2. 上海杉达学院体育教学部, 上海 201209;
3. 海军军医大学(第二军医大学)心理系基础心理学教研室, 上海 200433;
4. 扬州大学体育学院, 扬州 225100;
5. 浙江大学教育学院, 杭州 310063
2. Department of Physical Education, Sanda University, Shanghai 201209, China;
3. Department of Basic Psychology, Faculty of Psychology, Naval Medical University (Second Military Medical University), Shanghai 200433, China;
4. College of Physical Education, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225100, Jiangsu, China;
5. College of Education, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310063, Zhejiang, China
注意缺陷多动障碍(attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,ADHD)是一种常见于儿童时期的神经发育障碍,其核心症状表现为注意力不集中、多动/冲动行为[1]。ADHD若在儿童时期没有得到有效治疗,其症状将可能延续到青春期和成年期,对患者的日常生活产生严重影响[2]。近年来,大量临床研究已证实运动干预在ADHD康复中疗效确切且具有独特优势[3-5],相关文献量亦随临证经验的积累及科学研究的深入而获得迅速增长。本研究拟采用CiteSpace软件,对Web of Science数据库中1996-2022年收录的有关ADHD运动干预的文献进行知识图谱可视化分析,挖掘其研究热点及前沿主题演化脉络,以期为未来研究方向提供参考和建议。
1 材料和方法 1.1 数据来源以Web of Science核心合集(包括SCI-E、SSCI、A & HCI)为来源数据库进行检索。检索语言为“English”,文献类型为“Article”,检索时间跨度为1996-2022年(检索与下载截止日期为2022年12月31日)。在主题词一栏输入TS=(“Physical activity” OR “Physical exercise” OR “physical fitness” OR “physical education” OR “fitness” OR “acute exercise” OR “chronic exercise” OR “healthy exercise” OR “aerobic exercise” OR “resistance exercise” OR “anaerobic exercise” OR “exercise” OR “sport*”),得到1 016 033条记录,记录为#1;再次在主题词一栏输入TS=(“attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity” OR “attention deficit disorders with hyperactivity” OR “attention deficit hyperactivity disorders” OR “attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder” OR “hyperkinetic syndrome” OR “syndromes hyperkinetic” OR “ADDH” or “ADHD”),得到61 881条记录,记录为#2;然后进行组配检索,组配检索式为“#1 AND #2”,得到1 475条记录。除去会议论文、书评及与研究主题无关的记录后,最终得到1 153篇文献。
1.2 知识图谱可视化分析采用美国德雷赛尔大学陈超美博士开发的CiteSpace可视化软件绘制科学知识图谱[6]。首先下载1 153篇有关ADHD运动干预的文献信息(包括题名、作者、关键词、摘要、参考文献、出版机构等),保存为纯文本格式,并导出到空文件夹data内;然后将data文件夹导入CiteSpace 6.2.R2软件,对文献的基本现状、研究热点及前沿主题演进内容进行知识图谱可视化分析。
2 结果 2.1 发文量与被引频次的时间分布1996-2022年有关ADHD运动干预疗法研究的年发文量和被引频次整体呈现上升趋势(图 1)。1996-2008年,年发文量呈波浪式攀升,处于平稳上升期;2009-2016年,年发文量呈逐年增加趋势,处于快速发展期;2017-2022年,年发文量增速迅猛,并在2019年出现井喷式增长,处于高速发展期,但2022年增长趋缓。1996-2022年1 153篇文献总被引频次为37 380次,篇均被引频次为32.42次,提示有关ADHD运动干预疗法研究的文献总体质量和关注度较高。
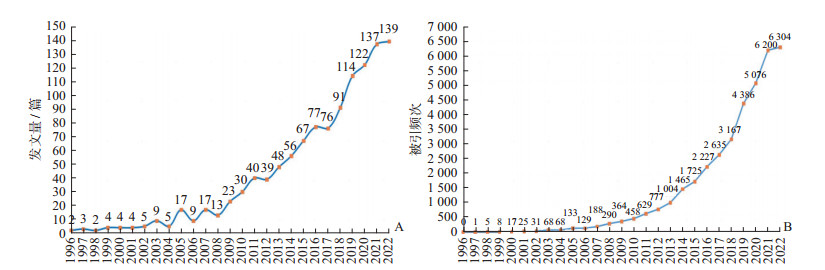
|
图 1 1996-2022年注意缺陷多动障碍运动干预研究发文量(A)与被引频次(B)的时间分布 |
2.2 国家(地区)和研究机构分布
美国发文量最高,为564篇;其次是加拿大,为118篇;英国的发文量为87篇,排在第3位。高产机构排在第1位的是美国哈佛大学医学院(86篇),第2、第3位分别为美国哈佛大学(71篇)和美国加州大学(48篇)。从合作网络特征来看,高产机构之间形成了较为紧密的合作网络聚类簇,并呈现出局部性特征,代表着本研究领域的国际权威和知识中心。
2.3 学科分布从出现频次来看,精神病学(209次)排在第1位,儿科学(170次)和神经科学(132次)分别排在第2和第3位,体育科学(125次)排在第4位。从中介中心性来看,心理学(0.29)排在第1位,精神病学(0.19)和工程学(0.18)分别排在第2和第3位。可以看出,多学科交叉融合是当前ADHD运动干预疗法领域的重要学科表征。
