2. 青岛鱼水雷仓库二分库, 山东青岛 266042;
3. 海军工程大学, 湖北武汉 430033
2. Torpedo and Mine warehouse of Qingdao, Qingdao 266042, China;
3. Naval University of Engineering, Wuhan 430033, China
由于科学技术的发展,航空航天、船舶等领域对结构的振动和声辐射提出了更高的要求,隔振是控制机械振动向结构传递的常用手段之一。由于制造、装配、部件的不平衡等因素的存在,旋转机械与设备振动传至结构的激励力逐渐成为结构振动、噪声的激励源,影响水下航行体的声隐身性。因此,将发动机、隔振器、结构、介质考虑在同一个系统中,研究系统的振动与声辐射特性,对于降低结构的振动与噪声、提高水下结构的声隐身性具有重要意义。
隔振是指在振动源与基础、基础与仪器设备间加入具有一定弹性的装置以减少振动量的传递。为了降低旋转机械与设备振动传至结构的激励力,旋转机械或设备与结构之间通常设置不同类型及不同数目的隔振器。钱家昌等[1]通过有限元法和导纳法间接估算出机械设备对基座的输出激励力;朱正道等[2]将自由速度作为描述振源激励特性的参数,通过对机器-隔振器-基座系统的分析,得到了作用于基座结构的激励力与机器自由速度之间的关系;王宇等[3]针对舰船设备普遍采用隔振器与基座相连的连接方式,研究了隔振器类型及隔振器数量对舰船基座振动特性的影响。
对于平板结构的声振特性研究,Williams[4] 根据边界条件,将速度势展开为特征函数的级数叠加形式,然后由最小平均误差原则将其转化为含待定系数的有限项级数,导出了3种边界条件下有声障板及无声障板2种情形下平板结构声辐射阻抗的半解析表达式。Atalla[5] 考虑模态间耦合作用对声辐射阻抗的影响,采用坐标变换法将表达式中的四重积分转化为二重积分,给出了采用 Gaussian 公式求解二重积分的具体步骤。为解决任意波数下矩形平板声辐射阻抗的积分奇异性问题,Li[6] 和 Gibeling[7] 采用坐标变换法和级数逼近法导出简支矩形板声辐射阻抗的计算公式,并讨论了自辐射阻抗和互辐射阻抗对平板辐射声功率的影响。沈苏等[8]在此基础上,推导并给出声辐射阻抗的一重积分表达式与计算步骤。
隔振器的隔振性能、结构的声辐射在不同的领域单独进行研究,目前将隔振器与结构视为一个系统并研究系统声振特性的工作鲜有报道。针对发动机隔振器的隔振与降噪问题,综合考虑振动激励力与声压力,本文将建立发动机-隔振器-平板结构-介质系统的动力学模型,根据谐波平衡法推导系统的振动控制方程,研究隔振器的刚度、阻尼对系统振动与声辐射特性的影响。
1 动力学建模与求解研究发动机、隔振器、平板结构及周围流体介质组成系统的声振耦合问题,如图 1 所示,假定发动机的质量为 m,隔振器的刚度为 k,阻尼为 c,隔振器与平板在$({x_0} ,\,\,{y_0}) $ 处相连。平板的结构参数:弹性模量为 E,密度为 ρ ,泊松比为 μ ;几何参数:长度为 a,宽度为 b,厚度为 h,作用在平板表面的声压为$p(x\text{,}y\text{,}0\text{,}t)$ 。假设平板中面上各点仅作沿 z 轴方向的微幅振动,位移为 w,发动机的振动位移为${\tau_{i}}(t)$ 。
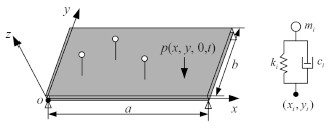
|
图 1 含动力吸振器平板的声振模型 Fig. 1 Vibro-acoustic model of the dynamic vibration absorbers-plate system |
根据 Hamilton 变分原理可推导出发动机-隔振器-平板-介质系统的声振耦合动力学方程为
| $ \begin{aligned} m\ddot{\eta }(t) + & c\left( {{{\dot{u}}}_{0}}(t)-{{\left. {\dot{w}} \right|}_{({{x}_{0}},{{y}_{0}})}} \right)+{{k}_{i}}\left( {{u}_{0}}(t)-{{\left. w \right|}_{({{x}_{0}},{{y}_{0}})}} \right)= \\ & me{{\omega }^{2}}\cos (\omega t) D{{\left( {{\nabla }^{2}}w \right)}^{2}}+\\ & \rho h\frac{{{\partial }^{2}}w}{\partial {{t}^{2}}}+p(x,y,t)\begin{matrix} - \\ \end{matrix}\bigg( c\big( {{{\dot{u}}}_{0}}(t) - \\ & {{\left. {\dot{w}} \right|}_{({{x}_{0}},{{y}_{0}})}} \big)+k\left( {{u}_{0}}(t)-{{\left. w \right|}_{({{x}_{0}},{{y}_{0}})}} \right) \bigg) \times \\ & \delta (x-{{x}_{0}})\delta (y-{{y}_{0}})=0 \text{。}\ \end{aligned} $ | (1) |
