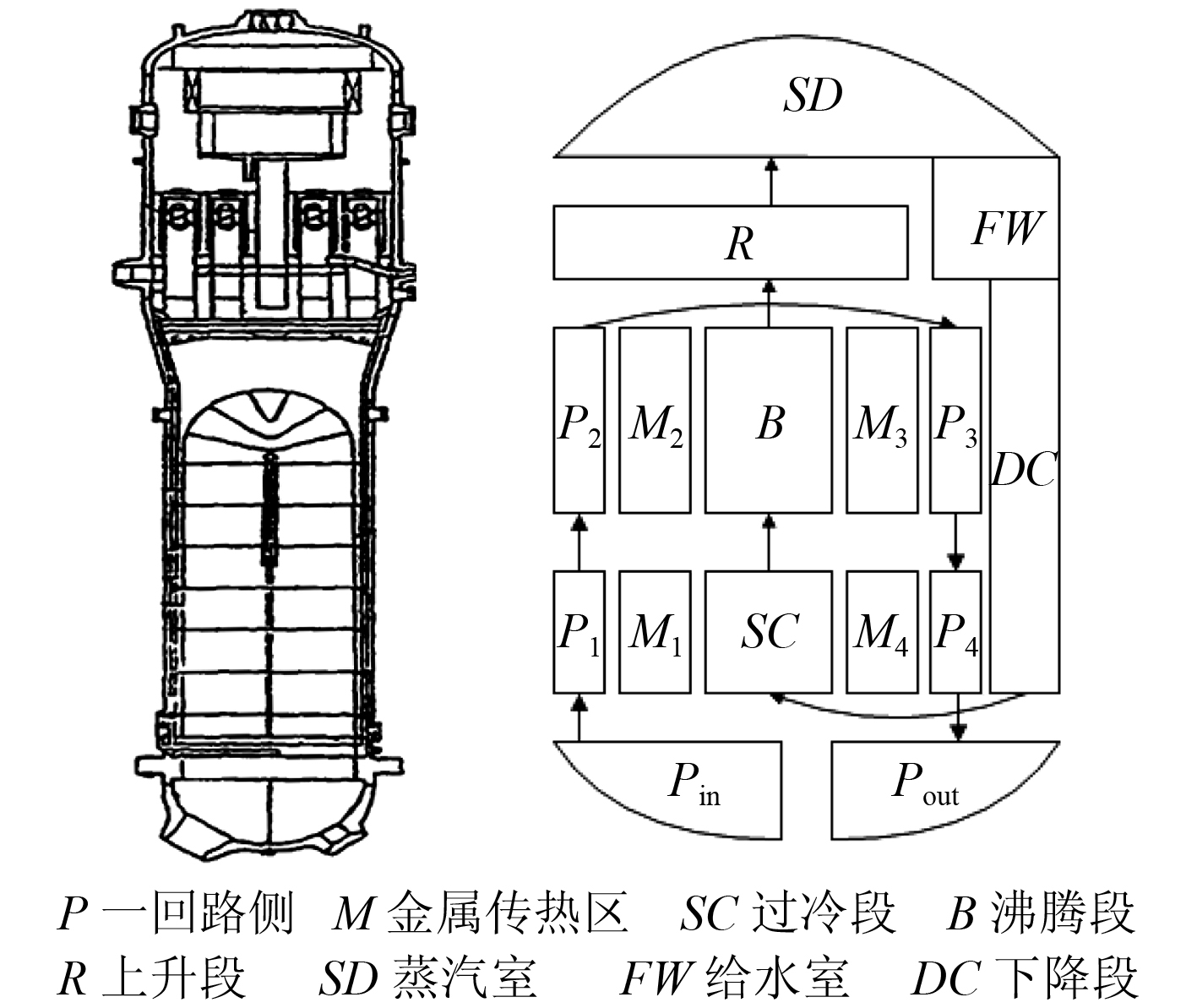
立式自然循环蒸汽发生器是目前核电站与舰船核动力系统中常用的一种蒸汽发生器,结构如图 1 所示,这种蒸汽发生器具有如下特点:传热管呈倒 U 型,套筒将蒸汽发生器二次侧隔离成上升通道和下降通道,给水经位于上筒体的给水管进入后与同汽水分离器分离出的再循环水混合,一起进入下降通道,经套筒底部的缺口进入上升通道在二次侧的循环回路中,下降段流动的是单向过冷水,上升通道流动的温度较高的汽水混合物,在统一系统压力下,两者密度差形成自然循环的驱动力。
蒸汽发生器是核动力系统中一二回路的枢纽,它的运行特性对舰船核动力装置有重大的影响。为了对蒸汽发生器的动态特性进行研究需要准确建立蒸汽发生器的数学模型。目前国内外发展的蒸汽发生器热工水力瞬态分析模型主要有均相流模型[1]与漂移流模型[2],均相流具有简单、在低含汽率时具有较高的准确性等特点;漂移流模型是对均相流的发展,考虑了汽液两相流动时的相互作用与影响,涉及到众多两相流经验公式,模型准确与否取决于经验公式的选取,由于舰船用核动力系统中蒸汽发生器的大部分工况的含汽率比较低,故采用均相流模型。
1 蒸汽发生器简介立式自然循环蒸汽发生器主要由一回路水室、管板、U 型管束、汽水分离器和筒体构成。蒸汽发生器外壳由上下 2 个筒体构成,直径不同,中间由锥形过渡,上端为椭球形上封头,其顶端中心为主蒸汽出口,下端为球形封头,该封头与管板相连,构成一回路水室。一回路管板采用低合金钢锻造,球形封头采用低合金钢或锻件冲压制造。U 型管束上有支撑板,管束周围装有套筒将筒,体与管束隔开分为上升及下降通道。管束与套筒上方安装有汽水分离器[3]。
2 蒸汽发生器数学模型 2.1 蒸汽发生器数学模型模块划分建立该模型的目的主要是解决水位控制问题,为了便于分析将蒸汽发生器划分为一回路侧和二回路侧,其中一回路侧为双流程结构,划分为冷却剂入口室、冷却剂第Ⅰ流程、过渡室、冷却剂第Ⅱ流程、冷却剂出口室;二回路侧根据流体在 U 型管内的流动和传热特性分为给水室、下降段、过冷段、上升段、蒸汽空间,如图 1 所示。
|
图 1 蒸汽发生器建模结构 Fig. 1 The model structure of steam generator |
采用机理建模[4 –5]方法建立蒸汽发生器模型[6 –8],建模时假设一回路侧认为流体不可压缩,只能建立能量平衡方城,流通的横截面积不变;二回路侧把上升段两相流问题简化,认为工质比焓和密度可以用平均值表示,认为两相流体为蒸汽与水的单纯混合物,蒸汽干度是垂直距离的线性函数;忽略动态过程中蒸汽区和给水腔空间的传热和传质;忽略下降段与上升段的热交换;忽略蒸汽发生器的排污。
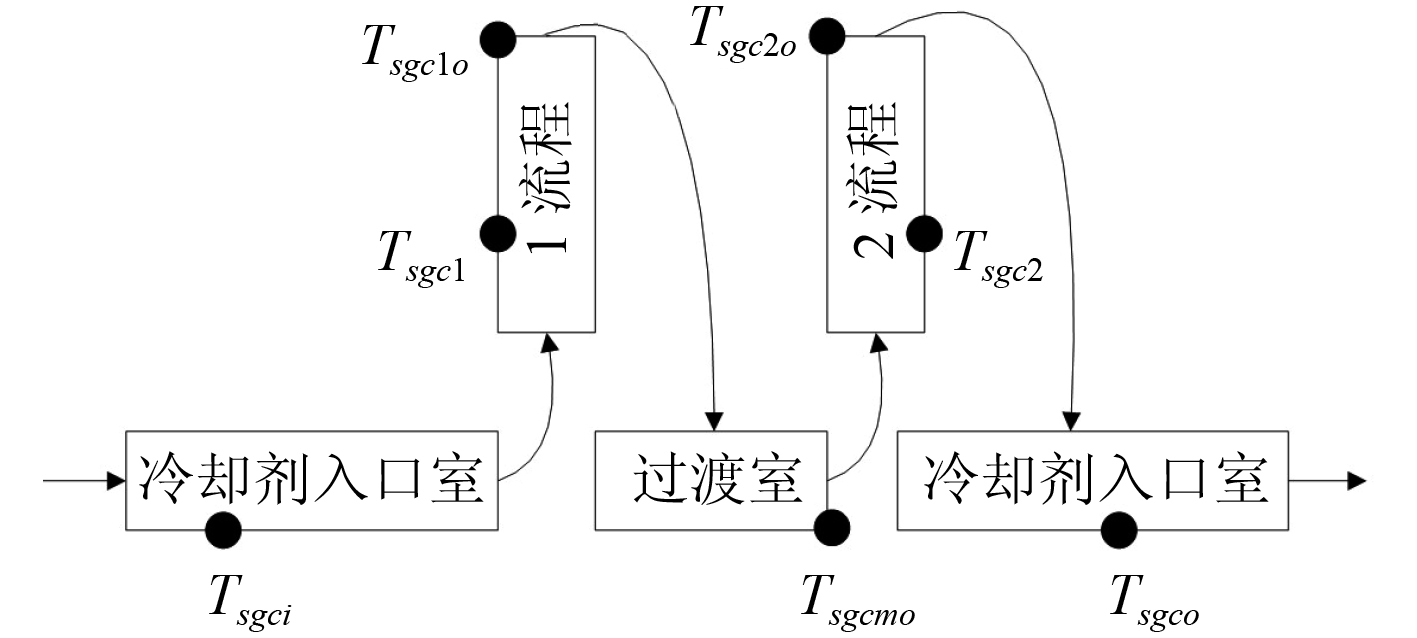
2.3 蒸汽发生器一次侧数学模型在建立模型时对通用符号作以下约定:C 为比热,F 为流通截面积,G 为质量流量,h 为比焓,L 为水位,M 为质量,P 为压力,q 为热流密度,Q 为换热量,T 为温度,τ 为时间,V 为体积,x0 为蒸汽干度,ρ 为密度,UF 为等效换热系数,fw 为给水,fwv 为给水室,wd 为下降段,bv 为沸腾段,ph 为预热段,sgs 为蒸汽空间,se 为汽水分离器,ξ 为阻力系数,sgc 为冷却剂,0 为稳态值,sgpa 为平均值,sgc1 为冷却剂第Ⅰ流程,sgc2 冷却剂第Ⅱ流程,sgci 为冷却剂入口室,sgco 为冷却剂入口室,sgm 为换热管,sgmc1o 为冷却剂第Ⅰ流程出口,sgmc2o 为冷却剂第Ⅱ流程出口,sgmcmo 为冷却剂过渡室出口。
对一回路侧各段列出以下能量平衡方程:
冷却剂入口室:
| ${(MC)_{sgci}}\frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgci}}}}{{\rm{d}\tau }} = \frac{1}{2}{G_{sgc}}{C_{sgc}}({T_{sgci}} - {T_{sgc1}}) \text{;}$ | (1) |
冷却剂Ⅰ流程:
| $\begin{array}{l}\displaystyle{(MC)_{sgc1}}\frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgc1}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = \frac{1}{2}{G_{sgc}}{C_{sgc}}({T_{sgci}} - {T_{sgc1}}) - \\[5pt]{(UF)_{sgc1}}({T_{sgc1}} - {T_{sgm1}})\text{,}\\[5pt]\displaystyle {(MC)_{sgm1}}\frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgm1}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = {(UF)_{sgc1}}({T_{sgc1}} - {T_{sgm1}}) - \\[5pt]{(UF)_{sgp1}}({T_{sgm1}} - {T_{sgpa}}) - {(UF)_{sgs1}}({T_{sgm1}} - {T_s})\text{;}\end{array} $ | (2) |
过渡室:
| ${(MC)_{sgc2}}\frac{{ {\rm d}}{T_{sgcmo}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = \frac{1}{2}{G_{sgc}}{C_{sgc}}({T_{sgc1o}} - {T_{sgcmo}}) \text{;}$ | (3) |
冷却剂Ⅱ流程:
