影响船舶动力的主要因素为船舶电力推进系统性能好坏和灵活程度等。船舶推进系统采用电动机带动船体螺旋桨推进船舶行驶。传统的电动机装置带有位置传感器,位置传感器的使用无疑增加经济成本,且噪声大,不易维护,运行条件苛刻等均影响船舶的稳定行驶和安全操作。为提高船舶的稳定性、可靠性等安全因素,采用无位置传感器永磁同步电机来带动螺旋桨以达到平稳推进船舶行驶。永磁同步电机(PMSM)具有结构简易、运行稳定等诸多优点[1],在高性能调速系统中得到了广泛的应用。国外对永磁同步电机无传感器控制技术的研究相对来说起步较早,M.L.Corley 和 R. D. Lorenz 等[2]率先从事无传感器控制研究,澳大利亚的 M. F. Rahman 教授、丹麦的 F. Blaabjerg 等相继在无传感器控制技术上做出相关研究成果。郭庆鼎等[3]在无传感器控制领域深入研究,并取得相应研究成果。
本文设计并实现了高频方波注入下的船舶电机控制系统。阐述高频方波注入船舶电机控制系统的结构,分析系统的控制策略和控制原理,并通过试验结果验证系统设计的有效性。
1 永磁同步电机数学模型建模时为计算简便,忽略铁芯的磁饱和,不计涡流损耗和磁滞损耗和无阻尼绕组[4]。
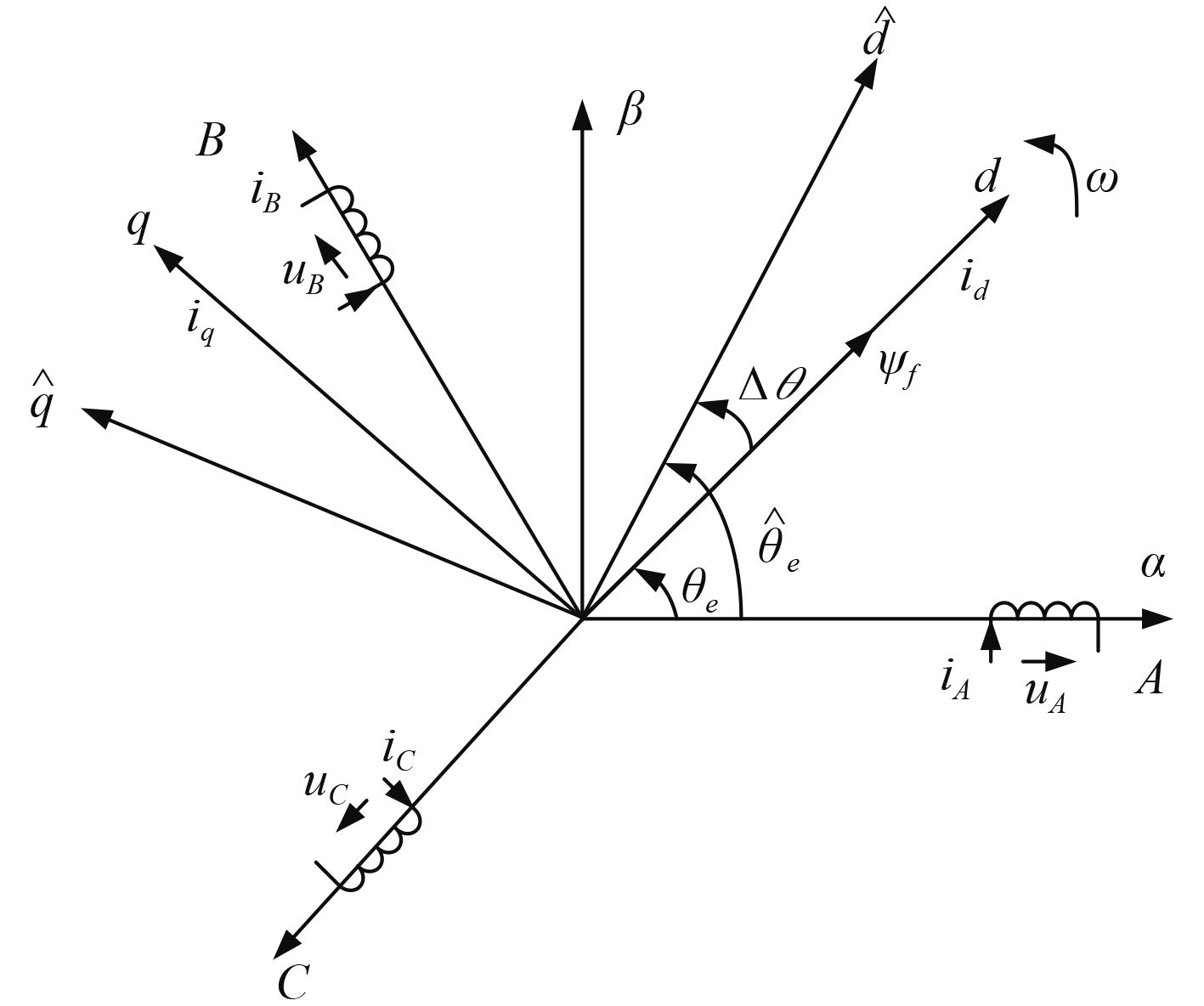
|
图 1 永磁同步电机矢量坐标及转子估计坐标系 Fig. 1 PMSM vector coordinates and rotor estimated coordinate system |
1)d-q 坐标系定子电压方程
