2. 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 北京 100029
2. Institute of Geology and Geophysics CAS, 100029, China
P-SV地震勘探技术在气云下成像、PP反射差地区目标成像、碎屑岩岩性构图及提高浅层分辨率(小于1000m深度)等方面已证实有效,并且在各向异性参数求取、弹性反演方面有着重要前景[1-4],尤其是在裂缝检测[5-6]、储层预测[7]和探测隐伏活动断裂[8]方面已取得较好成果.随着三维地震勘探[9-10]在很多地区的成功实践应用,P-SV静校正将成为一个很有挑战性的课题,它远比P波复杂,是因为近地表低速带的厚度、速度和密度的横向变化对P与S来说是不同的,在同一位置上S波静校正的数值通常比P波的大2~10倍[11].因此,P-SV波静校正的难点在于接收点的S波静校正.P-SV波静校正可以分为反射波法和折射波法两大类,对于反射波法,比较有代表性的有:P.W.Cary [12]提出的共检波点叠加道相关法,主要用来求取短波长静校正量,郭桂红[13]用曲线拟合圆滑消除构造影响、潘树林[14]用构造校正分别对其进行了改进,随后潘树林[15]用初至叠加法拾取初至,根据纵波和转换波的初至时差计算了转换波的静校正量,并在宣汉地区得到很好效果;对于折射波法,比较有代表性的有:Armin W Schafter[16]提出的转换波折射静校正法,主要用来求取长波长静校正量,李彦鹏[17]提出的转换波延迟时静校正法,它根据P波和S波的初至时差来求取S波静校正,Heelan[18]很好的计算了折射波的振幅强度,为转换波静校正提供了便利,LIU[19]对折射波法进行了深入研究,得出大波阻抗差是产生折射横波的条件,李彦鹏[20]将转换波延迟时和共检波点叠加相关结合,得出一个针对厚风化层覆盖区的有效转换波静校正方法.这些方法在一定条件下均取得了不错的效果,为研究转换波静校正提供了理论基础.
频率波数域偏移是一种效率高、效益好的方法,DanKosloff[21]、BengtFornberg [22]等人对其做了很多改进,JohnR.Berryhill[23]最早指出可以将其应用到P波静校正中,随后很多学者在这方面做了工作,Reshef[24]用相移法以逐步累加向下波场延拓的方式完成了起伏地表的基准面校正,BevcD [25]用克希霍夫算子以波场向上外推的方式完成了起伏地表的基准面校正,王祥春[26]通过对起伏地表进行变换,用双平方根法将地震波场向下延拓完成了起伏地表的静校正,杨锴[27]用有限差分法以逐步累加向下延拓实现了非水平观测面的基准面校正,随后又将其应用到三维波动方程的基准面校正中[28],李录明[29]做了基于复杂表层模型的三维波场延拓研究,卢回忆[30]用快速Fourier变换相移、分裂步和一阶退化三种不同的算子完成了波动方程的基准面校正,王红落[31]研究分析了波动方程基准面延拓的进展,陈树文[32]研究了复杂地质体的波动方程基准面技术,王建民[33]研究了波场延拓的速度分析,李翔[34]用变换坐标系的方法推导出一种新的延拓算子,用近地表速度向上延拓完成了复杂地表的静校正,可见,频率波数域波场延拓在P波静校正中已取得良好效果,Li[35]提出可以将其应用到转换波静校正中.另外,许多学者在转换波的其他方面也做了深入研究,崔杰[36]提出了高分辨率的P-SV波速度分析方法,冯晅[37-38]分别研究了P-SV波转换点的最佳角度搜索方法和P-SV波的AVO反演,李天成[39]研究了P-SV波转换点和各向异性参数的关系,蔡晓刚[40]研究了P-SV波的反投射系数,陈学良[41]研究了场地钻井台阵观测中P-SV波的分离方法,芦俊[42]设计了P-SV波的采集观测系统,这都为转换波的静校正提供了理论帮助.本文在此基础上,提出基于波场延拓的变换坐标转换波静校正,首先对起伏地表函数进行坐标变换,将炮点和检波点映射到同一水平面上,使地震数据的频率波数域和时间空间域能够相对应;接着波场分离,提取出P-SV地震数据,将P-SV地震数据分成共炮点道集和共检波点道集;然后根据新坐标系下的波动方程延拓公式向上延拓P-SV地震数据到基准面,共炮点道集用近地表S波速度,共检波点用P波速度,恢复起伏地表到基准面之间的真实波场;最后还原到原始坐标系,取出基准面P-SV地震数据并完成校正.该方法不但适用于起伏平缓地区,而且可以在地形复杂地区应用.
