2. 海军潜艇学院军事体育与技能教研室,青岛 266000;
3. 中国人民解放军东部战区总医院骨科,南京 210002
2. Department of Military Sports and Skills, Navy Submarine Academy, Qingdao 266000, Shandong, China;
3. Department of Orthopaedics, General Hospital of Eastern Theater Command of PLA, Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu, China
晕动症是水上作业人员和海军官兵常见的生理障碍,船舶在海上航行过程中的异常加速度刺激所诱发的头晕、头痛、恶心、呕吐等症状可严重影响人员的认知和操作能力[1-2]。研究发现,对于旋转椅或视觉诱导的晕动症易感性,黄种人显著高于白种人和黑种人[3-5]。在风力6级条件下航行1 h、长距离连续航渡8 h以上或在南海湿热条件下连续航行,晕动症发生率均可达85%以上[6-7]。经过一定时间的海上航行或陆上抗晕训练,可产生症状消失、认知能力恢复的习服现象[8-9]。生活常识和研究均证明,主动开车时的晕动症发生率显著低于被动坐车时,被动运动引起的感觉冲突是晕动症的主要诱因[10]。同时,上下垂荡运动是引起晕动症的首要因素,单独的左右或前后摇摆不能引起晕动症,而3种运动同时作用却能引起明显的晕动症症状[11]。目前,最常用的陆上防晕动症专项训练方法有滚轮、浪木、旋梯和模拟舱等[12-14],主要包括回环、翻腾、旋转、摆荡等主动运动动作,可有效提高身体的平衡控制力,但以上训练方法以水平和旋转运动为主,缺乏垂荡运动,且均为主动运动,训练效果欠佳。本课题组结合现有浪木器械和海上船舶运动特点,设计了一种基于被动运动的仰姿浪木训练法,此法通过训练时体位的变化,可把横向的水平运动转化为人体纵向的垂荡运动。本研究旨在检验新型浪木训练法的训练效果,为今后改进陆上浪木训练法、提高人体对海上舰船运动环境的耐受能力提供试验依据。
1 对象和方法 1.1 对象及分组从成年男性100人[年龄为17~38(23.39±3.35)岁]中,根据40 min正弦垂直振荡期间的晕动症症状筛选出晕动症敏感者,并根据Graybiel评分分为轻度敏感组(Graybiel评分为1~15分)和重度敏感组(Graybiel评分≥16分)。所有参与者在最近3个月内无海上航行和抗晕动症训练经历,无眩晕相关疾病,在训练期间未服用抗晕药物,不进行高强度体能训练,并保证每天7 h以上的睡眠时间。研究方案通过海军军医大学(第二军医大学)医学研究伦理委员会审核批准,每位参与者均签署知情同意书。
1.2 试验流程试验总时长为7 d,训练时长为5 d。试验第1天,给予100名参与者正弦垂荡刺激,根据Graybiel评分筛选出晕动症敏感者并分组。试验第2~6天为训练日,受训者进行连续5 d、30 min/d的仰姿浪木训练,记录训练期间受训者的Graybiel评分和浪木的运动参数。试验第7天,给予受训者正弦垂荡刺激以验证训练效果。在训练期间,受训者若出现呕吐症状则立即停止训练并下器械休息。试验第2、6天,训练前后进行静态平衡功能测试。
1.3 试验方法 1.3.1 Graybiel评分按国际上常用的Graybiel量表[15]进行晕动症症状评估,包括恶心综合征、皮肤颜色、出冷汗、流涎、嗜睡和中枢神经系统体征等6类症状[16]。每类症状的最高得分相加得到该名参与者的Graybiel评分,分值越高表明晕动症症状越严重,晕动症敏感性越高。晕动症严重程度按照Graybiel分级标准分为无晕动症(0分)、轻度晕动症(1~2分)、中度晕动症(3~7分)、重度晕动症(8~15分)、极重度晕动症(≥16分)。
1.3.2 正弦垂荡刺激正弦垂荡刺激由本研究组自行设计的垂荡模拟器[17]提供,垂荡参数为频率0.3 Hz、加速度0.2 g、时间40 min。在垂荡训练期间,经过专业培训的评估员使用对讲机和安装在舱内的摄像机与受训者进行实时通信,每10 min按照Graybiel量表评估1次晕动症症状,以4次评估时的最高Graybiel评分作为其分级依据。
1.3.3 仰姿浪木训练浪木训练3~5人为1组,以制式浪木为训练器材。受训者上半身仰躺于铺满瑜伽垫或褥子(防止训练过程中人体滑动)的浪木板上,双腿盘于浪木板上,在浪木的4根摆杆上系4根长1.5~2.0 m的牵引绳,2名助训者位于浪木两端牵拉绳子,尽量保持浪木的来回摆动角度为60°左右,每3 s摆动1次。将ADXL375型三轴加速度计的ADXL345姿态传感器模块(深圳维特智能科技有限公司)固定于浪木板的一侧,实时记录浪木的运动频率和加速度。由1名数据记录者每10 min按照Graybiel量表评估1次受训者的晕动症症状,并根据运动频率和加速度读数告知助训者调整牵引力度。
