2. 新加坡国立大学药学系, 新加坡 119077;
3. 海军军医大学(第二军医大学)基础医学院生物物理学教研室, 上海 200433;
4. 上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院辅助生殖科, 上海 200011
2. Department of Pharmacy, National University of Singapore, Singapore 119077, Singapore;
3. Department of Biophysics, College of Basic Medical Sciences, Naval Medical University (Second Military Medical University), Shanghai 200433, China;
4. Department of Assisted Reproduction, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200011, China
溃疡性结肠炎(ulcerative colitis,UC)是一种慢性炎症性胃肠道疾病,临床表现为腹泻、腹痛、黏液脓血便等,往往反复发作,病程迁延,目前仍无法治愈。Toll样受体(Toll-like receptor,TLR)4能够识别来自肠道菌群的病原相关分子模式(pathogen-associated molecular pattern,PAMP),通过髓样分化因子88(myeloid differentiation factor 88,MyD88)激活NF-κB等炎症信号通路[1]。TLR4在正常黏膜原代肠上皮细胞中表达量极低,而在UC患者肠上皮细胞和固有层细胞中表达明显上调[2-5]。干预TLR4信号能够在一定程度上缓解肠道炎症[6-13]。然而,相对野生型小鼠,肠上皮细胞TLR4或MyD88基因敲除小鼠在葡聚糖硫酸钠(dextran sulfate sodium,DSS)诱导下表现出更高的急性结肠炎发病率和死亡率[14-17]。在肠上皮细胞和多种固有免疫细胞表面表达的TLR4是肠道病原体入侵的第一道防线,是肠道在遗传和环境因素作用下发生损伤时机体维持肠上皮屏障和肠黏膜免疫稳态不可缺少的保护因子[18]。本研究通过制备TLR4-Ig融合蛋白竞争性阻断TLR4,验证TLR4信号在UC发生早期调节肠道固有免疫反应和修复肠黏膜损伤中的关键作用。
1 材料和方法 1.1 UC患者样本收集和检测收集UC患者结直肠活检组织样本63例(来自22例UC患者,年龄15~66岁,平均35.6岁),其中4例取自直肠,7例取自盲肠,8例取自升结肠,8例取自横结肠,9例取自降结肠,27例取自乙状结肠。样本用4%多聚甲醛溶液固定24 h后,脱水,石蜡包埋,制成厚5~6 μm的切片。切片进行常规H-E染色,于光学显微镜下观察肠组织炎症细胞浸润情况。按照Matts组织病理学分级标准[19]分为5级,代表不同炎症程度。1级:外观正常;2级:黏膜或固有层细胞浸润,呈圆形或多态形;3级:黏膜、固有层和黏膜下层均有细胞浸润;4级:黏膜、固有层和黏膜下层均有细胞浸润,存在隐窝脓肿;5级:黏膜溃疡、糜烂或坏死,部分或全部黏膜层均有细胞浸润。
采用免疫组织化学染色检测TLR4的表达。组织切片室温脱蜡和水化,热修复抗原,并灭活内源性过氧化物酶和生物素。加入山羊血清进行非特异性封闭,加入鼠源TLR4抗体(货号ab22048,英国Abcam公司)4 ℃孵育过夜,再用二抗(HRP标记山羊抗小鼠IgG,上海碧云天生物技术股份有限公司)室温孵育10 min,DAB显色和复染后,于光学显微镜下观察。根据细胞染色强度,将无阳性着色(阴性)和淡黄色(弱阳性)视为TLR4低表达,棕黄色(阳性)和棕褐色(强阳性)视为TLR4高表达。
1.2 TLR4-Ig融合蛋白的制备及体外中和活性评估参照既往研究报道的方法[20]制备TLR4-Ig融合蛋白。将编码小鼠TLR4细胞外结构域的DNA序列与编码小鼠IgG2a铰链CH2-CH3片段的DNA序列相连,插入pcDNA3.4表达载体,用FreeStyle 293表达系统(美国Invitrogen公司)表达TLR4-Ig融合蛋白,用ASepharose(英国Abcam公司)纯化蛋白。使用紫外分光光度计和PAGE测定蛋白质浓度和纯度。
以牛血清白蛋白(bovine serum albumin,BSA)和实验室前期制备储存的T细胞免疫受体(T cell Ig and ITIM domain,TIGIT)-Ig融合蛋白作为阴性对照,参照既往研究报道的方法[21]将抗鼠Fc多克隆抗体固定在CM5芯片上,目标偶联量为150响应值(response unit,RU),利用脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide,LPS)或BSA(12.5~200 nmol/L)捕获TLR4-Ig或TIGIT-Ig。使用Biacore-T200(美国Cytiva公司)测定融合蛋白的单价亲和力。
体外培养健康者来源的外周血单个核细胞(peripheral blood mononuclear cell,PBMC),细胞稳定传代后用于实验。设置空白对照组、LPS刺激组(LPS组)和TLR4-Ig干预组(LPS+TLR4-Ig组),后两组分别向培养基中加入100 μg/mL LPS或100 μg/mL LPS+100 μg/mL TLR4-Ig,培养12 h。收集培养基,使用细胞因子分析仪Human Cytokine 10-Plex Panel(美国ThermoScientific公司)检测粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor,GM-CSF)、干扰素γ(interferon γ,IFN-γ)、IL-1β、IL-2、IL-4、IL-5、IL-6、IL-8、IL-10和TNF-α的分泌水平。
1.3 TLR4-Ig融合蛋白抗小鼠急性结肠炎作用评估 1.3.1 DSS诱导小鼠急性结肠炎模型的构建选用8周龄雌性C57BL/6小鼠[购自上海吉辉实验动物饲养有限公司,实验动物生产许可证号为SCXK(沪)2022-0009],在相对湿度40%~60%、室温20~22 ℃的SPF级动物房饲养。用小鼠饮用水配制浓度为3%的DSS(分子量36 000~50 000,美国MP Biomedicals公司)溶液,装入小鼠饲养笼的水瓶中,小鼠通过自由饮水摄入DSS,每2 d更换新鲜的3% DSS溶液。
