地球是多物理场(如渗流场、电磁场等)的综合体,火山地区是地质构造活跃区域,在火山地区的自然电位(Sill, 1983;张贵宾等, 1996;Yasukawa et al., 2003;Friedel et al., 2004;Finizola et al., 2004;Aizawa et al., 2005;Tort and Finizola, 2005;Bennati et al., 2011)、磁场(Del Negro et al., 2004;Aizawa et al., 2005)、温度(Friedel et al., 2004;Aizawa et al., 2005)、渗流(Yasukawa et al., 2003;Finizola et al., 2004;Bennati et al., 2011)、幔源气体(上官志冠和孙明良, 1996;Bennati et al., 2011)和地震信号(马明志等,1996;明跃红等,2009)等物性参数变化明显,可采用多种地球物理方法探测火山,如大地电磁探测(汤吉等,1997;仇根根等,2014)、自然电位测量(Sill, 1983;Yasukawa et al., 2003)、地震(郭履灿等,1996;马明志等,1996;杨卓欣等,2005)、重力磁法勘探(Del Negro et al., 2004)等.
根据已有的地质资料和物性资料,可通过建立地下介质模型进行数值模拟,分析地下介质物理性质变化及多物理场响应的变化规律.张贵宾等(1996)采用线性反演理论与正则化法对火山地区自然电位异常进行多次反演计算,从而确定火山地区地下视极化强度分布和源区中心位置;赵阳升等(2002)提出了高温岩体地热开发的块裂介质固流热耦合数学模型及其数值模拟求解方法,为高温岩体地热开发决策、技术方案选择提供了技术支持;Adler等(1999)将La Fournaise火山概化为由断裂带组成的二维地质体,通过数值模拟来验证在火山裂隙流水产生电磁场;Titov等(2005)通过建立地下水模型,验证在抽水实验过程中可以采用自然电位监测地下水流动;程旭等(2014)采用有限元及有限差分的方法数值模拟地壳内岩浆房或岩浆囊中的岩浆沿已有断层向上运移的动力学过程.
本文以长白山天池为例,基于COMSOL Multiphysics建立长白山天池二维数值模型,模拟大气降水和天池水不断补给地下水,地下水流动产生自然电磁场,再现长白山天池的流场、电磁场的多物理场耦合响应,研究结果有助于理解长白山天池地区地下水循环过程及电磁异常出现的机理,为火山地区勘查、监测与开发提供技术支持.
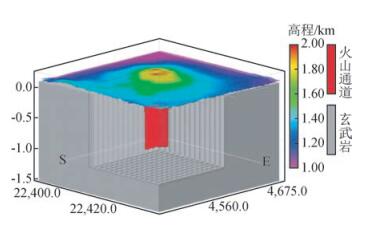
1 研究区简介长白山天池位于吉林省东南部,是火山喷发自然形成的中国最大的火山口湖(42°0′17.17′N,128°3′11.93″E),为松花江、图们江和鸭绿江的源头.天然地震监测(马明志等, 1996)、大地电磁测深(汤吉等,1997;仇根根等,2014)、三维空间深地震测深技术(杨卓欣等,2005)都探测到在长白山火山口及其附近地下埋深约10~15 km处存在局部三维异常体,初步推测是火山岩浆囊(马明志等, 1996;汤吉等, 1997;杨卓欣等, 2005;仇根根等, 2014) (图 1),火山通道/断层及其破碎带透水性较好,与地下水联系密切.以长白山天池为中心左右各取15 km作为二维模拟剖面(方向从南向北),建立长白山二维模型,底部取地下15 km,顶部采用长白山天池实际地形.长白山二维模型分为玄武岩区、火山通道/断层及其破碎带区和天池区(图 2).
|
图 1 长白山天池三维地质模型 Figure 1 3D Geological model of Tianchi lake in Changbaishan volcano |

|
图 2 长白山天池二维地质模型剖面图(单位:m) Figure 2 2D Geological model profile of Tianchi lake in Changbaishan volcano (unit:m) |
稳定态流场可由连续方程描述,Δ·u=0,由Darcy定律(薛禹群,1997),流速u(m/s)可由地下水流动产生的水头压力p(Pa)表示,公式为

|
(1) |
其中k为介质的渗透率;η为流体的动态黏滞度(Pa·s).这里仅考虑地下水流场流动产生电场,忽略电场对流场的拖曳.
边界条件:模型顶部为内流量边界,其中天池边界为大气降水补给边界,非天池边界大气降水在重力作用下入渗补给地下水,底部边界与顶部边界补给量相等;天池北侧天文峰与龙门峰之间有一缺口,池水由此缺口溢出,即乘搓河(又称白河、天河),天河流量为1.32 m/s;火山北侧有温泉出露.两侧边界假设为不透水的,即u·n=0.