2 方法要点 2.1 变换坐标转换波波场延拓静校正变换坐标转换波波长延拓静校正方法可简单分为四步:
1)坐标变换,将炮点和检波点映射到同一水平面上;
2)波场分离,提取P-SV地震数据,P-SV地震数据分成共炮点道集和共检波点道集;
3)根据新坐标系下的波动方程延拓公式向上延拓P-SV地震数据到基准面,共炮点道集用近地表S波速度,共检波点用P波速度;
4)将延拓到基准面的波场还原到原始坐标系,即是校正到基准面的P-SV地震数据.
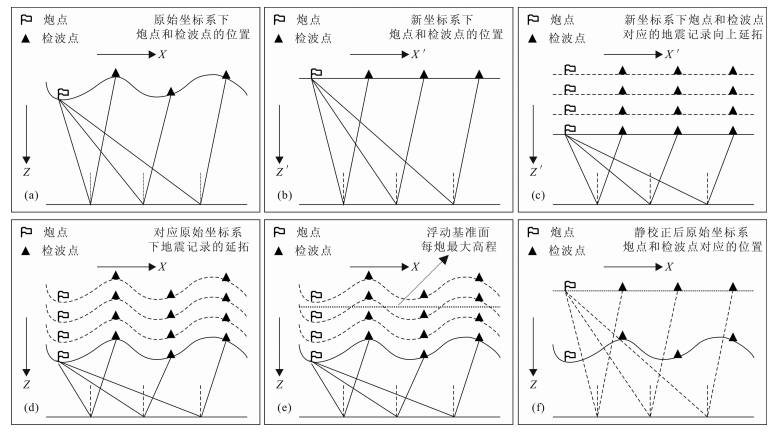
|
图 1 基于波场延拓的变换坐标转换波静校正原理图 (a)原始坐标下炮点和检波点空间位置;(b)变换坐标下炮点和检波点空间位置;(c)变换坐标系下延拓炮点和检波点;(d)原始坐标系下延拓炮点和检波点;(e)在原始坐标系下选取浮动水平基准面;(f)完成转换波静校正. Fig. 1 The schematic diagram of transformating coordination converted wave static correction based on wavefiled continuation |
公式推导的目的是为了将炮点和检波点映射到水平面上,解决延拓静校正频率波数域和时间空间域相对应的问题.假设地表函数为f(x),f(x)可以通过拉格朗日插值函数求取,由二维波动方程出发,有
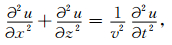
|
(1) |
式(1)中,x和z为二维坐标,v是速度,u是波场.
新旧坐标转换关系式为
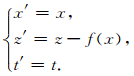
|
(2) |
式(2)中,x′和z′为新二维坐标,将(2)式根据波动方程(1)进行转变,可得
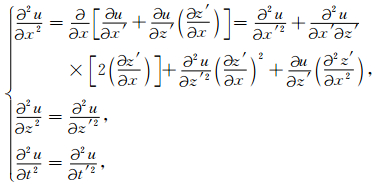
|
(3) |
将(3)式代入(1)式,得波动方程式

|
(4) |
公式(4)称为变换坐标系下的波动方程,其中

|
对公式(4)两边做二维傅里叶变换,得到变换坐标系下的频率波数域波动方程
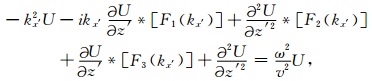
|
(5) |
式中F1(kx′),F2(kx′),F3(kx′)代表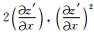
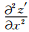
为解决波场延拓问题,需对公式(5)进行求解.边界条件是
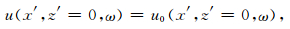
|
(6) |
式(6)中u0(x′,z′=0,t′)为已知变换坐标系下的地震数据.
