2. 长城钻探工程技术有限公司测井公司, 盘锦 124011
2. Well Logging, CNPC-GWDC, Panjin, Liaoning 124011, China
针对目前日益复杂的地质构造的研究需要,薄层、薄互层已经成为测井分析家的一项重要课题.提高薄层、薄互层的认识必须提高地球物理测井的分辨率.通常采用以下两种方法来提高测井的分辨率:其一,研制开发高分辨率的测井仪器;其二,通过研究高分辨率处理技术来提高测井评价的正确性(周远田和付友生,1999),采用高分辨率技术会增加人为的影响因素,在某些地层中会出现虚假的分辨率信息的现象.
双侧向测井是常规电阻率测井方法,在油田勘探开发中发挥了重要作用.国内著名电法测井家张庚骥先生利用有限元方法分析了双侧向计算理论(张庚骥,1986),后来的学者对双侧向仪器在裂缝性地层测井响应开展了研究(汪涵明等,1995;邓少贵等,2010),对大斜井井以及水平井中双侧向响应以及快速井眼校正进行了仿真(肖加奇和张庚骥,1996;高杰和谢然红,2000;朱大伟等,2005;邓少贵等,2009);在此基础上对阵列侧向正反演计算(李智强等,2010),也对水平井中盐水泥浆响应及快速计算方法进行研究(谭茂金等,2012).总之,国内外主要工作是针对原有仪器开展测井响应和快速井眼计算方法,重点针对原有双侧向仪器的探测特性开展响应规律研究,随着油田开发程度的不断提高,原有双侧向测井仪受垂直分辨率影响,无法充分反映所研究的地层信息,遗漏掉薄层以及薄互层中的储层,从而低估了储量,解释可信度降低.本文重点对高分辨率双侧向仪器开展了理论设计研究以及高分辨率双侧向的探测响应研究.
1 电极系排列工作原理国内外测井公司推出多种双侧向测井仪,虽然它们的电极系尺寸不同,但电极系结构和电极排列方式基本上是一样的.其中供电电极都是由A0、A1、A1′、A2、A2′组成,而监督电极为2对对称监督电极M1(M1′)、M2(M2′)或者3对对称监督电极M1(M1′)、M2(M2′)、M3(M3′);有的采用1对取样电极(A1*、A1*′),有的没有取样电极.几种典型的常规双侧向电极系如图 1所示.尽管电极排列方式有所不同以及各电极尺寸也不一样,但它们的探测性能差别不大,分层能力为0.6~0.9 m;探测深度深侧向为1.2~1.5 m、浅侧向为0.35~0.45 m,井眼影响的特征也相似.
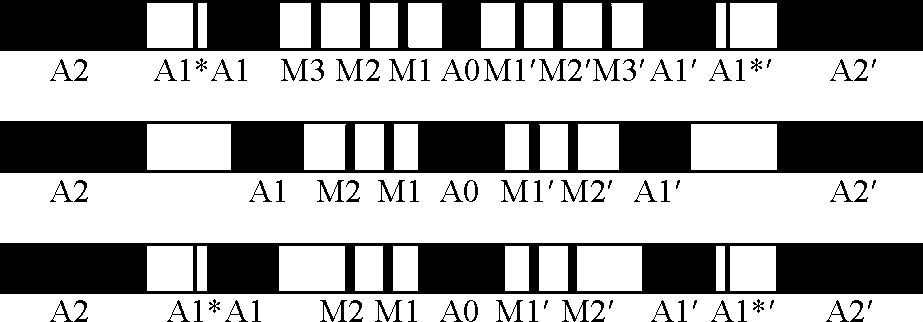
|
图 1 常规双侧向电极系示意图 Figure 1 The schematic diagram of dual laterolog electrode system |
高分辨率双侧向采用与原来双侧向测井仪器结构相同的形式,采用了两对监督电极M1(M1′)、M2(M2′)以及A1*(A1*′)取样电位,只是在结构尺寸中进行了调整,调整后仪器长度为5.80 m.在提高分辨率的同时,缩短仪器长度,更加有利于实际施工过程以及减小仪器施工的风险.
在CSU双侧向中采用了反馈回路使监督电极M1、M2等电位,在高分辨率双侧向中采用了软聚焦合成原理使M1、M2保证始终等电位.