1.3.4 静态平衡功能测试静态平衡功能测试是使用荷兰HUR公司的HUR SmartBalance系统进行的标准版Romberg测试[18]。该套系统把检测平台(BTG4-FE)的力学传感器测定到的压力中心(center of pressure,CoP)的实时变化数据通过特定数据线传入一体式计算机(HP EliteOne 800 G2 23-in Touch Aio,中国惠普有限公司)中,并采用HUR SmartBalance软件(Balance Support Station,芬兰HUR公司)对数据进行量化。Romberg测试包括4种模式,分别为睁眼-硬底(eyes open-firm surface,EO-FIRM)、睁眼-软底(eyes open-compliant surface,EO-COMP)、闭眼-硬底(eyes closed-firm surface,EC-FIRM)、闭眼-软底(eyes closed-compliant surface,EC-COMP),整体测试时间为2 min。硬底模式时,受训者被要求睁眼或闭眼站在60 cm×60 cm的检测平台坚硬表面上各30 s;软底模式时,在检测平台上放置1个51.5 cm×42.5 cm的矩形泡沫板,受训者闭眼或睁眼站在泡沫板上各30 s。睁眼测试时,受训者需将视线聚焦在正前方3 m处1个直径5 cm的黑色圆圈上。研究表明,穿多只袜子或穿厚袜子会显著增加身体的摇摆,而穿着与可穿戴生物反馈系统相结合的鞋子可减少身体的摇摆[19-21]。为了避免误差,受训者被要求除去鞋袜,光脚站在检测平台上,按检测平台上的图形放置脚的位置,并在测试期间保持双臂自然垂于身体两侧。
根据HUR SmartBalance软件说明,检测平台记录的CoP数据可计算多种姿势变量,此次测试使用的变量为平均速度(mean velocity)和摇摆面积(sway area)。通过对每100 ms(10 Hz)收集的连续CoP点的直线段的长度求和计算总迹线长度,然后用总迹线长度除以30 s的测试持续时间来计算平均速度(mm/s)。摇摆面积(cm2)定义为置信椭圆的面积,包含30 s记录过程中90%的CoP采样点。
1.4 统计学处理采用SPSS 27.0软件进行统计分析。计量资料以x±s表示,计数资料以人数和百分数表示。年龄、身高、体重、人员筛选时的Graybiel评分等基础数据的比较采用独立样本t检验。训练期间Graybiel评分和静态平衡功能测试数据的比较采用两因素多水平重复测量数据的方差分析,两两比较采用最小显著性差异法。晕动症发生率的比较采用Pearson χ2检验或Fisher确切概率法(理论频数<5),两两比较采用Z检验。检验水准(α)为0.05。
2 结果 2.1 人员分组及基础数据通过正弦垂荡期间Graybiel评分筛选出61名晕动症敏感者,其中轻度敏感组28例、重度敏感组33例,两组的年龄、身高、体重、BMI差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05),重度敏感组的Graybiel评分高于轻度敏感组(P<0.001)。见表 1。
|
|
表 1 两组晕动症敏感者的基础特征比较 Tab 1 Comparison of baseline characteristics of motion sickness sensitive individuals between 2 groups |
将三轴加速度计的ADXL345姿态传感器模块连接至笔记本电脑,通过配套软件读取训练期间的加速度和运动频率数据,每1 min读取1次数据进行作图。从图 1可知,经过训练后,助训者可掌握使用牵引绳拉拽浪木的力度规律,将加速度保持在0.15~0.25 g,运动频率保持在0.25~0.35 Hz。
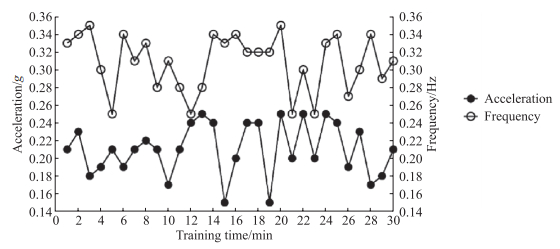
|
图 1 浪木的运动频率和加速度 Fig 1 Frequency and acceleration of ripple wood |
2.2 训练期间Graybiel评分
采用两因素多水平重复测量数据的方差分析对训练期间Graybiel评分进行检验,结果显示,训练天数(F(2.29,135.12)=81.659,偏η2=0.072,P=0.009)、组别(F(1,59)=44.442,偏η2=0.086,P=0.022)主效应均有统计学意义,不存在交互作用(F(2.29,135.12)=2.290,偏η2=0.044,P=0.062)。两两比较结果显示,重度敏感组的Graybiel评分随着训练天数的增加而下降,于训练第3天接近习服水平(P>0.05);轻度敏感组的Graybiel评分一直较低,与训练天数无关。同一训练日组间比较结果显示,重度敏感组训练第1天的Graybiel评分高于轻度敏感组(P<0.01),训练第2、3、4、5天两组间比较差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。见图 2。
