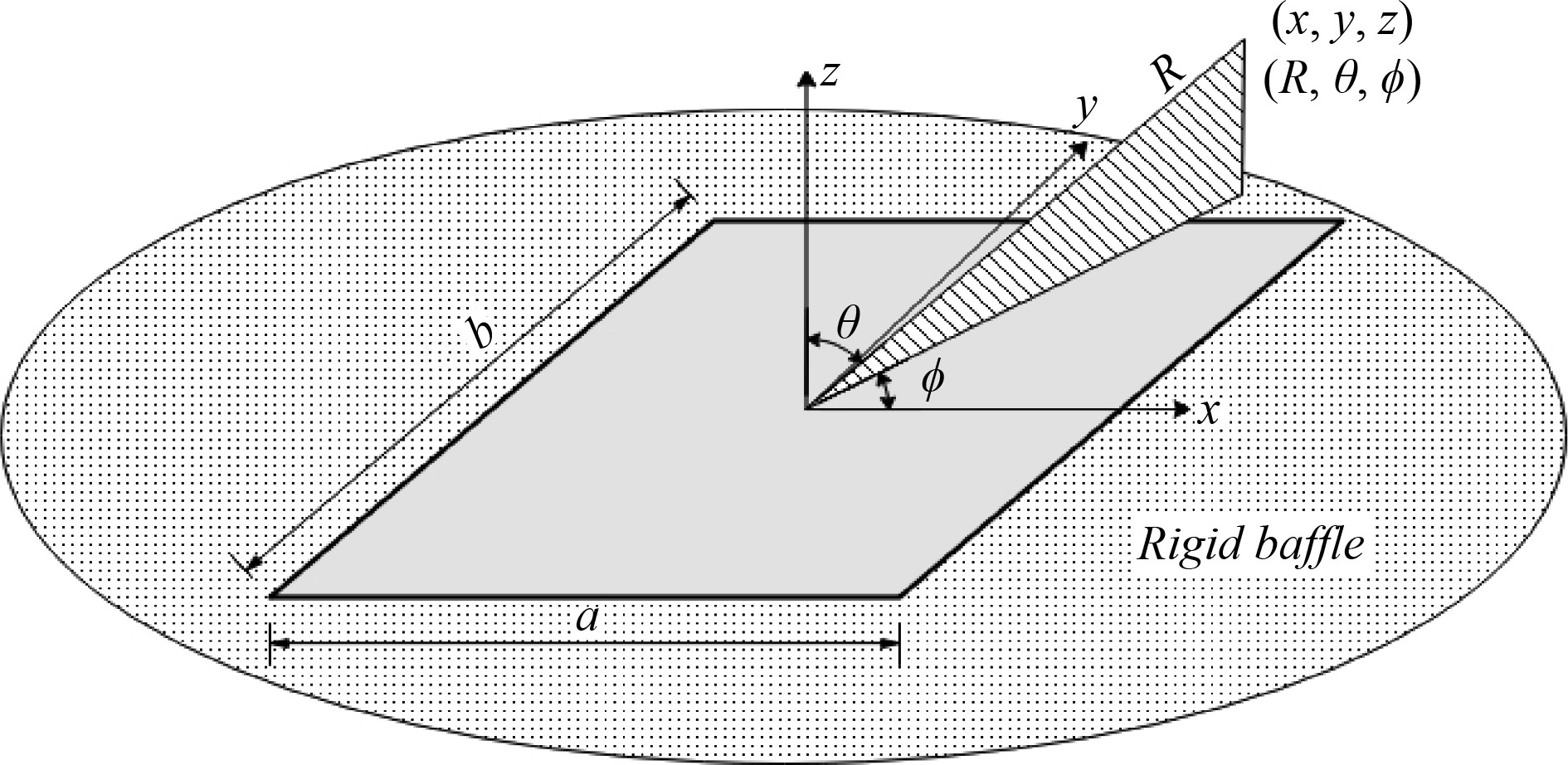
2 加筋/夹层板壳声振特性研究 2.1 板壳结构普通板壳结构声振特性研究是加筋/夹层板壳结构声振特性研究的基础,从普通板壳到加筋/夹层板壳再到复合材料加筋/夹层板壳,模型所考虑的因素逐渐增多,但模型基本特征未变,所采用的研究方法也是不断继承和发展的。以经典的矩形简支薄板的声振计算为例 [33],假设矩形薄板四周为无限大刚需障板,板受外部激励
| $ D{\nabla ^4}w(x,y) - {\rho _D}h{\omega ^2}w(x,y) = F(x,y) - {p_0}(x,y) 。$ | (1) |
其中:
| $ {p_0}(x,y) = \frac{{i{\rho _0}\omega }}{{2{\text π} }}\int_{{S_p}} {\dot \omega (x',y')} \frac{{{e^{ - i{k_0}R}}}}{R}{\rm{d}}x'{\rm{d}}y'。$ | (2) |
其中:
| $ Z_{mn}^M{a_{mn}} + i\omega \sum\limits_{m = 1}^\infty {\sum\limits_{n = 1}^\infty {{Z_{mnpq}}{a_{mn}} = {F_{mn}}} } 。$ | (3) |
其中:
|
图 1 矩形板声振计算示意图 Fig. 1 Diagram of vibroacoustic calculation of rectangular plate |
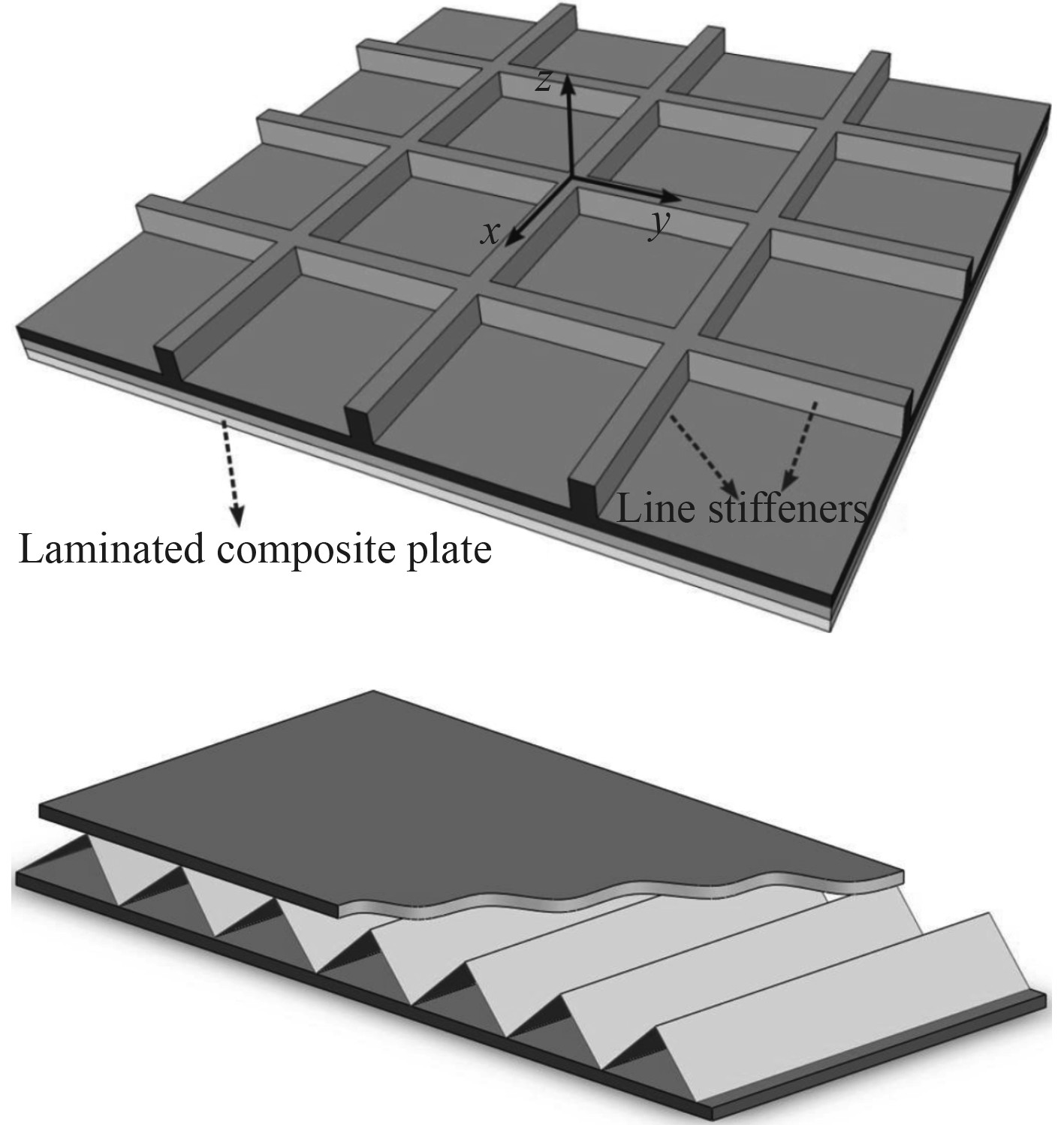
相较于普通板壳结构,加筋/夹层板壳通常有更好的力学和声学性能,在工程应用中极为广泛[34],在研究其声振特性时,理论模型通常会根据实际情况进行一定程度简化。例如,对于加筋板壳,可简单地将加强筋视为作用在面板上的线力[16],或者等效为弹簧的横向支撑和扭簧的旋转支撑[2,18],亦或者考虑弯曲和扭转的同时还考虑加强筋与板的耦合作用[1];对于夹层板壳,若夹芯层为非连续形式,如点阵结构、格栅结构、波纹结构等离散夹芯[35],还需要进行层芯受力简化。例如将波纹夹芯简化为具有平移刚度和扭转刚度的弹簧[36-37],并假设芯层的质量时均布于上下面板,或者将夹层进行均质化等效,得到等效的弹性参数[5,38]。
在考虑加筋/夹层板壳结构声振特性时,研究对象通常有无限大周期结构和有限尺寸结构之分[39],这两者的关注重点不同,前者主要着眼于结构波在加筋/夹层板上的传播特性,如Mead和Pujara等[13-14,40-41]研究了声波在周期弹性支撑梁和无限大周期加筋板中的传播问题,应用空间谐波法求解了周期加筋结构的声传递特性,并讨论不同加筋参数对振声响应的影响。此类研究偏向于揭示声振特性形成机理,并对结构进行波动分析[22]。相对地,对有限尺寸结构则主要关注结构在特定激励作用下的振声响应,有限尺寸加筋/夹层板有明确的边界,可以建立起封闭的理论模型,求解得到特定频率下振动和声辐射的封闭解[42-44,9]。
对于呈现周期排列的加筋/夹层结构,还可以通过周期结构Floquet-Bloch理论[45]建立声振耦合方程。例如,Zhou[25]在研究将正交加筋板的声辐射特性时,将加筋视为周期排列的十字交叉点进行分析,但这种方法用于分布稀疏周期加筋结构时会带来较大误差。对于周期加筋/夹层结构,还可以利用等效方法计算出胞元结构的等效性质[5,38],典型方法有代表体单元法(RVE)[46]和渐进均匀化法(AH)[47-49]等。
