2. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049;
3. 中国石油大学(北京)盆地与油藏研究中心, 北京 102249;
4. 成都理工大学能源学院, 成都 610059
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China;
3. Research Center of Basin and Reservoir, China University of Petroleum, Beijing 102249, China;
4. College of Energy Resources, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu 610059, China
盆地地层热历史主要受埋藏和热体制控制,岩浆活动作为非稳态的热源,其在地球内部积聚、上涌以及在近地表喷发的过程也是能量释放的过程,会对盆地内有机质的演化产生影响. 研究表明塔里木盆地古地温梯度自震旦纪以来整体呈下降趋势,其中志留纪至晚古生代从拉张盆地时期过渡到稳定地壳热演化时期,地温梯度逐渐降低;中生代地温梯度较稳定;新生代则叠加了盆地边缘强烈挠曲热演化过程(Chang et al.,2014; Li et al.,2010; Qiu et al.,2012; 李成等,2000; 刘绍文等,2006; 邱楠生等,2004; 左银辉等,2015). 二叠纪岩浆岩喷发于早、中二叠世,约300—275 Ma,其中大规模玄武岩发育在290—288 Ma(Li et al.,2012b; Polyakov et al.,2008; Wei et al.,2014; Xu et al.,2014; Yu et al.,2011; Zhang et al.,2010,2013; 陈汉林等,1997,2009; 杨树锋等,2014),然而目前针对该期岩浆活动对古地温的影响范围和时间存在明显争议. 由于有机质成熟演化的不可逆性,其与非稳态高温热事件的可能关系值得关注. 为此,本文通过分析塔里木盆地Ro值随深度的演化规律,恢复典型单井热历史,探讨了石炭-二叠纪异常热演化及其成因,这将为进一步认识盆地深部构造-岩浆活动及其石油地质意义提供重要基础.
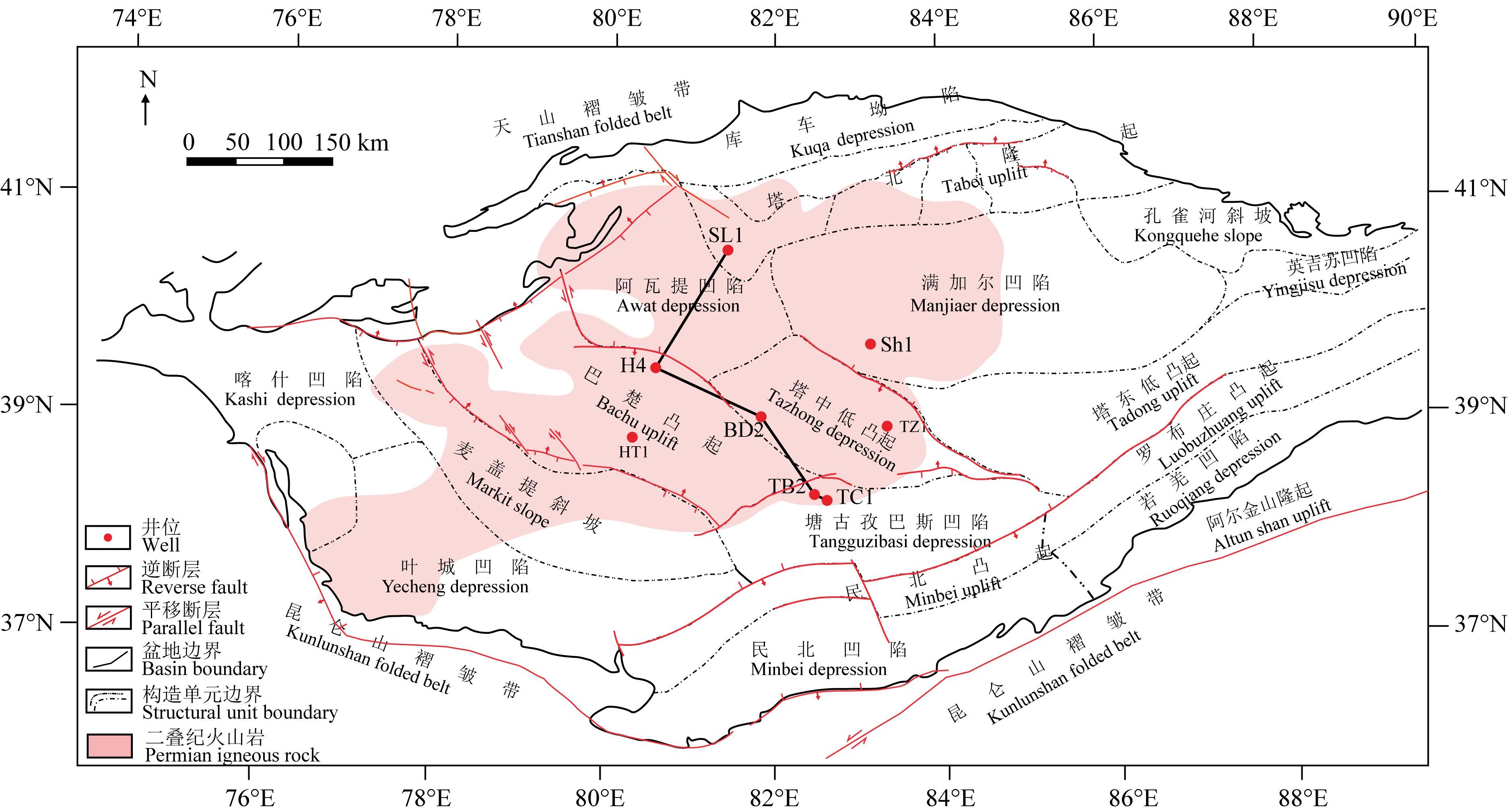
2 地质背景塔里木盆地是中国最大的沉积盆地,位于天山和昆仑山褶皱带之间,是在古老基底之上震旦纪-古生代克拉通叠覆中新生代前陆盆地而成的大型叠合盆地(贾承造,2004; 贾承造和魏国齐,2002),经历了震旦纪-中泥盆世、晚泥盆世-三叠纪和侏罗纪-第四纪3个伸展-聚敛演化旋回(何碧竹等,2011; 何登发等,2005),构造环境发生了多次重大变革. 复杂的构造运动导致了多期岩浆活动,盆地内主要发育四期火山岩,分别在震旦-寒武纪、晚奥陶世-志留纪、二叠纪、白垩纪,其中晚古生代火山活动强度很大(陈汉林等,1997; 温声明等,2005; 徐汉林等,2006; 张水昌等,2004). 晚古生代是塔里木盆地演化过程的一个重要阶段,此时塔里木克拉通处于强烈的拉张状态,盆地内部发育了大量岩浆岩,以基性岩类为主,如玄武岩、辉绿岩、玄武安山岩和超镁质岩类等,在满加尔凹陷西段、塔北隆起西段、塔中隆起、巴楚隆起和塔西南坳陷中段均有分布,面积达2.5×105 km2以上(图 1)(刘晓等,2011; 潘赘等,2013; 杨树锋等,2005,2014).