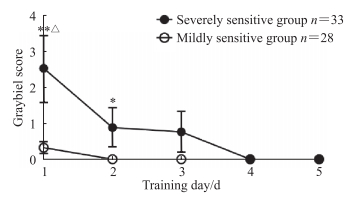
|
图 2 训练期间晕动症敏感者的Graybiel评分 Fig 2 Graybiel scores of motion sickness sensitive individuals during training period *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs training day 5 in the same group; △P < 0.05 vs mildly sensitive group on the same training day. |
表 2展示了浪木训练期间两组受训者的晕动症发生情况。重度敏感组在训练第1天的晕动症发生率为33.33%(11/33),随着训练天数的增加发生率逐渐下降,并于训练第4天全员习服。轻度敏感组在训练第1天5名(17.86%)受训者出现晕动症症状,在训练第2天全员习服。采用χ2检验比较两组每日晕动症的发生率,仅在训练第2天两组的晕动症发生率差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),在训练第1、3、4、5天两组之间差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。
|
|
表 2 不同训练日晕动症敏感者的晕动症发生率 Tab 2 Motion sickness incidence in motion sickness sensitive individuals on different training days |
2.3 训练期间静态平衡功能
两因素多水平重复测量数据的方差分析结果显示,重度敏感组的平均速度在4种平衡测试模式下均显示出垂荡主效应和交互效应(均P<0.05),仅在EO-FIRM、EC-FIRM、EO-COMP模式下显示出习服主效应(均P<0.05)。重度敏感组的摇摆面积及轻度敏感组的摇摆面积和平均速度在4种平衡测试模式下均不存在垂荡和习服主效应(均P>0.05)。见表 3。
|
|
表 3 两组晕动症敏感者的静态平衡功能测试分析结果 Tab 3 Statistical analysis results of static balance function tests of motion sickness sensitive individuals in 2 groups |
对重度敏感组4种平衡测试模式下的平均速度进行两两比较,第1天训练后的平均速度比第1天训练前增加(均P<0.01),而第5天训练后与第5天训练前相比差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05);第5天训练后的平均速度与第1天训练后相比均下降(均P<0.05),而与第1天训练前相比差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。轻度敏感组在4种平衡测试模式下,第1、5天训练前后的平均速度差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05),训练第1天和第5天的平均速度差异也无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。见图 3。
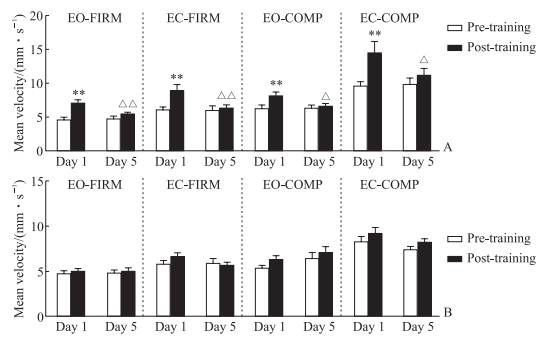
|
图 3 两组晕动症敏感者在4种平衡功能测试模式下的平均速度变化 Fig 3 Mean velocity changes of motion sickness sensitive individuals in 2 groups under 4 balance function test modes A: Severely sensitive group (n=33); B: Mildly sensitive group (n=28). **P < 0.01 vs pre-training on the same day in the same mode; △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.01 vs post-training on the training day 1 in the same mode. x±s. EO-FIRM: Eyes open-firm surface; EC-FIRM: Eyes closed-firm surface; EO-COMP: Eyes open-compliant surface; EC-COMP: Eyes closed-compliant surface. |