2 数值模拟理论 2.1 地层模型在二维轴对称情况下,采用柱坐标系,此时高分辨率双侧向测井方法所计算的场可以简化为如图 2所示的二维非均匀介质模型.

|
图 2 高分辨率双侧向及地层模型 Figure 2 High resolution dual laterolog tool and formation model |
图 2中,Rxo为侵入带电阻率,Rt为原状地层电阻率,H为目的层第j层的层厚,Rs为围岩电阻率,Rm为泥浆电阻率.
2.2 数学模型在柱坐标系(ρ,φ,z)下,由地层旋转轴对称性,高分辨率双侧向测井响应的求解简化为图 2所示的1/2空间.在二维柱坐标系下,高分辨率双侧向测井响应中连续而且光滑的电场函数U满足公式为
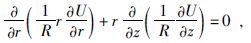
|
(1) |
式中:R为不同区域的电阻率;在恒压电极,U满足第一类边界条件;在恒流电极表面上,U满足第二类边界条件


为求取(1),需将偏微分方程问题转化成求泛函的极值问题:

|
(2) |
式中,IE,UE是各电极上电流和电位.通过有限元方法求得电位后,高分辨率双侧向测井响应值满足公式为

|
(3) |
式中:K为仪器参数;UM1为M1电极上的电位值;I0为仪器发射电流强度.
2.3 伪几何因子及侵入的影响高分辨率双侧向的径向探测深度和侵入影响可以用伪几何因子来描述,深侧向(Jd)、浅侧向(Js)测井伪几何因子J表示为
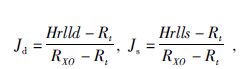
|
(4) |
其中,Jd,Js分别为高分辨率深浅侧向伪几何因子.
图 3的模拟条件为:井径8 inch(20 cm),泥浆电阻率1.0 Ω·m,冲洗带电阻率10.0 Ω·m,原状地层电阻率50.0 Ω·m.图 3中横坐标表示侵入深度,纵坐标为伪几何因子.以径向伪几何因子为0.50对应的侵入深度作为探测深度,CSU浅探测深度为0.37 m,深探测深度为1.20 m,计算得到的CSU深浅侧向电极系数分别为0.89,1.45.利用有限元方法对CSU双侧向的探测深度计算与CSU的探测深度以及电极系数相一致(张庚骥,2013,电法测井;),表明了该算法的正确性与准确性.
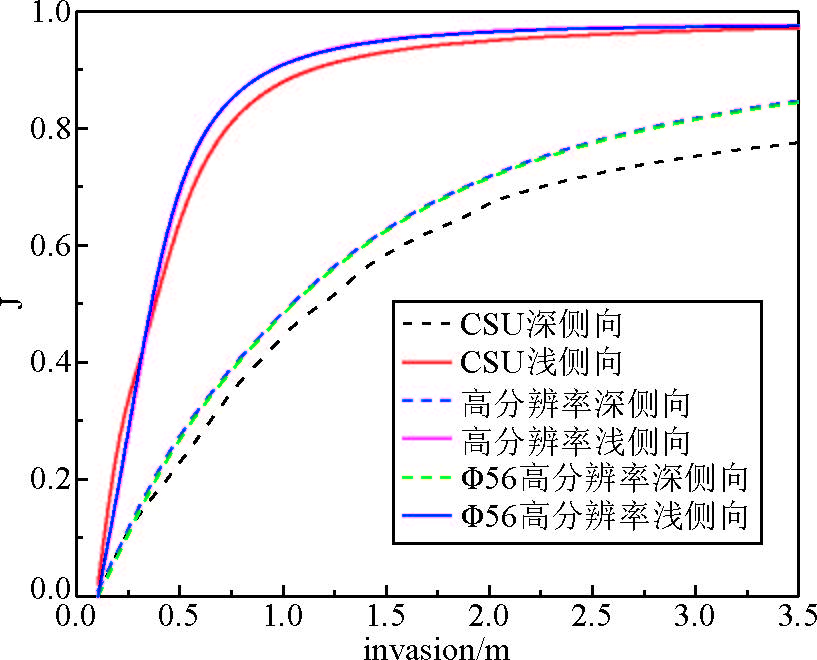
|
图 3 高分辨率双侧向与常规双侧向伪几何因子对比 Figure 3 Comparison of pseudo geometry factors of high resolution dual laterolog with that of dual laterolog |
高分辨率深侧向的探测深度为1.03 m,高分辨率浅侧向探测深度为0.35 m.高分辨率侧向在仪器外径变为57 mm时,探测深度与外径为100 mm的高分辨率侧向相一致.可见经过优化之后的高分辨双侧向电极系在保证探测深度的同时还缩短仪器长度.
