2. 海军军医大学(第二军医大学)海军医学系防化医学教研室,上海200433
2. Department of Chemical Defense Medicine, Faculty of Naval Medicine, Naval Medical University (Second Military Medical University), Shanghai 200433, China
芥子气(sulfur mustard,SM)是难防难治化学战剂的典型代表,自第一次世界大战期间被引入战场后,又多次被用于各种冲突和恐怖袭击[1-2]。尽管目前存在毒性更强的化学战剂,但是SM具有易于工业化生产、难以预防和治疗的特点,仍然具有较大的军事威胁。肺是SM损伤的主要靶器官之一,急性肺损伤是导致SM中毒患者死亡的主要原因之一[3-4]。研究者们认为氧化应激是SM中毒的关键环节[5-6]。研究表明,炎症因子如IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α等与SM引起的肺损伤密切相关[7-9]。SM中毒的机制尚未完全阐明,目前还没有特效治疗药物,以对症治疗为主。基于SM的军事威胁和毒性特点,推进SM中毒机制的研究、寻找新型有效的治疗药物具有重要意义。
虎杖苷(polydatin,PD)是一种白藜芦醇的苷类衍生物,从传统中药虎杖(Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb)的根部分离得到。PD分布广泛,存在于许多常见的食品中,如葡萄、葡萄酒及花生等。研究表明PD具有抗氧化和抗炎活性,能发挥对肾脏、肝脏和肺功能的保护作用[10-12],可作用于多个系统且不良反应小,具有巨大的应用潜力。Shu等[13]研究发现PD可阻断磷脂酶A2的活性,下调分泌型磷脂酶A2 ⅡA mRNA的表达,改善内毒素休克大鼠的急性肺损伤。王方岩等[14]观察到PD可通过降低超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)活性和丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)含量来减轻缺血/再灌注引起的肺损伤。现有文献中未见PD对SM所致肺损伤作用的相关报道。本研究以雄性ICR小鼠为研究对象,建立SM肺损伤模型,探究PD对SM肺损伤的改善作用,并初步探索其作用机制。
1 资料和方法 1.1 动物分组与造模ICR小鼠(雄性,6~8周龄,体重25~30 g)由昭衍(苏州)新药研究中心有限公司[生产许可证号:SCXK(苏)2018-0006]提供。小鼠在12 h光照/12 h黑暗循环、室温(20±2)℃、自由进食和饮水的条件下饲养1周后使用。在存活率实验中,将小鼠随机分为6组(n=15):对照(Ctrl)组、SM组、PD低剂量(SM+PD100)组、PD中剂量(SM+PD200)组、PD高剂量(SM+PD400)组和阳性对照药N-乙酰半胱氨酸(N-acetyl-L-cysteine,NAC)治疗(SM+ NAC)组。SM以40 mg/kg的剂量皮下注射给药。在SM暴露30 min后,SM+PD100、SM+PD200、SM+PD400组分别以100、200、400 mg/kg PD每天灌胃给药1次,持续给药7 d。SM+NAC组在SM暴露30 min后,以200 mg/kg的剂量每天灌胃给药1次,持续给药7 d。连续观察14 d,每天按时记录小鼠的存活情况。
在除存活率外的其他实验中,小鼠被随机分为4组(n=15):Ctrl组、SM组、SM+PD200组和SM+NAC组。SM以30 mg/kg的剂量皮下注射给药。PD在SM暴露30 min后,以200 mg/kg(SM+ PD200组)的剂量每天灌胃给药1次,持续给药5 d。SM+NAC组在SM暴露30 min后,以200 mg/kg的剂量每天灌胃给药1次,持续给药5 d。于第1、3、5、7、10天处死小鼠,取各组小鼠肺组织制作H-E切片进行组织病理学观察。另取一批小鼠随机分为上述4组(n=15),处理同前,持续给药5 d后处死小鼠进行后续实验。
1.2 试剂SM(纯品)由军事科学院防化研究院提供;PD(纯度为95%)和NAC(纯度为99%)购自美国Sigma-Aldrich公司,货号分别为15721-25G和A9165。
1.3 肺组织病理学观察处死小鼠后,取左侧最大叶肺组织,在4%多聚甲醛组织固定液中固定24 h,按顺序放入梯度乙醇和二甲苯溶液中脱水(75%乙醇4 h → 85%乙醇2 h → 90%乙醇2 h → 95%乙醇1 h →无水乙醇Ⅰ 30 min →无水乙醇Ⅱ 30 min →二甲苯Ⅰ 10 min →二甲苯Ⅱ 10 min),透明处理后将肺组织浸蜡包埋并切成5 µm厚的切片,H-E染色。规避分组信息后邀请上海市肺科医院谢惠康副主任医师和高彩霞、张伟2位中级技师根据肺水肿、肺出血、肺组织炎症细胞浸润、肺泡壁结构、支气管结构和病变面积等情况对H-E切片进行评分:未见任何病变记为0分;病理改变轻微、病变面积≤25%记为1分;病理改变轻度、病变面积>25%~50%记为2分;病理改变中度、病变面积>50%~75%记为3分;病理改变重度、病变面积>75%记为4分。
