基于秦四清等(2010a,b)提出的孕震断层多锁固段脆性破裂理论与相关预测方法,我们先后成功地对中缅边境地震区(秦四清和薛雷,2011; 秦四清等,2014a)、昭通地震区(秦四清等,2012b)、汶川地震区(秦四清等,2014h)、海原地震区(秦四清等,2013c)、于田地震区(秦四清等,2014e)和普洱地震区(秦四清等,2014g)的未来震情进行了前瞻性预测,表明该理论经得起重复性检验.在地震区精细划分的基础上(秦四清等, 2013a,2014b),作者逐步完善了基于该理论进行强震预测的方法体系,先后提出了较大事件震级预测方法(秦四清等, 2012a,2014h)、不同震级标度之间的转换关系(秦四清等,2013b)、最小完整性震级Mc确定方法(秦四清等,2014d)以及孕育周期界定和主震事件判识方法(秦四清等, 2014b,c).将改进后的预测方法应用于板间地震区大地震预测研究(秦四清等,2014f),效果良好.这不仅增强了该理论的实际可操作性,同时也可提高预测精度.
秦四清等(2014d)的研究表明:地震目录的完整性直接影响CBS(Cumulative Benioff Strain)值计算结果,进而影响对特定地震区强震发生时间窗口的判断.对某些地震区数据分析时若考虑Mc,则可大大降低预测临界CBS值和实际值之间的误差.
鉴于此,本文考虑Mc,重新研判新疆及其邻区某些地震区(图 1)强震、大震或巨震发震时间窗口,其中包括:中吉边境、新源-阿拉木图、库尔勒、拜城、昆仑山口西与若羌地震区.鉴于我们近期分析哈密-阿勒泰-斋桑与阿图什地震区震情时已考虑了Mc(秦四清等,2014c),而对于田地震区的前瞻性预测也已得到验证(秦四清等,2014e),故本文不再涉及.
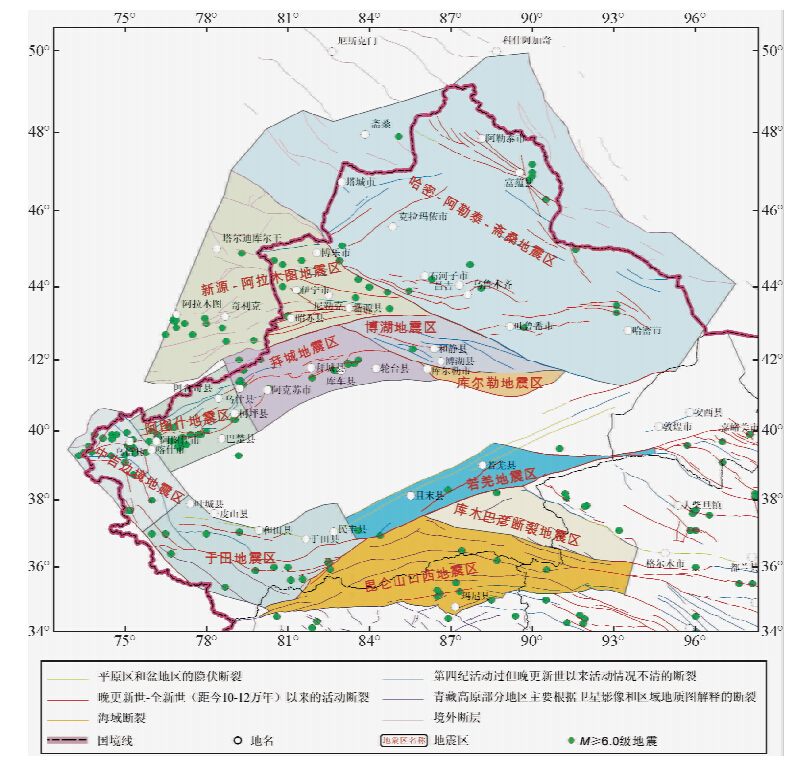 | 图 1 已划定的新疆及其邻区地震区构造图 Fig. 1 Seismotectonic map of the delimited seismic zones in Xinjiang region and its adjacent regions |
数据分析时,中吉边境、昆仑山口西与若羌地震区的地震目录均引自中国地震信息网站;新源-阿拉木图、拜城与库尔勒地震区2010年8月3日前的地震目录由新疆地震局提供,之后数据引自中国地震信息网站.
