环肋圆柱壳在航空航天、船舶、机械、土木等工程领域具有广泛的应用,如何准确预报环肋圆柱壳的振动特性对该结构的减振降噪具有重要意义。目前,关于环肋圆柱壳振动特性分析方法主要包含解析法、数值法及模型试验。解析法在预报环肋圆柱壳振动特性中,环肋主要采用平摊法[1-2]、梁模型[3]和壳体模型[4-6]。以有限元为主的数值法分析中,模拟环肋的单元主要采用梁单元、而非壳体单元。文献[7]中对比采用Beam188和Shell181单元分析环肋圆柱壳自由振动时指出:2种环肋建模方法得到的环肋圆柱壳固有频率存在一定差异,且差异随着模态阶数增加而增加。尽管采用Beam188单元模拟环肋可使有限元建模过程大为简化,但实际工程中的环肋主要采用钢板。在此背景下,通过研究Ansys中采用Beam188单元和Shell181单元模拟环肋对圆柱壳振动特性影响、揭示2种建模方法差异将具有重要工程价值。
本文在Ansys中建立2种环肋圆柱壳模型,其差异主要在环肋分别采用Beam188单元和Shell181单元处理,通过分析不同边界条件、不同环肋类型(内环肋、对称环肋和外环肋)及不同环肋尺寸下2种环肋建模方法对圆柱壳固有频率、模态振型影响,研究2种环肋建模方法的异同。
1 结构有限元法应用有限元方法对环肋圆柱壳进行振动特性分析,其振动控制方程可表示为:
| $ {{M}}\ddot{\delta}+{{C}}\dot{\delta}+{{K}}\delta={{F}}{\text{。}} $ | (1) |
式中:
进行自由振动分析,对于工程中常用的钢等材料,可忽略阻尼的影响,并考虑结构作简谐振动时,式(1)可进一步简化为:
| $ \left({{K}}-\omega^{2}\boldsymbol{{M}}\right){\delta}={0}\text{。} $ | (2) |
式中:
在Ansys中建立环肋圆柱壳有限元模型并求解固有频率和模态振型,讨论2种环肋建模方法对圆柱壳自由振动特性影响。
2.1 模型说明圆柱壳半径、长度和厚度分别为3.5 m,9.6 m和0.03 m;矩形截面环肋的厚度和高度分别为0.03 m和0.3 m;壳体和环肋均由钢组成,其杨氏模量、密度和泊松比为2.1×1011 N/m2,7800 kg/m3和0.3。在Ansys 16.0中建立环肋圆柱壳有限元模型时,圆柱壳采用Shell181单元,环肋分别采用Beam188和Shell181两种单元。采用Beam188单元模拟环肋时,通过设置不同的偏心距以区分内环肋、对称环肋和外环肋,如图1所示。采用Shell181单元模拟环肋时,通过建立与环肋对应的圆环面后划分网格即可。

|
图 1 环肋圆柱壳有限元模型(Beam188) Fig. 1 Finite element models of ring stiffened cylindrical shell (Beam188) |