对波场函数U(kx′,z′,ω)进行分离变量,有

|
(7) |
将式(7)代入方程(5),可得

|
(8) |
式中
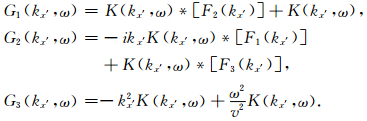
|
(9) |
式(8)为针对z的二阶线性常微分方程,通过求解,可以得到最后的延拓公式
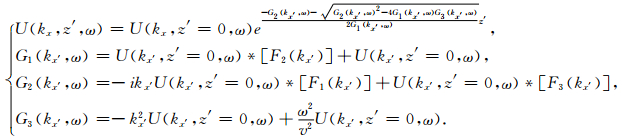
|
(10) |
公式(10)即为转换波频率波数域波动方程延拓静校正的公式,它根据地表起伏函数,通过变换坐标将炮点和检波点映射到水平面上,解决了地震数据的频率波数域和时间空间域的相对应问题.在延拓过程中不仅易于选择基准面,而且还能真实的还原波场,能够得到准确的静校正结果.
3 模拟数据处理图 2是1000 m×1000 m大小的模型数据,在400m和700m处各有一反射层,每层纵波和横波速度分别是:1500 m/s和900 m/s、2000 m/s和1150m/s、2500m/s和1450m/s.图 3是地表高程,最大高程和最小高程相差60m.
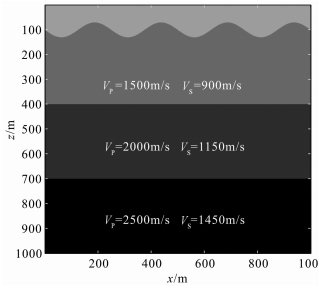
|
图 2 正演模型 Fig. 2 正演模型 |
|
图 3 地表高程 Fig. 3 The surface elevation |
图 4是模型正演结果.通过Tesseral软件模拟得到,中间放炮,99道接收,10m道间距,0.3ms采样率,1.2s总采样时间,共4000个采样点.从图 4中可以看出,由于地形起伏较剧烈,造成有些地方直达波也接收不到,能量断断续续,但地下500 ms和750ms处的两条P-P波看的还是很清楚,700ms和1000ms处的两条P-S波隐隐可见,接近900ms处的是一条多次波.
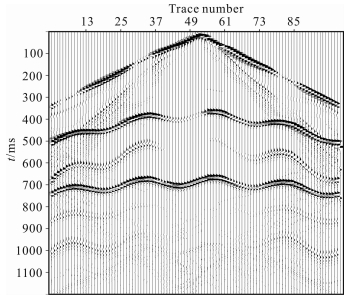
|
图 4 正演结果 Fig. 4 The result of forward modeling |
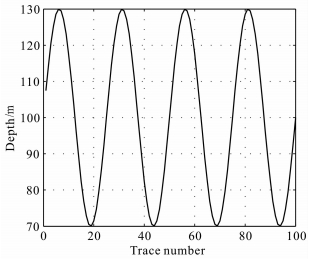
图 5是通过波场分离得到的P-SV地震数据,采用的方法是τ-p变换法[43].图 6是地震数据的延拓过程,根据高程最大差60m,可以选择延拓60步,每一步1m.图 7是本方法静校正结果,根据最大高程-70m,把最佳基准面选定在-69m水平位置,从图中可以看出校正结果呈现伪双曲线的形状,符合转换波理论特征.