|
|
表 1 Mc对新疆及其邻区某些地震区预测临界CBS值和实际监测值的影响 Table 1 The influence of Mc on the predicted critical values and actual monitored ones of CBS for some seismic zones in Xinjiang region and its adjacent regions |
根据秦四清等(2014d)提出的最小完整性震级确定方法,我们确定了上述6个地震区的Mc值,并计算了相应的临界CBS值和截止到2014年11月14日的实际监测值.作为对比,不考虑Mc的相应数值也一并示于表 1.容易看出:(1)考虑Mc与否,对拜城与库尔勒地震区的临界值和监测值影响不大.鉴于这两个地震区当前监测值距临界值尚远(图 2~3),故预测发震时间窗口均为中长期,而其他要素预测结果可参见文献(秦四清等,2013b).(2)考虑Mc与否,对中吉边境地震区、新源-阿拉木图地震区、昆仑山口西与若羌地震区的临界值和监测值有较大影响,故我们重点重新研判这四个地震区的发震时间窗口及其他要素.
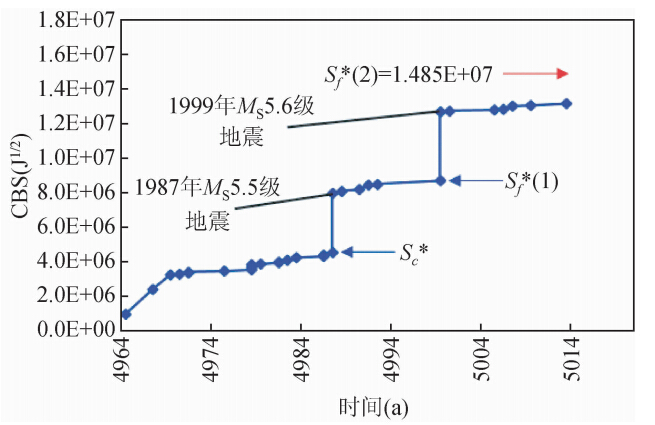 |
图 2 库尔勒地震区1964.11.23-2014.11.14之间CBS值与时间关系 (数据分析时选取MS≥3.0级地震事件;横坐标对应的时间减去3000年为实际年份;误差修正已被考虑.) Fig. 2 Temporal distribution of CBS in the period from 23 November 1964 to 14 November 2014 for the Korla seismic zone (The earthquake events with MS ≥3.0 are selected for data analysis.The real time is the value on the horizontal axis minus 3000 years. The error correction is also considered.) |
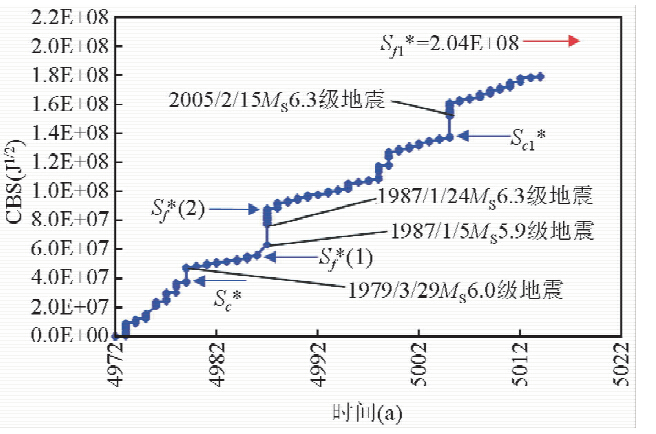 |
图 3 拜城地震区1972.10.10-2014.11.14之间CBS值与时间关系 (数据分析时选取MS≥3.0级地震事件;横坐标对应的时间减去3000年为实际年份;误差修正已被考虑.) Fig. 3 Temporal distribution of CBS in the period from 10 October 1972 to 14 November 2014 for the Baicheng seismic zone (The earthquake events with MS ≥3.0 are selected for data analysis.The real time is the value on the horizontal axis minus 3000 years. The error correction is also considered.) |
对该地震区发震时间窗口的判断,我们前后有过两次失误.由震级标度换算关系不合理引起的误判,已于2013年10月份得以纠正(秦四清等,2013b);由未考虑Mc导致的误判,已于2014年4月份得以初步纠正(http://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-575926-789411.html).
