2. 上海市杨浦区控江医院神经内科,上海 200433
2. Department of Neurology, Kongjiang Hospital of Yangpu District, Shanghai 200433, China
痴呆是导致老年人群行动障碍和生活依赖的主要原因,全球目前约有5 000万例痴呆患者,并且患病人数以每年约1 000万例的速度持续增加[1]。研究表明,女性痴呆的患病率和发病率约为男性的2倍[2],对女性人群痴呆影响因素的研究尤为重要。年龄对痴呆的发生和发展有重要影响,认知功能损伤多在中年以后开始出现,但常见于老年人[3],因此本研究以老年女性作为研究对象,探究影响老年女性认知功能的因素。
脑白质损伤(white matter lesion,WML)又称为脑白质疏松,影像学表现为MRI T2加权像和液体抑制反转恢复(fluid attenuated inversion recovery,FLAIR)像高信号[4],常被认为是脑功能衰退的征象。研究表明WML和认知功能下降显著相关[5],但是何种程度的WML会引起认知功能损伤尚不清楚,且在已存在WML的患者中哪些因素可能会加剧认知损伤亦未明确。在可能加剧WML患者认知功能障碍的潜在因素中,炎症、激素和维生素D水平等逐渐受到关注。随着年龄的增长,女性体内雌激素水平下降,引起催乳素、卵泡刺激素、黄体生成素水平增高,但目前关于催乳素和黄体生成素水平与WML患者认知功能障碍的关系尚不明确。此外,文献报道目前全球范围约有50%的老年人患有维生素D缺乏症[6],亦有研究表明维生素D水平与认知功能呈正相关[7],但此类研究多局限于将认知功能损伤人群与健康人群进行比较分析,所得结论是否适用于WML老年女性患者仍有待证实。本研究通过分析WML老年女性患者炎症、激素和维生素D水平与其认知损伤的相关性,期望找到此类人群患痴呆的潜在生物学标志物,为早期预防和干预提供借鉴。
1 资料和方法 1.1 研究对象选择2020年1-6月在海军军医大学(第二军医大学)第一附属医院和上海市杨浦区控江医院神经内科门诊及病房就诊的WML老年女性为研究对象。纳入标准:(1)年龄≥ 60岁;(2)头颅MRI检查显示FLAIR像存在脑白质高信号;(3)患者或其家属签署研究入组知情同意书;(4)能够配合完成认知功能量表评估。排除标准:(1)既往有明确病因的脑白质病变者,如感染性、遗传性、中毒、多发性硬化、结节病、特异性脑白质病等脑白质变性疾病者;(2)严重失语,不能配合者;(3)严重心肺功能障碍,不能完成认知功能量表评估及其他检查者;(4)近3个月内服用影响体内维生素D及性激素水平药物的患者;(5)患有神经内分泌肿瘤等。
纳入同期就诊的48例无WML老年女性患者作为对照组,不限制疾病类型。纳入标准:(1)年龄≥ 60岁;(2)头颅MRI检查显示FLAIR像不存在脑白质高信号;(3)患者或其家属签署研究入组知情同意书;(4)能够配合完成认知功能量表评估。排除标准同WML患者入组时的排除标准。本研究经海军军医大学(第二军医大学)第一附属医院和上海市杨浦区控江医院伦理委员会审批。
1.2 一般资料收集使用自制标准化量表收集患者的一般资料,记录年龄、受教育年限、吸烟史、饮酒史、高血压病史、糖尿病史、冠心病史等。根据颈动脉超声检查结果记录颈动脉斑块情况。
1.3 血标本采集及检测采集患者晨起空腹静脉血进行血常规、血生物化学和血激素水平检测, 并用电化学发光法检测血清25-羟维生素D[25-hydroxyvitamin D,25(OH)D]水平。另采集4 mL静脉血,取血清储存于-80 ℃冰箱,在所有样本收集完成后,采用ELISA检测血清炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α的水平。
1.4 认知功能评估使用简易精神状态评估(mini-mental state exam,MMSE)量表对患者的认知功能进行评估。所有评估医师均经过量表标准化评分培训以保证量表评估的相对一致性。痴呆的诊断标准根据受教育程度的不同有所差异,受教育水平为文盲(未受过教育)且MMSE量表评分≤ 17分、受教育水平为小学且MMSE量表评分≤ 20分、受教育水平为初中及以上且MMSE量表评分≤ 24分时诊断为痴呆[8]。
1.5 脑白质病变评分患者行头颅MRI检查,在FLAIR像上利用Fazekas评分对脑白质病变情况进行评分,根据脑室旁高信号和深部白质高信号分布情况计0~3分:脑室旁高信号0分为无病灶,1分为帽状或铅笔样薄层病变,2分为病灶呈光滑的晕圈,3分为不规则的脑室旁高信号、延伸到深部白质;深部白质高信号0分为无病变,1分为点状病变,2分为病变融合,3分为病变大面积融合。脑室旁高信号与深部白质高信号得分之和为该患者的脑白质病变得分,总分为0~6分[9]。根据脑白质病变评分结果,将WML患者分为轻度WML组(1~2分)和中重度WML组(3~6分)。