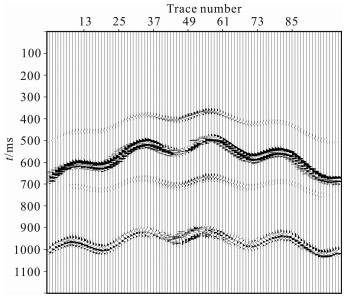
|
图 5 波场分离结果 Fig. 5 The result of wavefield separation |
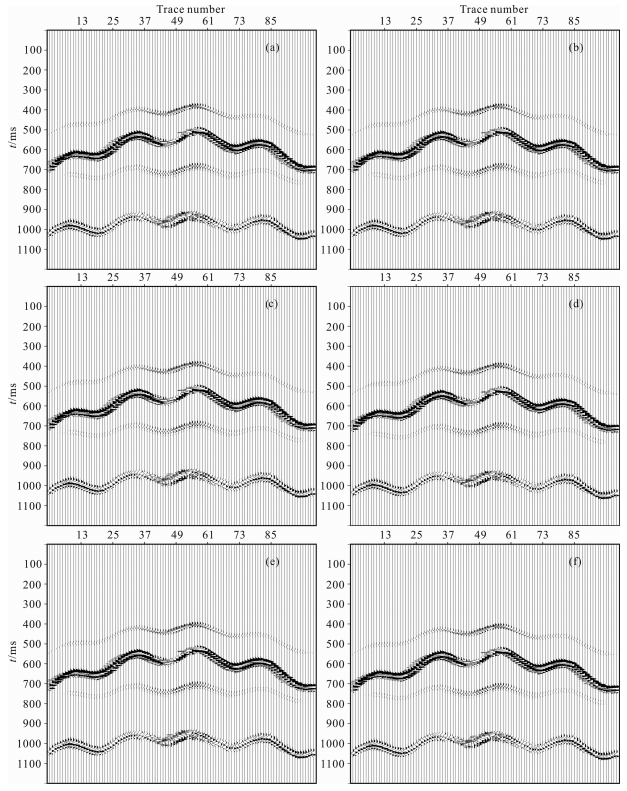
|
图 6 延拓过程 (a)10步;(b)20步;(c)30步;(d)40步;(e)50步;(f)60步. Fig. 6 The process of wavefield continuation (a)10 steps; (b)20 steps; (c)30 steps; (d)40 steps; (e)50 steps; (f)60 steps. |
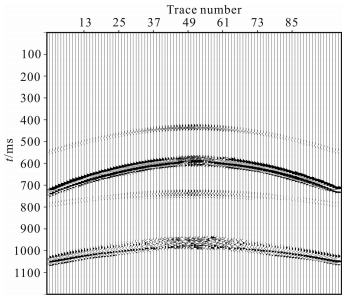
|
图 7 校正结果 Fig. 7 The result of P-SV static correction |
为了验证本方法的可靠性和精确性,我们在延拓过程中随机抽取了第40道的单道数据,蓝色和红色分别表示原始地震记录和延拓了30步的地震记录(图 9),从图中可以得知在延拓过程中地震子波的振幅(A)、频率、相位等属性并没有改变,能量也没有损失,波形依然是零相位子波.随后,我们将炮点和检波点在基准面上的正演数据和本方法的静校正结果数据相减(图 8),得出振幅最大误差不超过0.12,这对正演子波的平均振幅来说是非常低的,达到了可以忽略的程度.这表明了本方法的可行性.

|
图 9 第40道原始记录(蓝色)和延拓30步(红色)记录比较 Fig. 9 The comparison of original (blue) and 30 steps (red) continuity seismic data in the 40th gather |

|
图 8 误差分析结果 Fig. 8 The result of error analysis |
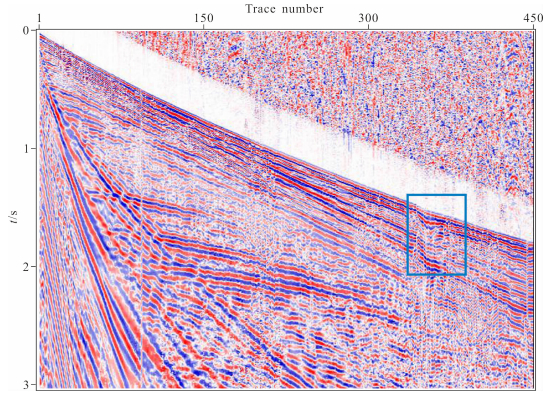
为了验证本方法的实用性,本文对东北某油田的一炮P-S波原始数据做了简单处理,该地区地表有起伏,低降速带S波变化剧烈,并且有较强的面波干扰.可以利用初至波自动拾取技术,通过共炮检距校正统计方法,获取近地表P波和SV波的速度.观测系统道间距为10m,共450道接收,图 10为其中S1测线上的第20炮记录,从原始记录中的S波反射不够光滑以及地下S波反射曲线连续不明显可以看出地形起伏对地震记录是有一定影响的.