1.4 肺湿重/干重(W/D)比值检测将小鼠的肺组织完整取出,用吸水纸擦掉肺表面残余的血渍后称量,记为湿重(W)。将肺组织在70 ℃烘箱中干燥72 h后称量,记为干重(D),计算W/D比值。
1.5 肺泡灌洗液(bronchoalveolar lavage fluid,BALF)蛋白浓度检测小鼠末次给药后,腹腔注射10%的水合氯醛进行麻醉,固定小鼠后打开腹腔,剪断两侧腹主动脉进行放血,钝性分离出小鼠气管,通过气管将1 mL预冷的生理盐水缓缓注入小鼠肺中,然后缓慢回抽,循环3次,最后回抽600 µL生理盐水。将获得的BALF离心(4 ℃,400×g,15 min),收集上清,于-80 ℃保存备用。
1.6 氧化应激指标与炎症因子检测采用SOD活性检测试剂盒(WST-8法)检测小鼠肺组织中SOD活性,用脂质氧化检测试剂盒检测MDA含量,用过氧化氢(H2O2)检测试剂盒检测H2O2含量。以上试剂盒均购自上海碧云天生物技术有限公司,货号分别为S0103、S0131S、S0038。还原型谷胱甘肽(glutathione,GSH)含量检测试剂盒与髓过氧化物酶(myeloperoxidase,MPO)活性检测试剂盒均购自南京建成生物工程研究所,货号分别为A006-2-1、A044-1-1。所有检测步骤均依据试剂盒说明书进行。
采用IL-1β ELISA试剂盒检测小鼠肺组织中IL-1β水平,IL-6 ELISA试剂盒检测IL-6水平,TNF-α ELISA试剂盒检测TNF-α水平,以上试剂盒均购自美国R&D公司,货号分别为SMLB00C、SM6000B、SMTA00B。所有检测步骤均依据试剂盒说明书进行。
1.7 氧化应激与炎症反应相关蛋白表达水平的检测将组织放入含有蛋白酶抑制剂的RIPA缓冲液(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司,货号P0013D)中剪碎,在预冷的组织研磨仪上匀浆至没有肉眼可见的组织块,离心(4 ℃,13 000×g,20 min)后将上清小心转移到新的EP管中。依据哺乳动物细胞核和细胞质蛋白提取试剂盒(北京全式金生物技术有限公司,货号DE201-01)的说明书提取细胞核和细胞质蛋白。采用BCA蛋白浓度检测试剂盒(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司,货号P0012S)测定蛋白浓度。将蛋白(40 µg)上样于12% SDS-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶上,电泳分离后转至PVDF膜(美国Millipore公司,货号ISEQ00010)。用5%脱脂牛奶封闭2 h,TBST(TBS购自武汉塞维尔生物科技公司,货号G0001-2L;吐温购自上海博光生物科技有限公司,货号BL-SJ-0763)洗膜后用相应一抗在4 ℃孵育过夜,洗膜后放入HRP标记的二抗(1∶3 000 TBST稀释)中在室温下孵育1 h,TBST清洗,经化学发光法得到条带。GAPDH、β-微管蛋白(β-tubulin)、核因子E2相关因子2(nuclear factor E2-related factor 2,Nrf2)、NAD(P)H: 醌氧化还原酶(NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1,NQO1)、Toll样受体4(Toll-like receptor 4,TLR4)、NF-κB p65总蛋白抗体均购自Proteintech中国公司,货号分别为60004-1-Ig、11224-1-AP、16396-1-AP、11451-1-AP、19811-1-AP、10745-1-AP;TATA盒结合蛋白(TATA box binding protein,TBP)、沉默信息调节因子1(silencing information regulator 1,SIRT1)、血红素加氧酶1(heme oxygenase 1,HO-1)抗体均购自上海碧云天生物技术有限公司,货号分别为AF5321、AF0282、AF1333;磷酸化NF-κB p65抗体购自美国CST公司,货号3039;HRP标记的山羊抗兔/鼠抗体购自上海碧云天生物技术有限公司,货号为A0208、A0216。
1.8 统计学处理应用GraphPad Prism 9软件进行分析和绘图。数据以x±s表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,多样本均数两两之间比较采用SNK-q检验。用Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线,存活率的比较采用log-rank检验。检验水准(α)为0.05。
2 结果 2.1 PD可以提高SM染毒小鼠的存活率,改善SM所致肺损伤如图 1所示,Ctrl组无小鼠死亡,SM组小鼠存活率为11.33%(与Ctrl组比较,P<0.01);与SM组相比,SM+NAC组小鼠与SM+PD400组小鼠存活率均提升至26.84%(P均<0.05);SM+PD200组小鼠存活率提高至48.62%(与SM组相比,P<0.01;与SM+NAC组相比,P<0.05);SM+PD100组小鼠存活率与SM组相比无明显提升(P>0.05)。以上结果表明,PD可以提高SM染毒小鼠的存活率,且PD最佳给药剂量为200 mg/kg,选用此剂量进行后续PD作用评价实验。
