2. 国家儿童健康与疾病临床医学研究中心, 重庆 400014;
3. 儿童发育疾病研究教育部重点实验室, 重庆 400014;
4. 儿科学重庆市重点实验室, 重庆 400014
2. National Clinical Research Center for Child Health and Disorders, Chongqing 400014, China;
3. Key Laboratory of Child Development and Disorders of Ministry of Education, Chongqing 400014, China;
4. Chongqing Key Laboratory of Pediatrics, Chongqing 400014, China
新生儿感染往往导致脑损伤的发生, 并且伴随少突胶质细胞(oligodendrocyte, OL)成熟障碍和髓鞘形成受损[1]。OL在中枢神经系统中的主要作用是促进髓鞘生成, 若其成熟发生障碍则会引起髓鞘生成障碍, 发生脱髓鞘疾病, 导致认知、行为和感觉功能下降[2]。miRNA是一类小的非编码RNA分子, 由许多真核生物表达, 能调节体内大多数生物学进程[3-4]。微RNA-219(microRNA-219, miR-219)可以调控少突胶质祖细胞的分化, 并在已成熟的OL中大量表达[5-7], 在脊髓损伤等脱髓鞘疾病动物模型脑部过表达miR-219可以促进OL成熟, 但相关机制并不明确[5-6]。本研究在模拟炎症的新生SD大鼠侧脑室注射miR-219 agomir(一种miR-219模拟物), 同时于空白对照的新生SD大鼠侧脑室注射miR-219 antagomir(一种miR-219拮抗物), 观察OL的成熟情况并探究miR-219促进OL成熟的机制, 为临床治疗新生儿感染所致脑损伤提供新的线索。
1 材料和方法 1.1 材料脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide, LPS; 上海希格玛高技术有限公司), miR-219 agomir和miR-219 antagomir [生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司], 反转录和qPCR试剂(美国MCE公司), TRIzol(美国Invitrogen公司), 全蛋白质提取试剂盒(江苏凯基生物技术股份有限公司), β微管蛋白抗体、髓鞘碱性磷脂蛋白(myelin basic protein, MBP)抗体、ERK 1/2抗体(美国Cell Signaling Technology公司), TRITC荧光二抗、FITC荧光二抗和山羊抗兔IgG H & L [艾博抗(上海)贸易有限公司], BCA试剂盒、ERK 1/2通路抑制剂U0126(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司)。
1.2 动物分组与处理将60只新生SD大鼠随机分为5组: 对照组、miR-219 antagomir组、LPS组、LPS+miR-219 agomir组和LPS+miR-219 agomir+U0126组, 每组12只。3组炎症模型SD大鼠出生24 h后腹腔注射0.15 mg/kg LPS, 连续2 d; 对照组和miR-219 antagomir组则在相同时间腹腔注射等体积生理盐水。LPS+miR-219 agomir和LPS+miR-219 agomir+U0126组大鼠, 腹腔注射LPS 12 h后, 定位于大鼠前囟后0.6 mm、中线左(右)0.8 mm、颅骨下2.4 mm使用微量注射器注射miR-219 agomir, 将注射体积设置为3 μL, 注射速度设置为3 μL/min, 留针1 min。U0126(30 mg/kg)溶于DMSO, 并于侧脑室注射miR-219 agomir前30 min腹腔注射。miR-219 antagomir的注射方法与miR-219 agomir相同。
分别于大鼠出生后7 d和14 d断头处死大鼠, 于冰上迅速剥离脑组织并一分为二, 一份冻存于-80 ℃, 另一份用4%多聚甲醛溶液固定。
1.3 qPCR检测脑组织炎症因子IL-1β和TNF-α的mRNA表达水平取-80 ℃冻存的脑组织, 采用TRIzol法提取总RNA, 根据试剂使用说明书反转录成cDNA, 再进行qPCR扩增。IL-1β上游引物序列为5'-CCAGCTTCAAATCTCACAGCAG-3', 下游引物序列为5'-CTTCTTTGGGTATTGCTTGGGATC-3';TNF-α上游引物序列为5'-TTCCGAATTCACTG-GAGCCTCGAA-3', 下游引物序列为5'-TGC-ACCTCAGGGAAGAATCTGGA-3';内参基因GAPDH上游引物序列为5'-TGAAGCAGGCAT-CTGAGGG-3', 下游引物序列为5'-CGAAGGT-GGAAGAGTGGGAG-3'。qPCR反应条件: 95 ℃ 3 min; 95 ℃ 30 s、55 ℃ 20 s, 40个循环。所用引物均由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成。
