肾透明细胞肉瘤(clear cell sarcoma of the kidney,CCSK)多在3岁以下儿童中发病,是儿童肾癌中第二大常见肿瘤[1-2]。单纯的CCSK在成人肾癌中所占比例较低,部分成人典型肾癌如肾透明细胞癌、乳头状肾细胞癌及嫌色细胞癌也可发生肉瘤样变[3]。尽管CCSK发病率较肾母细胞瘤低,但起病隐匿,鉴别诊断困难,患者常在诊断初期已发生局部进展或远处转移[4-6]。CCSK的临床典型表现与肾母细胞瘤类似,以腹胀、腹痛、腹部肿块及血尿多见,呕吐、摄食量骤减、发热、便秘及高血压等症状少见[7]。CCSK的治疗方案以手术联合放化疗为主,多数患者预后较差[1, 3],目前缺乏针对CCSK的特异性诊疗标志物。此外,CCSK的治疗方式较为单一,缺乏特异性药物,发生肿瘤局部进展或转移的患者预后极差,因此临床亟待探索新的治疗手段。近年来免疫治疗的兴起为肿瘤治疗提供了新方向,该治疗方案在多数肿瘤中发挥了显著疗效,但对CCSK的疗效尚未见报道。本研究通过对基因表达汇编(Gene Expression Omnibus,GEO)数据库中GSE49972及GSE2712数据集的联合分析,鉴定CCSK特异性标志物及信号通路,以期为CCSK的早期诊断提供线索;并进一步通过对CCSK中免疫细胞浸润程度的评估,分析CCSK肿瘤微环境组成,为CCSK治疗提供新思路。
1 材料和方法 1.1 数据来源及处理从GEO数据库中下载GSE49972数据集(Illumina HumanHT-12 V4.0芯片,由Jenny等提供,包括22个CCSK组织样本和4个正常胚肾组织样本)和GSE2712数据集(Affymetrix Human Genome U133A芯片,由Elizabeth等提供,包括18个CCSK组织样本及3个正常胚肾组织样本),通过R 3.6.3软件limma包对数据进行背景校正,数据经过log2转化[8-9]后用于后续分析。
1.2 差异表达基因分析利用limma包对GSE49972及GSE2712数据集进行分析,采用秩和检验分析CCSK组织和正常胚肾组织之间的基因水平差异(|log2差异倍数|>1且P<0.01),获取2个数据集的差异表达基因,然后对差异表达基因取交集,用于后续的功能富集分析及蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络构建。
1.3 功能与通路分析利用R 3.6.3软件clusterProfiler包对差异表达基因进行基因本体(Gene Ontology,GO)功能分析,基于京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,KEGG)对CCSK相关通路进行分析[10-11]。
1.4 蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络构建将得到的差异表达基因导入STRING蛋白数据库,调整关联度(>0.8)获取关联度较高的差异表达基因,再通过Cytoscape软件中CytoHubba插件的加权算法鉴定核心蛋白网络[12]。
1.5 免疫细胞浸润分析利用R 3.6.3软件GSVA包对GSE49972及GSE2712数据集中的CCSK组织和正常胚肾组织进行免疫细胞浸润分析。用R 3.6.3软件pheatmap包绘制免疫细胞浸润热图,用ggplot2包分析两组间免疫浸润细胞差异,用corplot包绘制免疫细胞的关联图。