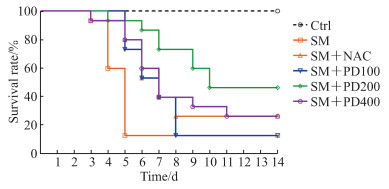
|
图 1 PD处理对SM染毒小鼠存活率的影响 Fig 1 Effect of PD on survival rate of SM-exposed mice n=15. PD: Polydatin; SM: Sulfur mustard; Ctrl: Control; NAC: N-acetyl-L-cysteine; PD100, PD200, PD400: 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg PD, respectively. |
H-E染色观察PD对SM所致肺损伤的影响,结果如图 2、3所示,Ctrl组小鼠肺组织形态正常,肺泡和支气管结构完整;SM组小鼠肺损伤先加重后减轻,在SM暴露后的第5天肺组织损伤最为严重(评分与Ctrl组比较,P<0.01),可见明显的支气管结构破坏和肺间隔增厚,炎症细胞浸润增加;与SM组相比,SM+NAC组小鼠肺损伤程度有轻微改善,肺泡腔内有部分炎症细胞浸润,可见少量出血和肺间隔增厚,支气管结构轻微破坏;SM+PD200组小鼠肺损伤有明显缓解(第5天评分与SM组比较,P<0.05),肺泡腔仅有少量的炎症细胞浸润和渗出物,偶见支气管结构轻微破坏。结果表明PD和NAC对SM所致肺损伤均具有一定的保护作用,且前者效果优于后者。
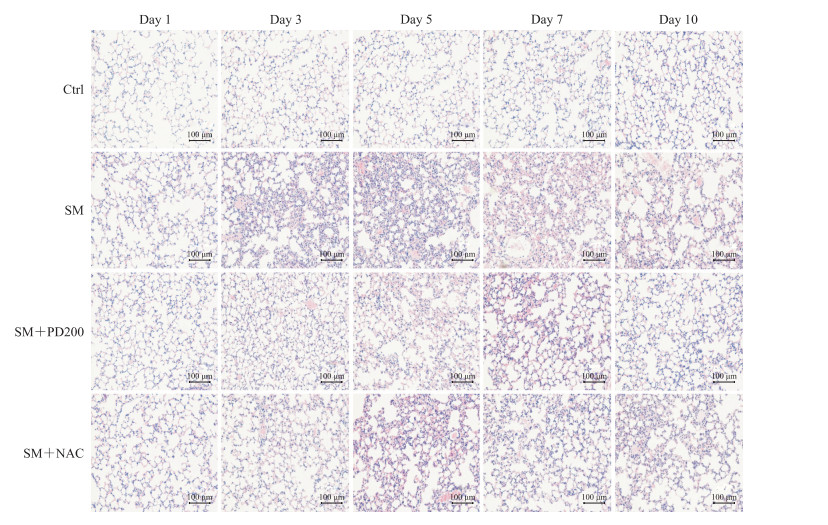
|
图 2 各组小鼠肺组织病理变化 Fig 2 Histopathological changes of lung issues in mice in each group Hematoxylin-eosin staining. Ctrl: Control; SM: Sulfur mustard; PD200: 200 mg/kg polydatin; NAC: N-acetyl-L-cysteine. |
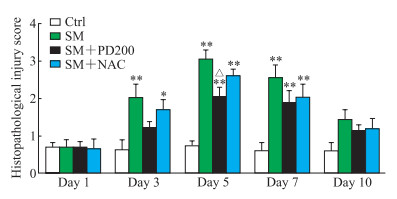
|
图 3 各组小鼠肺组织病理损伤评分 Fig 3 Histopathological injury scores of lung tissues in mice in each group *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs Ctrl group; △P < 0.05 vs SM group. n=3, x±s. Ctrl: Control; SM: Sulfur mustard; PD200: 200 mg/kg polydatin; NAC: N-acetyl-L-cysteine. |
通过小鼠肺W/D比值和BALF蛋白浓度来评判肺损伤程度(n=5)。Ctrl组W/D比值为4.22± 0.22,BALF蛋白浓度为(349.90±110.14)μg/mL。与Ctrl组相比,SM组小鼠W/D比值(4.91±0.16)和BALF蛋白浓度[(869.23±73.85)μg/mL]升高(P<0.01),提示SM可引起肺组织损伤。采用PD200干预可降低W/D比值(4.44±0.23)和BALF蛋白浓度[(545.67±64.28)μg/mL](与SM组相比,P<0.05或P<0.01),采用NAC干预不能降低W/D比值(4.67±0.26;与SM组相比,P>0.05)但可降低BALF蛋白浓度[(645.77±127.46)μg/mL,与SM组相比,P<0.05],提示PD和NAC可降低SM染毒小鼠的肺水肿,对SM所致肺损伤具有保护作用,且PD的作用效果优于NAC。
2.2 PD可以降低SM染毒小鼠的氧化应激相关指标水平如图 4所示,与Ctrl组相比,SM组小鼠肺组织中MDA含量、H2O2含量及MPO活性均升高(P均<0.01),GSH含量、SOD活性均降低(P均<0.01);NAC处理可提高GSH含量和SOD活性(与SM组相比,P均<0.05);PD200处理后可降低MDA含量、H2O2含量及MPO活性(与SM组相比,P<0.05或P<0.01),提高GSH含量、SOD活性(与SM组相比,P均<0.01)。结果表明PD和NAC可以不同程度地改善SM引起的氧化应激。
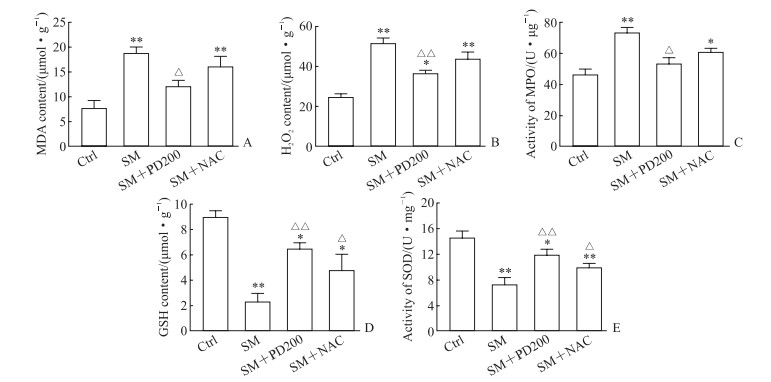
|
图 4 各组小鼠肺组织中氧化应激相关指标检测结果 Fig 4 Results of oxidative stress indexes in lung tissues of mice in each group Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay results. A: MDA; B: H2O2; C: MPO; D: GSH; E: SOD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs Ctrl group; △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.01 vs SM group. n=3, x±s. Ctrl: Control; SM: Sulfur mustard; PD200: 200 mg/kg polydatin; NAC: N-acetyl-L-cysteine; MDA: Malondialdehyde; H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; GSH: Glutathione; SOD: Superoxide dismutase. |
