船舶和海洋结构物的波浪载荷计算是结构物设计、疲劳分析、安全性分析的基础。20世纪50年代提出的切片理论为船舶的运动和载荷预报提供了一种实用、较精确、经济的手段。随着计算处理能力的增强,完全的三维水动力计算成为了可能。三维波浪载荷计算方法可分为频域或者时域方法;按照所选取的Green函数不同,也可以分为自由面Green函数或者Rankine源方法。目前三维频域理论已经相当成熟。三维时域理论能有效处理有航速和非线性问题,但是也面临着时域Green函数复杂、计算耗时等问题。
采用三维时域自由面Green函数计算外飘船型时可能遇到计算发散的问题,一般需要结合Rankine源对流场进行划分。内域采用Rankine源,外域采用自由面Green函数[1-2]。Shukui Liu等[3]采用时域混合源法对零航速的长方体驳船、半球、Wigley、系列60船型进行数值计算,并将计算的水动力系数和其他数值方法进行比较,结果显示该方法与其他数值方法计算结果基本一致,但是作者并未给出运动和载荷的RAO比较;唐恺等[4-5]使用混合源法对Wigley型船、S175等船进行了时域模拟,并探讨了时间步长、面元密度划分等对计算结果的影响,并在此基础上对一艘LNG船进行了运动响应的计算,运动RAO的计算结果和试验值吻合良好;汪雪良等[6]采用混合源法对一超大型油船在规则波中的运动响应和波浪载荷进行了预报,同时进行了该大型油船的模型试验,理论计算与试验得到的传递函数符合较好。
本文对三维时域混合源法开展了研究,针对1艘散货船,计算了在规则波随浪和顶浪、无航速和有航速海况下的运动和载荷响应,与WASIM计算结果进行了对比。给出有航速的海况下将2种数值计算结果和试验结果的比较。
1 三维时域混合源法理论简介为了避免在船体表面布置自由面Green函数使得计算发散,需要在船体表面布置Rankine源(简单源1/r),但是若整个边界布置Rankine源,又将面临辐射条件难以满足、布置的源数量较大等问题,为了解决这些问题,利用一假想的控制面将流域分为内外域,内域布置Rankine源,外域布置自由面Green函数。
内域速度势设为
| $ {\Phi _I}(x,y,z,t) = {\Phi _w}(x,y,z,t) + {\Phi _d}(x,y,z,t). $ | (1) |
式中:
| $ \left\{ \begin{array}{l} {\nabla ^2}{\Phi _d} = 0{\rm{ }}\left( {在内域中} \right),\\ \frac{{\partial {\Phi _d}}}{{\partial n}} = {V_n} - \frac{{\partial {\Phi _w}}}{{\partial n}}\left( {在船体湿表面} \right),\\ \frac{{{\partial ^2}{\Phi _d}}}{{\partial {t^2}}} + g\frac{{\partial {\Phi _d}}}{{\partial z}} = 0{\rm{ }}\left( {在自由面上} \right),\\ {\Phi _d} = \frac{{\partial {\Phi _d}}}{{\partial t}} = 0{\rm{ }}\left( {t = 0} \right). \end{array} \right. $ | (2) |
式中:n为船体表面外单位法向矢量;Vn为船体表面的法向速度。
内域采用Rankine源,边界积分方程为:
| $ 2\pi {\Phi _{\text{d}}}(P) + \iint_{SI} {\left[{{\Phi _{\text{d}}}(Q)\frac{{\partial \left( {\frac{1}{r}} \right)}}{{\partial n}} - \frac{{\partial {\Phi _{\text{d}}}(Q)}}{{\partial n}}\;\frac{1}{r}} \right]}{\text{d}}S = 0 $ | (3) |
式中:Green函数取
在外域,扰动势
| $ \left\{ \begin{array}{l} {\nabla ^2}{\Phi _t} = 0\;\;\left( {在外域中} \right),\\ \frac{{{\partial ^2}{\Phi _t}}}{{\partial {t^2}}} + \frac{{\partial \Phi }}{{\partial z}} = 0\;\;\left( {在自由面上} \right),\\ \nabla {\Phi _t} \to 0\;\;\left( {在无穷远处} \right)\\ {\Phi _t} = \frac{{\partial {\Phi _t}}}{{\partial z}} = 0\;\;\left( {t = 0} \right) \end{array} \right. $ | (4) |
同样,外域扰动势
| $ 2\pi {\Phi _t}(P) + \iint_{SII} {\left[{{\Phi _t}(Q)\frac{{\partial G}}{{\partial n}} - \frac{{\partial {\Phi _t}(Q)}}{{\partial n}}G} \right]}dS = 0. $ | (5) |
