2. 中国石油化工股份有限公司中原油田分公司, 濮阳 457001
2. Zhongyuan Oilfield Company, SINOPEC, Puyang 457001, China
储层岩石的微观孔隙结构特征决定储层宏观特征及宏观特性参数,储层孔隙结构也是控制油气藏采收率及剩余油气分布的重要因素(吴小斌等,2011;杨少春等,2012;张创等,2012;刘堂晏等,2013;邓继新等,2015).储层孔喉参数是储层孔隙结构的定量表征,目前对于储层微观孔喉参数的定量预测还未见报道(Weingarten et al., 1995; Radlinski et al., 2004; Ding and Kantzas, 2007; Petunin et al., 2011; 王瑞飞等,2012;陈萍等,2013).
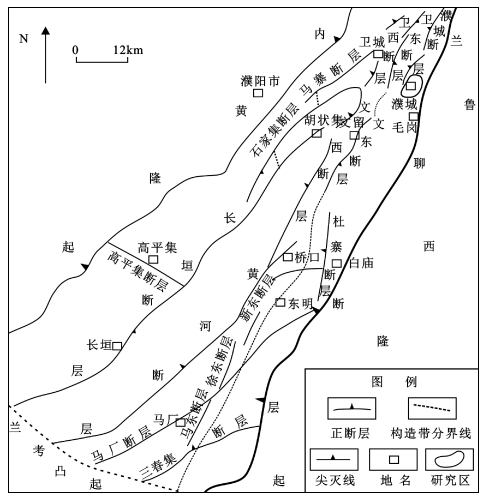
本文以渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷濮城油田沙河街组深层砂岩油藏为研究对象,应用铸体图像技术、高压压汞技术探讨了深层砂岩油藏储层孔喉参数特征,并对孔喉参数进行了定量预测.研究区位于渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷中央隆起带北部,南与文留构造带相接,北与古云集-陈营构造相连,东与濮城洼陷相邻,西与卫城-户部寨构造隔洼相望(图 1).
|
图 1 濮城油田构造位置 Figure 1 Tectonic position of Pucheng oil field |
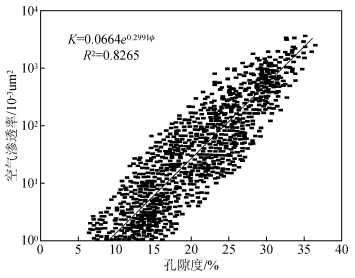
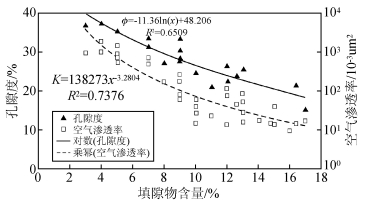
统计濮城油田沙河街组油层44口井6733组物性数据,得到孔隙度、渗透率的相关关系(图 2).分析图 2,渗透率与孔隙度总体呈指数函数的正相关关系.随孔隙度的增大,渗透率参数也增大.孔隙度分布范围有限,渗透率分布范围较宽.储层样品孔、渗关系的差异在于储层微观孔隙结构特征的不同.统计储层物性参数与填隙物含量的相关关系(图 3),储层物性参数与填隙物含量有较好的相关性,填隙物含量与渗透率参数的相关性好于其与孔隙度参数的相关性.这也说明储层物性参数中渗透率参数较孔隙度参数敏感,与图 2孔隙度参数分布范围有限,渗透率参数分布范围较大相吻合.表征储层物性的孔隙度、渗透率两参数存在较大差异.孔隙度既不限制于砂岩孔隙系统壁上小规模粗糙度所给予流体的拖曳作用,也不限制于砂岩内两点间流体必须流经的长度,这两者或两者之一的变化均能改变渗透率而不改变孔隙度.这就是研究中经常发现,同样孔隙度具有不同的渗透率以及孔隙度变化较小而渗透率变化较大的现象.
|
图 2 孔隙度与渗透率的关系 Figure 2 Relation between the porosity and the permeability |
|
图 3 濮城油田储层岩石填隙物含量与物性参数关系 Figure 3 Relation between the interstitial material content and the physical parameters |
岩心样品铸体薄片、普通薄片镜下观测结果表明,岩石孔隙、喉道类型多样,分布不均匀,孔、喉大小相差悬殊.孔隙类型主要有残余粒间孔、溶孔、晶间孔.喉道类型主要有缩径型喉道、点状喉道、片状喉道三种.
