2. 海洋国家实验室海洋矿产资源评价与探测技术功能实验室, 青岛 266071;
3. 中国石化石油勘探开发研究院, 北京 100083
2. Laboratory for Marine Mineral Resources, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao 266071, China;
3. Exploration & Production Research Institute, SINOPEC, Beijing 100083, China
裂缝性储层在碳酸盐岩、火山岩等地层中极为常见(司马立强,2005;李宁等,2009).受沉积、构造、成岩和改造作用等多因素影响,裂缝发育规模不等、分布不均、充填物类型和充填程度变化大,使得储集空间非均质性强、各向异性严重,加大了测井评价的难度.
双侧向测井由于其具有较强的电流聚焦能力和较大的探测范围,对井旁地质异常体较敏感,是除了电成像和阵列声波等特殊测井之外,最经济实用的裂缝识别与表征的常规测井方法.国内外学者基于模式匹配法、有限元法等开展了双侧向测井的数值模拟并研究了裂缝地层的双侧向测井响应,建立了基于深浅侧向电阻率的裂缝评价图版,在实际应用中取得一定效果(Chew et al., 1991;聂在平和陈思渊,1994;杨峰和聂在平,1997;李大潜等,1980;高杰和谢然红,2000;范宜仁等,2009;Tan et al., 2011; 谭茂金等,2012).
物理模拟是数值仿真和测井评价的重要桥梁,对深入分析裂缝地层的双侧向测井响应规律和测井评价具有极为关键的指导作用.受技术手段、设计思路等因素的综合制约,国内外鲜有开展裂缝地层的双侧向物理模拟研究.四川石油管理局测井公司用石蜡作为模拟地层,建立了国内首个研究裂缝双侧向测井响应的物理模拟平台,得到了不同角度裂缝的双侧向测井响应,被国内外广泛应用(赵良孝和补勇,1994).柯式镇等(1996, 2003)、乔德新等(2005)分别开展了裂缝地层的测井响应物理模拟研究.然而,现有物理模拟条件过于简单,难以满足复杂裂缝地层测井研究的需要.本文将数值仿真与物理实验结合,在验证数值模拟的基础上,开展井旁裂缝不同规模、倾角和走向等情况的双侧向测井物理模拟,总结典型裂缝的双侧向测井响应特征,为裂缝识别与评价奠定物理基础.
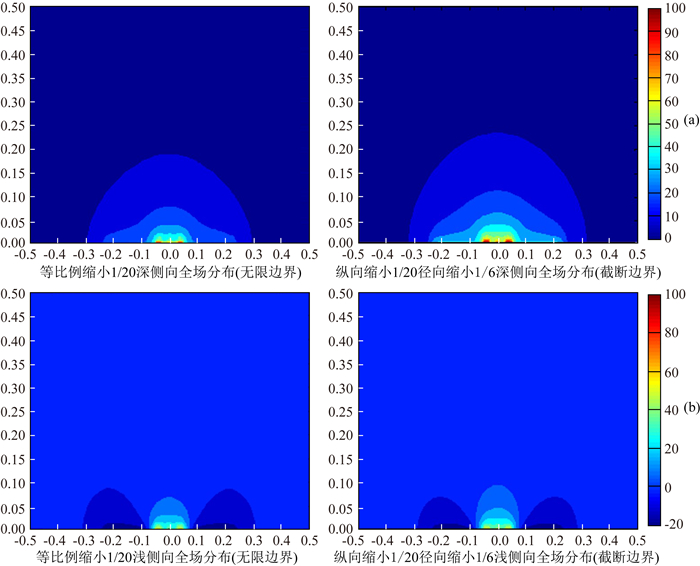
1 实验平台及模型简介为方便实验测量,仪器及地层模型需在不改变探测性能的基础上,按照一定比例进行缩小.根据前期研究成果,我们以1229型双侧向测井仪为例,采用三维有限元素法分别考察了仪器等比例缩小和不等比例缩小的双侧向电场特征,仪器纵横向等比例缩小为1/20时的深浅侧向电场分布与仪器纵向缩小为1/20、横向缩小为1/6时基本一致,如图 1.因此,物理模拟中的相关参数设置为:地层径向半径为1 m,纵向高度为2 m,仪器纵向缩小为1/20,径向缩小为1/6(范宜仁等,2016).