1.6 统计学处理应用SPSS 22.0软件进行统计学分析,两组间差异分析采用独立样本t检验,免疫浸润细胞之间的关系采用Spearman秩相关分析。检验水准(α)为0.05。
2 结果 2.1 差异表达基因分析结果CCSK组织和正常胚肾组织之间的差异表达基因由GSE49972数据集分析可得1 793个,由GSE2712数据集分析可得1 565个。对这2个数据集差异表达基因取交集,共获得740个共同差异表达基因(300个上调基因、440个下调基因)进行后续分析。
2.2 差异表达基因GO功能及KEGG通路富集分析通过clusterProfiler包对740个差异表达基因进行GO功能分析,分别注释到生物学过程、细胞成分及分子功能3个模块,发现差异表达基因集中在细胞外结构组织、细胞外胶原基质、细胞黏附分子结合等功能模块上。KEGG通路分析结果显示,差异表达基因参与的主要信号通路富集于PI3K/Akt信号通路、肿瘤转录失调、黏着斑、钙离子信号通路及肿瘤蛋白多糖等(图 1)。
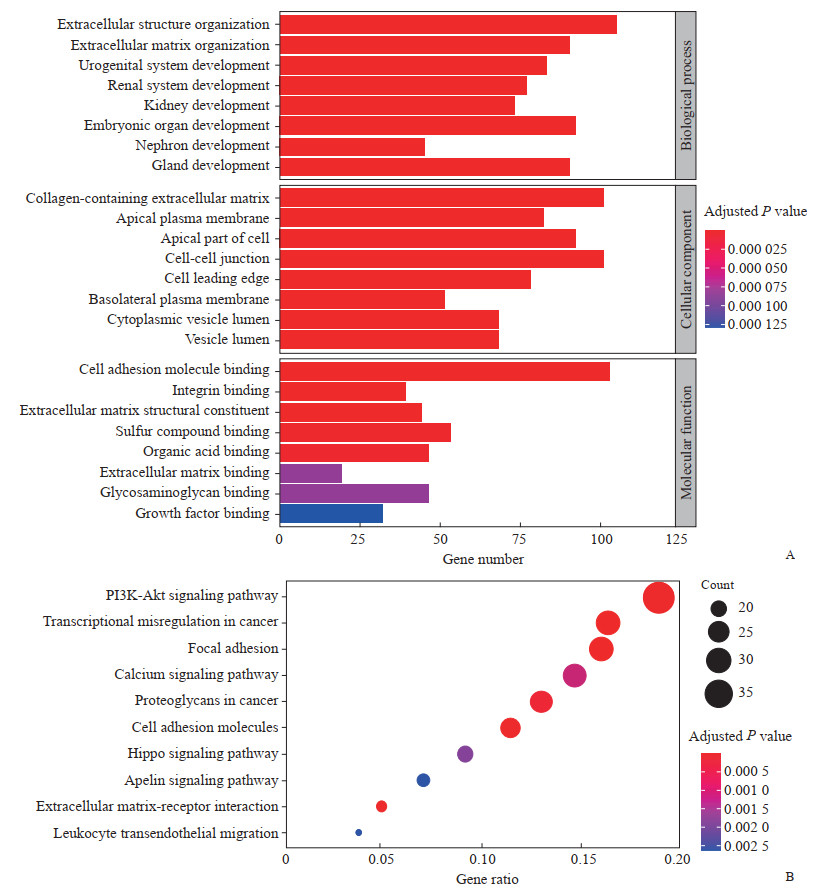
|
图 1 740个差异表达基因的GO功能及KEGG通路富集分析 Fig 1 GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of 740 differentially expressed genes A: GO enrichment analysis; B: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. GO: Gene Ontology; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; PI3K/Akt: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B. |
2.3 差异表达基因蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络分析
将差异表达基因导入string蛋白数据库,选择关联度>0.8的互作蛋白,将筛选后的蛋白导入Cytoscape软件中进行重注释,得到蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络图(图 2A)。使用CytoHubba插件对蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络进行子网络提取,获得核心模块(图 2B),其中密封蛋白家族[claudin(CLDN)10、CLDN3、CLDN8、CLDN11]和钙黏着蛋白家族[cadherin(CDH)1、CDH2,CDH4]在CCSK组织中权重较大,红色到黄色代表蛋白在相互作用网络中的权重排序(红色权重值最大,黄色权重值最小)。
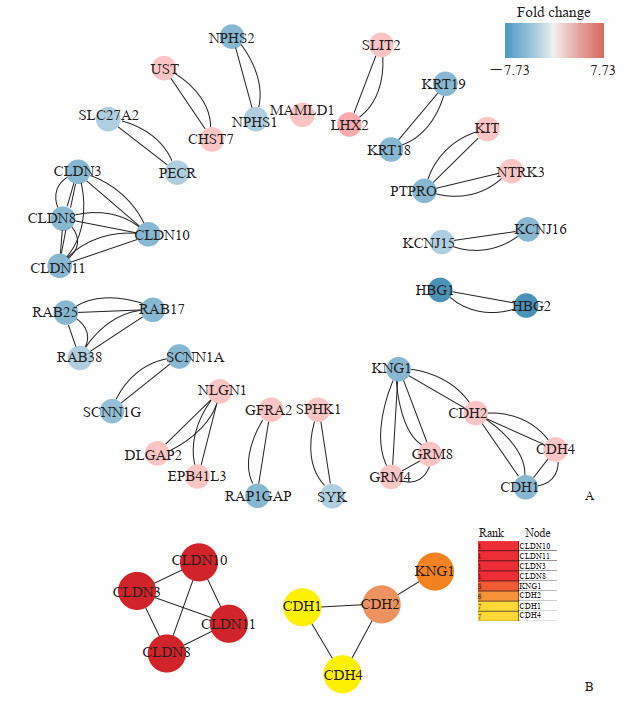
|