2.4 作者分布发文量排在第1位的是美国哈佛大学医学院的Iverson教授(23篇),被引频次排在第1位的是美国普林斯顿大学的Putukian教授(1 228次)。由图 2可以看出,高产作者之间形成了关系密切的合作网络,其中以高产作者Iverson教授等为主的学术共同体合作关系最为密切,成为这一领域最为活跃的研究团队,研究主要涉及ADHD运动干预的生理生化机制;其次是以高产作者Chang教授(发文量16篇)为主的学术团队,研究涉及单次有氧运动或长期有氧运动对ADHD患儿核心症状及其他功能的改善作用;以高产作者Oosterlaan教授(发文量11篇)为主的研究团队主要侧重于运动与脑电神经反馈训练联合干预对ADHD患儿神经认知功能影响的影像学分析。

|
图 2 1996-2022年注意缺陷多动障碍运动干预研究高产作者合作网络分布图 |
2.5 高频关键词聚类和突现分析
1996-2022年关于ADHD运动干预疗法的研究紧紧围绕着改善ADHD患儿精神功能、运动功能和社会功能等主题展开;研究对象主要包括儿童和青少年人群,其中针对男性患儿的研究较多;干预方式主要集中在抗阻训练、悬吊训练,以及自行车、太极、武术、瑜伽等有氧运动;研究方法主要包括随机对照试验、横断面研究和meta分析。见表 1。
|
|
表 1 1996-2022年注意缺陷多动障碍运动干预研究高频关键词分类 |
2.6 研究前沿主题聚类分析
1996-2022年关于ADHD运动干预研究的文献被引网络聚类共凝练出21个前沿主题知识群,分别为clinical recovery(临床恢复,111篇)、young people(青年人,105篇)、ADHD symptom(ADHD症状,93篇)、neurofeedback/methylphenidate(神经反馈/哌甲酯,69篇)、open trial(开放试验,55篇)、adverse effect(副作用,45篇)、biological basis(生物学基础,42篇)、adult patient(成年患者,41篇)、mental health issue(精神健康问题,31篇)、emotional behavioural(情绪行为,16篇)、psychological aspect(心理方面,12篇)、social support(社会支持,11篇)、sport(体育运动,10篇)、separate norm(独立规范,9篇)、school-based health survey(基于学校的健康调查,8篇)、difference(差异性,8篇)、neurocognitive function(神经认知功能,7篇)、digital media use(数字媒体应用,7篇)、behavioral development(行为发展,7篇)、behavioral(行为,5篇)、energy expenditure(能量消耗,5篇),其轮廓系数为0.873~1.000。各前沿主题知识群出现的时间序列较明显地揭示了ADHD运动干预研究主题沿着ADHD诱因机制-运动干预生理生化机制-运动干预功能效果的演进脉络展开。
3 讨论本研究结果显示,1996-2022年关于ADHD运动干预疗法的研究急剧增长。发文量最多的国家(地区)为美国、加拿大、英国,高产作者间形成了凝聚力比较强的合作网络,多学科交叉融合是该研究领域重要学科表征,前沿主题主要聚焦于ADHD诱因机制、运动干预治疗生理生化机制及运动干预治疗功能效果。
ADHD诱因机制的研究主要集中于遗传及环境因素、脑结构和功能异常两方面。ADHD是一种以遗传为主的多基因疾病,遗传率高达40%左右[7]。ADHD患儿的多巴胺和多巴胺转运体存在异常,它们在ADHD发病中起着重要作用[8]。一项meta分析结果显示,母亲孕期及围产期的抑郁、肥胖、超重和糖尿病等都会增加新生儿患ADHD的概率[9]。早产或出生时体重偏低的婴儿后期被诊断为ADHD的概率也比较高[10]。ADHD患者脑部微结构存在异常,皮质厚度和尾状核大小与正常人群相比存在差异[11]。ADHD患儿无论处在任务态或静息态,其大脑左半球额下回活动均比较弱,执行功能和注意力呈现低激活表现[12]。O’Halloran等[13]研究发现,ADHD患儿在执行持续性注意反应任务中,大脑前部与后部血流分配存在差异,诱发电位波幅降低,反映了其持续注意障碍的神经机制。
ADHD运动干预相关机制的研究主要围绕神经营养因子与神经递质、大脑功能与结构等方面展开。研究发现运动干预能够增强大鼠海马等脑组织中脑源性神经营养因子的表达并减轻ADHD大鼠空间学习能力障碍[14-15],18周的中等强度马术运动与神经反馈训练联合运动干预能够提高ADHD患儿血液中脑源性神经营养因子表达水平[16]。运动可以使ADHD患儿脑区之间的功能网络连接加强,提高神经递质和皮质醇水平[17]。Tantillo等[18]对8~12岁ADHD儿童(男10例、女8例)实施急性运动干预,结果显示只有ADHD男性患儿的运动功能得到改善、多巴胺能活动水平得到提高,提示性别和运动强度之间存在相互作用。Ludyga等[19]采用随机交叉试验设计方案,对16例ADHD患儿和18名正常儿童分别实施了20 min中等强度的功率自行车运动和传统协调性运动,结果显示与传统的协调性运动干预相比,20 min中等强度的功率自行车运动可以显著提高ADHD患儿的P300振幅,改善ADHD患儿的抑制控制和注意力分配能力。Choi等[20]采用3-T功能磁共振成像技术探究了6周有氧运动对ADHD患儿大脑活动的影响,结果显示运动干预能够增加ADHD患儿右额叶和颞叶皮质内大脑活动。
ADHD运动干预功能效果的研究涉及精神功能、运动功能、情感功能和社会功能等多个方面。运动干预可以有效改善ADHD儿童和青少年的整体执行功能,其中对抑制性和认知灵活性有着中等至较大的积极影响[21]。高强度间歇运动训练与中等强度的联合运动干预均能够有效提高ADHD患儿的注意力表现[22-23]。Chang等[24]研究结果显示中等强度跑台运动(1次/周,20~30 min/次)使ADHD患儿的反应时间明显缩短。Kosari等[25]研究指出,Spark体育锻炼(45 min/次,共计18次)可以显著提高ADHD患儿在速度素质、灵活性、平衡性、协调性和力量素质等方面的运动表现。Smith等[26]对17例ADHD患儿进行了为期8周的有氧运动干预(5次/周,30 min/次),结果显示有氧运动可以显著改善ADHD患儿的粗大和精细运动技能。一项meta分析结果显示,运动对ADHD患儿的冲动、焦虑和压力等方面具有改善作用[27]。30 min的中高强度急性运动和5~15周的长期运动干预不仅可以改善ADHD患儿的多动、烦躁等负面心理问题,还使ADHD患儿的教室行为和学习成绩得到明显提升[28]。运动还能改善ADHD患儿的生活质量和社会交往能力[29]。Zhang等[30]研究指出,12周的运动干预对ADHD儿童父母感知育儿压力有积极影响,证明运动干预对促进ADHD患者的家庭关系和谐有益。