|
图 1 缩小比例样机双侧向测井电场分布(以仪器中心点为原点,检测点位于仪器中心点之上时距离为负,位于中心点之下时距离为正) (a)深侧向电场分布;(b)浅侧向电场分布. Fig. 1 Reduced dual laterolog electric field distribution of proportional prototype (The center of the instrument is the origin. When the measuring point is above the instrument center, the distance is negative; when the measuring point is below the instrument center, the distance is positive.) (a) Electric field distribution of deep laterolog; (b) Electric field distribution of shallow laterolog. |
以往的物理模拟均采用石蜡或致密岩石为基岩,每更换一次基岩需重新选择模型材料,数据测量与采集十分不便.为方便测量,实现实验过程的可视化观测,我们将具一定矿化度的地层水作为基岩,采用镀锌板作为裂缝.全新的物理模型更加全面地考虑井眼、地层和裂缝对测量结果的影响,丰富了物理实验的模拟条件,极大地满足了研究需要,图 2是实验平台示意和实物图.

|
图 2 缩小比例双侧向测井实验平台示意及实物图 (a)示意图;(b)实物图. Fig. 2 Reduced schematic and real object of the dual laterolog experimental platform (a) Schematic diagram; (b) Physical diagram. |
用厚度为0.22 mm镀锌板(良导体,电阻率未测)作为高导裂缝模型,将裂缝设计正方形,裂缝模型尺寸及编号如表 1所示.研究三种不同产状裂缝的双侧向响应(图 3所示),基岩电阻率约为830 Ωm,不考虑井眼影响.由于实验室缺乏精密定位系统,采用马达控制测速,马达的测量速度为0.01 m·s-1.在测量过程中容易产生毛刺现象,对所测数据进行七点平滑滤波.
|
|
表 1 实验所用裂缝模型基本参数 Table 1 Basic parameters of fracture model used in experiment |

|
图 3 裂缝产状示意图 (a)垂直缝;(b)倾斜缝;(c)水平缝. Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of fracture occurrence (a) Vertical fractures; (b) Inclined fractures; (c) Horizontal fractures. |
实验主要研究了井旁裂缝的双侧向测井响应特征,重点研究了不同规模的裂缝与井壁距离、与井眼相对倾角等典型条件的深、浅侧向电阻率变化规律.
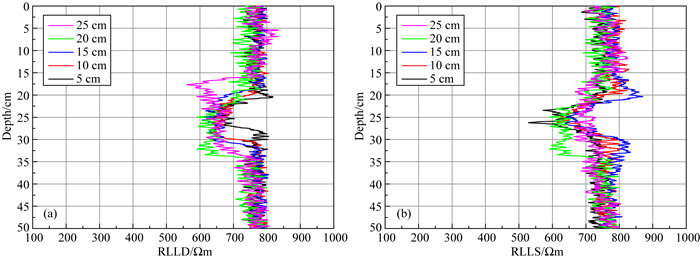
2.1 裂缝延伸为考察裂缝延伸对双侧向测井响应的影响,制作了五种不同边长的正方形裂缝模型.图 4分别为垂直缝贴井壁时,测量不同裂缝规模的深浅侧向电阻率.从图中可知,深浅侧向在不同边长的裂缝处视电阻率值基本相同,说明裂缝的延伸对双侧向响应影响较小;边长较大的裂缝,双侧向测井曲线的异常幅度面积越大,反之亦然.实验表明,双侧向测井响应可有效判断井旁垂直裂缝纵向延伸,双侧向测井曲线的异常幅度面积越大,裂缝纵向延伸越大.