图 2 蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络图及核心模块 Fig 2 Protein-protein interaction network diagram and core modules A: Protein-protein interaction network diagram of differentially expressed genes. Circles represent genes and lines represent associations between genes. Red represents up-regulated genes and blue represents down-regulated genes. B: In the core modules of protein-protein interaction network, claudin family and cadherin family have large weighted values, and the order of weighted values is shown on the right (the red weighted value is the largest, and the yellow weighted value is the smallest). |
2.4 免疫细胞浸润分析
利用GSVA包对GSE49972数据集中的组织样本进行免疫细胞浸润评估,共涉及28种免疫细胞(活化B细胞、活化CD4 T细胞、活化CD8 T细胞、活化树突状细胞、CD56bright自然杀伤细胞、CD56dim自然杀伤细胞、中心记忆CD4 T细胞、中心记忆CD8 T细胞、效应记忆CD4 T细胞、效应记忆CD8 T细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞、γδ T细胞、幼稚B细胞、未成熟树突状细胞、巨噬细胞、肥大细胞、骨髓来源抑制性细胞、记忆B细胞、单核细胞、自然杀伤细胞、自然杀伤T细胞、中性粒细胞、浆细胞样树突状细胞、调节性T细胞、滤泡辅助性T细胞、1型辅助性T细胞、17型辅助性T细胞、2型辅助性T细胞)。结果发现多数免疫细胞在CCSK组织中浸润程度较低(图 3A),其中活化B细胞、活化树突状细胞、CD56dim自然杀伤细胞、中心记忆CD8 T细胞、效应记忆CD8 T细胞、γδ T细胞、未成熟树突状细胞、巨噬细胞、肥大细胞、骨髓来源抑制性细胞、自然杀伤细胞、自然杀伤T细胞、中性粒细胞、调节性T细胞、滤泡辅助性T细胞、1型辅助性T细胞、17型辅助性T细胞在CCSK组织中下调(P<0.05,P<0.01),而活化CD4 T细胞和效应记忆CD4 T细胞在CCSK组织中上调(P<0.05,P<0.01),见图 3B。
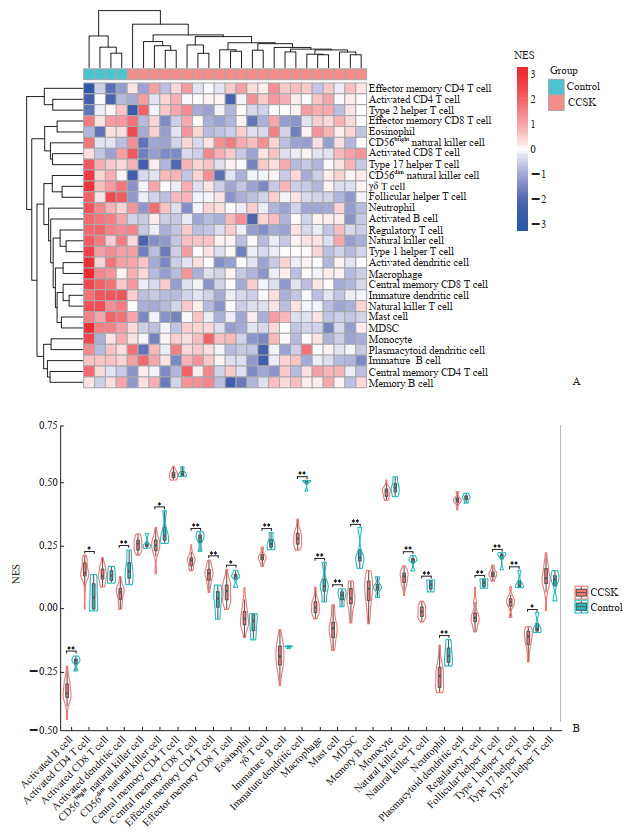
|