|
图 1 塔里木盆地构造单元和研究井位分布图 二叠纪火山岩分布据杨树锋等(2005). Fig. 1 Sketch map of structural units in the Tarim basin and well locations The distribution of Permian igneous rock is drawn according to Yang et al.(2005). |
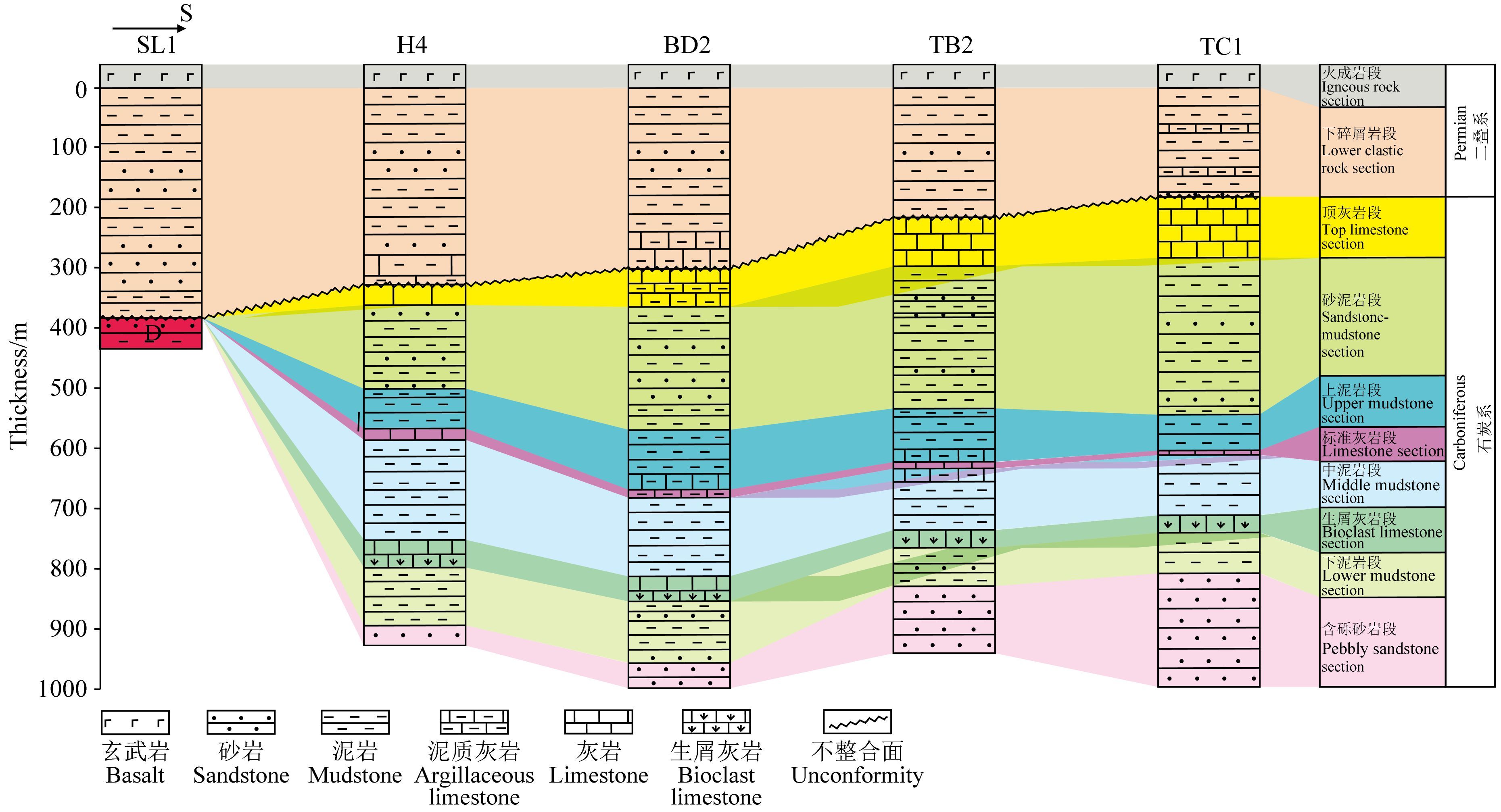
石炭-二叠纪是塔里木盆地内部沉积演化的重要时期. 塔里木盆地经历了震旦纪-中泥盆世活跃的构造变迁之后,在晚泥盆世进入了相对稳定的演化阶段,发育了由西南向东北的海侵,并在石炭纪初急剧扩张(何登发等,2005). 晚泥盆世-石炭纪总体上以海平面相对上升的海侵为主,期间出现两次快速下降和两次缓慢小幅度下降(王毅,1998; 朱如凯等,2002),海平面的频繁变化造就了碳酸盐岩与碎屑岩交互发育的特点,自下而上依次沉积了含砾砂岩段、下泥岩段、生屑灰岩段、上泥岩段、砂泥岩段、顶灰岩段. 前期相对稳定的构造环境使得盆地内含砾砂岩段-砂泥岩段保存较完整,直至顶灰岩段在盆地内部及周缘地区出现不同程度的缺失,且向北向西愈加严重(朱如凯等,2002),上石炭统剥蚀发生于石炭纪末小海子组沉积后-二叠纪初碎屑岩段沉积前,剥蚀量可达到800 m以上(Li et al.,2014). 本文选取了岩浆岩分布区中8口井进行研究(图 1),自北向南的地层连井剖面显示石炭系顶剥蚀程度具有北强南弱的趋势,残余顶灰岩段向南增厚(图 2). 二叠纪是塔里木板块构造-沉积演化一个重要的转折期,早二叠世结束了海相沉积,进入了陆相沉积阶段,发育了以陆相碎屑岩为主的沉积以及火山岩和火山碎屑岩.
|
图 2 石炭系-下二叠统连井剖面 Fig. 2 Stratigraphic profile of Carboniferous and Lower Permian |
镜质体反射率是目前应用最广泛的古温标之一,是本文研究塔里木盆地晚古生代热事件的依据. Ro值受控于有机质受热温度和受热时间,以温度影响为主(Buchardt and Lewan,1990; Burnham and Sweeney,1989; 邱楠生等,2004),稳定沉降的状态下Ro与深度(温度)在对数坐标中表现出线性关系(Baker and Pawlewicz,1986; Baker and Goldstein,1990; Sweeney and Burnham,1990);有机质热演化具有不可逆性,能够指示如岩浆活动异常高温热事件,非稳态高热源侵入浅部地层引起Ro增大,若后期正常沉积下地层温度不超过非稳态热效应对有机质的影响,Ro演化不连续. 另外,Ro值演化可揭示地层的沉降-抬升信息,在相同的热状态下,地层抬升剥蚀是导致Ro在深度剖面上呈现不连续演化的主要原因.