式中:
其中:
| $ \begin{gathered} {G^0} = \frac{1}{r} - \frac{1}{{r'}},r = \left| {PQ} \right|,r' = \left| {PQ'} \right|,P = (x,y,z),\hfill \\ Q = (\xi ,\eta ,\zeta ),Q{\text{'}} = (\xi ,\eta ,- \zeta ),\hfill \\ \end{gathered} $ | (6) |
| $ {G^f} = 2\mathop \smallint \nolimits_0^\infty [1 - \cos (\sqrt {gk} (t - \tau ))]{e^{k(z + \zeta )}}{J_0}(kR){\text{d}}k $ | (7) |
| $ \begin{gathered} P \ne Q,t \geqslant \tau ,\hfill \\ R = \sqrt {{{(x - \xi )}^2} + {{(y - \eta )}^2}} . \hfill \\ \end{gathered} $ | (8) |
式中:J0为零阶Bessel函数。最终相应的边界积分方程为:
| $ 2\pi \pi {\Phi _d}(P) + \iint_m {({\Phi _d}(Q)\frac{{\partial {G^0}}}{{\partial n}} - \frac{{\partial {\Phi _d}(Q)}}{{\partial n}}{G^0})dS = M(P,t),} $ | (9) |
| $ \begin{gathered} M(P,t) = \mathop \smallint \nolimits_0^t {\text{d}}\tau \left\{ {\smallint \int\limits_{{S_m}} {({\Phi _t}\frac{{{\partial ^2}{G^f}}}{{\partial n\partial \tau }}} } \right. - \frac{{\partial {\Phi _t}}}{{\partial n}}\frac{{\partial {G^f}}}{{\partial \tau }}){\text{d}}S + \hfill \\ \quad \quad \quad \quad {\kern 1pt} \,\frac{1}{{\text{g}}}\int_{\Gamma m} {({\Phi _t}\frac{{{\partial ^2}{G^f}}}{{\partial {\tau ^2}}} - \frac{{\partial {\Phi _t}}}{{\partial \tau }}\;\frac{{\partial {G^f}}}{{\partial \tau }})} \left. {{V_N}dL} \right\}. \hfill \\ \end{gathered} $ | (10) |
式中:
| $\left\{ \begin{gathered} {\Phi _d} = {\Phi _t}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \hfill \\ \frac{{\partial {\Phi _d}}}{{\partial n}} = \frac{{\partial {\Phi _t}}}{{\partial n}},\left( {在控制面上} \right). \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \right. $ | (11) |
要注意内外域外法线方向的不同。将式(11)代入式(9)中,并与方程(2)联立,可以求出各个表面的面元中心的速度势或者速度势的法向导数。
船体表面的速度势
| $ \left\{ \begin{gathered} \frac{{D\zeta }}{{Dt}} = \frac{{\partial {\Phi _d}}}{{\partial z}} + U \cdot \nabla \zeta {\text{,}} \hfill \\ \frac{{D{\Phi _d}}}{{Dt}} = - g\zeta + U \cdot \nabla {\Phi _d}. \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \right. $ | (12) |
其中,U为自由面面元速度。式(12)需要在时间上积分。为保证计算的稳定性,在时间积分中采用预估校正格式。
扰动速度势一旦求出,总的力和力矩可通过Bernoulli方程求解:
| $ p = - \rho (\frac{{\partial \Phi }}{{\partial t}} + gz{\text{ + }}\frac{{{{\left| {\nabla \Phi } \right|}^2}}}{2}){\text{.}} $ | (13) |