| $\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{u_d}}\\{{u_q}}\end{array}} \right) = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{R_s} + p{L_d}\;\;\; - {\omega _e}{L_q}}\\{{\omega _e}{L_d}\;\;\;\;\;\;{R_s} + p{L_q}}\end{array}} \right)\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{i_d}}\\{{i_q}}\end{array}} \right) + \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}0\\{{\omega _e}{\psi _f}}\end{array}} \right)\text{。}$ | (1) |
2)定子磁链方程
| $\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{\psi _d}}\\{{\psi _q}}\end{array}} \right){\rm{ = }}\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{L_d}}&{{L_q}}\end{array}} \right)\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{i_d}}\\{{i_q}}\end{array}} \right){\rm{ + }}\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{\psi _f}}\\0\end{array}} \right)\text{。}$ | (2) |
式中:ud、uq,id、iq,Ld、Lq 分别为 d-q 坐标系中的电压分量、电流分量和电感分量;Rs 为定子电枢绕组的电阻;ωe 为转子的电角速度;Ψd,Ψq 为定子磁链;Ψf 为永磁体磁链。
3)转矩方程
| ${T_e} = \frac{3}{2}{n_p}\left( {{\psi _d}{i_q} - {\psi _q}{i_d}} \right)\text{。}$ | (3) |
4)运动方程
| ${T_m} = {T_e} + J\frac{{{\rm d}{\omega _e}}}{{{\rm d}t}}\text{。}$ | (4) |
式中:Te 为电磁转矩;np 为电机极对数;Te 为电磁转矩;J 为转动惯量。
5)高频注入电压电流方程
在转子坐标系的估计轴
| ${u_{dph}} = {L_{dq}}p{i_{dph}}\text{,}$ | (5) |
其中:
| ${L_{dq}} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{L_0} + {L_1}\cos 2(\mathop {{\theta _e}}\limits^ \wedge - {\theta _e})}&{{L_1}\sin 2(\mathop {{\theta _e}}\limits^ \wedge - {\theta _e})}\\{{L_1}\sin 2(\mathop {{\theta _e}}\limits^ \wedge - {\theta _e})}&{{L_0} - {L_1}\cos 2(\mathop {{\theta _e}}\limits^ \wedge - {\theta _e})}\end{array}} \right)\text{,}$ |
式中:
经 park 逆变换[5],高频励磁电压方程变换为:
| $\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{i_{\alpha h}}}\\{{i_{\beta h}}}\end{array}} \right) = \frac{V}{{{L_0} + {L_1}}}\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{\cos {\theta _e}}\\{\sin {\theta _e}}\end{array}} \right)\text{,}$ | (6) |
因电机转子位置信号为正值,所以需对高频响应电流进行符号一致化处理(即符号取正),再进行归一化[6] 得到如下高频响应电流:
| $\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{{i_{\alpha h}}}\\{{i_{\beta h}}}\end{array}} \right) = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{\cos {\theta _e}}\\{\sin {\theta _e}}\end{array}} \right)\text{。}$ | (7) |
利用锁相环[7] 对式(7)跟踪处理,估算出电机转子位置信号,进而估算出速度信号。
2 高频方波注入的船舶电机控制系统设计 2.1 永磁同步电机系统组成图 2 为永磁同步电机无位置传感器控制系统结构,系统由 PMSM、功率驱动、速度调节器、电流调节器、位置观测器组成。电流内环、速度环构成双闭环[8] 控制系统。位置观测器是基于高频方波信号注入估算转子位置和转速信号[9]。
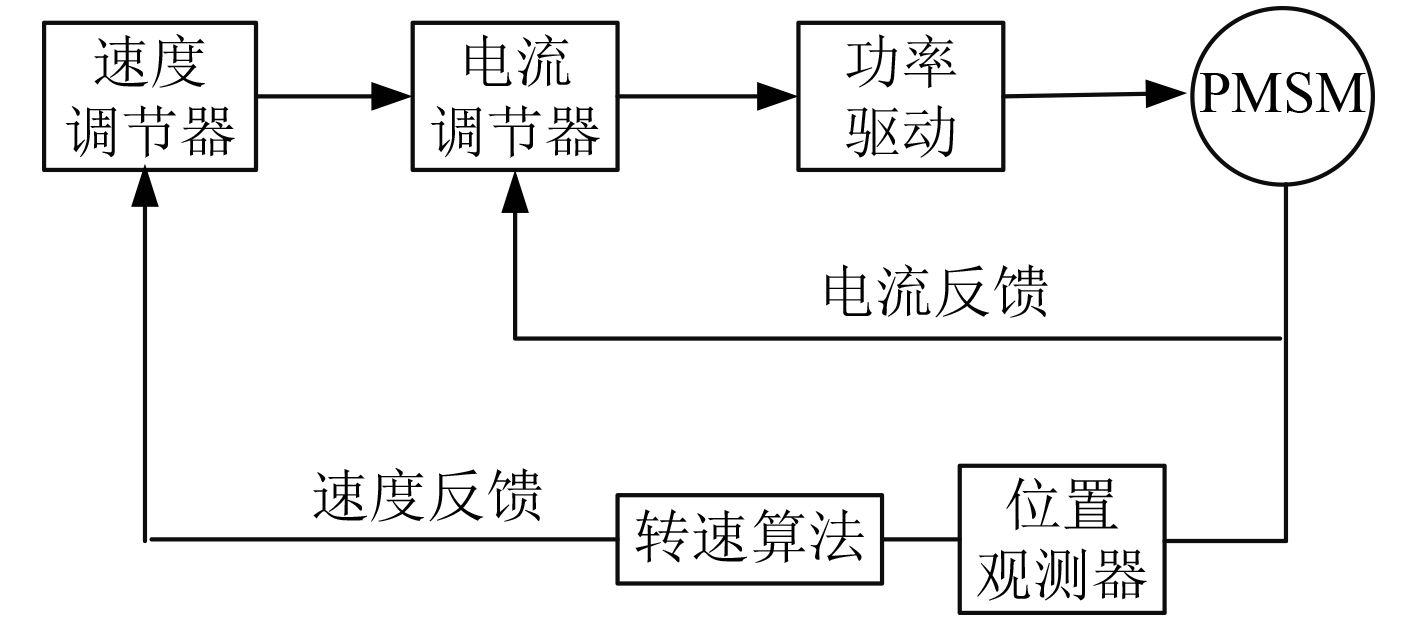
|
图 2 永磁同步电机无位置传感器控制系统框图 Fig. 2 PMSM sensor-less control system structure |
图 3为高频方波信号注入的系统原理框图。

|
图 3 高频方波信号注入的系统原理框图 Fig. 3 High frequency square wave signal injection system principle block diagram |
基于高频方波注入的船舶电机控制系统主要有主控模块,桨叶驱动模块驱动螺旋桨,驱动电机,控制电机,电源等。船舶电机控制结构框图如图 4所示。
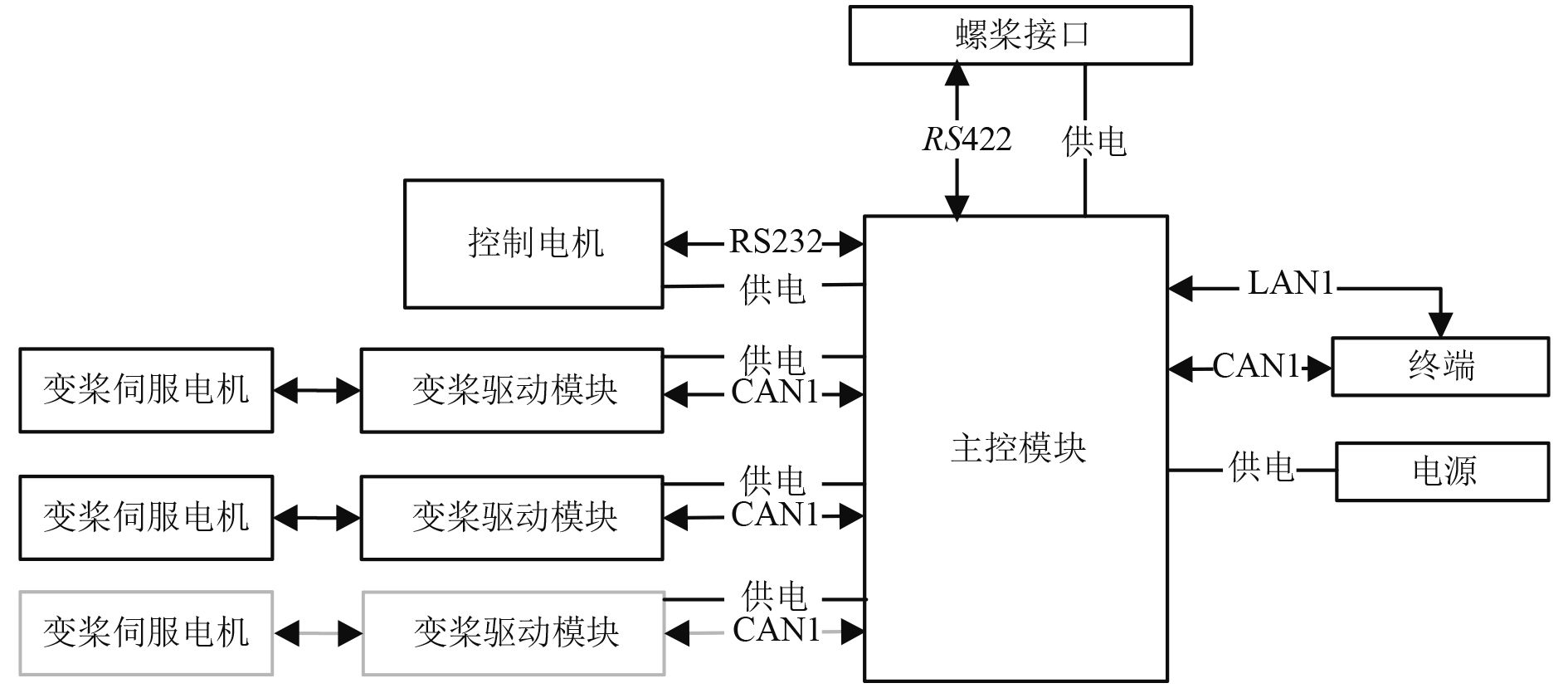
|
图 4 船舶电机控制结构框图 Fig. 4 Marine motor control structure |