图 3 CCSK组织与正常胚肾组织间免疫细胞浸润热图及浸润差异(基于GSE49972数据集) Fig 3 Heatmap and infiltration difference of immune cells between CCSK and normal embryonic kidney tissues (based on GSE49972 dataset) *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. A: Heatmap of immune cells between CCSK and normal embryonic kidney tissues (control); B: Difference of immune cell infiltration between CCSK (n=22) and normal embryonic kidney tissues (n=4). CCSK: Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney; MDSC: Myeloid-derived suppressor cell; NES: Normalized enrichment score. |
对免疫浸润细胞进行相关性分析,结果发现在CCSK组织中活化CD4 T细胞、效应记忆CD4 T细胞及2型辅助性T细胞与多数免疫浸润细胞呈负相关关系(P均<0.01)。见图 4。
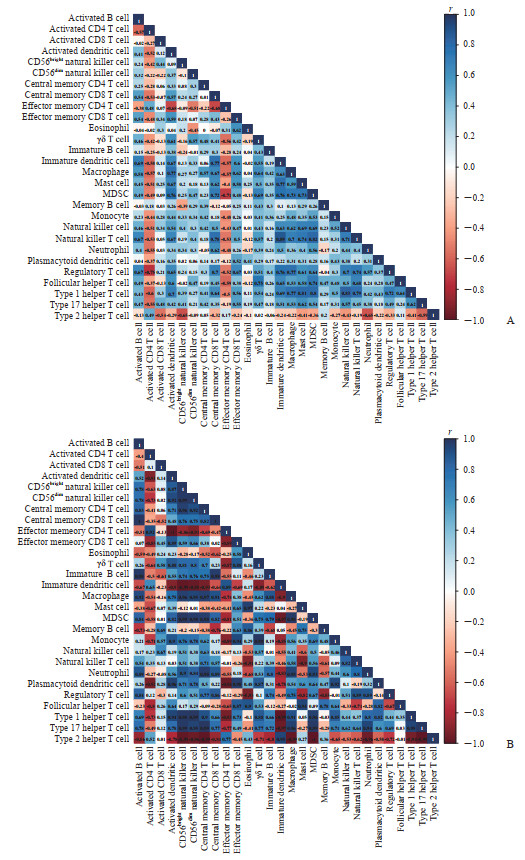
|
图 4 CCSK和正常胚肾组织中28种免疫细胞的相关性(基于GSE49972数据集) Fig 4 Correlation of 28 immune cells in CCSK or normal embryonic kidney tissues (based on GSE49972 dataset) A: Correlation matrix of immune cells in CCSK tissues; B: Correlation matrix of immune cells in normal embryonic kidney tissues. Red represents negative correlation and blue represents positive correlation. The darker the color is, the more significant the correlation is. CCSK: Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney; MDSC: Myeloid-derived suppressor cell. |
3 讨论
目前CCSK的治疗以手术联合放化疗为主,但疗效欠佳,且毒副作用明显[1, 4]。发生肿瘤转移的患者5年生存率极低,常见的转移部位包括颅脑、骨及肺,因此临床亟待CCSK特异性治疗方案[7, 13]。过去10年,免疫治疗在肾癌治疗研究中取得重大进展,免疫检查点抑制剂作为晚期肾癌的二线治疗方案于2015年获得批准,自此肾癌治疗迈入免疫治疗时代[14-16]。有研究发现免疫治疗联合靶向药物可显著提升晚期肾癌患者的总体生存期,抗血管生成药物(如阿昔替尼、舒尼替尼)和免疫检查点抑制剂联用可促进两类药物各自的疗效[17-18]。CCSK缺乏特异性标志物及治疗靶标,免疫治疗或许有望成为该类患者的治疗手段。