1.6 统计学处理应用SPSS24.0软件进行统计学分析。呈正态分布的计量资料以x±s表示,组间比较采用独立样本t检验或方差分析;非正态分布的计量资料以中位数(下四分位数,上四分位数)表示,组间比较采用Mann-Whitney检验或Kruskal-Wallis检验。计数资料以例数和百分数表示,组间比较采用χ2检验。根据MMSE量表评分将149例WML患者分为无痴呆组及痴呆组,采用二元logistic回归模型分析包括WML严重程度在内的多个因素与WML患者认知功能的相关性,并绘制ROC曲线进一步研究相关因素对WML患者痴呆的潜在诊断价值。所有检验均为双侧检验,检验水准(α)为0.05。
2 结果 2.1 不同程度WML患者与对照组患者各指标的比较共纳入149例WML患者和48例对照患者,其中海军军医大学(第二军医大学)第一附属医院WML患者98例、对照组13例,上海市杨浦区控江医院WML患者51例、对照组35例。根据Fazekas评分,轻度WML组72例,中重度WML组77例。年龄与老年女性WML有关(P < 0.001),轻度及中重度WML组患者的年龄均大于对照组(P均 < 0.01)。MMSE量表评分在3组间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001),中重度WML组MMSE量表评分低于对照组(P < 0.01),而轻度WML组MMSE量表评分与对照组相比差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。血清25(OH)D水平在3组间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001),轻度及中重度WML组患者的血清25(OH)D水平均低于对照组(P均 < 0.01)。血清炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α水平在3组间差异均有统计学意义(P均 < 0.001),轻度及中重度WML组患者的血清IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α水平均高于对照组(P均<0.01),而轻度与中重度WML组血清IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α水平差异均无统计学意义(P均>0.05)。3组患者的受教育年限、颈动脉斑块、既往病史(糖尿病、冠心病、高血压)、CRP、白细胞计数、降钙素原、血糖、血脂、尿酸、同型半胱氨酸、雌二醇、卵泡刺激素、黄体生成素、催乳素、孕酮、睾酮、皮质醇等差异均无统计学意义(P均>0.05)。见表 1。
|
|
表 1 不同程度WML组及对照组相关变量的比较 Tab 1 Comparison of variables between control group and different degree-WML groups |
2.2 无痴呆组和痴呆组WML患者各指标的比较
与无痴呆组相比,痴呆组WML患者的年龄较大,受教育年限较长,血尿酸、25(OH)D、催乳素和皮质醇水平均较低(P均 < 0.05)。两组颈动脉斑块、CRP、白细胞计数、降钙素原、血糖、血脂、同型半胱氨酸、血清炎症因子(IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α)、雌二醇、卵泡刺激素、黄体生成素、孕酮、睾酮等差异均无统计学意义(P均>0.05)。见表 2。
|
|
表 2 痴呆组和无痴呆组WML患者相关变量的比较 Tab 2 Comparison of variables between dementia and non-dementia WML patients |
2.3 25(OH)D、催乳素水平与WML老年女性痴呆发生的关系
将表 2中差异有统计学意义的变量纳入多因素logistic回归模型,在对年龄进行校正后分析发现,WML严重程度与老年女性患者认知功能障碍相关,WML严重程度是WML老年女性患痴呆的危险因素(OR=2.337,95% CI 1.057~5.167,P=0.036);25(OH)D(OR=0.821,95% CI 0.717~0.940,P=0.004)和催乳素(OR=0.994,95% CI 0.989~1.000,P=0.042)是WML老年女性患者认知功能的保护因素。
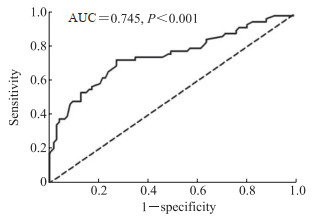
2.4 25(OH)D联合催乳素对WML老年女性痴呆的诊断效力ROC曲线(图 1)分析显示,25(OH)D联合催乳素判断WML老年女性患有痴呆的AUC为0.745(P < 0.001),灵敏度为72.41%,特异度为72.53%,具有中度诊断价值。
|
图 1 25(OH)D联合催乳素诊断WML老年女性患有痴呆的ROC曲线 Fig 1 ROC curve of the combination of 25(OH)D and prolactin for diagnosis of dementia in elderly women with WML 25(OH)D: 25-hydroxyvitamin D; WML: White matter lesion; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; AUC: Area under curve. |