表1~表3分别给出了简支、固支和自由3种边界条件下不同环肋建模方法对圆柱壳固有频率影响。分析表中数据可知,3种边界条件下,采用Beam188和Shell181两种单元模拟环肋得到环肋圆柱壳固有频率均存在一定差异,且内、外环肋的差异明显高于对称环肋。此外,进一步分析表2中内环肋圆柱壳的固有频率可知,采用Beam188和Shell181模拟环肋时基频模态对应的周向模态数n不再一致,分别为3和2。
|
|
表 1 简支边界条件下环肋不同建模方法对固有频率影响(Hz) Tab.1 Effects of the modeling method of ring stiffeners on natural frequencies of the simply supported cylindrical shell (Hz) |
|
|
表 2 固支边界条件下环肋不同建模方法对固有频率影响(Hz) Tab.2 Effects of the modeling method of ring stiffeners on natural frequencies of the clamped cylindrical shell (Hz) |
|
|
表 3 自由边界条件下环肋不同建模方法对固有频率影响(Hz) Tab.3 Effects of the modeling method of ring stiffeners on natural frequencies of the free cylindrical shell (Hz) |
为进一步讨论2种环肋建模方法对圆柱壳固有振动特性的影响,图2对比了简支边界条件下模态振型(n=4, m=1)。结合表1中固有频率可知,尽管2种环肋建模方得到的固有频率差异显著,但圆柱壳的法向模态振型曲线完全重合,即表明不同环肋建模方法主要影响壳体固有频率、而对模态振型几乎无影响。进一步分析可知,外环肋时模态振型不再是光滑曲线、而存在明显波动,如图2(c)所示,即表明环肋作用导致圆柱壳模态振型发生变化。
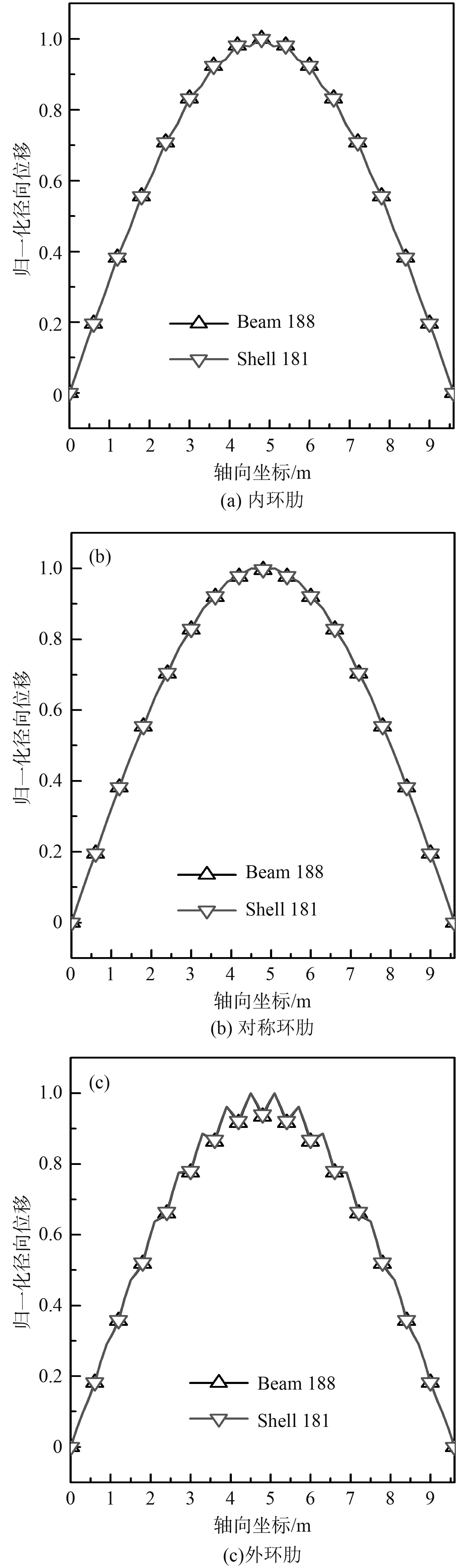
|
图 2 不同环肋建模方法对简支圆柱壳模态振型影响(n=4, m=1) Fig. 2 Effects of the method of modeling of ring stiffeners on mode shapes (n=4, m=1) |