| $\begin{array}{l}\displaystyle{(MC)_{sgc2}}\frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgc2}}}}{{\rm{d}\tau }} = \frac{1}{2}{G_{sgc}}{C_{sgc}}({T_{sgcmo}} - {T_{sgc2}}) - \\[5pt] \displaystyle {(UF)_{sgc2}}({T_{sgc2}} - {T_{sgm2}})\text{,}\\[5pt]\displaystyle{(MC)_{sgm2}}\frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgm2}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = {(UF)_{sgc2}}({T_{sgc2}} - {T_{sgm2}}) - \\[5pt]\displaystyle {(UF)_{sgp2}}({T_{sgm2}} - {T_{sgpa}}) - {(UF)_{sgs2}}({T_{sgm2}} - {T_s}) \text{;} \end{array}$ | (4) |
冷却剂出口室:
| ${(MC)_{sgco}}\frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgco}}}}{{\rm{d}\tau }} = \frac{1}{2}{G_{sgc}}{C_{sgc}}({T_{sgc2o}} - {T_{sgco}}) \text{。}$ | (5) |
对于蒸汽发生器一次侧温度的含义如图 2 所示,图中温度点取在各段中间的为该段温度的平均值,取在各段末端的为该段出口温度。在求平均温度时下式成立:
| ${T_{sgc2o}}{\rm{ = }}2{T_{sgc2}} - {T_{sgcmo}},{T_{sgc1o}} = 2{T_{sgc1}} - {T_{sgc{i}}}\text{。}$ | (6) |
|
图 2 一回路冷却剂温度示意图 Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of primary system coolant temperatures |
蒸汽发生器的二次侧模型包括动力学方程与动力学方程,动力学方程包括二回路各段的质量平衡方程、能量平衡方程,运动学方程主要体现了工质运动时下降通道与上升通道流体重力压头与阻力相平衡的特性。
给水腔:
| $\begin{array}{l}\displaystyle \frac{{{\rm d}{M_{fwv}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = {G_{fw}} + \left( {1 - {x_0}} \right){G_{bvo}} - {G_{wd}}\text{,}\\[5pt]\displaystyle L = {L_{wd}} + {M_{fwv}}/({\rho _{fwv}}{F_{fwv}})\frac{{\rm d}}{{{\rm d}\tau }}\left( {{M_{fwv}}{h_{fwv}}} \right) = \\[5pt]{G_{fw}}{h_{fw}} + (1 - {x_0}){G_{bvo}}h' - {G_{wd}}{h_{fwv}}\text{;}\end{array}$ | (7) |
下降段:
| $\begin{array}{l}\displaystyle \frac{{\rm d}}{{{\rm d}\tau }}\left( {{M_{wd}}{h_{wdo}}} \right) = {G_{wd}}({h_{fwv}} - {h_{wdo}})\text{,}\\[5pt]{M_{wd}} = {V_{wd}}{\rho _{wd}} \text{;}\end{array} $ | (8) |
预热段:
| $\begin{array}{l}\displaystyle\frac{{\rm d}}{{{\rm d}\tau }}\left( {{L_{ph}}{F_r}{\rho _{ph}}{h_{ph}}} \right) = {G_{wd}}\left( {{h_{wdo}} - h'} \right) + {Q_{ph}}{Q_{ph}} = \\[5pt]{(UF)_{sgp1}}({T_{sgm1}} \!-\! {T_{sgma}})\! +\! {(UF)_{sgp2}}({T_{sgm2}}\!\! -\! {T_{sgpa}}) \text{;}\!\!\end{array}$ | (9) |
沸腾段:
| $\begin{array}{l}\displaystyle \frac{{\rm d}}{{{\rm d}\tau }}\left( {{V_{bv}}{\rho _{bv}}} \right) = {G_{wd}} - {G_{bvo}}\text{,}\\[5pt]{V_{bv}} \!=\! ({L_h} - {L_{ph}}){F_r}\text{,}\\[5pt]\displaystyle {V_{bv}}\frac{{\rm d}}{{{\rm d}\tau }}\left( {{\rho _{bv}}{h_{bv}}} \right)\! =\! {G_{wd}}h' - {G_{bvo}}{h_{bvo}} + {Q_{bh}}\text{,}\\[5pt]{Q_{bh}}\!\! =\! \!{(UF)_{sgs1}}({T_{sgm1}}\! - \!{T\!_s}) \!\!+\! {(UF)_{sgs2}}({T_{sgm2}} \!-\! {T_s}) \text{;}\!\!\end{array}$ | (10) |
蒸汽区:
| $\begin{array}{l}\displaystyle \frac{{\rm d}}{{{\rm d}\tau }}\left( {{V_{SGS}}\rho ''} \right) = {G_{bvo}} - {G_s}/2 - (1 - {x_0}) \cdot {G_{bvo}}\text{,}\\[5pt]{V_{sgs}} = {V_{sgs0}} + ({L_0} - L) \cdot {F_{fwv}} \text{;}\end{array} $ | (11) |
工质的运动方程为:
| $\begin{array}{l}\displaystyle \left[ {{\zeta _d}\left( {\frac{1}{{F_{wd}^2{\rho _{wd}}}} + \frac{1}{{F_{fwv}^2{\rho _{fwv}}}}} \right) + {\zeta _{ph}}\left( {\frac{1}{{F_r^2{\rho _{ph}}}}} \right)} \right]\frac{{G_{wd}^2}}{{2g}} + \\[8pt]\displaystyle \left( {{\zeta _{bv}}\frac{1}{{F_r^2{\rho _{bv}}}} + {\zeta _{se}}\frac{1}{{F_{se}^2{\rho _{bvo}}}}} \right)\frac{{G_{bvo}^2}}{{2g}} + \left( {\frac{{L - {L_{wd}}}}{{{F_{fwv}}g}} + \frac{{{L_{wd}}}}{{{F_{wd}}g}} + \frac{{{L_{ph}}}}{{{F_r}g}}} \right)\\[8pt]\displaystyle \frac{{{\rm d}{G_{wd}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} + \left( {\frac{{{L_{bh}}}}{{{F_r}g}} + \frac{{{L_{se}}}}{{{F_{se}}g}}} \right)\frac{{{\rm d}{G_{bvo}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = \left( {L - {L_{wd}}} \right){\rho _{fwv}} + \\[8pt]{L_{wd}}{\rho _{wd}} - {L_{ph}}{\rho _{ph}} - {L_{bh}}{\rho _{bh}} - {L_{se}}{\rho _{bvo}}\text{。}\qquad\qquad\qquad (12)\end{array} $ | (12) |
一次侧模型方程比较简单,经整理后是 7 个一阶微分方程,二次方程比较复杂,要对二次侧方程进行推导,首先考虑建立模型时的假设,假设沸腾段工质干度随空间容积线性变化,有如下方程成立:
| $\displaystyle re = 1 + \frac{{\rho '}}{{\rho ''}}{x_0}, {\rho _{bv}} = \frac{{\rho ''}}{{{x_0}}}\ln re, {\rho _{bvo}} = \frac{{\rho ''}} {\displaystyle {{1 + {x_0}\frac{{\rho '}}{{\rho ''}}}}}\text{,}$ | (13) |
综合以上 3 式,对时间求导数,经推导可得:
| $\frac{{{\rm d}{\rho _{bv}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = (\frac{{re{\rho _{bv}} - \rho '}}{{re\rho ''}})\frac{{{\rm d}\rho ''}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} + (\frac{{\rho ' - re{\rho _{bv}}}}{{{x_0}re}})\frac{{{\rm d}{x_0}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }}\text{,}$ | (14) |
又因为沸腾段工质包括水与水蒸汽,考虑到模型推导时的假设,焓值为水的焓值与蒸汽焓值的平均值,对焓值求时间的导数可得:
| $\begin{array}{l}{h_{bv}} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {h' + {x_0}h'' + (1 - {x_0})h'} \right)\text{,}\\[5pt] \displaystyle \frac{{{\rm d}{h_{bv}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = \frac{{{\rm d}h'}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} + \frac{{{x_0}}}{2}\left( {\frac{{{\rm d}h''}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} - \frac{{{\rm d}h'}}{{{\rm d}\tau }}} \right) + \frac{{h'' - h'}}{2}\frac{{{\rm d}{x_0}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }}\text{。}\end{array}$ | (15) |
得出沸腾段工质密度、比焓随时间的变化率就可以对其他方程化简,经整理,蒸汽发生器二次侧模型包括 5 个一阶微分方程:
| $\begin{split}\\[-14pt]& \displaystyle \left( {{\rho _{fwv}} + \frac{{1 - {x_0}}}{{{x_0}}}\rho ''} \right){F_{fwv}}\frac{{{\rm d}L}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} - \frac{{1 - {x_0}}}{{{x_0}}} \cdot {V_{SGS}} \cdot \\& \quad\quad\quad \displaystyle \frac{{{\rm d}\rho ''}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}} \cdot \frac{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = {G_{fw}} + \frac{{1 - {x_0}}}{{2{x_0}}}{G_s} - {G_{wd}}\text{,}\\& \displaystyle \left( {{V_{bv}}(\frac{{re{\rho _{bv}} - \rho '}}{{re\rho ''}}) + \frac{{{V_{SGS}}}}{{{x_0}}}} \right) \cdot \frac{{{\rm d}\rho ''}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}} \cdot \frac{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} - \frac{{{F_{fwv}}\rho ''}}{{{x_0}}} \times \\ & \quad\quad \displaystyle \frac{{{\rm d}L}} {{{\rm d}\tau }}+ {V_{bv}}(\frac{{\rho ' - re{\rho _{bv}}}}{{{x_0}re}})\frac{{{\rm d}{x_0}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = {G_{wd}} - \frac{1}{{2{x_0}}}{G_s}\text{。}\end{split}$ | (16) |
| $\begin{split}\\[-12pt]\displaystyle {F\!_{fwv}}& \left( {{\rho _{fwv}} \cdot {h_{fwv}} \!+\! \frac{{1 \!-\! {x_0}}}{{{x_0}}}\rho ''h'} \right)\frac{{{\rm d}L}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} \!\!-\! \frac{{1 - {x_0}}}{{{x_0}}}{V_{SGS}}\\& \displaystyle h'\frac{{{\rm d}\rho ''}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}} \cdot \frac{{\rm{d}{p_s}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} + {\rho _{fwv}} \cdot {F_{fwv}}\left( {L - {L_{wd}}} \right)\frac{{{\rm d}{h_{fwv}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = \\& \displaystyle {G_{fwv}}{h_{fwv}} + \frac{{1 - {x_0}}}{{2{x_0}}}{G_s}h' - {G_{wd}}{h_{fwv}}\\& \displaystyle {M_{wd}}\frac{{{\rm d}{h_{wd0}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = {G_{wd}}\left( {{h_{fwv}} - {h_{wd0}}} \right)\text{。}\end{split}$ | (17) |
| $\begin{split}& \left\{ \begin{array}{l}\displaystyle\!\! {\!\!V_{bv}}{\rho _{bv}}\left[ {\frac{{{\rm d}h'}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}\!\!+\!\! \frac{{{x_0}}}{2}\left( {\frac{{{\rm d}h''}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}\! -\! \frac{{{\rm d}h'}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}} \right)}\! \right] \!+\! \frac{1}{2}{l_{ph}}{F_r}{\rho _{ph}}\frac{{{\rm d}h'}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}\!\!\\\displaystyle +\left[ {{V_{bv}}{h_{bv}}(\frac{{re{\rho _{bv}} - \rho '}}{{re\rho ''}}) + \frac{{{V_{SGS}}}}{{{x_0}}}{h_{bvo}}} \right] \cdot \frac{{{\rm d}\rho ''}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}\end{array} \right\} \cdot \\& \quad\quad\displaystyle \frac{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} - \frac{{\rho ''{F_{fwv}}}}{{{x_0}}}{h_{bvo}}\frac{{{\rm d}L}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} + \frac{1}{2}{L_{ph}}{F_r}{\rho _{ph}}\frac{{{\rm d}{h_{wdo}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} + \\& \quad\quad \displaystyle {V_{bv}}\left[ {{h_{bv}}(\frac{{\rho ' - re{\rho _{bv}}}}{{{x_0}re}}) + \frac{1}{2}{\rho _{bv}}\left( {h'' - h'} \right)} \right]\frac{{{\rm d}{x_0}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = \\& \quad\quad \displaystyle {G_{wd}}{h_{wdo}} - \frac{1}{{2{x_0}}}{G_s}{h_{bvo}} + Q\text{。}\end{split}\!\!\!\!$ | (18) |