2.4 层厚影响与纵向分辨率图 4为Φ100高分辨率双侧向、Φ57高分辨率双侧向以及CSU双侧向的层厚校正曲线,其模拟条件为:Rs=1.0 Ω·m,层厚为0.20~10.0 m.其中Rt为地层真电阻率,Rhlld0、Rhlls0为Φ100高分辨率深浅侧向的测井响应值.Rhlld1、Rhlls1为Φ57高分辨率深浅侧向的测井响应值.Rlld、Rlls为双侧向的测井响应值.

|
图 4 (a)Φ100高分辨率浅侧向层厚影响校正曲线;(b)Φ100高分辨率深侧向层厚影响校正曲线; (c)Φ57高分辨率浅侧向层厚影响校正曲线;(d)Φ57高分辨率深侧向层厚影响校正曲线; (e)CSU浅侧向层厚影响校正曲线;(f)CSU深侧向层厚影响校正曲线 Figure 4 (a)Bed correction curve of high-resolution shallow investigation laterolog tool with Φ100; (b)Bed correction curve of high-resolution deep investigation laterolog tool with Φ100; (c)Bed correction curve of high-resolution shallow investigation laterolog tool with Φ57; (d)Bed correction curve of high-resolution deep investigation laterolog tool with Φ57; (e)Bed correction curve of CSU shallow investigation laterolog; (f)Bed correction curve of CSU deep investigation laterolog |
从图 4中可以看出,Φ100高分辨率双侧向、Φ57高分辨率双侧向以及CSU双侧向的层厚影响校正系数均表现为非线性变化,但是高分辨率双侧向在层厚为0.20 m时,其校正系数远小于CSU双侧向的校正系数.
图 5的模拟条件:井眼为8 in,泥浆电阻率为1.0 Ω·m,层厚分别为0.20 m、0.50 m、1.0 m,围岩为4.0 Ω·m,目的层为30.0 Ω·m.从模拟结果分析在层厚为0.20 m时,Φ100高分辨率双侧向、Φ57高分辨率双侧向测量结果可以分别为20.0 Ω·m以及17.0 Ω·m,而CSU双侧向测量结果仅在8.0 Ω·m,对于薄层中地层的视电阻率,高分辨率双侧向要高于CSU双侧向.