3 讨论
近年来,多项神经影像和临床标志物已被确定可用来预测认知功能损伤或认知功能障碍的进展,在这些标志物中WML与认知损伤的相关性已经得到广泛认可,但是在老年女性群体中何种程度的WML会引起认知损害或痴呆尚不明确。本研究结果表明,与对照组相比,中重度WML老年女性的认知功能下降。文献报道,体内炎症和激素水平与认知功能有关[10]。本研究通过检测患者的血清炎症因子和激素水平发现,与对照组相比,轻度和中重度WML患者的血清炎症因子水平升高;然而除25(OH)D外,WML患者的激素水平与对照组相比无明显变化。为进一步研究影响WML老年女性认知功能的因素,本研究根据认知功能评分将WML老年女性分为痴呆组和无痴呆组,相较于无痴呆组,痴呆组患者的年龄较大、受教育年限较长。研究表明年龄越大痴呆发生风险越高,受教育时间越长痴呆发生风险越低[11]。本研究中痴呆组患者受教育年限长于非痴呆组,这可能是由于痴呆组患者年龄偏大而对受教育程度这一因素的结果产生了干扰。另外,痴呆组催乳素、皮质醇和25(OH)D水平均较无痴呆组下降,但两组间炎症因子水平差异无统计学意义。在校正年龄后,多因素logistic回归分析显示血清催乳素和25(OH)D是WML老年女性患者认知功能的独立保护因素。进一步绘制ROC曲线发现,血清25(OH)D与催乳素联合应用对WML老年女性是否患痴呆有较好的诊断价值。
维生素D是人体必需营养素,血清25(OH)D是反映其水平的金标准。随着社会结构的老龄化,越来越多的人受到维生素D缺乏的影响,近50%的老年人患有维生素D缺乏症[6],维生素D缺乏可能会增加心血管疾病及神经精神疾病的患病风险[12-13],并且维生素D缺乏可能是认知损害发生及轻度认知损害进展为阿尔茨海默病过程中的重要环节[14-15]。研究发现维生素D可能通过抗炎、抗氧化应激及改善神经可塑性等改善认知损害[16-17]。本研究观察到WML严重程度是WML老年女性患痴呆的危险因素,25(OH)D是WML老年女性认知功能的保护因素,并且老年女性WML的严重程度与血清25(OH)D水平呈负相关,提示维生素D在维持老年女性认知功能中发挥重要作用,但其具体作用机制仍不明确。Beydoun等[18]研究了成人血清25(OH)D水平与颅容量和白质完整性之间的关联,在对性别、年龄、种族和经济水平进行分层后发现血清25(OH)D始终与区域特异性白质完整性有关;De la Fuente等[19]研究发现维生素D能够促进少突胶质细胞前体细胞分化,并且在大鼠毒性脱髓鞘模型中可以通过促进少突胶质细胞前体细胞分化帮助髓鞘再生,这些研究结果证明了维生素D在维持白质完整性中的重要作用。一项队列研究结果显示血清25(OH)D水平每增加1 ng/mL,WML体积减少1%[20],表明25(OH)D水平降低是WML的危险因素,提示WML可能介导了由低维生素D引起的认知功能障碍。
催乳素主要由垂体前叶合成和分泌,参与调控血管生成、免疫应答、渗透调节和乳糖生成等生理过程。催乳素的受体在皮质、海马及杏仁核等多个脑区均有分布,提示催乳素可能参与脑内多种生理调控环节。尽管临床证据表明催乳素水平过高可能与认知损害有关[21],但现有的研究结论仍存在一定争议。一方面,催乳素水平和记忆、执行功能之间存在负相关[22],Henry和Sherwin[23]研究也发现高水平的催乳素对执行功能有不利影响。在针对精神病高危人群和患者的多因素线性回归分析中,控制潜在混杂因素后分析发现催乳素水平增加与早期精神病患者的处理速度受损有关[24]。另一方面,催乳素缺乏的成年小鼠海马产生的神经球数量减少了大约80%,标准化的行为测试结果提示缺乏催乳素导致其学习和记忆能力受损,并且将重组催乳素直接注入海马可以改善这种行为缺损,表明成年小鼠海马中催乳素缺乏可能与学习和记忆受损有关[25]。此外,在体外培养的原代海马神经元中,催乳素可以对抗神经兴奋毒性而发挥神经保护作用[26]。总的来说,在现有的研究中,由于实验设计及研究对象的差异,催乳素与认知功能的关系并未被阐明,本研究结果提示催乳素对于WML老年女性的认知功能有保护作用。
本研究通过分析老年女性WML患者血清炎症因子、激素和维生素D水平与痴呆的相关性发现,血清25(OH)D和催乳素是老年女性WML患者认知功能的保护因素,两者联合应用对老年女性WML患者痴呆有潜在的诊断价值。本研究将研究对象限定于老年女性,消除了性别对结果的影响,但是作为横断面研究,结果仅能反映25(OH)D和催乳素与WML及认知功能障碍的关联性,今后仍需要开展队列研究进一步明确这2个指标在老年女性WML患者认知功能障碍发展过程的因果关系。
| [1] |
World Health Organization. Global action plan on the public health response to dementia 2017-2025[EB/OL]. (2017-12-08)[ 2022-01-21]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241513487.