2.4 训练效果验证
对筛选和验证试验时两组的Graybiel评分进行两因素多水平重复测量数据的方差分析,结果显示,习服主效应(F(1,59)=1 362.891,偏η2=0.708,P<0.001)、组别主效应(F(1,59)=2 532.122,偏η2=0.744,P<0.001)有统计学意义,且存在交互作用(F(1,59)=810.236,偏η2=0.591,P<0.001)。两两比较结果显示,重度敏感组在筛选和验证试验期间的Graybiel评分均高于轻度敏感组(均P<0.01),重度敏感组在浪木训练后Graybiel评分降低(P<0.01),而轻度敏感组无变化(P>0.05,表 4)。对筛选和验证试验期间两组受训者的晕动症严重程度进行χ2检验,结果显示,重度敏感组(χ2=64.837,P<0.001)和轻度敏感组(χ2=33.041,P<0.001)在浪木训练后的晕动症严重程度均下降(表 4)。晕动症总体发生率从61.00%(61/100)降至37.00%(37/100),极重度晕动症发生率从33.00%(33/100)降至2.00%(2/100),呕吐发生率从32.00%(32/100)降至2.00%(2/100)。轻度敏感组的晕动症发生率从100.00%(28/28)降至35.71%(10/28);重度敏感组的极重度晕动症发生率从100.00%(33/33)降至6.06%(2/33),呕吐发生率从96.97%(32/33)降至6.06%(2/33)。
|
|
表 4 筛选和验证试验期间两组晕动症敏感者的晕动症发生率及严重程度 Tab 4 Incidence and severity of motion sickness in motion sickness sensitive individuals of 2 groups during screening and verification periods |
3 讨论
船舶在海上航行可产生纵摇、横摇、垂荡、横滚、俯仰和偏航等6个自由度的复杂同步运动。海上实航和实验室模拟研究均表明,当船只以0.08~0.4 Hz的频率进行周期性垂荡运动时,会诱发晕动症症状[22-23]。而俯仰和横滚在单独出现时没有晕动症的诱导潜力,在与垂荡运动相结合时才可产生显著的晕动症反应[11]。在一定的频率范围内,晕动症严重程度随着加速度的增加而加重[24]。因此,低频的垂直线性振荡可能是陆上抗晕训练的一种良好选择。既往研究表明,对中国男性来说,0.42 Hz/0.22 g的垂荡刺激比0.25 Hz/0.44 g的刺激能诱发更高的晕动症发生率[17],此结果与以白种人为主的国外研究结果[25]不同。所以,本研究采用自行设计的垂荡模拟器(运动参数为频率0.3 Hz、加速度0.2 g、时间40 min)进行筛选和验证试验,筛选时晕动症发生率为61.00%,极重度晕动症发生率为33.00%。
陆上抗晕专项训练包括徒手抗晕操、滚轮、浪木、旋梯、手动模拟舱、电动四柱秋千和各类模拟器,如汽车模拟器、飞行模拟器、垂荡模拟器、航空模拟器、虚拟现实模拟器等[26-28]。各类模拟器训练趋向于真实环境,训练效果好,但耗资大,单次训练人数少,不适合部队官兵或水上专业人员的大批量抗晕训练。因此,最常用的陆上训练方案仍是使用浪木等低成本器材[12-13]。研究发现,经过体能、心理和陆上抗晕专项训练后,海上实航晕动症发生率可从71.3%降至39.6%[29];经过20节训练课的浪木、固定滚轮专项训练后,人体的肌肉协调能力和平衡能力可得到明显改善,且存在向海上抗眩晕能力的正迁移效果,这种迁移作用以浪木训练最为突出[30]。若采用防晕体操、弹力绳被动运动训练和心理训练的综合训练法进行14次或28次训练,陆上四柱秋千诱发的晕动症发生率可从93.48%分别降至58.62%和61.54%,Graybiel评分均值从11.37分分别降至4.05分和3.88分,极重度晕动症人数从12人降至3人;同时,经过综合训练法训练后,在3~4级海况下的Graybiel评分显著降低,效果显著优于普通浪木训练[31]。