下面讨论Mc值选取对该地震区CBS值的影响.如表 1所示,若不考虑Mc时,则截止到2014年11月14日,该区CBS监测值约为1.57E+09J1/2,已超过临界值1.52E+09J1/2,但预期中的大震事件仍未发生;若考虑Mc(取ML4.0级)时,截止到2014年11月14日,该区CBS监测值约为1.41E+09J1/2,距临界值1.52E+09J1/2尚有一定距离(图 4),故预测发震时间窗口为中长期.对该区未来大震其他要素的预测结果如下:震级:MS 7.5~7.9级;震中位置:北纬38.7°,东经75.8°;震源深度:7~20 km.我们将密切跟踪该区地震活动性动态,期望对震中位置和发震时间有更准确的判断.预计向临界状态演化过程中,该地震区还将发生不超过MS 6.8级的preshock或foreshock事件.
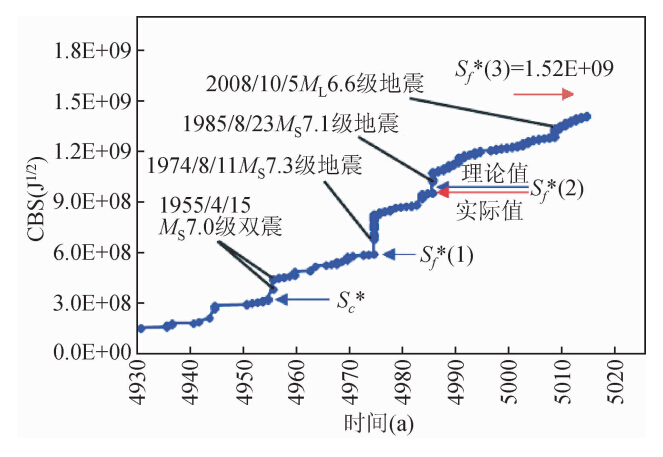 |
图 4 中吉边境地震区1853.11.1-2014.11.14之间CBS与时间关系 (数据分析时选取ML≥4.0级地震事件;为使图件清晰,1930.2.8前的应变值作为初值;横坐标对应的时间减去3000年为实际年份;误差修正已被考虑.) Fig. 4 Temporal distribution of CBS in the period from 1 November 1853 to 14 November 2014 for the China-Kyrgyzstan seismic zone (The earthquake events with ML≥4.0 are selected for data analysis.The strain value prior to 8February 1930 is regarded as an initial one for seeing a more clear figure. The real time is the value on the horizontal axis minus 3000 years. The error correction is also considered.) |
1.2 新源-阿拉木图地震区
因当时数据处理时未考虑Mc,当发现CBS监测值超越临界上限值时,秦四清等(2013b)预测该地震区的巨震应在2014年底前发生.目前看来,这种可能性不大.
如表 1所示,当该区Mc取MS 5.4级时,截止到2014年11月14日,该区实际CBS监测值约为1.86E+09J1/2,已接近临界值1.89E+09J1/2(图 5).考虑到该区近期地震活动性动态,故预测发震时间窗口为中长期.对该区未来巨震其他要素的预测结果如下:震中位置:中吉哈边境地区(北纬43°、东经80°左右);震源深度:10~30 km;震级:MS 8.3~8.7级,为MS 8.5~8.6级的可能性大.我们将密切跟踪该区地震活动性动态,期望对震中位置和发震时间有更准确的判断.预计向临界状态演化过程中,该地震区还将发生不超过MS 7.2级的preshock 或foreshock事件.