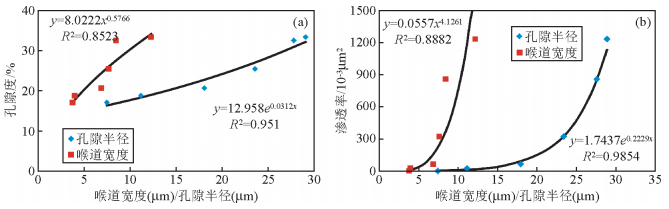
3 孔喉特征参数 3.1 铸体图像技术铸体图像技术研究孔隙结构是根据岩石颗粒和孔喉间颜色的差异描述孔喉大小及其配置情况,并进行数据处理与统计.根据29块样品的铸体图像分析资料(表 1),其储层孔隙空间结构参数具有以下特征:①不同类型储层物性与其孔隙半径、喉道宽度呈正相关,且相关性较好(图 4).②面孔率与孔隙度、渗透率参数相关性较好.但面孔率数值均较相应的孔隙度参数小,这主要是由于孔隙迂曲度造成的,可能还与图像分析仪分辨率低、注环氧树脂压力低等有关.③比表面范围为0.32~0.47 μm-1,形状因子范围为0.56~0.69,比表面、形状因子与其物性参数不相关,说明储层岩石孔喉形状的无规律性.④从特低渗透到高渗透储层,孔喉比无明显变化趋势,孔喉配位数呈增大趋势,说明从特低渗透储层到高渗透储层,孔隙半径、喉道宽度变化不大,但有效喉道数量增多,致使有效孔隙增多,无效孔隙减少,孔喉连通性变好,平面非均质性减弱.⑤各类储层孔喉均质系数、分选系数、变异系数规律性不强,也说明储层微观非均质性强,储层特性参数规律性较弱.
|
|
表 1 铸体图像孔隙特征参数分析统计表 Table 1 The pore-throat parameters by the casting image |
|
图 4 储层物性与孔隙半径(喉道宽度)的相关关系 Figure 4 Relation between the physical parameters and the pore radius (throat width) |
毛管压力曲线是研究储层微观孔隙结构特征的一种较好方法(李海燕等,2012;毛伟和杜朋举,2012;赖锦等,2015),有关储层孔喉的大部分特征参数都可由毛管压力资料确定,研究区样品高压压汞测试中最大进汞压力为45 MPa.
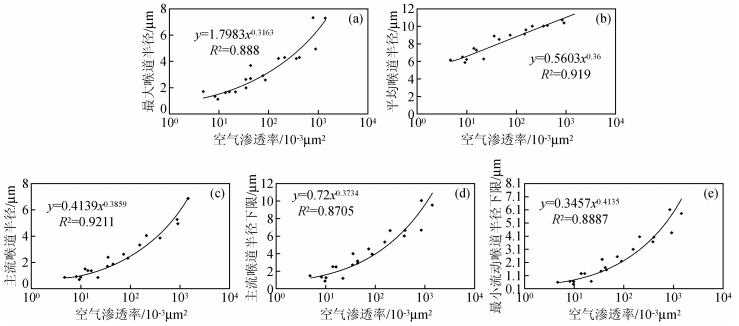
3.2.1 微观孔隙结构特征参数根据研究区储层20块样品的高压压汞资料,最大喉道半径、平均喉道半径、主流喉道半径、主流喉道半径下限值、最小可流动喉道半径等均与储层岩石渗透率参数呈正相关关系,其相关性如图 5所示.