| $ \left\{ \begin{gathered} F = \iint\limits_S {np{\text{d}}S}{\text{, }} \hfill \\ {M_G} = \iint\limits_S {(r \times n)p{\text{d}}S}. \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \right. $ | (14) |
| $ \left\{ \begin{gathered} \frac{{{\text{d}}(MV)}}{{{\text{d}}t}} = F,\hfill \\ \frac{{{\text{d}}(I\omega + Mr \times V)}}{{{\text{d}}t}} = {M_G},\hfill \\ \end{gathered} \right. $ | (15) |
式中:Φ包括了入射势以及扰动势;M为船体质量矩阵;V和r分别为质心速度和位移;I为船体相对重心惯性矩。式(14)计算力和力矩时面积分为船体平均湿表面。
2 算例分析 2.1 船舶主尺度以1艘散货船为例[8-9],计算该散货船在随浪和顶浪、无航速和有航速(V=7.61 m/s)下垂荡、纵摇、船中垂向弯矩,并和WASIM计算结果进行了比较。该散货船的主尺度如表 1所示。散货船船体表面网格划分如图 1所示。
|
|
表 1 散货船主尺度 Tab.1 Principal characteristics of the bulk carrier |
|
图 1 散货船网格示意图 Fig. 1 Grids on the surface of the bulk carrier |
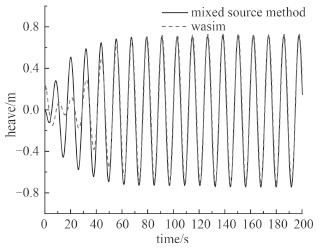
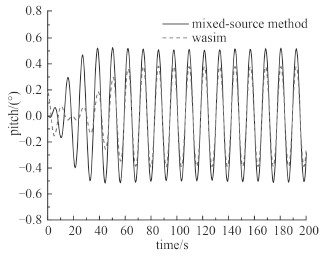
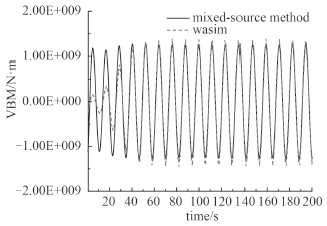
分别采用混合源法和WASIM[10]对同一条船舶进行规则波下的时域计算。这里给出一规则波计算结果。入射波频率为0.530 1 rad/s,浪向角为180°,波幅为2 m。图 2~图 4给出了无航速下该散货船的垂荡、纵摇和船舯垂向弯矩的时域曲线。
|
图 2 垂荡时域曲线 Fig. 2 The time history of heave |
|
图 3 纵摇时域曲线 Fig. 3 The time history of pitch |
|
图 4 船中垂向弯矩时域曲线 Fig. 4 The time history of vertical bending moment at midship |
从图中可看出,混合源法得到的垂荡、弯矩响应和WASIM的结果频率、幅值上基本一致,纵摇响应则是频率一致,但幅值较WASIM计算结果偏大。
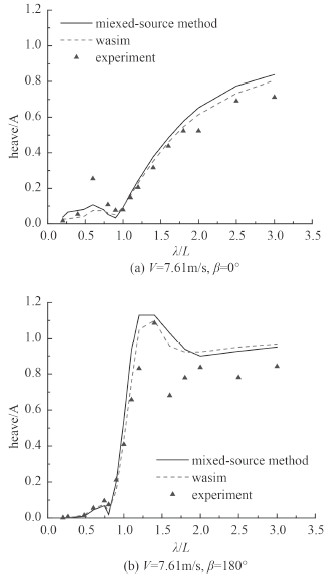
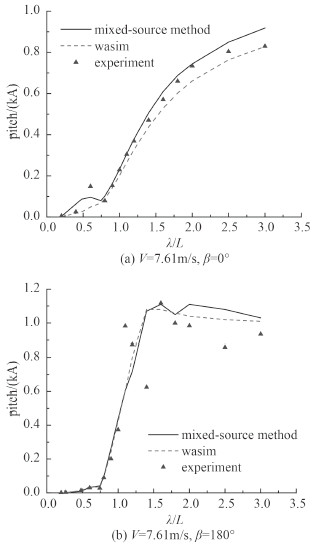
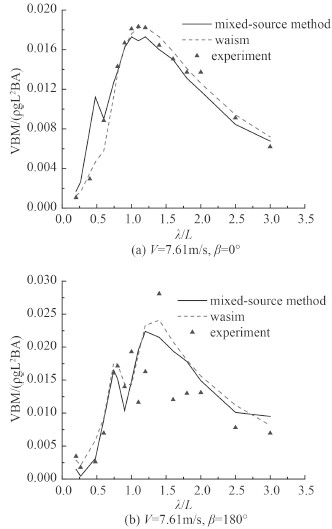
2.3 频域分析将时域结果转化到频域内,比较垂荡、纵摇、船中垂向弯矩的响应幅值算子(RAO)。在这里给出有航速、随浪和顶浪工况下的比较结果。横坐标为波长船长比,纵坐标为无量纲化的RAO。A为波幅,k为波数。
|
图 5 垂荡RAO Fig. 5 The RAO of heave |
从上述图中可以得到以下结论:
1)在随浪和顶浪海况下,l/L较小时(比如小于1.5),混合源结果和WASIM结果、模型试验符合地较好,l/L较大时,理论计算与试验结果之间有差别。总的来说,随浪工况理论计算结果与试验值符合地更好;波长船长比较大时顶浪工况2种理论计算结果和试验值相差较大。
|
图 6 纵摇RAO Fig. 6 The RAO of pitch |
|
图 7 船中垂向弯矩RAO Fig. 7 The RAO of the vertical bending moment at midship |
2)运动和载荷的RAO比较都显示出了这样规律:波长较短时,数值计算结果与模型试验结果值较接近,波长较长时,则差别较大。原因可能是混合源法和WASIM都需要对一定范围的自由面进行网格划分,而且自由面的尺寸不能太小,当波长增大后,自由面的范围没有相应进行调整,这需要进一步的研究。
3 结语本文基于三维时域混合源法,计算了一艘散货船的运动和波浪载荷响应,并将计算结果与WASIM和试验结果进行了比对,得到了以下结论:
1)混合源法的计算结果和WASIM结果大体一致,均与试验结果相符,验证了该方法的可行性,可用于实际船舶载荷预报。
2)该方法在波长船长比小于1.2时与试验值很好地吻合,当波长较大时,则预报结果与试验值有一定差别;随浪计算结果比顶浪更贴近试验值。
| [1] | LIN W M, ZHANG S, WEEMS K, et al. A mixed-source formulation for nonlinear ship-motion and wave-load simulations[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Numerical Ship Hydrodynamics. Nantes, France: NSH, 1999: 131-122. |