随着测序技术及生物信息学的进步,对既往芯片数据进行整合挖掘成为探究CCSK的发病机制、推测可能的诊疗标志物的重要手段。本研究对GEO数据库中数量较多的两组CCSK芯片数据集GSE49972及GSE2712进行整合分析,共筛选出740个差异表达基因。GO功能分析发现差异表达基因集中富集在细胞外结构组织、细胞外胶原基质、细胞黏附分子结合等功能模块上,可见细胞外成分参与了CCSK的疾病进程,提示破坏细胞外基质成分可能有助于提高CCSK疗效。KEGG通路分析表明差异表达基因参与的主要信号通路富集于PI3K/Akt信号通路、肿瘤转录失调、黏着斑、钙离子信号通路及肿瘤蛋白多糖等,其中PI3K/Akt-哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)信号通路参与调控恶性肿瘤细胞的增殖、存活、代谢及相关基因的转录、翻译等过程,靶向该通路的经典药物(如西罗莫司、依维莫司)已在肾透明细胞癌的治疗中取得一定效果,但存在一定毒副作用且收益人群特征有限[19-21]。PI3K/Akt-mTOR信号通路抑制剂对CCSK的疗效尚未见报道,本研究发现该通路参与CCSK疾病进展,提示靶向该通路可能使CCSK患者获益。通过蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络分析,本研究鉴定出在众多差异表达基因中起关键作用的核心基因,即CLDN蛋白家族(CLDN10、CLDN3、CLDN8、CLDN11)和CDH蛋白家族(CDH1、CDH2、CDH4)基因,这些基因可能在CCSK的发生、发展中发挥重要作用。CLDN蛋白家族参与多种肿瘤进程,尤其是肿瘤转移[22]。细胞间黏附结构及功能改变与肿瘤远处转移密切相关,同时细胞间黏附结构及细胞极性的破坏将促进肿瘤上皮细胞发生上皮-间质转化[23-25]。有研究表明CLDN蛋白家族在消化道肿瘤及乳腺癌中低表达,破坏组织渗透屏障,使细胞间黏附力降低,导致肿瘤转移[26-28]。本研究发现CLDN蛋白家族在CCSK组织中显著下调,符合该肿瘤易发生远处转移的临床特征;同时分析结果显示该蛋白家族是蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络的核心模块,可推测CLDN蛋白家族参与了CCSK的发生、发展及远处转移,该蛋白家族有望成为CCSK术前诊断及术后监测的新型分子标志物。CDH蛋白家族可发挥功能性钙离子依赖性黏附分子作用,通过连接邻近细胞在疾病中发挥作用,该家族蛋白功能的紊乱可促进肿瘤细胞局部浸润及远处转移[29-30]。有研究发现CDH17可作为消化系统肿瘤(包括胃癌、肝癌及结直肠癌等)的诊断及预后标志物[31-33]。本研究发现CDH蛋白家族在CCSK和正常胚肾组织间存在差异表达,推测该蛋白家族成员可能参与了CCSK的进展及转移。
鉴于CCSK治疗的靶向药物较少,尤其是对局部进展或发生转移的CCSK患者,当前的治疗手段效果不佳,患者预后较差,新兴的免疫治疗方法可能有助于CCSK的治疗,因此本研究对CCSK免疫细胞浸润情况进行了分析。本研究共涉及28种免疫细胞,其中活化CD4 T细胞和效应记忆CD4 T细胞在CCSK组织中上调,活化B细胞、活化树突状细胞、CD56dim自然杀伤细胞、中心记忆CD8 T细胞、效应记忆CD8 T细胞、γδ T细胞、未成熟树突状细胞、巨噬细胞、肥大细胞、骨髓来源抑制性细胞、自然杀伤细胞、自然杀伤T细胞、中性粒细胞、调节性T细胞、滤泡辅助性T细胞、1型辅助性T细胞、17型辅助性T细胞在CCSK组织中下调,提示CCSK属于“冷肿瘤”,即免疫细胞浸润程度较低,符合既往认为肾癌属于低负荷突变类肿瘤的发现。