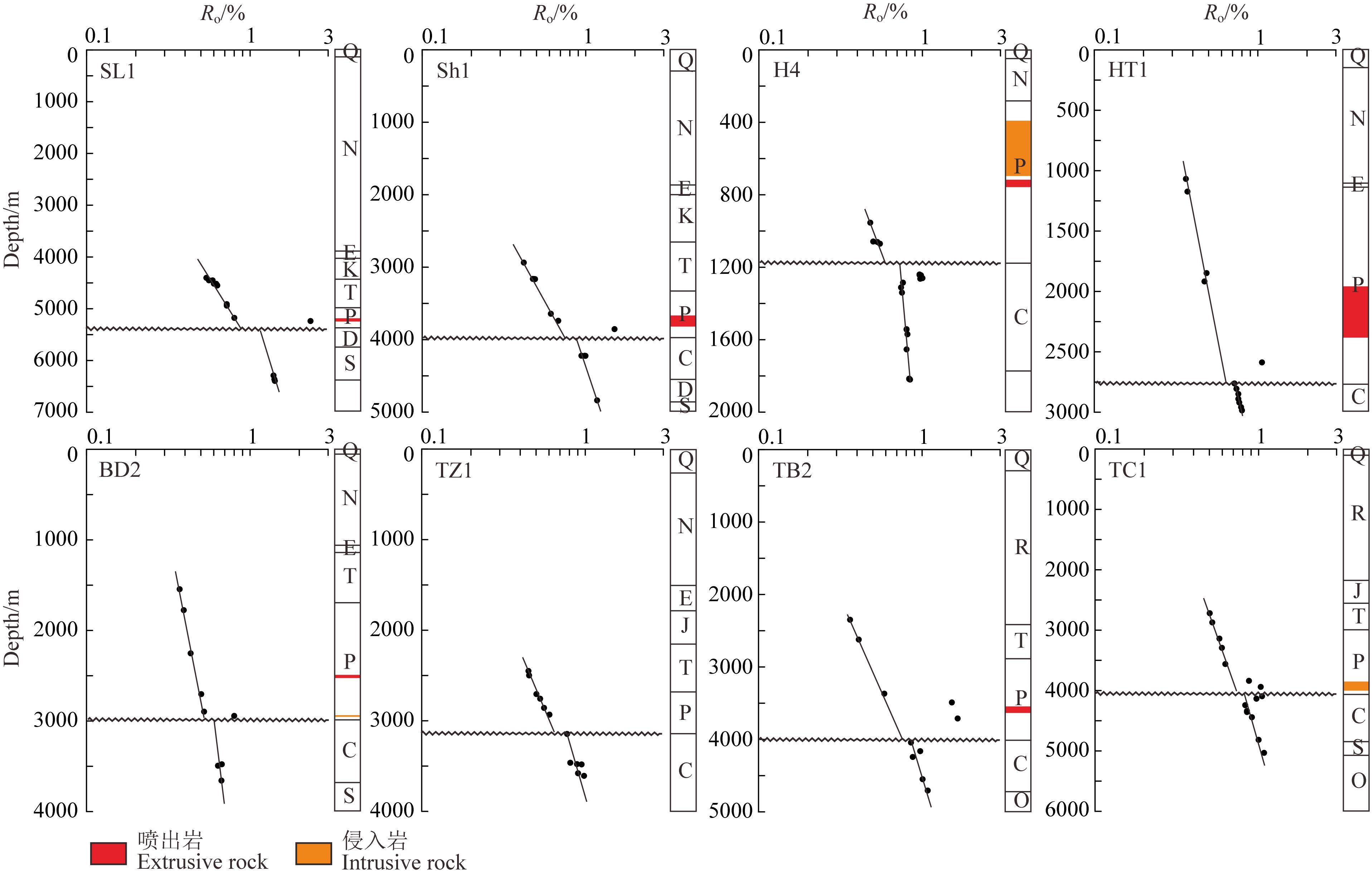
综合分析塔里木盆地不同地区的大量实测Ro数据,多口钻井的Ro值在深度剖面上的分布具有规律性. 二叠系与前二叠系(SL1井为泥盆系,其余井为石炭系)中的Ro值不连续,不整合面附近多具零星的极高Ro异常值,记录了明显的构造-热事件,揭示出石炭纪末地层经历了较高的古地温(表 1、图 1和图 3).
|
|
表 1 塔里木盆地镜质体反射率 Table 1 Vitrinite reflectance in Tarim basin |
|
图 3 塔里木盆地典型井镜质体反射率随深度的演化关系 Fig. 3 Ro versus depth of typical wells in Tarim basin |
本文根据EasyRo%模型(Burnham and Sweeney,1989; Sweeney and Burnham,1990),利用Ro值进行热史反演. 为探讨二叠系与石炭系之间Ro值不连续与古地温和地层剥蚀量的关系,选择不同构造单元中4口井为基础进行详细模拟. 如巴楚隆起H4井二叠系与石炭系间Ro的差值若仅由地层抬升剥蚀造成的情况下,模拟结果显示石炭系顶的剥蚀量需超过3500 m(图 4a),综合前人研究成果其剥蚀量为~1000 m(Li et al.,2014;Lin et al.,2012; 齐永安和刘国臣,1999; 张一伟等,2000; 李丽贤等,2011; 丛培泓等,2015). 若存在高温热事件的条件下,考虑岩浆上涌释放充沛热量烘烤地层,限定剥蚀量为1000 m,模拟结果显示石炭纪末地层温度显著升高,达到峰值,促进了有机质的热演化;而后地层温度逐渐下降,到中二叠世恢复到正常热状态(图 4b). Sh1井、HT1井和TB2井模拟亦揭示出相同的结果:石炭-二叠系间Ro值的不连续演化是高温热事件与抬升剥蚀共同作用的结果,石炭纪末地温出现短暂的高峰;二叠纪初地层温度快速降低,之后地层温度主要受埋藏深度的控制.

|
图 4 H4井、Sh1井、TZ1井和TB2井埋藏史和热史模拟结果 (a,c,e,g)分别为H4井、Sh1井、TZ1井和TB2井仅有剥蚀的假设情况;(b,d,f,h) 分别为H4井、Sh1井、TZ1井和TB2井在剥蚀和热事件控制下的实际情况. Fig. 4 Burial and thermal history of wells H4,Sh1,TZ1 and TB2 (a,c,e,g)are simulated results only with erosion for Well H4,Sh1,TZ1 and TB2,respectively.(b,d,f,h)are simulated results controlled by erosion and magmatic activity for wells H4,Sh1,TZ1 and TB2,respectively. |
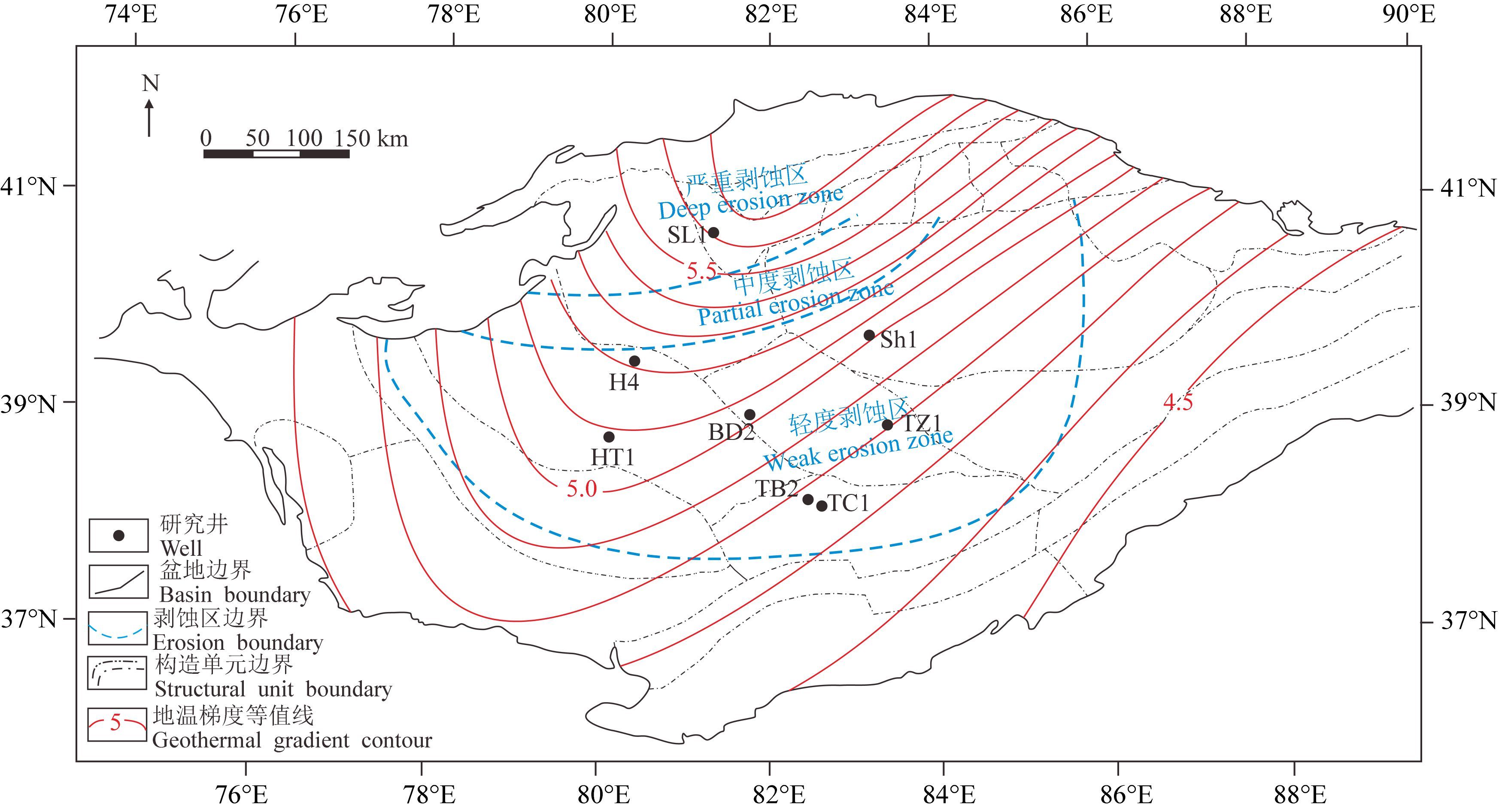
塔里木盆地自震旦纪至今总体上逐渐变冷,前石炭纪稳定演化,邱楠生等(2004)研究成果显示出地温梯度逐渐降低的规律. 研究井热史模拟显示石炭纪末盆地地温梯度短暂地快速提升,至300 Ma左右达到高峰值,分布在4.8~5.6 ℃/100 m之间. 距今约285 Ma时高地温梯度快速回落至3 ℃/100 m左右,进入持续缓慢降低的阶段(图 4). 地温梯度高峰期在区域上呈现出西北高东南低的规律:在塔北地区(SL1井)最高,巴楚隆起北部(H4井)次之,塔中地区(TZ1井)最低(图 5). 由于塔里木盆地地质历史复杂,多期构造运动叠加使得盆地内地层遭受了不同程度的剥蚀,东部大部分地区二叠系缺失,南部二叠系则俯冲至昆仑山下,因此盆地东南部对石炭-二叠纪热事件的记录缺失,有待进一步分析确认.