|
图 4 不同宽度的垂直裂缝双侧向测井响应特征 (a)深侧向曲线;(b)浅侧向曲线. Fig. 4 Dual laterolog response characteristics of vertical fractures with different widths (a) Deep laterolog curve; (b) Shallow laterolog curve. |
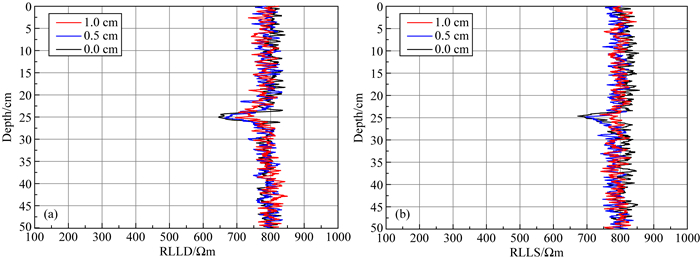
井眼与裂缝距离不同时,它们的双侧向测井中也会有不同响应,这是双侧向测井在径向探测范围的直接体现.为研究裂缝与仪器间距离大小对双侧向测井响应的影响,对每一个裂缝模型的任意产状都进行了不同距离的测量.代表性地选取边长为10 cm的垂直缝在不同距离下的实验结果,如图 5所示.由图可知,随着裂缝与井壁距离的增大,深浅侧向电阻率都增大,裂缝与井壁距离越远,双侧向的测井响应特征越不明显,异常幅度降低.深侧向具有较深的径向探测深度,当裂缝距井壁1 cm时,仍能观测到一定的幅度异常.
|
图 5 10 cm边长裂缝不同发育位置的双侧向测井响应特征 (a)深侧向曲线;(b)浅侧向曲线. Fig. 5 Dual laterolog response characteristics of different developmental position in a 10 cm-long fracture (a) Deep laterolog curve; (b) Shallow laterolog curve. |
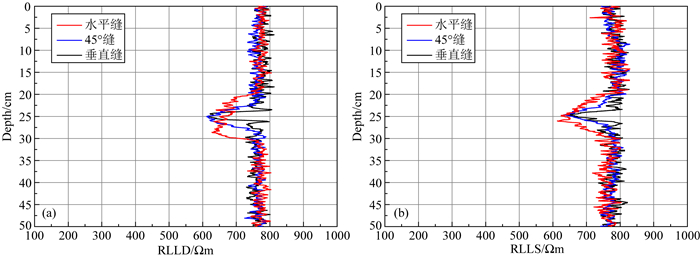
大量数值模拟结果表明,裂缝产状对双侧向测井响应有较大影响.为研究裂缝产状对双侧向测井响应的影响,设计了三种不同产状的对比实验,图 6是10 cm边长的裂缝产状分别为0°、45°和90°所测的深浅侧向电阻率.从图中可知,随着裂缝倾角的增大,深侧向在裂缝处电阻率增大,浅侧向电阻率无明显变化.
|
图 6 不同产状的裂缝双侧向测井响应特征 (a)深侧向曲线;(b)浅侧向曲线. Fig. 6 Dual laterolog response characteristics of fractures with different occurrences (a) Deep laterolog curve; (b) Shallow laterolog curve. |
将裂缝边长为5 cm的深浅侧向电阻率值进行组合,可得到不同产状下的双侧向测井响应,如图 7所示.从图中可知,水平缝深浅侧向视电阻率值接近,且深浅侧向为较小的负幅度差,45°倾角缝深浅侧向视电阻率值也较接近,深浅侧向仍为负幅度差,但与水平缝相比,深浅侧向电阻率更接近,表现为幅度差值减小;随着裂缝倾角增大,当裂缝为垂直缝时,深浅侧向在裂缝处表现为正幅度差.实验结果与大部分数值模拟结果相似,随着裂缝倾角的增大,双侧向电阻率从负幅度差向正幅度差过渡.受实验条件等限制,我们未观测到明显的临界角现象,这主要受裂缝孔隙度、基岩和泥浆电阻率等因素的综合影响(高杰等,2012;潘秀萍,2012).