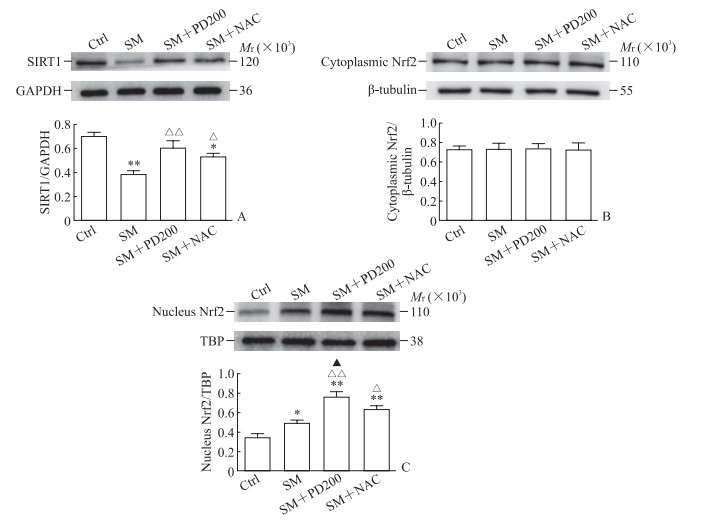
2.3 PD可上调SM染毒小鼠SIRT1蛋白的表达,促进Nrf2的核转移,上调HO-1和NQO1蛋白的表达
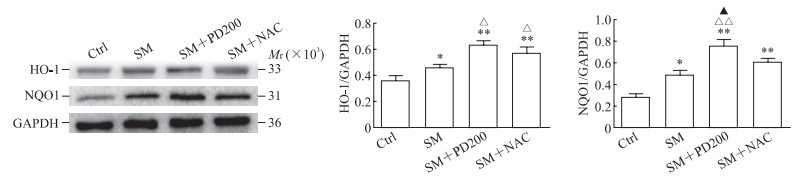
如图 5A所示,与Ctrl组相比,SM组SIRT1蛋白的表达水平下降(P<0.01)。与SM组相比,SM+PD200组和SM+NAC组SIRT1蛋白的表达水平均有所上升(P<0.01,P<0.05),证明PD和NAC都可能通过激活SIRT1蛋白来发挥其保护作用。如图 5B、5C所示,各组细胞胞质的Nrf2总蛋白水平没有明显变化,但SM+PD200组和SM+ NAC组Nrf2蛋白的核转移与SM组相比增加(P<0.01,P<0.05)。如图 6所示,与SM组相比,SM+PD200组HO-1和NQO1蛋白的表达水平增加(P<0.05或P<0.01),SM+NAC组的HO-1蛋白表达水平增加(P<0.05),且SM+PD200组的变化均较SM+NAC组更为显著。结果表明PD可能通过激活SIRT1蛋白的表达来调控Nrf2及其下游蛋白发挥抗氧化作用。
|
图 5 各组小鼠肺组织中SIRT1与Nrf2蛋白的表达 Fig 5 Protein expression of SIRT1 and Nrf2 in lung tissues of mice in each group Western blotting results. A: SIRT1; B: Cytoplasmic Nrf2; C: Nucleus Nrf2. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs Ctrl group; △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.01 vs SM group; ▲P < 0.05 vs SM+NAC group. n=3, x±s. Ctrl: Control; SIRT1: Silencing information regulator 1; Nrf2: Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2; SM: Sulfur mustard; PD200: 200 mg/kg polydatin; NAC: N-acetyl-L-cysteine; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; TBP: TATA box binding protein. |
|
图 6 各组小鼠肺组织中HO-1和NQO1蛋白的表达 Fig 6 Protein expression of HO-1 and NQO1 in lung tissues of mice in each group Western blotting results. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs Ctrl group; △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.01 vs SM group; ▲P < 0.05 vs SM+NAC group. n=3, x±s. Ctrl: Control; SM: Sulfur mustard; PD200: 200 mg/kg polydatin; NAC: N-acetyl-L-cysteine; HO-1: Heme oxygenase 1; NQO1: NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. |
2.4 PD可降低SM染毒小鼠炎症因子水平
通过ELISA试剂盒检测小鼠肺组织中炎症因子TNF-α、IL-1β和IL-6的水平变化,结果如图 7所示。与Ctrl组相比,SM组TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6的表达水平均升高(P均<0.01),提示SM作用后可引起肺组织的炎症反应;PD或NAC处理降低了TNF-α、IL-1β的表达水平(与SM组相比,P均<0.05)。SM+PD200组IL-6水平较SM组降低(P<0.05),SM+NAC组IL-6水平降低不明显。结果说明PD可以降低SM染毒小鼠肺组织内的炎症水平,改善小鼠SM肺损伤。

|