对于蒸汽发生器二次侧的对流传热计算采用大空间泡核沸腾放热处理,计算时采用 Kutateraze 推荐的公式:
| $Nu = A\mathop {Pr}\limits_f^{{n_1}} P_e^{{n_2}}K_p^{{n_3}}K_t^{{n_4}}\text{,}$ | (19) |
其中
| $\begin{aligned}& \displaystyle Nu = \frac{\alpha }{{{\lambda _f}}}\sqrt {\frac{\sigma }{{g\left( {{\rho _f} - {\rho _g}} \right)}}} \text{,}\\& \displaystyle {P_e} = \frac{q}{{{h_{fg}}{\rho _g}{\alpha _f}}}\sqrt {\frac{\sigma }{{g\left( {{\rho _f} - {\rho _g}} \right)}}} \text{,}\\& \displaystyle {K_p} = \frac{p}{{\sqrt {\sigma \rho \left( {{\rho _f} - {\rho _g}} \right)} }}\text{,}\\& \displaystyle {K_t} = \frac{{{{\left( {{h_{fg}}{\rho _g}} \right)}^2}}}{{{\rho _f}{c_{p,f}}{T_s}\sqrt {\sigma \rho \left( {{\rho _f} - {\rho _g}} \right)} }}\text{。}\end{aligned}$ | (20) |
式中:P 为饱和液体压力 ,N/m2;αf 为液体热扩散率, m2/s;经验常数A = 7.0 × 10–4;n1 = –0.35;n2 = 0.7;n3 = 0.7;n4 = 0;Nu 为努谢尔特数;Pr 为普朗特数。
3.2 模型计算将蒸汽发生器一次侧模型的 7 个方程与二次侧模型的 5 个方程联立可得导独立的 12 个一阶微分方程,可以求解 12 个独立变量,包括一次侧的冷却剂入口室平均温度Tsgci ,冷却剂Ⅰ流程平均温度Tsgc 1,冷却剂Ⅰ流程换热管平均温度Tsgm 1,冷却剂过渡室出口温度Tsgcmo ,冷却剂Ⅱ流程平均温度Tsgc 2,冷却剂Ⅱ流程换热管平均温度Tsgm 2,冷却剂出口室平均温度Tsgco ,二次侧压力ps ,水位L,给水室工质焓值hfwv ,下降段出口焓值hwdo 。
取向量
| $\begin{array}{l}X = ({T_{sgci}},{T_{sgc1}},{T_{sgm1}},{T_{sgcmo}},{T_{sgc2}},\\[5pt]{T_{sgm2}},{T_{sgco}},{p_s},L,{x_0},{h_{fwv}},{h_{wdo}}{)^{\rm{T}}}\text{,}\\[5pt]\displaystyle \frac{{{\rm d}X}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = (\frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgci}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }},\frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgc1}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }},\frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgm1}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }},\frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgcmo}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }},\frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgc2}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }},\\[10pt]\displaystyle \frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgm2}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }},\frac{{{\rm d}{T_{sgco}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }},\frac{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }},\frac{{{\rm d}L}}{{{\rm d}\tau }},\frac{{{\rm d}{x_0}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }},\frac{{{\rm d}{h_{fwv}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }},\frac{{{\rm d}{h_{wdo}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }}{)^{{\rm d}}}\text{,}\end{array}$ | (21) |
该蒸汽发生器模型可以表示为:
| $A = \left[ {\frac{{\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}{{E_{11}}} & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & {{E_{22}}} & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & {{E_{33}}} & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & 0 & {{E_{44}}} & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & {{E_{55}}} & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & {{E_{66}}} & 0\\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & {{E_{77}}}\end{array}}}{{\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \\0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \\0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \\0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \\0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \end{array}}}\left| {\frac{{\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: \\0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \\0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \\0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \\0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \\0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \\0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0 & \: \: 0\end{array}}}{{\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}{{C_{11}}} & {{C_{12}}} & 0 & 0 & 0\\{{C_{21}}} & {{C_{22}}} & {{C_{23}}} & 0 & 0\\{{C_{31}}} & {{C_{32}}} & 0 & {{C_{34}}} & 0\\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & {{C_{45}}}\\{{C_{51}}} & {{C_{52}}} & {{C_{53}}} & 0 & {{C_{55}}} \text{,}\end{array}}}} \right.} \right]\text{。}$ | (22) |
其中
| $\begin{array}{l}\! {E_{11}}\!\! = \!\!{(MC)_{sgci}}, {E_{22}} \!\!=\!\! {(MC)_{sgc1}}, {E_{33}} \!\!=\!\! {(MC)_{sgm1}}\text{,}\!\!\\[5pt]\! {E_{44}} \!\!=\!\! {(MC)_{sgcmo}}\text{,}\!\!\!\!\!{E_{55}}\!\! =\!\! {(MC)_{sgc2}}\text{,}\!\!\!\!\!\!{E_{66}}\!\! =\! {(MC)_{sgm2}}\text{,}\\[5pt]\! {E_{77}} = {(MC)_{sgco}},\end{array}$ | (23) |
| $\begin{split}\\[-12pt]& \displaystyle{C_{11}} = - \frac{{1 - {x_0}}}{{{x_0}}} \cdot {V_{SGS}} \cdot \frac{{\rm{d}\rho ''}}{{\rm{d}{p_s}}}\text{,}\\[-1pt]& \displaystyle{C_{12}} = {K_{z12}} = \left( {{\rho _{fwv}} + \frac{{1 - {x_0}}}{{{x_0}}}\rho ''} \right){F_{fwv}}\text{,}\\[-1pt]& \displaystyle{C_{21}} = \left( {{V_{bv}}(\frac{{re{\rho _{bv}} - \rho '}}{{re\rho ''}}) + \frac{{{V_{SGS}}}}{{{x_0}}}} \right) \cdot \frac{{\rm{d}\rho ''}}{{\rm{d}{p_s}}} {C_{22}} = - \frac{{{F_{fwv}}\rho ''}}{{{x_0}}}\text{,}\\[-1pt]& \displaystyle {C_{23}} = {V_{bv}}(\frac{{\rho ' - re{\rho _{bv}}}}{{{x_0}re}}), {C_{31}} = - \frac{{1 - {x_0}}}{{{x_0}}}{V_{SGS}}h'\frac{{\rm{d}\rho ''}}{{\rm{d}{p_s}}}\text{,}\\[-1pt]& \displaystyle {C_{32}} = {F_{fwv}}\left( {{\rho _{fwv}} \cdot {h_{fwv}} + \frac{{1 - {x_0}}}{{{x_0}}}\rho ''h'} \right)\text{,}\\[-1pt]& \displaystyle {C_{34}} = {\rho _{fwv}} \cdot {F_{fwv}}\left( {L - {L_{wd}}} \right), {C_{45}} = {M_{wd}}\text{,}\qquad\qquad\quad\:\:(24)\end{split}$ | (24) |