|
图 5 孔喉特征参数与渗透率的相关关系 (a)最大喉道半径与空气渗透率的关系;(b)平均喉道半径与空气渗透率的关系;(c)主流喉道半径与空气渗透率的关系;(d)主流喉道半径下限与空气渗透率的关系;(e)最小流动喉道半径下限与空气渗透率的关系. Figure 5 Relation between the pore-throat parameters and the permeability (a) Relation between the maximal radiuses of pore throats and the permeability; (b) Relation between the average pore throat radius and the permeability; (c) Relation between the mainstream throat radius and the permeability; (d) Relation between the lower limit of mainstream throat radius and the permeability; (e) Relation between the lower limit of the minimum flowing throat radius and the permeability. |
研究中还进行了岩石平均水力半径(K/ϕ)1/2与平均喉道半径的对比,如图 6所示.研究表明,岩石平均水力半径(K/ϕ)1/2与平均喉道半径间以线性关系拟合精度为最高.设置常数项为零,其精度也很高,其统计规律公式为

|

|
图 6 平均喉道半径与平均水力半径的关系 Figure 6 Relation between the average throat radius and the average hydraulic radius |
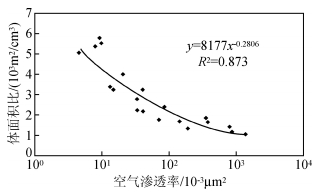
式中:K为空气渗透率,μm2;ϕ为孔隙度,%;R为平均喉道半径,μm.该式反映岩石平均水力半径与平均喉道半径呈正相关关系,由常规物性资料经系数校正后可估算岩石平均喉道半径.储层岩石比表面与渗透率呈负相关关系,如图 7.
|
图 7 比表面与空气渗透率的关系 Figure 7 Relation between the surface area and the air permeability |
比较这些喉道特征参数~渗透率的相关性与喉道特征参数~平均水力半径的相关性.储层渗透率参数的差异主要体现在孔喉系统中喉道的差异(主要体现在喉道的几何形态和喉道数量方面),这充分说明储层层间非均质程度和岩石微观非均质程度是由其油藏类型决定的.从绝对数值的角度分析,高渗透油藏的非均质程度明显高于低渗透油藏的非均质程度.但是,高渗透油藏的渗透率下限值远远高于低渗透油藏,这也是高渗透油藏驱油效率和采收率均高于低渗类型油藏的一个重要原因.
4 孔喉参数预测模型应用毛管压力资料研究储层孔隙结构(王瑞飞等,2012;章海宁等,2015),因受取心井所在区块、井点、层位等的限制,相当部分区块无压汞资料,给研究储层孔隙结构带来困难.本研究拟在毛管压力资料的基础上,建立地区性的储层孔喉参数预测模型.由毛管压力资料,不同类型储层岩心在相同的进汞压力下(即相同的喉道半径),进汞饱和度相差很大,说明不同类型岩心对应的孔隙度大小不同;探讨不同类型储层,不同喉道半径下进汞饱和度的变化规律,可以揭示储层微观孔隙结构特征.
|
|
表 2 储层孔喉特征参数预测模型 Table 2 The prediction model of the pore-throat parameters |
根据毛管压力资料,同一喉道半径下的汞饱和度与孔隙度、渗透率间有较好的相关关系,由压汞资料统计汞饱和度与空气渗透率参数的相关关系,得到研究区储层孔喉特征参数预测模型如表 2.