|
| [2] |
GBD 2019 Dementia Forecasting Collaborators. Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J/OL]. Lancet Public Health, 2022, 7: e105-e125. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-2667(21)00249-8.
|
| [3] |
AARTSEN M J, SMITS C H, VAN TILBURG T, KNIPSCHEER K C, DEEG D J. Activity in older adults: cause or consequence of cognitive functioning? A longitudinal study on everyday activities and cognitive performance in older adults[J]. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci, 2002, 57: 153-162. DOI:10.1093/geronb/57.2.P153 |
| [4] |
KLOPPENBORG R P, NEDERKOORN P J, GEERLINGS M I, VAN DEN BERG E. Presence and progression of white matter hyperintensities and cognition: a meta-analysis[J]. Neurology, 2014, 82: 2127-2138. DOI:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000505 |
| [5] |
REIJMER Y D, SCHULTZ A P, LEEMANS A, O'SULLIVAN M J, GUROL M E, SPERLING R, et al. Decoupling of structural and functional brain connectivity in older adults with white matter hyperintensities[J]. NeuroImage, 2015, 117: 222-229. DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.05.054 |
| [6] |
HOSSEIN-NEZHAD A, HOLICK M F. Vitamin D for health: a global perspective[J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2013, 88: 720-755. DOI:10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.05.011 |
| [7] |
YANG T, WANG H L, XIONG Y, CHEN C, DUAN K R, JIA J Y, et al. Vitamin D supplementation improves cognitive function through reducing oxidative stress regulated by telomere length in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a 12-month randomized controlled trial[J]. J Alzheimer's Dis, 2020, 78: 1509-1518. DOI:10.3233/JAD-200926 |
| [8] |
LI H Z, JIA J P, YANG Z Q. Mini-mental state examination in elderly Chinese: a population-based normative study[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2016, 53: 487-496. DOI:10.3233/JAD-160119 |
| [9] |
ZHU S G, QIAN S F, XU T, PENG H, DONG R G, WANG D J, et al. White matter hyperintensity, immediate antihypertensive treatment, and functional outcome after acute ischemic stroke[J]. Stroke, 2020, 51: 1608-1612. DOI:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.028841 |
| [10] |
AU A, FEHER A, MCPHEE L, JESSA A, OH S, EINSTEIN G. Estrogens, inflammation and cognition[J]. Front Neuroendocrinol, 2016, 40: 87-100. DOI:10.1016/j.yfrne.2016.01.002 |
| [11] |
SUBRAMANIAM M, CHONG S A, VAINGANKAR J A, ABDIN E, CHUA B Y, CHUA H C, et al. Prevalence of dementia in people aged 60 years and above: results from the WiSE study[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2015, 45: 1127-1138. DOI:10.3233/JAD-142769 |
| [12] |
P I L Z S, V E R H E Y E N N, G R Ü B L E R M R, TOMASCHITZ A, MÄRZ W. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease prevention[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2016, 13: 404-417. DOI:10.1038/nrcardio.2016.73 |
| [13] |
HÄUSLER D, TORKE S, PEELEN E, BERTSCH T, DJUKIC M, NAU R, et al. High dose vitamin D exacerbates central nervous system autoimmunity by raising T-cell excitatory calcium[J]. Brain, 2019, 142: 2737-2755. DOI:10.1093/brain/awz190 |
| [14] |
ANNWEILER C, MILEA D, WHITSON H E, CHENG C Y, WONG T Y, IKRAM M K, et al. Vitamin D insufficiency and cognitive impairment in Asians: a multi-ethnic population-based study and meta-analysis[J]. J Intern Med, 2016, 280: 300-311. DOI:10.1111/joim.12491 |
| [15] |