|
图 5 (a)Φ100高分辨率双侧向在薄层中的响应;(b)Φ57高分辨率双侧向在薄层中的响应; (c)双侧向在薄层中的响应图 Figure 5 (a)Response of high-resolution dual laterolog tool with Φ100 in thin bed; (b)Response of high-resolution dual laterolog tool with Φ57 in thin bed; (c)Response of dual laterolog tool in thin bed |
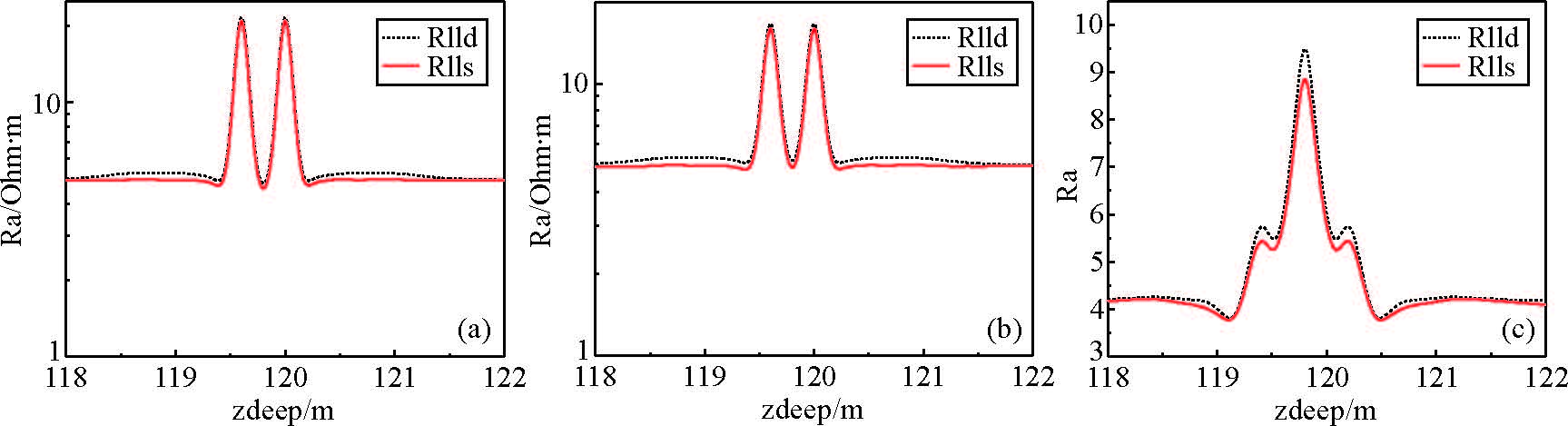
图 6的模拟条件:井眼为8 in,泥浆电阻率为1.0 Ω·m,层厚分别为0.20 m、0.20 m、0.20 m,低阻层电阻率为4.0 Ω·m,夹层为30.0 Ω·m.从模拟结果分析Φ100高分辨率双侧向、Φ57高分辨率双侧向测量可以明显的分辨两个夹层,测量的电阻率分别为20.0 Ω·m、17.0 Ω·m,而CSU双侧向测井响应曲线仅能反映出一个夹层且与原始地层模型具有较大的差别.
|
图 6 (a)Φ100高分辨率双侧向在薄互层中的响应;(b)Φ57高分辨率双侧向在薄互层中的响应; (c)双侧向在薄互层中的响应 Figure 6 (a)Response of high-resolution dual laterolog tool with Φ100 in thin interbed; (b)Response of high-resolution dual laterolog tool with Φ57 in thin interbed; (c)Response of dual laterolog tool in thin interbed |
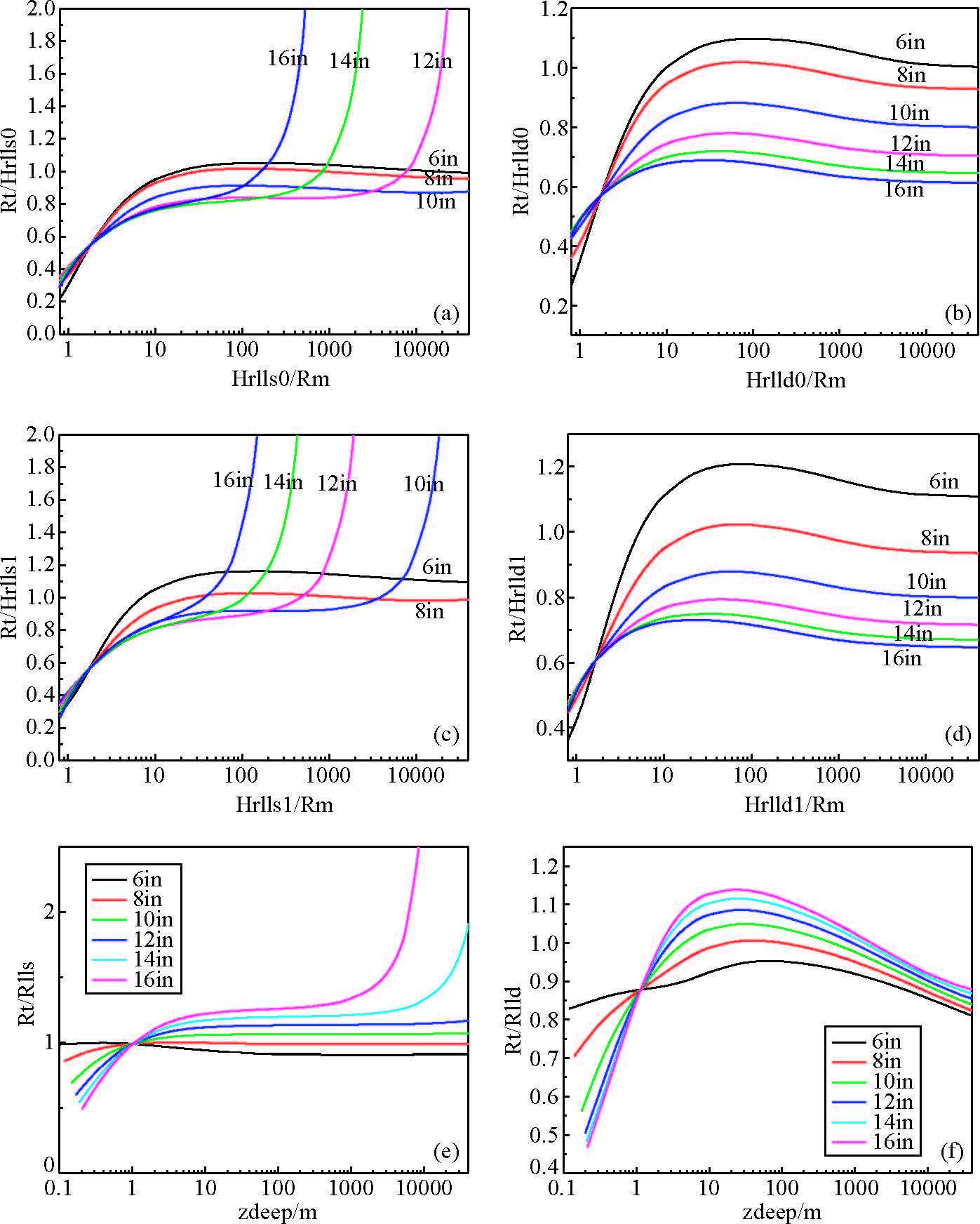
高分辨率双侧向的井眼影响校正曲线见图 7,图中横轴为视电阻率(Ra)与泥浆(Rm)的比值,纵轴为原状地层与视电阻率的比值Rt/Ra,不同的曲线代表不同的井眼大小.
|