图 7 各组小鼠肺组织中炎症因子的检测结果 Fig 7 Results of inflammatory factors in lung tissues of mice in each group Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay results. A: TNF-α; B: IL-1β; C: IL-6. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs Ctrl group; △P < 0.05 vs SM group. n=4, x±s. Ctrl: Control; SM: Sulfur mustard; PD200: 200 mg/kg polydatin; NAC: N-acetyl-L-cysteine; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; IL-1β: Interleukin 1β; IL-6: Interleukin 6. |
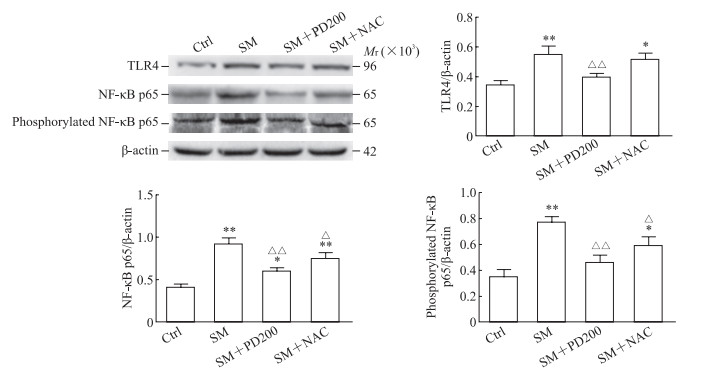
2.5 PD可降低SM染毒小鼠TLR4蛋白、NF-κB p65总蛋白表达及NF-κB p65磷酸化水平
如图 8所示,与Ctrl组相比,SM组小鼠肺组织中TLR4蛋白和NF-κB p65总蛋白表达及NF-κB磷酸化水平升高(P<0.01);与SM组相比,PD或NAC处理后NF-κB p65总蛋白及其磷酸化水平降低(P<0.01或P<0.05),SM+NAC组TLR4蛋白水平下降不明显。结果表明PD可能通过TLR4/NF-κB通路来抑制SM所致的炎症反应。
|
图 8 各组小鼠肺组织中TLR4、NF-κB p65和磷酸化NF-κB p65蛋白的表达 Fig 8 Protein expression of TLR4, NF-κB p65 and phosphorylated NF-κB p65 in lung tissues of mice in each group Western blotting results. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs Ctrl group; △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.01 vs SM group. n=3, x±s. TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; NF-κB: Nuclear factor κB; Ctrl: Control; SM: Sulfur mustard; PD200: 200 mg/kg polydatin; NAC: N-acetyl-L-cysteine. |
3 讨论
在SM暴露模型选择上,研究者们根据研究目的选择了不同的染毒方式[15-20],或将SM制成气溶胶对眼、皮肤和呼吸系统进行直接染毒,或将液态SM直接滴注到气管进行染毒,或通过皮下、腹腔或静脉注射的方式进行染毒,或通过皮肤涂抹进行染毒,以这些方式进行SM染毒均可引起肺损伤。本实验选择皮下注射SM为染毒模型,主要原因是我们认为皮肤暴露可能是SM中毒更主要的威胁方式,因为和佩戴防毒面具相比及时穿戴好全身防护服的难度更大、更难以实现。由于受实验条件限制,仅能实现皮肤涂抹和皮下注射2种方式进行SM皮肤暴露,我们认为皮下注射可以更好地保证动物染毒剂量的一致性。
目前还没有针对SM损伤的特效治疗药物,减少SM所致损伤的最好方法是在2 min内对暴露部位进行去污处理,否则SM被吸收将造成机体损伤。目前对于SM损伤主要采用支持性疗法,如抗生素治疗和皮肤烧伤护理等[21]。NAC也可以通过多种机制减轻SM损伤,具有较好的效果[22-23],因此本研究选用NAC作为阳性对照药物。本实验中首先观察了PD对于SM肺损伤的作用,结果表明PD可以提高SM染毒小鼠的生存率、降低SM染毒小鼠肺W/D比值和BALF蛋白浓度,这与其他PD对肺损伤保护作用的报道[24-25]一致;NAC也可缓解SM所致肺损伤,但整体效果不及PD。
氧化应激是SM肺损伤的起始和关键环节之一,SM及其类似物能与各种细胞成分和低分子量代谢物反应,形成单功能和双功能加合物,最终导致活性氧过量产生、脂质过氧化、抗氧化体系失活等[26-27]。MPO可以将H2O2转化为更高活性的次氯酸;MDA含量高低用以评价细胞质膜的受损程度;GSH和SOD是重要的抗氧化剂,同时也是SM的靶标分子,SM可以使它们耗损从而加重氧化应激水平,导致毒性效应[28-30]。Liu等[31]证明PD可以通过抑制MPO和MDA的水平提高SOD活性,抑制大鼠特发性肺纤维化。Fu等[32]发现PD可以提高谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase, GSH-Px)和SOD的活性,缓解百草枯对人胚胎肺成纤维细胞造成的损伤。在本研究中,SM组小鼠肺组织MDA含量、H2O2含量和MPO活性均高于Ctrl组,而SOD活性、GSH含量均低于Ctrl组;与SM组比较,PD组MDA含量、H2O2含量和MPO活性降低,SOD活性、GSH含量升高。本研究结果表明PD可以通过降低氧化酶水平,提高抗氧化酶活性来抑制SM所致肺损伤的氧化应激反应。