数值方法可以很好地解决复杂结构和复杂边界结构的声振计算问题[50-52],数值与解析相结合的方法,可以灵活适用不同结构且具有较高的计算效率。Laurent[53]在研究水下不规矩加筋壳的振声响应时,将受流压作用的壳和肋骨框架视为不同的子系统并分别求解导纳,通过圆周导纳方法(CAA)将各子系统变成一个耦合系统,用解析和数值相结合的方法分析了水下耐压艇体在较宽频率范围内的振声性能。Yang[15]提出一种可以预测周期结构振声响应的模型,将行波法和有限元法相结合,用有限元法建立周期结构的单元模型,求得单元的质量矩阵和刚度矩阵后代入解析模型进行分析,极大简化了声振计算过程。文献[54-57]也采用了类似的研究思路,利用有限元与等效法相结合简化计算模型。
2.3 复合材料加筋/夹层板壳结构本文所讨论的复合材料特指纤维增强树脂基体复合材料,其最大的特点是具有分层特性和各向异性的材料属性,在研究结构声振特性时多基于复合材料力学和层合板理论考虑这一材料特性。Yin[19]研究了双周期加筋复合材料层合板的声辐射特性,考虑加筋板受简谐点激励作用,利用层合板理论考虑复合材料面板的各向异性特性,同时利用空间谐波法求解辐射声压,最后分析加筋对不同频段声辐射的影响。Shen[58]研究了无限大正交加筋复合材料层合板在声波和外力激励下声辐射特性,其中复合材料层合板横向位移采用一阶剪切的分层理论考虑,并过傅里叶变换法求解得到不同激励下的结构声辐射。Shen[17]通过相似的方法研究了复合材料加筋层合板的声传递特性,并分析了不同截面形式加筋的影响。Mejdi[59]基于模态叠加法研究了复合材料加筋板的声振特性,使用一阶剪切变形理论考虑复合材料面板和复合材料加强筋的横向变形,并将加强筋等效为作用于面板的弯矩和剪力,利用连续关系集成在面板的阻抗表达式中,分析了3种截面形式加强筋的不同影响,以及不规则加筋板和周期性加筋板的振声响应。与有限元法/边界元法计算进行比较,结果具有良好的一致性。Ghinet[60-61]基于分层理论提出了一种通用的复合材料夹层板壳理论模型,其中每个分层采用一阶剪切理论,考虑分层的弯曲变形、横向剪切变形以及转动惯量和各向异性铺层角影响,最后用行波法求解了无限大夹层板在散射场作用下的传声损失,并用有限元法和谱有限元法分别验证了模型的有效性。Cherif[62]对该模型进行了详细的实验验证,对结构波数、模态密度、阻尼损耗因子、辐射效率、传声损失等指标进行比较,验证了该理论模型预测复合材料夹层板壳声振特性的准确性。
|
图 2 典型复合材料加筋板和复合材料夹芯板示意图 Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of typical stiffened composite plate and sandwich composite plate |
复合材料加筋/夹层板壳结构声振特性研究所考虑的因素很多,采用的研究方法是从普通板壳、加筋/夹层板壳结构声振研究的方法中继承和发展的。在研究加筋/夹层板壳结构声振特性时,通常需要进行一定的模型简化,或者使用等效参数和周期理论。在各种研究方法中,空间谐波法和傅里叶变换法适合无限大周期结构的声振分析,模态叠加法适用于有限尺寸结构的声振响应计算,行波法可以用来分析结构的频散特性,带隙特性[22]。数值法和解析法相结合进行声振分析,既能解决结构外形复杂难以解析求解的问题,也能避免计算资源消耗过大的问题。
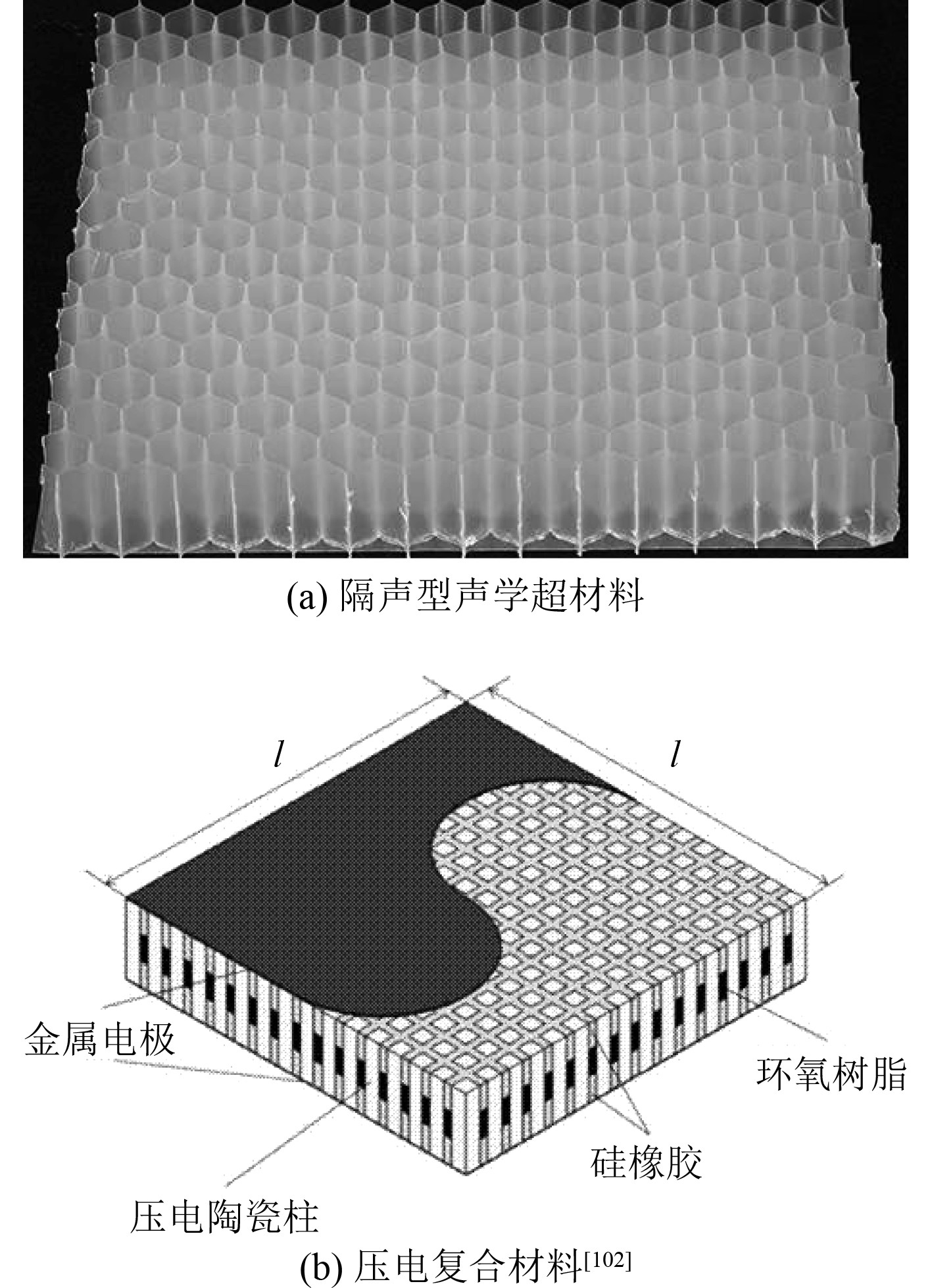