为讨论不同环肋尺寸下2种环肋建模方法对圆柱壳固有振动特性影响,表4~表6对比了环肋高度为0.2m,0.3m和0.4m时内环肋、对称环肋和外环肋3种模型固有频率,表中环肋厚度保持不变、仅高度变化。分析可知,除少数几阶模态外,环肋高度为0.2 m时采用Beam188和Shell181单元模拟环肋得到的固有频率差异明显小于其他2种情况,且随着环肋高度增加采用Beam188和Shell181模拟环肋得到圆柱壳固有频率差异快速增加。另外,对于3种尺寸的环肋,采用Beam188和Shell181单元模拟对称环肋时差异整体上小于内环肋和外环肋。
|
|
表 4 不同环肋高度时环肋建模方法对固有频率影响(Hz, 内环肋) Tab.4 Effects of the modeling method of ring stiffeners on natural frequencies for the stiffeners with different height (Hz, interior) |
|
|
表 5 不同环肋高度时环肋建模方法对固有频率影响(Hz, 对称环肋) Tab.5 Effects of the modeling method of ring stiffeners on natural frequencies for the stiffeners with different height (Hz, concentric) |
|
|
表 6 不同环肋高度时环肋建模方法对固有频率影响(Hz, 外环肋) Tab.6 Effects of the modeling method of ring stiffeners on natural frequencies for the stiffeners with different height (Hz, exterior) |
除表4~表6给出的固有频率外,图3~图5分别给出了不同环肋高度下采用Beam188和Shell181单元模拟环肋时对圆柱壳模态振型影响。无论是内环肋、对称环肋还是外环肋,不同环肋尺寸时采用Beam188和Shell181模拟环肋时壳体模态振型曲线完全重合,此结论与图2中结论一致。进一步分析图5可知,随着环肋高度增加,图中曲线波动愈发显著。
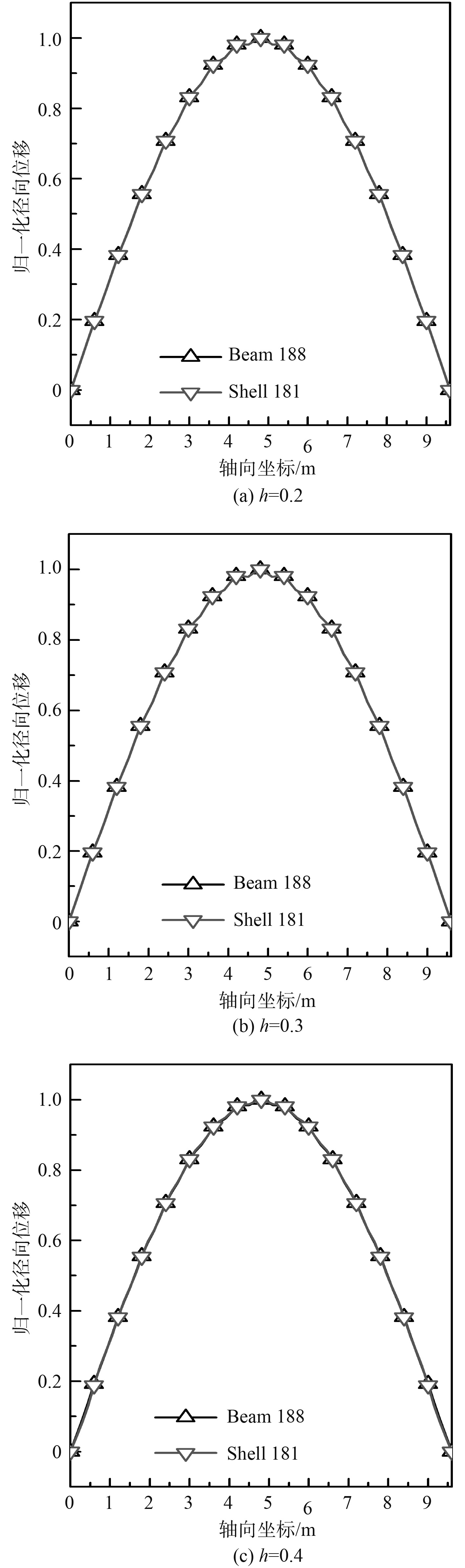
|
图 3 不同环肋高度时2种环肋建模方法对内环肋圆柱壳模态振型影响(n=4, m=1) Fig. 3 Effects of the modeling of ring stiffeners on mode shapes for the shell with interior rings of different height (n=4, m=1) |
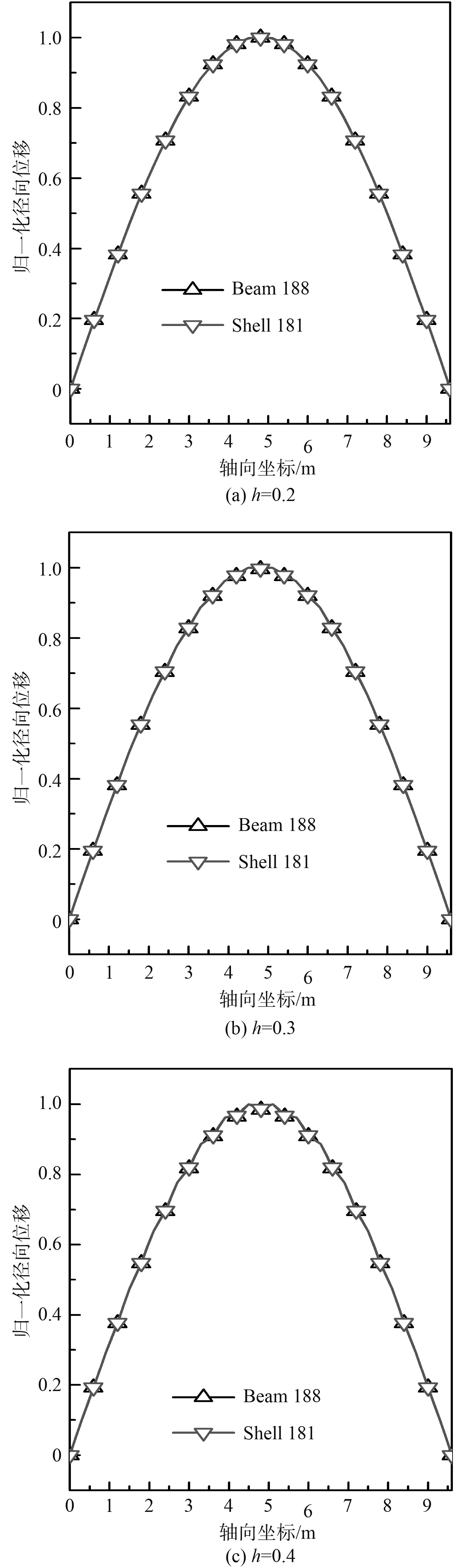
|
图 4 不同环肋高度时2种环肋建模方法对对称环肋圆柱壳模态振型影响(n=4, m=1) Fig. 4 Effects of the modeling of ring stiffeners on mode shapes for the shell with concentric rings of different height (n=4, m=1) |