|
图 5 塔里木盆地石炭纪末地温梯度等值线图 剥蚀区据Li et al.(2014). Fig. 5 Thermal gradient contours at end of Carboniferous in Tarim basin The erosion zone is from Li et al.(2014). |
镜质体是由高等植物演化而来,陆生植物大发展始于晚古生代. 泥盆纪晚期植物界完成脱离水体的变革,乔木型植物已占相当的优势,并可形成小型森林;石炭纪陆生植物进一步繁荣,地球上首次出现大规模的森林;晚二叠世开始,全球许多地区裸子植物兴起,占主导地位(杜远生和童金南,1998; 刘本培和全秋琦,1996; 肖传桃,2007). 因此晚志留世之后的沉积地层中包含镜质体,可以直接测量;而晚古生代之前沉积的地层中只含有沥青、镜状体等,这些古温标必须通过公式转换成等效镜质体反射率,准确性相对较差. 在文中重点比较的二叠系、石炭系和上泥盆统中的Ro值是直接测量的结果,采用这些测量值进行研究具有较高的可靠性.
4.2 石炭-二叠纪热事件对塔里木盆地地温场的影响盆地内岩浆活动对地温场的影响范围和程度一直有争议,本文中-下二叠统和上石炭统中零星Ro极高值点和石炭-二叠系Ro值错断的现象为这一问题提供了解释的切入点. 侵入体对围岩热影响的范围与岩体性质和规模有关. 酸性岩浆的温度约为700~900 ℃,中性岩浆的温度约为900~1000 ℃,基性岩浆的温度约为1000~1300 ℃,高温熔融物质在浅部地层运移过程中冷却结晶成岩释放的热量作用于围岩有机质热成熟演化,导致Ro值急剧上升,可达6%以上,远远超出有机质正常热演化所能达到的程度(Annen and Sparks,2002; Fjeldskaar et al.,2008; Galushkin,1997; 王民,2010). 岩浆沿构造薄弱带上涌时以不同形式侵入浅部地层或喷出地表,研究表明受火山岩体热影响的围岩厚度约为其厚度的0.3~4倍,通常火山侵入体规模较小,对多个地区火山侵入体周边围岩内有机质成熟程度统计结果显示距侵入体数米至百米范围内的围岩被严重烘烤,有机质演化程度明显增高(Fjeldskaar et al.,2008; Galushkin,1997; Stewart et al.,2005; 陈荣书等,1989; 高福红等,2009; 朱传庆等,2010a). 本文研究井中除TZ1井外均钻遇了岩浆岩,以玄武岩为主,安山岩、英安岩和辉绿岩也可见,厚度范围在63~429 m之间,岩浆岩附近出现了Ro高值“漂点”(如Sh1井4913 m测量点为1.70%),离岩浆岩距离越近Ro值越高,但高温作用范围有限,距岩浆岩较远的有机质演化正常,Ro值不受影响(图 3). 塔里木盆地中邻近岩浆岩的Ro演化与前人研究规律一致:围岩温度随与岩体距离的增加急剧降低,导致围岩内Ro值随着快速下降,呈陡倾状连续演化(图 6)(Clayton and Bostick,1986; Galushkin,1997; Simoneit et al.,2004; Simonet et al.,1981). 岩浆活动难以大范围提高地层温度,尤其是在盆地尺度上,仅能作为局部热源. 塔里木盆地石炭-二叠系之间Ro值不连续,热史模拟显示塔里木盆地北部及西部地区石炭纪末地层温度升高,意味着在岩浆喷发前盆地大范围地区处于高地热背景下. 地球内部活动性大的岩浆易向低压区域聚集形成岩浆房,其分布范围远远超出岩浆侵入带的范围,该阶段岩浆熔融形成过程中积聚的热量通过热传导作用于上部地层,对区域热演化有一定的影响,且影响时间超过岩浆侵入的影响时间(范桃园等,1999; 朱传庆等,2010a). 塔里木盆地石炭纪末岩浆自地球深部携带热量上涌的过程导致了区域性地温升高,而二叠纪岩浆喷发活动对地温场的影响局限在岩体周围但效果显著.