3 新材料应用与声振特性研究新材料的应用给复合材料加筋/夹层结构声振研究带来了新的发展[63]。例如,声学超材料被用来改善加筋/夹层板壳结构的声传递特性[64],智能材料[65-66]被用来实现加筋/夹层结构的振动主动控制,这些材料的应用使声振计算变得更复杂,也使得加筋/夹层结构有了更大的设计空间。
声学超材料是一类具备超常物理特性的人工复合材料,具有如负等效质量密度、负等效弹性模量等特性,声学超材料的概念最早是Liu等[67-68]在研究局部共振声学材料时提出的,通过对材料组成和结构构型进行设计,可以实现小尺寸结构对大波长声波的传播抑制。从而实现对声波的调谐[69],这给声振特性研究带来新的变量,增大了结构声学的设计空间。Chen[70]研究了声学薄膜板的低频吸声能力,通过建立薄膜板的声振耦合理论模型,揭示了平面入射波作用下的声能吸收机理。不同于一般声传递特性研究,局域共振(薄膜上附着质量的共振和反共振运动)是声学超材料产生低频吸声能力的关键,Chen通过求解声振耦合的积分-微分方程,准确地对结构吸声能力进行定量测定,其结果与有限元预测结果吻合较好。
智能材料也是研究的热点之一,所谓智能材料的定义相当模糊,通常这些材料都具有一些常规材料所不具备的材料特性,且有一定的可调节性,比如压电材料[71-72]、温控阻尼材料[73]、形状记忆合金[74]等。就研究结构的声振特性而言,这些材料的应用主要是实现结构振动的主动控制,进而影响声振特性。文献[71-72]研究了如何利用压电纤维主动阻尼约束层来控制夹层结构振动,其中贴敷于层合梁上的约束阻尼分为压电材料层和粘弹性阻尼层2层,通过对压电纤维层实施适当的电压控制,可以主动调节粘弹性阻尼材料层的横向剪切变形,增大对结构的阻尼约束作用,从而抑制夹层梁振动,更多地耗散结构动能。文献[73]利用高分子聚合材料在玻璃化转变区具有更高的阻尼性能这一特性,提出一种温控变阻尼技术,通过主动调节芯层温度控制其阻尼性能,从而实现对夹层结构振动的控制,实验表明温控变阻尼技术抑振效果明显。
|
图 3 新材料在夹层结构的应用 Fig. 3 Typical applications of new materials in sandwich structures |
实际工程结构的边界一般都是非理想状态的,即结构的边界是一种弹性状态,对于有限尺寸复合材料加筋/夹层板壳,边界对其声振特性的影响是无法回避的,因而研究任意边界条件下的声振特性具有重要意义。目前对复合材料板壳结构的声振特性研究,很多都是以简支为边界条件的,这是因为在简支边界下更容易获得解析解[75],还有不少文献虽然也进行任意边界条件下的研究,但实质却是不同经典边界的任意组合[76]。
研究任意边界条件下复合材料加筋/夹层板壳结构的声振特性,既考虑复合材料的各向异性同时还要考虑结构的弹性边界,这使得声振求解变得异常困难,因而大部分文献未能考虑所有条件进行综合分析,而是退而求其次地研究结构的自由振动特性[77-78],或结合数值方法和实验方法来进行研究。