1.3.2 实验分组和处理第一阶段实验探索不同浓度TLR4-Ig对DSS诱导急性结肠炎的影响。将75只小鼠随机分为5组(n=12),其中空白组小鼠仅饮普通饮用水;DSS+生理盐水(normal saline,NS)组、DSS+IgG组、DSS+20 mg/kg TLR4-Ig组、DSS+40 mg/kg TLR4-Ig组小鼠均饮3% DSS溶液,并分别于实验第1、3、5、7天腹腔注射NS、40 mg/kg小鼠IgG、20 mg/kg TLR4-Ig融合蛋白或40 mg/kg TLR4-Ig融合蛋白。所有小鼠均于第9天停止给药及饮水,并采用颈椎脱臼法处死。
第二阶段实验探索肠道菌群对DSS诱导急性结肠炎的影响。将60只小鼠随机分为6组(n=10)。参照既往报道的方法[22],用小鼠饮用水配制含1 g/L氨苄青霉素、1 g/L新霉素、0.25 g/L甲硝唑、0.5 g/L万古霉素的“抗生素鸡尾酒”(antibiotic cocktail,AC)。AC+DSS+IgG组、AC+DSS+TLR4-Ig组小鼠均于DSS诱导前连续4周饮用AC。随后,除空白组小鼠仅饮普通饮用水外,其余各组均饮3% DSS溶液,并分别于实验第1、3、5、7天腹腔注射NS(DSS+NS组)、40 mg/kg小鼠IgG(DSS+IgG组、AC+DSS+IgG组)或40 mg/kg TLR4-Ig融合蛋白(DSS+TLR4-Ig组、AC+DSS+TLR4-Ig组)。所有小鼠均于第7天停止给药及饮水,并采用颈椎脱臼法处死。
1.3.3 体重、疾病活动和生存情况观察每日固定时间称取小鼠体重,收集小鼠粪便观察粪便形态,使用粪便隐血检测试剂盒(氨基比林法,北京伊塔生物科技有限公司)检测粪便隐血情况。根据公式计算疾病活动指数(disease activity index,DAI)[19]:DAI=(S1+S2+S3)/3。其中,S1为体重下降率,<1%计0分,1%~5%计1分,6%~10%计2分,11%~15%计3分,>15%计4分;S2为粪便形态,颗粒状计0分,疏松稀软计2分,水样便计4分;S3为便血情况,粪便隐血阴性计0分,粪便隐血阳性计2分,肉眼可见便血计4分。记录小鼠存活情况,以体重下降率达30%作为处死标准。
1.3.4 结肠长度测量和组织病理学检测处死小鼠后,取完整结肠组织测量长度。取肛门向上1 cm处长约5 mm的结肠组织,用4%多聚甲醛溶液固定,进行石蜡包埋、切片、H-E染色,在光学显微镜下观察。根据公式计算病理学评分[23]:病理学评分=(A1+A2+A3)/3。其中,A1为损伤深度,无损伤计0分,黏膜层损伤计1分,黏膜下层损伤计2分,穿透性损伤计3分;A2为隐窝损伤,无损伤计0分,1/3隐窝缺失计1分,2/3隐窝缺失计2分,仅上皮完整计3分,上皮损伤计4分;A3为损伤面积,<1%计0分,1%~25%计1分,26%~50%计2分,51%~75%计3分,76%~100%计4分。
1.4 统计学处理使用GraphPad Prism 8.0软件分析实验数据。计量资料以x±s表示,两组间比较采用独立样本t检验,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析;计数资料以例数和百分数表示,组间比较采用Fisher确切概率法。检验水准(α)为0.05。
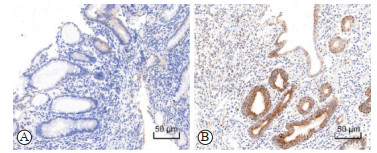
2 结果 2.1 UC患者肠组织TLR4表达水平与炎症程度相关对UC患者结直肠组织样本进行免疫组织化学染色,63例样本中有35例(55.6%)检测到TLR4高表达。当肠组织炎症程度较轻时,肠上皮细胞和间质细胞中TLR4低表达(图 1A);而当炎症十分严重时,TLR4表达明显上调(图 1B)。根据Matts组织病理学分级标准分为5级,1~5级病变样本中TLR4高表达比例分别为0(0/7)、26.7%(4/15)、62.5%(10/16)、82.4%(14/17)、87.5%(7/8),差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。以上结果表明,Matts组织病理学分级越高TLR4高表达的样本比例越高,TLR4表达水平与肠组织的炎症程度相关。
|
图 1 溃疡性结肠炎患者肠组织TLR4免疫组织化学染色 Fig 1 Immunohistochemical staining of TLR4 in colon tissues of patients with ulcerative colitis A: TLR4 was stained weakly either in epithelium and stroma with mild inflammation (Matts grade 2); B: TLR4 was stained strongly in the epithelial cells with severe inflammation (Matts grade 4). TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4. |
2.2 TLR4-Ig融合蛋白对TLR4有竞争性阻断作用
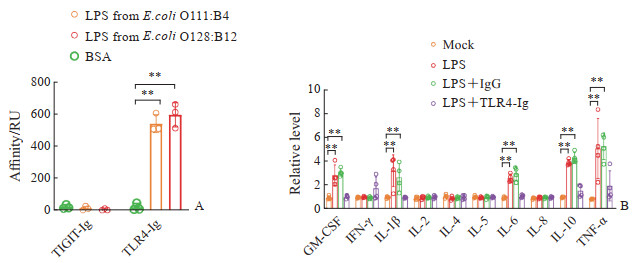
选取来源于2株不同大肠埃希菌(E. coli O111:B4和E. coli O128:B12)的LPS,用Biacore-T200实验评估TLR4-Ig对LPS的亲和力,结果表明2种LPS和TLR4-Ig均能够以高亲和力结合,而对照TIGIT-Ig不与LPS结合(图 2A)。体外培养的PBMC在LPS刺激下分泌的GM-CSF、IL-1β、IL-6、IL-10和TNF-α水平均上调(均P<0.01),在培养基中添加TLR4-Ig时PBMC的活化和炎症细胞因子的分泌被阻断(图 2B)。以上结果表明,TLR4-Ig融合蛋白具有良好的配体中和活性,能够竞争性阻断细胞表面的TLR4激活。
|
图 2 TLR4-Ig融合蛋白的体外中和活性 Fig 2 Neutralizing activity in vitro of TLR4-Ig fusion protein A: The affinity of the TLR4-Ig fusion protein detected using Biacore-T200; B: The effect of TLR4-Ig fusion protein on the secretion levels of inflammatory factors of PMBCs when stimulating by LPS. **P<0.01. n=4, x±s. TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; Ig: Immunoglobulin; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; TIGIT: T cell Ig and ITIM domain; BSA: Bovine serum albumin; RU: Response unit; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN-γ: Interferon γ; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; PBMC: Peripheral blood mononuclear cell. |