本文采用永磁同步电机与谐波减速器配合的方法,结合矢量控制[10] 方法和 id = 0 的控制策略[11],电流、速度闭环控制实现高频方波注入下的船舶电机无位置传感器控制。
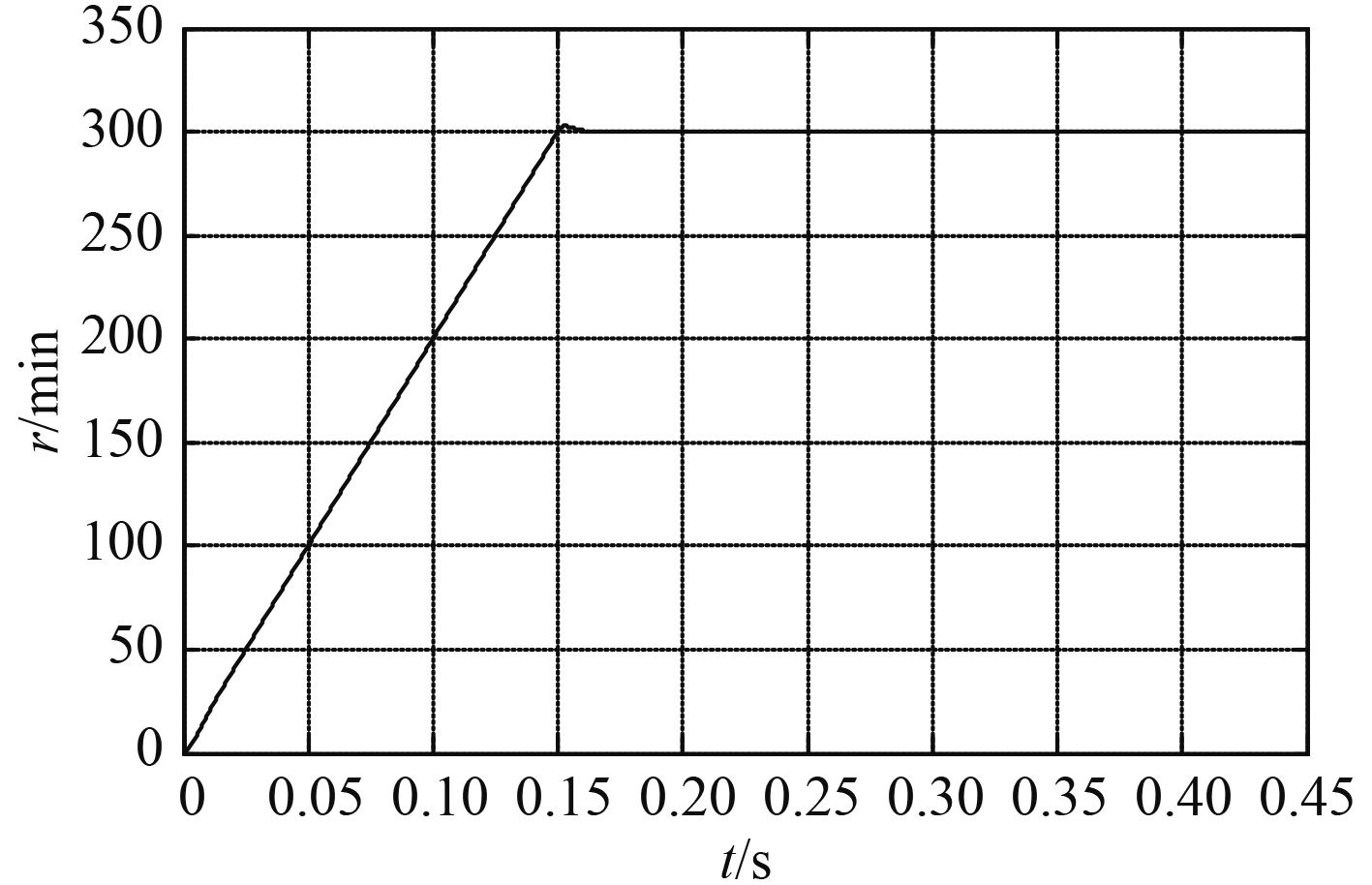
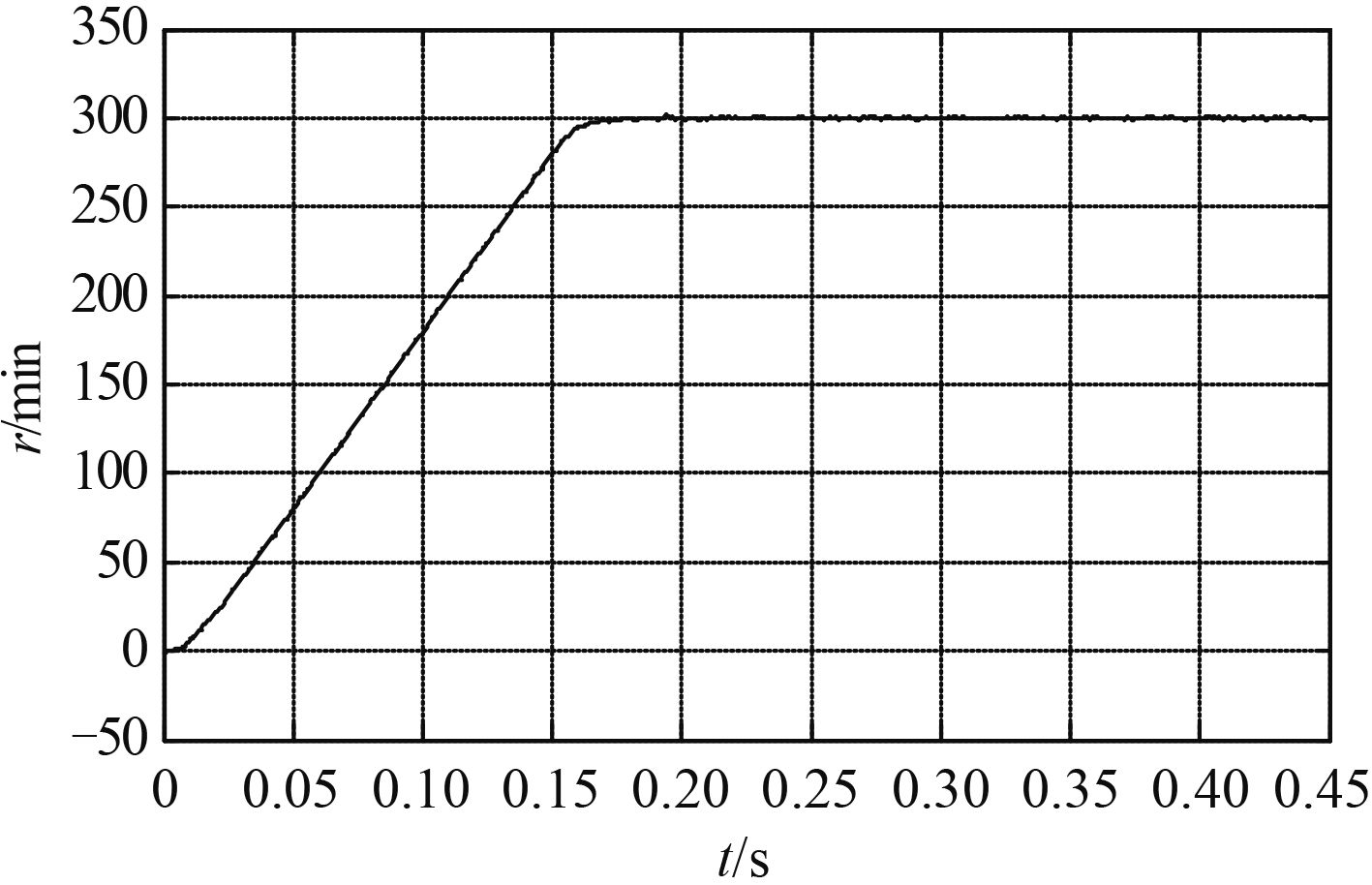
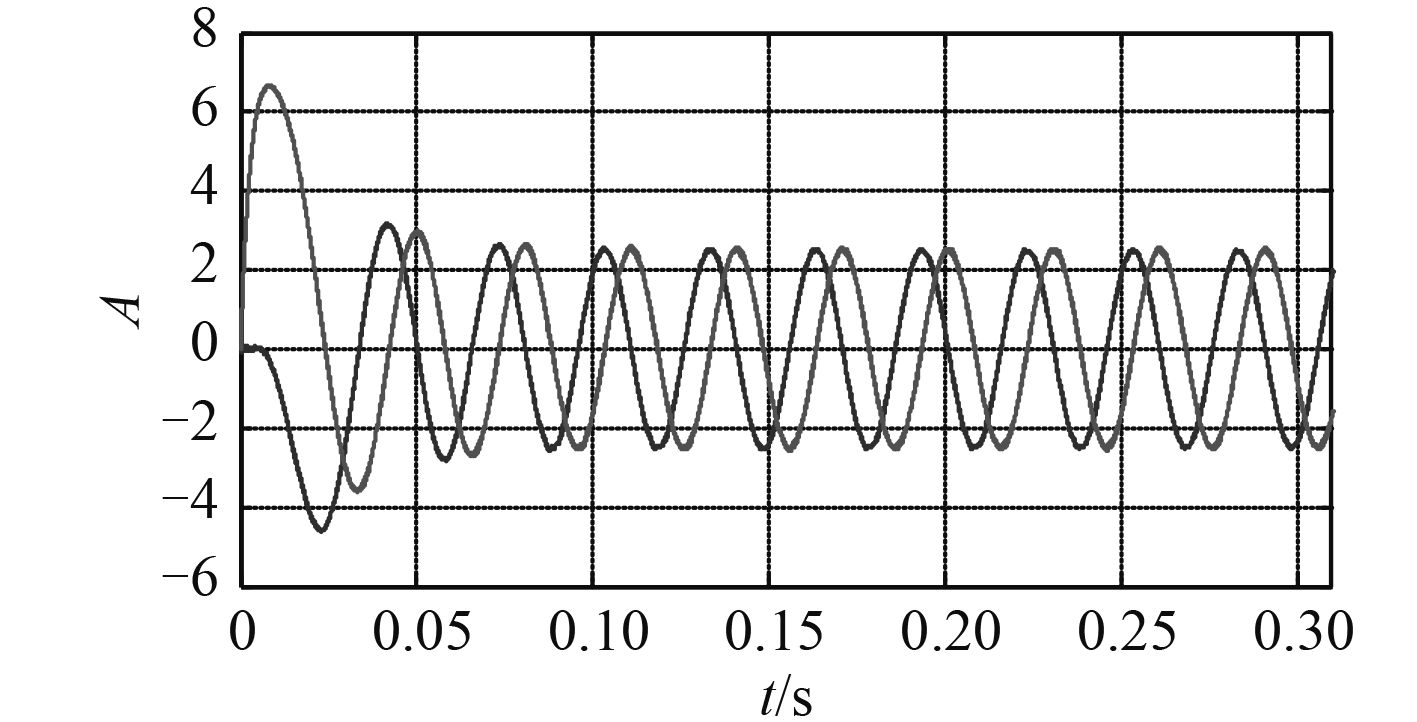
3 实验验证为验证高频方波注入的船舶电机无位置传感器控制系统的可靠性和有效性,在 Simulink 仿真环境[12] 下建立基于高频方波注入的永磁同步电机无位置传感器控制系统,采用 id = 0 矢量控制,电机参数选取为:R = 0.8 Ω,Ld = 0.008 H,Lq = 0.021 H,Ψf = 0.175 Wb,J = 0.000 46 kg·m2,极对数 Pn = 2,额定功率 PN = 1.4 kW,额定转速 n = 300 r/min。PI 控制器系数分别为 kp = 285,ki = 100。电机仿真模型如图 5所示;图 6为电机实际速度曲线,曲线较为平滑,电机由静止平滑运行至额定转速并稳定运行于额定转速 300 r/min 处;图 7为电机估计速度曲线, 估计转速曲线较为平滑,并与实际转速曲线相似接近,误差小,且运行稳定;图 8为定子电流波形,电机能顺利平稳启动,并快速启动至稳定状态;图 9为转子位置曲线;图 10为转子位置误差曲线。由图可以看出转子位置误差很小。
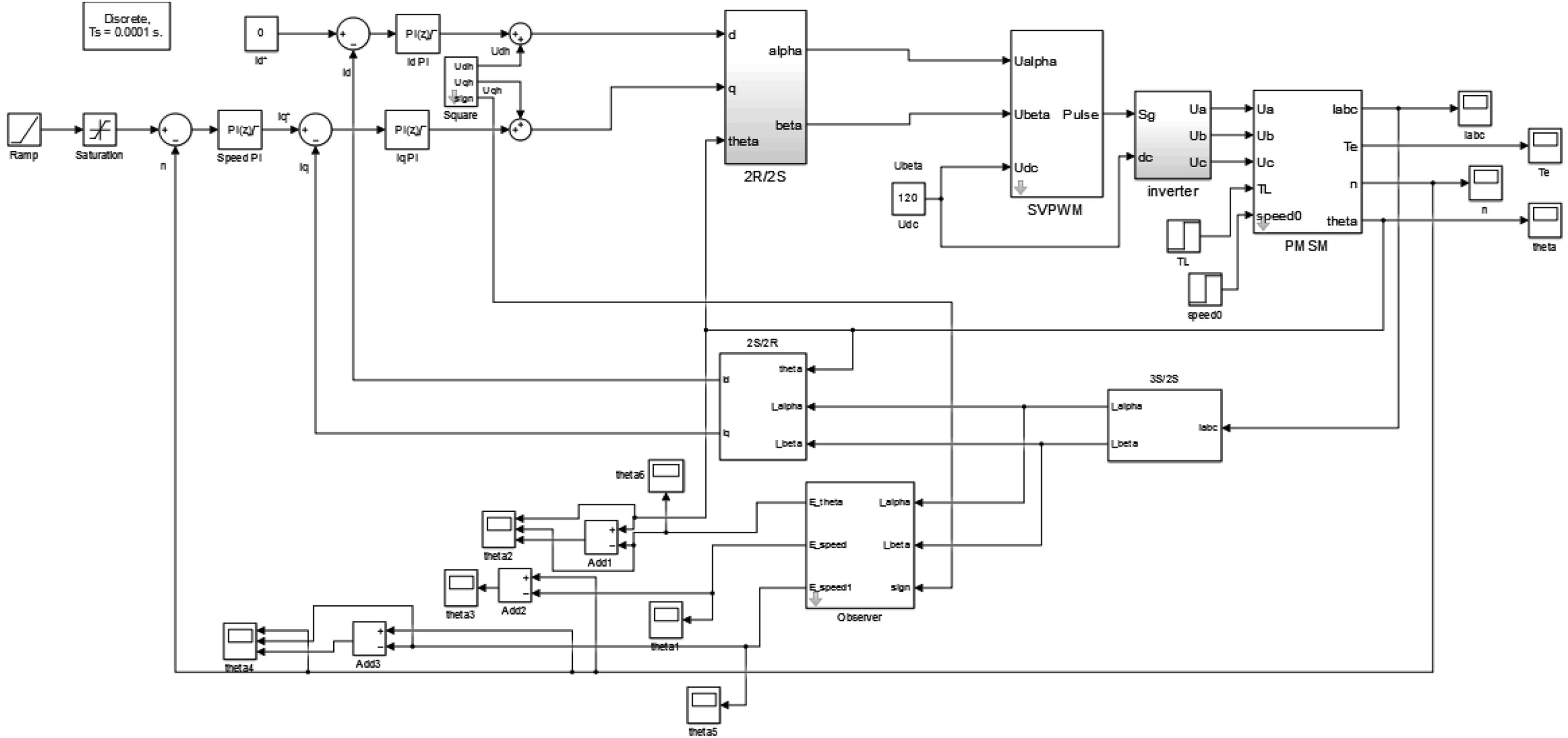
|
图 5 永磁同步电机的仿真模型 Fig. 5 Permanent magnet synchronous motor simulation model |
|
图 6 永磁同步电机的实际速度曲线 Fig. 6 Permanent magnet synchronous motor actual speed curve |
|
图 7 永磁同步电机的估计速度曲线 Fig. 7 Permanent magnet synchronous motor estimated speed curve |
|
图 8 永磁同步电机的定子电流波形 Fig. 8 Permanent magnet synchronous motor current curve |

|
图 9 永磁同步电机的转子位置曲线 Fig. 9 Permanent magnet synchronous motor position curve |

|
图 10 永磁同步电机的转子位置误差曲线 Fig. 10 Permanent magnet synchronous motor position error curve |
本文对船舶电机无位置传感器控制的研究得出以下结论:
1)采用高频方波注入法实现,缓解了位置延迟现象;
2)高频方波注入结合矢量控制 id = 0,电机控制系统启动平缓稳定;
3)与锁相环结合控制,提高系统估计精度。
以上证明了此方案的可行性。
| [1] |
金光哲, 徐殿国, 高强. 高频注入电压预估同步电机转子位置检测方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 09 : 1376–1383.