|
图 6 受岩浆岩影响的Ro值演化剖面 图中实线为Ro变化趋势. Fig. 6 Vitrinite reflectance profile influenced by igneous rocks Solid line shows changing trend of Ro. |
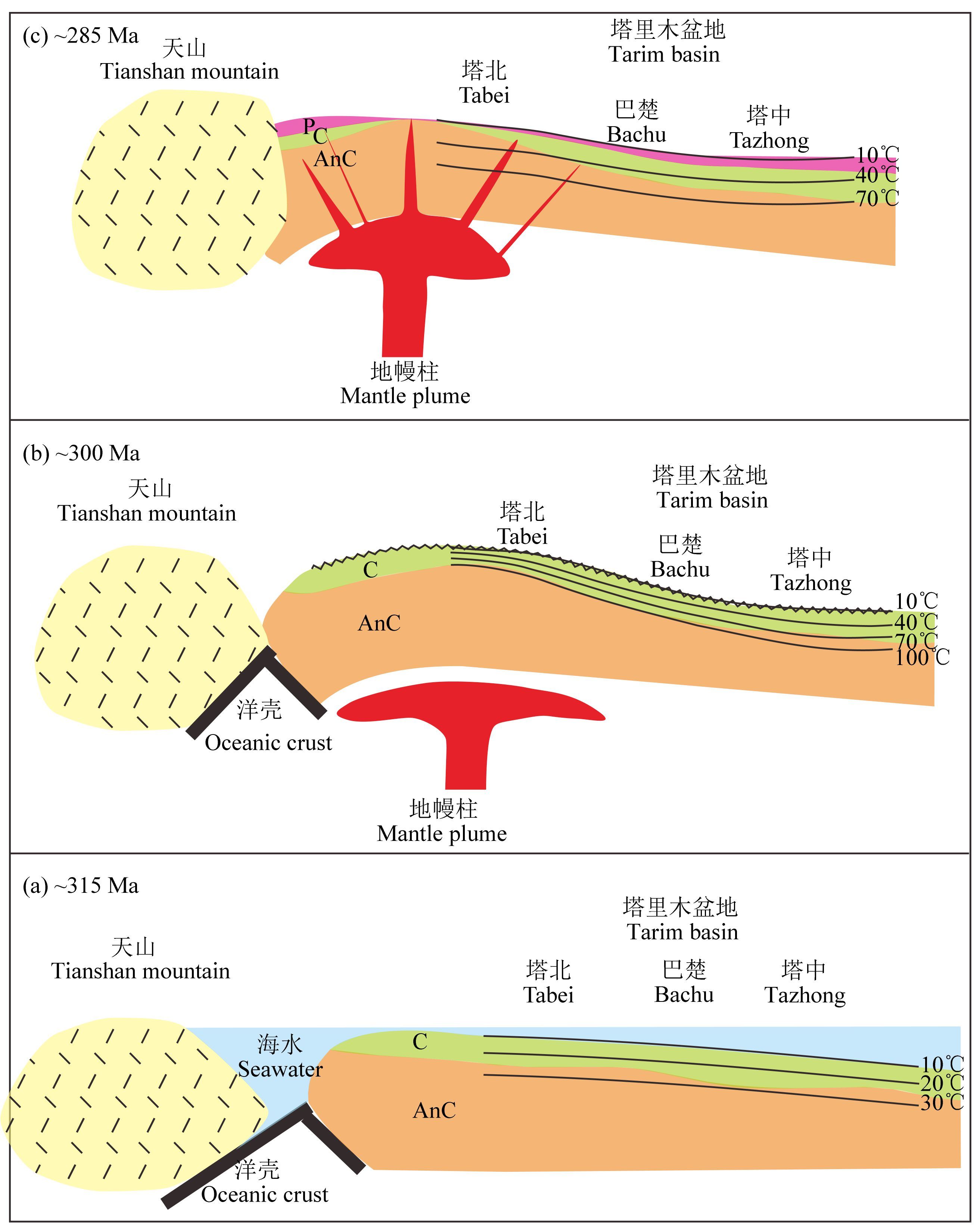
塔里木早-中二叠世大火成岩省是在我国继峨眉山大火成岩省之后相对比较确认的又一个大火成岩省,随着研究的深入越来越多的证据指出塔里木大火成岩省与地幔柱关系密切. 朱传庆等(2010a,2010b)在恢复四川盆地热流演化史的基础上,证实古热流的时间演化规律、空间分布特征与峨眉山岩浆活动密切相关,为峨眉山地幔柱在上扬子地区的存在提供地热学依据.塔里木盆地构造-热演化亦具有相似的特征. 通常认为地幔柱起源于核幔边界,地幔柱柱头直径最大可达千米以上,具有异常高的温度(Campbell,2001),由于上升地幔柱对岩石圈的动力和能量冲击,可造成大规模的地壳抬升和地层温度升高(Griffiths and Campbell,1990),有别于一般的岩浆活动和地层抬升.塔里木盆地近半区域内异常的构造-热历史从地热学角度一定程度地指示出大火成岩省与地幔柱的关系. 塔里木盆地大火成岩省的岩浆喷出在300—275 Ma(Li et al.,2012b; Polyakov et al.,2008; Wei et al.,2014; Xu et al.,2014; Yu et al.,2011; Zhang et al.,2010,2013; 陈汉林等,1997,2009; 杨树锋等,2014),大规模玄武质岩浆岩形成于290—288 Ma. 通过沉积地层学研究确定塔里木岩浆喷发前地壳快速大幅度抬升,强烈隆升发生于~300 Ma(Li et al.,2014),造成石炭-二叠系之间的不整合. 盆地地温梯度值自石炭纪末期开始迅速升高,最高值出现在~300 Ma,与地层强烈隆升的时间一致,呼应了高温地幔柱柱头的上升过程(图 7b). 热史模拟显示石炭纪末期塔里木盆地地温受热效应的影响程度自北向南方向减弱(图 5),该时期地层剥蚀程度亦表现出北强南弱的特点,热史演化和地层剥蚀在空间上相呼应. 随后地温梯度开始迅速降低(图 7c),这是由于地幔柱的热量在与塔里木岩石圈地幔发生持续作用和岩浆喷发的短暂过程中大量损耗. 由于地幔柱与岩石圈地幔的相互作用,大火成岩省从早期的玄武岩到晚期的侵入岩体现出从富集地幔组分转变为亏损地幔组分的演化趋势,侵入岩均具有源于亏损地幔源区的特征(Li et al.,2012a; 励音骐,2013; 余星,2009). 前人通过沉积学、岩石学和地球化学方法得出,地幔柱中心柱头位于盆地北部地区(Tian et al.,2010; Zhang et al.,2013; 陈汉林等,2006);值得注意的是天山二叠系玄武岩与塔里木玄武岩具有相似的地球化学特征,推断是同一地幔柱的产物,但天山玄武岩低钛高镁、高εNd(t)值的特点表明其可能是来自高程度部分熔融的岩石圈地幔的产物,与地幔柱头更为邻近,塔里木盆地玄武岩高钛低镁、低εNd(t)值的特点意味着其可能来自于柱头边缘低程度部分熔融的区域(Qin et al.,2011; 夏林圻等,2004). 塔里木盆地石炭纪末地温梯度自北向南降低,反映出异常热作用北强南弱的特点,这种空间上的分布规律应是对石炭纪末地幔柱柱头烘烤浅部地层的响应,意味着盆地西北部更靠近热源中心.
|
图 7 ~315—285 Ma塔里木盆地古地温和地幔柱演化示意图 Fig. 7 Schematic illustration for ~315—285 Ma evolution of thermal history and mantle plume in Tarim basin |
(1) 塔里木盆地西北部多口钻井显示二叠系与前二叠系内镜质体反射率(Ro)值随埋深出现不连续演化,Ro分析和热史模拟表明,盆地内自晚石炭世发育一期高温热事件,岩浆喷出前岩浆房的烘烤对盆地地温场产生了重要影响,导致区域地温升高,并在~300 Ma达到峰值,随后至早二叠世温度迅速下降;而二叠纪大规模岩浆喷发过程(290—288 Ma)的热效应仅能作用有限区域.