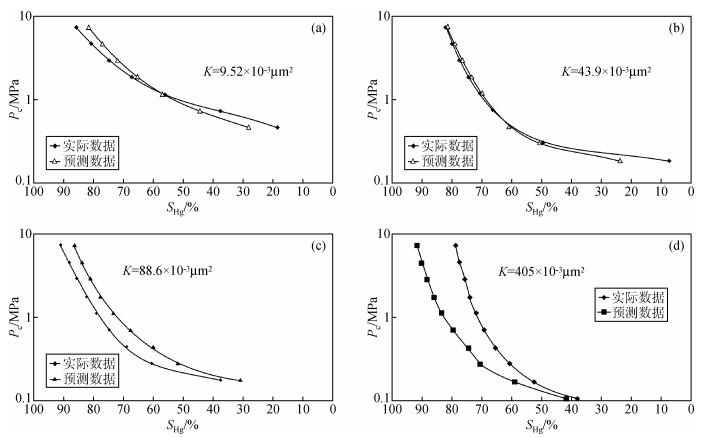
根据统计分析原理,在置于0.01显著水平上,n=20-2=18的相关系数至少应不低于0.5610.由表中的相关系数值分析可知,每个方程都满足统计意义.各类型储层样品实测压汞曲线与预测模型对比如图 8所示.分析对比结果,预测模型对低渗、特低渗样品符合程度较高,而与中高渗、高渗样品符合程度较低.由前述分析,储层趋于致密渗透性变差时孔喉比参数无明显变化趋势,即孔隙半径及喉道宽度变化不大;孔喉配位数减小,有效喉道数量减少,无效喉道数量增多,孔喉连通性变差,孔隙与喉道间的对应性变好.故渗透率越低,有效孔隙与有效喉道的关联性越强.高压压汞测试中,饱和度参数对应有效孔隙,渗透率参数对应有效喉道.故储层渗透率越低,预测模型与实测样品的符合程度越高.
|
图 8 高压压汞曲线与预测模型对比 (a)特低渗储层压汞曲线与预测模型对比;(b)低渗储层压汞曲线与预测模型对比;(c)中低渗储层压汞曲线与预测模型对比;(d)中渗储层压汞曲线与预测模型对比. Figure 8 Comparison of the high pressure mercury curve and the prediction model (a) Comparison of the high pressure mercury curve and the prediction model in Ultra-low permeability reservoir; (b) Comparison of the high pressure mercury curve and the prediction model in Low permeability reservoir; (c) Comparison of the high pressure mercury curve and the prediction model in Medium to Low permeability reservoir; (d) Comparison of the high pressure mercury curve and the prediction model in Medium permeability reservoir. |
应用铸体图像分析技术、高压压汞技术对深层砂岩油藏储层孔喉特征参数进行了研究.
5.2铸体图像技术研究表明,储层物性与孔隙半径、喉道宽度呈正相关;面孔率与孔隙度、渗透率参数相关性好,面孔率参数较相应的孔隙度参数小;比表面、形状因子与其物性参数不相关,储层孔隙、喉道形状无规律;由特低渗到高渗储层,孔喉比无明显变化趋势,孔喉配位数呈增大趋势,孔喉均质系数、分选系数、变异系数变化的规律性不强.
5.3毛管压力曲线资料分析表明,储层最大喉道半径、平均喉道半径、主流喉道半径、主流喉道半径下限值、最小可流动喉道半径等均与岩石渗透率参数呈正相关;平均水力半径与平均喉道半径呈正相关关系;储层岩石比表面与渗透率参数呈负相关关系.基于毛管压力资料,建立东濮凹陷濮城油田深层砂岩油藏储层孔喉参数预测模型.
致谢 感谢审稿专家的支持和编辑的辛勤工作.| [] | Chen P, Tao G, Dong M Z, et al .2013. The effects of the pore throat roughness on the water-oil flow in rock reservoirs[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 28 (2) : 824–829. DOI:10.6038/pg20130232 |
| [] | Deng J X, Wang H, Zhou H, et al .2015. Microtexture, seismic rock physical properties and modeling of Longmaxi Formation shale[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58 (6) : 2123–2136. DOI:10.6038/cjg20150626 |
| [] | Ding M, Kantzas A. 2007. Capillary number correlations for gas-liquid systems[C].//SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Washington, DC:Society of Ptrolleum Engineers, 1-6. |
| [] | Lai J, Wang G W, Meng C Q, et al .2015. Pore structure characteristics and formation mechanisms analysis of tight gas sandstones[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 30 (1) : 217–227. DOI:10.6038/pg20150133 |
| [] | Li H Y, Yue D L, Zhang X J .2012. Characteristics of pore structure and reservoir evaluation of low permeability reservoir in Sulige gas field[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 19 (2) : 133–140. |
| [] | Liu T Y, Tang T Z, Du H H, et al .2013. Study of rock conductive mechanism based on pore structure[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 56 (8) : 2818–2826. DOI:10.6038/cjg20130830 |
| [] | Mao W, Du P J .2012. Characteristics of pore structure of Xing'anling pay zone in Suderte Oilfield[J]. Geoscience, 26 (3) : 575–580. |
| [] | Petunin V V, Yin X L, Tutuncu A N. 2011. Porosity and permeability changes in sandstones and carbonates under stress and their correlation to rock texture[C].//SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Calgary, Alberta, Canada:Society of Ptrolleum Engineers, 1-10. |