自由振动求解难度低,且能反映结构固有频率随质量、刚度分布变化的情况,是声振特性研究的基础。Qin[79]研究了圆柱壳在任意边界条件下自由振动,通过设置不同刚度的支撑弹簧来模拟任意边界条件,采用Sanders壳理论计算壳体弹性应变能,并使用Rayleigh-Ritz法推导控制方程,最后分析了圆柱壳在任意条件下的自由振动特性。Berry[80]研究了矩形薄板在任意边界条件下的振动和声辐射特性,同样是利用Rayleigh-Ritz法推导获得矩形板的振动控制方程,并利用Rayleigh积分公式进行远场辐射声压计算,最后得到结论:矩形板受到的边界约束越小,板的辐射效率就越低。文献[79,81-84]均为研究各类板壳结构在任意边界下的振动,其中既有夹层结构、加筋结构、格栅结构等不同结构形式的,也有功能梯度材料,粘弹性材料等不同材料特性,但都是通过Rayleigh-Ritz法和Hamilton原理来进行振动分析的,这样可以避开复杂结构和边界带来的复杂力学分析,较为简便地得到振动控制方程。同时,上述文献在处理板壳结构的任意边界时,多是参考结构的弯曲刚度来表示边界约束条件,这样可以保证最后得到振动控制方程可解,当板壳结构是具有各向异性的复合材料层合结构时,由于耦合刚度的存在,不便直接利用弯曲刚度的表示边界约束条件,因而不少文献中都是直接假设一个刚度参数[85-86]来模拟边界条件。
用有限元方法特别是利用商用有限软件模拟任意边界条件是非常方便的[87],不少文献中都将有限元计算作为理论计算的验证,但和理论分析一样,边界的刚度约束虽然可以方便地假定为任意数值,但难以合理地模拟和还原实际结构的边界约束条件,这方面的研究需要针对性的试验作为支撑。
5 结 语随着复合材料加筋/夹层结构被不断地应用于航空航天、船舶、汽车、高速列车等不同领域,对其声振特性的研究也逐步深入。复合材料加筋/夹层板壳结构声振问题较为复杂,需要考虑的因素较多,本文从介绍声振特性研究内容和研究方法开始,先后归纳总结了加筋/夹层板壳结构声振特性研究、考虑新材料应用的声振特性研究、任意边界条件下的声振特性研究的相关文献,通过综述上述研究文献,可以发现:
1)解析与数值相结合的研究方法有更好的应用灵活性和计算效率,是研究复合材料加筋/夹层结构声振特性的有效方法,也是重要的发展方向;
2)新材料的应用为复合材料加筋/夹层结构的声振特性研究带来了新变化,增大了结构动力学设计和声学设计的设计空间;
3)现有的分析方法可以模拟出任意边界条件而无法还原出实际边界条件,因而需要结合试验研究作为支撑。
| [1] |
SHENG P, ZHANG X, LIU Z, et al. Locally resonant sonic materials[J]. Physica B:Condensed Matter, 2003, 338(1): 201-205. |
| [2] |
LIU ZY, CHAN CT, SHENG P. Analytic model of phononic crystals with local resonances[J]. Physical review B Condensed matter and materials physics, 2005(1): 71. |
| [3] |
BIRMAN VICTOR, KARDOMATEAS GEORGE-A. Review of current trends in research and applications of sandwich structures[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2018, 142: 221-240. DOI:10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.01.027 |
| [4] |