|
图 10 原始数据 Fig. 10 The original seismic data |
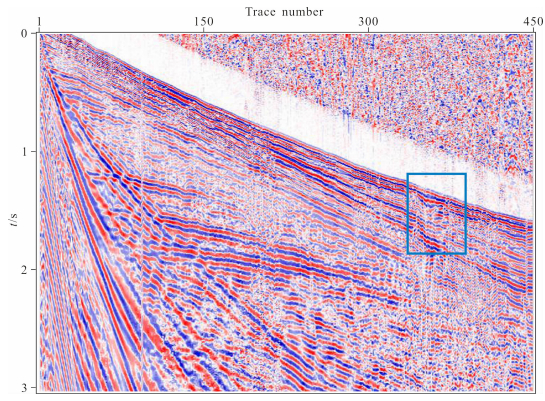
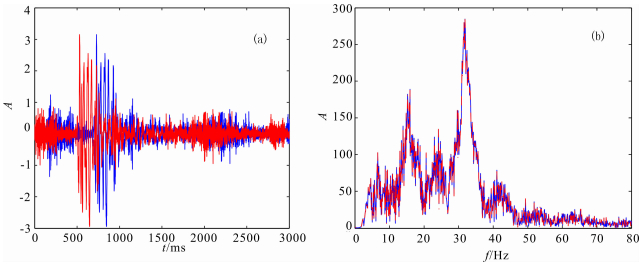
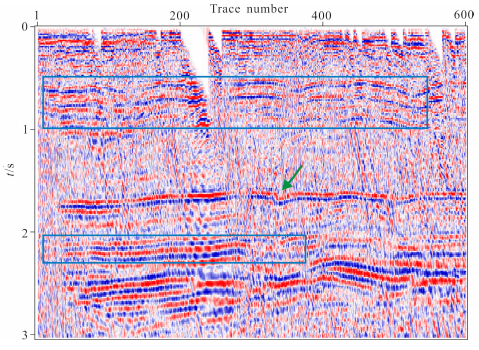
图 11为通过本文方法静校正的结果,延拓填充速度为真实地表速度.从图中可以看出,本方法校正的S波同相轴很明显,线条圆润光滑,连续性很好,信噪比也很高,并且把350道附近有明显凹陷的P波直达波也较平.图 12为随机抽取的第200道的原始单道数据(蓝色)和延拓20步(红色)后的记录比较,从图中可以得知在延拓过程中地震子波的振幅(A)、频率、相位等属性基本没有改变,能量也没有损失.图 13为转换波静校正前的叠加数据,图 14为转换波静校正后的叠加数据,通过对比我们可以发现,校正后的反射层更清晰,连续性更好,同相轴更光滑,尤其是100道左右中间层的位置,同相轴明显的显现了出来.此结果充分验证了变换坐标系下频率波数域波动方程延拓静校正的真实性和可行性.
|
图 11 本方法校正后数据 Fig. 11 The result of seismic data through wavefiled continuation static correction |
|
图 12 第200道原始记录(蓝色)和延拓20步(红色)记录比较 Fig. 12 The comparison of original (blue) and 20 steps (red) continuity seismic data in the 200th gather |
|
图 13 静校正前叠加数据 Fig. 13 The stacked seismic data before static correction |
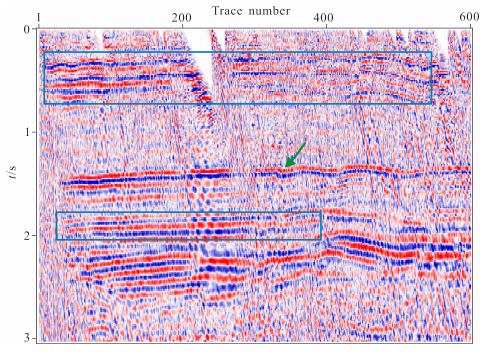
|
图 14 静校正后叠加数据 Fig. 14 The stacked seismic data after static correction |
频率波数域波场延拓静校正已在纵波静校正中取得了一定成果,主要针对地形起伏剧烈,地表条件复杂的地区,这恰好为转换波静校正提供了思路.本文根据此思路研制新方法,通过坐标变换解决了起伏地表地震数据的频率波数域和时间空间域的相对应问题,在延拓过程中使用真实的近地表P波和S波速度,恢复了真实的波场,保证了转换波静校正的精度,同时解决了基于地表一致性假设带来的校正畸变问题.虽然将频率波数域波场延拓应用到转换波静校正中,还存在不少问题尚待进一步解决,但仍可为多波多分量后续处理研究提供思路和方法.