2.2 水流方程和电场耦合方程及其边界条件稳定电流场中电流是连续的(赵凯华和陈熙谋,2003;李金铭,2005;刘国兴,2005;Zimmerman和中仿科技公司,2007),用公式表达即为
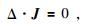
|
(2) |
其中J=σE+Je,即Δ·(σE+Je)=0.J为总的电流密度(A/m2);σ为岩石电导率(S/m);E为电场强度(V·m-1);Je表示流体产生的电流密度,Je=-αΔp,α代表动电耦合系数.
边界条件:所有边界设为绝缘边界条件,即J·n=0.
2.3 磁场方程及其边界条件为了计算由流场驱动产生的自然电场进而产生的磁场,利用准静态近似,根据法拉第定律(赵凯华和陈熙谋,2003;李金铭,2005;刘国兴,2005;Zimmerman和中仿科技公司,2007):

|
(3) |
用安培定律来定义电流密度,公式为
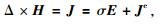
|
(4) |
其中H是磁场强度(A/m).
将式(4) 代入(3),磁场控制方程可进一步写为

|
(5) |
边界条件:所有边界设为绝缘边界条件,即Hz=0.
3 基于COMSOL Multiphysics建立流场、电场和磁场模型本研究采用COMSOL Multiphysics (Zimmerman和中仿科技公司,2007)研究流场、电场和磁场之间的响应.涉及COMSOL Multiphysics两个模块:地球科学模块Earth Science Module和AC/DC模块(AC/DC Module),其中Earth Science Module用于模拟长白山天池周边地区的地下水流场,AC/DC Module用于模拟流场产生的电场和磁场,通过α动电耦合系数使流场的渗透压力和电场耦合,电场产生磁场,使三个物理场耦合计算成为可能.导入dxf格式的长白山天池模型至COMSOL Multiphysics,将长白山天池模型子域属性和边界条件按上述赋值,网格自动三角剖分(图 3),采用广义最小残量方法(Saad and Schultz, 1986)求解线性方程组.

|
图 3 长白山天池2D模型三角剖分(单位:m) Figure 3 2D model Triangle subdivision of Tianchi lake in Changbaishan volcano (unit:m) |
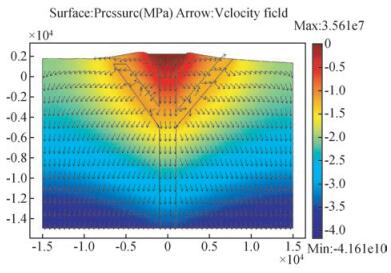
图 4是COMSOL Multiphysics计算所得的流场压力和流速图.其中彩图为流场压力分布图,箭头为流场流速分布.流场压力分布由天池向天池周围逐渐减少,在火山通道/断层区渗透系数大,地下水沿着火山通道向下运移,流场底部积累的多年大气降水,遇到地下致密岩体后,沿着火山通道向上运移,一部分补给天池,一部分在地质构造、岩性薄弱的地方,在流场压力作用下,涌出地表成泉.
|
图 4 长白山天池2D地下水流场压力分布(彩色)和流速(箭头)剖面图(单位:m) Figure 4 2D groundwater flow field pressure distribution (surface plot) and velocities (arrows) profile around Tianchi lake of Changbaishan volcano(unit:m) |
图 5是电场自然电位和总电流密度分布图.其中彩图为自然电场电位图,箭头为总电流密度.从自然电场彩虹图中可以看出,由于地下水向下流动产生电位差.当地下水静止时,整个系统呈电性平衡,不产生外电场.当天池和大气降水入渗补给地下水,地下水在重力作用下向下流动时,带走溶液中的部分正离子,在水流上游即天池和近地表有多余的“负离子”,电位呈现负值,而在2D模型底部有多余的“正离子”,电位为正值,形成极化,从而形成自然电场;在火山通道/断层外侧电流密度方向由地表指向地下,而在火山通道/断层区地下水向上涌出,电流密度方向相反.