这一结果提示单一的免疫治疗对该类患者的效果可能并不显著。针对低负荷突变的“冷肿瘤”,有研究证实靶向激活特定激酶,可使“冷肿瘤”转为“热肿瘤”,从而增强免疫检查点抑制剂抗体的疗效[34-35]。Noman等[36]通过在“冷肿瘤”中抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶催化亚基3型(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 3,PIK3C3)激酶活性,促进多种免疫细胞在肿瘤组织中的浸润和肿瘤炎性环境的形成,使免疫检查点抑制剂对多种“冷肿瘤”发挥杀伤效果。
综上所述,本研究通过GEO数据挖掘,鉴定CCSK中核心基因及特异信号通路,发现CLDN蛋白家族及CDH蛋白家族显著下调,结合KEGG通路富集分析结果推测黏着斑及钙离子依赖通路在CCSK疾病进程中发挥作用,上述基因及信号通路可作为CCSK的潜在治疗靶点。通过分析CCSK组织中免疫细胞浸润情况,发现多数免疫细胞在CCSK组织中的浸润程度极低(包括CD8 T细胞、自然杀伤T细胞等抗肿瘤免疫细胞),但CD4 T细胞浸润程度较高,提示CCSK免疫微环境中免疫起始阶段正常,但缺乏有效的肿瘤抗原递呈,未能募集相关效应T细胞。免疫检查点与特定激酶抑制剂的联合应用可能会提高效应T细胞的浸润程度,进而提高免疫治疗疗效。
| [1] |
宋宏程, 黄澄如, 孙宁, 张潍平, 何乐建, 白继武, 等. 儿童肾细胞癌的临床、病理特点及预后分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2013, 34: 810-813. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2013.11.003 |
| [2] |
CAI J B, HE M, WANG F L, XIONG J N, MAO J Q, GUAN Z H, et al. Paraplegia after transcatheter artery chemoembolization in a child with clear cell sarcoma of the kidney: a case report[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2020, 8: 2332-2338. DOI:10.12998/wjcc.v8.i11.2332 |
| [3] |
ZHANG Y, LI J, WANG Y. Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney in a 62-year-old patient presenting with generalized pruritus[J/OL]. BMC Cancer, 2019, 19: 1034. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-6212-1.