| [] | Radlinski A P, Ioannidis M A, Hinde A L, et al .2004. Angstrom-to-millimeter characterization of sedimentary rock microstructure[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 274 (2) : 607–612. DOI:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.02.035 |
| [] | Wang R F, Lv X H, Guo D B .2012. Feature parameters of micro pore throat in deep section high pressure and low-permeability sandstone reservoir[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 41 (1) : 64–68. |
| [] | Weingarten J S. Perkins T K .1995. Prediction of sand production in gas wells:Methods and gulf of mexico case studies[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 47 (7) : 596–600. DOI:10.2118/24797-PA |
| [] | Wu X B, Hou J G, Sun W .2011. Microstructure characteristics and quantitative analysis on porosity evolution of ultra-low sandstone reservoir[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 42 (11) : 3438–3446. |
| [] | Yang S C, Wang H J, Luo H N, et al .2012. Nanoscale pore structure characteristics of clastic rock in Shengli Oilfield[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 36 (1) : 8–12. |
| [] | Zhang C, Sun W, Yang J P, et al .2012. Pore and pore-throat size distributions of low permeability sandstone reservoir and their differential origin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86 (2) : 335–348. |
| [] | Zhang H N, Tang T Z, Liu T Y, et al .2015. A saturation evaluating method based on pore structure[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 30 (2) : 709–717. DOI:10.6038/pg20150231 |
| [] | 陈萍, 陶果, 董明哲, 等.2013. 岩石孔喉道中表面粗糙度对油水两相流动的影响[J]. 地球物理学进展, 28 (2) : 824–829. DOI:10.6038/pg20130232 |
| [] | 邓继新, 王欢, 周浩, 等.2015. 龙马溪组页岩微观结构、地震岩石物理特征与建模[J]. 地球物理学报, 58 (6) : 2123–2136. DOI:10.60388/cjg20150626 |
| [] | 赖锦, 王贵文, 孟辰卿, 等.2015. 致密砂岩气储层孔隙结构特征及其成因机理分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 30 (1) : 217–227. DOI:10.6038/pg20150133 |
| [] | 李海燕, 岳大力, 张秀娟.2012. 苏里格气田低渗透储层微观孔隙结构特征及其分类评价方法[J]. 地学前缘, 19 (2) : 133–140. |
| [] | 刘堂晏, 汤天知, 杜环虹, 等.2013. 考虑储层孔隙结构的岩石导电机制研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 56 (8) : 2818–2826. DOI:10.6038/cjg20130830 |
| [] | 毛伟, 杜朋举.2012. 苏德尔特油田兴安岭油层微观孔隙结构特征[J]. 现代地质, 26 (3) : 575–580. |
| [] | 王瑞飞, 吕新华, 国殿斌.2012. 深层高压低渗砂岩储层微观孔喉特征参数研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 41 (1) : 64–68. |
| [] | 吴小斌, 侯加根, 孙卫.2011. 特低渗砂岩储层微观结构及孔隙演化定量分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 42 (11) : 3438–3446. |
| [] | 杨少春, 王惠娟, 罗海宁, 等.2012. 胜利油区碎屑岩纳米尺度孔隙结构特征[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 36 (1) : 8–12. |
| [] | 张创, 孙卫, 杨建鹏, 等.2012. 低渗砂岩储层孔喉的分布特征及其差异性成因[J]. 地质学报, 86 (2) : 335–348. |
| [] | 章海宁, 汤天知, 刘堂晏, 等.2015. 基于地层孔隙结构的饱和度评价方法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 30 (2) : 709–717. DOI:10.6038/pg20150231 |
 2016, Vol. 31
2016, Vol. 31