Sirtuin家族是烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸(nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide,NAD+)依赖的组蛋白去乙酰化酶家族,其生物学功能多样。SIRT1作为Sirtuin家族的重要成员之一,主要负责调控机体氧化应激与能量代谢等多条信号通路[33]。Nrf2是抗氧化应激通路中发挥抗氧化作用的关键分子,通常情况下与特异性抑制受体Keap1相结合,大部分以无活性的形式存在于细胞质中;当机体受到刺激时会导致Nrf2与Keap1解离,解离的Nrf2向核转移并激活其下游通路蛋白的表达,以此来调节机体的氧化应激[6]。研究表明,PD可以特异性激活SIRT1蛋白的表达,调节SIRT1/Nrf2通路发挥抗氧化作用[34-35]。Meng等[5]还发现Nrf2与其下游抗氧化蛋白HO-1和NQO1均参与了SM肺损伤的调节。本实验结果表明,SM染毒小鼠肺组织的SIRT1蛋白下调,Nrf2少量入核。PD可提升SM染毒小鼠肺组织中SIRT1蛋白的表达,促进Nrf2入核,上调HO-1和NQO1蛋白的表达,从而减轻SM的损伤作用,提示PD在SM染毒后可能通过调节SIRT1/Nrf2通路改善SM引起的肺损伤。
炎症反应也是SM继发性损伤的重要标志之一。SM引起的肺损伤会导致TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6、IL-8等炎症因子大量释放和炎性细胞的浸润,最终导致炎症反应[36-37]。TLR4是Toll样受体家族的成员之一,主要在免疫和炎症反应中发挥作用[38]。NF-κB是TLR4通路激活炎症反应的下游关键分子,细胞应激可导致TLR4蛋白表达提高,从而激活下游NF-κB通路[39]。NF-κB p65是NF-κB家族的成员之一,其表达和磷酸化可间接反映NF-κB的活性[40-41]。研究表明SM可以增加肺组织中TLR4的表达[42],PD可以通过TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB通路保护脂多糖诱导的急性肺损伤[24]。本实验结果表明SM暴露小鼠肺组织中TLR4、NF-κB p65及磷酸化NF-κB水平升高,PD处理可逆转上述变化,表明PD可能通过调节TLR4/NF-κB通路对SM诱导的肺损伤产生抗炎作用。
综上所述,本研究首次明确了PD对SM肺损伤具有改善作用,初步阐明PD治疗SM肺损伤的机制主要与调节氧化应激、抑制炎症反应有关,为今后PD治疗SM肺损伤的临床研究提供了实验依据。
| [1] |
GHABILI K, AGUTTER P S, GHANEI M, ANSARIN K, PANAHI Y, SHOJA M M. Sulfur mustard toxicity: history, chemistry, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics[J]. Crit Rev Toxicol, 2011, 41: 384-403. DOI:10.3109/10408444.2010.541224 |
| [2] |
SAWYER T W. N-Acetylcysteine as a treatment for sulphur mustard poisoning[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2020, 161: 305-320. DOI:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.09.020 |
| [3] |
TANG F R, LOKE W K. Sulfur mustard and respiratory diseases[J]. Crit Rev Toxicol, 2012, 42: 688-702. DOI:10.3109/10408444.2012.698405 |
| [4] |
AMINI H, SOLAYMANI-DODARAN M, MOUSAVI B, ALAM BELADI S N, SOROUSH M R, ABOLGHASEMI J, et al. Long-term health outcomes among survivors exposed to sulfur mustard in Iran[J/OL]. JAMA Netw Open, 2020, 3: e2028894. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.28894.
|
| [5] |
MENG W Q, PEI Z P, FENG Y W, ZHAO J, CHEN Y C, SHI W W, et al. Neglected role of hydrogen sulfide in sulfur mustard poisoning: Keap1 S-sulfhydration and subsequent Nrf2 pathway activation[J/OL]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 9433. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-09648-6.