2.3 TLR4-Ig融合蛋白加重DSS诱导的小鼠急性结肠炎
相比于DSS+NS和DSS+40 mg/kg IgG组,DSS+20 mg/kg TLR4-Ig和DSS+40 mg/kg TLR4-Ig组小鼠体重下降更严重(P<0.01,图 3A),DAI更高(P<0.01,图 3B),总生存率更低(图 3C),结肠组织表现出水肿、充血(图 3D),平均结肠长度更短(图 3E),结肠组织可见杯状细胞缺失、隐窝肿胀破坏及上皮细胞损伤(图 3F),结肠组织病理学评分更高(P<0.01,图 3G)。DSS+20 mg/kg TLR4-Ig组和DSS+40 mg/kg TLR4-Ig组间上述指标均无明显差异,表明20 mg/kg TLR4-Ig融合蛋白即能够有效阻断TLR4。以上结果初步表明,TLR4-Ig融合蛋白对TLR4信号的阻断加重了DSS诱导的小鼠急性结肠炎。

|
图 3 不同浓度TLR4-Ig融合蛋白干预下DSS诱导的小鼠急性结肠炎表现 Fig 3 DSS-induced acute colitis in mice after treatment with different concentrations of TLR4-Ig fusion protein A: Body weight loss analysis; B: Disease activity index analysis; C: Survival rate analysis; D: Colonic morphology; E: Colon length analysis; F: Hematoxylin-eosin staining of colon tissue; G: Colonic pathological score analysis. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. n=8-12, x±s. TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; Ig: Immunoglobulin; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; NS: Normal saline. |
2.4 抗生素干预能够缓解TLR4信号阻断造成的小鼠急性结肠炎加重
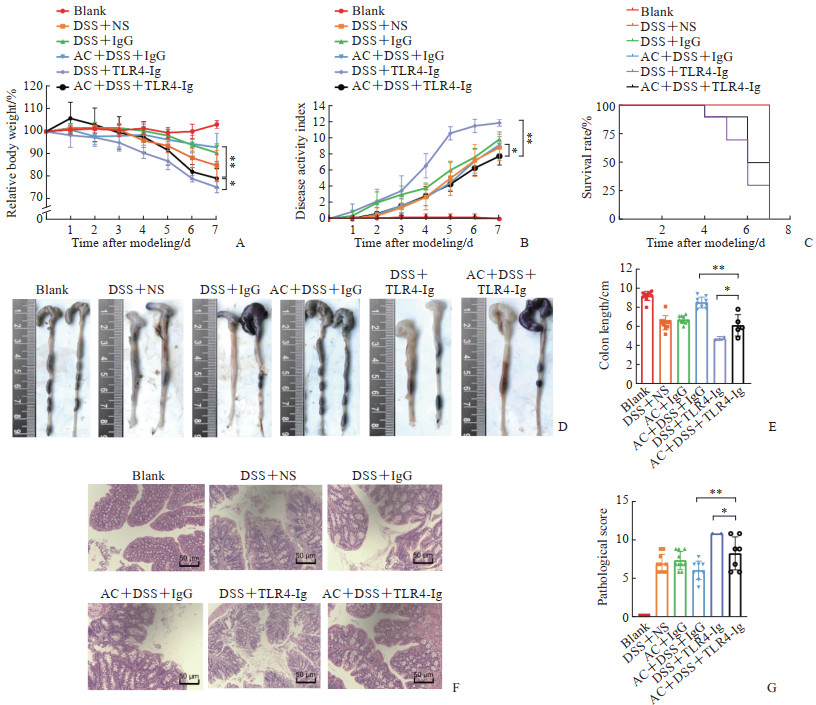
相比于DSS+TLR4-Ig组,AC+DSS+TLR4-Ig组小鼠体重下降较轻(P<0.05,图 4A),DAI更低(P<0.01,图 4B),总体生存率更高(图 4C),结肠水肿充血情况有所缓解(图 4D),结肠长度更长(P<0.05,图 4E),结肠组织中杯状细胞缺失、隐窝肿胀破坏及上皮细胞损伤情况有所缓解(图 4F),结肠组织病理学评分更低(P<0.05,图 4G)。以上结果表明,TLR4信号缺失时肠道菌群的入侵是造成肠道急性炎症的重要因素,而在急性结肠炎早期给予抗生素能够缓解DSS引起的肠上皮损伤。
|
图 4 抗生素和TLR4-Ig融合蛋白共同干预下DSS诱导的小鼠急性结肠炎表现 Fig 4 DSS-induced acute colitis in mice after combined intervention with antibiotics and TLR4-Ig fusion protein A: Body weight loss analysis; B: Disease activity index analysis; C: Survival rate analysis; D: Colonic morphology; E: Colon length analysis; F: Hematoxylin-eosin staining of colon tissue; G: Colonic pathological score analysis. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. n=3-10, x±s. TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; Ig: Immunoglobulin; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; NS: Normal saline; AC: Antibiotic cocktail. |
3 讨论
UC和克罗恩病(Crohn disease,CD)是炎症性肠病(inflammatory bowel disease,IBD)的2种类型。一直以来,TLR4表达水平与IBD发生、发展的相关性被广泛研究。TLR4在正常的肠上皮细胞和固有层细胞中低表达,而在UC和CD患者体内表达水平显著升高[2, 24-28]。在小鼠模型中,肠上皮细胞组成型表达TLR4的转基因小鼠更容易发生化学诱导的结肠炎[29-31]。因此,大量研究以TLR4作为IBD的治疗靶点,通过干预TLR4及其信号通路缓解IBD相关炎症[7-9, 11-13]。然而,研究发现TLR4信号缺失对肠道炎症的发生、发展具有完全相反的作用,且与肠道菌群有关。例如,靶向敲除肠上皮细胞TLR4基因的小鼠表现出肠道菌群多样性降低、细菌聚集性改变和炎症基因表达差异[32],靶向敲除肠上皮细胞MyD88基因的小鼠体内具有肠道保护作用的抗菌肽表达下调[33-34],当利用这些基因缺陷小鼠构建化学诱导的结肠炎模型时,其表现出比野生型小鼠更高的易感性和死亡率。