1.4 qPCR检测脑组织miR-219表达水平以上述cDNA为模板采用qPCR扩增miR-219, miR-219上游引物序列为5'-AGGCGCATTGATTGTCCAA-ACG-3', 下游引物序列为5'-ATCCAGTGCAGGG-TCCGAGG-3';内参基因U6上游引物序列为5'-GCAGCTACCTCAGTGCA-3', 下游引物序列为5'-GCGAACGCAGGAATTTGTGT-3'。qPCR反应条件: 95 ℃ 10 min; 95 ℃ 2 s、60 ℃ 20 s、70 ℃ 10 s, 40个循环。所用引物均由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成。
1.5 蛋白质印迹法检测OL标志物MBP和ERK 1/2通路蛋白表达水平取-80 ℃冻存的脑组织, 按全蛋白质提取试剂盒说明书提取蛋白质, 用BCA法测蛋白质浓度。取40 μg蛋白质用SDS-PAGE分离, 转至PVDF膜上(105 V、105 min); 用5%脱脂牛奶封闭1 h, TBST洗3次, 每次5 min; 加MBP、ERK 1/2抗体(稀释比例均为1∶1 000)于4 ℃摇床孵育14 h, TBST洗3次, 每次5 min; 加山羊抗兔IgG H & L(稀释比例为1∶3 000)于26 ℃孵育1.5 h, TBST洗5次, 每次3 min。显影后用ImageJ软件对条带灰度值进行分析。
1.6 免疫荧光法检测胼胝体成熟OL数量取4%多聚甲醛溶液固定的脑组织制成冰冻切片, 将冰冻切片用山羊血清封闭30 min; 吸弃山羊血清, PBS洗2次, 加MBP和ERK 1/2抗体(稀释比例均为1∶200)于4 ℃湿盒孵育24 h, PBS洗3次; 用TRITC荧光二抗和FITC荧光二抗(稀释比例均为1∶500)室温孵育2 h, PBS洗3次; 用DAPI染核, PBS洗3次。采用荧光淬灭剂封片, 在荧光显微镜下观察。
1.7 统计学处理应用SPSS 24.0软件进行统计学分析。数据以x±s表示, 采用Dunnett’s t检验进行组间比较, 检验水准(α)为0.05。
2 结果 2.1 LPS导致大鼠全身炎症反应并使其脑组织内miR-219表达降低大鼠腹腔注射LPS后脑组织内IL-1β mRNA(1.34±0.12 vs 0.31±0.07)和TNF-α mRNA(1.46±0.21 vs 0.46±0.03)的表达与对照组相比均升高, 而miR-219表达减少(0.42±0.12 vs1.40±0.05), 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01)。
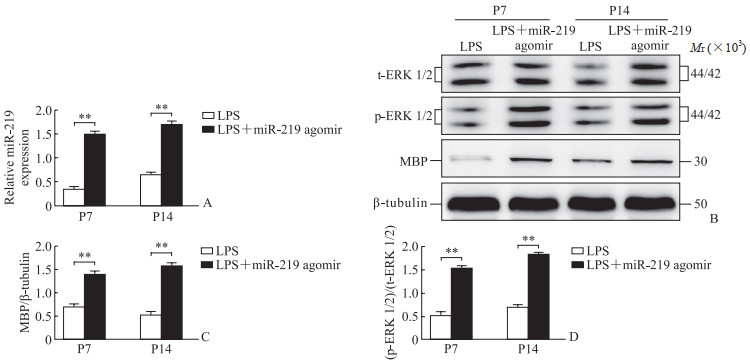
2.2 miR-219 agomir可促进OL成熟qPCR和蛋白质印迹法检测结果显示, 与LPS组大鼠对比, LPS+miR-219 agomir组大鼠脑组织内miR-219、MBP、ERK 1/2表达均升高(P<0.01, 图 1), 免疫荧光法检测结果显示大鼠胼胝体OL数量增加(图 2)。
|
图 1 miR-219 agomir干预前后炎症模型SD大鼠脑组织中miR-219、MBP、ERK 1/2的表达 Fig 1 Expression of miR-219, MBP, and ERK 1/2 in brain tissue of SD rats of inflammation model before and after intervention with miR-219 agomir A: Expression of miR-219 detected by quantitative polymerase chain reaction; B-D: Expression of MBP and ERK 1/2 detected by Western blotting. **P < 0.01. n=6, x±s. miR-219: MicroRNA-219; MBP: Myelin basic protein; ERK 1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; t-ERK 1/2: Total ERK 1/2; p-ERK 1/2: Phosphorylated ERK 1/2; P7: Postnatal day 7; P14: Postnatal day 14. |

|
图 2 免疫荧光法检测miR-219 agomir干预前后炎症模型SD大鼠胼胝体少突胶质细胞(20×) Fig 2 Oligodendrocytes in corpus callosum of SD rats of inflammation model before and after intervention with miR-219 agomir detected by immunofluorescence (20×) miR-219: MicroRNA-219; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; DAPI: 4', 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; MBP: Myelin basic protein; ERK 1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. |
2.3 miR-219 antagomir可抑制OL成熟
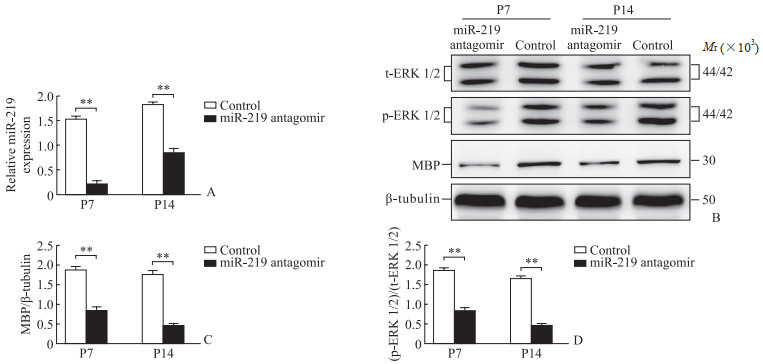
qPCR和蛋白质印迹法检测结果显示, 与对照组大鼠对比, miR-219 antagomir组大鼠脑组织内miR-219、MBP、ERK 1/2表达均降低(P<0.01, 图 3); 免疫荧光法检测结果显示大鼠胼胝体OL数量减少(图 4)。