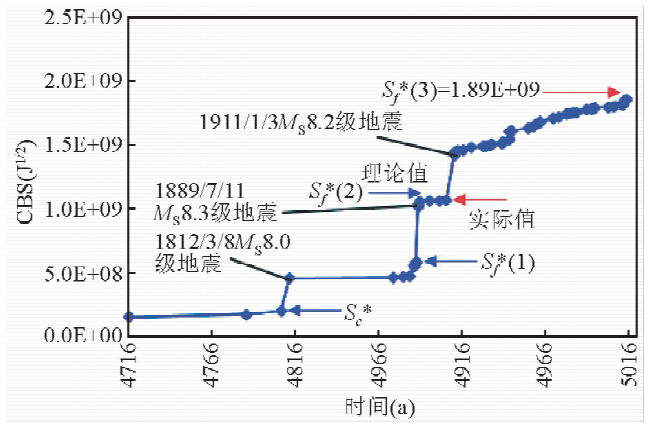 |
图 5 新源-阿拉木图地震区250-2014.11.14之间CBS值与时间关系 (数据分析时选取MS≥5.4级地震事件;为使图件清晰,1716.1.1前的应变值作为初值;横坐标对应的时间减去3000年为实际年份;误差修正已被考虑.) Fig. 5 Temporal distribution of CBS in the period from 250 to 14 November 2014 for the Xinyuan-Alma-Ata seismic zone (The earthquake events with MS ≥5.4 are selected for data analysis.The strain value prior to 1 January 1716 is regarded as an initial one for seeing a more clear figure. The real time is the value on the horizontal axis minus 3000 years. The error correction is also considered.) |
1.3 昆仑山口西地震区
如表 1所示,当Mc取ML3.7级时,截止到2014年11月14日,该区CBS监测值约为1.57E+08J1/2,距临界值1.61 E+08J1/2较近(图 6),结合该区近期地震活动性判断,预测发震时间窗口为中短期.对该区强震其他要素的预测结果如下:震级:MS 6.4~6.8级,为MS 6.5~6.6级的可能性大;震中位置:北纬36.6°,东经84.1°;震源深度:5~20 km.我们将密切跟踪该区地震活动性动态,期望对震中位置和发震时间有更准确的判断.预计向临界状态演化过程中,该地震区还将发生不超过MS 5.8级的preshock或foreshock事件.
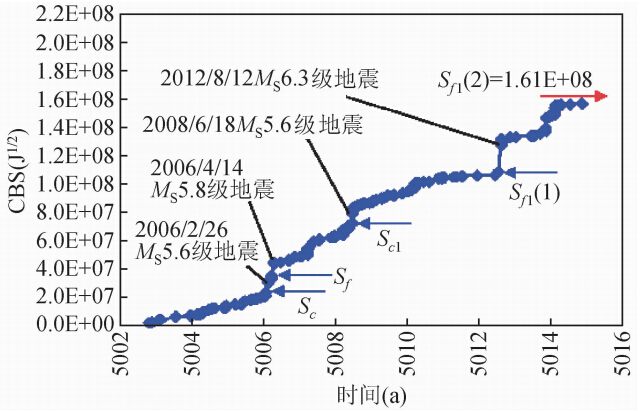 |
图 6 昆仑山口西地震区2002.10.19-2014.11.14之间CBS值与时间关系 (数据分析时选取ML≥3.7级地震事件;横坐标对应的时间减去3000年为实际年份.) Fig. 6 Temporal distribution of CBS in the period from 19 October 2002 to 14 November 2014 for the Kunlunshankouxi seismic zone (The earthquake events with ML≥3.7 are selected for data analysis.The real time is the value on the horizontal axis minus 3000 years.) |
表 2为该地震区有地震记录以来M≥5.0级的地震目录.可看出,1924年7月12日新疆民丰东MS 7.2级地震,是该区有史以来记录到的最大地震,故初步认为该震是若羌地震区的一次主震事件,而1933年9月26日新疆且末东MS 6.75级地震则是主震后的一次强余震事件.由于该周期地震目录严重缺失,难以根据我们的理论分析主震事件的孕育过程.根据上述分析,我们认为该地震区至少已经历一个完整的孕育周期,目前处于第二轮孕育周期.图 7示出了考虑Mc(取ML 3.0级)时,该区当前孕育周期中强震事件之间的力学联系.