LIU Bilong, FENG Leping, NILSSON Anders. Sound transmission through curved aircraft panels with stringer and ring frame attachments[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2007, 300(3−5): 949−973.
|
| [5] |
LEE J H, KIM J. Analysis of sound transmission through periodically stiffened panels by space-harmonic expansion method[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2002, 251(2): 349−366.
|
| [6] |
LEE JH, KIM J. Sound transmission through periodically stiffened cylindrical shells[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2002, 251(3): 431−456.
|
| [7] |
ZHAO Dong, SQUICCIARINI G, FERGUSON N. Vibroacoustic response of stiffened thin plates to incident sound[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2021, 172: 107578.
|
| [8] |
ARUNKUMAR M P, PITCHAIMANI JEYARAJ, GANGADHARAN K V. Vibro-acoustic response and sound transmission loss characteristics of truss core sandwich panel filled with foam[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2018, 78(Jul): 1−11.
|
| [9] |
ISAAC CW, PAWELCZYK M, WRONA S. Comparative study of sound transmission losses of sandwich composite double panel walls[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(4): 1543.
|
| [10] |
MEJDI A, ATALLA N, GHINET S. Wave spectral finite element model for the prediction of sound transmission loss and damping of sandwich panels[J]. Computers & Structures, 2015, 158: 251-258. |
| [11] |
JEYARAJ P. Vibro-acoustic behavior of an isotropic plate with arbitrarily varying thickness[J]. European Journal of Mechanics - A/Solids, 2010, 29(6): 1088−1094.