总之,近年来关于ADHD运动干预疗法的研究呈现出热点多元化、内容精细化、主题深入化的研究趋势。不同研究的运动干预方式多样,主要集中在抗阻训练、悬吊训练以及自行车、太极、武术、瑜伽等有氧运动,但最佳运动干预形式和干预剂量还未形成共识。建议在未来研究中,各学术群体间加强跨地区及跨国家的合作;除了对热点学科的重视外,还应积极主动地将相关的新学科融入进来,并提高对基础学科的重视;加强对各种运动干预形式及强度的研究,寻找最佳的运动干预方案;大力开展大样本量的随机对照试验研究,以期为ADHD运动干预疗法的临床应用提供强有力的依据。
| [1] |
AKUTAGAVA-MARTINS G C, SALATINO-OLIVEIRA A, KIELING C C, et al. Genetics of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: current findings and future directions[J]. Expert Rev Neurother, 2013, 13(4): 435-445. DOI:10.1586/ern.13.30 |
| [2] |
RUSHTON S, GIALLO R, EFRON D. ADHD and emotional engagement with school in the primary years: investigating the role of student-teacher relationships[J]. Br J Educ Psychol, 2020, 90(S1): 193-209. DOI:10.1111/bjep.12316 |
| [3] |
VYSNIAUSKE R, VERBURGH L, OOSTERLAAN J, et al. The effects of physical exercise on functional outcomes in the treatment of ADHD: a meta-analysis[J]. J Atten Disord, 2020, 24(5): 644-654. DOI:10.1177/1087054715627489 |
| [4] |
JEYANTHI S, ARUMUGAM N, PARASHER R K. Effect of physical exercises on attention, motor skill and physical fitness in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review[J]. Atten Defic Hyperact Disord, 2019, 11(2): 125-137. DOI:10.1007/s12402-018-0270-0 |
| [5] |
LUDYGA S, GERBER M, PÜHSE U, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis investigating moderators of long-term effects of exercise on cognition in healthy individuals[J]. Nat Hum Behav, 2020, 4(6): 603-612. DOI:10.1038/s41562-020-0851-8 |
| [6] |
CHEN C. CiteSpace Ⅱ: detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature[J]. J Am Soc Inf Sci, 2006, 57(3): 359-377. DOI:10.1002/asi.20317 |
| [7] |
FARAONE S V, BONVICINI C, SCASSELLATI C. Biomarkers in the diagnosis of ADHD: promising directions[J]. Curr Psychiatry Rep, 2014, 16(11): 497. DOI:10.1007/s11920-014-0497-1 |
| [8] |
DEMONTIS D, WALTERS R K, MARTIN J, et al. Discovery of the first genome-wide significant risk loci for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder[J]. Nat Genet, 2019, 51(1): 63-75. DOI:10.1038/s41588-018-0269-7 |
| [9] |
KONG L, NILSSON I A K, BRISMAR K, et al. Associations of different types of maternal diabetes and body mass index with offspring psychiatric disorders[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2020, 3(2): e1920787. DOI:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.20787 |
| [10] |
FRANZ A P, BOLAT G U, BOLAT H, et al. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and very preterm/very low birth weight: a meta-analysis[J]. Pediatrics, 2018, 141(1): e20171645. DOI:10.1542/peds.2017-1645 |