|
图 5 长白山天池2D电位分布(彩色)和总电流密度(箭头)剖面图(单位:m) Figure 5 2D electric potential (surface plot) and current density (arrows) profile around Tianchi lake of Changbaishan volcano(unit:m) |
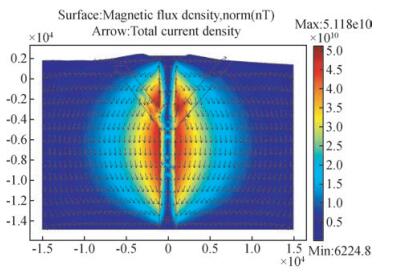
图 6为长白山2D磁通量密度分布(彩色)和总电流密度(箭头)剖面图.流动的地下水产生自然电位,进而产生磁场.由此计算的磁通量密度高值主要分布在长白山天池火山通道/断层区外侧,在火山通道/断层区向下运移的地下水受到底部致密岩石隔水阻挡,地下水向上流动,产生向上运移的电流,磁通量密度呈现低值,显示为蓝色.
|
图 6 长白山天池2D磁通量密度分布(彩色)和总电流密度(箭头)剖面图(单位:m) Figure 6 2D magnetic flux (surface plot) and current density (arrows) profile around Tianchi lake of Changbaishan volcano(unit:m) |
基于COMSOL Multiphysics建立多物理场模型,研究长白山天池流场特征、电位分布和磁场响应.数值模拟了长白山天池大气降水向下运移补给地下水,地下水在重力作用下向下运移产生自然电位,进而产生磁场.渗透性不同导致水流场变化、自然电位场和磁场响应不同,在强渗透区如火山通道或者断层区,呈现出流速加大,电位增大,电流密度增大,随着地下水补给的增加,若地下水遇到致密岩层,地下水流动方向发生改变,电流密度方向相反,进而影响到磁通量密度的分布.
5.2本研究通过模拟再现了地下水流动产生自然电磁场,可以看出地下水对流扩散是形成自然电磁场的场源之一;在地下水运移的过程中,可将深部幔源气体带到地表,地下水与深部岩浆热交换形成温泉群.若考虑在地下岩浆囊高温高压驱动下,多物理场响应更明显.研究长白山地区地下水多物理参数响应特征,有助于进一步理解长白山天池地区地下水循环过程及电磁异常出现的机理,亦可用于指导火山地区勘查、监测与开发.
致谢 感谢审稿专家提出的修改意见和编辑部的大力支持!| [] | Adler P M, Le Mouel J L, Zlotnicki J. 1999. Electrokinetic and magnetic fields generated by flow through a fractured zone:A sensitivity study for La Fournaise volcano[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 26(6): 795–798. DOI:10.1029/1999GL900095 |
| [] | Aizawa K, Yoshimura R, Oshiman N, et al. 2005. Hydrothermal system beneath Mt. Fuji volcano inferred from magnetotellurics and electric self-potential[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 235(1-2): 343–355. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.03.023 |
| [] | Bennati L, Finizola A, Walker J A, et al. 2011. Fluid circulation in a complex volcano-tectonic setting, inferred from self-potential and soil CO2 flux surveys:The Santa María-Cerro Quemado-Zunil volcanoes and Xela caldera (Northwestern Guatemala)[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 199(3-4): 216–229. DOI:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2010.11.008 |
| [] | Cheng X, Chen Z A, Bai W M. 2014. A numerical simulation of magma migration in crust fracture-an application to Changbaishan Tianchi volcano[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 57(5): 1522–1533. DOI:10.6038/cjg20140516 |
| [] | DelNegro C, Currenti G, Napoli R, et al. 2004. Volcanomagnetic changes accompanying the onset of the 2002-2003 eruption of Mt. Etna (Italy)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 229(1-2): 1–14. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2004.10.033 |
| [] | Finizola A, Lénat J F, Macedo O, et al. 2004. Fluid circulation and structural discontinuities inside Misti volcano (Peru) inferred from self-potential measurements[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 135(4): 343–360. DOI:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2004.03.009 |
| [] | Friedel S, Byrdina S, Jacobs F, et al. 2004. Self-potential and ground temperature at Merapi volcano prior to its crisis in the rainy season of 2000-2001[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 134(3): 149–168. DOI:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2004.01.006 |
| [] | Guo L C, Ma S Z, Zhang Y S. 1996. Research on "Magma Chamber" of Changbai mountain volcano by means of seismic tomography[J]. CT Theory and Applications (in Chinese), 5(1): 47–52. |
| [] | Li J M. 2005. Geoelectric Field and Electrical Exploration (in Chinese)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. |
| [] | Ma M Z, Zhang X K, Hou L P. 1996. Volcanic earthquake types and distributior at Tianchi, Changbai Shan[J]. Seismological and Geomangnetic Observation and Research (in Chinese), 17(6): 39–44. |
| [] | Ming Y H, Wu J P, Fang L H, et al. 2009. Volcanic seismic signals and tremor source models[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 24(2): 382–390. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2009.02.003 |
| [] | Qiu G G, Pei F G, Fang H, et al. 2014. Analysis of magma chamber at the Tianchi volcano area in Changbai mountain[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 57(10): 3466–3477. DOI:10.6038/cjg20141032 |