|
| [4] |
HADLEY G P, SHEIK-GAFOOR M H. Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney in children: experience in a developing country[J]. Pediatr Surg Int, 2010, 26: 345-348. DOI:10.1007/s00383-010-2554-0 |
| [5] |
TREECE A L. Pediatric renal tumors: updates in the molecular era[J]. Surg Pathol Clin, 2020, 13: 695-718. DOI:10.1016/j.path.2020.08.003 |
| [6] |
夏宇, 黄滔, 徐丹枫, 杨安卿, 楚晨龙, 赵晨晖, 等. 转移型肉瘤样肾癌的生存分析研究及治疗进展[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 35: 984-990. |
| [7] |
BALAREZO F S, JOSHI V V. Clear cell sarcoma of the pediatric kidney: detailed description and analysis of variant histologic patterns of a tumor with many faces[J]. Adv Anat Pathol, 2001, 8: 98-108. DOI:10.1097/00125480-200103000-00006 |
| [8] |
KARLSSON J, HOLMQUIST MENGELBIER L, CIORNEI C D, NARANJO A, O'SULLIVAN M J, GISSELSSON D. Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney demonstrates an embryonic signature indicative of a primitive nephrogenic origin[J]. Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 2014, 53: 381-391. DOI:10.1002/gcc.22149 |
| [9] |
CUTCLIFFE C, KERSEY D, HUANG C C, ZENG Y, WALTERHOUSE D, PERLMAN E J, et al. Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney: up-regulation of neural markers with activation of the sonic hedgehog and Akt pathways[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2005, 11: 7986-7994. DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1354 |
| [10] |
YU G C, WANG L G, HAN Y Y, HE Q Y. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters[J]. Omics, 2012, 16: 284-287. DOI:10.1089/omi.2011.0118 |
| [11] |
KANEHISA M, FURUMICHI M, TANABE M, SATO Y, MORISHIMA K. KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(D1): D353-D361. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkw1092 |
| [12] |
SMOOT M E, ONO K, RUSCHEINSKI J, WANG P L, IDEKER T. Cytoscape 2.8:new features for data integration and network visualization[J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27: 431-432. DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btq675 |
| [13] |
RADULESCU V C, GERRARD M, MOERTEL C, GRUNDY P E, MATHIAS L, FEUSNER J, et al. Treatment of recurrent clear cell sarcoma of the kidney with brain metastasis[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2008, 50: 246-249. DOI:10.1002/pbc.21131 |
| [14] |
HSIEH J J, PURDUE M P, SIGNORETTI S, SWANTON C, ALBIGES L, SCHMIDINGER M, et al. Renal cell carcinoma[J/OL]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2017, 3: 17009. DOI: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.9.
|
| [15] |
KUMAR R, KAPOOR A. Current management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: evolving new therapies[J]. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care, 2017, 11: 231-237. DOI:10.1097/SPC.0000000000000277 |
| [16] |
BEDKE J, GAULER T, GRÜNWALD V, HEGELE A, HERRMANN E, HINZ S, et al. Systemic therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma[J]. World J Urol, 2017, 35: 179-188. DOI:10.1007/s00345-016-1868-5 |
| [17] |
MOTZER R J, PENKOV K, HAANEN J, RINI B, ALBIGES L, CAMPBELL M T, et al. Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380: 1103-1115. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa1816047 |
| [18] |
MCDERMOTT D F, HUSENI M A, ATKINS M B, MOTZER R J, RINI B I, ESCUDIER B, et al. Clinical activity and molecular correlates of response to atezolizumab alone or in combination with bevacizumab versus sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Nat Med, 2018, 24: 749-757. DOI:10.1038/s41591-018-0053-3 |
| [19] |
GUO H, GERMAN P, BAI S, BARNES S, GUO W, QI X, et al. The PI3K/AKT pathway and renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Genet Genomics, 2015, 42: 343-353. DOI:10.1016/j.jgg.2015.03.003 |
| [20] |
KAJIWARA M, MASUDA S. Role of mTOR inhibitors in kidney disease[J/OL]. Int J Mol Sci, 2016, 17: 975. DOI: 10.3390/ijms17060975.