图 7 (a)Φ100高分辨率浅侧向井眼影响校正曲线;(b)Φ100高分辨率深侧向井眼影响校正曲线; (c)Φ57高分辨率浅侧向井眼影响校正曲线;(d)Φ57高分辨率深侧向井眼影响校正曲线; (e)浅侧向井眼影响校正曲线;(f)深侧向井眼影响校正曲线 Figure 7 (a)Borehole correction curve of high-resolution shallow investigation laterolog tool with Φ100; (b)Borehole correction curve of high-resolution deep investigation laterolog tool with Φ100; (c)Borehole correction curve of high-resolution shallow investigation laterolog tool with Φ57; (d)Borehole correction curve of high-resolution deep investigation laterolog tool with Φ57; (e)Borehole correction curve of shallow investigation laterolog; (f)Borehole correction curve of deep investigation laterolog |
从图 7b、图 7d分析,高分辨率深侧向随着井眼的变大,校正系数逐渐变小;从图 7f分析,随着井眼的变大,深侧向的校正系数逐渐变大;这是由于高分辨率双侧向为了增加纵向分辨率,采用了“过聚焦”的聚焦方式,导致了井眼校正关系的反序现象.从图 7可知,Hrlld/Rm比值在10~1000内,大井眼中高分辨率深侧向测量值会大于地层的真电阻率值,而深侧向Rlld/Rm比值在10~1000内时测量值会小于地层的真电阻率值,为了更好的对比两种测井曲线,高分辨率双侧向必须进行井眼校正.由图 7b、图 7d可知随着仪器直径的缩小,高分辨率双侧向受井眼的影响也变大.
3 结 论利用有限元方法编制了计算高分辨率双侧向测井仪器响应的数值模拟程序,并对高分辨率双侧向测井仪进行理论优化设计;
经过数值模拟可知,高分辨率浅侧向的探测深度与浅侧向相同,高分辨率深侧向探测深度可以达到1.03 m;
通过层厚影响、薄层以及薄互层分析可知,高分辨率双侧向分辨率可以达到0.20 m,可以识别储层厚度大于0.20 m的地层;
通过井眼校正模拟可知,高分辨率深侧向的井眼校正关系与深侧向的井眼校正关系趋势相反,两者在井眼较大时视电阻率值差异也较大,高分辨率双侧向必须经过井眼校正;
高分辨率双侧向仪器做到100 mm的外径,与常规测井系列进行组合测井,已经达到仪器推广阶段;该仪器还可以缩小为57 mm的外径满足泵出式仪器系列.