实际上,TLR4信号通过多种机制在肠黏膜稳态中发挥保护作用。有研究表明,肠上皮不同部位的TLR4发挥不同的生物学功能,肠上皮基底外侧区域的TLR4能够识别来自于肠道的LPS等致病物质,引发炎症反应,而顶端膜的TLR4促进免疫耐受,TLR4介导的免疫活化和免疫耐受平衡维持肠黏膜稳态[35]。TLR4信号通过调控环氧合酶表达[34, 36-37]、维持细胞间紧密连接[18, 38]、调控IgA的合成、增强树突状细胞的抗原呈递功能及介导抗菌肽和凝集素的分泌等机制[30, 39-41]促进肠道损伤修复。此外,TLR4还是多种固有免疫细胞与肠道菌群之间信号交流的重要媒介,TLR4和TLR7/8的协同激活可以诱导未成熟的树突状细胞分化为成熟的树突状细胞,并促进活化T细胞分化为具有记忆细胞功能的CD8+ T细胞[42],而在TLR4基因缺失的小鼠体内树突状细胞无法被病原体活化[43]。总的来说,TLR4信号在IBD发生、发展中起到“双刃剑”作用,一方面TLR4过度激活会导致免疫反应过度活化、肠道炎症反应加重,另一方面TLR4又在肠黏膜修复中发挥重要作用。
在此前的研究中,虽然敲除小鼠的TLR4基因实现了TLR4信号的完全阻断,但不符合临床UC患者的实际情况,此外,也无法确定TLR4信号缺失对免疫系统发育的影响。本研究创新性地利用了TLR4-Ig融合蛋白,其能够在不激活免疫反应的基础上竞争性地阻断TLR4信号,并通过与IgG的Fc段相融合有效延长TLR4的体内半衰期,发挥持续的阻断作用。自1989年有研究者首次将CD4细胞外结构域与人IgG1的Fc结构域相融合构建CD4-Ig融合蛋白并用于HIV感染的治疗[44]以来,抗体融合蛋白的治疗潜力得到了广泛的探索。Fc结构域能够与吞噬细胞表面的新生儿Fc受体(neonatal Fc receptor,FcRn)结合,避免被体循环快速清除,从而使多种生物活性分子包括蛋白质和多肽药物的半衰期得到有效延长[45]。目前美国FDA已经批准了13种抗体融合蛋白药物,用于治疗包括癌症、自身免疫病、血液病、急慢性炎症和移植排斥在内的多种疾病[46]。
本研究分析了UC患者结肠组织样本中TLR4的表达水平,发现TLR4表达量越高结肠组织炎症程度越高,表明TLR4表达上调在UC的发生、发展中发挥重要作用;成功制备了TLR4胞外段和人IgG Fc段相融合的TLR4-Ig重组蛋白,其能够在体外有效阻断LPS诱导的PMBC活化和细胞因子分泌;利用3% DSS溶液构建小鼠急性结肠炎模型,发现TLR4-Ig融合蛋白给药组小鼠的急性结肠炎严重程度更高,这一结果与另一项利用TLR4特异性单克隆抗体干预TLR4信号的实验结果一致,该研究发现给予小鼠TLR4抗体可导致肠黏膜修复受损[47]。此外,提前给予小鼠抗生素处理能够有效减缓TLR4-Ig导致的结肠损伤加重。实际上,随着微生物组和代谢组分析技术的发展,已明确肠道微生物亚群能通过TLR4与肠上皮细胞进行信号交流[48-49],因此,在肠黏膜发生损伤时,肠道菌群中的病原体通过与肠黏膜上皮细胞表面TLR4间的信号交流激活肠黏膜的固有免疫反应,清除病原体并进行损伤组织的快速修复。在本研究中,TLR4-Ig融合蛋白对TLR4的竞争性阻断使DSS诱导的肠黏膜急性损伤更严重,表明TLR4表达上调是肠上皮发生急性损伤时的重要保护机制,TLR4信号在UC发生、发展中起着重要作用。
| [1] |
GRIBAR S C, RICHARDSON W M, SODHI C P, et al. No longer an innocent bystander: epithelial Toll-like receptor signaling in the development of mucosal inflammation[J]. Mol Med, 2008, 14(9/10): 645-659. DOI:10.2119/2008-00035.Gribar |
| [2] |
CARIO E, PODOLSKY D K. Differential alteration in intestinal epithelial cell expression of Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and TLR4 in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Infect Immun, 2000, 68(12): 7010-7017. DOI:10.1128/IAI.68.12.7010-7017.2000 |
| [3] |
BANK S, SKYTT ANDERSEN P, BURISCH J, et al. Polymorphisms in the inflammatory pathway genes TLR2, TLR4, TLR9, LY96, NFKBIA, NFKB1, TNFA, TNFRSF1A, IL6R, IL10, IL23R, PTPN22, and PPARG are associated with susceptibility of inflammatory bowel disease in a Danish cohort[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(6): e98815. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0098815 |
| [4] |
FROLOVA L, DRASTICH P, ROSSMANN P, et al. Expression of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), TLR4, and CD14 in biopsy samples of patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: upregulated expression of TLR2 in terminal ileum of patients with ulcerative colitis[J]. J Histochem Cytochem, 2008, 56(3): 267-274. DOI:10.1369/jhc.7a7303.2007 |
| [5] |
SZEBENI B, VERES G, DEZSÕFI A, et al. Increased expression of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4 in the colonic mucosa of children with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2008, 151(1): 34-41. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03531.x |
| [6] |