本次训练采用仰姿浪木训练法,经过严格培训后的助训者有规律地拉动浪木摆杆上的牵引绳,使浪木的横向线性加速度保持在0.15~0.25 g、运动频率保持在0.25~0.35 Hz,而受训者训练期间的仰躺姿势可使浪木的横向线性运动变为垂荡运动,加上浪木弧线运动过程中所产生的少量纵摇和横摇刺激,最终使训练参数接近对中国男性有效的晕动症诱发参数。本次仰姿浪木训练周期为5 d,从训练期间Graybiel评分和晕动症发生率的变化来看,重度敏感组的适应时间为4 d,轻度敏感组的适应时间为2 d;从垂荡模拟器验证结果来看,轻度敏感组的晕动症发生率从100.00%(28/28)降至35.71%(10/28),重度敏感组的晕动症发生率从100.00%(33/33)降至81.82%(27/33)、极重度晕动症发生率从100.00%(33/33)降至6.06%(2/33)、呕吐发生率从96.97%(32/33)降至6.06%(2/33),可见仰姿浪木训练在晕动症发生率和症状严重程度方面均有显著的习服效果。从训练时间和效果看,仰姿浪木训练法均优于普通陆上抗晕专项训练,可极大地节约训练成本,提高训练效率。
研究表明,船舶在海上的运动对人体的姿势控制有重大影响,无论是新手还是有经验的水手,在海上时双腿站立宽度都比在陆地上宽[32]。在模拟器训练期间和/或之后,身体摇摆路径长度、平均速度、摇摆面积均可显著增加[33-34]。另有报道,人体接受视觉感觉冲突后平衡能力立即轻度下降,在脱离该环境后10 min恢复[35]。使用滚轮、浪木、悬梯、四柱秋千和旋转秋千5种器械进行为期2周的训练后,动态姿势平衡能力明显提高,重心晃动显著降低,线性加速度引起的平衡能力改变得到恢复[36]。采用眩晕诊断治疗系统进行10次阶梯性习服训练后,静态平衡能力显著改善,晕动症Graybiel评分显著降低[37]。本次训练采用静态平衡功能测试观察受训者训练前后的平衡功能,结果提示单次训练后重度敏感组的姿势稳定性下降,习服后可恢复,而轻度敏感组在整个训练过程中无显著变化,说明仰姿浪木训练引起的平衡能力变化与晕动症敏感性有关,且其变化规律与习服规律相似。
| [1] |
DIELS C, BOS J E. Self-driving carsickness[J]. Appl Ergon, 2016, 53(Pt B): 374-382. DOI:10.1016/j.apergo.2015.09.009 |
| [2] |
MATSANGAS P, MCCAULEY M E, BECKER W. The effect of mild motion sickness and sopite syndrome on multitasking cognitive performance[J]. Hum Factors, 2014, 56(6): 1124-1135. DOI:10.1177/0018720814522484 |
| [3] |
STERN R M, HU S, UIJTDEHAAGE S H, et al. Asian hypersusceptibility to motion sickness[J]. Hum Hered, 1996, 46(1): 7-14. DOI:10.1159/000154318 |
| [4] |
MARTINGANO A J, BROWN E, TELAAK S H, et al. Cybersickness variability by race: findings from 6 studies and a mini meta-analysis[J]. J Med Internet Res, 2022, 24(6): e36843. DOI:10.2196/36843 |
| [5] |
KLOSTERHALFEN S, KELLERMANN S, PAN F, et al. Effects of ethnicity and gender on motion sickness susceptibility[J]. Aviat Space Environ Med, 2005, 76(11): 1051-1057. |
| [6] |
鲁云敏, 汪鸿, 凃永久, 等. 陆军渡海作战演习晕船情况及其预防措施[J]. 人民军医, 2002, 45(9): 503-504. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-9736.2002.09.005 |
| [7] |
滕伟强, 张才云, 郑宏良. 某岛礁作业人员航行期间晕船状况调查[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2021, 42(10): 1175-1178. TENG W Q, ZHANG C Y, ZHENG H L. Survey on seasickness of island-reef personnel during navigation[J]. Acad J Sec Mil Med Univ, 2021, 42(10): 1175-1178. DOI:10.16781/j.0258-879x.2021.10.1175 |