|
| [21] |
SÁNCHEZ-GASTALDO A, KEMPF E, GONZÁLEZ DEL ALBA A, DURAN I. Systemic treatment of renal cell cancer: a comprehensive review[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2017, 60: 77-89. DOI:10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.08.010 |
| [22] |
WINOGRAD-KATZ S E, FÄSSLER R, GEIGER B, LEGATE K R. The integrin adhesome: from genes and proteins to human disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2014, 15: 273-288. DOI:10.1038/nrm3769 |
| [23] |
SUN Z, TSENG H Y, TAN S, SENGER F, KURZAWA L, DEDDEN D, et al. Kank2 activates talin, reduces force transduction across integrins and induces central adhesion formation[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2016, 18: 941-953. DOI:10.1038/ncb3402 |
| [24] |
HUANG R, ROFSTAD E K. Integrins as therapeutic targets in the organ-specific metastasis of human malignant melanoma[J/OL]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37: 92. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-018-0763-x.
|
| [25] |
ERSHAID N, SHARON Y, DORON H, RAZ Y, SHANI O, COHEN N, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome in fibroblasts links tissue damage with inflammation in breast cancer progression and metastasis[J/OL]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10: 4375. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-12370-8.
|
| [26] |
TORRES-MARTÍNEZ A C, GALLARDO-VERA J F, LARA-HOLGUIN A N, MONTAÑO L F, RENDÓN-HUERTA E P. Claudin-6 enhances cell invasiveness through claudin-1 in AGS human adenocarcinoma gastric cancer cells[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2017, 350: 226-235. DOI:10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.11.025 |
| [27] |
MATSUDA Y, SEMBA S, UEDA J, FUKU T, HASUO T, CHIBA H, et al. Gastric and intestinal claudin expression at the invasive front of gastric carcinoma[J]. Cancer Sci, 2007, 98: 1014-1019. DOI:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00490.x |
| [28] |
LUO Y, KISHI S, SASAKI T, OHMORI H, FUJIWARA-TANI R, MORI S, et al. Targeting claudin-4 enhances chemosensitivity in breast cancer[J]. Cancer Sci, 2020, 111: 1840-1850. DOI:10.1111/cas.14361 |
| [29] |
VAN ROY F. Beyond E-cadherin: roles of other cadherin superfamily members in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2014, 14: 121-134. DOI:10.1038/nrc3647 |
| [30] |
CANEL M, SERRELS A, FRAME M C, BRUNTON V G. E-cadherin-integrin crosstalk in cancer invasion and metastasis[J]. J Cell Sci, 2013, 126(Pt 2): 393-401. |
| [31] |
ALTREE-TACHA D, TYRRELL J, HAAS T. CDH17 is a more sensitive marker for gastric adenocarcinoma than CK20 and CDX2[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2017, 141: 144-150. DOI:10.5858/arpa.2015-0404-OA |
| [32] |
LIU X J, HUANG Y, YUAN H, QI X Q, MANJUNATH Y, AVELLA D, et al. Disruption of oncogenic liver-intestine cadherin (CDH17) drives apoptotic pancreatic cancer death[J]. Cancer Lett, 2019, 454: 204-214. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2019.04.022 |
| [33] |
MARSHALL J F. Targeting CDH17 in cancer: when blocking the ligand beats blocking the receptor?[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 24: 253-255. DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2823 |
| [34] |
MALEKI VAREKI S. High and low mutational burden tumors versus immunologically hot and cold tumors and response to immune checkpoint inhibitors[J/OL]. J Immunother Cancer, 2018, 6: 157. DOI: 10.1186/s40425-018-0479-7.
|
| [35] |
YARMARKOVICH M, MARIS J M. When cold is hot: immune checkpoint inhibition therapy for rhabdoid tumors[J]. Cancer Cell, 2019, 36: 575-576. DOI:10.1016/j.ccell.2019.11.006 |
| [36] |
NOMAN M Z, PARPAL S, VAN MOER K, XIAO M, YU Y, VIKLUND J, et al. Inhibition of Vps34 reprograms cold into hot inflamed tumors and improves anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy[J/OL]. Sci Adv, 2020, 6: eaax7881. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aax7881.
|
 2021, Vol. 42
2021, Vol. 42