| [] | Saad Y, Schultz M H. 1986. GMRES:A generalized minimal residual algorithm for solving nonsymmetric linear system[J]. Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing, 7(3): 856–869. DOI:10.1137/0907058 |
| [] | Shangguan Z G, Sun M L. 1996. Mantle-derived rare-gas releasing features at the Tianchi volcanic area, Changbaishan Mountains[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 42(9): 768–771. |
| [] | Sill W R. 1983. Self-potential modeling from primary flows[J]. Geophysics, 48(1): 76–86. DOI:10.1190/1.1441409 |
| [] | Tang J, Liu T S, Jiang Z, et al. 1997. Preliminary observations of the Tianchi volcano area in Changbaishan Mountain by MT method[J]. Seismology and Geology (in Chinese), 19(2): 164–170. |
| [] | Titov K, Revil A, Konosavsky P, et al. 2005. Numerical modelling of self-potential signals associated with a pumping test experiment[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 162(2): 641–650. DOI:10.1111/gji.2005.162.issue-2 |
| [] | Tort A, Finizola A. 2005. The buried caldera of Misti volcano, Peru, revealed by combining a self-potential survey with elliptic Fourier function analysis of topography[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 141(3-4): 283–297. DOI:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2004.11.005 |
| [] | Yang Z X, Zhang X K, Zhao J R, et al. 2005. Tomographic imaging of 3-D crustal structure beneath Changbaishan-Tianchi volcano region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 48(1): 107–115. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2005.01.016 |
| [] | Yasukawa K, Mogi T, Widarto D, et al. 2003. Numerical modeling of a hydrothermal system around Waita volcano, Kyushu, Japan, based on resistivity and self-potential survey results[J]. Geothermics, 32(1): 21–46. DOI:10.1016/S0375-6505(02)00048-2 |
| [] | Zhang G B, Aubert M, Qi J L. 1996. Inversion of a two-dimensional self-potential anomaly in volcanic area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 39(6): 835–844. |
| [] | Zhao Y S, Wang R F, Hu Y Q, et al. 2002. 3D numerical simulation for coupled THM of rock matrix-fractured media in heat extraction in HDR[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering (in Chinese), 21(12): 1751–1755. |
| [] | 程旭, 陈祖安, 白武明. 2014. 地壳中岩浆沿已有断层运移的数值模拟——在长白山天池火山的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(5): 1522–1533. DOI:10.6038/cjg20140516 |
| [] | 郭履灿, 马石庄, 张禹慎. 1996. 应用地震CT技术研究长白山火山的岩浆囊[J]. CT理论与应用研究, 5(1): 47–52. |
| [] | 李金铭. 2005. 地电场与电法勘探[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. |
| [] | 刘国兴. 2005. 电法勘探原理与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. |
| [] | 马明志, 张兴科, 侯立平. 1996. 长白山天池火山地震类型与地震分布[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 17(6): 39–44. |
| [] | 明跃红, 吴建平, 房立华, 等. 2009. 火山地震信号和火山颤动震源模型[J]. 地球物理学进展, 24(2): 382–390. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2009.02.003 |
| [] | 仇根根, 裴发根, 方慧, 等. 2014. 长白山天池火山岩浆系统分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(10): 3466–3477. DOI:10.6038/cjg20141032 |
| [] | 上官志冠, 孙明良. 1996. 长白山天池火山区幔源稀有气体释放特征[J]. 科学通报, 41(18): 1695–1698. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1996.18.019 |
| [] | 汤吉, 刘铁胜, 江钊, 等. 1997. 长白山天池火山区大地电磁测深初步观测[J]. 地震地质, 19(2): 164–170. |
| [] | 薛禹群. 1997. 地下水动力学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. |
| [] | 杨卓欣, 张先康, 赵金仁, 等. 2005. 长白山天池火山区三维地壳结构层析成像[J]. 地球物理学报, 48(1): 107–115. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2005.01.016 |
| [] | 张贵宾, AubertM, 齐剑玲. 1996. 火山地区二维自然电位异常反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 39(6): 835–844. |
| [] | 赵凯华, 陈熙谋. 2003. 电磁学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社. |
| [] | 赵阳升, 王瑞凤, 胡耀青, 等. 2002. 高温岩体地热开发的块裂介质固流热耦合三维数值模拟[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 21(12): 1751–1755. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2002.12.001 |
| [] | ZimmermanW B J, 中仿科技公司. 2007. Comsol Multiphysics有限元法多物理场建模与分析[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社. |
 2017, Vol. 32
2017, Vol. 32