|
| [6] |
BEIGI HARCHEGANI A, TAHMASBPOUR E, BORNA H, IMAMY A, GHANEI M, SHAHRIARY A. Free radical production and oxidative stress in lung tissue of patients exposed to sulfur mustard: an overview of cellular and molecular mechanisms[J]. Chem Res Toxicol, 2018, 31: 211-222. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrestox.7b00315 |
| [7] |
MARIAPPAN N, HUSAIN M, ZAFAR I, SINGH V, SMITHSON K G, CROWE D R, et al. Extracellular nucleic acid scavenging rescues rats from sulfur mustard analog-induced lung injury and mortality[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2020, 94: 1321-1334. DOI:10.1007/s00204-020-02699-1 |
| [8] |
MAJD A M M, FAGHIHZADEH S, POURFARZAM S, EGHTEDARDOOST M, JAMALI D, MIRSHARIF E S, et al. Serum and sputum levels of IL-17, IL-21, TNFα and mRNA expression of IL-17 in sulfur mustard lung tissue with long term pulmonary complications (28 years after sulfur mustard exposure)[J/OL]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2019, 76: 105828. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105828.
|
| [9] |
SMITH L C, VENOSA A, GOW A J, LASKIN J D, LASKIN D L. Transcriptional profiling of lung macrophages during pulmonary injury induced by nitrogen mustard[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2020, 1480: 146-154. DOI:10.1111/nyas.14444 |
| [10] |
LI R, LI J Z, HUANG Y J, LI H, YAN S S, LIN J X, et al. Polydatin attenuates diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2018, 14: 1411-1425. DOI:10.7150/ijbs.26086 |
| [11] |
ZHAO X J, YU H W, YANG Y Z, WU W Y, CHEN T Y, JIA K K, et al. Polydatin prevents fructose-induced liver inflammation and lipid deposition through increasing miR-200a to regulate Keap1/Nrf2 pathway[J]. Redox Biol, 2018, 18: 124-137. DOI:10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.002 |
| [12] |
MA Y, GONG X, MO Y L, WU S Z. Polydatin inhibits the oxidative stress-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells by activating the ENOS/SIRT1 pathway[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2016, 37: 1652-1660. DOI:10.3892/ijmm.2016.2554 |
| [13] |
SHU S Y, WANG X Y, LING Z Y, LU Z Y. Effect of polydatin on phospholipase A2 in lung tissues in rats with endotoxic shock[J]. Chin J Traumatol, 2004, 7: 239-243. |
| [14] |
王方岩, 徐正衸, 张晓隆, 王万铁, 郝卯林, 汪洋. 虎杖甙抗肺缺血/再灌注损伤作用及其机制初探[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志, 2008, 24: 62-65. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6834.2008.01.013 |
| [15] |
TRIPATHI R, BALNE P K, SINHA N R, MARTIN L M, KAMIL S, LANDRENEAU J R, et al. A novel topical ophthalmic formulation to mitigate acute mustard gas keratopathy in vivo: a pilot study[J/OL]. Transl Vis Sci Technol, 2020, 9: 6. DOI: 10.1167/tvst.9.12.6.
|
| [16] |
BARILLO D J, CROUTCH C R, BARILLO A R, THOMPSON C K, ROSEMAN J, REID F. Debridement of sulfur mustard skin burns: a comparison of three methods[J]. J Burn Care Res, 2020, 41: 159-166. DOI:10.1093/jbcr/irz140 |
| [17] |
MENG W Q, SUN M X, XU Q Q, CEN J F, CAO Y B, LI Z J, et al. Development of a series of fluorescent probes for the early diagnostic imaging of sulfur mustard poisoning[J]. ACS Sens, 2019, 4: 2794-2801. DOI:10.1021/acssensors.9b01424 |
| [18] |
MENG W Q, ZHANG H, XIAO L, CHEN X T, SUN M X, XU Q Q, et al. Visualization of sulfur mustard in living cells and whole animals with a selective and sensitive turn-on fluorescent probe[J/OL]. Sens Actuat B Chem, 2019, 296: 126678. DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.126678.