LIU B, PIAO X, NIU W, et al. Kuijieyuan decoction improved intestinal barrier injury of ulcerative colitis by affecting TLR4-dependent PI3K/AKT/NF-κB oxidative and inflammatory signaling and gut microbiota[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 1036. DOI:10.3389/fphar.2020.01036 |
| [7] |
LI C, AI G, WANG Y, et al. Oxyberberine, a novel gut microbiota-mediated metabolite of berberine, possesses superior anti-colitis effect: impact on intestinal epithelial barrier, gut microbiota profile and TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2020, 152: 104603. DOI:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104603 |
| [8] |
CHEN Y, LU Y, PEI C, et al. Monotropein alleviates secondary liver injury in chronic colitis by regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2020, 883: 173358. DOI:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173358 |
| [9] |
LUO X, YU Z, DENG C, et al. Baicalein ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis by suppressing TLR4/MyD88 signaling cascade and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in mice[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 16374. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-12562-6 |
| [10] |
YOUSEFI-MANESH H, DEJBAN P, MUMTAZ F, et al. Risperidone attenuates acetic acid-induced colitis in rats through inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol, 2020, 42(5): 464-472. DOI:10.1080/08923973.2020.1808987 |
| [11] |
DEJBAN P, SAHRAEI M, CHAMANARA M, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of amitriptyline in a rat model of acetic acid-induced colitis: the involvement of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Fundam Clin Pharmacol, 2021, 35(5): 843-851. DOI:10.1111/fcp.12642 |
| [12] |
刘凯丽, 都新新, 张文琴, 等. 过表达miR-31对结肠炎模型小鼠TLR4/NF-κB信号通路及凋亡蛋白的调控[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志, 2020, 36(3): 211-215, 239, 289-191. |
| [13] |
WANG J P, DONG L N, WANG M, et al. MiR-146a regulates the development of ulcerative colitis via mediating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23(5): 2151-2157. DOI:10.26355/eurrev_201903_17260 |
| [14] |
RAKOFF-NAHOUM S, PAGLINO J, ESLAMI-VARZANEH F, et al. Recognition of commensal microflora by Toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis[J]. Cell, 2004, 118(2): 229-241. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2004.07.002 |
| [15] |
FUKATA M, MICHELSEN K S, ERI R, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 is required for intestinal response to epithelial injury and limiting bacterial translocation in a murine model of acute colitis[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2005, 288(5): G1055-G1065. DOI:10.1152/ajpgi.00328.2004 |
| [16] |
ARAKI A, KANAI T, ISHIKURA T, et al. MyD88-deficient mice develop severe intestinal inflammation in dextran sodium sulfate colitis[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2005, 40(1): 16-23. DOI:10.1007/s00535-004-1492-9 |