|
图 3 miR-219 antagomir干预前后SD大鼠脑组织中miR-219、MBP、ERK 1/2的表达 Fig 3 Expression of miR-219, MBP, and ERK 1/2 in SD rat brain tissue before and after intervention with miR-219 antagomir A: Expression of miR-219 detected by quantitative polymerase chain reaction; B-D: Expression of MBP and ERK 1/2 detected by Western blotting. **P < 0.01. n=6, x±s. miR-219: MicroRNA-219; MBP: Myelin basic protein; ERK 1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; t-ERK 1/2: Total ERK 1/2; p-ERK 1/2: Phosphorylated ERK 1/2; P7: Postnatal day 7; P14: Postnatal day 14. |

|
图 4 免疫荧光法检测miR-219 antagomir干预前后大鼠胼胝体少突胶质细胞(20×) Fig 4 Oligodendrocytes of rat corpus callosum before and after intervention with miR-219 antagomir detected by immunofluorescence (20×) miR-219: MicroRNA-219; DAPI: 4', 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; MBP: Myelin basic protein; ERK 1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. |
2.4 U0126对OL成熟的影响
蛋白质印迹法检测结果显示, 用ERK 1/2通路抑制剂U0126处理后, 大鼠脑组织内ERK 1/2、MBP蛋白表达均减少(P<0.01, 图 5), 表明miR-219对MBP表达的促进作用因ERK 1/2通路被抑制而减弱。

|
图 5 蛋白质印迹法检测各组大鼠脑组织内MBP和ERK 1/2蛋白的表达水平 Fig 5 Protein expression of MBP and ERK 1/2 in rat brain tissue of each group detected by Western blotting U0126 is an inhibitor of ERK 1/2 pathway. **P < 0.01. n=6, x±s. MBP: Myelin basic protein; ERK 1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; t-ERK 1/2: Total ERK 1/2; p-ERK 1/2: Phosphorylated ERK 1/2; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; miR-219: MicroRNA-219; P7: Postnatal day 7; P14: Postnatal day 14. |
3 讨论
新生儿免疫系统尚未成熟, 极易遭受各种感染[8]。相关研究显示, 新生儿的急性和慢性炎症都可以导致脑损伤[9-10]。新生儿感染导致的脑损伤类型虽多种多样, 但都伴随OL成熟障碍, 因此, 炎症被认为是OL成熟发生障碍的主要原因之一[8, 11]。OL分布于中枢神经系统有髓神经纤维之间, 构成髓鞘, 其主要功能是形成MBP、维持和保护神经元的正常功能[12-14]。OL发育异常会使髓鞘形成受损, 进而导致中枢神经系统多种疾病如多发性硬化、脑白质损伤等, 甚至可能引发精神类疾病[2]。
miRNA是一类内生的、长度为20~24个核苷酸的RNA, 在体内各个系统中具有多种重要的调节作用[15-16]。相关研究显示, miR-219、miR-338等在OL的分化过程中表达量急剧增加, 尤其是miR-219, 作为OL特有表达的miRNA在OL分化过程中表达达到峰值[5-6]。在体外实验及脊髓损伤动物模型中, miR-219可以促进少突胶质祖细胞分化为成熟的OL, 从而促进髓鞘再生, 改善疾病的症状[6, 17-18]。本实验结果也证实, 在新生SD大鼠炎症模型中miR-219表达降低, 过表达miR-219可以促进OL成熟, 而抑制miR-219表达后OL的成熟受到了抑制。
ERK 1和ERK 2是MAPK家族的成员, 能影响OL的增殖和分化[19]。在缺血缺氧性疾病中, ERK通路的激活可以促进少突胶质祖细胞分化为成熟的OL; 在模拟精神压力性疾病小鼠的海马区, 激活5-羟色胺以抑制ERK通路的活性后海马区OL的分化遭受损害[20-21]。但在炎症导致的脑损伤尤其是动物实验中, ERK通路的作用研究相对较少。本实验结果证实, 在炎症新生大鼠脑内随着miR-219表达增多ERK 1/2活性增加, 促进了OL成熟, 而用U0126抑制ERK 1/2活性后miR-219对OL的促成熟作用受到抑制; 并且在空白新生大鼠脑内随着miR-219表达减少ERK 1/2活性减弱, OL成熟受到抑制。