致谢感谢北京吉奥菲斯科技有限责任公司的大力支持和李翔博士富有意义的建议.
| [1] | 何樵登. 地震勘探原理和方法. 北京: 地质出版社, 1986 . He Q D. The Principles and Methods of the Seismic Exploration (in Chinese). Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1986 . |
| [2] | 黄绪德, 杨文霞. 转换波地震勘探. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008 . Huang X D, Yang W X. The Converted Wave Seismic Exploration (in Chinese). Beijing: The Petroleum Industry Press, 2008 . |
| [3] | Luynn H, Stewart R R, Garotta R, et al. 4C-in the future-a word from the "gurus". The Leading Edge , 2001, 20(9): 978. DOI:10.1190/1.1487319 |
| [4] | Stewart R R, Gaiser J E, Brown R J, et al. Converted-wave seismic exploration:applications. Geophysics , 2003, 68(1): 40-57. DOI:10.1190/1.1543193 |
| [5] | 程冰洁, 徐天吉. 转换波方位各向异性裂缝检测技术研究及应用. 地球物理学进展 , 2012, 27(2): 575–581. Cheng B J, Xu T J. Research and application of fracturedetection technique using azimuthal anisotropy of C-wave. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2012, 27(2): 575-581. |
| [6] | 杨晓, 王真理, 喻岳钰. 裂缝型储层地震检测方法综述. 地球物理学进展 , 2010, 25(5): 1785–1794. Yang X, Wang Z L, Yu Y Y. The overview of seismic techniques in prediction of fracture reservoir. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2010, 25(5): 1785-1794. |
| [7] | 单刚义, 韩立国, 张丽华, 等. 转换波在储层预测中的研究分析. 地球物理学进展 , 2010, 25(1): 282–287. Shang G Y, Han L G, Zhang L H, et al. Research and analysis of converted wave in reservoir prediction. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2010, 25(1): 282-287. |
| [8] | 刘保金, 赵成彬, 酆少英, 等. 应用三分量浅层地震反射方法探测隐伏活动断裂. 地球物理学报 , 2012, 55(8): 2676–2686. Liu B J, Zhao C B, Feng S Y, et al. Application of the three-component shallow seismic reflection method to probing buried active faults. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2012, 55(8): 2676-2686. |
| [9] | 付雷, 刘财, 王建民, 等. 大庆地区P-SV波地震资料处理技术. 地球物理学进展 , 2004, 19(2): 414–419. Fu L, Liu C, Wang J M, et al. Seismic processing of P-SV wave in Daqing area. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2004, 19(2): 414-419. |
| [10] | 耿丽娟. 新疆哈密戈壁滩区煤层三维地震勘探实践. 地球物理学进展 , 2005, 20(2): 393–398. Geng L J. 3D seismic wave survey for coal layer in Hami desert area of Xinjiang. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2005, 20(2): 393-398. |
| [11] | Tatham R H, McCormack M D, Neitzel E B, et al. Multicomponent Seismology in Petroleum Exploration. Tulsa: Soc. Expl. Geophys., 1991 . |
| [12] | Cary P W, Eaton D W S. A simple method for resolving large converted-wave (P-SV) static. Geophysics , 1993, 58(3): 429-433. DOI:10.1190/1.1443426 |
| [13] | 郭桂红, 王德利, 何樵登, 等. 转换波的静校正. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版) , 2003, 33(4): 542–544. Guo G H, Wang D L, He Q D, et al. Statics of converted wave. The Journal of Jilin University (Earth Sciences Edition) (in Chinese) , 2003, 33(4): 542-544. |
| [14] | 潘树林. P-SV转换波静校正方法研究. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2008 . Pan S L. The research for P-SV converted-wave static correction (in Chinese). Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2008 . |
| [15] | 潘树林, 高磊, 吴波, 等. 初至叠加法在宣汉地区转换波静校正中的应用. 地球物理学进展 , 2010, 25(3): 932–938. Pal S L, Gao L, Wu B, et al. Application on the superposition method of the first arrival in P-SV static correction in the Xuanhan area. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2010, 25(3): 932-938. |