由于不考虑耦合系统中的非线性因素,系统在发动机不平衡激振力作用下将作周期运动,由于考虑隔振器中的阻尼,因此可将发动机的振动位移表示为
| $ \eta (t)=A\cos \left( \omega t \right)+B\sin \left( \omega t \right) \text{,} $ | (2) |
平板在发动机振动激励下运动,根据发动机的运动形式和模态展开法,可将平板在发动机振动激励下的横向振动位移表示为
| $ \begin{array}{l} w(x,y,t) = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{m = 1}^\infty {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = 1}^\infty {{\psi _{mn}}\left( {x\text{,}y} \right)} } \times \\ \left( {{w_{cmn}}\cos \left( {\omega t} \right) + {w_{smn}}\sin \left( {\omega t} \right)} \right)\text{。} \end{array} $ | (3) |
其中,${{\psi }_{mn}}\left( x\text{,}y \right) $ 为振型函数,对于四边简支平板:
| $ {{\psi }_{mn}}(x,y)=\sin {{k}_{m}}x\sin {{k}_{n}}y \text{。} $ | (4) |
其中,${{k}_{m}}=m\pi /a$ ,${{k}_{n}}=n\pi /b$ 。结构在受到外部激励力作用时,将发生机械振动,向外压缩周围介质并辐射噪声。根据 Rayleigh 积分公式,平板表面声压可由其表面位移表示为
| $ \begin{array}{l} p(x,y,0,t) = - \displaystyle\frac{{{\omega ^2}{\rho _0}}}{{2\pi }}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{m = 1}^\infty {\sum\limits_{n = 1}^\infty {\left( {{w_{c1mn}}\sin \left( {\omega t} \right) - } \right.} } \\ \left. {{w_{s1mn}}\cos \!\left( {\omega t} \right)} \right) \displaystyle\int \!\!\!\! {\int\limits_S {\frac{{{\psi _{mn}}({x^{'}},{y^{'}}){2{e}^{ - {j}k\left| {r - r{'}} \right|}}}}{{\left| {r - {r^{'}}} \right|}}} } 2{\rm d}{x^{'}}2{\rm d}{y^{'}} \text{。} \end{array} $ | (5) |
其中,$\left| r-{r}' \right|=\sqrt{{{(x-{x}')}^{2}}+{{(y-{y}')}^{2}}}$,k,ω,ρ0 分别表示波数、振动频率、流体介质密度。
将式(2)、式(3)、式(5)代入式(1),用式(2)两端乘以${{\psi }_{{{m}^{'}}{{n}^{'}}}}$,并沿平板表面积分,根据振型函数的正交性可得
| $ \begin{array}{l} \left( { - {\omega ^2}m + k} \right)A + \omega cB - k{w_c} - \omega c{w_s} = 0 \text{,}\\ - \omega cA + \left( { - {\omega ^2}m + k} \right)B + \omega c{w_s} - k{w_c} = 0 \text{,}\\ D{\left( {k_m^2 + k_n^2} \right)^2}{w_{cmn}} - \rho h{\omega ^2}{w_{cmn}} + {Z_{mn}}{w_{smn}}\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} - \end{array}\\ \displaystyle\frac{{4{\psi _{mn}}}}{{ab}}\left( {\omega c\left( {B - {w_s}} \right) + k\left( {A - {w_c}} \right)} \right) = 0 \text{,}\\ D{\left( {k_m^2 + k_n^2} \right)^2}{w_{smn}} - \rho h{\omega ^2}{w_{smn}} - {Z_{mn}}{w_{cmn}}\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} - \end{array}\\ \displaystyle\frac{{4{\psi _{mn}}}}{{ab}}\left( { - \omega c\left( {A - {w_c}} \right) + k\left( {B - {w_s}} \right)} \right) = 0 \text{,} \end{array} $ | (6) |