Jin Guangzhe, Xu Dianguo, Gao Qiang. A Synchronous Motor Rotor Position Detection Method Based on High-frequency Injection Voltage Prediction[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 09 : 1376–1383. |
| [2] | 王高林, 杨荣峰, 李刚. 基于高频信号注入的IPMSM无位置传感器控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2012, 11 : 62–68. |
| [3] | 周扬忠, 龙世鹏. 基于转子高频脉动电流注入的同步电动机无位置传感器型直接转矩控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 01 : 223–230. |
| [4] |
朱喜华, 李颖晖, 张敬. 基于一种新型滑模观测器的永磁同步电机无传感器控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2010, 13 : 6–10.
Zhu Xihua, LI Yinghui, Zhang Jing. Sensorless Control of PMSM Based on a Novel Sliding Mode Observer[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2010, 13 : 6–10. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3415.2010.01.002 |
| [5] | 王志新, 林环城, 陆斌锋. 脉振高频电压注入PMSM凸极特性实验检测研究[J]. 电机与控制应用, 2015, 03 : 20–24. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6540.2015.07.005 |
| [6] | 周恒. 基于空间矢量PWM控制的永磁同步电机驱动系统的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2012. |
| [7] |
张杰, 柴建云, 孙旭东. 双三相异步电机反相高频注入无速度传感器控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 23 : 6162–6171.
Zhang Jie, Chai Jianyun, Sun Xudong. Sensorless Control of Dual Three Phase Induction Machines by Antiphase High Frequency Signal Injection[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 23 : 6162–6171. |
| [8] |
李华阳, 王涛, 林环城. 基于高频注入的PMSM无传感器控制的误差分析[J]. 微特电机, 2013, 11 : 64–70.
Li Huayang, Wang Tao, Lin Huancheng. Analysis of Position Errors in High Frequency Carrier Signal Injection Based Sensorless Control of PMSM[J]. Small & Special Electrical Machines, 2013, 11 : 64–70. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7018.2013.06.018 |
| [9] |
彭亚为, 杜彬, 陈娟. 基于Ackermann公式的滑模控制设计方法[J]. 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 04 : 128–133.
Peng Yawei, Du Bin, Chen Juan. Sliding Mode Control Design Method Based on Ackermann Formula[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2011, 04 : 128–133. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4628.2011.04.026 |
| [10] |
周大鹏, 张自友. 基于卡尔曼和改进滑模观测器的永磁电机无位置控制[J]. 中国测试, 2013, 03 : 104–107.
Zhou Dapeng, Zhang Ziyou. Sensorless Control of PMSM Based on Improved Sliding Mode Observer and Kalman Filter[J]. China Measurement and Test, 2013, 03 : 104–107. |
| [11] |
谢红普, 李宏, 郑勇. 基于状态观测器的永磁同步电动机超低速控制[J]. 微特电机, 2011, 10 : 48–51.
Xie Hongjin, Li Hong, Zheng Yong. Ultra-Low Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on State Observer[J]. Micro Motor, 2011, 10 : 48–51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7018.2011.03.015 |
| [12] |
刘纯金, 梁晖. 交流同步发电机无位置传感器矢量控制[J]. 电力电子技术, 2009, 07 : 26–27+65.
Liu Chunjin, Liang Hui. AC Synchronous Generator Sensorless Vector Control[J]. Power Electronics, 2009, 07 : 26–27+65. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-100X.2009.03.011 |
 2017, Vol. 39
2017, Vol. 39