| [16] | Schafer A W. The determination of converted-wave statics using P refractions together with SV refractions. CREWS Research Report , 1991, 13: 51-66. |
| [17] | Li Y P. A new method for converted wave statics correction. 72nd Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstract , 2002: 979-981. |
| [18] | Hall D. Converted waves in refraction surveys over markers with variable depth. Geophysics , 1964, 29(5): 733-744. DOI:10.1190/1.1439412 |
| [19] | Liu Y, Wei X C. Propagation characteristics of converted refracted wave and its application in static correction of converted wave. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences , 2008, 51(S2): 226-232. DOI:10.1007/s11430-008-6004-y |
| [20] | 李彦鹏, 马在田, 孙鹏远, 等. 厚风化层覆盖区转换波静校正方法. 地球物理学报 , 2012, 55(2): 614–621. Li Y P, Ma Z T, Sun P Y, et al. Converted-wave static correction method for thick weathering area. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2012, 55(2): 614-621. |
| [21] | Dan K, John S, Zvi K, et al. Velocity and interface depth determination by tomography of depth migrated gathers. Geophysics , 1996, 61(5): 1511-1523. DOI:10.1190/1.1444076 |
| [22] | Bengt F. The pseudospectral method:Accurate representation of interfaces in elastic wave calculations. Geophysics , 1998, 53(5): 625-637. |
| [23] | Berryhill J R. Wave-equation datuming. Geophysics , 1979, 44(8): 1329-1344. DOI:10.1190/1.1441010 |
| [24] | Reshef M. Depth migration from irregular surfaces with depth extrapolation methods. Geophysics , 1991, 56(1): 119-122. DOI:10.1190/1.1442947 |
| [25] | Bevc D. Flooding the topography:Wave-equation datuming of land data with rugged acquisition topography. Geophysics , 1997, 62(5): 1558-1569. DOI:10.1190/1.1444258 |
| [26] | 王祥春, 刘学伟. 变换坐标系下相移法起伏地表地震波场延拓. 地球物理学进展 , 2005, 20(3): 677–680. Wang X C, Liu X W. Downward continuing the seismic record of topography using coordination transformated method. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2005, 20(3): 677-680. |
| [27] | 杨锴, 王华忠, 程玖兵, 等. 非水平观测面有限差分法叠前波动方程基准面校正. 石油地球物理勘探 , 2002, 37(2): 154–162. Yang K, Wang H Z, Cheng J B, et al. Prestack wave equation datum correction from non-flat surface with finite-difference scheme. Oil Geophysical Prospecting (in Chinese) , 2002, 37(2): 154-162. |
| [28] | 杨锴, 程玖兵, 刘玉柱, 等. 三维波动方程基准面校正方法的应用研究. 地球物理学报 , 2007, 50(4): 1232–1240. Yang K, Cheng J B, Liu Y Z, et al. A study on the application of the 3-D wave-equation-datuming. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2007, 50(4): 1232-1240. |
| [29] | 李录明, 罗省贤. 三维波场延拓复杂表层模型校正方法及应用. 地球物理学进展 , 2005, 20(4): 1027–1034. Li L M, Luo S X. The Method and application of 3D wave field continuation correction based on complicated surface layer model. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2005, 20(4): 1027-1034. |
| [30] | 卢回忆, 符力耘, 蒋韬. 快速Fourier变换波动方程基准面校正方法研究. 地球物理学进展 , 2010, 25(4): 1313–1322. Lu H Y, Fu L Y, Jiang T. Wave-equation datuming based on fast fourier transform. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2010, 25(4): 1313-1322. |