| $\begin{aligned}& {C_{51}}\!\! =\!\! \left\{ \begin{array}{l}\displaystyle {V_{bv}}{\rho _{bv}}\left [ {\frac{{{\rm d}h'}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}} + \frac{{{x_0}}}{2}\left( {\frac{{{\rm d}h''}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}} - \frac{{{\rm d}h'}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}} \right)} \right]\!\!\\ + \left[ \begin{array}{l}\displaystyle {V_{bv}}{h_{bv}}(\frac{{re{\rho _{bv}} - \rho '}}{{re\rho ''}})\!\!\\ \displaystyle + \frac{{{V_{SGS}}}}{{{x_0}}}{h_{bvo}}\end{array} \right] \displaystyle \cdot \frac{{{\rm d}\rho ''}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}\!\!\\ \displaystyle + \frac{1}{2}{l_{ph}}{F_r}{\rho _{ph}}\frac{{{\rm d}h'}}{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}\end{array} \right\}\displaystyle \cdot \frac{{{\rm d}{p_s}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }}\text{,}\\& \displaystyle {C_{52}} = - \frac{{\rho ''{F_{fwv}}}}{{{x_0}}}{h_{bvo}}\text{,} \displaystyle {C_{55}} = \frac{1}{2}{L_{ph}}{F_r}{\rho _{ph}}\text{,}\\& \displaystyle {C_{53}} = {V_{bv}}\left[ {{h_{bv}}(\frac{{\rho ' - re{\rho _{bv}}}}{{{x_0}re}}) + \frac{1}{2}{\rho _{bv}}\left( {h'' - h'} \right)} \right]\text{,}\quad\qquad(25)\end{aligned}$ | (25) |
B
为时变矩阵,包含参变量的非线性项。
| $\begin{aligned}& {B_1} \!=\! \left[ \!\!{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}\displaystyle {\frac{1}{2}{G_{sgc}}{C_{sgc}}({T_{sgci}} - {T_{sgc1}})}\\[8pt] \displaystyle \!\!\!{\frac{1}{2}{G_{sgc}}{C_{sgc}}({T_{sgci}} - {T_{sgc1}}) - {{(UF)}_{sgc1}}({T_{sgc1}} - {T_{sgm1}})}\\[8pt] \displaystyle \begin{array}{l}\displaystyle {(MC)_{sgm1}}\frac{{d{T_{sgm1}}}}{{{\rm d}\tau }} = {(UF)_{sgc1}}({T_{sgc1}} - {T_{sgm1}}) - \\[8pt]\displaystyle {(UF)_{sgp1}}({T_{sgm1}} - {T_{sgpa}}) - {(UF)_{sgs1}}({T_{sgm1}} - {T_s})\end{array}\\[8pt]\displaystyle {\frac{1}{2}{G_{sgc}}{C_{sgc}}({T_{sgc1o}} - {T_{sgcmo}})}\\[8pt]\displaystyle {\frac{1}{2}{G_{sgc}}{C_{sgc}}({T_{sgcmo}} - {T_{sgc2}}) - {{(UF)}_{sgc2}}({T_{sgc2}} - {T_{sgm2}})}\\[8pt]\begin{array}{l}\displaystyle {(UF)_{sgc2}}({T_{sgc2}} - {T_{sgm2}}) - {(UF)_{sgp2}}({T_{sgm2}} - {T_{sgpa}})\\[8pt]\displaystyle - {(UF)_{sgs2}}({T_{sgm2}} - {T_s})\end{array}\\[8pt]\displaystyle \!\!{\frac{1}{2}{G_{sgc}}{C_{sgc}}({T_{sgc2o}} - {T_{sgco}})}\end{array}}\!