| [17] |
BROWN S L, RIEHL T E, WALKER M R, et al. MyD88-dependent positioning of PTGS2-expressing stromal cells maintains colonic epithelial proliferation during injury[J]. J Clin Invest, 2007, 117(1): 258-269. DOI:10.1172/JCI29159 |
| [18] |
ABREU M T. Toll-like receptor signalling in the intestinal epithelium: how bacterial recognition shapes intestinal function[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2010, 10(2): 131-144. DOI:10.1038/nri2707 |
| [19] |
JEENGAR M K, THUMMURI D, MAGNUSSON M, et al. Uridine ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 3924. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-04041-9 |
| [20] |
SHEN X, FU W, WEI Y, et al. TIGIT-Fc promotes antitumor immunity[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2021, 9(9): 1088-1097. DOI:10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-20-0986 |
| [21] |
FU W, WANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Insights into HER2 signaling from step-by-step optimization of anti-HER2 antibodies[J]. mAbs, 2014, 6(4): 978-990. DOI:10.4161/mabs.28786 |
| [22] |
HERNÁNDEZ-CHIRLAQUE C, ARANDA C J, OCÓN B, et al. Germ-free and antibiotic-treated mice are highly susceptible to epithelial injury in DSS colitis[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2016, 10(11): 1324-1335. DOI:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw096 |
| [23] |
MOSLI M H, FEAGAN B G, SANDBORN W J, et al. Histologic evaluation of ulcerative colitis: a systematic review of disease activity indices[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2014, 20(3): 564-575. DOI:10.1097/01.MIB.0000437986.00190.71 |
| [24] |
ABREU M T, ARNOLD E T, THOMAS L S, et al. TLR4 and MD-2 expression is regulated by immune-mediated signals in human intestinal epithelial cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(23): 20431-20437. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M110333200 |
| [25] |
PEDERSEN G, ANDRESEN L, MATTHIESSEN M W, et al. Expression of Toll-like receptor 9 and response to bacterial CpG oligodeoxynucleotides in human intestinal epithelium[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2005, 141(2): 298-306. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02848.x |
| [26] |
ECKMANN L, NEBELSIEK T, FINGERLE A A, et al. Opposing functions of IKKβ during acute and chronic intestinal inflammation[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(39): 15058-15063. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0808216105 |
| [27] |
ABREU M T, VORA P, FAURE E, et al. Decreased expression of Toll-like receptor-4 and MD-2 correlates with intestinal epithelial cell protection against dysregulated proinflammatory gene expression in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide[J]. J Immunol, 2001, 167(3): 1609-1616. DOI:10.4049/jimmunol.167.3.1609 |