|
| [12] |
LEGAULT J, MEJDI A, ATALLA N. Vibro-acoustic response of orthogonally stiffened panels: The effects of finite dimensions[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2011, 330(24): 5928-5948. DOI:10.1016/j.jsv.2011.07.017 |
| [13] |
LI Xiangyang, YU Kaiping, ZHAO Rui. Vibro-acoustic response of a clamped rectangular sandwich panel in thermal environment[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2018, 132: 82−96.
|
| [14] |
A N S, A T R M, B S K P. Vibro-acoustic behaviour of shear deformable laminated composite flat panel using BEM and the higher order shear deformation theory - ScienceDirect[J]. Composite Structures, 2017, 180: 116−129.
|
| [15] |
金叶青. 基于不同理论模型的加筋层合板壳声振特性研究[D]: 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2013.
|
| [16] |
MEAD D J, PUJARA K K. Space-harmonic analysis of periodically supported beams: response to convected random loading[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1971, 14(4): 525−541.
|
| [17] |
MEAD DENYS-J. Plates with regular stiffening in acoustic media: Vibration and radiation[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1990, 83(1): 391−401.
|
| [18] |
YANG Yi, MACE B R, KINGAN M J. Vibroacoustic analysis of periodic structures using a wave and finite element method[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 457: 333−353.
|
| [19] |
MACE B R. Sound radiation from fluid loaded orthogonally stiffened plates[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1981, 79(3): 439−452.
|
| [20] |
SHEN Cheng, XIN Fengxian, LU Tianjian. Transmission loss of orthogonally stiffened laminated composite plates[C]//Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology: China Science Literature Publishing House, 2015: 275.
|
| [21] |
XIN FengXian, LU TianJian. Sound radiation of parallelly stiffened plates under convected harmonic pressure excitation[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2012, 55(2): 496-500. DOI:10.1007/s11431-011-4698-0 |
| [22] |
YIN X W, GU X J, CUI H F. et al. Acoustic radiation from a laminated composite plate reinforced by doubly periodic parallel stiffeners[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2007, 306(3−5): 877−869.
|
| [23] |
TITZE Maik, MISOL Malte, MONNER Hans-Peter. Examination of the vibroacoustic behavior of a grid-stiffened panel with applied passive constrained layer damping[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 453.
|
| [24] |
Shahgholian-ghahfarokhi Davoud, Aghaei-ruzbahani Milad, Rahimi Gholamhossein. Vibration correlation technique for the buckling load prediction of composite sandwich plates with iso-grid cores[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2019, 142: 392-404. DOI:10.1016/j.tws.2019.04.027 |
| [25] |
汤冬. 舰船典型板架结构弹性波动力学特性研究[D]: 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2018.
|
| [26] |
TARKASHVAND A, DANESHJOU K, GOLMOHAMMADI A. Fg and viscoelastic models combination for vibroacoustic modeling of sandwich structures made of open and closed cell foam materials[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 259. |
| [27] |
卢天健, 辛锋先. 轻质板壳结构设计的振动和声学基础(第一版) [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.
|
| [28] |
ZHOU Haian, ZHAO Yugang, WU Huayong, et al. The vibroacoustic analysis of periodic structure-stiffened plates[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2020, 481: 115402.
|
| [29] |
DROZ C, ZERGOUNE Z, BOUKADIA R, et al. Vibro-acoustic optimisation of sandwich panels using the wave/finite element method[J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 156: 108−114.
|
| [30] |
RAFIEE M, NITZSCHE F, LABROSSE M. Dynamics, vibration and control of rotating composite beams and blades: A critical review[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2017, 795-819. |
| [31] |
刘洋, 刘宝, 王蕾. 一种分析水中结构声振耦合特性的等效源方法[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2021, 33(1): 34-40. DOI:10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2021.01.007 |
| [32] |
孙雪荣, 朱锡. 船舶水下结构噪声的研究概况与趋势[J]. 振动与冲击, 2005(1): 108-115,140. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2005.01.029 |
| [33] |
MAXIT L, EGE K, TOTARO N, et al. Non resonant transmission modelling with statistical modal energy distribution analysis[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2014, 333(2): 499−519.
|
| [34] |
LANGLEY R S, SMITH J R D, FAHY F J. Statistical energy analysis of periodically stiffened damped plate structures[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1997, 208(3): 407−426.
|
| [35] |
SEÇGIN Abdullah, KARA Murat, OZANKAN Altay. A modal impedance-based statistical energy analysis for vibro-acoustic analysis of complex systems having structural uncertainty[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2019, 233(6): 1972−1989.
|
| [36] |
胡昊灏. 复合平板结构水下声辐射预报方法研究[D]: 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2014.
|
| [37] |
D'ALESSANDRO V, PETRONE G, FRANCO F, et al. A review of the vibroacoustics of sandwich panels: Models and experiments[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials, 2013, 15(5): 541−582.
|
| [38] |
朱子旭, 朱锡, 李永清, 等. 复合材料夹芯结构研究现状及其在船舶工程的应用[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2018, 40(3): 1-7. DOI:10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2018.01.001 |
| [39] |
SHEN C, XIN F X, LU T J. Theoretical model for sound transmission through finite sandwich structures with corrugated core[J]. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 2012, 47(10): 1066−1072.
|
| [40] | |
| [41] |
C SHEN. Sound transmission loss of adhesively bonded sandwich panels with pyramidal truss core: theory and experiment[J]. International Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2015, 7(1): 1550013.