FEART C, HELMER C, MERLE B, HERRMANN F R, ANNWEILER C, DARTIGUES J F, et al. Associations of lower vitamin D concentrations with cognitive decline and long-term risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease in older adults[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2017, 13: 1207-1216. DOI:10.1016/j.jalz.2017.03.003 |
| [16] |
AL-AMIN M, BRADFORD D, SULLIVAN R K P, KURNIAWAN N D, MOON Y, HAN S H, et al. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with reduced hippocampal volume and disrupted structural connectivity in patients with mild cognitive impairment[J]. Hum Brain Mapp, 2019, 40: 394-406. DOI:10.1002/hbm.24380 |
| [17] |
MEHRI N, HADDADI R, GANJI M, SHAHIDI S, SOLEIMANI ASL S, TAHERI AZANDARIANI M, et al. Effects of vitamin D in an animal model of Alzheimer's disease: behavioral assessment with biochemical investigation of hippocampus and serum[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2020, 35: 263-274. DOI:10.1007/s11011-019-00529-7 |
| [18] |
BEYDOUN M A, SHAKED D, HOSSAIN S, BEYDOUN H A, KATZEL L I, DAVATZIKOS C, et al. Vitamin D, folate, and cobalamin serum concentrations are related to brain volume and white matter integrity in urban adults[J/OL]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2020, 12: 140. DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.00140.
|
| [19] |
DE LA FUENTE A G, ERREA O, VAN WIJNGAARDEN P, GONZALEZ G A, KERNINON C, JARJOUR A A, et al. Vitamin D receptor-retinoid X receptor heterodimer signaling regulates oligodendrocyte progenitor cell differentiation[J]. J Cell Biol, 2015, 211: 975-985. DOI:10.1083/jcb.201505119 |
| [20] |
SCHRAMM S, SCHLIEPHAKE L, HIMPFEN H, CASPERS S, ERBEL R, JÖCKEL K H, et al. Vitamin D and white matter hyperintensities: results of the populationbased Heinz Nixdorf Recall Study and 1000BRAINS[J]. Eur J Neurol, 2021, 28: 1849-1858. DOI:10.1111/ene.14810 |
| [21] |
YAO S, SONG J, GAO J F, LIN P, YANG M, ZAHID K R, et al. Cognitive function and serum hormone levels are associated with gray matter volume decline in female patients with prolactinomas[J/OL]. Front Neurol, 2017, 8: 742. DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2017.0074210.3389/fneur.2017.00742.
|
| [22] |
CASTANHO T C, MOREIRA P S, PORTUGALNUNES C, NOVAIS A, COSTA P S, PALHA J A, et al. The role of sex and sex-related hormones in cognition, mood and well-being in older men and women[J]. Biol Psychol, 2014, 103: 158-166. DOI:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2014.08.015 |
| [23] |
HENRY J F, SHERWIN B B. Hormones and cognitive functioning during late pregnancy and postpartum: a longitudinal study[J]. Behav Neurosci, 2012, 126: 73-85. DOI:10.1037/a0025540 |
| [24] |
MONTALVO I, GUTIÉRREZ-ZOTES A, CREUS M, MONSENY R, ORTEGA L, FRANCH J, et al. Increased prolactin levels are associated with impaired processing speed in subjects with early psychosis[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2014, 9: e89428. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089428.
|
| [25] |
WALKER T L, VUKOVIC J, KOUDIJS M M, BLACKMORE D G, MACKAY E W, SYKES A M, et al. Prolactin stimulates precursor cells in the adult mouse hippocampus[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2012, 7: e44371. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044371.
|
| [26] |
VERGARA-CASTAÑEDA E, GRATTAN D R, PASANTES-MORALES H, PÉREZ-DOMÍNGUEZ M, CABRERA-REYES E A, MORALES T, et al. Prolactin mediates neuroprotection against excitotoxicity in primary cell cultures of hippocampal neurons via its receptor[J]. Brain Res, 2016, 1636: 193-199. DOI:10.1016/j.brainres.2016.02.011 |
 2022, Vol. 43
2022, Vol. 43