综上所述, miR-219可以改善由炎症导致的新生SD大鼠脑部OL成熟障碍, 且这一作用是通过ERK 1/2通路而发挥的。本研究结果为早产儿脑损伤的治疗研究提供了新的线索。
| [1] |
SCHNEIDER J, MILLER S P. Preterm brain injury: white matter injury[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2019, 162: 155-172. DOI:10.1016/B978-0-444-64029-1.00007-2 |
| [2] |
VAN TILBORG E, HEIJNEN C J, BENDERS M J, et al. Impaired oligodendrocyte maturation in preterm infants: potential therapeutic targets[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2016, 136: 28-49. DOI:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.11.002 |
| [3] |
TAO J, XIA L, CAI Z, et al. Interaction between microRNA and DNA methylation in atherosclerosis[J]. DNA Cell Biol, 2021, 40(1): 101-115. DOI:10.1089/dna.2020.6138 |
| [4] |
MA Q, DASGUPTA C, LI Y, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-210 provides neuroprotection in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2016, 89: 202-212. DOI:10.1016/j.nbd.2016.02.011 |
| [5] |
JI J, SUN Y Q, ZHA Z, et al. Bu Shen Yi Sui capsules promote remyelination by regulating microRNA-219 and microRNA-338 in exosomes to promote oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2022, 2022: 3341481. DOI:10.1155/2022/3341481 |
| [6] |
HARRIS V K, STARK J, VYSHKINA T, et al. Phase Ⅰ trial of intrathecal mesenchymal stem cell-derived neural progenitors in progressive multiple sclerosis[J]. EBioMedicine, 2018, 29: 23-30. DOI:10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.02.002 |
| [7] |
NAZARI B, NAMJOO Z, MORADI F, et al. miR-219 overexpressing oligodendrocyte progenitor cells for treating compression spinal cord injury[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2021, 36(5): 1069-1077. DOI:10.1007/s11011-021-00701-y |
| [8] |
NOVAK C M, OZEN M, BURD I. Perinatal brain injury: mechanisms, prevention, and outcomes[J]. Clin Perinatol, 2018, 45(2): 357-375. DOI:10.1016/j.clp.2018.01.015 |
| [9] |
LEAVY A, JIMENEZ MATEOS E M. Perinatal brain injury and inflammation: lessons from experimental murine models[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(12): 2640. DOI:10.3390/cells9122640 |
| [10] |
RISBROUGH V B, VAUGHN M N, FRIEND S F. Role of inflammation in traumatic brain injury-associated risk for neuropsychiatric disorders: state of the evidence and where do we go from here[J]. Biol Psychiatry, 2022, 91(5): 438-448. DOI:10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.11.012 |