|
| [19] |
MENG W Q, CHEN Y C, FENG Y W, ZHANG H, XU Q Q, SUN M X, et al. An off-on fluorescent probe for the detection of mitochondria-specific protein persulfidation[J]. Org Biomol Chem, 2018, 16: 6350-6357. DOI:10.1039/C8OB01608A |
| [20] |
YU D, BEI Y Y, LI Y, HAN W, ZHONG Y X, LIU F, et al. In vitro the differences of inflammatory and oxidative reactions due to sulfur mustard induced acute pulmonary injury underlying intraperitoneal injection and intratracheal instillation in rats[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2017, 47: 78-87. DOI:10.1016/j.intimp.2017.02.013 |
| [21] |
BOBB A J, ARFSTEN D P, JEDERBERG W W. N-acetyl-L-cysteine as prophylaxis against sulfur mustard[J]. Mil Med, 2005, 170: 52-56. DOI:10.7205/MILMED.170.1.52 |
| [22] |
BALSZUWEIT F, MENACHER G, SCHMIDT A, KAI K H, POPP T, WOREK F, et al. Protective effects of the thiol compounds GSH and NAC against sulfur mustard toxicity in a human keratinocyte cell line[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2016, 244: 35-43. DOI:10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.09.002 |
| [23] |
JUGG B, FAIRHALL S, SMITH A, RUTTER S, MANN T, PERROTT R, et al. N-acetyl-L-cysteine protects against inhaled sulfur mustard poisoning in the large swine[J]. Clin Toxicol (Phila), 2013, 51: 216-224. DOI:10.3109/15563650.2013.780208 |
| [24] |
JIANG Q, YI M, GUO Q Q, WANG C M, WANG H M, MENG S S, et al. Protective effects of polydatin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2015, 29: 370-376. DOI:10.1016/j.intimp.2015.10.027 |
| [25] |
LI T, LIU Y T, LI G C, WANG X, ZENG Z H, CAI S M, et al. Polydatin attenuates ipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2014, 7: 8401-8410. |
| [26] |
KAI K H, SZINICZ L. Medical aspects of sulphur mustard poisoning[J]. Toxicology, 2005, 214: 198-209. DOI:10.1016/j.tox.2005.06.014 |
| [27] |
KEHE K, BALSZUWEIT F, STEINRITZ D, THIERMANN H. Molecular toxicology of sulfur mustard-induced cutaneous inflammation and blistering[J]. Toxicology, 2009, 263: 12-19. DOI:10.1016/j.tox.2009.01.019 |
| [28] |
TSENG H W, TSENG H H, LIOU H H, TSAI K W, GER L P, SHIUE Y L. The association between immunoexpression levels of oxidant and antioxidant enzymes and lip squamous cell carcinoma[J]. APMIS, 2018, 126: 403-412. DOI:10.1111/apm.12824 |
| [29] |
RYMASZEWSKI A L, TATE E, YIMBESALU J P, GELMAN A E, JARZEMBOWSKI J A, ZHANG H, et al. The role of neutrophil myeloperoxidase in models of lung tumor development[J]. Cancers, 2014, 6: 1111-1127. DOI:10.3390/cancers6021111 |
| [30] |
SONI A K, BHASKAR A S B, PATHAK U, NAGAR D P, GUPTA A K, KANNAN G M. Pulmonary protective efficacy of S-2[2-aminoethylamino]ethyl phenyl sulphide (DRDE-07) and its analogues against sulfur mustard induced toxicity in mice[J/OL]. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol, 2020, 76: 103333. DOI: 10.1016/j.etap.2020.103333.
|
| [31] |
LIU Y L, CHEN B Y, NIE J, ZHAO G H, ZHUO J Y, YUAN J, et al. Polydatin prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad/ERK signaling pathway[J/OL]. Exp Ther Med, 2020, 20: 62. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9190.
|
| [32] |
FU Y, YAN M, XIE C M, HU J L, ZENG X X, HU Q H. Polydatin relieves paraquat-induced human MRC-5 fibroblast injury through inhibiting the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome[J/OL]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8: 765. DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-4570.
|
| [33] |
SINGH V, UBAID S. Role of silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) in regulating oxidative stress and inflammation[J]. Inflammation, 2020, 43: 1589-1598. DOI:10.1007/s10753-020-01242-9 |
| [34] |
ZENG Z H, CHEN Z Q, XU S Q, SONG R, YANG H, ZHAO K S. Polydatin alleviates small intestine injury during hemorrhagic shock as a SIRT1 activator[J/OL]. Oxidative Med Cell Longev, 2015, 2015: 965961. DOI: 10.1155/2015/965961.
|
| [35] |
LI P Y, WANG X M, ZHAO M, SONG R, ZHAO K S. Polydatin protects hepatocytes against mitochondrial injury in acute severe hemorrhagic shock via SIRT1-SOD2 pathway[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2015, 19: 997-1010. DOI:10.1517/14728222.2015.1054806 |
| [36] |
MALAVIYA R, SUNIL V R, VENOSA A, VAYAS K N, HECK D E, LASKIN J D, et al. Inflammatory mechanisms of pulmonary injury induced by mustards[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2016, 244: 2-7. DOI:10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.10.011 |
| [37] |
WAGNER S, LANG S, POPP T, SCHMIDT A, THIERMANN H, STEINRITZ D, et al. Evaluation of selective and non-selective cyclooxygenase inhibitors on sulfur mustard-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine formation in normal human epidermal keratinocytes[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2019, 312: 109-117. DOI:10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.03.012 |
| [38] |
VERSTREPEN L, BEKAERT T, CHAU T L, TAVERNIER J, CHARIOT A, BEYAERT R. TLR-4, IL-1R and TNF-R signaling to NF-κB: variations on a common theme[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2008, 65: 2964-2978. DOI:10.1007/s00018-008-8064-8 |
| [39] |
ROCHA D M, CALDAS A P, OLIVEIRA L L, BRESSAN J, HERMSDORFF H H. Saturated fatty acids trigger TLR4-mediated inflammatory response[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2016, 244: 211-215. DOI:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.11.015 |
| [40] |
VIATOUR P, MERVILLE M P, BOURS V, CHARIOT A. Phosphorylation of NF-κB and IκB proteins: implications in cancer and inflammation[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2005, 30: 43-52. DOI:10.1016/j.tibs.2004.11.009 |
| [41] |
KARIN M, GRETEN F R. NF-κB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2005, 5: 749-759. |
| [42] |
FENG Y W, XU Q Q, YANG Y Y, SHI W W, MENG W Q, ZHANG H, et al. The therapeutic effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in the acute lung injury induced by sulfur mustard[J/OL]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2019, 10: 90. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-019-1189-x.
|
 2022, Vol. 43
2022, Vol. 43