|
|
表 2 若羌地震区M≥5.0级地震事件 Table 2 The earthquake events with M≥5.0 in the Ruoqiang seismic zone |
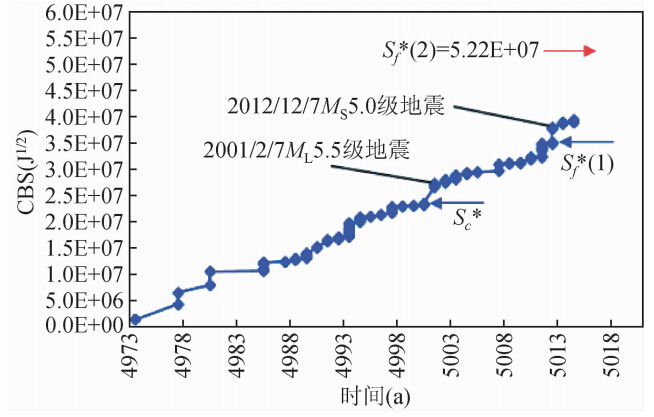 |
图 7 若羌地震区1973.4.19-2014.11.14之间CBS值与时间关系 (数据分析时选取ML≥3.0级地震事件;横坐标对应的时间减去3000年为实际年份;误差修正已被考虑.) Fig. 7 Temporal distribution of CBS in the period from 19 April 1973 to 14 November 2014 for the Ruoqiang seismic zone (The earthquake events with ML≥3.0 are selected for data analysis.The real time is the value on the horizontal axis minus 3000 years.The error correction is also considered.) |
如表 1所示,Mc对该区临界CBS值有较大影响.不论考虑Mc与否,实际CBS监测值均距相应的临界CBS值较远,故预测发震时间窗口为中长期.对该区未来中强震其他要素的预测结果如下:震级:MS 5.4~5.8级;震中位置:北纬39.2°,东经88.8°;震源深度:5~20 km.我们将密切跟踪该区地震活动性动态,期望对震中位置和发震时间有更准确的判断.预计向临界状态演化过程中,该地震区还将发生不超过MS 5.2级的preshock或foreshock事件. 2 结 论
考虑最小完整性震级Mc,对新疆及其邻区某些地震区未来震情进行了重新研判,得出如下结论:
(1)Mc对不同地震区预测临界CBS值和监测值的影响程度不同,其对拜城与库尔勒地震区的影响不大,而对中吉边境、新源-阿拉木图、昆仑山口西与若羌地震区则有较大影响.
(2)拜城、库尔勒与若羌地震区目前距临界状态较远,故预测发震时间窗口均为中长期.
(3)中吉边境地震区未来将发生MS 7.5~7.9级地震,目前距临界状态尚有一定距离,故预测发震时间窗口为中长期.
(4)新源-阿拉木图地震区未来将发生MS 8.3~8.7级地震,目前已接近临界状态,结合该区近期地震活动性判断,预测发震时间窗口为中长期.
(5)昆仑山口西地震区未来将发生MS 6.5~6.9级地震,目前已接近临界状态,结合该区近期地震活动性判断,预测发震时间窗口为中短期.
建议有关部门根据本文四要素预测结果,加强相关地震区前兆异常监测,以及时作出判断.