| [8] |
HUPPERT D, BENSON J, BRANDT T. A historical view of motion sickness—a plague at sea and on land, also with military impact[J]. Front Neurol, 2017, 8: 114. DOI:10.3389/fneur.2017.00114 |
| [9] |
KESHAVARZ B, GOLDING J F. Motion sickness: current concepts and management[J]. Curr Opin Neurol, 2022, 35(1): 107-112. DOI:10.1097/WCO.0000000000001018 |
| [10] |
REUTEN A J C, SMEETS J B J, RAUSCH J, et al. The (in)effectiveness of anticipatory vibrotactile cues in mitigating motion sickness[J]. Exp Brain Res, 2023, 241(5): 1251-1261. DOI:10.1007/s00221-023-06596-8 |
| [11] |
WERTHEIM A H, BOS J E, BLES W. Contributions of roll and pitch to sea sickness[J]. Brain Res Bull, 1998, 47(5): 517-524. DOI:10.1016/s0361-9230(98)00098-7 |
| [12] |
唐磊, 彭友, 叶泽. 开展海上抗晕陆上训练的研究[J]. 科技视界, 2013(21): 12. DOI:10.19694/j.cnki.issn2095-2457.2013.21.007 |
| [13] |
朱飞. 水上专业学生习练预防晕船专项技能实用功效研究[J]. 体育科技, 2019, 40(1): 6-7. DOI:10.14038/j.cnki.tykj.2019.01.004 |
| [14] |
姜淑芳, 孟昭刚, 单守勤. 我国晕船病的调查和防治研究进展[J]. 海军医学杂志, 2020, 41(2): 235-238. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-0754.2020.02.041 |
| [15] |
GRAYBIEL A, WOOD C D, MILLER E F, et al. Diagnostic criteria for grading the severity of acute motion sickness[J]. Aerosp Med, 1968, 39(5): 453-455. |
| [16] |
TAMURA A, IWAMOTO T, OZAKI H, et al. Wrist-worn electrodermal activity as a novel neurophysiological biomarker of autonomic symptoms in spatial disorientation[J]. Front Neurol, 2018, 9: 1056. DOI:10.3389/fneur.2018.01056 |
| [17] |
毛宇奇, 潘磊磊, 苏阳, 等. 上下垂荡运动刺激下大鼠及人体模拟晕船的反应规律[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2020, 45(3): 298-303. DOI:10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2020.03.12 |
| [18] |
FORBES J, MUNAKOMI S, CRONOVICH H. Romberg test[M/OL]//StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2023: 1-6(2023-08-13)[2024-01-19]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563187/?report=reader.