|
| [42] |
付涛. 复合夹层筋板结构声振特性分析及抑制研究[D]: 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.
|
| [43] |
MEAD D J. Free wave propagation in periodically supported, infinite beams[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1970, 11(2): 181−197.
|
| [44] |
MEAD D J. A new method of analyzing wave propagation in periodic structures; Applications to periodic timoshenko beams and stiffened plates[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1986, 104(1): 9−27.
|
| [45] |
LIN Tian-Ran. An analytical and experimental study of the vibration response of a clamped ribbed plate[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2012, 331(4): 902−913.
|
| [46] |
LIN Tian-Ran, PAN Jie. A closed form solution for the dynamic response of finite ribbed plates[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2006, 119(2): 917−925.
|
| [47] |
FU Tao, CHEN Zhaobo, YU Hongying, et al. An analytical study of the vibroacoustic response of a ribbed plate[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2017, 73(FEB): 96−104.
|
| [48] |
BRILLOUIN L. Wave propagation in periodic structures: electric filters and crystal lattices[J]. Mcgraw Hill Book Company Inc New York, 1953.
|
| [49] |
蔡园武. 周期性板结构的渐近均匀化方法及微结构优化[D]: 大连: 大连理工大学, 2014.
|
| [50] |
高涛. 基于渐近均匀化法的格栅结构振动特性研究[D]: 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2017.
|
| [51] |
HASSANI B, HINTON E. A review of homogenization and topology opimization II-analytical and numerical solution of homogenization equations[J]. Computers & Structures, 1998, 69(6): 719−738.
|
| [52] |
KALAMKAROV ALEXANDER L. Asymptotic homogenization of composite materials and structures[J]. Alexander L. Kalamkarov, 2009(1): 3-5. |
| [53] |
REDDY R K K, ARUNKUMAR M P, BHAGAT V. Vibro-acoustic characteristics of viscoelastic sandwich panel: effect of inherent damping[J]. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2021, (1).
|
| [54] |
CLAUDE B, DUIGOU L, GIRAULT G. Study of damped vibrations of a vibroacoustic interior problem with viscoelastic sandwich structure using a high order newton solver[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 462: 114947.
|
| [55] |
SHARMA N, MAHAPATRA T R, PANDA S K. Evaluation of vibroacoustic responses of laminated composite sandwich structure using higher-order finite-boundary element model[J]. Steel & Composite Structures, 2018, 28(5): 629−639.
|
| [56] |
MAXIT Laurent, GINOUX Jean-Marc. Prediction of the vibro-acoustic behavior of a submerged shell non periodically stiffened by internal frames[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2010, 128(1): 137−151.
|
| [57] |
CAI Yuanwu, XU Liang, CHENG Gengdong. Novel numerical implementation of asymptotic homogenization method for periodic plate structures[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2014, 57(1): 284−292.
|
| [58] |
DUTRA T A, FERREIRA R T Luiz, Resende H B. A complete implementation methodology for Asymptotic Homogenization using a finite element commercial software: preprocessing and postprocessing[J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 245: 112305.
|
| [59] |
CLAUDE B, DUIGOU L, GIRAULT G, et al. Study of a vibroacoustic interior problem with viscoelastic sandwich structure using the asymptotic numerical method[C]. 2018.
|
| [60] |
ZHOU XQ, YU D Y, SHAO X Y. Asymptotic analysis on flexural dynamic characteristics for a laminated composite plate with embedded and perforated periodically viscoelastic damping material core[J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 154: 616-633. DOI:10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.07.054 |
| [61] |
SHEN C, XIN F X, CHENG L. Sound radiation of orthogonally stiffened laminated composite plates under airborne and structure borne excitations[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2013, 84(4): 51−57.
|
| [62] |
MEJDI A, ATALLA N. Vibroacoustic analysis of laminated composite panels stiffened by complex laminated composite stiffeners[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2012, 58(1): 13−26.
|
| [63] |
GHINET S, ATALLA N, OSMAN H. Diffuse field transmission into infinite sandwich composite and laminate composite cylinders[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006, 289(4): 745-778. |
| [64] |
GHINET S, ATALLA N. Modeling thick composite laminate and sandwich structures with linear viscoelastic damping[J]. Computers & Structures, 2011, 89(15): 1547−1561.
|
| [65] |
CHERIF R, ATALLA N. Experimental investigation of the accuracy of a vibroacoustic model for sandwich-composite panels[J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2015, 137(3): 1541.
|
| [66] |
WU X, SU Y, SHI J. Perspective of additive manufacturing for metamaterials development[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2019, 28(9): 093001.