致 谢 感谢国家自然科学基金委重点项目(41030750)对研究工作的资金支持.| [1] | Qin S Q, Li G L, Xue L, et al. 2013a. Reanalysis of the future earthquake situation for some seismic zones in the region of Southwest China. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese), 28(5): 2407-2432, doi: 10.6038/pg20130521. |
| [2] | Qin S Q, Li G L, Xue L, et al. 2013b. Reanalysis of the future earthquake situation for some seismic zones in the Xinjiang region and its border areas. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese), 28(5): 2376-2391, doi: 10.6038/pg20130519. |
| [3] | Qin S Q, Li G L, Xue L, et al. 2014c. Analysis of the future earthquake situation for some seismic zones in the northwest China and Tibet. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese), 29(3): 1046-1067, doi: 10.6038/pg20140308. |
| [4] | Qin S Q, Li G L, Xue L, et al. 2014d. Analysis of the future earthquake situation for some seismic zones in the northeast China, north China and Taiwan. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese), 29(2): 535-554, doi: 10.6038/pg20140210. |
| [5] | Qin S Q, Li G L, Xue L. 2012a. A statistical relation between the symbolic earthquake magnitude and the earthquake magnitude at peak strength point during the failure process of looked patch. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese), 27(5): 1841-1844, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.05.002. |
| [6] | Qin S Q, Li P, Xue L, et al. 2014a. The definition of seismogenic period of strong earthquakes for some seismic zones in southwest China. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese), 29(4): 1526-1540, doi: 10.6038/pg20140407. |
| [7] | Qin S Q, Li P, Xue L, et al. 2014b. Analysis of the future earthquake situation for some seismic zones in the east China, south China and southwest China. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese), 29(3): 1033-1045, doi: 10.6038/pg20140307. |
| [8] | Qin S Q, Xu X W, Hu P, et al. 2010a. Brittle failure mechanism of multiple locked patches in a seismogenic fault system and exploration on a new way for earthquake prediction. Chinese J.Geophys. (in Chinese), 53(4): 1001-1014, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.04.025. |
| [9] | Qin S Q, Xue L, Li G L, et al. 2012b. The verification of prospective prediction for the ZhaoTong earthquakes on 7 September 2012. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese), 27(5): 1837-1840, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.05.001. |
| [10] | Qin S Q, Xue L, Li G L, et al. 2013c. The verification of prospective prediction for the Minxian- Zhangxian MS 6.6 earthquake in Gansu province and an analysis on the future earthquake situation. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese), 28(4): 1860-1868, doi: 10.6038/pg20130427. |
| [11] | Qin S Q, Xue L, Li G l, et al. 2014h. The verification of prospective prediction for the Lushan MS 7.0 earthquake on 20 April 2013 and an analysis on future earthquake situation. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese), 29(1): 141-147, doi: 10.6038/pg20140118. |
| [12] | Qin S Q, Xue L, LI P, et al. 2014e. A review of prospective prediction for the Yutian 7.3 earthquake in Xinjiang province and an analysis on future earthquake situation. Chinese J.Geophys. (in Chinese), 57(2): 679-684, doi: 10.6038/cjg20140231 |