| [28] |
OTTE J M, CARIO E, PODOLSKY D K. Mechanisms of cross hyporesponsiveness to Toll-like receptor bacterial ligands in intestinal epithelial cells[J]. Gastroenterology, 2004, 126(4): 1054-1070. DOI:10.1053/j.gastro.2004.01.007 |
| [29] |
FUKATA M, SHANG L, SANTAOLALLA R, et al. Constitutive activation of epithelial TLR4 augments inflammatory responses to mucosal injury and drives colitis-associated tumorigenesis[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2011, 17(7): 1464-1473. DOI:10.1002/ibd.21527 |
| [30] |
SHANG L, FUKATA M, THIRUNARAYANAN N, et al. Toll-like receptor signaling in small intestinal epithelium promotes B-cell recruitment and IgA production in lamina propria[J]. Gastroenterology, 2008, 135(2): 529-538. DOI:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.04.020 |
| [31] |
DHEER R, SANTAOLALLA R, DAVIES J M, et al. Intestinal epithelial Toll-like receptor 4 signaling affects epithelial function and colonic microbiota and promotes a risk for transmissible colitis[J]. Infect Immun, 2016, 84(3): 798-810. DOI:10.1128/IAI.01374-15 |
| [32] |
LU P, SODHI C P, YAMAGUCHI Y, et al. Intestinal epithelial Toll-like receptor 4 prevents metabolic syndrome by regulating interactions between microbes and intestinal epithelial cells in mice[J]. Mucosal Immunol, 2018, 11(3): 727-740. DOI:10.1038/mi.2017.114 |
| [33] |
FRANTZ A L, ROGIER E W, WEBER C R, et al. Targeted deletion of MyD88 in intestinal epithelial cells results in compromised antibacterial immunity associated with downregulation of polymeric immunoglobulin receptor, mucin-2, and antibacterial peptides[J]. Mucosal Immunol, 2012, 5(5): 501-512. DOI:10.1038/mi.2012.23 |
| [34] |
BRANDL K, SUN L, NEPPL C, et al. MyD88 signaling in nonhematopoietic cells protects mice against induced colitis by regulating specific EGF receptor ligands[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010, 107(46): 19967-19972. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1014669107 |
| [35] |
VAMADEVAN A S, FUKATA M, ARNOLD E T, et al. Regulation of Toll-like receptor 4-associated MD-2 in intestinal epithelial cells: a comprehensive analysis[J]. Innate Immun, 2010, 16(2): 93-103. DOI:10.1177/1753425909339231 |
| [36] |
STENSON W F, CIORBA M A. Nonmicrobial activation of TLRs controls intestinal growth, wound repair, and radioprotection[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 11: 617510. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2020.617510 |
| [37] |
FUKATA M, CHEN A, KLEPPER A, et al. Cox-2 is regulated by Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) signaling: role in proliferation and apoptosis in the intestine[J]. Gastroenterology, 2006, 131(3): 862-877. DOI:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.06.017 |
| [38] |