|
图 5 不同环肋高度时2种环肋建模方法对外环肋圆柱壳模态振型影响(n=4, m=1) Fig. 5 Effects of the modeling of ring stiffeners on mode shapes for the shell with exterior rings of different height (n=4, m=1) |
为进一步讨论不同环肋尺寸对圆柱壳模态振型影响,图6对比了不同环肋高度对圆柱壳模态振型。分析图中结果可知,对于内环肋、外环肋及对称环肋,环肋高度增加后圆柱壳模态振型曲线波动愈发显著,且较小尺寸的环肋圆柱壳模态振型同样存在影响。进一步分析图中曲线可知,当内环肋变为对称环肋、外环肋时,增加环肋高度对圆柱壳模态振型影响显著增加。
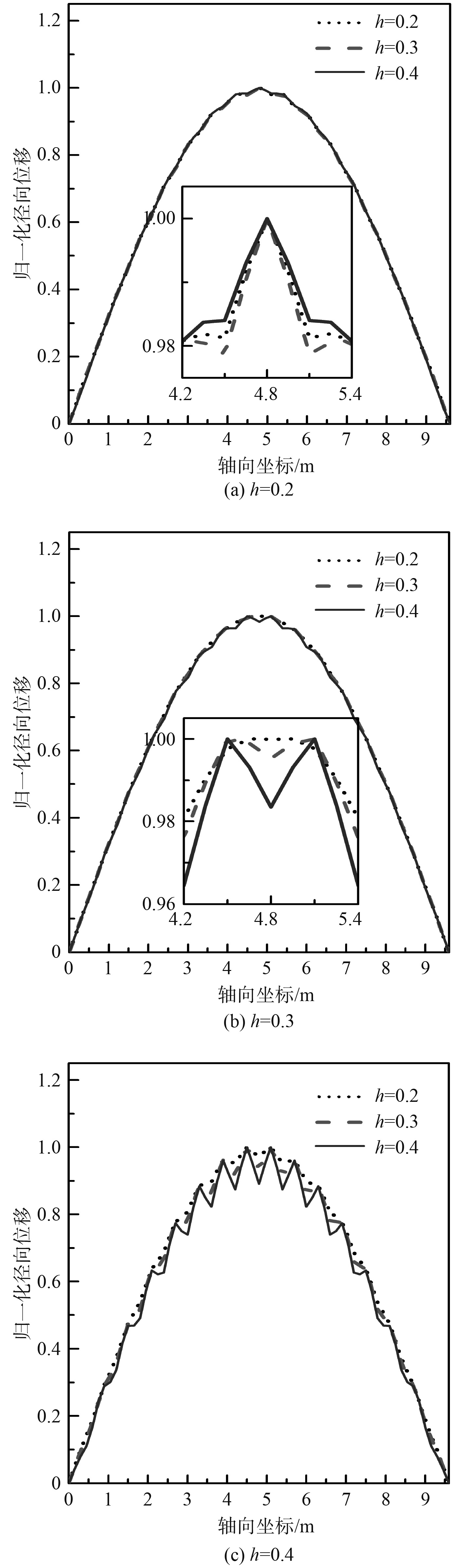
|
图 6 不同环肋高度对圆柱壳模态振型影响(n=4, m=1, Beam188) Fig. 6 Effects of the height of ring stiffeners on mode shapes (n=4, m=1, Beam188) |
本文研究Ansys中2种常见环肋建模方法(Beam188单元和Shell181单元)对计算环肋圆柱壳自由振动特性的影响,结果表明:
1)采用Beam188单元和Shell181单元模拟环肋时会导致环肋圆柱壳固有频率计算存在差异,且对称环肋差异明显小于内环肋和外环肋;
2)随着环肋截面高度增加,Beam188单元和Shell181单元得到的计算结果差异愈发显著;
3)尽管Beam188单元和Shell181单元会导致环肋圆柱壳固有频率计算存在差异,但2种环肋建模方法并不影响圆柱壳模态振型。
| [1] |
CARESTA M, KESSISSOGLOU N J. Structural and acoustic responses of a fluid-loaded cylindrical hull with structural discontinuities[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2009, 70(7): 954-963. DOI:10.1016/j.apacoust.2008.11.004 |
| [2] |
CARESTA M, KESSISSOGLOU N J. Acoustic signature of a submarine hull under harmonic excitation[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2010, 71(1): 17-31. DOI:10.1016/j.apacoust.2009.07.008 |
| [3] |
PAN Z, LI X, MA J. A study on free vibration of a ring-stiffened thin circular cylindrical shell with arbitrary boundary conditions[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 314(1): 330-342. |
| [4] |
XIE K, CHEN M, DENG N, et al. Free and forced vibration of submerged ring-stiffened conical shells with arbitrary boundary conditions[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2015, 96: 240-255. DOI:10.1016/j.tws.2015.08.013 |
| [5] |
WEI J, CHEN M, HOU G, et al. Wave based method for free vibration analysis of cylindrical shells with nonuniform stiffener distribution[J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics-Transactions of the ASME, 2013, 135(0610116). |
| [6] |
CHEN M, WEI J, XIE K, et al. Wave based method for free vibration analysis of ring stiffened cylindrical shell with intermediate large frame ribs[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2013, 20(3): 459-479. DOI:10.1155/2013/382589 |
| [7] |
谢坤. 纵向激励下桨-轴-艇耦合模型声振响应半解析计算方法及特性研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2018.
|
 2021, Vol. 43
2021, Vol. 43