| [31] | 王红落, 陈中州, 常旭. 波动方程基准面延拓研究进展. 地球物理学进展 , 2004, 19(2): 230–234. Wang H L, Cheng Z Z, Chang X. The recent progress in wave-equation datuming. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2004, 19(2): 230-234. |
| [32] | 陈树文, 刘洪. 可用于复杂地质体的波动方程基准面技术. 地球物理学进展 , 2002, 17(3): 365–369. Cheng S W, Liu H. The usability of the wave-equation datuming for complicated geological body. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2002, 17(3): 365-369. |
| [33] | 王建民, 刘财, 杨宝俊, 等. 地质雷达技术在巴彦查干地区地震勘探中的应用. 地球物理学进展 , 2002, 17(4): 745–752. Wang J M, Liu C, Yang B J, et al. The application of ground penetrating radar for seismic exploration in Bayanchagan area. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2002, 17(4): 745-752. |
| [34] | 李翔. 基于复杂地表波场延拓的静校正方法研究. 长春: 吉林大学, 2009 . Li X. Static correction based on wavefield continuation in complex area (in Chinese). Changchun: Jilin University, 2009 . |
| [35] | Li G F, Peng S P. Static corrections for low S/N ratio converted-wave seismic data. Applied Geophysics , 2008, 5(1): 44-49. DOI:10.1007/s11770-008-0009-3 |
| [36] | 崔杰, 韩立国, 廉玉广, 等. 高分辨率P-SV波速度分析. 地球物理学进展 , 2009, 24(6): 2036–2043. Cui J, Han L G, Lian Y G, et al. High resolution velocity analysis of P-SV wave. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2009, 24(6): 2036-2043. |
| [37] | 冯晅, 刘财, 郭继茹, 等. 多层倾斜层状介质P-SV转换波转换点计算的最佳角度搜索法. 地球物理学报 , 2011, 54(2): 320–328. Feng X, Liu C, Guo J R, et al. Estimation of P-SV conversion point by searching optimal angle in a dipping or horizontal layered medium. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2011, 54(2): 320-328. |
| [38] | 冯晅, 舒梦珵, 王兆国, 等. P-P波和P-SV波联合AVO反演研究. 地球物理学进展 , 2008, 23(5): 1556–1559. Feng X, Shu M C, Wang Z G, et al. Joint AVO inversion using P-P and P-SV seismic data. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2008, 23(5): 1556-1559. |
| [39] | 李天成, 牛滨华, 孙春岩, 等. VTI介质中P-SV波转换点与各向异性参数关系. 地球物理学进展 , 2007, 22(5): 1522–1526. Li T C, Niu B H, Sun C Y, et al. The relationship of VTI media P-SV wave converted Point and anisotropy parameters. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2007, 22(5): 1522-1526. |
| [40] | 蔡晓刚, 陈晓非. 倾斜裂隙介质反透射系数研究. 地球物理学报 , 2009, 52(5): 1253–1262. Cai X G, Chen X F. Study on the reflection-transmission coefficients of elastic waves in the media with dipping fractures. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2009, 52(5): 1253-1262. |
| [41] | 陈学良, 金星. 场地钻井台阵观测中斜入射P波和SV波的近似剥离方法. 地球物理学进展 , 2009, 24(5): 1636–1645. Cheng X L, Jin X. Approximate decomposition method of oblique incidence P, SV wave fields in observation of site borehole array. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2009, 24(5): 1636-1645. |
| [42] | 芦俊, 王赟, 孟召平, 等. 优化P-P、P-SV波联合采集观测系统设计方法. 地球物理学进展 , 2003, 18(4): 715–723. Lu J, Wang Y, Meng Z P, et al. Method of optimizing joint P-P、P-SV acquisition geometry design. Progress in Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2003, 18(4): 715-723. |
| [43] | 冯晅, 张先武, 刘财, 等. 带有多道相关的抛物线Radon变换法分离P-P、P-SV波. 地球物理学报 , 2011, 54(2): 304–309. Feng X, Zhang X W, Liu C, et al. Separating P-P and P-SV wave by parabolic Radon transform with multiple coherence. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese) , 2011, 54(2): 304-309. |
 2013, Vol. 56
2013, Vol. 56