|
| [19] |
MA C Z, WAN A H, WONG D W, et al. A vibrotactile and plantar force measurement-based biofeedback system: paving the way towards wearable balance-improving devices[J]. Sensors (Basel), 2015, 15(12): 31709-31722. DOI:10.3390/s151229883 |
| [20] |
YALLA S V, CREWS R T, FLEISCHER A E, et al. An immediate effect of custom-made ankle foot orthoses on postural stability in older adults[J]. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon), 2014, 29(10): 1081-1088. DOI:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2014.10.007 |
| [21] |
MA C Z, WONG D W, WAN A H, et al. Effects of orthopedic insoles on static balance of older adults wearing thick socks[J]. Prosthet Orthot Int, 2018, 42(3): 357-362. DOI:10.1177/0309364617752982 |
| [22] |
GOLDING J F, GRESTY M A. Biodynamic hypothesis for the frequency tuning of motion sickness[J]. Aerosp Med Hum Perform, 2016, 87(1): 65-68. DOI:10.3357/AMHP.4295.2016 |
| [23] |
GRIFFIN M J, MILLS K L. Effect of frequency and direction of horizontal oscillation on motion sickness[J]. Aviat Space Environ Med, 2002, 73(6): 537-543. |
| [24] |
O'HANLON J F, MCCAULEY M E. Motion sickness incidence as a function of the frequency and acceleration of vertical sinusoidal motion[J]. Aerosp Med, 1974, 45(4): 366-369. |
| [25] |
BOS J E, BLES W. Modelling motion sickness and subjective vertical mismatch detailed for vertical motions[J]. Brain Res Bull, 1998, 47(5): 537-542. DOI:10.1016/s0361-9230(98)00088-4 |
| [26] |
BLUE R S, ONG K M, RAY K, et al. Layperson physiological tolerance and operational performance in centrifuge-simulated spaceflight[J]. Aerosp Med Hum Perform, 2023, 94(8): 584-595. DOI:10.3357/AMHP.6237.2023 |
| [27] |
SALIMI Z, FERGUSON-PELL M W. Motion sickness and sense of presence in a virtual reality environment developed for manual wheelchair users, with three different approaches[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(8): e0255898. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0255898 |
| [28] |
GEYER D J, BIGGS A T. The persistent issue of simulator sickness in naval aviation training[J]. Aerosp Med Hum Perform, 2018, 89(4): 396-405. DOI:10.3357/AMHP.4906.2018 |
| [29] |
吴爱平, 林衔亮, 付桂强, 等. 抗眩晕预适应强化训练对预防晕船的作用[J]. 海军医学杂志, 2007, 28(1): 12-13. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-0754.2007.01.006 |
| [30] |
林建棣, 陈南生. 特项训练对提高机体平衡协调能力和心血管功能效应与训练效果的迁移作用[C]//第五届全国体育科学大会论文摘要汇编. 北京: 中国体育科学学会, 1997: 434-435.
|
| [31] |
杨月珍, 包瀛春, 黄矛, 等. 综合训练法预防晕船病效果评估[J]. 解放军预防医学杂志, 2006, 24(3): 179-182. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5248.2006.03.007 |
| [32] |
STOFFREGEN T A, CHEN F C, VARLET M, et al. Getting your sea legs[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6): e66949. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0066949 |
| [33] |
CHANG C H, CHEN F C, KUNG W C, et al. Effects of physical driving experience on body movement and motion sickness during virtual driving[J]. Aerosp Med Hum Perform, 2017, 88(11): 985-992. DOI:10.3357/AMHP.4893.2017 |
| [34] |
CHANDER H, SHOJAEI A, DEB S, et al. Impact of virtual reality-generated construction environments at different heights on postural stability and fall risk[J]. Workplace Health Saf, 2021, 69(1): 32-40. DOI:10.1177/2165079920934000 |
| [35] |
COBB S V, NICHOLS S C. Static posture tests for the assessment of postural instability after virtual environment use[J]. Brain Res Bull, 1998, 47(5): 459-464. DOI:10.1016/s0361-9230(98)00104-x |
| [36] |
王林杰, 孙洪义, 裴静琛, 等. 某些体训项目对人体前庭功能的影响[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2000, 13(6): 405-409. DOI:10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2000.06.004 |
| [37] |
张琦, 冷辉. 阶梯习服方案治疗晕动病的临床研究[J]. 中医眼耳鼻喉杂志, 2018, 8(2): 85-87. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9006.2018.02.008 |
 2024, Vol. 45
2024, Vol. 45