(2) 塔里木盆地石炭纪末-二叠纪初的构造-热事件,从地热学角度提供了塔里木地幔柱存在的证据,盆地地温梯度具有北高南低的特点,异常热事件对盆地的影响向南部地区减弱,指示塔里木盆地北部更靠近热源中心区.
| Annen C, Sparks R S J. 2002. Effects of repetitive emplacement of basaltic intrusions on thermal evolution and melt generation in the crust. Earth & Planetary Science Letters , 203 (3-4) : 937-955. | |
| Barker C E, Goldstein R H. 1990. Fluid-inclusion technique for determining maximum temperature in calcite and its comparison to the vitrinite reflectance geothermometer. Geology , 18 (10) : 1003-1006. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<1003:FITFDM>2.3.CO;2 | |
| Barker C E, Pawlewicz M J. 1986. The correlation of vitrinite reflectance with maximum temperature in humic organic matter.//Paleogeothermics. Berlin Heidelberg:Springer, 79-93. | |
| Buchardt B B, Lewan M. 1990. Reflectance of vitrinite-like macerals as a thermal maturity index for Cambrian-Ordovician Alum Shale, Southern Scandinavia. AAPG Bulletin , 74 (4) : 394-406. | |
| Burnham A K, Sweeney J J. 1989. A chemical kinetic model of vitrinite maturation and reflectance. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta , 53 (10) : 2649-2657. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(89)90136-1 | |
| Campbell I H. 2001. Identification of ancient mantle plumes.//Mantle Plumes:their identification through time. Geological Society of America Special Papers, 352:5-21. | |
| Chang J, Brown R W, Yuan W M, et al. 2014. Mesozoic cooling history of the "Bachu Uplift" in the Tarim Basin, China:Constraints from zircon fission-track thermochronology. Radiation Measurements , 67 : 5-14. DOI:10.1016/j.radmeas.2014.05.019 | |
| Chen H L, Yang S F, Dong C W, et al. 1997. Confirmation of Permian basite zone in Tarim Basin and its tectonic significance. Geochimica (in Chinese) , 26 (6) : 77-87. | |
| Chen H L, Yang S F, Wang Q H, et al. 2006. Sedimentary response to the Early-Mid Permian basaltic magmatism in the Tarim plate. Geology in China (in Chinese) , 33 (3) : 545-552. | |
| Chen H L, Yang S F, Li Z L, et al. 2009. Spatial and temporal characteristics of Permian large igneous province in Tarim Basin. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology (in Chinese) , 30 (2) : 179-182. | |
| Chen R S, He S, Wang Q L, et al. 1989. A Preliminary discussion of magma activity on the maturation of organic matter-taking Geyucheng-Wenan area of Hebei Province as an example. Petroleum Exploration and Development (1) : 29-37. | |
| Clayton J L, Bostick N H. 1986. Temperature effects on kerogen and on molecular and isotopic composition of organic matter in Pierre Shale near an igneous dike. Organic Geochemistry , 10 (1-3) : 135-143. DOI:10.1016/0146-6380(86)90017-3 | |
| Cong P H, Wang H F, Qi K B, et al. 2015. Study on strata denudation quantity based on the seismic data. Geophysical Exploration Technology Seminar of CPS (in Chinese) : 276-279. | |
| Du Y S, Dong J N. Paleotology and Geochronic Geology (in Chinese). (in Chinese) Wuhan: China University of Geoscience Press, 1998 . | |
| Fan T Y, Shi Y L, Zhou Y R. 1999. Effect of magma intrusion on the thermal evolution in a sedimentary basin. Journal of the Graduate School Academia Sinica (in Chinese) , 16 (1) : 63-69. | |
| Fjeldskaar W, Helset H M, Johansen H, et al. 2008. Thermal modelling of magmatic intrusions in the Gjallar Ridge, Norwegian Sea:implications for vitrinite reflectance and hydrocarbon maturation. Basin Research , 20 (1) : 143-159. DOI:10.1111/bre.2008.20.issue-1 | |
| Galushkin Y I. 1997. Thermal effects of igneous intrusions on maturity of organic matter:a possible mechanism of intrusion. Organic Geochemistry , 26 (1-2) : 645-658. | |
| Gao F H, Gao H M, Zhao L. 2009. Effects of volcanic eruptions on characteristics of source rocks:taking Shangkuli Formation of Labudalin basin as an example. Acta Petrologica Sinica (in Chinese) , 25 (10) : 2671-2678. | |
| Griffiths R W, Campbell I H. 1990. Stirring and structure in mantle starting plumes. Earth & Planetary Science Letters , 99 (1-2) : 66-78. | |
| He B Z, Xu Z Q, Jiao C L, et al. 2011. Tectonic unconformities and their forming:implication for hydrocarbon accumulations in Tarim basin. Acta Petrologica Sinica (in Chinese) , 27 (1) : 253-265. | |
| He D F, Jia C Z, Li D S, et al. 2005. Formation and evolution of polycyclic superimposed Tarim Basin. Oil & Gas Geology (in Chinese) , 26 (1) : 64-77. | |
| Jia C Z. Plate Tectonics and Continental Dynamics of Tarim Basin (in Chinese). (in Chinese) Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press., 2004 . | |
| Jia C Z, Wei G Q. 2002. Tectonic characteristics and oil-gas potential of Tarim Basin. Chinese Science Bulletin (in Chinese) , 47 (S1) : 1-8. | |
| Li C, Wang L S, Guo S P, et al. 2000. Thermal evolution in Tarim Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica (in Chinese) , 21 (3) : 13-17. | |
| Li D X, Yang S F, Chen H L, et al. 2014. Late Carboniferous crustal uplift of the Tarim plate and its constraints on the evolution of the Early Permian Tarim Large Igneous Province. Lithos , 204 : 36-46. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.05.023 | |
| Li L X, Li Y, Li G H, et al. 2011. Restoration method and application discussion of strata denudation quantity in Kongque river area of Tarim Basin. Petroleum Geology and Engineering (in Chinese) , 25 (3) : 43-52. | |
| Li M J, Wang T G, Chen J F, et al. 2010. Paleo-heat flow evolution of the Tabei Uplift in Tarim Basin, northwest China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 37 (1) : 52-66. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.07.007 | |
| Li Y Q, Li Z L, Chen H L, et al. 2012a. Mineral characteristics and metallogenesis of the Wajilitag layered mafic-ultramafic intrusion and associated Fe-Ti-V oxide deposit in the Tarim large igneous province, northwest China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 49 : 161-174. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.11.026 | |