\! \right]\text{,}\\[8pt]& {B_2} = \left[ \displaystyle {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}\displaystyle {{G_{fw}} + \frac{{1 - {x_0}}}{{2{x_0}}}{G_s} - {G_{wd}}}\\[8pt]\displaystyle {{G_{wd}} - \frac{1}{{2{x_0}}}{G_s}}\\[8pt]\displaystyle {{G_{fwv}}{h_{fwv}} + \frac{{1 - {x_0}}}{{2{x_0}}}{G_s}h' - {G_{wd}}{h_{fwv}}}\\[8pt]\displaystyle {{G_{wd}}\left( {{h_{fwv}} - {h_{wd0}}} \right)}\\[8pt]\displaystyle {{G_{wd}}{h_{wdo}} - \frac{1}{{2{x_0}}}{G_s}{h_{bvo}} + Q}\end{array}} \right]\text{。}\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad(26) \end{aligned}$ | (26) |
求解蒸汽发生器的动态特性,采用 4 阶变步长 Runge-Kutta 法,并采用面向对象的方法,用 VC++6.0 开发了蒸汽发生器类。
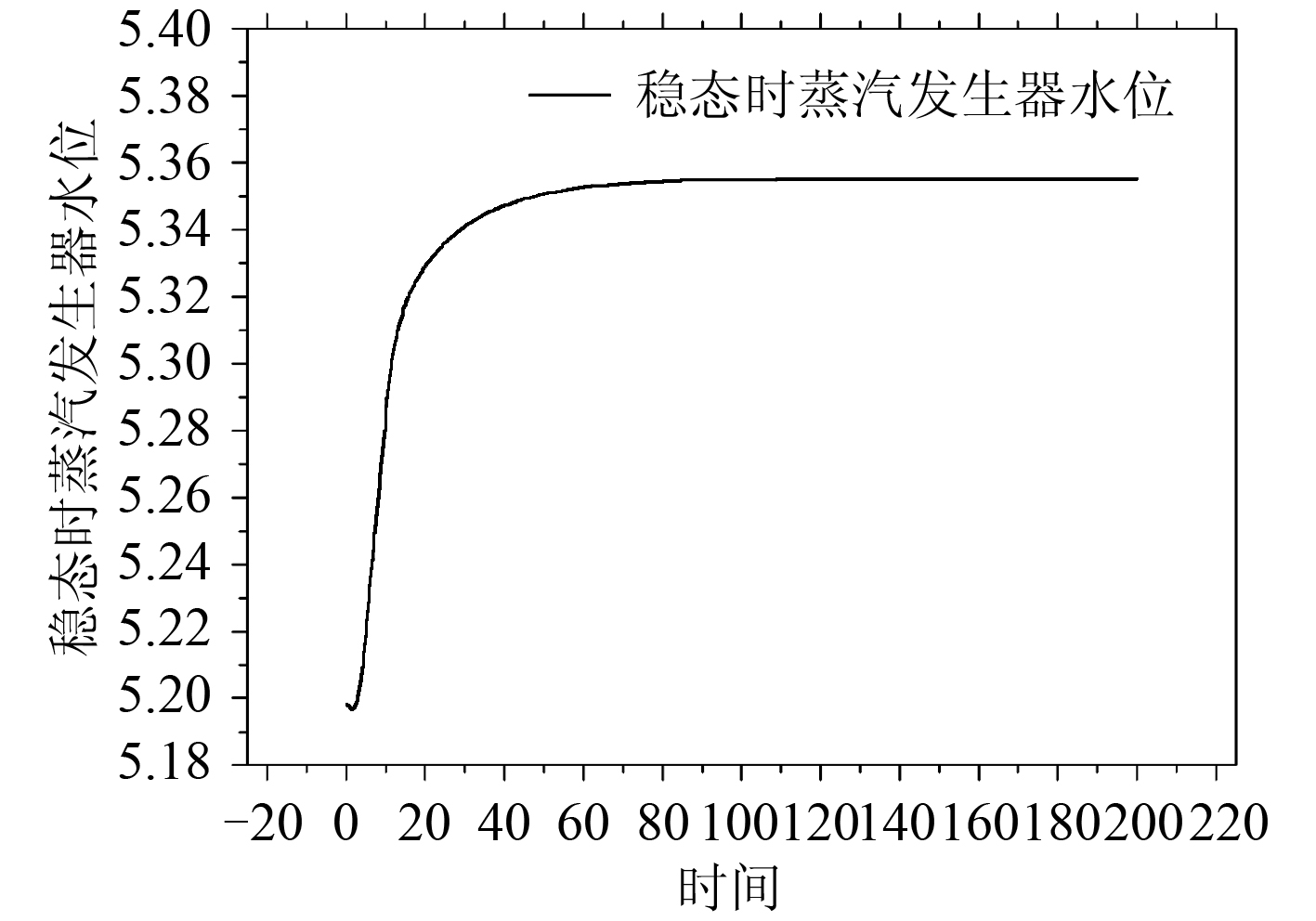
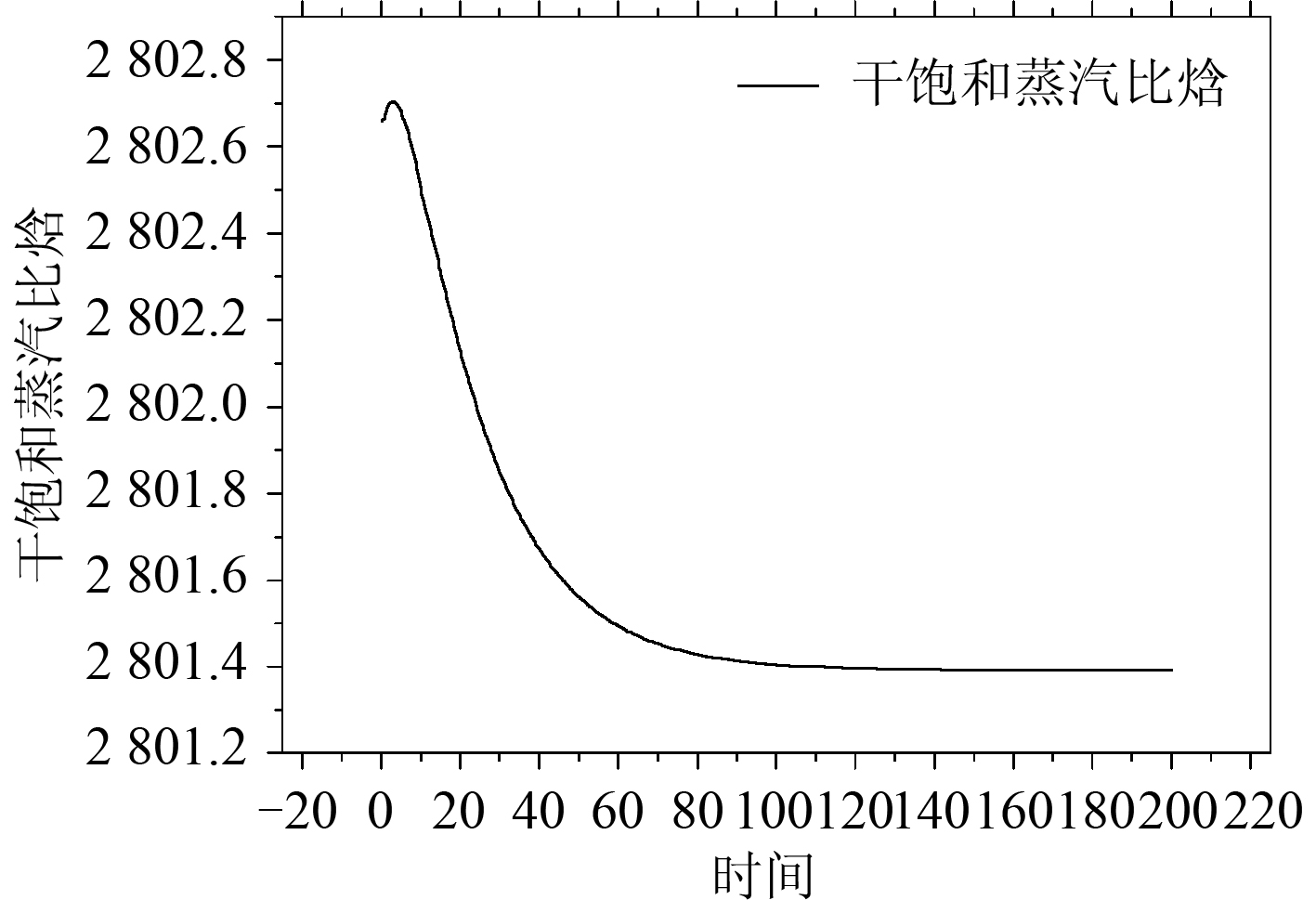
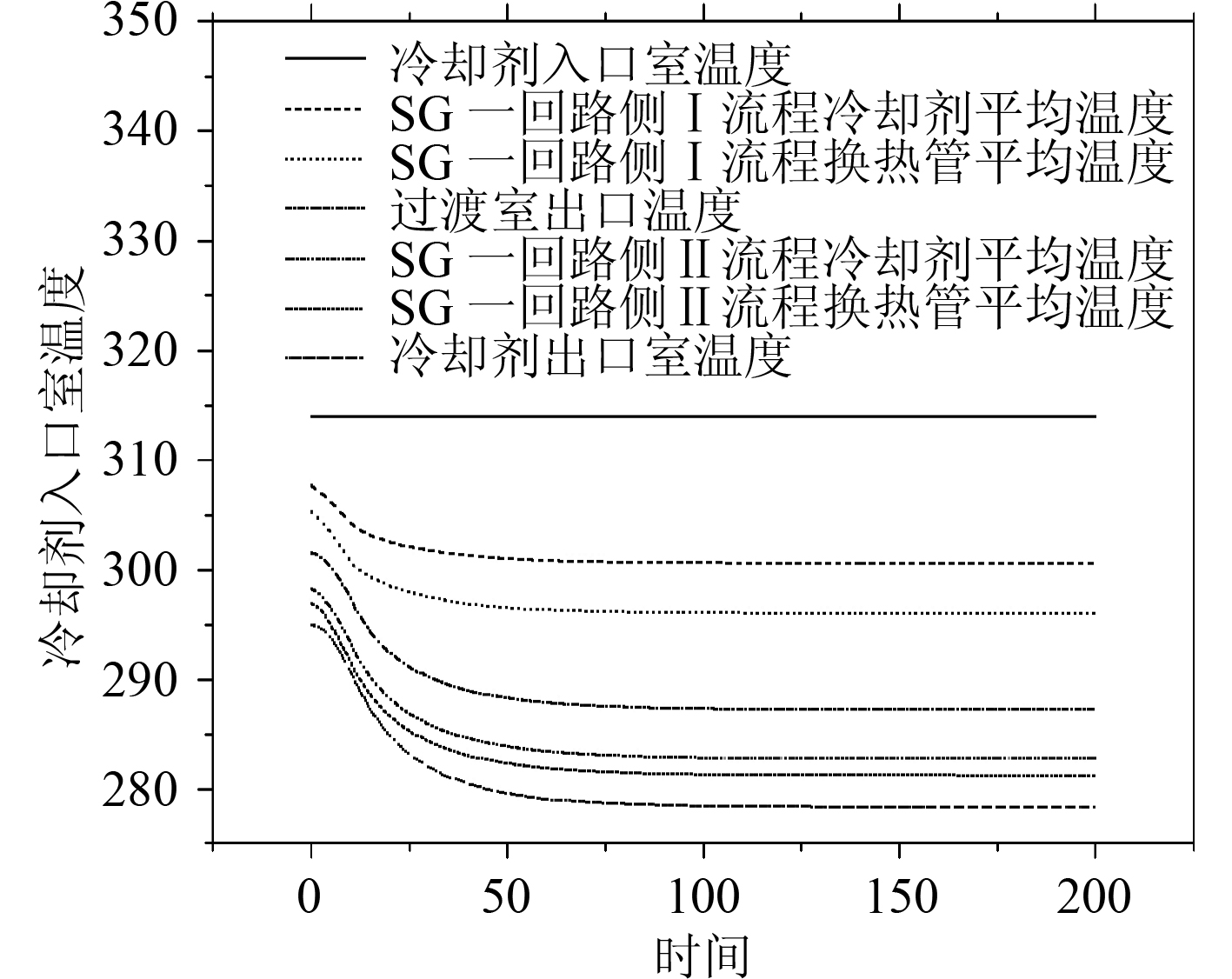
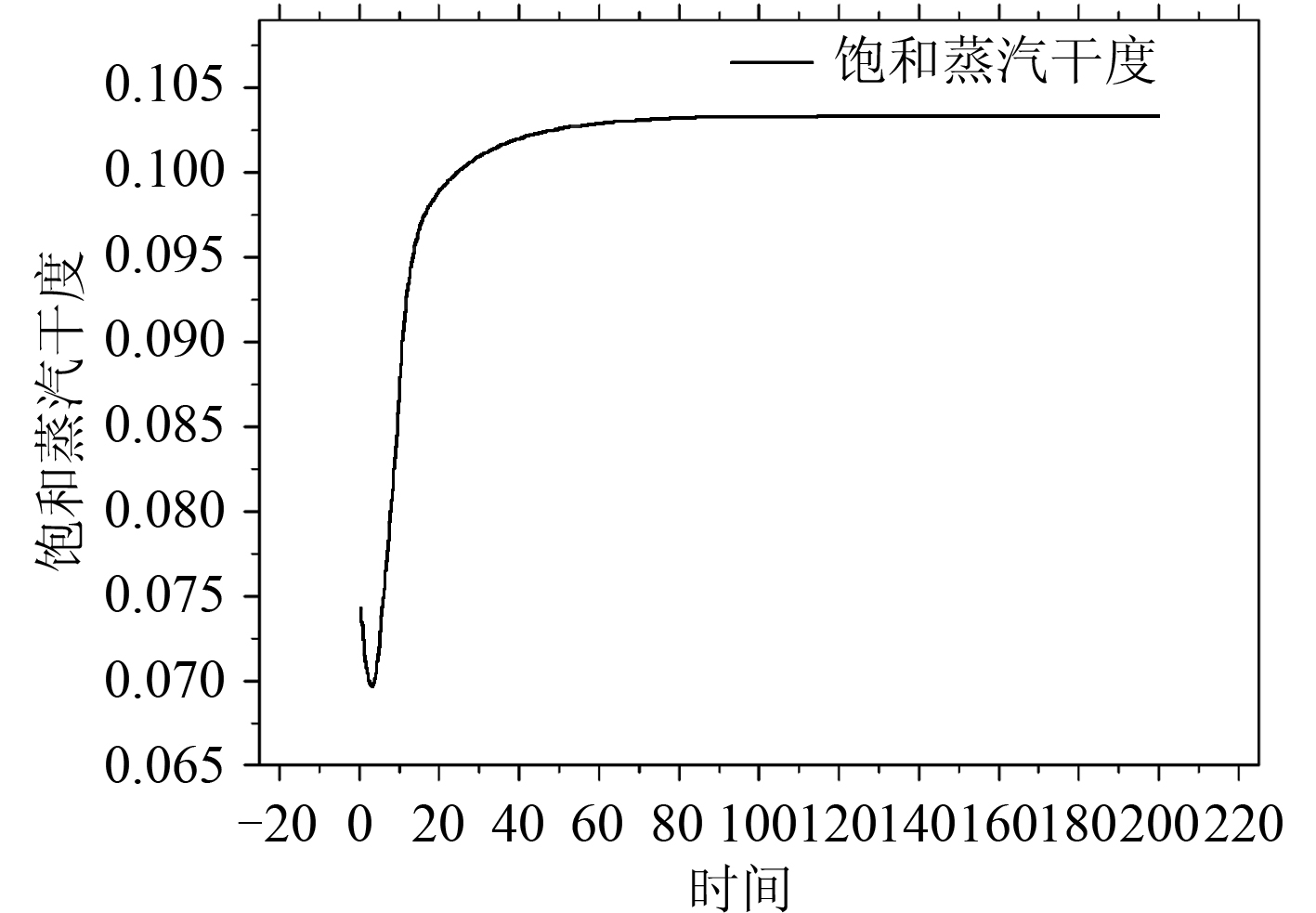
4 仿真试验为了验证立式自然循环蒸汽发生器模型的正确性,对该模型进行仿真验证试验。蒸汽发生器在稳态时对负荷加入 10% 扰动。蒸汽发生器水位不采用自动控制,对蒸汽发生器水位、蒸汽比焓、一回路冷却剂温度、给水比焓、饱和蒸汽干度等变量进行仿真,结果如图 3~图 7 所示。随着给水流量的增加蒸汽发生器水位逐渐增加、一次侧温度随之降低,由于温度的变化使得蒸汽与给水的比焓降低。饱和蒸汽干度上升。
|
图 3 蒸汽发生器水位 Fig. 3 Water level of steam generator |
|
图 4 蒸汽发生器蒸汽比焓 Fig. 4 Steam enthalpy of steam generator |
|
图 5 一回路冷却剂温度 Fig. 5 Primary system coolant temperatures |

|
图 6 蒸汽发生器给水比焓 Fig. 6 Feedwater enthalpy of steam generator |
|
图 7 蒸汽发生器饱和蒸汽干度 Fig. 7 Saturated steam dryness of steam generator |
蒸汽发生器仿真结果与理论分析相符,验证了该数学模型的正确性。该模型对立式自然循环蒸汽发生器进行模块划分,划分了 16 个控制体,对每个控制体采用集总参数法建立数学模型并进行推导与解算,得到了拥有 12 个状态变量的数学模型。通过对该模型进行仿真,验证了该模型的动态特性,利用该模型可以分析蒸汽发生器的动态特性,设计蒸汽发生器控制器,并对控制算法进行验证,具有一定的工程应用价值。
| [1] | SUN Bao-zhi, HAN Wen-jing, BAO Jie, et al. Dynamic characteristics analysis of steam generator based on drift-flux [J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2013, 64(S1): 64–52. |
| [2] | ZHANG Yu, SUN Bao-zhi, ZHANG Guo-lei, et al. One-dimensional homogeneous flow model and heat transfer performance of steam generator [J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2012, 46(1): 57–62. |
| [3] | 《Steam Generator》Drafting group of steam generator [M]. BeiJing: Atomic Energy Press, 1982. |
| [4] | GUIMARAES L N F, OLIVERIRA Jr. N S, BORGES E M. Derivation of a nine variable model of a U-tube steam generator coupled with a three-element controller[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2008, 32: 1027–1043 |
| [5] | WALTER. Dynamic modeling of vertical U-tube steam generators for operational safety system [D]. U.S.A: MIT, 1982: 20–33. |
| [6] | GUO Hai-hong, Working process dynamic simulation of steam generator [D]. Haerbin: Harbin Engineering University. 2007. |
| [7] | ZHANG Hai-xia. PWR steam generator modeling and dynamic analysis[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2007. |
| [8] | ZHANG Long-fei, ZHANG Da-fa. U-tube steam generator model and dynamic simulation [J]. Boiler Technology, 2006(4): 9–12. |
 2017, Vol. 39
2017, Vol. 39