其中,${{w}_{c}}\,=\,\displaystyle\sum\limits_{m=1}^{\infty }\,\,{\sum\limits_{n=1}^{\infty }{{{w}_{cmn}}\,\,{{\psi }_{mn}}\left( {{x}_{0}},\,\,{{y}_{0}} \right)}}$,${w_c} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{m = 1}^\infty \,\,{\sum\limits_{n = 1}^\infty } $${w_{cmn}}{\psi _{mn}}\left( {{x_0},{y_0}} \right)$,$\displaystyle{{\psi }_{mn0}}={{\psi }_{mn}}\left( {{x}_{0}},{{y}_{0}} \right)$,${{Z}_{mn}}=\displaystyle\frac{2{{\omega }^{2}}{{\rho }_{0}}}{\pi \ ab}$ $\displaystyle\sum\limits_{{m^ {'} } = 1}^\infty {\sum\limits_{{n^ {'}} = 1}^\infty {\int \!\!\! {\int\limits_S \!\!\! {\int \!\!\! {\int\limits_S {\frac{{{\psi _{mn}}{\psi _{{m^ {'} }{n^ {'} }}}{2{e}^{ - 2{j}k\left| {r - r {'} } \right|}}}}{{\left| {r - r {'} } \right|}} 2{{{\rm{d}}}x} {'} 2{{{\rm{d}}}y} {'} 2{{{\rm{d}}}x} 2{{{\rm{d}}}y}}}}}}} $ 为平板的声辐射阻抗,具体求解方法见文献[7]。将式(6)写为矩阵形式,即
| $ \left[ \begin{array}{l} {M_Q}\\ {M_p} \end{array} \right]x = F。 $ | (7) |
其中,$ {\bf{x}} \!= \!\left[{A\text{,}\!B\text{,}\!{w_{c11}}\text{,}\!{w_{c12}}\text{,}\! \cdots \text{,}\!{w_{cMN}}\text{,}\!{w_{s11}}\text{,}\!{w_{s12}}\text{,}\!} \right. $ $ {\left. { \cdots \text{,}{w_{sMN}}} \right]^{\rm{T}}} $ ${{{M}}_1} = \left[{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} { - {\omega ^2}m + k} & {c\omega }\ { - c\omega } & { - {\omega ^2}m + k} \end{array}} \right]\text{,}$ ${{{M}}_{o1}} = \left[{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} { - k{ {C}}} & { - c\omega { {C}}}\ {c\omega { {C}}} & {k{ {C}}} \end{array}} \right]\text{,}$ ${ {C}} = \left[{{\psi _{11}}\text{,}{\psi _{12}}\text{,} \cdots \text{,}{\psi _{MN}}} \right]\text{,} \quad {{ {M}}_p} = \left[{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{ {M}}_{o1}}} & {{{ {M}}_{pp}}} \end{array}} \right]\text{,}$ ${{{M}}_{pp}} = \left[{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{{M}}_{p1}}} & {{{{Z}}_{mn}}}\ { - {{{Z}}_{mn}}} & {{{{M}}_{p1}}} \end{array}} \right] \text{,}$ ${{{M}}_{p1}} = \left[{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{M_{11}}}& {}& {}& {{0}}\ {}& {{M_{12}}}& {}& {}\ {}& {}& \ddots & {}\ {{0}}& {}& {}& {{M_{MN}}} \end{array}} \right] + k{{C}}_{}^{'}{{C}} \text{,}$ ${M_{mn}} = {K_{mn}} - \rho h{\omega ^2}\text{,}\quad {K_{mn}} = D{\left( {k_m^2 + k_n^2} \right)^2}\text{,}$ ${{{Z}}_{mn}} = \left[{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{Z_{1111}}}& {{Z_{1112}}}& \cdots & {{Z_{11MN}}}\ {{Z_{1211}}}& {{Z_{1212}}}& \cdots & {{Z_{12MN}}}\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \\ {{Z_{MN11}}}& {{Z_{MN12}}}& \cdots & {{Z_{MNMN}}} \end{array}} \right] + \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^Q {\frac{4}{{ab}}} c\omega {{C}}_i^{'}{{{C}}_i}\text{,}$
式(7)中,${{{M}}_{oi}}$ 和${{{M}}_{o}}$ 是隔振器与平板振动的耦合项。求解耦合方程(7)即可获得平板与隔振器的振动位移,然后由平板的声辐射阻抗与振动速度获得其声辐射特性。
平板的辐射声功率级和表面平均振速级可定义为
| $ Lw=10\lg \frac{W}{{{W}_{0}}}\text{,}Lv=10\lg \frac{V_{{}}^{2}}{v_{0}^{2}} \text{。} $ | (8) |
其中,参考声功率为${W_0} = 0.67 \times {10^{ - 18}}\,{\rm{W}}$,参考振速为v0 = 5 × 10 -8 m/s。
2 案例分析研究发动机、隔振器、平板结构的声振特性。选取发动机的参数为:质量 m = 40 kg,偏心距 e = 0.02 m,隔振器与平板相连的位置为(a/2,b/2)。平板的参数为:长度 a = 0.8 m,宽度 b = 0.6 m,厚度 h = 0.003 m;杨氏模量$E=2.1\times {{10}^{11}} \,\mathrm{N}\cdot {{\mathrm{m}}^{-2}}$ ,密度$\rho = 7.8 \times {10^3}\,{\rm{kg}} \cdot {\rm{m}^{ - 3}} $,泊松比$\upsilon = 0.3$;平板置于水中,水密度${\rho _0} \! = \! 1 \!\times \!{10^3}\,{\rm{kg}} \cdot {\rm{m}^{ - 3}}$,声速${c_0} \! = \! 1.5 \!\times \!{10^3}\,\rm{m} \cdot {\rm{s}^{ - 1}}$ 。研究隔振器刚度 k,阻尼 c 对系统振动与声辐射特性的影响。
研究隔振器刚度对发动机振动、平板结构声振特性的影响。图 2 给出了 c = 200 N·s·m -1 时,平板辐射声功率级和表面平均振速级随刚度 k 的变化情况;图 3 给出了 c = 200 N·s·m -1 时,发动机振动幅度随刚度 k 的变化情况。当 k = 1 × 10 6 N·m -1 时,隔振器的固有频率 f = 25.16 Hz;当 k = 1 × 10 7 N·m -1 时,隔振器的固有频率 f = 79.58 Hz;当 k = 5 × 10 7 N·m -1 时,隔振器的固有频率 f = 177.94 Hz。由图 2 知,平板的辐射声功率级和表面平均振速级在隔振器的固有频率处的峰值最大,辐射声功率级分别为 219.07 dB,238.63 dB,253.72,表面平均级分别为 137.74 dB,150.54 dB,171.92 dB;当 k = 1 × 10 6 N·m -1 时,在整个研究频段,除了低频段隔振器固有频率附近处,平板的辐射声功率级和表面平均振速级最低,这是由于当隔振器的刚度增大时,发动机不平衡力通过隔振器传至平板的激励力增大。图 3 中,发动机的振幅在隔振器固有频率处取得最大值;k = 5 × 10 7 N·m -1 时,发动机的振幅中存在2个峰值,其中的低峰值由隔振器与平板耦合振动产生。因此设计隔振器时,应降低隔振器系统的固有频率,并确保发动机的工作频率为隔振器系统固有频率的5倍以上。
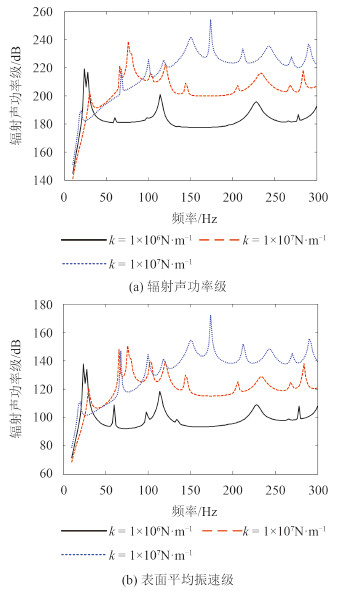
|
图 2 刚度对平板声振特性的影响 Fig. 2 Computational grid |
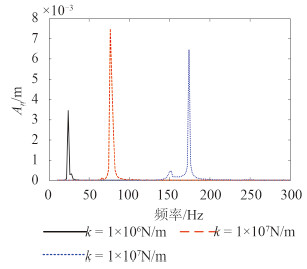
|
图 3 刚度对发动机振动幅值的影响 Fig. 3 Influence of the stiffness to the vibration amplitude of the engine |