| Li Y Q. 2013. Study on magma dynamics and ore potential of the Early Permain Tarim Large Igneous Province[Ph. D. thesis] (in Chinese). Hangzhou:Zhejiang University. | |
| Li Z L, Li Y Q, Chen H L, et al. 2012b. Hf isotopic characteristics of the Tarim Permian large igneous province rocks of NW China:Implication for the magmatic source and evolution. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 49 : 191-202. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.11.021 | |
| Lin C S, Yang H J, Liu J Y, et al. 2012. Distribution and erosion of the Paleozoic tectonic unconformities in the Tarim Basin, Northwest China:Significance for the evolution of paleo-uplifts and tectonic geography during deformation. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 46 : 1-19. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.10.004 | |
| Liu B P, Quan Q Q. Geochromic Geology. (in Chinese) Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1996 . | |
| Liu S W, Wang L S, Li C, et al. 2006. Lithospheric thermo-rheological structure and Cenozoic thermal regime in the Tarim Basin, Northwest China. Acta Geologica Sinica (in Chinese) , 80 (3) : 344-350. | |
| Liu X, Guan P, Pan W Q, et al. 2011. Meticulous characterization of Permian volcanic Rocks' spatial distribution and its geological significance in the Tarim Basin. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis (in Chinese) , 47 (2) : 315-320. | |
| Pan Y, Pan M, Tian W, et al. 2013. Redefined distribution of the Permian basalt in the central Tarim area:a new approach based on down hole logging data explanation. Acta Geologica Sinica (in Chinese) , 87 (10) : 1542-1550. | |
| Polyakov G V, Izokh A E, Borisenko A S. 2008. Permian ultramafic-mafic magmatism and accompanying Cu-Ni mineralization in the Gobi-Tien Shan belt as a result of the Tarim plume activity. Russian Geology and Geophysics , 49 (7) : 455-467. DOI:10.1016/j.rgg.2008.06.001 | |
| Qi Y A, Liu G C. 1999. Wave process analysis of sedimentary basin and erosion quantity of unconformities. Journal of Jiaozuo Institute of Technology (in Chinese) , 18 (3) : 161-165. | |
| Qin K Z, Su B X, Sakyi P A, et al. 2011. SIMS zircon U-Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd isotopes of Ni-Cu-bearing mafic-ultramafic intrusions in eastern Tianshan and Beishan in correlation with flood basalts in Tarim Basin (NW China):Constraints on a ca. 280 Ma mantle plume. American Journal of Science , 311 (3) : 237-260. | |
| Qiu N S, Hu S B, He L J. Theory and Application of the Thermal Regime of the Sedimentary Basin (in Chinese). (in Chinese) Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004 . | |
| Qiu N S, Chang J, Zuo Y H, et al. 2012. Thermal evolution and maturation of lower Paleozoic source rocks in the Tarim Basin, northwest China. AAPG Bulletin , 96 (5) : 789-821. DOI:10.1306/09071111029 | |
| Simonet B R T, Brenner S, Peters K E, et al. 1981. Thermal alteration of Cretaceous black shale by diabase intrusions in the eastern Atlantic. Ⅱ-Effects on bitumen and kerogen. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta , 45 (9) : 1581-1602. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(81)90287-8 | |
| Simoneit B R T, Peters K E, Rohrback B G, et al. 2004. Thermal alteration of Cretaceous black shale from the Eastern Atlantic. Ⅲ:Laboratory simulations. Geochemical Society Special Publications,9:321-340. | |
| Stewart A K, Massey M, Padgett P L, et al. 2005. Influence of a basic intrusion on the vitrinite reflectance and chemistry of the Springfield (No. 5) coal, Harrisburg, Illinois. International Journal of Coal Geology , 63 (1-2) : 58-67. DOI:10.1016/j.coal.2005.02.005 | |
| Sweeney J J, Burnham A K. 1990. Evaluation of a Simple Model of Vitrinite Reflectance Based on Chemical Kinetics. AAPG Bulletin , 74 (10) : 1559-1570. | |
| Tian W, Campbell I H, Allen C M, et al. 2010. The Tarim picrite-basalt-rhyolite suite, a Permian flood basalt from northwest China with contrasting rhyolites produced by fractional crystallization and anatexis. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology , 160 (3) : 407-425. | |
| Wang M. 2010. Research on hydrocarbon generation kinetics and thermal effect of volcanism, its application[Ph. D. thesis] (in Chinese). Daqing:Northeast Petroleum University. | |
| Wang T G, Dai S F, Li M J, et al. 2011. Stratigraphic thermohistory and its implications for regional geoevolution in the Tarim Basin, NW China. Science China Earth Science (in Chinese) , 40 (10) : 1331-1341. | |
| Wang Y. 1998. Stratigraphic sequence of Tarim Basin in Neodevonian Carboniferous period. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Sciences) (in Chinese) , 22 (6) : 14-20. | |
| Wei X, Xu Y G, Feng Y X, et al. 2014. Plume-lithosphere interaction in the generation of the Tarim large igneous province, NW China:Geochronological and geochemical constraints. American Journal of Science , 314 (1) : 314-356. DOI:10.2475/01.2014.09 | |
| Wen S M, Wang J Z, Wang G Z, et al. 2005. The development characteristic of the igneous rock in the Tarim Basin and its influence on the hydrocarbon accumulation. Oil Geophysical Prospecting (in Chinese) , 40 (Suppl) : 33-39. | |
| Xia L Q, Xia Z C, Xu X Y, et al. 2004. Carboniferous Tianshan igneous megaprovince and mantle plume. Geological Bulletin of China (in Chinese) , 23 (9-10) : 903-910. | |
| Xiao C T. Theories of Paleontology and Historical Geology (in Chinese). (in Chinese) Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2007 . | |
| Xiao X M, Wu Z J, Liu D H, et al. 1995. Evolution of maturity of the Early Paleozoic marine hydrocarbon source rocks on the basis of organic petrology. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica (in Chinese) , 13 (2) : 112-119. | |
| Xu H L, Fang L H, Zhang X, et al. 2006. Characteristics of Early Permian magmatic rocks and their impact on hydrocarbon accumulation in Tarim Basin. Acta Geoscientica Sinica (in Chinese) , 27 (3) : 235-240. | |