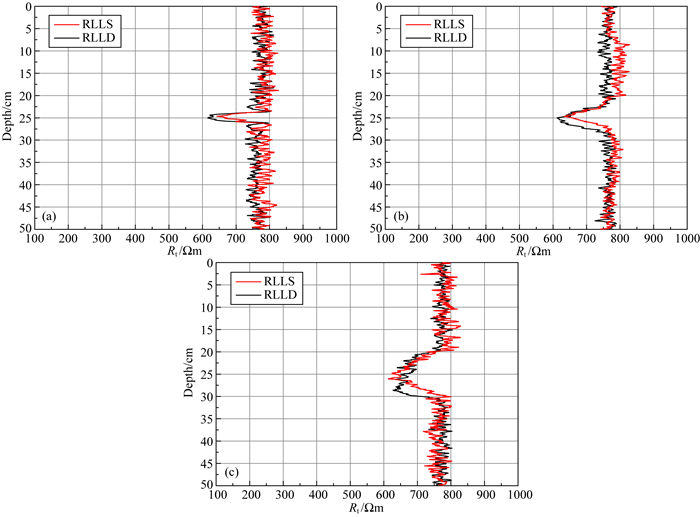
|
图 7 不同产状的裂缝双侧向测井响应特征 (a)水平缝深浅侧向测井响应;(b)斜交缝(45°)深浅侧向测井响应;(c)垂直缝深浅侧向测井响应. Fig. 7 Dual laterolog responses characteristics of fractures with different occurrences (a) Deep and shallow laterolog responses of horizontal fractures; (b) Deep and shallow laterolog responses of oblique fractures (45°); (c) Deep and shallow laterolog responses of vertical fractures. |
基于数值仿真确定了缩小比例双侧向测井实验平台的关键参数,开展了井旁裂缝的物理模拟,通过分析不同裂缝规模、裂缝发育位置和裂缝产状的深浅侧向电阻率差异,得到以下结论:
(1) 按不等比例缩小仪器的纵横向参数,仪器的电场分布及探测性能变化不大,可满足实验需求.
(2) 裂缝发育规模越大,双侧向测井异常幅度的面积也越大,基于双侧向测井曲线的形态,可大致评估裂缝发育规模.
(3) 裂缝离井越远,双侧向的探测能力越弱,与数值模拟和实际测井基本一致;深浅侧向电阻率随着裂缝与井壁距离的增大而增大,但深侧向电阻率增大幅度小于浅侧向,可依据深浅侧向电阻率幅度差定性判断垂直裂缝的发育位置.
(4) 一般地,随着裂缝倾角增大,深浅侧向电阻率从负幅度差向正幅度差过渡.高角度缝的深侧向电阻率明显大于浅侧向,但临界角很难判断.在应用双侧向测井幅度差判别裂缝倾角时,需特别注意其使用条件.
受实验条件所限,许多更复杂、与地层实际情况更接近的物理模拟还未展开,这也将是我们今后即将开展的重要工作.
致谢 感谢中石油测井重点实验室中国石油大学(华东)研究室邓少贵教授的指导,以及刘玺、周声明、刘家雄、刘建宇等同学在实验和数据处理过程中提供的帮助.
Chew W C, Nie Z P, Liu Q H, et al. 1991. An efficient solution for the response of electrical well logging tools in a complex environment. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 29(2): 308-313. DOI:10.1109/36.73673 |
Fan Y R, Jiang J L, Deng S G, et al. 2009. Numerical simulation of high resolution array lateral logging responses. Well Logging Technology (in Chinese), 33(4): 333-336. |
Fan Y R, Wang L, Ge X M, et al. 2016. Response simulation and corresponding analysis of dual laterolog in cavernous reservoirs. Petroleum Exploration and Development (in Chinese), 43(2): 237-243. |
Gao J, Xie R H. 2000. 3D numerical forward modeling and fast correction of dual-laterolog for high angle deviated wells. Petroleum Exploration and Development (in Chinese), 27(2): 69-71. |
Gao J, Liu C Q, Wan J B. 2012. Effect factors on critical angle of dual laterolog responses in fractured reservoir. Logging Technology (in Chinese), 36(5): 456-459. |
Ke S Z, Feng Q N, Shang Z Y. 1996. Experimental instrument for physical analogy of dual laterolog. Well Logging Technology (in Chinese), 20(4): 282-286. |
Ke S Z, Feng Q N, Yuan X H, et al. 2003. On scale modeling of dual laterolog responses to fractured formation. Well Logging Technology (in Chinese), 27(5): 253-355. |
Li D Q, Zheng S M, Tan Y J. 1980. Application of Finite Element Method in Electric Well Logging (in Chinese). Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press.