|
| [67] |
LOJA M, SOARES C, BARBOSA J. Analysis of functionally graded sandwich plate structures with piezoelectric skins, using b-spline finite strip method[J]. Composite Structures, 2013, 96: 606-615. DOI:10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.08.010 |
| [68] |
NATH JK, KAPURIA S. Assessment of improved zigzag and smeared theories for smart cross-ply composite cylindrical shells including transverse normal extensibility under thermoelectric loading[J]. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 2012, 82(7): 859-877. DOI:10.1007/s00419-011-0597-x |
| [69] |
许伟龙, 彭伟才, 张俊杰, 等. 声隐身超材料发展综述[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2020, 15(4): 19-27,35. DOI:10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.01624 |
| [70] |
CHEN Y, HUANG G, ZHOU X, et al. Analytical coupled vibroacoustic modeling of membrane-type acoustic metamaterials: plate model.[J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2014, 136(6): 2926-2934. DOI:10.1121/1.4901706 |
| [71] |
KUMAR RS, RAY MC. Smart damping of geometrically nonlinear vibrations of functionally graded sandwich plates using 1–3 piezoelectric composites[J]. Mechanics of Compesite Materials and Structure, 2016, 23(6): 652-669. |
| [72] |
GHOSH S, AGRAWAL S, PRADHAN AK, et al. Performance of vertically reinforced 1-3 piezo composites for active damping of smart sandwich beams[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials, 2015, 17(3): 258-277. |
| [73] |
高海昌, 梅志远, 杨国威, 等. 夹层结构主动温控变阻尼振动控制技术[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(4): 816-823. DOI:10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190617.004 |
| [74] |
KHALILI S, BOTSHEKANAN dehkordi M, CARRERA E. A nonlinear finite element model using a unified formulation for dynamic analysis of multilayer composite plate embedded with sma wires[J]. Composite Structures, 2013, 106: 635-645. DOI:10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.07.006 |
| [75] |
周振龙, 梅志远, 徐嘉启, 等. 水下湍流激励复合材料板的振声特性研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(3): 105-112. |
| [76] |
杜圆, 李海超, 庞福振, 等. 任意边界条件下矩形板薄板自由振动特性分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(19): 70-76. DOI:10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2019.19.012 |
| [77] |
李秋红, 刘广明, 薛开, 等. 圆形薄板在任意弹性边界条件下的自由振动分析[J]. 船舶力学, 2015, 19(Z1): 162-168. |
| [78] |
曾军才, 王久法, 姚望, 等. 正交各向异性矩形板的自由振动特性分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2015, 34(24): 123-127,143. DOI:10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2015.24.021 |
| [79] |
QIN Zhaoye, CHU Fulei, ZU Jean. Free vibrations of cylindrical shells with arbitrary boundary conditions: A comparison study[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2017: 91−99.
|
| [80] |
BERRY A, GUYADER J L, NICOLAS J. A general formulation for the sound radiation from rectangular, baffled plates with arbitrary boundary conditions[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1990, 88(6): 2792−2802.
|
| [81] |
SONG Xuyuan, HAN Qingkai, ZHAI Jingyu. Vibration analyses of symmetrically laminated composite cylindrical shells with arbitrary boundaries conditions via Rayleigh–Ritz method[J]. Composite Structures, 2015, 134(DEC.): 820−830.
|
| [82] |
刘均, 程远胜. 考虑芯层离散特性的方形蜂窝夹层板自由振动分析[J]. 固体力学学报, 2009, 30(1): 90-94. DOI:10.19636/j.cnki.cjsm42-1250/o3.2009.01.016 |
| [83] |
LIU L, CAO D, SUN S. Vibration analysis for rotating ring-stiffened cylindrical shells with arbitrary boundary conditions[J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 2013, 135(6): 061010.
|
| [84] |
LIU X, BANERJEE J R. Free vibration analysis for plates with arbitrary boundary conditions using a novel spectral-dynamic stiffness method[J]. Computers & Structures, 2016, 164: 108−126.
|
| [85] |
HE Dongze, SHI Dongyan, WANG Qingshan, et al. Wave based method (WBM) for free vibration analysis of cross-ply composite laminated cylindrical shells with arbitrary boundaries[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 213(apr): 284−298.
|
| [86] | |
| [87] |
孙勇敢, 黎胜, 包振明. 弹性边界条件下弹性基础加筋板声辐射特性研究[J]. 噪声与振动控制, 2019, 16-23. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2019.01.004 |
| [88] |
MEJDI A, ATALLA N. Dynamic and acoustic response of bidirectionally stiffened plates with eccentric stiffeners subject to airborne and structure-borne excitations[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2010, 329(21): 4422−4439.
|
| [89] |
SANTONI A, SCHOENWALD S, FAUSTI P, et al. Modelling the radiation efficiency of orthotropic cross-laminated timber plates with simply-supported boundaries[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2019, 143: 112-124. DOI:10.1016/j.apacoust.2018.08.022 |
| [90] |
Documentation ABAQUS-6.14-1. Abaqus Documentation[Z], 2014.
|
| [91] |
张冠军, 朱翔, 李天匀, 等. 双层加筋板水下声振耦合特性研究[J]. 船舶力学, 2019, 23(1): 78-87. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2019.01.009 |
| [92] |
陈磊磊, 胡昊文, 张伟, 等. 水下结构振动特征值分析的有限元_边界元法研究[J]. 船舶力学, 2020, 24(9): 1196-1204. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2020.09.012 |
| [93] |
吴健, 何涛, 王纬波, 等. 基于Abaqus的舷间充水双层壳体水下声辐射计算方法验证[J]. 中国造船, 2019, 60(60): 175-184. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2019.01.017 |
| [94] |
吴健, 李泽成, 熊晨熙. 基于Abaqus的水下结构声辐射仿真方法[J]. 计算机辅助工程, 2015, 24(6): 37-41,65. DOI:10.13340/j.cae.2015.06.007 |
| [95] |
刘建良, 梅志远, 张焱冰, 等. 浮力材料和橡胶格栅夹层板振动响应试验对比研究[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2019, 14(4): 1-6,13. DOI:10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.01289 |
 2023, Vol. 45
2023, Vol. 45