| Xu Y G, Wei X, Luo Z Y, et al. 2014. The Early Permian Tarim Large Igneous Province:Main characteristics and a plume incubation model. Lithos , 204 : 20-35. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.02.015 | |
| Yang S F, Chen H L, Ji D W, et al. 2005. Geological process of Early to Middle Permian magmatism in Tarim Basin and its geodynamic significance. Geological Journal of China Universities (in Chinese) , 11 (4) : 504-511. | |
| Yang S F, Chen H L, Li Z L, et al. 2013. Early Permian Tarim large igneous province in northwest China. Science China:Earth Science , 56 (12) : 2015-2026. DOI:10.1007/s11430-013-4653-y | |
| Yu X. 2009. Magma evolution and deep geological processes of Early Permian Tarim larger igneous province[Ph. D. thesis] (in Chinese). Hangzhou:Zhejiang University. | |
| Yu X, Yang S F, Chen H L, et al. 2011. Permian flood basalts from the Tarim Basin, Northwest China:SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating and geochemical characteristics. Gondwana Research , 20 (2-3) : 485-497. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.11.009 | |
| Zhang C L, Xu Y G, Li Z X, et al. 2010. Diverse Permian magmatism in the Tarim Block. W China:genetically linked to the Permian Tarim mantle plume? Lithos , 119 (3-4) : 537-552. | |
| Zhang D Y, Zhang Z C, Santosh M, et al. 2013. Perovskite and baddeleyite from kimberlitic intrusions in the Tarim large igneous province signal the onset of an end-Carboniferous mantle plume. Earth & Planetary Science Letters , 361 : 238-248. | |
| Zhang S C, Liang D G, Zhang B M, et al. Petroleum Geology and Exploration of Tarim Basin (Vol. (in Chinese) Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004 . | |
| Zhang Y W, Jin Z J, Liu G C, et al. 2000. Study on the formation of unconformaties and the amount of eroded sedimentation in Tarim Basin. Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese) , 7 (4) : 449-457. | |
| Zhu C Q, Tian Y T, Xu M, et al. 2010a. The effect of Emeishan supper mantle plume to the thermal evolution of source rocks in the Sichuan basin. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese) , 53 (1) : 119-127. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.01.013 | |
| Zhu C Q, Xu M, Yuan Y S, et al. 2010b. Palaeogeothermal response and record of the effusing of Emeishan basalts in the Sichuan basin. Chinese Science Bulletin , 55 (10) : 949-956. DOI:10.1007/s11434-009-0490-y | |
| Zhu R K, Luo P, Luo Z. 2002. Lithofacies palaeogeography of the late Devonian and Carboniferous in Tarim Basin. Journal of Palaeogeography (in Chinese) , 4 (1) : 13-24. | |
| Zuo Y H, Li J W, Li W Z, et al. 2015. Mesozoic and Cenozoic "thermal" lithospheric thickness evolution in the Tarim Basin. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese) , 30 (4) : 1608-1615. DOI:10.6038/pg20150415 | |
| 陈汉林, 杨树锋, 董传万, 等. 1997. 塔里木盆地二叠纪基性岩带的确定及大地构造意义. 地球化学 , 26 (6) : 77–87. | |
| 陈汉林, 杨树锋, 王清华, 等. 2006. 塔里木板块早-中二叠世玄武质岩浆作用的沉积响应. 中国地质 , 33 (3) : 545–552. | |
| 陈汉林, 杨树锋, 厉子龙, 等. 2009. 塔里木盆地二叠纪大火成岩省发育的时空特点. 新疆石油地质 , 30 (2) : 179–182. | |
| 陈荣书, 何生, 王青玲, 等. 1989. 岩浆活动对有机质成熟作用的影响初探——以冀中葛渔城-文安地区为例. 石油勘探与开发 (1) : 29–37. | |
| 丛培泓, 王海峰, 齐昆博等. 2015. 基于地震数据的剥蚀量恢复方 法研究. 中国石油学会2015年物探技术研讨会论文集, 276-279. | |
| 杜远生, 童金南. 古生物地史学概论. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1998 . | |
| 范桃园, 石耀霖, 周炎如. 1999. 沉积盆地热演化过程中的岩浆作用. 中国科学院大学学报 , 16 (1) : 63–69. | |
| 高福红, 高红梅, 赵磊. 2009. 火山喷发活动对烃源岩的影响:以拉布达林盆地上库力组为例. 岩石学报 , 25 (10) : 2671–2678. | |
| 何碧竹, 许志琴, 焦存礼, 等. 2011. 塔里木盆地构造不整合成因及对油气成藏的影响. 岩石学报 , 27 (1) : 253–265. | |
| 何登发, 贾承造, 李德生, 等. 2005. 塔里木多旋回叠合盆地的形成与演化. 石油与天然气地质 , 26 (1) : 64–77. | |
| 贾承造. 塔里木盆地板块构造与大陆动力学. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004 . | |
| 贾承造, 魏国齐. 2002. 塔里木盆地构造特征与含油气性. 科学通报 , 47 (增刊) : 1–8. | |
| 李成, 王良书, 郭随平, 等. 2000. 塔里木盆地热演化. 石油学报 , 21 (3) : 13–17. | |
| 李丽贤, 李延, 李国辉, 等. 2011. 塔里木盆地孔雀河地区地层剥蚀量恢复方法及应用探讨. 石油地质与工程 , 25 (3) : 43–52. | |
| 励音骐. 2013. 塔里木早二叠世大火成岩省岩浆动力学及含矿性研究[博士论文]. 杭州:浙江大学. | |
| 刘本培, 全秋琦. 地史学教程. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996 . | |
| 刘绍文, 王良书, 李成, 等. 2006. 塔里木盆地岩石圈热-流变学结构和新生代热体制. 地质学报 , 80 (3) : 344–350. | |
| 刘晓, 关平, 潘文庆, 等. 2011. 塔里木盆地二叠系火山岩空间展布的精细刻画及其地质意义. 北京大学学报:自然科学版 , 47 (2) : 315–320. | |
| 潘赘, 潘懋, 田伟, 等. 2013. 塔里木中部二叠纪玄武岩分布的重新厘定:基于测井数据的新认识. 地质学报 , 87 (10) : 1542–1550. | |
| 齐永安, 刘国臣. 1999. 沉积盆地波动分析与不整合剥蚀量研究:以新疆塔里木盆地为例. 焦作工学院学报 , 18 (3) : 161–165. | |
| 邱楠生, 胡圣标, 何丽娟. 沉积盆地热体制研究的理论与应用. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004 . | |
| 王民. 2010. 有机质生烃动力学及火山作用的热效应研究与应用[博士论文]. 大庆:东北石油大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10220-2010156575.htm | |
| 王铁冠, 戴世峰, 李美俊, 等. 2011. 塔里木盆地台盆区地层有机质热史及其对区域地质演化研究的启迪. 中国科学:地球科学 , 40 (10) : 1331–1341. | |
| 王毅. 1998. 塔里木盆地晚泥盆世与石炭纪沉积演化. 石油大学学报:自然科学版 , 22 (6) : 14–20. | |
| 温声明, 王建忠, 王贵重, 等. 2005. 塔里木盆地火成岩发育特征及对油气成藏的影响. 石油地球物理勘探 , 40 (增刊) : 33–39. | |
| 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义, 等. 2004. 天山石炭纪大火成岩省与地幔柱. 地质通报 , 23 (9-10) : 903–910. | |
| 肖传桃. 古生物学与地史学概论. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2007 . | |
| 肖贤明, 吴治君, 刘德汉, 等. 1995. 早古生代海相烃源岩成熟度的有机岩石学评价方法. 沉积学报 , 13 (2) : 112–119. | |
| 徐汉林, 方乐华, 张昕, 等. 2006. 塔里木盆地早二叠世岩浆特征及其对油气成藏关系初探. 地球学报 , 27 (3) : 235–240. | |
| 杨树锋, 陈汉林, 冀登武, 等. 2005. 塔里木盆地早-中二叠世岩浆作用过程及地球动力学意义. 高校地质学报 , 11 (4) : 504–511. | |
| 杨树锋, 陈汉林, 厉子龙, 等. 2014. 塔里木早二叠世大火成岩省 , 44 (2) : 187–199. | |
| 余星. 2009. 塔里木早二叠世大火成岩省的岩浆演化与深部地质作用[博士论文]. 杭州:浙江大学. http://www.oalib.com/references/18990740 | |
| 张水昌, 梁狄刚, 张宝民, 等. 2004. 塔里木盆地石油地质与勘探丛书(卷七):塔里木盆地海相油气的生成 : 1–18. | |
| 张一伟, 金之钧, 刘国臣, 等. 2000. 塔里木盆地环满加尔地区主要不整合形成过程及剥蚀量研究. 地学前缘 , 7 (4) : 449–457. | |
| 朱传庆, 田云涛, 徐明, 等. 2010a. 峨眉山超级地幔柱对四川盆地烃源岩热演化的影响. 地球物理学报 , 53 (1) : 119–127. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.01.013 | |
| 朱传庆, 徐明, 袁玉松, 等. 2010b. 峨眉山玄武岩喷发在四川盆地的地热学响应. 科学通报 , 55 (6) : 474–482. | |
| 朱如凯, 罗平, 罗忠. 2002. 塔里木盆地晚泥盆世及石炭纪岩相古地理. 古地理学报 , 4 (1) : 13–24. | |
| 左银辉, 李佳蔚, 李文正, 等. 2015. 塔里木盆地中、新生代"热"岩石圈厚度演化. 地球物理学进展 , 30 (4) : 1608–1615. DOI:10.6038/pg20150415 | |
 2016, Vol. 59
2016, Vol. 59