| [11] |
STEPHENSON J, NUTMA E, VAN DER VALK P, et al. Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Immunology, 2018, 154(2): 204-219. DOI:10.1111/imm.12922 |
| [12] |
KIPP M. Oligodendrocyte physiology and pathology function[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(9): 2078. DOI:10.3390/cells9092078 |
| [13] |
KUHN S, GRITTI L, CROOKS D, et al. Oligodendrocytes in development, myelin generation and beyond[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(11): 1424. DOI:10.3390/cells8111424 |
| [14] |
ROSKO L, SMITH V N, YAMAZAKI R, et al. Oligodendrocyte bioenergetics in health and disease[J]. Neuroscientist, 2019, 25(4): 334-343. DOI:10.1177/1073858418793077 |
| [15] |
KITTELMANN S, MCGREGOR A P. Modulation and evolution of animal development through microRNA regulation of gene expression[J]. Genes, 2019, 10(4): 321. DOI:10.3390/genes10040321 |
| [16] |
WU Y, LI Q, ZHANG R, et al. Circulating microRNAs: biomarkers of disease[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2021, 516: 46-54. DOI:10.1016/j.cca.2021.01.008 |
| [17] |
INOJOSA H, PROSCHMANN U, AKGÜN K, et al. A focus on secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (SPMS): challenges in diagnosis and definition[J]. J Neurol, 2021, 268(4): 1210-1221. DOI:10.1007/s00415-019-09489-5 |
| [18] |
INAMURA N, GO S, WATANABE T, et al. Reduction in miR-219 expression underlies cellular pathogenesis of oligodendrocytes in a mouse model of Krabbe disease[J]. Brain Pathol, 2021, 31(5): e12951. DOI:10.1111/bpa.12951 |
| [19] |
GONSALVEZ D, FERNER A H, PECKHAM H, et al. The roles of extracellular related-kinases 1 and 2 signaling in CNS myelination[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2016, 110(Pt B): 586-593. DOI:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.04.024 |
| [20] |
XIE Y, ZHANG X, XU P, et al. Aberrant oligodendroglial LDL receptor orchestrates demyelination in chronic cerebral ischemia[J]. J Clin Invest, 2021, 131(1): e128114. DOI:10.1172/JCI128114 |
| [21] |
KUROKAWA K, TAKAHASHI K, MIYAGAWA K, et al. Activation of 5-HT1A receptor reduces abnormal emotionality in stress-maladaptive mice by alleviating decreased myelin protein in the ventral hippocampus[J]. Neurochem Int, 2021, 151: 105213. DOI:10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105213 |
 2023, Vol. 44
2023, Vol. 44