| [13] | Qin S Q, Xue L, LI P, et al. 2014f. Analysis on the seismogenic processes of large or great earthquakes for some seismic zones abroad based on the brittle failure theory of multiple locked patches(I). Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 29(4): 1541-1554, doi: 10.6038/pg20140408. |
| [14] | Qin S Q, Xue L, Li P, et al. 2014g. A review of prospective prediction for the Jinggu MS 6.6 earthquake in Yunnan province and an analysis on future earthquake situation. Progress in Geophysics (in chinese), 29(5): 2479-2482, doi: 10.6038/pg20140574 |
| [15] | Qin S Q, Xue L, Wang Y Y, et al. 2010b. Further verifications on the brittle failure theory of multiple locked patches along a seismogenic fault systemand discussions on some science issues. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese), 25(3): 749-758, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.03.002. |
| [16] | Qin S Q, Xue L. 2011. A summary of prediction for the Yingjiang MS 5.8 earthquake in Yunnan and the Burma MS 7.2 earthquake as well as the analysis on the earthquake situation after the earthquake. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese), 26(2): 462-468, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2011.02.010. |
| [17] | 秦四清,李国梁,薛雷,等. 2013a. 中国西南地区某些地震区未来震情研判. 地球物理学进展, 28(5): 2407-2432, doi: 10.6038/pg20130521. |
| [18] | 秦四清,李国梁,薛雷,等. 2013b. 中国新疆及邻区某些地震区未来震情研判. 地球物理学进展, 28(5): 2376-2391, doi: 10.6038/pg20130519. |
| [19] | 秦四清,李国梁,薛雷,等. 2014c. 西北与西藏地区某些地震区地震趋势分析. 地球物理学进展, 29(3): 1046-1067, doi: 10.6038/pg20140308. |
| [20] | 秦四清,李国梁,薛雷,等. 2014d. 东北、华北与台湾地区某些地震区地震趋势分析. 地球物理学进展, 29(2): 535-554, doi: 10.6038/pg20140210. |
| [21] | 秦四清,李国梁,薛雷. 2012a. 锁固体破裂标志性地震震级与峰值强度点地震震级的统计关系. 地球物理学进展, 27(5): 1841-1844, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.05.002. |
| [22] | 秦四清,李培,薛雷,等. 2014a. 中国西南地区某些地震区强震孕育周期界定. 地球物理学进展, 29(4): 1526-1540, doi: 10.6038/pg20140407. |
| [23] | 秦四清,李培,薛雷,等. 2014b. 华东、华南与西南地区某些地震区地震趋势分析. 地球物理学进展, 29(3): 1033-1045, doi: 10.6038/pg20140307. |
| [24] | 秦四清,徐锡伟,胡平,等. 2010a. 孕震断层的多锁固段脆性破裂机制与地震预测新方法的探索. 地球物理学报, 53(4): 1001-1014, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.04.025. |
| [25] | 秦四清,薛雷,李国梁,等. 2012b. 云南昭通“9·7 地震”的前瞻性预测验证. 地球物理学进展, 27(5): 1837-1840, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.05.001. |
| [26] | 秦四清,薛雷,李国梁,等. 2013c. 甘肃岷县漳县6.6级地震的前瞻性预测验证及震后趋势分析. 地球物理学进展, 28(4): 1860-1868, doi: 10.6038/pg20130427. |
| [27] | 秦四清,薛雷,李国梁,等. 2014h. 四川省芦山“4·20”7.0级地震的前瞻性预测验证及震后趋势分析. 地球物理学进展, 29(1): 141-147, doi: 10.6038/pg20140118. |
| [28] | 秦四清,薛雷,李培,等. 2014e. 新疆于田7.3级地震前瞻性预测回顾及其震后趋势分析. 地球物理学报, 57(2): 679-684, doi: 10.6038/cjg20140231 |
| [29] | 秦四清,薛雷,李培,等. 2014f. 国外某些地震区大地震孕育过程分析(I). 地球物理学进展, 29(4): 1541-1554, doi: 10.6038/pg20140408. |
| [30] | 秦四清,薛雷,李培,等. 2014g. 云南景谷MS 6.6级地震前瞻性预测回顾及其震后趋势分析. 地球物理学进展, 29(5): 2479-2482, doi: 10.6038/pg20140574 |
| [31] | 秦四清,薛雷,王媛媛,等. 2010b. 对孕震断层多锁固段脆性破裂理论的进一步验证及有关科学问题的讨论. 地球物理学进展, 25(3): 749-758, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.03.002. |
| [32] | 秦四清,薛雷. 2011. 云南盈江MS 5.8级地震和缅甸MS 7.2级地震预测总结及震后趋势分析. 地球物理学进展, 26(2): 462-468, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2011.02.010. |
 2014, Vol. 29
2014, Vol. 29