| [11] |
GARRETT A, PENNIMAN L, EPSTEIN J N, et al. Neuroanatomical abnormalities in adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder[J]. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry, 2008, 47(11): 1321-1328. DOI:10.1097/CHI.0b013e318185d285 |
| [12] |
SAMEA F, SOLUKI S, NEJATI V, et al. Brain alterations in children/adolescents with ADHD revisited: a neuroimaging meta-analysis of 96 structural and functional studies[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2019, 100: 1-8. DOI:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.02.011 |
| [13] |
O'HALLORAN L, CAO Z, RUDDY K, et al. Neural circuitry underlying sustained attention in healthy adolescents and in ADHD symptomatology[J]. NeuroImage, 2018, 169: 395-406. DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.12.030 |
| [14] |
KIM H, HEO H I, KIM D H, et al. Treadmill exercise and methylphenidate ameliorate symptoms of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder through enhancing dopamine synthesis and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in spontaneous hypertensive rats[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2011, 504(1): 35-39. DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2011.08.052 |
| [15] |
JEONG H I, JI E S, KIM S H, et al. Treadmill exercise improves spatial learning ability by enhancing brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder rats[J]. J Exerc Rehabil, 2014, 10(3): 162-167. DOI:10.12965/jer.140111 |
| [16] |
LEE N, PARK S, KIM J. Hippotherapy and neurofeedback training effect on the brain function and serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor level changes in children with attention-deficit or/and hyperactivity disorder[J]. J Exerc Nutr Biochem, 2017, 21(3): 35-42. DOI:10.20463/jenb.2017.0018 |
| [17] |
PONTIFEX M B, SALIBA B J, RAINE L B, et al. Exercise improves behavioral, neurocognitive, and scholastic performance in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder[J]. J Pediatr, 2013, 162(3): 543-551. DOI:10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.08.036 |
| [18] |
TANTILLO M, KESICK C M, HYND G W, et al. The effects of exercise on children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder[J]. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 2002, 34(2): 203-212. DOI:10.1097/00005768-200202000-00004 |
| [19] |
LUDYGA S, BRAND S, GERBER M, et al. An event-related potential investigation of the acute effects of aerobic and coordinative exercise on inhibitory control in children with ADHD[J]. Dev Cogn Neurosci, 2017, 28: 21-28. DOI:10.1016/j.dcn.2017.10.007 |
| [20] |