|
Li N, Qiao D X, Li Q F, et al. 2009. Theory on logging interpretation of igneous rocks and its application. Petroleum Exploration and Development (in Chinese), 36(6): 683-692. DOI:10.1016/S1876-3804(10)60002-X |
Nie Z P, Chen S Y. 1994. The numerical analysis for the response of dual lateral logging tool in a complex environment. Acta Electronica Sinica (in Chinese), 22(6): 30-38. |
Pan X P. 2012. Numerical simulation of dual laterolog in carbonate fractured reservoir[Master's thesis] (in Chinese). Hubei, Jingzhou: Yangtze University.
|
Qiao D X, Li N, Wei Z L, et al. 2005. Calibrating fracture width using circumferential borehole image logging data from model wells. Petroleum Exploration and Development (in Chinese), 32(1): 76-79. |
Sima L Q. 2005. Study on comprehensive evaluation method and application of carbonate fractured reservoir[Ph. D. thesis] (in Chinese). Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University.
|
Tan M J, Gao J, Wang X C, et al. 2011. Numerical simulation of the dual laterolog for carbonate cave reservoirs and response characteristics. Applied Geophysics, 8(1): 79-85. DOI:10.1007/s11770-011-0268-2 |
Tan M J, Gao J, Zou Y L, et al. 2012. Environment correction method of dual laterolog in directional well. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 55(4): 1422-1432. DOI:10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.04.038 |
Yang F, Nie Z P. 1997. A precise numerical simulation of DLL logging response. Well Logging Technology (in Chinese), 21(4): 265-268. |
Zhao L X, Bu Y. 1994. Logging Evaluation of Carbonate Reservoir (in Chinese). Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press.
|
范宜仁, 蒋建亮, 邓少贵, 等. 2009. 高分辨率阵列侧向测井响应数值模拟. 测井技术, 33(4): 333-336. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-1338.2009.04.005 |
范宜仁, 王磊, 葛新民, 等. 2016. 洞穴型地层双侧向测井响应模拟与特征分析. 石油勘探与开发, 43(2): 237-243. |
高杰, 谢然红. 2000. 大斜度井侧向测井三维正演数值模拟及曲线快速校正方法研究. 石油勘探与开发, 27(2): 69-71. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2000.02.019 |
高杰, 刘传奇, 万金彬. 2012. 裂缝性储层双侧向测井响应临界角影响因素分析. 测井技术, 36(5): 456-459. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-1338.2012.05.004 |
柯式镇, 冯启宁, 尚作源. 1996. 双侧向测井物理模拟实验仪器. 测井技术, 20(4): 282-286. |
柯式镇, 冯启宁, 袁秀荷, 等. 2003. 裂缝地层双侧向测井响应物理模拟研究. 测井技术, 27(5): 253-355. |
李大潜, 郑宋穆, 谭永基. 1980. 有限元素在电法测井中的应用. 北京: 石油工业出版社.
|
李宁, 乔德新, 李庆峰, 等. 2009. 火山岩测井解释理论与应用. 石油勘探与开发, 36(6): 683-692. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2009.06.002 |
聂在平, 陈思渊. 1994. 复杂介质环境中双侧向测井响应的高效数值分析. 电子学报, 22(6): 30-38. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1994.06.005 |
潘秀萍. 2012. 碳酸盐岩裂缝性储层双侧向测井数值模拟[硕士论文]. 湖北荆州: 长江大学.
|
乔德新, 李宁, 尉中良, 等. 2005. 利用模拟井研究用声波成像资料计算裂缝宽度问题. 石油勘探与开发, 32(1): 76-79. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.01.020 |
司马立强. 2005. 碳酸盐岩缝-洞性储层测井综合评价方法及应用研究[博士论文]. 成都: 西南石油大学.
|
谭茂金, 高杰, 邹友龙, 等. 2012. 盐水泥浆条件下定向井双侧向测井环境校正方法研究. 地球物理学报, 55(4): 1422-1432. DOI:10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.04.038 |
杨峰, 聂在平. 1997. 双侧向电极系测井响应的精确模拟. 测井技术, 21(4): 265-268. |
赵良孝, 补勇. 1994. 碳酸盐岩储层测井评价技术. 北京: 石油工业出版社.
|
 2019, Vol. 62
2019, Vol. 62