| [2] | ZHANG S G, LIN W M, WEEMS K. A hybrid boundary-element method for non-wall-sided bodies with or without forward speed[C]//Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Water Waves and Floating Bodies. Alphen aan den Rijn, Netherlands: IWWWFB, 1998: 178-182. |
| [3] | LIU S K, PAPANIKOLAOU A. A time-domain hybrid method for calculating hydrodynamic forces on ships in waves[C]//Proceedings of the 13th Congress of International Maritime Association of Mediterranean. Istanbul, Turkey: IMAM, 2009. |
| [4] |
唐恺, 朱仁传, 缪国平, 等. 应用混合格林函数法计算波浪中浮体运动及离散参数取值的算例分析[J]. 中国造船 , 2015, 56 (1) :102–113.
TANG Kai, ZHU Ren-chuan, MIAO Guo-ping, et al. Analysis of motions of floating body in waves by hybrid Green function method and discretization of parameters[J]. Shipbuilding of China , 2015, 56 (1) :102–113. |
| [5] |
唐恺, 朱仁传, 缪国平, 等.基于混合格林函数法的波浪中船舶时域运动计算[C]//2013年船舶水动力学学术会议论文集.西安:中国造船工程学会, 2013: 353-364.
TANG Kai, ZHU Ren-chuan, MIAO Guo-ping, et al. Hybird green function method for time-domain analysis of motions of floating body in waves[C]//Conference on Ship Hydrodynamics. Xi'an: China Shipbuilding Engineering Society, 2013: 353-364. |
| [6] |
汪雪良, 胡嘉骏, 顾学康, 等.基于混合源方法的船舶在波浪中的响应预报[C]//2008年船舶水动力学学术会议暨中国船舶学术界进入ITTC30周年纪念会.杭州:中国造船工程学会, 2008: 190-197.
WANG Xue-liang, HU Jia-jun, GU Xue-kang, et al. Numerical investigation on response of a ship in waves based on a mixed source formulation[C]//Conference on Ship Hydrodynamics. Hangzhou: China Shipbuilding Engineering Society, 2008: 190-197. |
| [7] | 刘应中, 缪国平. 船舶在波浪上的运动理论[M]. 上海: 海洋出版社, 1884 . |
| [8] | 丁军, 胡嘉骏. 20.5万吨散货船波激振动和砰击振动模型试验报告[R].中国船舶科学研究中心研究报告, 2013. |
| [9] |
丁军, 汪雪良, 田超, 等.大型散货船波激振动和砰击振动模型试验研究[C]//第二十五届全国水动力学研讨会暨第十二届全国水动力学学术会议文集(上册).北京:中国力学学会, 2013: 502-510.
DING Jun, WANG Xue-liang, TIAN Chao, et al. Experimental investigations of springing and slamming responses of a large bulk carrier[C]//Proceedings of the 25th National Conference on Hydrodynamics. Beijing: Chinese Society of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2013: 502-510. |
| [10] | SESAM. User Manual[Z]. Det Norsake Veritas, 2010. |
 2016, Vol. 38
2016, Vol. 38