CHOI J W, HAN D H, KANG K D, et al. Aerobic exercise and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: brain research[J]. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 2015, 47(1): 33-39. DOI:10.1249/MSS.0000000000000373 |
| [21] |
LIANG X, LI R, WONG S H S, et al. The impact of exercise interventions concerning executive functions of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactive disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int J BehavNutr Phys Act, 2021, 18(1): 68. DOI:10.1186/s12966-021-01135-6 |
| [22] |
MEßLER C F, HOLMBERG H C, SPERLICH B. Multimodal therapy involving high-intensity interval training improves the physical fitness, motor skills, social behavior, and quality of life of boys with ADHD: a randomized controlled study[J]. J Atten Disord, 2018, 22(8): 806-812. DOI:10.1177/1087054716636936 |
| [23] |
SILVA A P, PRADO S O S, SCARDOVELLI T A, et al. Measurement of the effect of physical exercise on the concentration of individuals with ADHD[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0122119. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0122119 |
| [24] |
CHANG Y K, LIU S, YU H H, et al. Effect of acute exercise on executive function in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder[J]. Arch Clin Neuropsychol, 2012, 27(2): 225-237. DOI:10.1093/arclin/acr094 |
| [25] |
KOSARI S, HEMAYATTALAB R, ARABAMERI E, et al. The effect of physical exercise on the development of gross motor skills in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder[J]. Zahedan J Res Med Sci, 2013, 15: 74-78. |
| [26] |
SMITH A L, HOZA B, LINNEA K, et al. Pilot physical activity intervention reduces severity of ADHD symptoms in young children[J]. J Atten Disord, 2013, 17(1): 70-82. DOI:10.1177/1087054711417395 |
| [27] |
CERRILLO-URBINA A J, GARCÍA-HERMOSO A, SÁNCHEZ-LÓPEZ M, et al. The effects of physical exercise in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials[J]. Child Care Health Dev, 2015, 41(6): 779-788. DOI:10.1111/cch.12255 |
| [28] |
CHRISTIANSEN L, BECK M M, BILENBERG N, et al. Effects of exercise on cognitive performance in children and adolescents with ADHD: potential mechanisms and evidence-based recommendations[J]. J Clin Med, 2019, 8(6): 841. DOI:10.3390/jcm8060841 |
| [29] |
GARCÍA-GÓMEZ A, RODRÍGUEZ-JIMÉNEZ M, GUERRERO-BARONA E, et al. Benefits of an experimental program of equestrian therapy for children with ADHD[J]. Res Dev Disabil, 2016, 59: 176-185. DOI:10.1016/j.ridd.2016.09.003 |
| [30] |
ZHANG Z, LI R, ZHOU Z, et al. The effect of physical activity on quality of life and parenting stress in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Disabil Health J, 2023, 16(1): 101377. DOI:10.1016/j.dhjo.2022.101377 |
 2023, Vol. 44
2023, Vol. 44