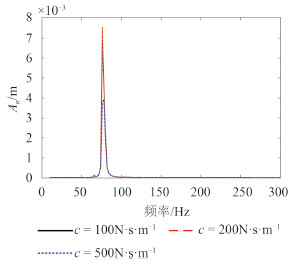
研究隔振器阻尼对发动机振动、平板结构声振特性的影响。图 4 给出了 k = 1 × 10 7 N·m -1 时,平板辐射声功率级和表面平均振速级随阻尼 c 的变化情况;图 5 给出了 k = 1 × 10 7 N·m -1 时,发动机振动幅度随阻尼 c 的变化情况。由图 4 知,平板的辐射声功率级和表面平均振速级在 f = 79.58 Hz 处取得最大值;阻尼主要改变 f = 76 Hz,206 Hz,284 Hz 处的峰值,且阻尼越大,峰值降低的越多。由图 5 知,阻尼主要影响发动机在固有频率 f = 79.58 Hz 处的峰值。上述分析表明,阻尼对发动机-隔振器-平板-介质系统的影响较小,可以忽略。
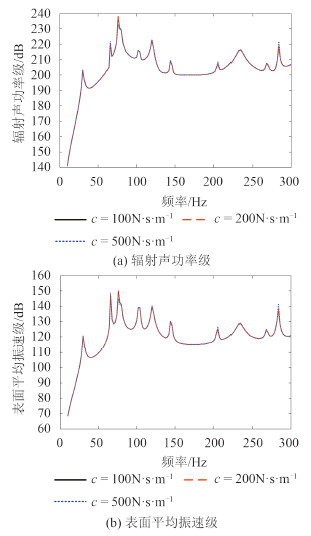
|
图 4 阻尼对平板声振特性的影响 Fig. 4 Influence of damping to the vibro-acoustic characteristics of plate |
|
图 5 阻尼对发动机振动幅值的影响 Fig. 5 Influence of the damping to the vibration amplitude of the engine |
针对发动机、隔振器、平板结构与介质组成的耦合系统,研究了隔振器的刚度、阻尼对系统振动与声辐射特性的影响规律。研究表明:隔振器的固有频率对系统声振特性有重要影响,而阻尼的影响可忽略;设计隔振系统时,为了控制系统的振动与声辐射,应降低隔振系统的固有频率,并确保发动机的工作频率为隔振系统固有频率的5倍以上。研究结果可为发动机隔振器的设计提供理论依据。
| [1] | 钱家昌, 彭旭, 陈明. 机械设备对基座激励力估算方法研究[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2008, 3(1):48-50. |
| [2] | 朱正道, 俞孟萨, 苗金林. 舰船机械设备振动激励特性测试方法研究[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2006, 28(S2):34-39. |
| [3] |
王宇, 陈兴林, 李光民. 隔振器对舰船基座振动特性的影响[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2012, 34(1):30-35, 49. WANG Yu, CHEN Xing-lin, LI Guang-min. Influence of vibration isolators to the vibration characteristics of a ship foundation[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2012, 34(1):30-35, 49. |
| [4] | WILLIAMS E G. A series expansion of the acoustic power radiated from planar sources[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1983, 73(5):1520-1524. |
| [5] | ATALLA N, NICOLAS J. A new tool for predicting rapidly and rigorously the radiation efficiency of plate-like structures[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1994, 95(6):3369-3378. |
| [6] | LI W L, GIBELING H J. Determination of the mutual radiation resistances of a rectangular plate and their impact on the radiated sound power[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2000, 229(5):1213-1233. |
| [7] | LI W L. An analytical solution for the self- and mutual radiation resistances of a rectangular plate[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2001, 245(1):1-16. |
| [8] | 沈苏, 刘碧龙, 李晓东, 等. 简支矩形板模态辐射抗的一种快速计算方法分析[J]. 声学学报, 2010, 35(2):126-133. |
 2016, Vol. 38
2016, Vol. 38