BRUNING E E, COLLER J K, WARDILL H R, et al. Site-specific contribution of Toll-like receptor 4 to intestinal homeostasis and inflammatory disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(2): 877-888. DOI:10.1002/jcp.29976 |
| [39] |
LU P, SODHI C P, HACKAM D J. Toll-like receptor regulation of intestinal development and inflammation in the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis[J]. Pathophysiology, 2014, 21(1): 81-93. DOI:10.1016/j.pathophys.2013.11.007 |
| [40] |
MENG D, ZHU W, SHI H N, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 in human and mouse colonic epithelium is developmentally regulated: a possible role in necrotizing enterocolitis[J]. Pediatr Res, 2015, 77(3): 416-424. DOI:10.1038/pr.2014.207 |
| [41] |
MALDONADO-CONTRERAS A L, MCCORMICK B A. Intestinal epithelial cells and their role in innate mucosal immunity[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2011, 343(1): 5-12. DOI:10.1007/s00441-010-1082-5 |
| [42] |
PUFNOCK J S, CIGAL M, ROLCZYNSKI L S, et al. Priming CD8+ T cells with dendritic cells matured using TLR4 and TLR7/8 ligands together enhances generation of CD8+ T cells retaining CD28[J]. Blood, 2011, 117(24): 6542-6551. DOI:10.1182/blood-2010-11-317966 |
| [43] |
MICHELSEN K S, AICHER A, MOHAUPT M, et al. The role of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in bacteria-induced maturation of murine dendritic cells (DCs)[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(28): 25680-25686. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m011615200 |
| [44] |
CAPON D J, CHAMOW S M, MORDENTI J, et al. Designing CD4 immunoadhesins for AIDS therapy[J]. Nature, 1989, 337(6207): 525-531. DOI:10.1038/337525a0 |
| [45] |
JAFARI R, ZOLBANIN N M, RAFATPANAH H, et al. Fc-fusion proteins in therapy: an updated view[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2017, 24(12): 1228-1237. DOI:10.2174/0929867324666170113112759 |
| [46] |
LAGASSÉ H A D, HENGEL H, GOLDING B, et al. Fc-fusion drugs have FcγR/C1q binding and signaling properties that may affect their immunogenicity[J]. AAPS J, 2019, 21(4): 62. DOI:10.1208/s12248-019-0336-8 |
| [47] |
UNGARO R, FUKATA M, HSU D, et al. A novel Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist antibody ameliorates inflammation but impairs mucosal healing in murine colitis[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2009, 296(6): G1167-G1179. DOI:10.1152/ajpgi.90496.2008 |
| [48] |
LIU Y, YANG M, TANG L, et al. TLR4 regulates RORγt+ regulatory T-cell responses and susceptibility to colon inflammation through interaction with Akkermansia muciniphila[J]. Microbiome, 2022, 10(1): 98. DOI:10.1186/s40168-022-01296-x |
| [49] |
MEI Q X, FU Y, HUANG Z H, et al. Intestinal TLR4 deletion exacerbates acute pancreatitis through gut microbiota dysbiosis and Paneth cells deficiency[J]. Gut Microbes, 2022, 14(1): 2112882. DOI:10.1080/19490976.2022.2112882 |
 2024, Vol. 45
2024, Vol. 45