致谢 感谢审稿专家和编辑老师对本文提出的宝贵意见和建议.| [1] | Deng S G, Li Z Q, Chen H.2010. The simulation and analysis of array lateral log response of fracture in coalbed methane reservoir[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration (in Chinese), 38 (3) : 55–60. |
| [2] | Deng S G, Li Z Q, Li Z Q.2009. Response of dual laterolog and fast correction for layer thickness and shoulder bed in horizontal wells[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development (in Chinese), 36 (6) : 725–729. DOI:10.1016/S1876-3804(10)60005-5 |
| [3] | Gao J, Xie R H.2000. 3D numerical forward modeling and fast correction of dual-laterolog for high angle deviated wells[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development (in Chinese), 27 (2) : 69–71. |
| [4] | Li Z Q, Fan Y R, Deng S G, et al.2010. Inversion of array laterolog by improved difference evolution[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition) (in Chinese), 40 (5) : 1199–1204. |
| [5] | Tan M J, Gao J, Zou Y L, et al.2012. Environment correction method of dual laterolog in directional well[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 55 (4) : 1422–1432. DOI:10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.04.038 |
| [6] | Wang H M, Zhang G J, Li S J, et al.1995. The dual laterolog response of the single dipping fracture[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China (in Chinese), 19 (6) : 21–24. |
| [7] | Xiao J Q, Zhang G J.1996. Computation of dual laterolog responses in highly deviated and horizontal wells with 3-D finite element method[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China (in Chinese), 20 (1) : 24–28. |
| [8] | Zhang G J.1986. Electrical Logging (in Chinese)[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press . |
| [9] | Zhang G J.2013. Electric Logging Algorithm (in Chinese)[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press . |
| [10] | Zhou Y T, Fu Y S.1999. High-resolution processing technique for geophysical logging data[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting (in Chinese), 34 (4) : 408–414. |
| [11] | Zhu D W, Deng S G, Fan Y R, et al.2005. Numerical simulation of dual laterolog response in highly deviated wells[J]. Well Logging Technology (in Chinese), 29 (3) : 208–211. |
| [12] | 邓少贵, 李智强, 陈华.2010. 煤层气储层裂隙阵列侧向测井响应数值模拟与分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 38 (3) : 55–60. |
| [13] | 邓少贵, 李竹强, 李智强.2009. 水平井双侧向测井响应及层厚/围岩影响快速校正[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 36 (6) : 725–729. |
| [14] | 高杰, 谢然红.2000. 大斜度井侧向测井三维正演数值模拟及曲线快速校正方法研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 27 (2) : 69–71. |
| [15] | 李智强, 范宜仁, 邓少贵, 等.2010. 基于改进差分进化算法的阵列侧向测井反演[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 40 (5) : 1199–1204. |
| [16] | 谭茂金, 高杰, 邹友龙, 等.2012. 盐水泥浆条件下定向井双侧向测井环境校正方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 55 (4) : 1422–1432. DOI:10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.04.038 |
| [17] | 汪涵明, 张庚骥, 李善军, 等.1995. 单一倾斜裂缝的双侧向测井响应[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 19 (6) : 21–24. |
| [18] | 肖加奇, 张庚骥.1996. 水平井和大斜度井中双侧向测井响应的正演[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 20 (1) : 24–28. |
| [19] | 张庚骥.年1986. 电法测井(下册)[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社 . |
| [20] | 张庚骥.2013. 电测井算法[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社 . |
| [21] | 周远田, 付友生.1999. 地球物理测井高分辨率处理技术[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 34 (4) : 408–414. |
| [22] | 朱大伟, 邓少贵, 范宜仁, 等.2005. 大斜度井双侧向测井响应的数值模拟[J]. 测井技术, 29 (3) : 208–211. |
 2016, Vol. 31
2016, Vol. 31

